UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 21st April 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Science and Technology
CROP: Comprehensive Remote Sensing Observation on Crop Progress
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has projected that wheat production in India, particularly from eight major wheat-producing states, is expected to reach approximately 122.724 million tonnes by March 31, 2025. This estimation utilizes advanced satellite-based remote sensing technologies.
- CROP is a semi-automated and scalable framework developed by the National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC).
- The main goal of CROP is to facilitate near real-time monitoring of crop sowing, growth, and harvesting, especially during the abi season in India.
Additional Details
- Technological Components: CROP integrates data from various remote sensing satellites, which include:
- EOS-04 (RISAT-1A): Provides Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data.
- EOS-06 (Oceansat-3): Offers optical remote sensing data.
- Resourcesat-2A: Utilized for high-resolution optical imaging of agricultural areas.
- The framework employs both optical and SAR datasets to accurately monitor crop progress under diverse weather and light conditions.
- Major Wheat-Producing States: The eight key states identified in the ISRO study include:
- Uttar Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh
- Rajasthan
- Punjab
- Haryana
- Bihar
- Gujarat
- Maharashtra
- These states play a vital role in ensuring national food security and contribute significantly to India's abi wheat harvest.
This initiative underscores the importance of technology in enhancing agricultural productivity and food security in India.
GS2/International Relations
Yellow Sea
 Why in News?
Why in News?
China has recently intensified its activities in the Yellow Sea following aggressive actions in the South China Sea, notably through the construction of a massive steel rig.
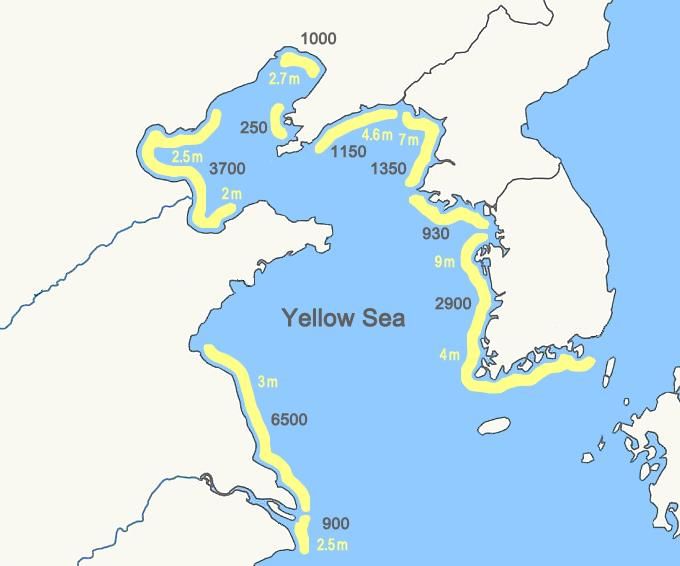
- The Yellow Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean, also known as Huang Hai in China and the West Sea in Korea.
- It is located to the north of the East China Sea and is bordered by mainland China to the north and west, and North Korea to the east.
Additional Details
- Geographical Significance: The Yellow Sea is named for the yellowish sand particles from the Gobi Desert that color its waters. It spans approximately 400,000 square kilometers and measures about 960 km from north to south and 700 km from east to west.
- Depth: The sea is relatively shallow, with an average depth ranging from 180 to 394 feet (55 to 120 meters), making it one of the largest areas of continental shelf submerged underwater.
- Climate: The region experiences very cold, dry winters and wet, warm summers, influencing its ecological dynamics.
- Major Rivers: Significant rivers that flow into the Yellow Sea include the Han, Yangtze, Datung, Yalu, Guang, and Sheyang, contributing to its hydrology and ecosystem.
- Islands: Notable islands in the Yellow Sea include Jeju Island (South Korea), various islands in the Shandong Peninsula (China), and Ganghwa Island (South Korea).
- Port Cities: Leading port cities surrounding the Yellow Sea are Qingdao and Dalian in China, Inch'ŏn in South Korea, and Namp'o in North Korea, which are crucial for trade and maritime activities.
The ongoing developments in the Yellow Sea reflect broader geopolitical maneuvers in the Indo-Pacific region, particularly as tensions in maritime areas continue to rise.
GS3/Science and Technology
Recycling Perovskite Solar Cells
Why in News?
Recent advancements in the recycling of perovskite solar cells have introduced a new water-based solution, which presents a more sustainable and efficient approach to solar energy production.
- Perovskite solar cells are known for their high power conversion efficiencies and low manufacturing costs compared to traditional silicon-based panels.
- These solar cells are lightweight, flexible, and made from inexpensive materials, making them a promising alternative in the solar energy market.
- Despite their efficiency, perovskite solar cells have a shorter lifespan and contain toxic materials like lead, posing environmental risks during disposal.
Additional Details
- Perovskite Solar Cells: These cells are utilized in various applications, including solar power generation, electric vehicles, and energy storage systems, due to their affordability and performance.
- New Recycling Method: Researchers have developed a water-based recycling solution that replaces harmful organic solvents with a non-toxic approach, utilizing three salts: sodium acetate, sodium iodide, and hypophosphorous acid to dissolve and regenerate perovskite crystals.
- This innovative process maintains nearly the same efficiency as fresh materials, even after five rounds of recycling, recovering 99% of the layers, thus promoting a circular economy and reducing waste.
This recycling method supports the environmentally friendly management of perovskite solar cells, enhancing sustainability in solar energy technology.
UPSC 2014
With reference to technologies for solar power production, consider the following statements:
- 1. ‘Photovoltaics’ is a technology that generates electricity through the direct conversion of light into electricity, while ‘Solar Thermal’ utilizes the Sun’s rays to generate heat, which is then used in the electricity generation process.
- 2. Photovoltaics generate Alternating Current (AC), whereas Solar Thermal generates Direct Current (DC).
- 3. India has a manufacturing base for Solar Thermal technology, but not for Photovoltaics.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- (a) 1 only*
- (b) 2 and 3 only
- (c) 1, 2 and 3
- (d) None
GS3/Science and Technology
Coenzyme Q: A Vital Molecule for Energy Production
Why in News?
A recent study published in Nature by researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences focused on genetically modifying rice plants to enhance the production of Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10).
- Coenzymes are organic molecules that enhance the efficiency of enzymes in biochemical reactions.
- Coenzyme Q (CoQ) is essential for cellular energy production and acts as an antioxidant.
- CoQ exists in ten forms (from CoQ1 to CoQ10) and is crucial within the respiratory chain of cells.
- CoQ10 is vital for mitochondrial energy production, particularly in high-energy organs such as the heart.
Additional Details
- Importance of CoQ9 and CoQ10: These coenzymes are found in various cereal crops, including wheat, rice, oats, and barley, as well as in plants like cinnamon, avocado, and pepper. They are commonly available in everyday foods, making them accessible nutrients.
- CoQ10 plays a significant role in health, especially for individuals with neurological disorders or age-related deficiencies.
- Research has shown that CoQ10 supplementation can improve health outcomes in patients with neurological disorders (Montini et al., 2008) and infants with CoQ10 deficiency (Shamima Ahmed, 2012).
CoQ10-based supplements are increasingly being recommended by healthcare professionals due to their health benefits and availability.
UPSC 2007
Question: Which one of the following is not a digestive enzyme in the human system?
- (a) Trypsin
- (b) Gastrin*
- (c) Pepsin
- (d) Amylase
GS3/Science and Technology
50 Years Since the Launch of Aryabhata
Why in News?
On April 19, 2025, India commemorates the 50th anniversary of the successful launch of Aryabhata, the country's first satellite. This event marked a significant milestone in India's space history and its journey towards becoming a notable player in space technology.
- Aryabhata was launched on April 19, 1975, with assistance from the Soviet Union.
- The satellite was named after the ancient Indian mathematician and astronomer Aryabhata.
- Aryabhata's design featured a unique 26-sided polyhedron with a diameter of 1.4 meters and a weight of 360 kg.
- It orbited the Earth every 96.3 minutes with an inclination of 50.7 degrees.
- Despite a power failure after 5 days, Aryabhata transmitted data for an impressive 17 years.
Additional Details
- Aryabhata's Design: The satellite's faces were covered with solar panels, enhancing its ability to harness solar energy.
- Scientific Missions: Aryabhata's mission focused on conducting experiments in solar physics and X-ray astronomy.
- Inception of India’s Space Program: Initiated in the 1960s under the leadership of Vikram Sarabhai, the program aimed to boost India’s technological and scientific capabilities.
- In 1972, India partnered with the Soviet Union for its initial satellite launch, marking the start of its journey into space exploration.
The launch of Aryabhata was pivotal in establishing India's space capabilities, leading to advancements in technology and further developments in the space program. The success of this mission laid the groundwork for future missions and achievements in the realm of space exploration.
GS3/Defence & Security
Indian Air Force Joins Exercise Desert Flag-10
Why in News?
The Indian Air Force (IAF) has recently participated in the esteemed Exercise Desert Flag-10, a multinational air combat exercise hosted at Al Dhafra Air Base in the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
- The exercise is designed to simulate complex aerial combat scenarios.
- IAF is deploying two types of aircraft: the MiG-29 and the Jaguar.
- Participating nations include several advanced air forces from across the globe.
Additional Details
- Exercise Desert Flag: This premier multinational air exercise aims to enhance the operational capabilities of participating air forces by providing realistic training environments.
- IAF Aircraft Participation: The IAF is showcasing its MiG-29, known for its air superiority capabilities, and the Jaguar, recognized for its ground attack and deep strike abilities.
- Participating Nations: The exercise includes air forces from Australia, Bahrain, France, Germany, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, South Korea, Turkey, the United Kingdom, the United States, and the host nation UAE.
- Objective: The primary aim is to conduct complex fighter engagements, focusing on operational knowledge exchange, sharing best practices, and enhancing air combat tactics among the world’s most advanced air forces.
This exercise not only strengthens bilateral ties among the participating nations but also fosters a collaborative environment for improving aerial combat strategies.
GS3/Economy
India’s Push for Higher Value Addition in Electronics Manufacturing
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Global smartphone leaders such as Apple and Samsung have established production facilities in India, motivated by the country's vast talent pool, government incentives, and the need to reduce reliance on China. While India has made strides in localizing smartphone assembly, the government is now shifting its focus towards enhancing domestic value addition.
- India aims to increase local value addition in electronics manufacturing from 15-20% to 40-50%.
- The government has launched the ₹76,000 crore India Semiconductor Mission and a ₹23,000 crore scheme for passive electronic components.
- India's trade deficit with China reached a record $100 billion in 2024-25, underscoring the urgency for these initiatives.
Additional Details
- Electronics Components Manufacturing Scheme: This scheme focuses on boosting domestic production of essential components for smartphones, laptops, and home appliances.
- India's mobile phone exports have surged dramatically, growing 77 times over the past decade, indicating a robust presence in global electronics manufacturing.
- Currently, the domestic production of key components like PCBs has significantly decreased imports, showcasing the effectiveness of local manufacturing initiatives.
- With the new incentive scheme worth ₹22,919 crore, the government aims to enhance the production capabilities of electronics components further.
The government's strategic push towards increasing domestic value addition in electronics manufacturing is set to reduce import dependency, especially on China, while creating high-quality jobs and fostering economic growth. By focusing on local component manufacturing, India is positioning itself as a significant player in the global electronics market.
GS3/Defence & Security
Anti-Satellite (ASAT) Weapons
 Why in News?
Why in News?
India is recognized as a significant player in shaping global norms for responsible behavior in space, as stated by Marjolijn van Deelen, the EU Special Envoy for Space.
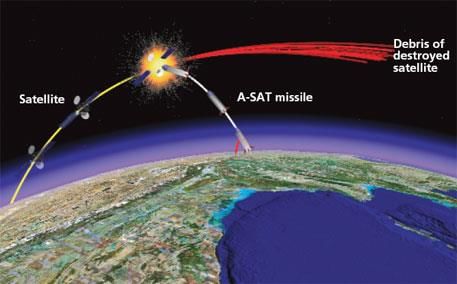
- ASAT weapons are designed to disable or destroy satellites in orbit for strategic purposes.
- India's ASAT capabilities were demonstrated in the 2019 Mission Shakti test.
- Concerns have been raised about space debris from ASAT tests, prompting calls for a ban on such activities.
Additional Details
- ASAT Weapons: These are specialized technologies aimed at disabling, destroying, or interfering with satellites for military or defensive purposes. They play a crucial role in space warfare by neutralizing enemy satellites that assist in surveillance, communication, navigation, and early warning systems.
- Classification of ASATs:ASAT weapons are broadly classified into two categories:
- Kinetic Energy ASATs: These involve direct physical impact, typically through missiles that collide with satellites, generating orbital debris as a byproduct.
- Non-Kinetic ASATs: These employ non-physical methods, such as cyber-attacks, jamming, spoofing, and directed energy weapons like lasers, to disrupt or blind satellites without physical destruction.
- ASAT weapons can be launched from ground stations, aircraft, or even other satellites, making them versatile and sometimes difficult to detect.
- Currently, four countries—the United States, Russia, China, and India—have demonstrated operational ASAT capabilities through various tests.
- India's ASAT Test (Mission Shakti) was conducted in March 2019, successfully destroying a live satellite in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) using a three-stage interceptor missile at an altitude of approximately 300 km in a "hit-to-kill" mode.
- The global community, especially the European Union, has expressed concerns regarding the space debris resulting from destructive ASAT tests and has advocated for a ban on such practices within a United Nations framework.
In addition to ASAT weapons, the concept of Rendezvous and Proximity Operations (RPO) involves maneuvering one spacecraft close to another in space for various objectives, including docking and inspection. Although RPOs are often utilized for scientific and repair missions, they can also be employed for espionage or to disable other satellites, particularly when conducted covertly by adversarial entities. This highlights the dual-use nature of space technologies and the need for international regulations to ensure responsible behavior in outer space.
GS2/Governance
Jal Jeevan Mission: Progress, Funding Challenges, and the Road Ahead
Why in News?
The Jal Shakti Ministry has requested Rs 2.79 lakh crore in Central funds to complete the Jal Jeevan Mission Scheme, highlighting significant funding challenges as the initiative approaches its final phase.
- Jal Jeevan Mission aims to provide Functional Household Tap Connections (FHTCs) to every rural household by 2024.
- As of March 31, 2025, approximately 14.56 crore rural households (73%) have received tap water connections.
- 13 states and Union Territories have achieved 100% tap water coverage.
- Funding gaps may delay progress in states with lower coverage rates.
Additional Details
- Background: Launched in August 2019, the Jal Jeevan Mission is a major initiative by the Government of India, spearheaded by the Ministry of Jal Shakti, to ensure equitable access to safe drinking water.
- Financial Requirement: The original outlay for the mission was Rs 3.60 lakh crore, but the current allocation is only Rs 1.58 lakh crore, leading to concerns over project sustainability and maintenance post-2024.
- Community Involvement: Village Water and Sanitation Committees (VWSCs) play a crucial role in the operation and maintenance of water supply systems, enhancing local governance.
- Challenges: Geographic diversity, water source sustainability, human resource gaps, and water quality issues pose significant challenges to the mission's success.
- Future Focus: The government aims to enhance long-term water supply infrastructure beyond the initial 2024 deadline, emphasizing the need for water quality monitoring and sustainable practices.
The Jal Jeevan Mission represents a vital step towards ensuring every household has access to safe drinking water. However, addressing funding challenges and local governance issues will be critical in achieving the mission's overarching goals.
GS3/Defence & Security
Sapsan Missile
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Russian Ministry of Defence has officially acknowledged the increasing threat posed by Ukraine's newly developed short-range ballistic missile, known as the Sapsan.
- The Sapsan missile, also referred to as Hrim-2 or Grom-2, is a Ukrainian tactical ballistic missile system.
- Its design integrates elements of a tactical missile system with those of a multiple rocket launcher.
- The system is capable of targeting stationary individual and group targets at ranges of 50 to 280 km, with an extended range of 700 km for Ukrainian forces.
Additional Details
- Sapsan System: It features a 10-wheeled Transporter-Erector-Launcher (TEL) that can transport two containerized missiles at once.
- Aero-Ballistic Capabilities: The missile can evade modern air defense systems, such as the S-300 and S-400, and is comparable to Russia's 9K720 Iskander missile complex.
- Versatility: The Hrim-2 can launch both ballistic and cruise missiles, making it adaptable for various missions, including air defense and coastal operations.
- Warhead: It carries a single-stage ballistic missile with a warhead mass of 480 kilograms, available in both unitary and cluster configurations.
- Navigation System: The onboard control system is inertial-based and integrates multiple navigation and guidance systems, including radar and optoelectronic components.
This missile system represents a significant advancement in Ukraine's military capabilities and poses a notable challenge to regional security dynamics.
GS3/Environment
Davis Strait Proto-Microcontinent
Why in News?
A recently discovered hidden landmass, known as the Davis Strait proto-microcontinent, lies beneath the icy waters separating Canada’s Baffin Island from Greenland. This finding has drawn attention due to its implications for geological and tectonic studies.
- The Davis Strait proto-microcontinent is hypothesized to have existed during the Paleozoic era.
- It consists of a 19-24 km thick thinned continental crust, flanked by narrow bands of 15-17 km thick continental crust.
- The landmass likely fractured due to tectonic movements.
- Geological evidence indicates similarities in rock formations and tectonic features between Greenland and parts of the Canadian Arctic.
- This proto-microcontinent is vital for understanding the tectonic processes that shaped the Atlantic Ocean and its surrounding regions.
About Davis Strait
- Davis Strait: A significant water body located between southeastern Baffin Island (Canada) and southwestern Greenland, forming a part of the Northwest Passage.
- It separates Baffin Bay to the north from the Labrador Sea to the south and connects to the Arctic Ocean through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago.
- This strait serves as an important maritime route for shipping and trade.
- Named after John Davis, the English explorer who navigated the area in the late 16th century, it plays a crucial role in the tectonic evolution of the Arctic region.
|
44 videos|5271 docs|1113 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 21st April 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of the CROP initiative in remote sensing for agriculture? |  |
| 2. How does recycling perovskite solar cells contribute to environmental sustainability? |  |
| 3. What role does Coenzyme Q play in energy production within the human body? |  |
| 4. What are the key milestones achieved by India in aerospace since the launch of Aryabhata? |  |
| 5. What are the implications of Anti-Satellite (ASAT) weapons for international security? |  |
















