UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 22nd April 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Science and Technology
Alamosaurus Fossil Discovery
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Geology students made a significant discovery at Big Bend National Park in the United States, where they uncovered a rare and nearly complete fossil of the Alamosaurus, one of the largest dinosaurs known to have existed.
- Alamosaurus is an herbivorous sauropod from the late Cretaceous period.
- It is recognized as the only known sauropod in North America from the Upper Cretaceous.
- The species was among the largest terrestrial animals, measuring up to 11 meters tall and 30.5 meters long.
Additional Details
- Alamosaurus: This dinosaur was characterized by its long neck, tail, and pillar-like limbs, which are typical features of its family. It weighed between 38 to 80 metric tons.
- Alamosaurus went extinct during the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event, marking it as one of the last non-avian dinosaurs to roam the Earth.
- This dinosaur was comparable in size to other giant sauropods, such as Argentinosaurus, which lived in South America around 97 to 92 million years ago.
This discovery not only sheds light on the physical characteristics and scale of the Alamosaurus but also enhances our understanding of the diversity of dinosaur species that existed in North America during the late Cretaceous period.
GS3/Science and Technology
SpaDeX Mission
Why in News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has recently marked a significant achievement by successfully completing the second docking of two satellites, SDX01 (Chaser) and SDX02 (Target), as part of the SpaDeX (Space Docking Experiment) mission.
- The SpaDeX mission is a technology demonstration initiative by ISRO.
- It aims to validate the capability of docking and undocking small satellites in low-Earth orbit.
- India is now the fourth country to successfully execute satellite docking operations.
Additional Details
- Mission Objectives:This mission has several objectives:
- Primary objective: To develop and demonstrate the capability for rendezvous and docking of spacecraft in low-Earth orbit.
- Secondary objectives include:
- Demonstrating the transfer of electric power between docked spacecraft, which is crucial for future in-space operations.
- Developing and validating composite spacecraft control systems.
- Testing payload operations after undocking, which is vital for deep-space missions.
- The satellites, each weighing approximately 220 kg, were launched into a 460 km circular orbit by PSLV-C60, with an inclination of 45 degrees.
- With this accomplishment, India joins the ranks of the United States, Russia, and China in successfully conducting satellite docking operations.
This achievement showcases India's advancing capabilities in space technology and positions ISRO as a key player in future space exploration endeavors.
GS3/Science and Technology
Science Behind Uterine Transplants
 Why in News?
Why in News?
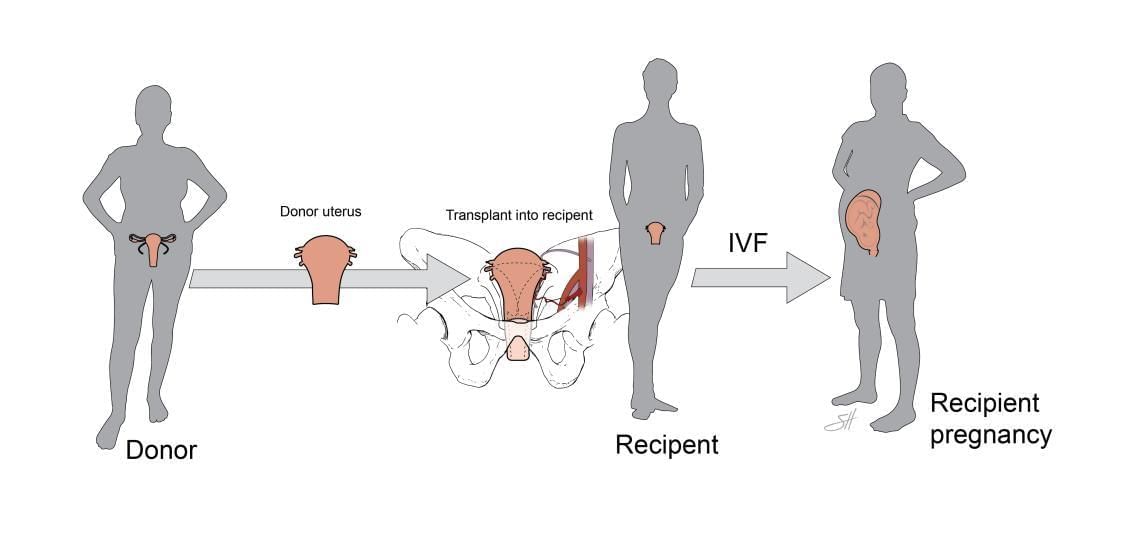
Uterine transplant surgery has emerged as a revolutionary solution for women suffering from absolute uterine infertility. This is underscored by the recent birth of the first child in the U.K. to a mother who received a donated uterus.
- Uterine transplantation allows women without a functional uterus to carry and give birth to children.
- The procedure is typically temporary, permitting one or two pregnancies before the uterus is removed to prevent complications.
Additional Details
- Donor Criteria:
- Age: Donors should be between 30 to 50 years old.
- Health: Donors must be in good overall health, with a BMI under 30, and no history of diabetes, cancer (within the last 5 years), or STIs.
- Exclusions: Women with HIV, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, or other significant health complications are not eligible to be donors.
- The surgery requires gynecological transplant surgeons with specialized training, and a recovery period of 6 months is necessary before attempting pregnancy.
In India, the first uterine transplant was conducted on May 18, 2017, at Galaxy Care Hospital in Pune. A 26-year-old woman received her mother’s uterus, leading to the birth of India's first baby via Caesarean section in October 2018, weighing 1.45 kg and in good health. This success symbolizes India’s advancements in reproductive medicine and provides hope for women seeking biological motherhood.
In light of recent advancements in human reproductive technology, the term “Pronuclear Transfer” is associated with:
- Options:
- (a) Fertilization of egg in vitro by donor sperm
- (b) Genetic modification of sperm-producing cells
- (c) Development of stem cells into functional embryos
- (d) Prevention of mitochondrial diseases in offspring
GS3/Science and Technology
Bullseye Galaxy
Why in News?
The Bullseye Galaxy (LEDA 1313424) has recently been identified by an international team of researchers using advanced astronomical tools such as the Hubble Space Telescope and the W.M. Keck Observatory. This discovery is particularly significant as it sheds light on the formation and characteristics of ringed galaxies.
- The Bullseye Galaxy features a unique ringed structure formed approximately 50 million years ago.
- This galaxy is nearly five times larger than the Milky Way, with a diameter of 250,000 light-years.
- It has been confirmed to have nine distinct rings, which is unusual for galaxies of its type.
Additional Details
- Formation: The ring structure is believed to have emerged from a head-on collision with a blue dwarf galaxy, resulting in gas waves that triggered star formation in concentric rings.
- Evolution Potential: The Bullseye Galaxy may evolve into a Giant Low Surface Brightness (GLSB) galaxy, a rare type associated with significant amounts of dark matter.
- GLSB Galaxy Features: These galaxies are characterized by diffuse, low-density stellar disks, contain large amounts of neutral hydrogen, and exhibit low star formation rates. An example is Malin 1, which is five times wider than the Milky Way.
- GLSB galaxies challenge the Standard Model of Cosmology due to their uniform central mass distribution, suggesting discrepancies in our understanding of cosmic structures.
The discovery of the Bullseye Galaxy not only highlights the complexity of galactic formations but also offers insights into the mysteries of dark matter, making it a significant topic in contemporary astrophysics.
GS2/Polity
Judiciary and Constitutional Boundaries: Vice-President’s Remarks Spark National Debate
Why in News?
Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar has recently raised significant concerns regarding the independence of the judiciary, its powers of judicial review, and the Supreme Court's directive on timelines for the President and Governor's actions related to state legislation. These remarks have ignited a national debate on the role and accountability of the judiciary in India.
- The judiciary serves as the guardian of the Constitution and citizens' rights.
- Concerns about judicial transparency and accountability have been highlighted.
- Mixed reactions from political and legal perspectives on the Vice-President's statements.
Additional Details
- Judiciary's Role: The judiciary's role in India is to ensure justice and accountability, primarily through mechanisms like judicial review and Article 142.
- Recent Remarks by Vice-President: At a public event, VP Dhankhar criticized judicial practices, addressing five key areas of concern:
- Transparency in Judicial Inquiries: He pointed out the lack of transparency in internal inquiries, citing a specific incident involving a Delhi High Court judge.
- Judicial Directives: He questioned a Supreme Court ruling that imposed timelines for constitutional authorities, emphasizing accountability.
- Accountability Deficit: The judiciary lacks a direct mechanism for public accountability, unlike the executive and legislature.
- Size of Constitution Benches: Suggested re-evaluating the requirement of five judges under Article 145(3) due to the current composition of the Supreme Court.
- Use of Article 142: Expressed concerns that the extensive powers under Article 142 might undermine democratic principles.
These remarks have prompted a spectrum of reactions, with some viewing them as an overreach, while others consider them a necessary critique reflecting public sentiments regarding judicial functioning.
Arguments in Favour of Greater Transparency
- Public concern persists regarding secrecy in judicial misconduct inquiries.
- Experts advocate for a transparent inquiry mechanism to enhance public trust in the judiciary.
Judicial Activism: Justified or Overstepped?
Judicial activism, especially through Article 142, has resulted in landmark rulings, including:
- Bhopal gas tragedy compensation (1989)
- Vishaka guidelines on sexual harassment (1997)
- Cancellation of illegal coal-block allocations (2014)
- Granting permanent commission to women officers in armed forces (2024)
- Guidelines on unlawful demolitions (2024)
These cases highlight the judiciary's evolving role in addressing justice where legislative or administrative actions have failed.
On Judicial Review and Timeline Mandates
The judiciary’s power of judicial review is pivotal within the Constitution's basic structure. Legal experts note that the Supreme Court's directive to set timelines for the President and Governors is supported by precedents and government guidelines.
Constitutional Bench Composition
According to Article 145(3), a minimum of five judges are required to adjudicate constitutional matters. Given the current backlog and the Supreme Court's bench strength, this number remains relevant.
Judicial Independence and Constitutional Sovereignty
The Indian constitutional framework integrates elements of both British parliamentary sovereignty and American judicial supremacy. Through judicial review, the Indian judiciary maintains constitutional supremacy, crucial for assessing the legality of legislative and executive actions. Ensuring transparency and inclusiveness in judicial appointments, possibly through a reformed National Judicial Appointments Commission, is essential for public confidence, though it must not compromise judicial independence.
In summary, the ongoing debate surrounding the judiciary's role, transparency, and accountability is vital for reinforcing democratic principles in India.
GS3/Environment
Why is Europe Warming Faster?
Why in News?
The 2024 European State of the Climate Report highlights that Europe is warming nearly twice as fast as the global average, with significant regional variations attributed to human-driven climate change.
- 2024 has been recorded as the warmest year in Europe, particularly affecting Eastern Europe.
- There are distinct climate conditions across regions, with Western Europe experiencing cloudier, wetter weather compared to the sunnier, warmer Eastern regions.
- Southeastern Europe faced its longest recorded heatwave, impacting countries like Bulgaria, Romania, Croatia, Kosovo, and Serbia.
Additional Details
- Proximity to the Arctic Region: Much of Europe lies close to the Arctic, where warming occurs three to four times faster than the global average, contributing to higher temperatures across Europe.
- Albedo Effect: The melting of Arctic ice reveals darker surfaces that absorb more solar radiation, thus accelerating warming in Europe.
- Reduction in Aerosols: Lower aerosol emissions in Europe have led to increased solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface, further enhancing warming.
- Land-Based Warming: Land areas in Europe warm more quickly than oceans, resulting in extreme weather events such as heatwaves, heavy rainfall, and flooding.
- Global Climate Dynamics: Europe's unique geographical and atmospheric characteristics make it particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change compared to other regions.
The scientific consensus indicates that the increase in global temperature should not exceed 2°C above pre-industrial levels. If temperatures rise beyond 3°C, significant impacts could include:
- Terrestrial biosphere trending towards a net carbon source.
- Widespread coral mortality.
GS3/Environment
National Yak Day in Nepal
 Why in News?
Why in News?
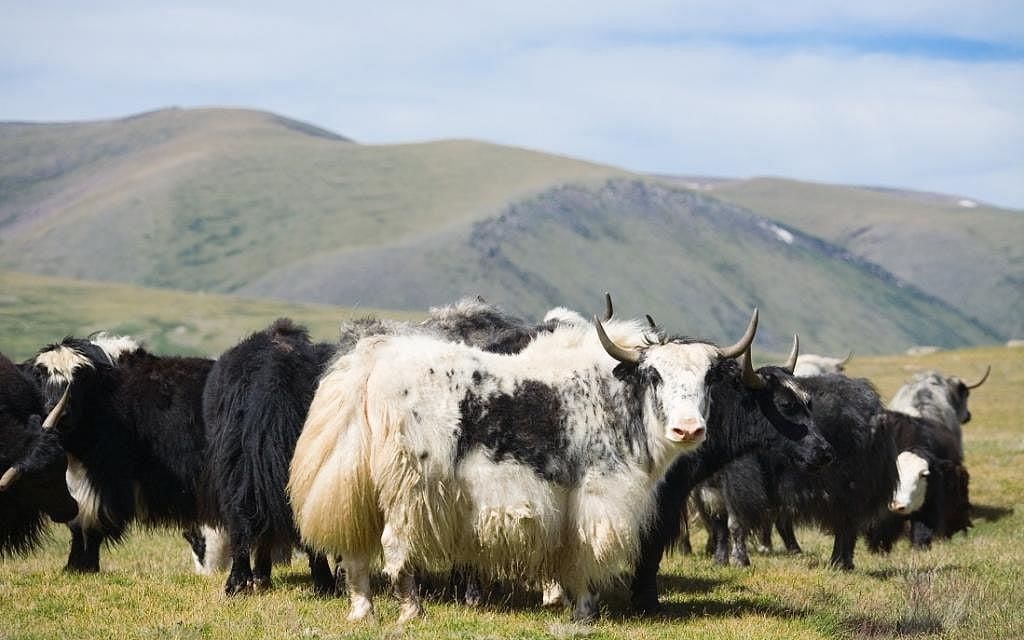
Nepal celebrated its inaugural 'National Yak Day' on April 20, 2025, to recognize the cultural, ecological, and economic significance of the yak in the Himalayan region. The International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) has called on stakeholders to elevate the yak's role within the sustainable development agenda, particularly in the Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) region. This initiative highlights the historical contributions of indigenous communities, such as the Sherpa, Tamang, Thakali, Rai, and Limbu, in protecting yak herding, which is intertwined with food security, cultural heritage, and biodiversity conservation.
- Nepal's first National Yak Day was observed on April 20, 2025.
- ICIMOD advocates for the yak's inclusion in sustainable development efforts.
- Indigenous communities have historically maintained yak herding practices.
Additional Details
- Biological and Geographic Features of Yak:
- Scientific Names: Wild yak (Bos mutus) and Domesticated yak (Bos grunniens).
- Habitat: Wild yaks live in alpine tundra at altitudes ranging from 5000 to 7000 meters, thriving in alpine meadows, steppes, and desert steppes.
- Geographic Distribution: Found across the Himalayan region, Tibetan plateau, and parts of South-Central Asia, with domesticated yaks raised in several Indian states including Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim.
- Physical Characteristics: Yaks typically stand around 2 meters tall at the shoulder, with domesticated yaks being smaller. They feature long, shaggy hair for insulation and distinctive curved horns, with males having larger horns. Notably, their lung capacity is nearly three times that of cattle, adapted for low-oxygen environments, and they are herbivorous, primarily feeding on grasses and alpine plants.
- Uses and Socio-Economic Importance: Domesticated yaks provide milk, meat, and serve as pack animals for transporting goods. They are also utilized in climbing and trekking expeditions, capable of ascending to 20,000 feet. Crossbreeding with domestic cattle produces dzo or chauri gai, which are hybrid animals utilized in agropastoralism.
- Conservation Status: Wild yaks are classified as 'Vulnerable' on the IUCN Red List, signaling the urgent need for conservation efforts to safeguard their habitats and genetic diversity.
The recognition of National Yak Day underscores the importance of yaks in sustaining local cultures and economies while promoting biodiversity conservation and sustainable development in the Himalayas.
GS3/Science and Technology
Gonorrhoea
Why in News?
A new oral antibiotic named gepotidacin has shown promising results in the treatment of persistent gonorrhoea infections, which has become a significant public health concern due to increasing resistance to existing antibiotics.
- Gonorrhoea is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhea.
- It can infect various parts of the body, including the urethra, rectum, throat, and eyes.
- Transmission primarily occurs through sexual activity, and infants can contract it during childbirth.
Additional Details
- Symptoms: Many individuals may not exhibit symptoms. If present, symptoms typically manifest between 1 to 14 daysafter infection. Common symptoms include:
- Sore throat
- Conjunctivitis
- Unusual discharge from the genital areas
- Pelvic and genital pain
- Complications:If left untreated, gonorrhoea can lead to serious health issues such as:
- Skin, joint, heart (endocarditis), and brain (meningitis) infections
- Infertility in both females and males
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Epididymitis and prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate)
- Prevention: Effective prevention strategies include practicing safe sex.
- Treatment: Most cases of gonorrhoea can be effectively treated with antibiotics.
With the emergence of gepotidacin as a potential treatment, there is hope for better management of gonorrhoea, particularly in cases resistant to traditional antibiotics.
GS3/Environment
World’s First Market for Particulate Emissions Trading in Gujarat
 Why in News?
Why in News?
A recent study published in the Quarterly Journal of Economics has highlighted the effectiveness of the world’s first market for trading particulate emissions, established in Surat’s industrial cluster. This study covered 162 textile plants over nearly two years and found that participants in the emissions trading system reduced pollution by 20–30%, outperforming those under traditional regulatory measures.
- The emissions trading system (ETS) resulted in participants holding permits for 99% of their emissions.
- Non-participating plants violated norms about one-third of the time.
- The findings affirm emissions trading as a viable tool for pollution control, modeled after successful international examples from Europe and China.
Additional Details
- Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS): This regulatory mechanism aims to reduce greenhouse gas or particulate emissions by providing financial incentives for industries to comply with pollution standards and invest in cleaner technologies.
- Working of ETS – The Cap-and-Trade Model:
- Cap on Emissions: Regulators set a limit on the total allowable emissions.
- Permits Allocation: Industries receive permits that allow them to emit a specified amount of pollutants.
- Trading System: Plants that successfully reduce emissions can sell their unused permits to create a financial incentive for cleaner operations.
- Benefits for Industries:
- Flexibility: Industries can gradually transition to cleaner technologies by purchasing permits.
- Revenue Opportunity: Efficient plants can profit by selling surplus permits.
- Price Controls and Penalties:
- Price Stability: Regulators establish minimum and maximum prices for permits to maintain market attractiveness.
- Enforcement: Industries exceeding their emission caps face penalties or must surrender permits.
- Long-Term Impact: As the ETS evolves, the total number of permits will be reduced, encouraging industries to adopt cost-effective, cleaner technologies.
The Surat ETS, launched in 2019, is a pioneering market-based initiative aimed at controlling particulate matter pollution, particularly targeting 342 highly polluting industries that primarily utilize coal, lignite, and diesel. Developed by the Gujarat Pollution Control Board (GPCB) in collaboration with researchers from J-PAL, EPIC, and Yale University, the scheme has significantly improved compliance and emission control, providing a cost-effective and transparent approach to pollution reduction.
In contrast to traditional command-and-control systems, which enforce uniform regulations across all industries, the ETS offers a more flexible and tailored approach that encourages industries to adopt cleaner technologies progressively. This shift from strict enforcement to market-driven solutions enhances efficiency and accountability within the industrial sector.
GS2/International Relations
India, China at 75 — A Time for Strategy, Not Sentiment
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The 75th anniversary of diplomatic relations between India and China serves as a crucial moment that goes beyond mere celebration; it signifies a critical juncture in both Asian and global geopolitics. The relationship, once based on idealistic notions of pan-Asian solidarity, has transformed into a strategic balancing act characterized by contested borders, economic interdependence, and geopolitical rivalry.
- The India-China relationship is marked by deep mistrust yet offers opportunities for cooperation.
- China significantly influences Indian foreign policy, affecting decisions on border security and economic strategy.
- India's approach is one of "competitive coexistence," balancing competition with dialogue.
- The U.S.-China rivalry complicates India's strategic calculations, necessitating a careful balance with the U.S.
Additional Details
- China Lens: The concept of the "China lens" encapsulates how nearly all of India's strategic decisions are influenced by its relationship with China, marking it as a structural challenge.
- Economic Interdependence: Despite geopolitical tensions, China remains a crucial trading partner for India, with a significant trade imbalance. Full economic decoupling is deemed unrealistic in the near term.
- Regional Influence: India's traditional dominance in South Asia is challenged by China's growing influence, necessitating proactive strategies to maintain regional leadership.
- Strategic Autonomy: The return of Donald Trump introduced pressures for India to align closely with U.S. interests, complicating its independent foreign policy stance.
As India and China observe 75 years of diplomatic interaction, it is essential to transition from nostalgia to strategic clarity. The relationship with China should be viewed not merely as a competition but as a framework for achieving an autonomous and influential role in a rapidly changing global landscape.
GS3/Environment
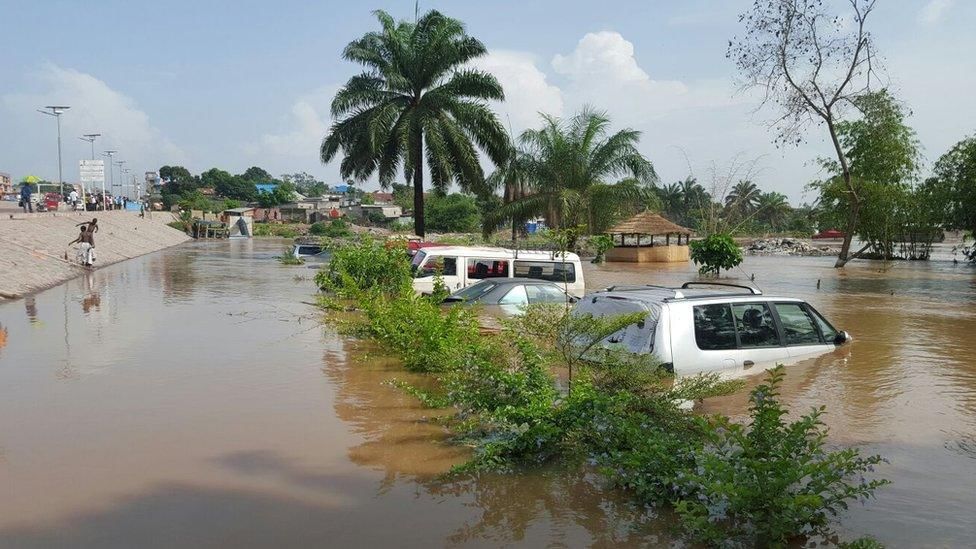
Flooding in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The recent flooding in April 2025 in Kinshasa, the capital of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), has drawn attention due to its severe impact on the urban population, primarily caused by urban mismanagement and infrastructure failures rather than excessive rainfall alone.
- The flooding was exacerbated by runoff from the Congo Central Province.
- Urban tributaries, specifically the Ndjili River and Lukaya tributary, were overwhelmed.
- The disaster resulted in significant casualties: 70 deaths and 150 injuries.
- Over 21,000 people were displaced, affecting 73 healthcare facilities and disrupting essential services.
- Current instability in eastern DRC due to the M23 armed group has led to further mass displacement.
Additional Details
- Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC): The DRC is the second largest country in Africa, following Algeria, and is the largest in Sub-Saharan Africa.
- Geography: The country features the Congo River, which is the second longest river in Africa, and is predominantly covered by tropical forests.
- Mineral Resources: The DRC is rich in various minerals including cobalt, copper, gold, lithium, iron ore, and coal.
- Flood Hotspots: Kinshasa is one of 38 identified flood hotspots in the Congo Basin.
This flooding incident highlights the urgent need for improved urban planning and infrastructure in Kinshasa to mitigate the effects of future flooding and support the well-being of its residents.
GS3/Environment
Nitrogen: A Double-Edged Sword for Life and Climate
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Nitrogen, a critical element for life, is also a significant contributor to climate change. India is the world’s second-largest emitter of nitrous oxide (N2O), a greenhouse gas with a global warming potential 300 times greater than carbon dioxide (CO2). This raises concerns about the implications of nitrogen management on climate risks.
- Nitrogen makes up approximately 78% of Earth's atmosphere.
- It is essential for the synthesis of DNA, ATP (the energy currency of cells), proteins, and chlorophyll.
- The nitrogen cycle is crucial for maintaining ecological balance.
- Excess nitrogen leads to significant environmental problems.
Additional Details
- Nitrogen Cycle: The nitrogen cycle is a natural process that converts atmospheric nitrogen (N2), which is inert and unusable by organisms, into forms that plants can absorb. This involves:
- Diazotrophs: Nitrogen-fixing bacteria that convert N2 into ammonia.
- Nitrification: The process where ammonia is converted into nitrites (NO2-) and then into nitrates (NO3-), which plants can utilize.
- Denitrification: Returns excess nitrates to the atmosphere, maintaining the nitrogen cycle.
- Haber-Bosch Process: Developed in the early 20th century, this process enabled the industrial fixation of nitrogen, leading to the production of synthetic fertilizers. It revolutionized agriculture and contributed to the Green Revolution, which supported exponential population growth.
- Environmental Risks of Excess Nitrogen:The overproduction of reactive nitrogen (ammonia, nitrate, nitrous oxide) through chemical fertilizers has led to:
- Eutrophication of water bodies, causing algal blooms and dead zones (e.g., Gulf of Mexico).
- Soil acidification and air pollution from nitrogen oxides (NOx) emissions.
- Formation of ground-level ozone and acid rain.
- N2O is now recognized as the third most potent greenhouse gas, following CO2 and methane (CH4).
Understanding nitrogen's role in both ecological balance and climate change is crucial for developing sustainable agricultural practices and mitigating environmental impacts.
|
44 videos|5271 docs|1113 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 22nd April 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of the Alamosaurus fossil discovery? |  |
| 2. What is the SpaDeX Mission, and what are its objectives? |  |
| 3. How do uterine transplants work, and what is their purpose? |  |
| 4. Why is the Bullseye Galaxy an important subject of study in astronomy? |  |
| 5. What are the implications of the world’s first market for particulate emissions trading in Gujarat? |  |
















