UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 4th March 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS2/Governance
SC Seeks Measures Against ‘Vulgarity’ Online
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court of India directed Solicitor General Tushar Mehta, representing the Central Government, to propose regulatory measures aimed at controlling the use of filthy language and vulgarity in online programmes. This initiative is intended to balance the need for decency and morality in public content while maintaining freedom of speech and expression.
- The Supreme Court urged the Solicitor General to suggest a regulatory framework to control vulgarity in online programs.
- The court emphasized the need to uphold societal moral standards without imposing outright censorship.
- Input from stakeholders is sought to foster a healthy debate on this issue.
Additional Details
- Public Decency and Morality: The court highlighted the importance of maintaining societal moral standards and preventing the spread of indecent content disguised as humour. For example, the court remarked that humour should be family-friendly and should not rely on vulgarity to demonstrate talent.
- Free Speech and Vulgarity: While it is crucial to protect freedom of expression, there is a need to curb vulgarity and perversity in public content. The court modified restrictions on YouTuber Ranveer Allahbadia, allowing him to broadcast but under the condition of adhering to decency norms.
- Protection of Vulnerable Audiences: The court stressed the necessity to shield minors and impressionable audiences from offensive and inappropriate humour. The Solicitor General noted that the content of "India Got Latent" was unsuitable for public viewing due to its perverse nature.
- Creativity and Responsibility: A balance must be struck between creative humour and responsible language. Justice Surya Kant observed that talented comedians can produce humour using ordinary words without breaching moral limits.
- Accountability of Online Platforms: The court called for regulatory oversight to ensure that online platforms are held accountable for the content they disseminate.
The impact of vulgar humour on society includes the erosion of social and moral values, negative influences on youth, public backlash and social division, undermining respect for institutions, and legal consequences for violating decency laws. Establishing a clear regulatory framework and promoting responsible content creation are essential steps moving forward.
GS3/Economy
Impact of LPG Access on Rural Women’s Employment and Time Allocation
Why in News?
Recent data from Periodic Labour Force Surveys (PLFS) indicates an increase in overall employment rates, particularly self-employment, among rural women since 2017-18. This trend raises critical questions regarding how these women are reallocating their time, especially in relation to domestic responsibilities.
- A significant portion of rural women are engaged as helpers in home-based enterprises.
- Women predominantly allocate their time to domestic work, with over 60 hours per week spent on various chores.
- Access to LPG through the Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) reduces time spent on cooking and fuel collection.
- Despite time savings, there is limited increase in women's income-generating activities.
- Challenges remain regarding regular LPG usage and women's financial empowerment.
Additional Details
- Women’s Domestic Work and Time Use Patterns: The 2019 Time Use Survey indicates that women spend a majority of their time on cooking. For instance, a survey in rural Indore found that women dedicate over 40 hours weekly to cooking and cleaning, with 75% relying on firewood and cow dung, which poses health risks due to smoke inhalation.
- LPG Access and Time Savings: LPG access significantly diminishes the time spent on cooking and fuel collection, saving approximately 30 minutes daily for households using LPG compared to those using solid fuels.
- Impact on Women’s Labour Force Participation: Despite time savings, there is no substantial increase in women's participation in income-generating activities, with saved time often redirected to leisure rather than employment.
- Challenges in Regular LPG Usage: Although PMUY has increased LPG connections, regular usage is hindered by mixed-fuel practices and low refill rates. Decision-making regarding LPG refills is typically male-dominated, affecting women's bargaining power.
- Recent Trends in Women’s Employment: The 2024 Time Use Survey shows a 1.5 percentage point increase in women's employment since 2019, yet the reasons for a significant rise in self-employment remain unclear.
In conclusion, while LPG access improves women's welfare by saving time, it does not significantly enhance their employment participation. Structural barriers such as the lack of job opportunities, inadequate skill levels, and gender-based decision-making challenges hinder genuine economic empowerment. Addressing these issues will necessitate comprehensive policy interventions, including skill development and better access to flexible, well-paying jobs for rural women.
GS3/Science and Technology
What is Planetary Alignment?
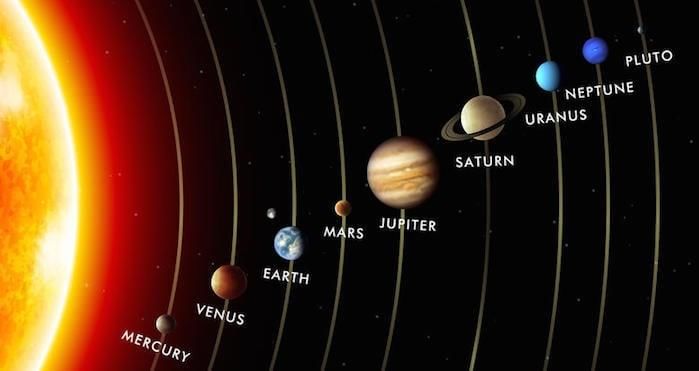 Why in News?
Why in News?
On February 29, 2024, skywatchers around the globe experienced a remarkable event as seven planets—Mars, Jupiter, Uranus, Neptune, Mercury, Saturn, and Venus—aligned in a spectacular display in the night sky.
- Planetary alignment occurs when multiple planets appear to line up from the perspective of Earth.
- This phenomenon is an optical illusion caused by the flat, disc-shaped plane of the planets' orbits around the Sun, known as the ecliptic.
- The alignment of planets can be referred to as a planet parade, where several planets are visible simultaneously.
Additional Details
- Types of Planetary Alignments:
- Conjunction: Two or more planets appear close together in the sky.
- Small Alignment: Three planets align in a visible line.
- Large Alignment: Four or more planets appear aligned from Earth's perspective.
- Full Alignment: All eight planets line up, which is very rare.
- Frequency of Alignments:
- Two- or Three-Planet Alignments: Occur multiple times a year.
- Four- or Five-Planet Alignments: Visible every few years.
- Six- or Seven-Planet Alignments: Appear every few decades.
- Full Alignment (All Eight Planets): Extremely rare, happens once every 170–200 years.
- Recent & Upcoming Alignments:
- August 2025: Anticipated four-planet alignment.
- May 2492: The next predicted full alignment of all eight planets.
Planetary alignments capture the imagination and interest of astronomers and enthusiasts alike, marking significant celestial events that are both visually stunning and scientifically intriguing.
GS2/International Relations
Australia, A Natural Partner for India’s Growth Trajectory
Why in News?
The relationship between Australia and India has entered a new era of economic and strategic cooperation, emphasizing Australia's confidence in India's growth trajectory. This partnership is founded on shared economic interests, strategic alignment, and historical ties, as outlined in the recently launched New Roadmap for Australia’s Economic Engagement with India.
- Australia predicts India will become the world's third-largest economy by 2030.
- Australia supports India's bid for a permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council.
- The Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (ECTA) has significantly boosted trade between the two nations.
- Key sectors for collaboration include clean energy, education, agribusiness, and tourism.
- Australia aims to assist India in addressing skill development needs.
- The Indian diaspora in Australia plays a crucial role in strengthening bilateral ties.
- The Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) aims to remove trade barriers and enhance cooperation.
Additional Details
- Australia’s Confidence in India’s Economic Growth: Australia firmly believes in India's economic potential, driven by robust growth and increasing global influence.
- Economic Engagement: Launched by Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese, the New Roadmap aims to deepen trade and economic cooperation, focusing on significant sectors.
- Skill Development Needs: India needs to skill 20 million people annually, and Australia is becoming a crucial partner by establishing campuses and providing vocational training.
- Role of the Indian Diaspora: With over 1 million Indian-Australians, this community serves as a cultural and economic bridge, enhancing bilateral relations.
- Future Agreements: While the ECTA has improved trade, the proposed CECA seeks to create a comprehensive framework for long-term economic collaboration.
In conclusion, Australia's proactive approach towards India's economic rise indicates a promising future for their partnership. The New Roadmap outlines a clear direction for mutual cooperation, ensuring both nations leverage each other's strengths for greater economic success.
GS3/Environment
Narwhals and Their Unique Hunting Techniques
Why in News?
Recent studies have provided unprecedented insights into the hunting behaviors of narwhals, the iconic marine mammals of the Arctic, revealing how they utilize their distinctive tusks during foraging.
- Narwhals are medium-sized toothed whales known for their long, horn-like tusks.
- The tusk is a tooth that possesses sensory capabilities, aiding in hunting and mating displays.
- They primarily inhabit Arctic waters, facing threats from climate change and industrial development.
Additional Details
- Narwhal Description: Narwhals, scientifically known as Monodon monoceros, have distinctive features that change with age, from a blue-gray color in newborns to a mottled gray or white in older individuals.
- Tusk Functionality: The tusk, which can contain up to 10 million nerve endings, is believed to play a crucial role in mating and is used to interact with prey such as Arctic char.
- Breeding Habits: Narwhals are polygynous, with mating occurring between March and May, and females typically give birth to a single calf, which emerges tail first.
- Diet: Their diet includes Greenland halibut, Arctic cod, squid, and shrimp, showcasing their adaptability in the harsh Arctic environment.
- Conservation Status: The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) lists narwhals as Near Threatened due to the impacts of climate change and oil and gas exploration in their habitats.
Understanding the behavior and biology of narwhals is crucial for their conservation, especially as environmental threats increase. Continued research can help inform strategies to protect these unique creatures of the Arctic.
GS3/Economy
Virtual Digital Assets: Income Tax Bill 2025
Why in News?
The Income Tax Bill, 2025, marks a significant development in India's taxation framework by explicitly categorizing Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs) as property and capital assets. This classification aligns India with global practices regarding the treatment of digital assets.
- VDAs, including crypto assets and Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), are recognized as property under the new bill.
- Gains from the sale or transfer of VDAs will be taxed under capital gains provisions.
- The bill imposes a flat 30% tax on income generated from VDA transactions.
- VDAs will be subject to regulations regarding undisclosed income and asset seizure.
Additional Details
- Capital Assets: VDAs will be classified as capital assets, similar to real estate and stocks. For instance, if an individual buys Bitcoin for ₹10 lakh and sells it for ₹20 lakh, the ₹10 lakh profit will incur capital gains tax, with rates dependent on the holding period.
- Tax Implications: Unlike traditional capital assets, no deductions—except for the cost of acquisition—are permitted when calculating taxable income on VDA transactions. For example, selling Ethereum bought for ₹5 lakh for ₹7 lakh results in a taxable profit of ₹2 lakh at a 30% tax rate, without deductions for transaction costs.
- Undisclosed Income Regulations: Failure to report VDA holdings can result in classification as undisclosed income, leading to additional taxation. Tax authorities are also empowered to seize VDAs during investigations, similar to cash or gold in tax evasion cases.
- Transaction Reporting: All entities dealing in crypto assets, such as exchanges and wallet providers, must report transactions in a specified format.
This legislative move aims to regulate and tax digital asset transactions, ensuring compliance with established financial frameworks and preventing misuse of these assets as unregulated financial instruments.
GS3/Environment
Lake Tanganyika Conservation Initiative
Why in News?
The nations surrounding the Lake Tanganyika Basin have initiated a five-year project aimed at evaluating and mitigating transboundary threats to the biodiversity of this significant ecological region.
- Lake Tanganyika is an ancient lake located in East Africa.
- It is bordered by four countries: Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Tanzania, and Zambia.
- The lake is renowned for being the longest and one of the deepest lakes in the world, stretching over 400 miles.
- A new initiative funded by the Global Environment Facility (GEF) aims to enhance biodiversity conservation and sustainable resource management in the basin.
Additional Details
- Geographic Significance: Lake Tanganyika lies at the southern end of the Western Rift Valley, with steep land rising from its shores. It serves as a natural divider between the floral regions of eastern and western Africa.
- Biodiversity and Economy: The lake supports various economic activities including fishing and agriculture, with rice and subsistence crops being cultivated along its banks.
- Recent Initiative: The project, led by the UN Environment Programme (UNEP), aims to foster cooperation among the four bordering countries to protect core conservation zones and promote sustainable practices.
- Efforts will also focus on restoring degraded landscapes and ensuring the sustainability of fishery resources.
This initiative represents a significant step towards preserving the biodiversity of Lake Tanganyika while promoting sustainable development practices among the nations that share this vital resource.
GS3/Economy
India’s Burden of Rising Obesity, the Hefty Cost to Pay
Why in News?
The prevalence of obesity in India is a growing concern, with significant implications for public health and the economy. The World Obesity Federation has reported alarming increases in childhood obesity, marking India as one of the nations facing the highest annual rise globally.
- Nearly one in four Indian adults is either overweight or obese, with varying rates across states.
- Obesity is linked to severe health issues, including diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases.
- The economic cost of obesity in India was estimated at $28.95 billion in 2019, projected to increase significantly by 2030.
Additional Details
- Rising Prevalence: Recent data indicates obesity rates vary widely, with some states reporting rates as low as 8% and others exceeding 50%. Urban populations are particularly affected due to lifestyle changes, leading to a concerning increase in childhood obesity.
- Health Consequences: Obesity contributes to a range of non-communicable diseases (NCDs), including diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and certain cancers, which together place immense pressure on the healthcare system.
- Economic Impact: The economic burden of obesity includes higher healthcare costs, lost productivity, and reduced workforce efficiency. Without intervention, these costs are expected to escalate significantly.
- Causes of Obesity: Key factors contributing to the obesity epidemic include poor dietary habits, increased consumption of high-fat and ultra-processed foods, sedentary lifestyles, and lack of physical activity.
Addressing the rising prevalence of obesity in India requires immediate and coordinated action from various stakeholders, including individuals, healthcare professionals, policymakers, and businesses. A comprehensive strategy focused on awareness, urban planning, healthcare integration, and community interventions is essential to mitigate this public health crisis.
GS3/Environment
MISHTI Scheme: A Step Towards Mangrove Restoration
Why in News?
Gujarat has recently achieved recognition as the national leader in mangrove afforestation, successfully covering 19,020 hectares in just two years under the Central Government’s MISHTI (Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats and Tangible Incomes) scheme.
- The MISHTI scheme was launched on June 5, 2023.
- It aims to restore 540 sq. km of mangrove forests over a 5-year period (2023–2028).
- The initiative focuses on 9 states and 3 union territories.
- Funding is through MGNREGS, CAMPA Fund, and community participation.
- It aligns with India’s commitment to the Mangrove Alliance for Climate at COP27 (2022, Egypt).
Additional Details
- Focus Areas: The scheme emphasizes restoration in regions such as the Sundarbans (West Bengal), Hooghly Estuary, and other coastal and wetland ecosystems.
- Gujarat's Leadership: Gujarat has become India's top state for mangrove cover, contributing 19,020 hectares (190 sq. km) under the MISHTI initiative.
- The Gulf of Kutch leads in mangrove coverage with 799 sq. km, followed by the Gulf of Khambhat and the Dumas-Ubhrat belt (134 sq. km).
- This initiative aims to expand mangrove cover by an additional 350 sq. km, enhancing climate resilience and coastal biodiversity.
The MISHTI scheme represents a significant effort to restore mangrove ecosystems, which are vital for biodiversity and climate resilience. Through community involvement and targeted funding, it aims to secure and enhance India's coastal environments for future generations.
GS3/Environment
Marbled Cat
Why in News?
The recently captured images of the elusive marbled cat through camera traps at Dehing Patkai National Park in Assam's Tinsukia district have generated significant interest and awareness about this rare species.
- The marbled cat (Pardofelis marmorata) is a small wild cat native to South and Southeast Asia.
- This species is closely related to the clouded leopard and the bay cat.
- Marbled cats are primarily found in India’s Northeastern states.
- Their current conservation status is listed as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List.
Additional Details
- Distribution: The marbled cat inhabits several countries including India, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand, and Laos. In India, it is predominantly located in the forests of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Meghalaya, and Nagaland.
- Physical Features: This small wild cat is characterized by its unique marbled fur pattern, which is typically brown or gray adorned with black spots and stripes. These features enable them to blend seamlessly into their forest surroundings.
- Behavior: Marbled cats are remarkable climbers, known for their ability to leap significant distances between trees. They are solitary creatures, marking their territory with urine and scent, and tend to spend most of their time alone.
- Size: Males are generally larger, weighing between 4.5 and 9 kg, while females weigh between 2.5 and 5 kg.
The sighting of marbled cats in their natural habitat highlights the importance of conservation efforts and the need to protect these unique creatures and their environment.
GS3/Environment
Gangetic Dolphin
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The first comprehensive estimate of Gangetic dolphins, the sole riverine dolphins found in India, has revealed a population of 6,327 individuals inhabiting the Ganga River and its tributaries.
- The Gangetic dolphin is a freshwater species and one of the few river dolphins in the world.
- It is recognized as the National Aquatic Animal of India.
Additional Details
- Habitat: This species resides in the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna and Karnaphuli-Sangu river systems across Nepal, India, and Bangladesh.
- Common Names: Known as the Blind dolphin, Ganges dolphin, Ganges susu, hihu, side-swimming dolphin, and South Asian River Dolphin.
- Scientific Classification: The scientific name for the Gangetic dolphin is Platanista gangetica.
- Description: The dolphin features a long, thin snout, a rounded belly, and a stocky body. It can weigh up to 150 kg, with females being larger than males.
- Coloration: At birth, calves are chocolate brown and transition to grayish brown as adults, possessing smooth and hairless skin.
- Feeding Habits: Gangetic dolphins primarily consume fish and are typically found in counter-current areas of the main river channel.
- Vision: Their eyes lack lenses, making them known as blind dolphins. They utilize a highly developed bio-sonar system to navigate and hunt in murky waters.
- Breathing: These dolphins cannot breathe underwater and must surface every 30-120 seconds, producing sounds while breathing, which contributes to their nickname 'Susu'.
- Conservation Status: The Gangetic dolphin is classified as Endangered by the IUCN and is protected under Schedule-I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act and listed in Appendix I of CITES.
This estimate highlights the critical need for conservation efforts to protect the Gangetic dolphin, given its endangered status and the threats posed by habitat degradation and pollution in river ecosystems.
|
44 videos|5271 docs|1113 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 4th March 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What measures is the Supreme Court considering to address online vulgarity? |  |
| 2. How has access to LPG impacted rural women's employment and time allocation? |  |
| 3. What is planetary alignment and why is it significant? |  |
| 4. What is the MISHTI Scheme and its objectives? |  |
| 5. What are the health implications of rising obesity rates in India? |  |
















