UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 5th March 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Environment
Threat to Native Biodiversity from Ruellia elegans
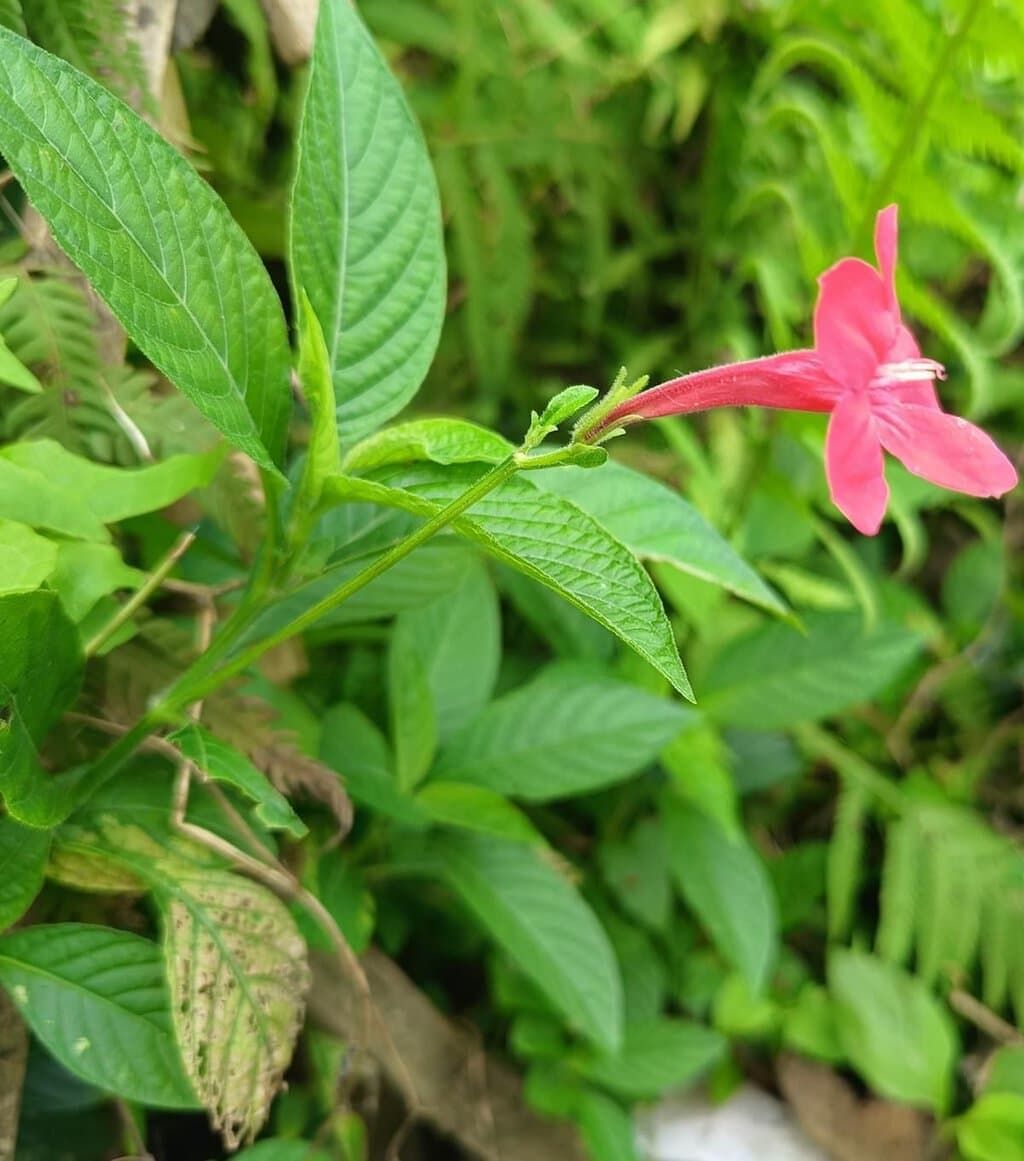 Why in News?
Why in News?
A recent study has highlighted the potential threat to native biodiversity posed by the invasive plant species Ruellia elegans, which is known for its aesthetic appeal.
- Origin: Ruellia elegans is native to Brazil and thrives primarily in wet tropical biomes.
- Common Names: This species is also referred to as the Brazilian petunia, Christmas pride, elegant Ruellia, red Ruellia, and wild petunia.
- Invasive Species: It is one of four invasive species in the Acanthoideae sub-family found in India.
- Geographical Spread: Ruellia elegans was introduced in the Andaman Islands and has been recorded in Odisha since nearly a decade ago.
Additional Details
- Invasive Plant Species: Invasive species like Ruellia elegans can quickly spread and outcompete native flora for essential resources such as sunlight, water, and nutrients.
- They disrupt local ecosystems by altering biodiversity, affecting wildlife habitats, and potentially leading to the decline or extinction of native species, which can result in significant economic and environmental damage.
This study serves as a crucial reminder of the impacts invasive species can have on biodiversity, urging for increased awareness and management strategies to protect native ecosystems.
GS3/Defence & Security
Taurus KEPD-350
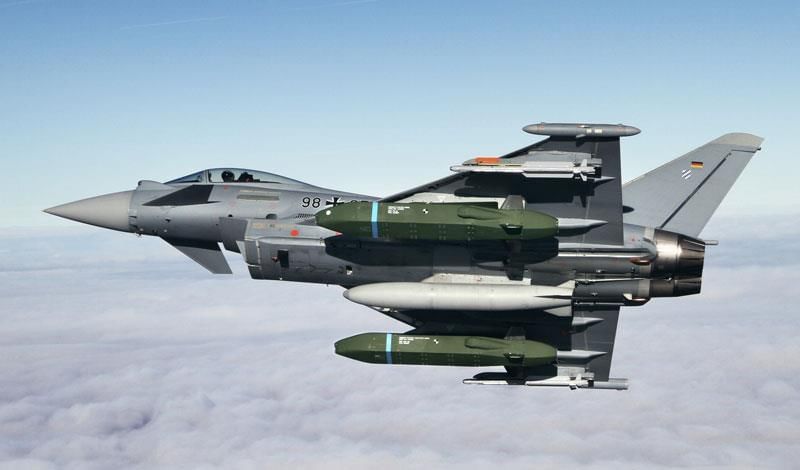 Why in News?
Why in News?
Sweden has made a significant advancement in enhancing its air force's long-range strike capabilities by opting for the Taurus KEPD-350 air-launched cruise missile to be integrated with its Gripen fighter jets.
- The Taurus KEPD-350 is a long-range, precision-guided cruise missile.
- Produced by Taurus Systems GmbH, a collaboration between Germany's MBDA Deutschland GmbH and Sweden's Saab Bofors Dynamics.
- It is capable of penetrating dense air defense systems to target hard and deeply buried military installations.
- The missile has been in operational use since 2005 and is utilized by air forces in various countries including Germany, Spain, and South Korea.
Additional Details
- Specifications: The missile measures 5 meters in length, has a wingspan of 2.1 meters, and weighs approximately 1,400 kilograms.
- Range: It possesses a range of over 500 kilometers, allowing for significant operational flexibility.
- Engine and Speed: Powered by a turbofan engine, it achieves a cruise speed ranging from Mach 0.6 to 0.95, while flying at low altitudes.
- Modularity: The missile's design incorporates modular sections and electronic systems, which can be tailored to specific missions.
- Operational Versatility: It is deployable during day or night and under all weather conditions, enhancing its operational effectiveness.
- Navigation System: The missile's navigation is managed through the Tri-Tec navigation system, which integrates data from an inertial navigation system (INS), military-grade GPS, terrain reference navigation (TRN), and an infrared seeker based on image-based navigation (IBN) sensors.
The integration of the Taurus KEPD-350 into Sweden's Gripen fighter jets marks a pivotal enhancement in the country's defense capabilities, enabling it to conduct more effective long-range strikes against critical military targets.
GS3/Environment
Mount Erebus
Why in News?
Mount Erebus, an active volcano in Antarctica, has drawn attention due to its unique geological features and the thriving microbial life found in its volcanic ice caves. This discovery offers insights into the potential for life on other celestial bodies.
- Mount Erebus is the world’s southernmost active volcano.
- Located on Ross Island in the Ross Sea, it is a glaciated intraplate stratovolcano.
- It features an active lava lake with alkalic lava, unique to a few volcanoes globally.
- Continuously active since 1972, it primarily experiences small eruptions of a Strombolian character.
- McMurdo Station, the largest Antarctic settlement, is situated about 40 kilometers (25 miles) from the volcano.
Additional Details
- Location: Mount Erebus is positioned on the western half of Ross Island, off the coast of Antarctica in the Ross Sea.
- Historical Significance: Discovered in 1841 by British explorer Sir James Clark Ross, the volcano was named after his ship, the Erebus.
- Height: The summit of Mount Erebus reaches 12,448 feet (3,794 meters) above sea level, making it the second tallest volcano in Antarctica, following Mount Sidley.
- Volcanic Activity: The lava lake within the volcano is characterized by its alkalic composition and has been a subject of study for understanding volcanic activity and life in extreme environments.
Mount Erebus not only serves as a significant geological feature but also as a point of interest for researchers exploring the possibilities of life in extreme conditions, both on Earth and potentially on other planets.
GS2/International Relations
Remodelling the UAE-India Aviation Partnership
Why in News?
The aviation partnership between India and the UAE is crucial as it reflects the growing air travel demand and the need for improved connectivity. However, existing limitations in bilateral air service agreements hinder the full potential of this collaboration.
- India is the world's third-largest domestic aviation market, emphasizing international collaboration.
- The UAE is a significant outbound travel destination for India, yet bilateral agreements restrict growth.
- Government initiatives and infrastructure expansion are critical for meeting rising air travel demand.
Additional Details
- Growing Demand for Air Travel: India's aviation industry has seen unprecedented growth, driven by economic development and rising incomes. The construction of major airports like Navi Mumbai International Airport signifies India's ambition to be a global aviation hub.
- Government Initiatives: Initiatives such as the UDAN program enhance regional connectivity, making air travel more affordable for smaller cities and towns. This addresses the travel needs of India's expanding middle class.
- International Connectivity: The India-UAE air corridor is among the busiest globally, yet the demand exceeds supply, leading to high ticket prices and limited options for travelers.
- Challenges: Key challenges include airport congestion, restrictive bilateral agreements, high airfares, and the need for workforce development to support the growing aviation sector.
- Way Forward: Both nations should prioritize cooperation over competition to create a synergistic aviation ecosystem that benefits economic and social development.
In conclusion, while infrastructural developments like the Navi Mumbai International Airport demonstrate India's commitment to expanding its aviation sector, regulatory barriers persist. A modernized open-skies policy is essential for both nations to capitalize on the growing travel demand, reduce costs, and enhance connectivity.
GS2/International Relations
Cities Coalition for Circularity (C-3)
Why in News?
India has initiated the Cities Coalition for Circularity (C-3), a multi-nation alliance aimed at fostering city-to-city collaboration, knowledge-sharing, and private sector partnerships to promote sustainable urban development.
- The initiative was launched at the 12th Regional 3R and Circular Economy Forum in Asia and the Pacific held in Jaipur.
- C-3 aims to facilitate collaboration among cities to adopt circular economy principles.
- It is spearheaded by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (India) in partnership with the United Nations Centre for Regional Development (UNCRD) and the Institute for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES).
- The forum will endorse the Jaipur Declaration (2025-2034), a non-political and non-binding commitment to enhance resource efficiency and sustainable urban growth over the next decade.
Additional Details
- Supported by International Organizations: C-3 is backed by UNESCAP, Japan’s Ministry of Environment, and various global partners.
- Circular Economy Focus: The initiative promotes practices such as reuse, recycling, remanufacturing, and composting to minimize waste.
- Global Collaboration: Involves local governments, private sector stakeholders, and academic institutions to drive innovation and policy development.
- Integration with SDGs: The coalition aligns with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those related to climate action and responsible consumption.
The establishment of the Cities Coalition for Circularity signifies India's commitment to sustainable urban development through collaborative efforts, aiming to integrate circular economy principles into urban planning and governance.
GS3/Environment
Species in News: Marbled Cat
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The elusive marbled cat (Pardofelis marmorata) has been recently spotted in Dehing Patkai National Park, located in Assam's Tinsukia district. This sighting has garnered attention due to the species' rarity and its ecological significance.
- The marbled cat is a small wild cat species native to South and Southeast Asia.
- It is classified as Near Threatened (NT) on the IUCN Red List due to habitat loss.
- Dehing Patkai National Park is known for its extensive lowland rainforests and diverse wildlife.
Additional Details
- Marbled Cat Characteristics: This species is characterized by its brown, gray, or yellowish fur adorned with distinctive black spots, marbled patterns, and stripes for effective camouflage. It primarily inhabits dense tropical and subtropical forests at elevations up to 2,500 meters.
- Nocturnal Behavior: The marbled cat is primarily nocturnal and crepuscular, indicating it is most active during dawn and dusk.
- Conservation Status: The species faces threats due to habitat loss and fragmentation, leading to its classification as Near Threatened by the IUCN and listed in CITES Appendix I.
- Dehing Patkai National Park: This national park, located in the Dibrugarh district of India, spans an area of 231.65 km². It was designated as a national park in 2020 and is part of the Dehing Patkai Elephant Reserve. The park features the largest stretch of lowland rainforests in India, hosting diverse flora and fauna, including seven species of wild cats.
- Indigenous Communities: The park is home to indigenous tribes such as the Tai Phake, Khamti, and Singpho, who have lived in harmony with the forest for generations.
In conclusion, the sighting of the marbled cat in Dehing Patkai National Park highlights the importance of conservation efforts in protecting this elusive species and its habitat. The park's rich biodiversity and indigenous cultures further emphasize the need for sustainable environmental practices.
GS1/Geography
Majuli Island
 Why in News?
Why in News?
A recent six-day survey has raised concerns regarding the increasing human-wildlife conflict (HWC) in the Majuli River Island district of Assam.
- Majuli is recognized as the world's largest river island.
- The island spans an area of 421 sq. km, located at the heart of Assam.
- It became the first island in India to be designated as a district in 2016.
Additional Details
- Geographical Features: Majuli is bordered by the Brahmaputra River to the south and the Kherkutia Xuti, an anabranch of the Brahmaputra, along with the Subansiri River to the north. Its landscape is marked by lush greenery, numerous water bodies, and expansive paddy fields.
- Cultural Significance: The island is a center of Assamese neo-Vaishnavite culture, which began in the 16th century with the influential Assamese saint-reformer Srimanta Sankerdeva and his disciple Madhavdeva. They established the tradition of Satras (monastic institutions) that have preserved various cultural elements such as Sattriya dance, literature, bhaona (theatre), mask-making, and boat-making.
- The majority of the island's residents belong to three tribes: Mishing, Deori, and Sonowal Kachari, while the remaining population consists of non-tribal Assamese.
- Majuli is renowned for its mask-making tradition and has a rich history of pottery making.
- Economy: The primary livelihood for the residents is rice cultivation, with unique varieties like Komal Saul and Bao Dhan being cultivated in the region.
This survey highlights the critical need to address the human-wildlife conflict to preserve the unique cultural and ecological heritage of Majuli Island.
GS2/Governance
Gond Tribes
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Gujarat High Court has recently requested responses from a power distribution company, the Ahmedabad district collector, and a residential society following an appeal by 95 families from the Rajgond tribe seeking directions for electricity connections to their homes.
- The Gond tribes are one of the largest tribal groups in India.
- They are primarily located in several Indian states, including Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh.
- The Gonds have a rich historical background, with significant contributions to Indian culture and governance.
Additional Details
- About Gond Tribe: The Gond, or Gondi, are a Dravidian ethno-linguistic group, with a population of nearly 11 million according to the 2001 census.
- Distribution: The majority of Gond populations are found in the states of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, and Odisha, with smaller communities in Uttar Pradesh, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Karnataka, Jharkhand, and West Bengal.
- Sub-groups: The Gonds are divided into four main tribes: Raj Gonds, Madia Gonds, Dhurve Gonds, and Khatulwar Gonds.
- History: The Gonds settled in the Gondwana region between the 9th and 13th centuries AD and ruled parts of central India in the 14th century, constructing forts, palaces, and temples.
- Language: Most Gond people speak dialects of Gondi, an unwritten Dravidian language, although some have adopted local languages such as Hindi, Marathi, or Telugu.
- Economy: The Gond economy is primarily based on agriculture, supplemented by animal husbandry and gathering wild plants.
- Religion: Gond religious beliefs center around clan and village gods, along with ancestor worship, with important festivals like Keslapur Jathra and Madai, as well as Hindu celebrations such as Dusshera.
This situation highlights the ongoing challenges faced by tribal communities in accessing basic services like electricity, which is crucial for their development and integration into the broader society.
GS3/Environment
What is Wallace Line?
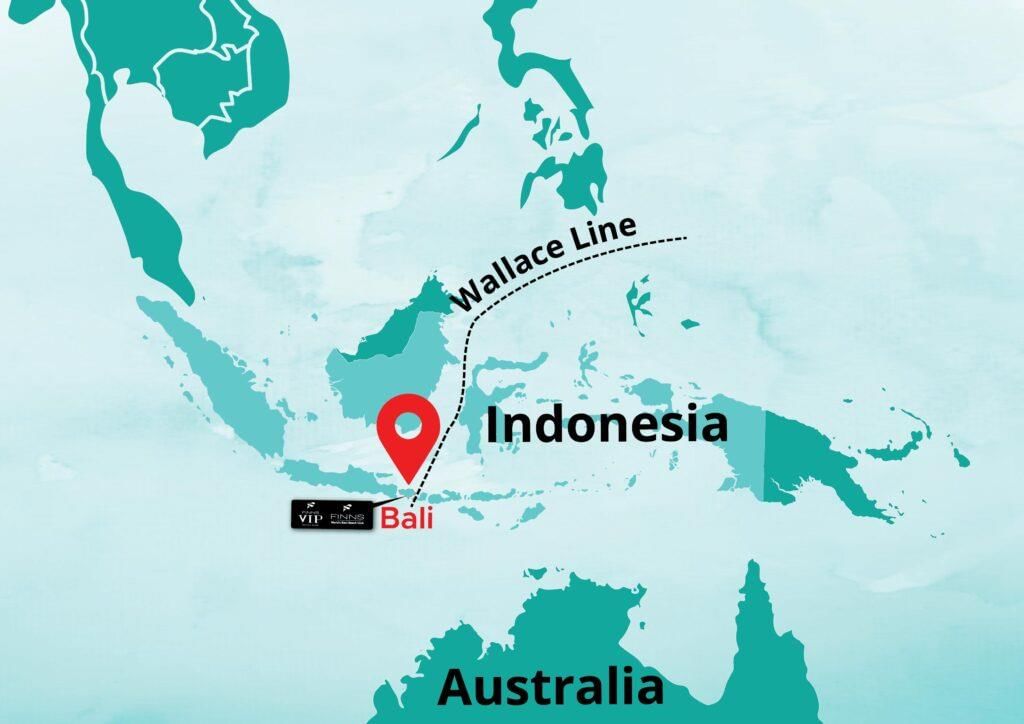 Why in News?
Why in News?
In the 19th century, the English naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace made a significant observation regarding biodiversity. As he traveled from Asia to Australia, he noted a distinct shift in species, which led him to propose an imaginary boundary known as the Wallace Line that separates the flora and fauna of these two regions.
- The Wallace Line serves as a bio-geographical boundary between Asia and Australia.
- Identified by Alfred Russel Wallace in 1863, it runs through the Lombok Strait and the Makassar Strait.
- Species on either side of the line have distinct evolutionary histories.
Additional Details
- Boundary Characteristics:
West of the line (Asia): Species such as tigers, elephants, and orangutans are found.
East of the line (Australia): Species like kangaroos, marsupials, and cockatoos are prevalent.
- Species Migration: Very few species, particularly birds and mammals, are known to cross the Wallace Line. This line acts as a barrier for land species but does not affect marine life.
- Formation Factors:
- Continental Drift: Australia separated from Antarctica about 35 million years ago, creating a deep-water channel that hindered species migration.
- Pleistocene Epoch Influence: Lower sea levels during this epoch exposed land bridges, but deep waters helped maintain the boundary.
- Scientific Relevance: The Wallace Line is considered more of a gradient than a strict boundary, aiding in the understanding of biogeography and predicting species adaptation to climate change.
- Comparison with Weber Line: The Weber Line provides a more accurate definition of the balance point where the influences of Asian and Australian species are nearly equal, while the Wallace Line marks a sharper division.
Understanding the Wallace Line is crucial for comprehending the biodiversity of the regions it separates and provides insights into the evolutionary processes that shape species distribution.
GS3/Science and Technology
Introduction of Dragon Copilot
Why in News?
Microsoft has recently launched a new voice-activated AI assistant named Dragon Copilot, which is integrated into Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare. This innovative tool aims to streamline the workflow of healthcare professionals by assisting in clinical documentation and information retrieval.
- Dragon Copilot is designed specifically for healthcare professionals.
- It utilizes advanced natural language processing and ambient listening technologies.
- The tool integrates with existing healthcare documentation systems.
Additional Details
- Natural Language Voice Dictation: Dragon Copilot employs sophisticated voice dictation technology from Nuance, enabling users to transcribe clinical notes and draft necessary paperwork efficiently.
- AI-Generated Notes: In addition to voice-to-text capabilities, users can create personalized notes by utilizing prompts or templates, enhancing the documentation process.
- Integrated Functionality: The assistant not only aids in documentation but also allows clinicians to search for medical information from reliable sources, ensuring comprehensive support in a centralized workspace.
- Dragon Copilot facilitates the automation of key tasks such as generating referral letters, after-visit summaries, and clinical evidence summaries, all while being accessible via mobile, desktop, or browser.
- It seamlessly integrates with various electronic health records, making it a versatile tool for healthcare settings.
In summary, Dragon Copilot represents a significant advancement in healthcare technology, aimed at enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of clinical documentation while providing valuable support to healthcare professionals.
GS2/International Relations
World Food Programme Closes Southern Africa Office
Why in News?
The World Food Programme (WFP), a key agency of the United Nations focused on eradicating hunger and promoting food security, is closing its southern Africa office in response to recent aid cuts by the Trump administration.
- The WFP operates in over 120 countries, providing food assistance during emergencies.
- The agency has been active in India since 1963 and collaborates with communities to improve nutrition and resilience.
- Funding for the WFP comes from voluntary donations from governments, corporations, and private donors.
- It is recognized as the largest humanitarian agency working to save lives in emergencies.
Additional Details
- Global Report on Food Crises: This report outlines the extent of acute hunger worldwide and analyzes the factors contributing to food crises. It is produced by the Global Network against Food Crises, which aims to tackle the root causes of extreme hunger.
- The WFP's mission includes helping communities achieve self-sufficiency and resilience to shocks.
The closure of the southern Africa office highlights the challenges faced by humanitarian organizations in light of funding cuts, further exacerbating the issue of food insecurity in the region.
GS3/Economy
Navratna Status for IRCTC and IRFC
Why in News?
The Indian Railway Catering and Tourism Corporation (IRCTC) and the Indian Railway Finance Corporation (IRFC) have recently been awarded Navratna status, becoming the 25th and 26th companies in India to achieve this prestigious recognition.
- IRCTC and IRFC are now recognized as Navratna companies.
- This status enhances their operational and financial independence.
- They join other significant Navratna companies within the Indian Railways sector.
Additional Details
- Navratna Status: Introduced in 1997, the Navratna scheme identifies high-performing Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs) and grants them greater financial and operational autonomy, enabling them to compete on a global scale while still being publicly owned.
- Categories of PSUs in India:
- Maharatna: The largest CPSEs with the highest financial powers.
- Navratna: Mid-tier CPSEs granted strategic autonomy.
- Miniratna: Emerging CPSEs with limited independence.
- Eligibility Criteria for Navratna Status: A CPSE must be a Miniratna-I company with an excellent rating in its Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) performance for three out of five years, and achieve a composite score of 60+ based on several financial metrics.
- Benefits of Navratna Status:
- Investment Autonomy: Can invest ₹1,000 crore or 15% of net worth in a single project without government approval.
- Strategic Expansion: Freedom to form joint ventures, subsidiaries, and pursue acquisitions.
- Operational Flexibility: Ability to make independent business and investment decisions.
- Enhanced Market Position: Attracts more investors and improves stock performance.
In summary, the Navratna status granted to IRCTC and IRFC marks a significant step in enhancing the operational capabilities of these enterprises, fostering a competitive edge in the global market while maintaining public sector ownership.
|
55 videos|5389 docs|1141 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 5th March 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is Ruellia elegans and how does it threaten native biodiversity? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the Wallace Line in biodiversity studies? |  |
| 3. What are the main features and cultural importance of Majuli Island? |  |
| 4. How does the UAE-India Aviation Partnership contribute to economic growth? |  |
| 5. What are the ecological and cultural roles of the Gond tribes in India? |  |
















