UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 23th March 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Economy
Parliamentary Panel Recommends Increased Fertilizer Subsidy and Domestic Production
Why in News?
The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Chemicals and Fertilizers has urged the Union Fertilizers Ministry to seek additional funding to facilitate the effective implementation of fertilizer subsidy schemes aimed at supporting farmers.
- The Committee recommends additional budget allocations to avoid negative impacts on farmers.
- It suggests expanding the production capacity of Nano Urea and Nano DAP fertilizers.
- There is a push for self-sufficiency in fertilizer supply through domestic mining initiatives.
- Concerns regarding underutilization of funds were highlighted.
- The continuation of the Urea Subsidy Scheme was emphasized due to its critical role in food production.
Additional Details
- Need for Additional Budget Allocation: The Committee stressed the importance of requesting more funds during the revised estimate stage to prevent adverse effects on farmers. The projected budget for the Department of Fertilizers for 2025-26 was ₹1,84,704.63 crore, which was cut by 7.38% to ₹1,71,082.44 crore, impacting the Nutrient-Based Subsidy (NBS) and Urea Subsidy Schemes.
- Expansion of Nano Fertilizer Production: Recommendations include increasing the production capacity of Nano Urea and Nano DAP, emphasizing timely establishment of production units to ensure availability and promoting these fertilizers among farmers due to their potential to enhance crop yields.
- Self-Sufficiency in Fertilizer Supply: The Committee noted the need for domestic exploration and production through mining lease agreements, highlighting that investment from government and private sectors is essential for achieving self-reliance.
- Addressing Underutilization of Funds: The Committee identified that significant portions of allocated funds were not utilized in 2024-25, including 20% under indigenous Phosphorus & Potassium fertilizers, and recommended full utilization of these funds for effective scheme implementation.
- Continuation of the Urea Subsidy Scheme: The importance of continuing the Urea Subsidy Scheme was reiterated due to urea's critical role in food grain production.
The recommendations from the Committee aim to ensure self-sufficiency in fertilizer production, continuity of subsidies, and enhanced agricultural productivity through advanced fertilizers like Nano Urea and Nano DAP. These initiatives focus on making fertilizers affordable, reducing dependency on imports, and promoting sustainable agricultural practices, which are vital for maintaining soil fertility and ensuring food security.
GS2/International Relations
India’s Push for Global Ban on Sikhs for Justice (SFJ) and the Challenges Ahead
Why in News?
During the Raisina Dialogue, the Indian government reaffirmed its call for a ban on the separatist group Sikhs for Justice (SFJ) in the United States and New Zealand. This comes as SFJ plans to conduct a "referendum" in Los Angeles on March 23, 2025, to garner support from the Sikh diaspora for its secessionist agenda.
- India is advocating for an international ban on SFJ amidst concerns about its separatist activities.
- SFJ is organizing a referendum in the U.S. to promote its agenda, raising questions about its legitimacy.
- Challenges exist in securing a ban due to differing international perspectives on free speech.
Additional Details
- India’s Diplomatic Efforts: Prime Minister Modi raised issues regarding anti-India activities during talks with New Zealand's PM Christopher Luxon, while Defence Minister Rajnath Singh urged the U.S. to classify SFJ as a terrorist entity.
- Legitimacy of SFJ Referendums: SFJ has held referendums in Western nations, which are criticized for their unverifiable voter identities, questioning their legitimacy.
- International Responses: New Zealand’s PM highlighted the nation's commitment to free speech, while the U.S. and Canada have shown caution due to past investigations linking Indian agents to threats against Khalistani activists.
- Potential Legal Designations: The U.S. could designate SFJ as a Foreign Terrorist Organization (FTO), which would lead to various legal actions including asset freezes. Similar actions are possible in the U.K. and Canada under their respective terrorism laws.
- Concerns Over Extremism: India has drawn parallels to historical events, warning that neglecting SFJ's activities might lead to serious security ramifications, similar to past incidents involving extremist groups.
In summary, while India continues to push for a global ban on SFJ to curb its influence, it faces significant challenges due to varying international views on free speech and the complexities of diplomatic relations. The situation remains dynamic, with implications for both India's security and international relations.
GS3/Science and Technology
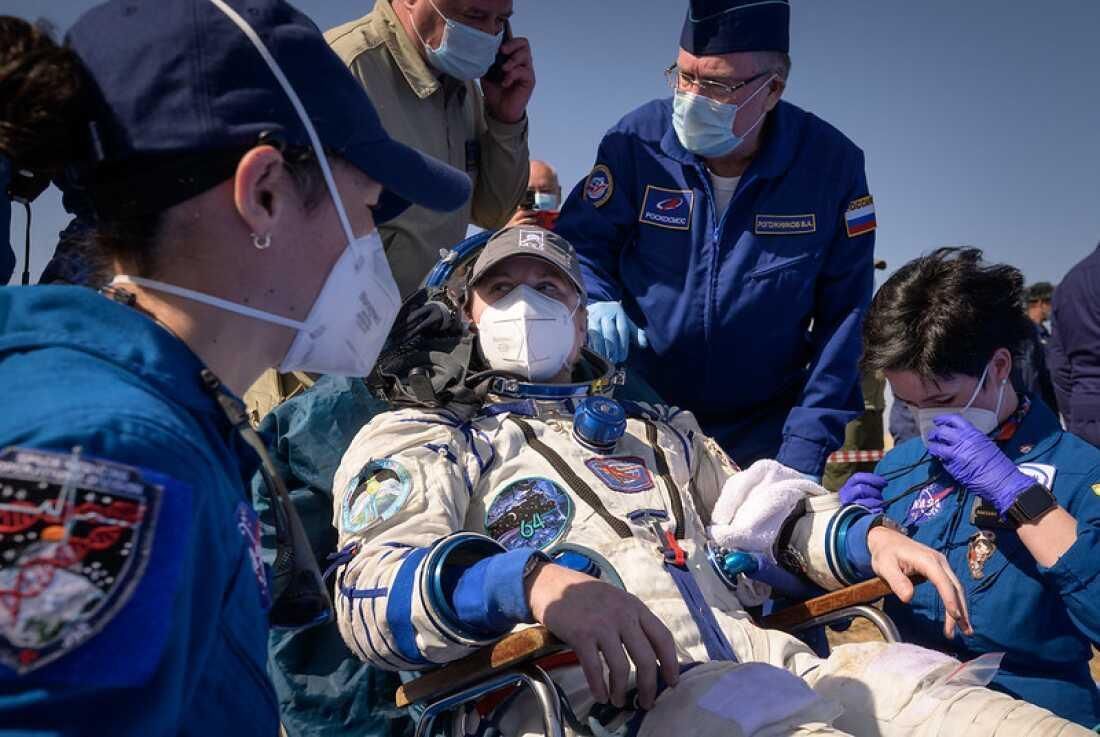
Astronauts' Recovery Process After Space Missions
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, a SpaceX capsule safely returned to Earth, carrying astronauts Sunita Williams, Barry Wilmore, Aleksandr Gorbunov, and Nick Hague, after their mission aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Ms. Williams and Mr. Wilmore spent nine months on the ISS, having arrived in June via Boeing’s Starliner capsule. NASA has established a structured recovery regimen for its astronauts, while Mr. Gorbunov follows the recovery protocols of Russia's Roscosmos.
- Astronauts experience various physiological changes due to extended spaceflight.
- Post-flight rehabilitation is critical for re-adapting to Earth's gravity.
- NASA and Roscosmos have different recovery protocols in place for their astronauts.
Additional Details
- Effects of Microgravity: Extended stays in space lead to fluid shifts, muscle weakening, and reduced bone density, which necessitate strict exercise and diet routines during missions.
- Monitoring of Astronauts: Astronauts undergo regular health assessments and psychological evaluations to manage both physical and mental well-being during long-duration missions.
- Rehabilitation Program: After returning, astronauts begin a rehabilitation program tailored to their individual needs, focusing on regaining fitness and strength.
- Recovery Timeline: Most astronauts regain their pre-flight fitness within 45 days, but some may require longer rehabilitation based on their recovery progress.
The recovery process is essential for ensuring that astronauts can readjust safely to life on Earth after exposure to microgravity. This involves a combination of medical assessments, physical therapy, and psychological support to address both the physical and mental challenges faced after long space missions.
GS2/Polity
Challenges in Uploading Voting Data: A Closer Look at Form 17C and Electoral Transparency
 Why in News?
Why in News?
In May 2024, during the Lok Sabha elections, the Supreme Court addressed a petition urging the Election Commission of India to publish booth-wise voter turnout data from Form 17C on its website within 48 hours after voting.
- The Supreme Court heard a petition from the Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR) demanding transparency in voter turnout data.
- The Election Commission of India (ECI) has been resistant to publishing this data publicly, citing legal obligations.
- Recent discrepancies in voter turnout figures have prompted discussions about potential policy changes.
Additional Details
- Form 17C: This is a two-part document required under the Conduct of Election Rules, 1961, filled out at every polling station. In 2024, there were over 10.5 lakh polling stations, leading to a vast amount of data.
- Part 1: This section, filled by the presiding officer, includes crucial data such as the booth’s EVM identification number, total electors, votes cast, and any discrepancies. Each copy is signed by polling agents before being sent to the returning officer.
- Part 2: Completed on counting day, it details candidate-wise vote counts and verifies if these align with what was recorded in Part 1, including necessary signatures from officials and candidate representatives.
- Opposition Demands: Activists and opposition parties are calling for the prompt online publication of Part 1 of Form 17C to ensure transparency, facilitate verification of vote counts, prevent manipulation, and bolster public trust in EVMs.
- ECI's Position: The ECI contends that it is not legally required to publish Form 17C online, as it only needs to share it with polling agents. They also express concerns about potential misuse of data if published online.
- Logistical Challenges: With 1 crore polling personnel and high-stress environments, data entry errors are likely. Post-election verification of data can lead to delays.
- Way Forward: Advocates suggest digitizing and publishing Form 17C data after verification, improving public access with safeguards, clarifying legal obligations of the EC, and creating a centralized database to enhance electoral transparency.
In conclusion, addressing the challenges associated with uploading voting data is crucial for enhancing electoral transparency and restoring public confidence in the electoral process in India.
GS3/Environment and Ecology
Dog-Faced Water Snake
Why is it in the News?
A dog-faced water snake has been spotted in Northeast India for the first time, well beyond its usual coastal habitat.
About the Dog-Faced Water Snake
- Scientific Classification:
- Family: Homalopsidae (Indo-Australian rear-fanged water snakes)
- Habitat: Typically found in mangroves, coastal mudflats, and estuarine environments across Southeast Asia and northern Australia. In India, it has been recorded in coastal areas such as Gujarat, Maharashtra, Kerala, Odisha, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Physical Characteristics:
- Length: Can grow up to about 1 meter.
- Head and Snout: Wide head and snout, giving it a "dog-faced" appearance.
- Coloration: Striped and dark brown with a white underbelly.
Behavior and Diet:
- Feeding: Hunts fish and crustaceans in shallow waters using a "sit-and-wait" strategy to ambush prey.
- Activity: Spends most of its life in water.
- Adaptation: Possesses salt glands that allow it to expel salt, enabling survival in marine environments.
Movement:
- Swimming: Well-adapted for swimming in slow-moving, shallow, and murky waters.
- On Land: Moves quickly by sidewinding on soft mud.
Conservation Status:
- Classified as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List.
GS3/ Environment and Ecology
Sheathia rosemalayensis
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Researchers have recently discovered a new species of freshwater algae called 'Sheathia rosemalayensis' in Rosemala, located in the Kollam district of Kerala.
About Sheathia rosemalayensis
- New Species: Sheathia rosemalayensis is a newly identified species of freshwater algae.
- Discovery Location: It was found in Rosemala, situated in the Western Ghats of Kerala. The species is named after this location.
- Rarity in India: The discovery is significant because species of the Sheathia genus are extremely rare in India. Prior to this, only one other Sheathia species was reported from the Himalayas.
- Geographical Distinction: Sheathia rosemalayensis has been documented only in the southern Western Ghats, a region with distinct geographical characteristics. In contrast, other Sheathia species like S. assamica, S. indonepalensis, and S. dispersa have wider distributions, including areas like Assam, Nepal, Indonesia, Taiwan, and even the Hawaiian Archipelago.
What Are Algae?
- Definition: Algae are a diverse group of aquatic organisms capable of photosynthesis. They can be unicellular (single-celled) or multicellular, ranging from tiny phytoplankton to large seaweeds like kelp.
- Structure: Algae do not have true roots, stems, or leaves, and they lack vascular tissues, which differentiates them from plants.
- Familiar Examples: Many people are familiar with certain types of algae, such as seaweeds (like kelp), pond scum, and algal blooms in lakes.
- Importance: While some algae are well-known, there is a vast and varied world of algae that is not only helpful to humans but also critical for our existence.
GS2/Polity and Governance
Doctrine of Precedent
Why is it News?
The Kerala High Court has recently reiterated that tax assessment orders made without considering binding precedents set by higher courts are a violation of the doctrine of precedent and are therefore unsustainable.
Understanding the Doctrine of Precedent
The doctrine of precedent, also known as 'stare decisis', is a principle followed by courts to maintain consistency in legal decisions. When a court decides on a point of law, that decision should be applied to future cases with similar facts.
- Binding Nature: Lower courts are required to follow the decisions made by higher courts. This ensures that similar cases are treated alike, promoting fairness and stability in the legal system.
- Article 141 of the Indian Constitution: The foundation of this doctrine in India is Article 141, which states that the law declared by the Supreme Court is binding on all courts within the country. Lower courts must adhere to the legal interpretations and judgments provided by the Supreme Court.
- Ratio Decidendi: This refers to the legal reasoning that constitutes the binding part of a judgment. Courts are obligated to follow this in similar cases to ensure uniformity in legal applications.
- Obiter Dicta: These are non-essential remarks made by the court during a judgment. While they are not binding, they can influence future cases and guide courts in their decisions.
Landmark Judgment: In the case of The State of Orissa v. Mamata Patnaik (1978), the Supreme Court highlighted the importance of following precedent in legal decisions. The court stressed that adhering to established legal principles is crucial for maintaining consistency in the application of law across similar cases.
GS1/Geography
Hemavathi River
Why in News?
Two young individuals tragically drowned while swimming in the Hemavati River close to Henli village in Sakleshpur.
Overview of the Hemavathi River- The Hemavathi River is a significant tributary of the Kaveri River.
- Origin: The river originates in the Western Ghats at an altitude of approximately 1219 meters above sea level, near Ballala Rayana Durga in the Chikmagalur District of Karnataka.
- Course: From its source, the river flows through the Tumkur and Hassan districts, where it is joined by its main tributary, the Yagachi River. It then continues into Mysore District before merging with the Kaveri River at Krishnarajasagara.
- Length and Drainage Area: The Hemavathi River is about 245 kilometers long, with a drainage area of approximately 5,410 square kilometers.
- Hemavati Reservoir:. masonry dam with a central spillway and earthen flanks, the Hemavati Reservoir is built across the river near Gorur village. It has a storage capacity of 37.1 tmcft. The water stored in this reservoir is used to irrigate 6.55 acres of land in the Mandya, Hassan, and Tumkur districts.
|
41 videos|5359 docs|1134 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 23th March 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the key recommendations made by the Parliamentary Panel regarding fertilizer subsidies? |  |
| 2. How is India addressing the issue of Sikhs for Justice (SFJ) and what challenges does it face? |  |
| 3. What recovery processes do astronauts undergo after returning from space missions? |  |
| 4. What is Form 17C and why is it significant in the context of electoral transparency? |  |
| 5. How can challenges in uploading voting data be resolved to enhance electoral integrity? |  |





















