UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 5th April 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS2/ Polity and Governance
Parliament passes Waqf (Amendment) Bill 2025 as Rajya Sabha grants approval

Why is it News?
After more than 12 hours of debate and voting late into the night, tensions increased over ministers taking a break, and Congress faced criticism from INDI allies for supporting a government-backed Bill.
Key Provisions of the Waqf (Amendment) Bill
- Inclusion of Non-Muslim Members: The Bill mandates the inclusion of at least two non-Muslim members in both the Central Waqf Council and State Waqf Boards. For instance, a State Waqf Board in Uttar Pradesh will now be required to have two non-Muslim members to ensure diversity and broader oversight.
- Enhanced Transparency and Accountability: The Bill requires the digitization of all Waqf records on a centralized portal, facilitating real-time monitoring and preventing unauthorized transactions. For example, Waqf institutions with annual earnings exceeding ₹1 lakh will be subject to audits by state-sponsored auditors.
- Women Must Receive Inheritance Before Waqf: The Bill stipulates that women must receive their rightful share of inheritance under Islamic law before any property is dedicated as Waqf. For instance, a man cannot donate ancestral property to a mosque as Waqf unless his daughters have first received their inheritance portions.
- Waqf Boards Cannot Arbitrarily Declare: The amendment removes the Waqf Board’s previous authority to unilaterally declare any property as Waqf without due process. For example, in cases of land disputes, the Waqf Board must now legally verify ownership instead of directly labeling the land as Waqf property.
- Restructuring of Waqf Tribunals: The structure of Waqf Tribunals is revised to include a district judge, a joint secretary-level government officer, and an expert in Muslim law. Appeals can be made to the High Court within 90 days. For instance, a property dispute resolved by the Waqf Tribunal in Delhi can now be appealed in the Delhi High Court within three months.
Opposition Criticism of the Bill
- Violation of Religious Freedom and Philanthropy Rights: The Opposition contended that prohibiting non-Muslims from creating Waqf infringes on their freedom to donate or support causes of different religions. For example, if a Hindu philanthropist wishes to donate land to a mosque for educational purposes, the law now prevents it from being classified as Waqf.
- Interference in Personal and Religious Affairs: Critics argued that the Bill represents excessive state intrusion into the religious practices of Muslims, particularly by restructuring Waqf Tribunals and mandating non-Muslim representation in Waqf Boards. For instance, the inclusion of non-Muslims in bodies managing Islamic religious endowments is perceived by some as an imposition on community autonomy.
- Lack of Consultation and Political Targeting: Opposition parties claimed that the Bill was introduced without sufficient consultation with stakeholders, including Muslim scholars, religious leaders, or civil society organizations. It was seen as part of a broader political narrative targeting minorities. For example, the abrupt change in Waqf creation criteria (only Muslims with five or more years of practice) was criticized for lacking meaningful dialogue with the affected community.
Current Status of Waqf Property in India
- Registered Properties: As of March 2025, Waqf boards in India oversee approximately 8.72 lakh (872,000) registered properties, covering over 38 lakh (3.8 million) acres of land. For instance, in Uttar Pradesh, there are about 2.1 lakh Waqf properties, while West Bengal has around 78,000 properties and Kerala has about 55,000 properties.
- Spread Across Urban and Rural Areas: Waqf land is distributed across prime urban locations and fertile rural areas, often facing challenges related to encroachment and mismanagement. For example, in cities like Delhi and Mumbai, many Waqf lands are situated in commercial hubs but are underutilized or illegally occupied.
Eligibility to Donate to Waqf Under the New Law
- Under the Waqf (Amendment) Bill, 2025, only practicing Muslims who have adhered to their faith for a minimum of five years are eligible to donate property as Waqf. This provision aims to ensure that donations are genuine and voluntary, reinstating a rule that was in place before 2013.
Future Directions
- Promote Inclusive Dialogue and Trust-building: Establish structured consultations with religious leaders, civil society, and legal experts to address concerns and foster transparency.
- Strengthen Implementation with Oversight: Ensure effective digitization, fair dispute resolution, and regular audits through independent oversight bodies to prevent misuse and encroachment.
GS2/International Relations
Heard and McDonald Islands
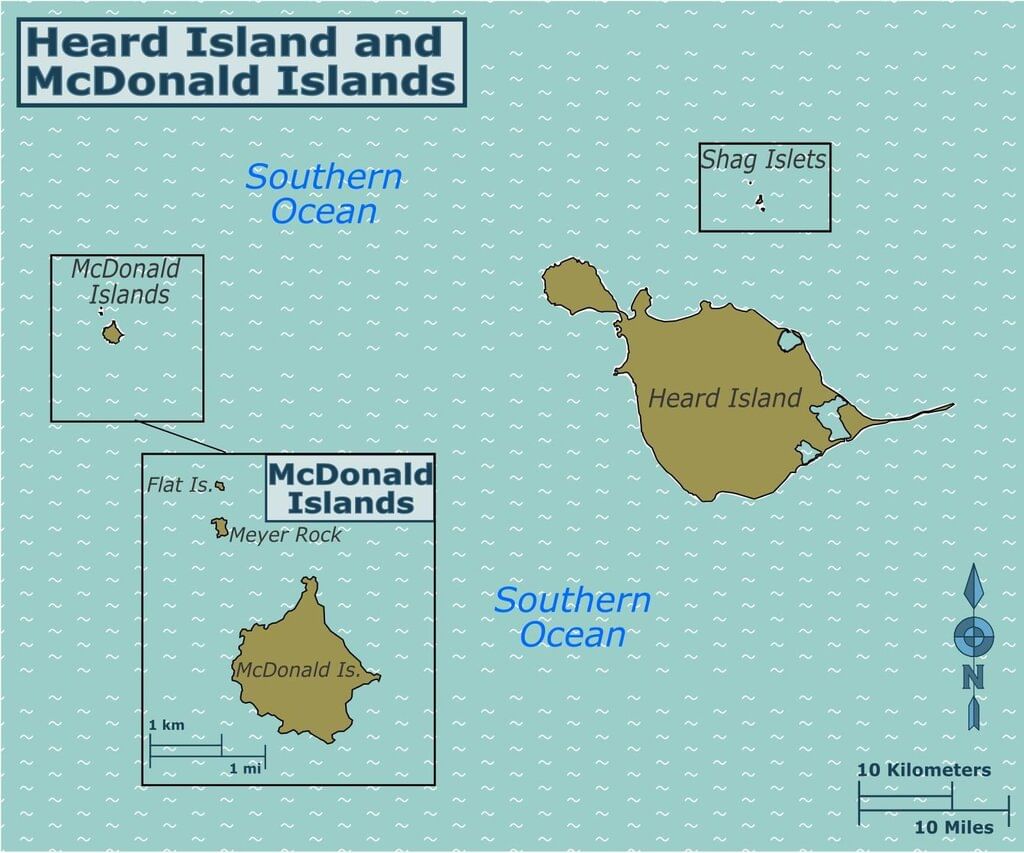
Why in News?
Donald Trump has implemented a 10% tariff on imports coming from the Heard and McDonald Islands. This decision is surprising considering that there has been no human presence on these islands for nearly a decade.
About the Heard and McDonald Islands
The Heard and McDonald Islands are situated in the Southern Ocean, roughly 4,100 kilometers south-west of Perth, Australia, and 1,600 kilometers north of the Antarctic coast.
- These islands are unincorporated external territories of Australia, meaning they are not part of any Australian state but are directly governed by the Australian government.
- The islands are ecologically significant, home to various wildlife such as seals, penguins, and albatrosses, and serve as crucial breeding grounds for these species.
- Due to their rich biodiversity and ecological importance, the islands have been recognized as UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
Heard Island
- Heard Island covers an area of about 368 square kilometers.
- The island’s tallest point is Mawson Peak, an active volcano that rises 2,745 meters (9,006 feet) above sea level.
- Mawson Peak is known for being one of the most active volcanoes in the southern hemisphere, with eruptions occurring as recently as 2016.
McDonald Islands
- McDonald Islands are significantly smaller, with a total area of only 2.5 square kilometers.
- Like Heard Island, McDonald Islands are also volcanic and part of the same volcanic chain.
Climate
- Both Heard and McDonald Islands experience an extremely cold subantarctic climate, characterized by strong winds, heavy snowfall, and ice for most of the year.
- Even during the summer months, temperatures on the islands rarely exceed 5°C (41°F).
Strategic Importance
- The Heard and McDonald Islands hold strategic significance due to their location between Australia and Antarctica. This position is vital for monitoring the Southern Ocean, which plays a crucial role in global biodiversity and climate studies.
- The islands are important for scientific research in areas such as volcanology, glaciology, and climate change. Australia operates a research station on Heard Island to facilitate this research.
- The islands are protected under the Antarctic Treaty System, which prohibits military activity and commercial exploitation in the region.
- The surrounding waters are rich in marine resources and are also protected to prevent overfishing and environmental damage.
- As international competition and territorial claims in Antarctica and the Southern Ocean increase, the geopolitical importance of the Heard and McDonald Islands is growing.
GS3/ Economics
India’s Subsea Cable Infrastructure
Why in News?
India is expanding its undersea cable infrastructure, aiming to boost international internet bandwidth with new systems like Airtel’s 2Africa Pearls and SEA-ME-WE-6.
What Are Undersea Cables?
- Undersea cables are fiber optic cables laid on the ocean floor, connecting internet networks between countries.
- These cables are heavily insulated and contain fiber optic strands for data transmission.
- They surface at landing points, connect to landing stations, and link to broader terrestrial networks.
- Approximately 600 undersea cables exist globally, handling 90% of global data, 80% of world trade, and $10 trillion in financial transactions.
India’s Current Undersea Cable Ecosystem
- India’s main hubs for subsea cables are Mumbai and Chennai.
- 17 international cables land in India, with 95% of subsea cables concentrated in a 6-km stretch in Versova, Mumbai.
- India has two domestic cable systems:
- Chennai–Andaman–Nicobar Islands (CANI)
- Kochi–Lakshadweep Islands
- Current bandwidth is considered sufficient, but rising data traffic may soon outpace capacity.
- India contributes only 1% of global cable landing stations and 3% of subsea cable systems, indicating underrepresentation in the global network.
Challenges in Undersea Cable Deployment in India
- High risk from cuts, especially at chokepoints like the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait in the Red Sea, where past disruptions have affected cables.
- Many cables follow traditional shipping routes, limiting redundancy and increasing the risk of large-scale outages.
- Deploying subsea cables requires navigating about 51 permissions from various departments, such as the Department of Telecom, Ministry of Environment, and Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Meta reports that 80% of project time is spent dealing with regulatory requirements in territorial waters.
- Lack of domestic repair capabilities, relying on foreign ships for cable repairs, makes the system vulnerable to prolonged outages.
GS3 / Defence and Security
Exercise INDRA 2025

Why is it News?
The Indian and Russian navies recently conducted the bilateral naval exercise INDRA 2025 from 28 March to 02 April 2025.
About Exercise INDRA
- INDRA is a joint military exercise held every two years, which started in 2003.
- Initially focused on specific areas, INDRA has evolved into a tri-service exercise involving the Army, Navy, and Air Force, making it more comprehensive.
Recent Editions of INDRA:
- 2021 (12th Edition): Took place in Volgograd, Russia, emphasizing counter-terrorism operations and operational synergy.
- 2023 (13th Edition): Held in the Bay of Bengal, India, focusing on naval forces and enhancing maritime cooperation.
- 2025 (14th Edition): Conducted in two phases: Harbour phase at Chennai and Sea phase in the Bay of Bengal.
Strategic Importance
- The exercise reinforced the collaborative capabilities of the Indian and Russian forces in maritime security operations.
- It underscored their commitment to upholding maritime order and promoting global peace and stability.
- The exchange of best practices during the exercise fostered a better understanding of each other’s operational doctrines, enhancing their responsiveness to contemporary maritime security challenges.
GS1/ Indian Society
Central Sector Scheme for Promotion of International Cooperation for AYUSH

Why is it News?
The Ministry of Ayush is promoting a scheme to enhance the global recognition and development of traditional Indian systems like Ayurveda, Yoga, Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, and Homeopathy.
About the Scheme
- The scheme aims to promote AYUSH systems internationally, contributing to their global growth.
- It is announced on the AYUSH website, inviting applications through open advertisements.
- Proposals are screened by a committee and approved for financial assistance based on needs and activity limits.
Key Components of the Scheme
- International Exchange of Experts & Officers: Facilitates the deputation of AYUSH experts for international conferences and training.
- Incentives for Drug Manufacturers: Provides financial support for international propagation and product registration.
- Market Development Support: Supports exhibitions, conferences, and market surveys for international market development.
- Promotion through Young Postgraduates: Deploys young postgraduates to promote AYUSH abroad through NGOs.
- Translation and Publication: Funds the translation and publication of AYUSH literature in foreign languages.
- AYUSH Information Cells/Health Centres: Establishes AYUSH cells and health centers in foreign countries through Indian missions.
- International Fellowship Programme: Offers fellowships to foreign nationals to study AYUSH courses in India.
Significance of Yoga and AYUSH in India’s International Outreach
- International Day of Yoga (IDY): Declared by the United Nations in 2014, with substantial investment in its promotion, spreading Yoga’s global message.
- National Curriculum Framework (NCF): Yoga is now part of the NCF, making it compulsory for students from Class I to Class X, ensuring its integration into education.
- Yoga Certification Board (YCB): Under the Ministry of Ayush, the YCB certifies yoga professionals and accredits institutions, maintaining quality and standards in Yoga practice.
- International Promotion of Indian Traditional Medicine: The Ministry of Ayush has signed numerous MoUs with countries and institutions to promote Indian traditional medicine systems globally, enhancing their recognition and practice worldwide.
GS1/ Geography
Ionian Islands

Why in News?
A significant archaeological discovery in Lefkada, Greece, has brought to light the first ancient Greek theater ever found in the Ionian Islands.
About Ionian Islands
- The Ionian Islands are a group of islands situated off the western coast of Greece, in the eastern part of the Ionian Sea.
- They cover a total land area of 2,306.94 square kilometers and consist of seven major islands along with several smaller ones.
- These islands are commonly referred to as “Heptanese” or “Seven Islands.”
- The major islands in this group include Kerkyra (Corfu), Paxi, Lefkada, Ithaki, Kefalonia, Zakynthos, and Kythira.
- Kefalonia, also known as Cephalonia, is the largest of the Ionian islands.
- The highest point in the Ionian Islands is Mount Ainos, which rises to an elevation of 1,628 meters.
History
- In the 15th and 16th centuries, the Ionian Islands were controlled by Venice.
- They were later taken by Russian and Turkish forces in 1799.
- The Treaty of Paris in 1815 placed the islands under British control.
- The British ceded the islands to Greece in 1864.
GS3/ Environment and Ecology
Pale-Chinned Flycatcher
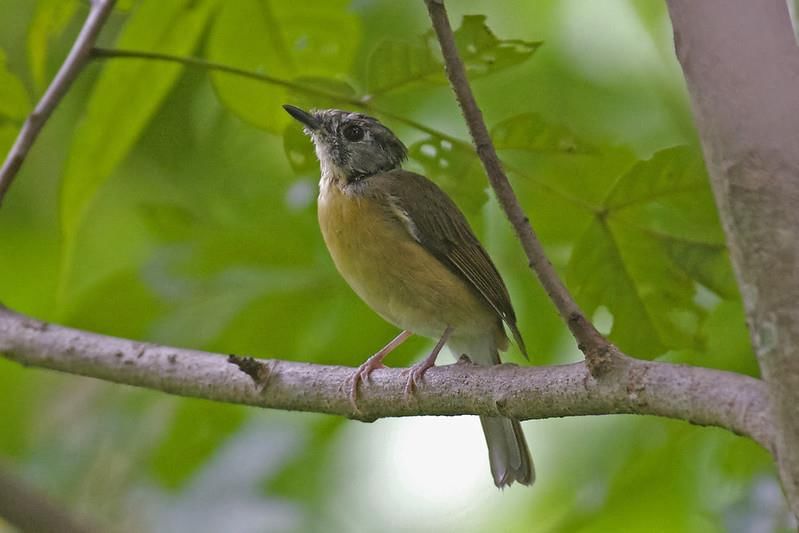

Why is it in the News?
Recently, the rare Pale-chinned Flycatcher. Cyornis poliogenys. was spotted in the Nong Loung (Bor Beel) forest area of Namsai district, adding to the rich avian diversity of Arunachal Pradesh.
About the Pale-Chinned Flycatcher
- Description: The Pale-Chinned Flycatcher is a small, insect-eating songbird known for its subtle beauty and unobtrusive behavior. It prefers the shady interiors of forests.
- Family: Muscicapidae
- Size: Sparrow-sized
- Scientific Name:Cyornis poliogenys
- Distribution:
- India: Found in the Eastern Ghats, northeastern states, Eastern Himalayas, and West Bengal.
- Other Countries: Bangladesh, Bhutan, Myanmar, and parts of Southeast Asia.
- Sundarbans: Rarely seen, but possible in suitable undisturbed patches.
- Habitat: Prefers dense, moist forest habitats, particularly evergreen and semi-evergreen forests with rich undergrowth.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Least Concern
Physical Features
- Size: Small, measuring about 13–14 cm (5.1–5.5 inches) in length.
- Weight: Approximately 10–12 grams.
- Males:
- Dull blue upperparts
- Greyish throat and chin
- Light olive or brownish wash on flanks
- Females:
- Similar to males but duller, with more brown tones and less distinct bluish hues
- Pale Chin or Throat Patch:. distinguishing feature that separates the dull blue-grey head and breast.
- Bill: Fine black bill, well-suited for foraging insects.
- Behavior: Frequently flicks its tail and flits low among vegetation.
GS1/ History and Culture
Kannadipaya

Why in News?
Kannadippaya, a distinctive tribal handicraft from Kerala, has recently been awarded the Geographical Indication (GI) tag. This recognition aims to protect its market and provide a global platform for this traditional product.
About Kannadipaya
- Kannadipaya is a traditional craft originating from Kerala, where artisans weave baskets, mats, and various daily use items using reed bamboo.
- This craft is carried out by the Urali, Mannan, and Muthuvan tribal communities, who use a specific type of bamboo called Teinostachyum wightii, locally known as ‘njoonjiletta’.
- The mats are known for their polished, mirror-like surface, which reflects light, giving rise to the name 'kannadipaya' (where 'kannadi' means mirror and 'paya' means mat).
- Typically measuring between 0.75-1.0 m × 2 m, these mats are highly flexible and can be rolled up into a bamboo culm with a diameter of less than 10 cm.
- Creating a kannadipaya mat is a labor-intensive process, taking over a month for a skilled weaver to complete one.
- The weaving involves a specific layer of ultra-thin and shiny slivers, usually the fourth or fifth layer, split from a reed bamboo species native to the region.
- Harvesting the bamboo is a ritual performed during a full moon, with each trip to the forest and back taking a full day and night.
GS3/ Defence and Security
Hansa-3 Trainer Aircraft
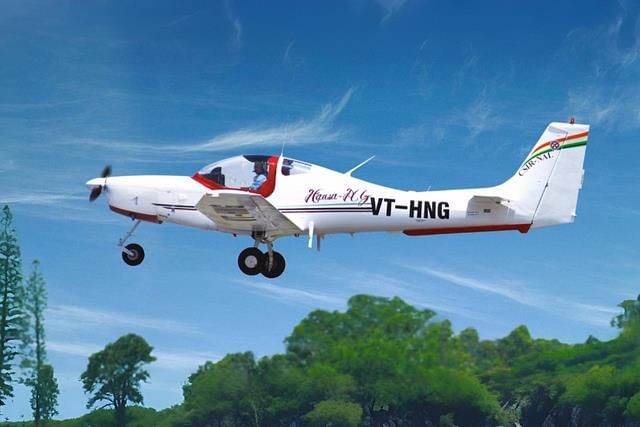

Why is it News?
The Hansa-3 trainer aircraft, developed in India, has received approval for training aircrew in obtaining pilot licenses.
- The aircraft will now be manufactured in India by the private sector.
About Hansa-3 Trainer Aircraft
- The Hansa-3 is India’s first indigenous flying trainer aircraft, designed and developed by CSIR-National Aerospace Laboratories in Bangalore, under the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
- It is specifically designed to meet the needs of Indian flying clubs and is considered ideal for Commercial Pilot Licensing (CPL) due to its low cost and fuel efficiency.
Features of Hansa-3 Trainer Aircraft
- Configuration: It is a two-seater, low-wing aircraft.
- Engine: Powered by a Rotax Digital Control Engine.
- Airframe: Features a lightweight composite airframe made using Just-In-Time Prepreg (JIPREG) technology.
- Cockpit: Equipped with a glass cockpit for better visibility and control.
- Canopy: Bubble canopy provides a wide panoramic view.
- Flaps: Electrically operated flaps for enhanced performance.
- Fuel System: Advanced electronic fuel injection system optimizes fuel and air mixtures at various altitudes.
GS3/ Environment and Ecology
Cauvery Wildlife Sanctuary
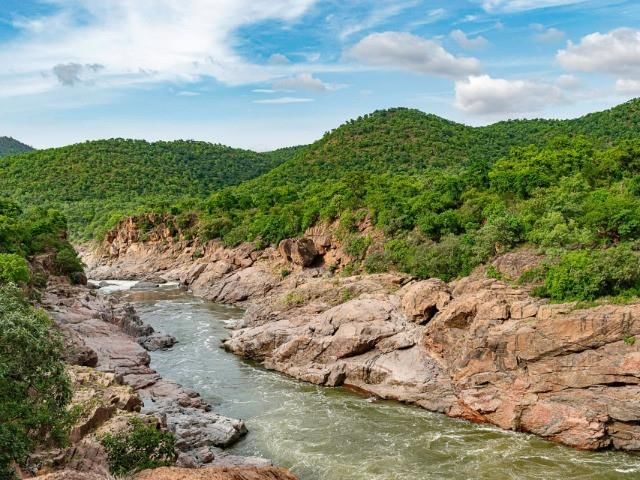

Why in News?
The Cauvery Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the Chamarajanagar and Ramanagara districts of Karnataka, India. It was established in 1987 to protect the rich biodiversity of the region. The sanctuary covers an area of 1,027.535 square kilometers and is traversed by the Cauvery River.
Location and Area
- Situated in Chamarajanagar and Ramanagara districts of Karnataka.
- Established in 1987, covering 1,027.535 square kilometers.
River and Forests
- The Cauvery River flows through the sanctuary, providing a vital water source.
- The central and eastern parts of the sanctuary are densely forested, primarily with South Indian dry deciduous trees.
Wildlife
The sanctuary is home to various mammals, including:
- Elephants
- Wild boars
- Leopards
- Dholes (wild dogs)
- Spotted deer
- Barking deer
- Four-horned antelopes
- Chevrotains (mouse deer)
- Common langurs
- Bonnet macaques
- Honey badgers
- Malabar giant squirrels
- Smooth-coated otters
- Grizzled giant squirrels
Reptiles and Fish
- The Cauvery River is home to reptiles such as:
- Mugger crocodiles
- Indian mud turtles
- Various snake species
- The river is also one of the few places where Mahseer fish are found.
Cultural and Tourist Sites
- Within the sanctuary, there are several sites of cultural, historical, and tourist interest, including:
- Hogenakkal Falls (known as "Smoking Rock" in Kannada)
- Mekedatu (meaning "Goat's Leap")
- Sangam (the confluence of the Arkavathi and Cauvery rivers)
- Muthathi (home to the Lord Anjaneya temple)
|
43 videos|5366 docs|1135 tests
|
















