UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 15th March 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Science and Technology
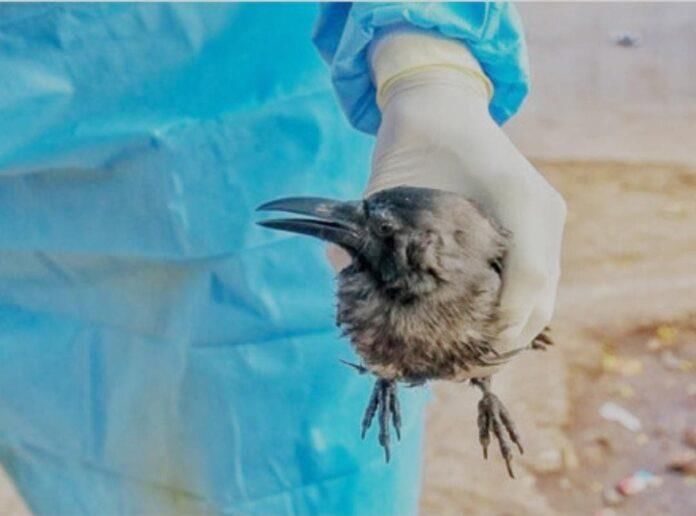
Bird Flu is Spreading in Bihar
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Bihar is currently grappling with an outbreak of bird flu; however, the state lacks a dedicated facility to test and confirm cases of this virus.
- The H5N1 strain of bird flu is highly contagious and has affected both birds and some mammals.
- First detected in China in 1996, H5N1 has since spread globally, including significant outbreaks in India.
- Climate change is worsening the spread of the virus by altering bird migration patterns.
Additional Details
- H5N1 Bird Flu: This avian influenza virus is known for its high pathogenicity and has led to outbreaks in various regions worldwide, including India where the first significant outbreak occurred in Maharashtra and Gujarat in 2015.
- Impact on Wildlife: The virus has primarily affected wild birds, particularly endangered species like the California condor, and has also begun to infect marine mammals such as sea lions and dolphins.
- Human Risk: While direct human infections are rare and typically occur through close contact with infected birds, experts have raised concerns about potential mutations that could facilitate human-to-human transmission in the future.
In summary, the ongoing bird flu outbreak in Bihar highlights the need for improved testing facilities and monitoring systems to combat the spread of H5N1 and protect both animal and human health.
GS2/Governance
Pradhan Mantri Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM)
Why in News?
The Delhi government is preparing to sign a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare to implement the Pradhan Mantri Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM).
- The scheme has a total outlay of Rs. 64,180 Crores for the period of 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- PM-ABHIM aims to reform and enhance health service delivery and public health actions across India.
- It focuses on strengthening health systems to provide comprehensive care at all levels: primary, secondary, and tertiary.
- The mission prepares health systems for effective responses to current and future health emergencies.
Additional Details
- Components of the Scheme:
- Construction of 17,788 sub-centres as Ayushman Bharat-Health & Wellness centres, now referred to as Ayushman Arogya Mandir (AAM).
- Establishment of 11,024 Health & Wellness Centres in urban areas, particularly targeting slum and slum-like regions.
- Creation of 3,382 Block Public Health Units (BPHUs) at the block level.
- Setting up of 730 District Integrated Public Health Labs (IPHL) across the country, ensuring each district has one lab.
- Establishing 602 Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs) in districts with a population exceeding 500,000.
- The CSS components of PM-ABHIM will be implemented using the existing framework and institutions under the National Health Mission.
- While public health and hospitals are under State jurisdiction, the implementation of the scheme falls under the State Government, with the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) providing necessary technical and financial support.
- Awareness generation and information, education, and communication (IEC) activities for the scheme will be conducted periodically by the State health department alongside other public health programs.
This initiative is a significant step toward enhancing the healthcare infrastructure in India, ensuring better health services for the population, especially in underserved areas.
GS2/Polity
Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry (APAAR) ID
Why in News?
The introduction of the Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry (APAAR) ID for school students has raised concerns among parents and activists. While the Ministry of Education has stated that the program is voluntary, there are fears that opting out may become increasingly difficult.
- The APAAR ID is a specialized identification system for students in India.
- This initiative is part of the 'One Nation, One Student ID' program, aligned with the National Education Policy of 2020.
Additional Details
- APAAR ID: This system assigns a unique and permanent 12-digit ID to every student, which consolidates their academic achievements, including degrees, scholarships, and awards.
- The APAAR ID serves as a lifelong academic passport, ensuring a seamless transition through different levels of education.
- How APAAR Works:
- Schools: Manage students' academic data and achievements within the APAAR framework.
- Higher Education Institutions (HEIs): Access students' academic records for admission and recruitment.
- Students: Can digitally store and retrieve their comprehensive academic and co-curricular accomplishments.
- Benefits to Students:
- Unified Academic Identity: A single platform to showcase academic records.
- Streamlining Student Records: Simplifying record-keeping for all stakeholders.
- Digital Repository: Securely storing academic data.
- Seamless Academic Mobility: Facilitating transitions between educational levels.
- Data Security and Confidentiality: Information is shared only with necessary government agencies, ensuring privacy.
- Academic Progress Tracking: Allows students to monitor their academic journey and adapt their study plans accordingly.
- Enrolment Process: The enrolment will be conducted by schools with parental consent, which can be withdrawn at any time.
- The government has pledged that student data will only be shared with relevant agencies when necessary, and all data will be stored in a centrally functioning District Information for Education portal.
In summary, while the APAAR ID aims to streamline academic records and enhance data security, concerns about its voluntary nature and potential for mandatory implementation remain a significant issue among parents and advocates.
GS3/Science and Technology
SpaDeX Mission Achievements
Why in News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has recently marked a significant milestone in space exploration with the successful undocking of two satellites as part of the Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) mission. This achievement highlights India's advancements in in-space docking technology.
- The SpaDeX mission successfully undocked two satellites on March 13, 2025, in a low-Earth orbit.
- India becomes the fourth nation globally to achieve in-space docking capabilities.
- The mission serves as a precursor to future space exploration initiatives, including lunar missions.
Additional Details
- SpaDeX Mission: This mission is designed as a cost-effective technology demonstrator for in-space docking. It involves two small spacecraft, SDX01 (the Chaser) and SDX02 (the Target), both launched by the PSLV-C60.
- Objectives:The primary goal is to develop technology for rendezvous, docking, and undocking operations. Secondary objectives include:
- Transfer of electric power between docked spacecraft, vital for future applications like in-space robotics.
- Composite spacecraft control and payload operations post-undocking.
- Recent Developments: The undocking occurred at an altitude of 460 km with a 45-degree inclination, and both satellites are now functioning independently with normal health status.
This successful operation not only demonstrates ISRO's capabilities in space technology but also sets the stage for India's future endeavors in space exploration, including potential lunar missions and establishing a Bharatiya Antariksha Station.
GS3/Science and Technology
Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs)
Why in News?
Recent observations by scientists from the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) have documented a flareless coronal mass ejection (CME) using the Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC) instrument aboard the Aditya-L1 mission, which is India's inaugural scientific endeavor aimed at solar studies.
- CMEs are large-scale ejections of solar plasma and magnetic fields from the Sun's corona.
- They can significantly affect Earth's magnetosphere and lead to various phenomena.
Additional Details
- Causes of CMEs:
- Intense magnetic field activity in the Sun's corona.
- Reconnection of magnetic field lines, which results in explosive energy releases.
- Increased solar activity, particularly during solar maximum phases of the 11-year solar cycle.
- Impacts of CMEs on Earth:
- Geomagnetic Storms: Interaction with Earth's magnetosphere can trigger geomagnetic storms, disrupting satellite communications and GPS signals.
- Auroras: Charged particles from CMEs collide with Earth's atmosphere, producing brilliant auroras, commonly known as the Northern and Southern Lights.
- Disruptions in Power Grids & Communication: Intense CMEs can generate electric currents in power grids, risking large-scale blackouts and disruption of HF radio communications.
- Satellite Damage: Increased radiation from CMEs can impair satellite operations or cause permanent damage.
- Health Risks to Astronauts: Increased radiation exposure poses health risks to astronauts operating in space during CME events.
In conclusion, understanding CMEs is crucial for mitigating their potentially harmful effects on technology and human activities on Earth.
GS2/Governance
Mission Amrit Sarovar
Why in News?
The Indian Railways is set to play a crucial role in the Union government's Mission Amrit Sarovar, a significant initiative aimed at combating the pressing issue of water scarcity across the nation.
- Launched in 2022, the mission aims to construct or rejuvenate 75 Amrit Sarovars (ponds) in each district, totaling 50,000 across India.
- Each Amrit Sarovar will cover a pondage area of at least 1 acre, with a water holding capacity of approximately 10,000 cubic meters.
Additional Details
- Community Involvement: The site for each Amrit Sarovar will be approved by a special Gram Sabha, which will also designate a Panchayat Partinidhi to supervise development efforts.
- Focus Areas: The initiative emphasizes water conservation, community participation, and the effective use of soil excavated from water bodies to support related infrastructure projects.
- Collaborative Approach: It operates on a "Whole of Government" approach, involving multiple ministries, including the Ministry of Rural Development and the Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- Financial Aspects: There is no separate financial allocation for Mission Amrit Sarovar, indicating a reliance on existing resources.
- Technical Support: The Bhaskar Acharya National Institute for Space Application and Geo-informatics (BISAG-N) has been appointed as a technical partner, overseeing the mission's implementation.
- Monitoring Tools: The progress of the mission will be tracked through the Amrit Sarovar Portal and Mobile App developed by BISAG-N.
Mission Amrit Sarovar represents a critical step towards addressing India's water crisis, particularly in rural areas, by fostering sustainable water management practices and encouraging community involvement in local governance.
GS3/Science and Technology
Centre Makes 'Quantum Hub' Operational
Why in News?
The Government of India has launched four Thematic Hubs (T-Hubs) dedicated to quantum computing research. Uttar Pradesh has received the highest allocation of ₹28.7 crore for quantum technology development in FY 2024-25, followed by Karnataka, Maharashtra, Delhi, and Tamil Nadu.
- Thematic Hubs (T-Hubs) are specialized research centres established under the National Quantum Mission (NQM).
- Four T-Hubs have been established in leading academic institutions focusing on various domains of quantum research.
Additional Details
- Quantum Hubs:These hubs are designed to drive innovation, research, and development in quantum technology. The specific areas of focus include:
- Quantum Computing: Located at IISc Bengaluru.
- Quantum Communication: Located at IIT Bombay.
- Quantum Sensing & Metrology: Located at IIT Delhi.
- Quantum Materials & Devices: Located at IIT Madras.
- Management Coordination: IIT Kanpur serves as the management coordinating center, overseeing administration and funding allocation.
- The hubs operate across 17 States and 2 Union Territories, with 14 technical research groups collaborating on various projects.
The National Quantum Mission (NQM) was launched by the Union Cabinet on April 19, 2023, with a total budget of ₹6,003.65 crore for a period of eight years (2023-2031). It is implemented by the Department of Science & Technology (DST), Ministry of Science & Technology. The mission aims to build intermediate-scale quantum computers, targeting:
- 20-50 qubits in 3 years,
- 50-100 qubits in 5 years, and
- 50-1,000 qubits in 8 years.
Additionally, it seeks to establish satellite-based quantum communication over 2,000 km within India, inter-city quantum key distribution (QKD), and multi-node quantum networks.
GS2/Governance
The Gender Budget: Bigger Allocations, Little Impact
Why in News?
The Union Budget 2025-26 has received attention for its increased financial allocations towards women-centric schemes, with the gender budget escalating to ₹4.49 lakh crore, marking a substantial 37.25% increase compared to the previous fiscal year. However, the distribution of benefits has not been equitable, especially for marginalized women belonging to Scheduled Caste (SC) and Scheduled Tribe (ST) communities. This necessitates a critical evaluation of the gender budget’s effectiveness, focusing on its shortcomings, structural barriers, and feasible solutions to enhance its impact.
- The gender budget reflects the government’s intent to bridge gender disparities, yet the economic benefits have not reached women proportionately, particularly marginalized groups.
- Targeted schemes like the PM Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM JANMAN) have had limited impact on SC/ST women.
- Lack of an intersectional approach in budgeting has hindered effective implementation.
Additional Details
- Digital Exclusion: Many women, particularly in rural and tribal regions, lack digital literacy, which obstructs their access to welfare benefits. Without investment in digital literacy programs, the push towards digitization may create new barriers.
- Outdated Census Data: The last Census conducted in India was in 2011, leading to policy decisions based on outdated data. This gap undermines accountability and complicates the assessment of fund allocation effectiveness.
- Bureaucratic Inefficiencies: Over 35% of funds earmarked for SC and ST Sub-Plans remain underutilized due to complex procedures and inadequate community involvement.
To reform the gender budget and ensure it serves as a tool for empowerment rather than a symbolic gesture, it is crucial to adopt an intersectional approach, strengthen local governance, and improve data transparency. Addressing structural barriers like digital exclusion and bureaucratic inefficiencies will be essential in achieving tangible benefits for marginalized women, particularly from SC/ST backgrounds.
GS2/Governance
A School Closure That Must be Called Out
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The decision to close the only Gondi-medium school in a village in Maharashtra raises crucial questions regarding the preservation of linguistic and cultural rights, the power dynamics in education policies, and the socio-political neglect of Adivasi communities. While the official rationale for the closure revolves around procedural aspects, a deeper analysis indicates a historical bias against tribal languages and cultures.
- The closure of the Gondi-medium school in Mohgaon village poses significant threats to linguistic diversity.
- Constitutional provisions exist to protect minority languages, yet these are often overlooked in practice.
- The non-recognition of tribal languages reflects systemic biases and historical marginalization of Adivasi communities.
Additional Details
- Constitutional Safeguards: The establishment of the Gondi-medium school aligned with Article 29 of the Indian Constitution, which guarantees minorities the right to preserve their distinct languages, scripts, and cultures. Article 350(a) further mandates provisions for education in the mother tongue.
- Political Context: The closure is justified by the administration's claim of non-registration under the Right to Education (RTE) Act. However, this raises concerns about the deeper implications of power dynamics and systemic bias against tribal education.
- Impact of Modernisation: Forces of modernisation and market-driven economies have accelerated the decline of Adivasi languages, pushing younger generations to abandon their native tongues for dominant regional languages.
- Urgency of Preservation: With Adivasi languages primarily existing in oral form, their extinction poses a significant risk, as the knowledge systems tied to these languages are vulnerable to loss.
The preservation of Adivasi languages is a critical issue that combines elements of constitutional rights, cultural preservation, and social justice. The state's failure to recognize and support these languages is indicative of broader societal neglect. Proactive measures are necessary to reverse the trend of linguistic decline, ensuring that India remains a pluralistic society that values and nurtures all its cultures.
GS2/International Relations
UN80 Initiative
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The UN Secretary-General, Antonio Guterres, has introduced the 'UN80 Initiative' as the United Nations approaches its 80th anniversary. This initiative addresses significant global challenges, including a liquidity crisis and resource constraints, amidst a climate of uncertainty.
- The UN80 Initiative is a reform program aimed at improving the efficiency and responsiveness of the UN.
- It seeks to identify operational inefficiencies and enhance the implementation of mandates from member states.
- The initiative will be led by Under-Secretary-General Guy Ryder and involves all UN entities globally.
Additional Details
- Objectives: The initiative focuses on optimizing operations, reviewing mandate implementations, and conducting structural evaluations within the UN system.
- Challenges: The UN is currently facing escalating conflicts, poverty, human rights issues, and difficulties stemming from unregulated technologies such as artificial intelligence.
- The liquidity crisis has persisted for over seven years, largely due to inconsistent payments from member states.
The UN80 Initiative aims to address these pressing challenges and improve the overall functionality of the UN as it prepares for its future.
|
52 videos|5374 docs|1136 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 15th March 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What measures are being taken to control the spread of Bird Flu in Bihar? |  |
| 2. What is the Pradhan Mantri Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM)? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry (APAAR) ID? |  |
| 4. What are the achievements of the SpaDeX Mission? |  |
| 5. How does the Gender Budget aim to create an impact despite larger allocations? |  |





















