UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 14th February 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS2/Polity
TRAI Tightens Rules Against Spam Calls and Text Messages
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?India’s telecom regulator, TRAI, has introduced new regulations under the Telecom Commercial Communications Customer Preference Regulations (TCCCPR), 2018, aimed at reducing spam calls and messages. These updated rules require telecom operators such as Airtel, Jio, and Vi to analyze call and SMS patterns in real time to identify spammers and report spam activity. Non-compliance may lead to fines ranging from ₹2 lakh for first-time offenses to ₹10 lakh for repeat violations.
- Introduction of stricter rules to combat spam communication.
- Telecom operators are mandated to act on spam reports within 5 days.
- Clear identification protocols for promotional and transactional calls.
- Enhanced monitoring mechanisms to detect spam activity.
Additional Details
- Reporting Spam: Users can now report spam more easily, with telecom operators required to act on these reports within 5 days, a significant reduction from the previous 30-day limit.
- Call Identification:Telemarketers are prohibited from using normal 10-digit numbers for promotional calls. Instead, specific number series are designated for different types of calls:
- 140 series for promotional calls.
- 1600 series for transactional and service calls (this is already being implemented).
- Opt-Out Mechanism: Telecom operators must provide users with an option to opt out of promotional communications, while users also have the option to opt in.
- Stricter Monitoring: Operators are required to monitor spam activity based on various factors including high call volumes, short call durations, and low incoming-to-outgoing call ratios.
- Verification and Penalties: Telemarketers must undergo stringent verification processes, including physical verification and biometric authentication. Repeated offenders will face suspension of their telecom resources, and operators must keep detailed records of complaints and sender information for prompt action.
Despite ongoing government efforts, millions of Indians still face persistent spam calls, particularly from sectors like banking and insurance. According to a LocalCircles survey conducted in February 2023 with 12,000 respondents:
- 60% receive 3 or more spam calls daily.
- 30% get 1-2 spam calls per day.
- 36% receive 3-5 calls daily.
- 21% get 6-10 calls daily.
- 3% receive over 10 unwanted calls daily.
The situation appears to be worsening, with telecom operators contributing to the surge in spam calls.
GS4/Ethics
India’s Got Latent Row
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Maharashtra cyber police have denied YouTuber Samay Raina’s request for more time to join the investigation into a case against him, podcaster Ranveer Allahbadia, and others. This case arose due to an “obscene joke” made by Allahbadia on Raina’s show.
- The case highlights the tension between freedom of expression and societal morality.
- There is ongoing debate regarding the definition and regulation of obscenity in media.
Additional Details
- What is an “obscene joke”: An obscene joke is characterized by sexually explicit, vulgar, or offensive content that may be deemed inappropriate or immoral by societal standards.
- Freedom of Expression vs. Public Morality: Content creators often face backlash when their work conflicts with societal norms, such as comedians making jokes about sensitive topics.
- Cultural Sensitivities: Standards of obscenity vary across cultures, complicating content regulation; for instance, nudity may be artistic in the West but often censored in India.
- Impact on Vulnerable Audiences: Explicit content can influence children and adolescents, affecting their views on relationships and social behavior.
- Accountability of Content Creators: Digital platforms and influencers must balance free speech with responsible content regulation.
The discussion surrounding obscenity emphasizes the need for clear legal definitions, stronger content moderation on digital platforms, and the promotion of media literacy among audiences. A balanced approach can ensure accountability while preserving creative freedom.
GS2/Polity
A Constant Legal Tussle Over Delhi's Unique Constitutional Status
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
The Aam Aadmi Party (AAP) government in Delhi has been embroiled in ongoing legal disputes with the Central Government regarding the unique constitutional status of the National Capital Territory (NCT) and the governance of the city.
- Delhi is a Union Territory (UT) with a legislative assembly and council of ministers, governed by Articles 239 and 239AA of the Indian Constitution.
- The governance structure involves three main power centers: the Chief Minister, the Lieutenant Governor (L-G), and the Union Home Ministry.
- Legal battles primarily revolve around control over bureaucratic services, law and order, and land administration.
Additional Details
- Constitutional Status: Delhi is classified as a Union Territory with a special status due to its legislative assembly, which allows it to make laws on certain subjects, except police, public order, and land. This unique arrangement is outlined in Article 239AA.
- Disputed Powers: The L-G, appointed by the President, has significant powers but must act according to the advice of the Council of Ministers, except in areas under the Centre's control. This has led to conflicts over bureaucratic appointments and governance.
- Legal Battles: The Supreme Court has intervened in several instances, ruling in favor of the Delhi government on issues like control over services, yet the Centre has responded by amending laws to restore L-G's authority.
- Impacts of Governance Crisis: Frequent clashes have resulted in administrative paralysis, policy delays, and reduced accountability, affecting initiatives like healthcare and water supply.
- Future Implications: Post-elections, if the BJP consolidates power, it may lead to stronger central control, potential rollbacks of AAP policies, and a clearer division of governance responsibilities.
The ongoing legal tussles highlight the complexities of Delhi's governance model and raise questions about the future of federal dynamics in India. Addressing these issues through constitutional amendments or judicial clarifications could pave the way for improved coordination between the different levels of government.
GS3/Economy
New Income-Tax Bill 2025: Simplified Structure and the New ‘Tax Year’ Concept
Source: Mint
Why in News?
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman has introduced the new Income Tax Bill in the Lok Sabha, aimed at reforming the existing tax system.
- The new Income-Tax Bill, 2025, aims to simplify tax laws and enhance compliance.
- Introduction of the concept of 'tax year', replacing the traditional 'assessment year'.
- Expected implementation date is April 1, 2026, if passed.
Additional Details
- Tax Year Concept: The tax year is defined as a 12-month period starting from April 1. This means income earned will be taxed in the same year, unlike the previous system which assessed income in the following year.
- Simplified Language: The bill reduces complex legal jargon and cross-referencing, decreasing the Income-Tax Act's length from 823 to 622 pages while maintaining the same number of chapters.
- Expanded Definition of Income: Virtual digital assets (VDAs) like cryptocurrencies and NFTs are now considered taxable capital assets, aligning them with traditional asset categories.
- Removal of Redundant Provisions: Outdated exemptions, such as those related to capital gains from before April 1992, have been eliminated.
- Improved Clarity: Provisions related to tax deductions and TDS rules have been consolidated into easily readable tables.
- Dispute Resolution Process: The new bill clarifies the roles and decisions of the Dispute Resolution Panel (DRP).
The new Income-Tax Bill aims to create a taxation system that is simpler and more comprehensible. While it improves clarity and structure, it does not introduce significant changes in tax rates or compliance mechanisms. The focus remains on ensuring a smooth transition to the new 'tax year' concept and preparing for future tax reforms.
GS2/Governance
The Problematic Globalisation of Medical Education
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The landscape of medical education is rapidly evolving across the globe, with a pronounced shortage of doctors coexisting with barriers to medical education access. This situation has prompted many students, particularly from India, to pursue medical training abroad, leading to significant internationalisation of medical education. However, this trend raises critical concerns regarding the quality and regulation of foreign medical programs.
- Growing shortage of doctors worldwide despite limited access to medical education.
- Indian students increasingly seek medical training abroad due to domestic constraints.
- Concerns exist about the quality of foreign medical programs and their regulation.
Additional Details
- Current Medical Education Crisis in India: India faces a severe shortage of doctors, with a doctor-to-patient ratio below the WHO recommended standard of 1:1000. Despite a high demand for medical professionals, the number of available medical seats is limited, intensifying competition.
- Intense Competition for Medical Seats: Approximately 2.3 million students take the NEET exam annually, with only about 700 medical colleges offering seats. This results in a success rate of about 1 in 22 students.
- High Fees in Private Institutions: Private medical colleges charge significantly high tuition fees, often between ₹50 lakh to ₹1 crore for an MBBS degree, making it unaffordable for many.
- Government Initiatives: The Indian government has announced plans to increase medical seats and establish new medical colleges through Public-Private Partnerships to address this issue.
- International Trends: The mobility of medical students is not limited to India; Western countries also face shortages, prompting students to study in neighbouring countries with English-medium medical programs.
The globalisation of medical education presents both opportunities and challenges. While it allows students to pursue their aspirations and addresses the global shortage of healthcare professionals, the lack of uniform quality standards poses risks. A coordinated global approach, prioritizing regulation and investment in medical training, is essential to ensure that medical education remains accessible and of high quality.
GS2/International Relations
Arab League: Overview and Current Developments
Source: ABC News
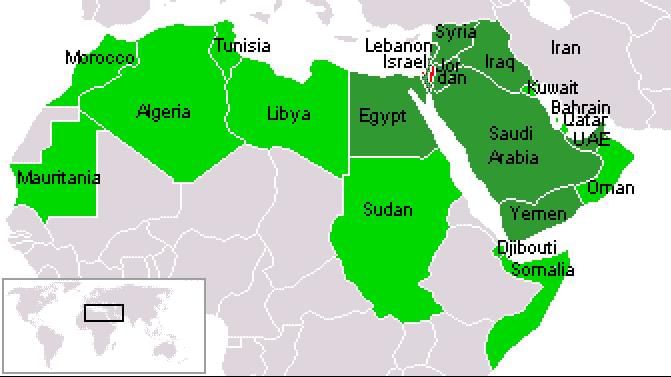 Why in News?
Why in News?The Arab League has recently voiced its strong disapproval of former US President Donald Trump’s proposal regarding the relocation of Gaza, labeling it as unacceptable.
- The Arab League was established on March 22, 1945, in Cairo, Egypt.
- Founding members included Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Lebanon, Saudi Arabia, and Syria.
- The League's primary objectives focus on economic, cultural, political, and military cooperation among member states.
Additional Details
- Consensus-Based Decision-Making: All member states must agree on significant resolutions, emphasizing collaboration.
- Member States: The Arab League currently comprises 22 member states, including Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Lebanon, Saudi Arabia, Syria, and more.
- Observer Nations: Several non-Arab countries, such as Brazil, Eritrea, India, and Venezuela, hold observer status but lack voting rights.
- Key Achievements:
- Arab Peace Initiative (2002): Proposed a two-state solution to address the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
- Military Coordination: Aided in joint military efforts during various regional conflicts.
- Economic Integration: Established the Arab Free Trade Area to foster intra-regional trade.
- Cultural and Educational Exchange Programs: Promoted cooperation in education, research, and cultural preservation.
The Arab League plays a crucial role in fostering collaboration among Arab states and addressing critical regional issues through diplomatic engagement.
Previous Year Question (PYQ):
[2023] Consider the following statements:
- Statement-I: Israel has established diplomatic relations with some Arab States.
- Statement-II: The ‘Arab Peace Initiative’ mediated by Saudi Arabia was signed by Israel and the Arab League.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- (a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- (b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- (c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
- (d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
GS3/Environment
New Fishing Grounds Discovered in Arabian Sea
Source: Deccan Herald
 Why in News?
Why in News?A deep-sea fishing expedition conducted by the Fishery Survey of India (FSI) has revealed several highly productive and previously
- The fishing survey was conducted at depths ranging from 300 to 540 meters using deep-sea trawlers.
- This initiative was funded under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY).
- Potential deep-sea fishing zones were mapped 100-120 nautical miles off India’s western coast, extending from Kollam in Kerala to Goa.
Additional Details
- Fishery Survey of India (FSI): Established in 1983 under the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying, FSI conducts fisheries research, resource surveys, and sustainable fishing assessments.
- Annual Resource Surveys: FSI conducts annual surveys to assist traditional fishermen, small and medium boat operators, and the deep-sea longlining tuna fleet.
- Historical Context: FSI originated from the “Deep Sea Fishing Station” project in 1946, was renamed the “Exploratory Fisheries Project” in 1974, and became the “Fishery Survey of India” in 1983. The Marine Engineering Division was integrated into FSI in 2005.
- Deep-Sea Fishing Project: Launched by PM Narendra Modi in 2017 to promote sustainable fishing practices across the Indian coastline.
India's Marine Fishing Industry
- India ranks second in global fish production after China, contributing 9.58 million tonnes.
- Production distribution: 70% from the west coast, 30% from the east coast.
- Major fish-producing states include Andhra Pradesh (20%), West Bengal (15%), Gujarat (8%), Kerala (7%), Maharashtra (6%), and Tamil Nadu (6%).
Exports and Global Trade
- India exports 1.05 million tonnes of marine fish, generating ₹334.4 billion ($5.57 billion) in revenue.
- Major export markets include the USA (26%), ASEAN nations (26%), EU (20%), Japan (9%), Middle East (6%), and China (4%).
This discovery of new fishing grounds emphasizes the importance of sustainable practices in enhancing India's fish production capabilities while also supporting local fishermen's livelihoods.
GS3/Environment
Brahmagiri Wildlife Sanctuary
Source: Deccan Herald
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Karnataka government's recent initiative to establish a tribal village in the buffer zone of Brahmagiri Wildlife Sanctuary has ignited discussions surrounding environmental conservation, tribal rights, and the potential for human-wildlife conflict.
- Brahmagiri Wildlife Sanctuary is located in Kodagu District, Karnataka, within the Western Ghats.
- It serves as a vital ecological corridor linking Nagarhole National Park and Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary.
- The sanctuary was designated as a protected area on June 5, 1974, to safeguard its diverse flora and fauna.
Additional Details
- Geographical Location: The sanctuary is approximately 250 km from Bengaluru and is named after Brahmagiri Peak, the highest point in the area.
- Flora: The region is characterized by the prevalence of bamboo species, which provide sustenance for herbivores like elephants and deer. The diverse plant life offers food, shelter, and nesting sites for numerous animal species.
- Fauna:
- Carnivores: Includes tigers, jungle cats, leopard cats, wild dogs, and sloth bears.
- Herbivores: Home to Indian elephants, gaurs, sambars, spotted deer, barking deer, mouse deer, and wild pigs.
- Primates: Features lion-tailed macaques, Nilgiri langurs, slender loris, bonnet macaques, and common langurs.
- Small Mammals & Rodents: Includes Malabar giant squirrels, giant flying squirrels, Nilgiri martens, common otters, brown mongooses, civets, porcupines, and pangolins.
- Reptiles: Notable species include king cobras, Indian cobras, pythons, and Malabar pit vipers.
- Birds: Home to various avian species, such as emerald doves, square-tailed bulbuls, and Malabar trogons.
This sanctuary plays a significant role in maintaining biodiversity and ecological balance in the region. The ongoing discussions regarding development in its buffer zone highlight the need for careful consideration of both conservation efforts and tribal rights.
GS3/Environment
Tackling Heatwaves - Strengthening Resilience in India
Source: Frontline magazine
 Why in News?
Why in News?Disasters are often viewed as distant threats; however, climate change has heightened the occurrence of extreme weather events. Among these, heatwaves have emerged as a silent killer in India, posing significant risks to public health, infrastructure, and economic stability. Alarmingly, public awareness surrounding the dangers of heatwaves remains low.
- Heatwaves in India are becoming more frequent, prolonged, and severe.
- January 2025 marked the 18th month in the last 19 with global temperatures surpassing the 1.5°C threshold.
- Impacts of heatwaves include public health crises, economic setbacks, and challenges in water supply and food security.
- Government initiatives aim to enhance preparedness and establish long-term mitigation strategies.
Additional Details
- Public Health Crisis: Approximately 90% of the Indian population is vulnerable to heat-related illnesses. Rural healthcare systems are particularly strained due to heat-induced health issues.
- Economic Consequences: Heat stress could lead to 34 million job losses in India by 2030, as per the World Bank. Outdoor workers frequently face productivity losses.
- Water Scarcity and Food Security: India holds only 4% of the world's freshwater but has 18% of the global population. Over 54% of India’s land experiences high to extreme water stress, jeopardizing agriculture due to declining groundwater levels and rising irrigation demands.
- Energy Sector Challenges: The increasing demand for cooling during heatwaves strains the energy supply, with 70% of India’s power generated by thermal plants that depend on water for cooling.
- Government Response: The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) recognizes heatwaves as a serious hazard, conducting workshops and implementing Heat Action Plans (HAPs) to mitigate impacts.
- National Framework for Heatwave Mitigation and Management (2024): This framework promotes local vulnerability assessments, community engagement, and mandates periodic updates to HAPs based on data-driven assessments.
With over 250 Heat Action Plans established, the next challenge lies in ensuring effective implementation and enhancing public awareness. India must prioritize transforming cities and communities into heat-resilient ecosystems to confront the rising temperatures of the future.
GS2/International Relations
China’s Dam Project Opens the Floodgates of Concern
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?China's initiative to build a significant hydroelectric dam on the Yarlung Zangbo River in Tibet, known as the Brahmaputra in India, has raised substantial concerns, particularly from India. The Brahmaputra River is vital for the livelihoods of millions across India's northeastern states and Bangladesh. Although China's shift towards renewable energy through such projects aligns with its environmental goals, the potential repercussions for downstream nations present serious environmental, geopolitical, and legal challenges.
- The dam's construction raises international legal concerns regarding water rights and responsibilities.
- Environmental risks include seismic hazards and ecological disruption, impacting biodiversity.
- Geopolitical tensions complicate water diplomacy between China and lower riparian states like India and Bangladesh.
Additional Details
- Legal Dimensions: The construction of the dam highlights critical issues under international water law, primarily the UN Watercourses Convention (1997). This convention emphasizes equitable utilization and cooperation among riparian states. However, both China and India are not signatories, complicating dispute resolutions over transboundary rivers.
- Environmental Risks: The dam's location in a high seismic activity zone raises concerns about its structural vulnerability. The potential for earthquakes and landslides could lead to catastrophic floods in downstream regions like Arunachal Pradesh and Assam, already prone to flooding.
- Impact on Biodiversity: The Yarlung Zangbo and Brahmaputra river basins are home to various endangered species. The dam could destroy habitats and block migration routes for species like the Gangetic river dolphin and the Bengal tiger, threatening their survival.
- Geopolitical Challenges: Water disputes are intertwined with broader geopolitical tensions in South Asia. Regional cooperation is hindered by political divisions, complicating negotiations on shared water resources.
In conclusion, while China asserts that the dam will not significantly affect downstream water flow, India remains apprehensive about its environmental, legal, and geopolitical implications. The lack of binding international agreements exacerbates the situation, necessitating renewed diplomatic efforts and regional cooperation to address these challenges.
|
51 videos|5377 docs|1138 tests
|
















