Geography: January 2025 Current Affairs | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Earthquake in Tibetan China and Nepal |

|
| Polar Vortex |

|
| Climate Change and African Easterly Waves |

|
| Artesian Well in Rajasthan and Tethys Sea |

|
| Record Global Warming and its Effect on India |

|
Earthquake in Tibetan China and Nepal
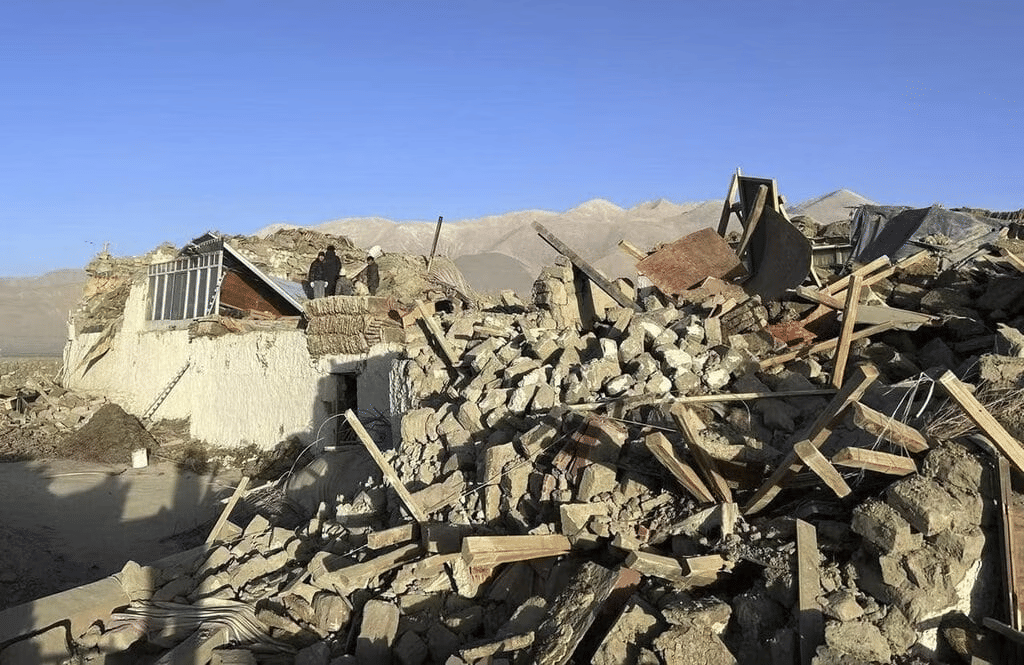

Why in News?
On January 7, 2025, a powerful earthquake measuring 7.1 struck the Tibetan region of China, affecting areas of Nepal as well. The earthquake had its epicenter approximately 10 km below the surface in Tingry County, located around 80 km north of Mount Everest. Initial reports indicated at least 95 fatalities and 130 injuries, along with extensive property damage, including the destruction of hundreds of houses. Tremors were felt in distant regions such as Kathmandu (Nepal), Thimphu (Bhutan), and Kolkata (India).
Key Takeaways
- The earthquake's epicenter was in Tingry County, Shigatse region, Tibet, a culturally significant area.
- Shigatse is home to about 800,000 residents and is a major spiritual center for Tibetan Buddhism.
- The region's tourism, particularly related to Mount Everest, has been severely impacted.
- Concerns arise over the Yarlung Tsangpo River dam project and its potential effects on water security in India.
Additional Details
- Geographical Context: The Tibetan region, known as the "third pole," plays a crucial role in global water resources, impacting millions of lives.
- Seismic Activity: The Himalayas are an active seismic zone due to the ongoing collision of the Indian and Eurasian tectonic plates, which continues to cause stress and earthquakes.
- Since 1950, the Lhasa terrane has recorded 21 earthquakes of magnitude 6 or higher, emphasizing the region's vulnerability.
- Humanitarian concerns include casualties, displacement of residents, and the need for disaster preparedness initiatives.
- Geological studies are essential for predicting future seismic events and understanding the dynamics of tectonic movements.
- The recent earthquake in Tibet underscores the complex interplay of geological, environmental, and geopolitical factors in the Himalayan region. Moving forward, a focus on disaster preparedness, sustainable development, and international collaboration will be vital to protect the region and its inhabitants.
Polar Vortex
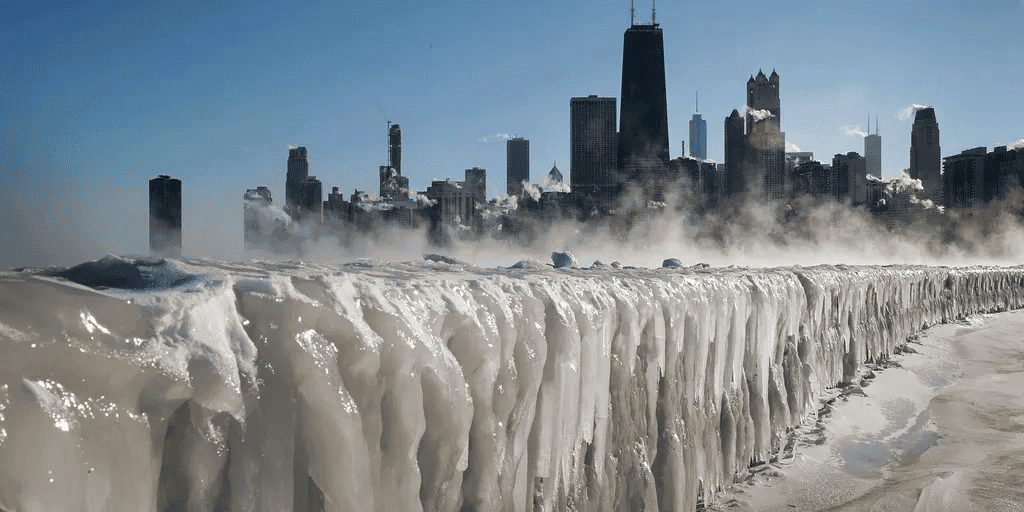

Why in News?
A severe winter storm has significantly impacted a large portion of the United States, affecting over 60 million people across 30 states. This extreme weather event is linked to the southward expansion of the polar vortex, which plays a critical role in producing frigid temperatures and severe storms.
Key Takeaways
- The polar vortex is a significant contributor to winter storms and extreme weather conditions.
- Winter storms are characterized by extreme cold, snow, sleet, or freezing rain, often accompanied by strong winds.
Additional Details
- What is the Polar Vortex: The polar vortex is a large area of low pressure and cold air that circulates around the Earth's polar regions. It exhibits a counter-clockwise flow of air, helping to confine colder air near the poles. While it exists year-round, it is stronger in winter and weaker in summer.
- Types of Polar Vortex:
- Tropospheric Polar Vortex: Located at the lowest atmospheric layer (up to 10-15 km) where most weather phenomena occur.
- Stratospheric Polar Vortex: Found at higher altitudes (15 km to 50 km), it is strongest during autumn and dissipates in summer.
- The stratospheric polar vortex is influenced by air movement and heat transfer in the polar region, with its strength increasing during autumn as circumpolar winds accelerate.
Mechanism of Extreme Cold
- When the polar vortex is strong, it stabilizes the jet stream, preventing cold air from moving southward.
- A weakened polar vortex disrupts the jet stream, causing it to become wavy and allowing Arctic air to flow further south, leading to extremely low temperatures and severe storms.
- This disruption can result in significant snowfall and freezing rain.
Global Warming and Polar Vortex
- Researchers have noted that the Arctic is warming at a rate faster than the rest of the planet, a phenomenon termed Arctic amplification.
- This warming reduces the temperature gradient between the poles and mid-latitudes, ultimately weakening the polar vortex.
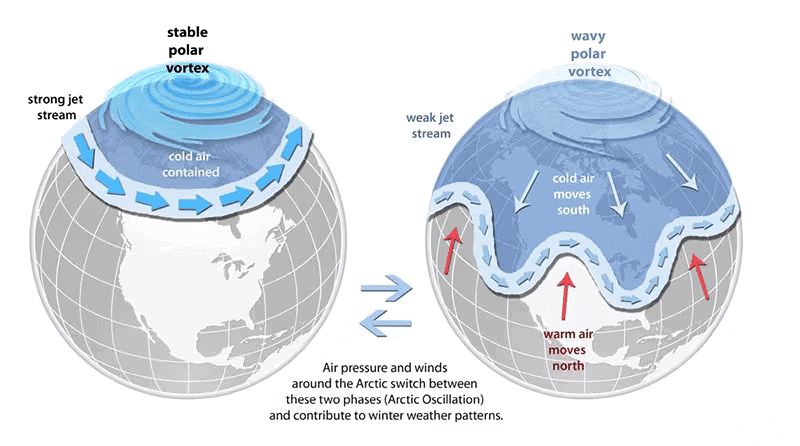
This phenomenon of the polar vortex and its effects on winter weather highlights the complexities of our climate system and the increasing impact of global warming on extreme weather events.
Climate Change and African Easterly Waves
 Why in News?
Why in News?
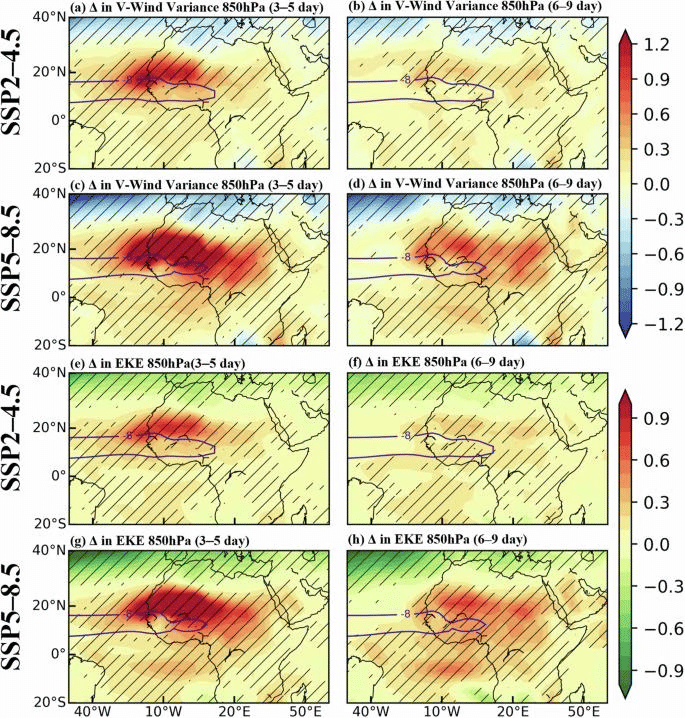
A recent study published in Communications Earth & Environment has highlighted the alarming effects of climate change on the Sahel region, predicting an increase in the intensity and frequency of extreme flooding. This phenomenon is largely attributed to changes in African easterly waves (AEWs).
Key Takeaways
- Increased AEW Activity: The study forecasts a rise in AEW occurrences over the Sahel-Sahara region by the end of the 21st century, driven by enhanced baroclinicity.
- Enhanced Monsoon Flow: Low-level warming is expected to strengthen the monsoon flow, leading to increased air convergence and altered AEW formation.
- Implications for Saharan Dust Transport: Strong winds associated with AEWs can transport dry Saharan air, affecting the development of tropical cyclones in the Atlantic.
- Connection to Mesoscale Convective Systems (MCSs): Increased AEW activity is anticipated to result in more frequent and intense flooding events in the Sahel.
Additional Details
- African Easterly Waves (AEWs): AEWs are weather systems that originate over northern Africa during the summer and typically move east to west towards the Atlantic Ocean. They are crucial for bringing rain to drought-affected areas and transport Saharan dust across the ocean, acting as precursors for hurricanes.
- Regional Hydroclimate Influence: AEWs significantly impact the hydroclimate of the Sahel, making it essential to study their behavior in the context of global warming.
Artesian Well in Rajasthan and Tethys Sea

Why in News?
Recently, large amounts of water began gushing out from underground in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, attributed to an artesian well in India. Experts have ruled out a connection to the ancient Saraswati River, suggesting that the water may be millions of years old, originating from the Tethys Sea during pre-Vedic times.
Key Takeaways
- Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, is experiencing significant water eruptions from underground.
- The water is believed to be ancient, with links to the Tethys Sea rather than the Saraswati River.
Additional Details
- What is an Artesian Well?: An artesian well is a type of well where water rises naturally to the surface under pressure, without the need for pumping. It occurs when water is trapped in a confined aquifer, creating pressure that forces the water to rise.
- Formation: Artesian wells are formed when a well penetrates a confined aquifer, a layer of permeable rock or sediment sandwiched between impermeable layers like clay or rock.
- Water Flow: Water in artesian wells may flow freely to the surface if the pressure is sufficient; otherwise, it can be extracted using a pump.
- Geological Significance: The Jaisalmer region, once bordering the Tethys Sea, has geological features and fossils indicating its ancient marine environment.
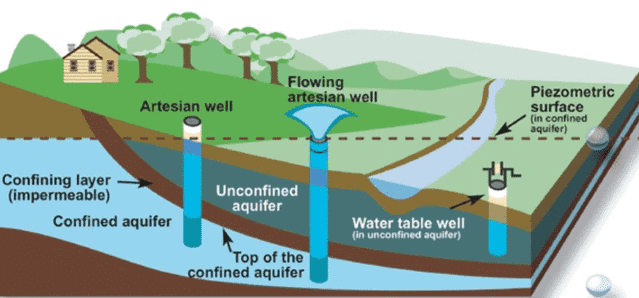
The water eruptions in Rajasthan highlight the geological history of the region, indicating connections to ancient seas rather than modern river systems.
What are the features of Artesian Well Found in Rajasthan?
- Water Eruption: In Rajasthan's desert regions, water is confined beneath a geological layer of sandstone, and when the top layer is punctured, water surges upwards due to pressure.
- Ancient Sea Evidence: The high salinity of the borewell water suggests similarities to ancient sea or saline groundwater sources.
- Presence of Marine Clay: Marine clay with skeletal remains supports the theory that groundwater is from an ancient sea.
- Geological Significance: The region's history as a boundary to the Tethys Sea is evidenced by giant shark fossils found exclusively in this area and a few others in Asia.
What are the Key Facts About the Tethys Sea?
- The Tethys Sea formed during the early Mesozoic Era, particularly in the Triassic period (about 250 to 201 million years ago).
- It existed between the landmasses of Gondwana and Laurasia, incorporating regions that are now continents.
- The Tethys Sea extended across parts of Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Middle East, connecting the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans.
- By the Late Cretaceous (around 66 million years ago), the Tethys Sea began to close, leading to the creation of new landmasses.
- The Tethys Sea was home to diverse marine life, significantly influencing the geological and fossil records.
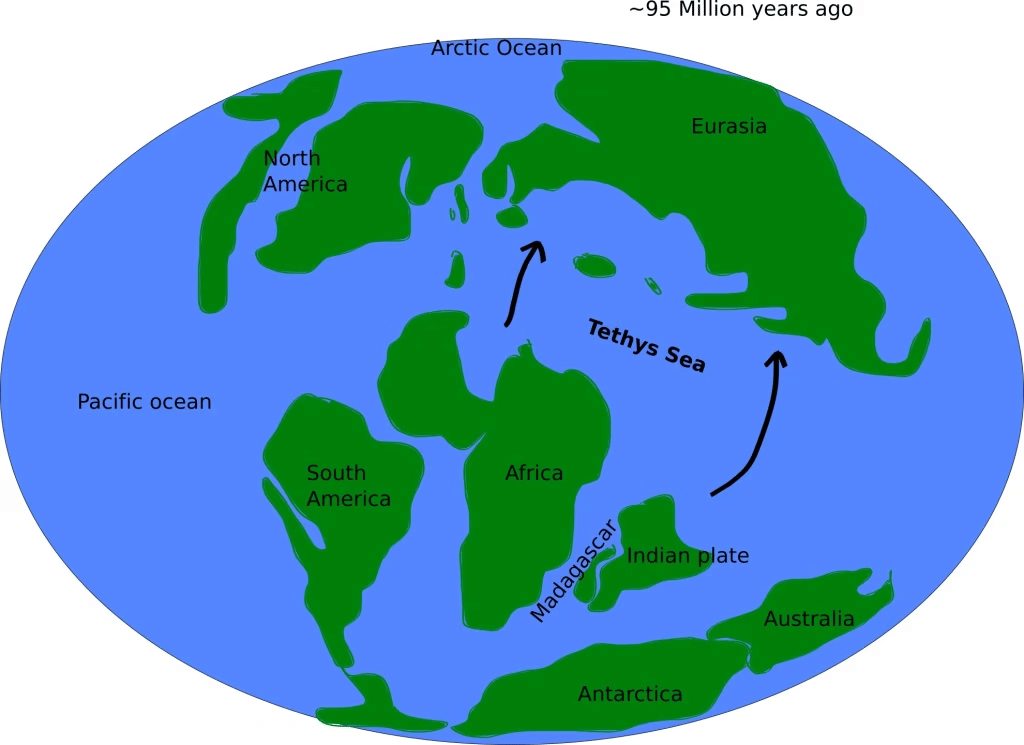
In conclusion, the recent artesian well activity in Rajasthan has led to important discussions about the region's geological past and its connections to ancient bodies of water, particularly the Tethys Sea.
Record Global Warming and its Effect on India

Why in News?
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has confirmed that 2024 is the warmest year on record.
- The past ten years 2015-2024 are the ten warmest years on record.
- According to IMD, the temperature increase in India is lower than the global average rise in temperature.
- However, concerns exist that global climate models don't accurately reflect changes in India, highlighting the need to improve its climate observation and impact assessment capabilities.
What are the Key Findings by the WMO?
- Record Global Temperature: In 2024, the global average surface temperature was 1.55°C above the pre-industrial levels (1850-1900 period), marking the first year with a temperature exceeding 1.5°C above this baseline.
- Ocean Heat: The top 2000 meters of ocean water absorbed a record 16 zettajoules of heat, roughly 140 times the total global electricity generation in 2023.
- Around 90% of excess heat from global warming is stored in the ocean.
- Temperature Assessment: Although 2024's temperature surpassed 1.5°C, the WMO assures that the Paris Agreement's goals remain intact.
- It emphasizes that every fraction of a degree worsens climate impacts on ecosystems and human systems.
- The Paris Agreement is a legally binding global agreement under UNFCCC to limit global warming to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels, with an ambition to limit warming to 1.5°C.
- Warming in India: India Meteorological Department (IMD) said that in 2024 India was 0.65 degrees Celsius higher than normal but lower than the global average of 1.55°C.
- IMD data shows that temperature over India in 2024 was about 1.2 °C higher than the 1901-1910 average.
What are the Reasons Behind Lower Warming Over India?
- Geographic Location: Global temperature rise has been more noticeable at higher latitudes, especially near the poles, due to heat transfer from the tropics through air circulation systems and the fact that higher latitudes already have lower temperatures.
- India is located in the tropical zone, closer to the equator which does not experience such geographical phenomenon.
- Albedo Effect: In the Arctic region, higher heating is caused by low albedo effect, where melting ice exposes land or water that traps more heat than ice-covered surfaces, which reflect sunlight.
- In India, albedo effect on snow is restricted to Himalayan areas.
- Aerosols and Pollution: The particulate matter and aerosols have a cooling effect because they scatter the solar radiation back into space.
- Aerosols also help in cloud formation which, in turn, help in reflecting sunlight back to space.
- High air pollution in India due particulate matter and aerosols have a small unintended consequence of lowering the temperature rise.
- Altitude Variations: India's landmass is not uniform, with distinct variations in temperature rise across regions.
- Some areas see more warming due to local climate and geography, but the national average temperature rise remains lower.
What are the Consequences of Rising Global Temperatures?
- Sea Level Rise: Global sea level has risen by about 8 inches since 1880 and is projected to rise by at least another foot by 2100 inundating coastal areas, displacing communities, and disrupting ecosystems.
- Oceans absorb significant CO2, increasing acidity and harming marine life.
- Droughts and Heat Waves: Droughts and heat waves are likely to intensify, while cold waves are expected to weaken and occur less frequently.
- Warming and prolonged drought have intensified wildfire seasons and increased fire risks.
- Biodiversity Loss: Rising temperatures and shifting weather disrupt ecosystems, driving many species toward extinction.
- Related Effects: Extreme weather disrupts food production, causing shortages and price hikes, while rising temperatures worsen air quality, increase heat illnesses, and spread diseases.
How India Can Better Observe Global Warming?
- Expansion of Weather Stations: India needs to expand its weather stations, especially in rural areas, with stations in every major panchayat under the Viksit Bharat vision for 2047, to gather real-time data for accurate climate assessments.
- Enhancing Computing Capabilities: India must invest in advanced computing and analysis infrastructure to process climate data for improved disaster management, agricultural forecasting, and climate resilience strategies.
- Regular Impact Assessments: India needs to conduct India-specific climate change impact assessments to track the evolving climate risks like sea level rise, and ecosystem changes.
- Mission Mausam: Mission Mausam should be strengthened and integrated with national and international systems for better weather prediction, especially in coastal and mountainous regions.
- Mission Mausam aims to enhance India’s ability to predict and respond to extreme weather events and the impacts of climate change.
- Localized Impact Studies: India needs to invest in localized studies that reflect the specific climate challenges faced by different regions such as the Himalayas, coastal areas, and urban centers for targeted adaptation strategies and policy interventions.
|
164 videos|800 docs|1155 tests
|
FAQs on Geography: January 2025 Current Affairs - General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce
| 1. What are the recent seismic activities reported in Tibetan China and Nepal, and how do they relate to the region's geological features? |  |
| 2. How does the polar vortex influence weather patterns in the Northern Hemisphere? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of African Easterly Waves in the context of climate change? |  |
| 4. How does the presence of artesian wells in Rajasthan relate to the historical Tethys Sea? |  |
| 5. What are the effects of record global warming on India’s climate and environment? |  |




















