UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 30th March 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Economy
Calls for GST 2.0 Grow Stronger Amidst Compliance Challenges and Refund Delays
Why in News?
A report to Parliament has prompted its Public Accounts Committee (PAC) to call for a thorough review of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) framework in India. The report highlights ongoing issues in GST implementation, which are affecting businesses, State finances, and the overall efficiency of the tax system.
- The PAC has recommended a comprehensive overhaul of the GST system, referred to as "GST 2.0."
- Transparency and timely audits in GST compensation disbursement to States remain critical concerns.
- Technical glitches and compliance complexities are causing delays in refunds, particularly impacting MSMEs and exporters.
- The absence of a functional GST Appellate Tribunal is causing legal bottlenecks in dispute resolution.
Additional Details
- Background: Introduced in 2017, India's GST aimed to unify the country's fragmented indirect tax system. However, a recent Parliamentary report reveals significant implementation challenges that persist nearly eight years later.
- Compensation to States: The PAC flagged the lack of transparency and audit in the disbursal of GST compensation, with the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) not auditing the GST Compensation Fund for over six years due to inadequate financial data.
- Compliance Complexities: Key issues include confusion over tax jurisdictions, unjustified cancellations of GST registrations, and delays in Input Tax Credit (ITC) refunds, which affect the cash flow of businesses.
- Institutional Reforms: The report emphasizes the need for a GST Appellate Tribunal to expedite dispute resolutions, as there are over 19,730 pending cases involving substantial tax implications.
- Way Forward: Recommendations include simplifying compliance, ensuring timely audits, and improving digital platforms for registrations and refunds.
In conclusion, while GST was intended to be a transformative indirect tax reform, ongoing implementation challenges have created hurdles for both businesses and State governments. Addressing these issues through a comprehensive overhaul and regular audits is essential for realizing the full potential of GST.
GS2/International Relations
Chicken’s Neck Corridor
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Bangladesh has invited China to participate in a river conservation initiative near the strategically important ‘Chicken’s Neck’ corridor, which serves as the vital link between India’s mainland and its northeastern states.
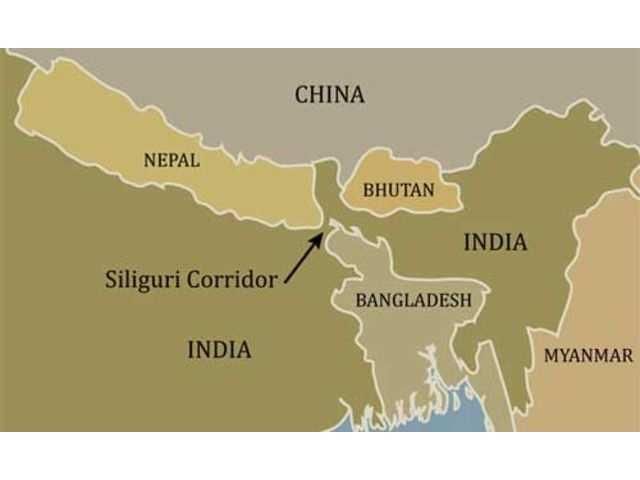
- The Chicken’s Neck, also referred to as the Siliguri Corridor, is a narrow strip of land in West Bengal.
- This corridor connects India's northeastern states to the rest of the country.
- Its geographical significance is heightened by its proximity to Nepal, Bhutan, and Bangladesh.
- Any disruption to this corridor could severely impact India's connectivity with its northeastern states.
Additional Details
- Geographic Significance: The corridor spans approximately 22 kilometers at its narrowest point, flanked by Nepal to the west, Bhutan to the north, and Bangladesh to the south.
- The Chicken’s Neck Corridor links the North-eastern Region (NER), consisting of eight states: Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, and Tripura, to mainland India.
- This region is geopolitically sensitive due to its strategic importance for military movements and logistics.
- In the event of conflict, there is a potential risk that China could target this corridor, thereby isolating India's northeastern states.
The significance of the Chicken’s Neck corridor highlights the need for careful diplomatic and strategic management in the region, particularly in light of the evolving relations between India, Bangladesh, and China.
GS2/International Relations
Operation Brahma: India's Humanitarian Response to Myanmar's Earthquake
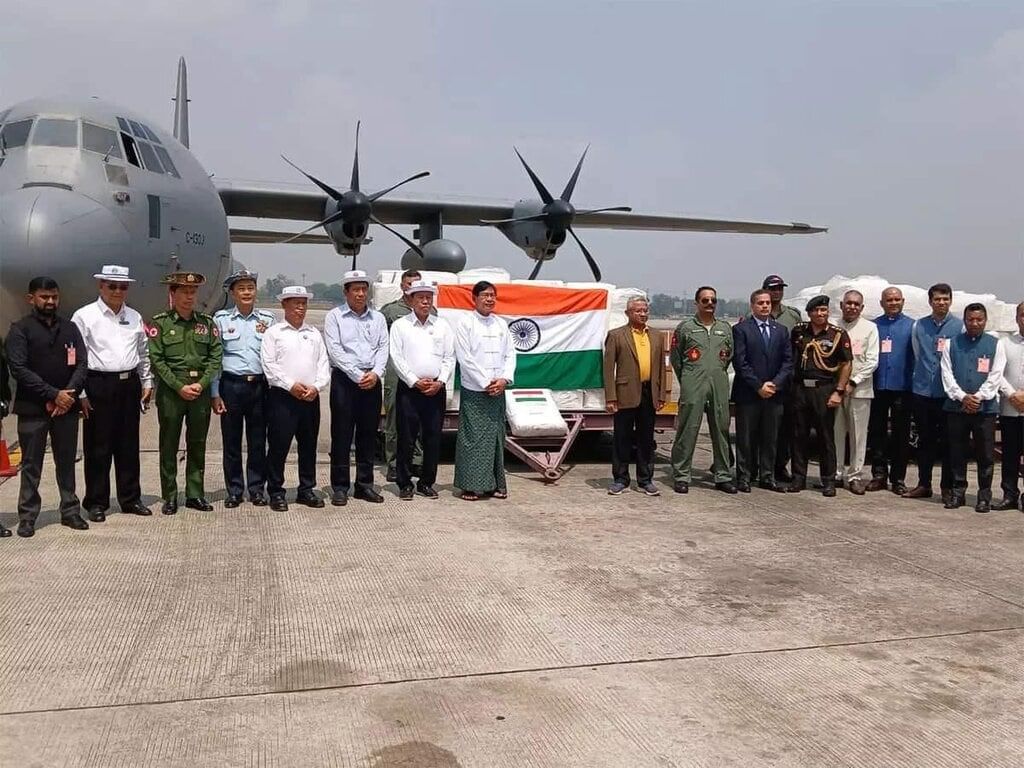 Why in News?
Why in News?
India has launched a significant humanitarian mission named Operation Brahma to aid Myanmar following a catastrophic earthquake. This initiative responds to the urgent need for relief and support after a devastating 7.7-magnitude earthquake struck the region on March 28, 2025.
- The earthquake resulted in over 1,600 fatalities and extensive destruction in Myanmar and neighboring Thailand.
- Operation Brahma encompasses rescue operations, medical assistance, and the distribution of relief supplies.
Additional Details
- National Disaster Response Force (NDRF): An 80-member team has been deployed with essential rescue equipment such as concrete cutters and drill machines.
- Indian Army's Involvement: A specialized 118-member medical team from the elite Shatrujeet Brigade Medical Responders is providing urgent humanitarian assistance.
- The Indian Army will establish a 60-bed Medical Treatment Centre to cater to trauma cases and emergency surgeries, supporting Myanmar's overwhelmed healthcare system.
- Two Indian naval ships, INS Satpura and INS Savitri, have been dispatched to deliver 40 tonnes of humanitarian aid to Yangon.
Operation Brahma underscores India's commitment to offering immediate support and relief to Myanmar during this challenging time, aiming to mitigate the humanitarian crisis worsened by the earthquake.
GS3/Environment
Kasampatty Sacred Grove: A New Biodiversity Heritage Site
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Tamil Nadu government has officially designated the Kasampatty (Veera Kovil) sacred grove as a Biodiversity Heritage Site, recognizing its ecological and cultural significance.
- The Kasampatty Sacred Grove is located in Kasampatti village, Dindigul District, Tamil Nadu.
- This site spans approximately 4.97 hectares and is surrounded by lush mango plantations.
- It is home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, including numerous species of plants, birds, and other wildlife.
- Kasampatty is the second site in Tamil Nadu to be recognized as a Biodiversity Heritage Site under the Biological Diversity Act, 2002.
Additional Details
- Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS): These are unique ecosystems characterized by rich biodiversity, which includes wild and domesticated species, high endemism, and the presence of rare or threatened species.
- The designation of BHS aims to enhance the quality of life for local communities through the conservation of significant ecological sites.
- The process for notifying BHS involves consultation between the State Government and local bodies, ensuring that local practices are respected unless voluntarily altered.
- The first BHS in India was the Nallur Tamarind Grove in Bengaluru, Karnataka, designated in 2007.
In summary, the declaration of Kasampatty Sacred Grove as a Biodiversity Heritage Site underscores the importance of conserving unique ecosystems and the benefits such conservation brings to local communities.
GS3/Environment
Amur Tigers
 Why in News?
Why in News?
A recent study published in Oryx has raised concerns about the increasing number of roadkill incidents involving Amur tigers. This trend poses a significant threat to their long-term survival in the wild.
- The Amur tiger, also known as the Siberian tiger, is classified as Endangered on the IUCN Red List.
- Population estimates suggest that there are between 265 and 486 Amur tigers in Russia, with a small population in China and potentially North Korea.
Additional Details
- Scientific Name: Panthera tigris altaica
- Habitat: These tigers primarily inhabit the birch forests of eastern Russia but can also be found in parts of China and North Korea.
- Diet: Being carnivorous, Amur tigers prey on large ungulates such as elk and wild boar.
- Size: They can grow up to 10.75 feet in length and weigh as much as 660 pounds.
- Lifespan: In the wild, Amur tigers live for about 10-15 years, while those in captivity can reach up to 20 years.
- Unique Adaptations: Their thick fur, large size, and lighter coat color are adaptations that help them survive in cold climates.
The ongoing threat from road infrastructure highlights the urgent need for conservation efforts to protect the Amur tiger population, ensuring their survival for future generations.
GS3/Science and Technology
Future Circular Collider (FCC)
Why in News?
The Future Circular Collider (FCC) is a proposed $30 billion project by CERN that has sparked considerable debate within the scientific community. The project aims to advance particle physics research significantly but comes with financial and strategic implications that have divided opinions among physicists.
- The FCC will feature a 91 km circular tunnel located beneath the Swiss-French border.
- Its goal is to achieve unprecedented particle collision energies, generating Higgs bosons in large quantities by around 2040, followed by high-energy proton collisions by 2070.
- The initial estimated cost is $30 billion, with ongoing funding considerations for future decades.
- Supporters, including CERN leadership and prominent physicists, argue it will be the most powerful tool for investigating fundamental aspects of nature.
- Critics express concern over potential funding shortages for other scientific endeavors due to the project's financial demands.
Alternative Proposals to FCC
- Linear Accelerators: These straight-line accelerators may provide a more cost-effective and flexible approach to particle physics research.
- Plasma Wave Technology: This innovative method uses plasma waves to accelerate particles in a compact design, potentially transforming collider technology within the next 20 years.
What is a Hadron?
- Hadrons: Subatomic particles comprised of quarks, held together by the strong nuclear force.
- Types of Hadrons:
- Mesons: Examples include pions and kaons.
- Baryons: An example is neutrons.
What is the Large Hadron Collider (LHC)?
- Location: Positioned on the Franco-Swiss border and operated by CERN.
- Size: A 27 km circular tunnel designed for high-energy proton collisions.
- Purpose: To investigate fundamental forces and particles through high-energy collisions.
- Discoveries: Notably, the Higgs boson was discovered in 2012, confirming the existence of the Higgs field that imparts mass to particles.
- Speed: Particles are accelerated to 99.9999% of the speed of light.
- Significance: The LHC plays a crucial role in replicating conditions similar to those of the Big Bang and testing theories such as supersymmetry and extra dimensions.
The discussions surrounding the Future Circular Collider highlight a critical juncture in particle physics research, balancing the potential for groundbreaking discoveries with the realities of funding and resource allocation within the scientific community.
GS3/Science and Technology
Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO) and ISRO’s Breakthrough in Semi-Cryogenic Engine Development for LVM3
Why in News?
ISRO has recently made significant advancements by successfully developing a semi-cryogenic engine that utilizes liquid oxygen and kerosene, achieving a high thrust of 2,000 kN (kilonewtons). The first successful hot test of the Engine Power Head Test Article (PHTA) was conducted at the ISRO Propulsion Complex in Mahendragiri, Tamil Nadu. This innovative engine will be incorporated into the semi-cryogenic booster stage of the Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM3), thereby enhancing India's capabilities in space launches.
- ISRO's semi-cryogenic engine development marks a substantial improvement in launch vehicle technology.
- The engine's first successful hot test validates its operational capabilities.
- The new engine will replace the existing L110 stage in the LVM3, increasing payload capacity to GTO.
Additional Details
- What is a Transfer Orbit? A transfer orbit is designed to transition a satellite from one circular orbit to another efficiently, commonly utilizing a Hohmann Transfer Orbit for such maneuvers.
- Characteristics of Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO):
- Perigee: The closest point to Earth, ranging from 180-200 km above the Earth's surface.
- Apogee: The farthest point from Earth, approximately 35,900 km, near geostationary orbit.
- GTO is crucial for placing satellites into their final geostationary orbits, reducing the energy required from the launch vehicle, thus enhancing fuel efficiency.
- What is a Semi-Cryogenic Engine? This type of engine operates using liquid oxygen (LOX) as an oxidizer and refined kerosene (RP-1) as fuel, stored at normal temperatures, unlike cryogenic engines that require ultra-cold storage.
The successful hot test of the PHTA, which lasted for 2.5 seconds, demonstrated the engine's ignition and boost strap mode performance, confirming that all parameters met expectations. The Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC) under ISRO developed this engine, with plans for further testing before the fully integrated engine is realized. This development is anticipated to significantly improve payload capacity in GTO from 4 tonnes to 5 tonnes.
GS3/Science and Technology
Xenotransplantation
 Why in News?
Why in News?
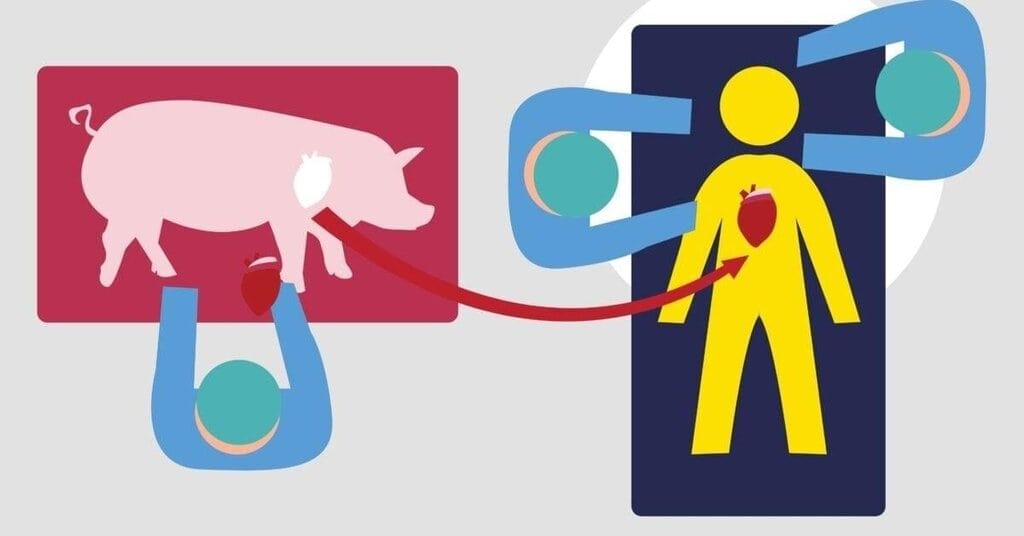
Researchers in China have made significant progress in the field of xenotransplantation by successfully transplanting a gene-modified pig liver into a human patient who was declared brain dead. This experiment aims to evaluate the survival and functionality of the transplanted organ.
- Xenotransplantation is the process of transplanting live cells, tissues, or organs from animals into human recipients.
- Genetic modifications in animal organs are necessary to prevent rejection by the human immune system.
- Recent advancements include the first genetically modified pig heart transplant in 2022 and the pig liver transplantation in 2025.
Additional Details
- Xenotransplantation: This refers to the transplantation, implantation, or infusion of live cells, tissues, or organs from one species (such as pigs) into a human recipient. It can also include human cells that have previously interacted with non-human animal cells.
- Why Pigs? Pigs are commonly used due to their anatomical and physiological similarities with humans, making them ideal organ donors. Additionally, their widespread farming makes organs more accessible and cost-effective.
- Recent Advancements:
- First genetically modified pig heart was transplanted into a human in 2022, showcasing the potential for using genetically altered pig organs for human transplantation.
- In 2025, Chinese researchers performed a pig liver transplant into a brain-dead human recipient, demonstrating the feasibility of this approach.
- Gene Modifications: Six genes in the pig liver were edited to prevent immune rejection, and human transgenes were added to enhance compatibility.
- Observations: Over a monitoring period of 10 days, the pig liver showed functionality by producing bile and albumin, maintaining stable blood flow, and exhibiting no signs of rejection due to immunosuppressants.
- Potential Uses: Gene-modified pig livers could serve as a "bridge therapy" for patients awaiting human organ transplants, though long-term viability and full functionality of the liver remain uncertain.
This groundbreaking work in xenotransplantation highlights the potential for overcoming organ shortages, while also emphasizing the need for further research to address long-term complications and ensure the safety of such procedures.
GS3/Environment
Frankincense: A Valuable Resin at Risk of Extinction
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has recently issued a warning regarding the alarming status of Frankincense-producing trees, specifically those belonging to the Boswellia genus, which are facing the threat of extinction.
- Five species of Frankincense on Socotra Island (Yemen) have transitioned from Vulnerable to Endangered, with one species now classified as Critically Endangered.
- Three other species have also been assessed as Critically Endangered for the first time.
What is Frankincense?
Frankincense is an aromatic resin extracted from the trees of the Boswellia genus. It has been historically prized for its use in:
- Incense
- Perfumes
- Traditional medicine
It holds significant cultural importance, being one of the three gifts (Gold, Frankincense, and Myrrh) presented to Jesus by the Magi, as recorded in the Bible.
Major Species of Boswellia
| Scientific Name | Common Name | Region Found |
|---|---|---|
| Boswellia serrata | Indian Frankincense | |
| Boswellia carterii | Somali Frankincense | Somalia, Ethiopia |
| Boswellia sacra | Arabian Frankincense | Oman, Yemen |
| Boswellia papyrifera | Sudanese Frankincense | Sudan, Eritrea |
| Boswellia frereana | Maydi Frankincense |
Why is Frankincense at Risk?
- Habitat destruction & overgrazing: Goats graze on young saplings, hindering the regeneration of these trees. Traditional rotational grazing practices have also diminished.
- Climate change & extreme weather: Events such as cyclones, flash floods, and landslides (notably in 2015 and 2018) have caused significant damage, uprooting many trees.
- Prolonged droughts: These conditions create challenges for sapling growth.
- Unsustainable harvesting: Excessive tapping for resin extraction weakens the trees and reduces their seed production.
- Limited conservation measures: There is a lack of effective protective measures, such as fencing and regulated harvesting, which has exacerbated the crisis.
In conclusion, the future of Frankincense and its significant cultural and economic value is in jeopardy. Effective conservation efforts are urgently needed to protect these endangered species and their habitats.
GS2/International Relations
India-US Civil Nuclear Deal - Commercial Implementation and Strategic Implications
Why in News?
The India-US civil nuclear deal, established two decades ago, has advanced significantly with the recent regulatory approval from the US Department of Energy (DoE). This approval enables Holtec International, a US-based company, to transfer Small Modular Reactor (SMR) technology—ranging in capacity from 30 MWe to 300 MWe per unit—to Indian private firms.
- Recent approval marks a critical milestone in the operationalization of the civil nuclear deal.
- The deal includes strategic and diplomatic implications for India and the US.
- It positions India to enhance its capabilities in the nuclear energy sector.
Additional Details
- US DoE authorisation: The regulation involved is "10CFR810" (Part 810 of Title 10, US Atomic Energy Act, 1954). The authorized recipients include Holtec Asia (an Indian subsidiary of Holtec), Tata Consulting Engineers Ltd (TCE), and Larsen & Toubro Ltd (L&T).
- Excluded entities: The Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL) and National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC) are excluded pending Non-proliferation assurances.
- Conditions of the deal: The agreement is set for a duration of 10 years, subject to reviews every 5 years, and includes restrictions on technology retransfer, access to enrichment technology, and military applications.
- The deal signifies a revival of the 123 Civil Nuclear Agreement, with implications for India's nuclear technology and private sector engagement.
This recent development in the India-US civil nuclear deal not only aligns with India's energy security goals but also enhances its strategic positioning in the global nuclear landscape. However, regulatory and legal challenges must be addressed to fully exploit the deal's potential.
GS3/Economy
Govt Scraps Gold Monetisation Scheme: RBI Clarifies Fate of Existing Deposits
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Indian government has announced the discontinuation of the medium- and long-term deposits of the Gold Monetisation Scheme (GMS) effective March 26, 2025, citing unfavorable market conditions and the scheme's overall performance. However, short-term deposits will continue based on the discretion of the banks.
- The GMS was introduced in November 2015 to make idle gold productive.
- Medium- and long-term deposits have been officially scrapped, but existing deposits will remain intact until maturity.
- The RBI is expected to release detailed guidelines concerning the closure of the scheme.
Additional Details
- Gold Monetisation Scheme (GMS): Aimed to integrate gold into the formal economy, reduce gold imports, and lower the current account deficit by allowing individuals and institutions to deposit gold with banks.
- Key Features of GMS:
- Allowed deposits from households, trusts, and institutions.
- Minimum deposit requirement is 10 grams of raw gold (including bars, coins, and jewelry without stones/metals).
- No upper limit on the amount of deposit.
- Types of Deposits:
- Short-term deposits (1-3 years) - managed by banks.
- Medium-term deposits (5-7 years) - managed by the government.
- Long-term deposits (12-15 years) - managed by the government.
- Interest Rates:
- Short-term deposits' interest rates are determined by banks based on market conditions.
- Medium- and long-term deposits' interest rates were set by the government in consultation with the RBI, with the Central government responsible for payments.
- Impact on Existing Deposits: Existing medium- and long-term deposits will not be affected and will continue until maturity unless withdrawn early.
- Total Gold Mobilised: As of November 2024, 31,164 kg of gold was mobilised under the scheme, with 7,509 kg in short-term deposits, 9,728 kg in medium-term deposits, and 13,926 kg in long-term deposits.
The discontinuation of the GMS follows a similar decision regarding the Sovereign Gold Bonds, indicating a shift in government strategy amidst rising gold prices. The government had previously indicated that the cut in gold import duty was intended to stimulate gold investment, which aligns with the goals of the GMS.
|
44 videos|5271 docs|1113 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 30th March 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the key challenges associated with the implementation of GST 2.0 in India? |  |
| 2. How does the Chicken's Neck Corridor impact India's strategic interests? |  |
| 3. What humanitarian efforts were undertaken by India in response to the earthquake in Myanmar under Operation Brahma? |  |
| 4. Why is the Kasampatty Sacred Grove important for biodiversity conservation? |  |
| 5. What are the potential benefits and challenges of xenotransplantation in medical science? |  |
















