UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 23rd April 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS1/History & Culture
Bamiyan Buddhas
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Bamiyan Buddhas, two monumental statues in central Afghanistan, are significant cultural and historical symbols. Recently, discussions around Afghanistan's heritage sites have intensified, particularly in the context of the Taliban's changing attitudes towards cultural preservation.
- The Bamiyan Buddhas were carved in the 6th century CE and stood at heights of 115 feet and 174 feet.
- They exemplified the Gandhara School of Buddhist Art, showcasing a blend of Indian, Persian, and Greco-Roman influences.
- The Taliban destroyed the statues in February 2001, marking a significant act of cultural vandalism.
- In 2003, UNESCO designated the Bamiyan Valley as a World Heritage Site despite the destruction.
- In 2021, a 3D holographic projection temporarily recreated the statues, aiming to engage with the lost heritage.
Additional Details
- Bamiyan Buddhas: These statues, known as Salsal and Shamama, represented a fusion of artistic styles, including Gupta, Sassanian, and Hellenistic elements, highlighting the confluence of various civilizations.
- The Taliban's destruction of the Buddhas was based on their extremist interpretation of Islamic law, which prohibited art and public expressions deemed un-Islamic.
- Despite the destruction, the Bamiyan Valley remains a site of cultural significance and ongoing discussions about heritage and preservation.
The Bamiyan Buddhas serve as a reminder of the rich cultural history of Afghanistan and the importance of preserving heritage sites against the backdrop of extremism and cultural erasure.
GS3/Environment
Earth Day and the Urgent Call for Sustainable Stewardship
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Earth Day, celebrated annually on April 22, serves as a vital reminder of humanity's responsibility to preserve the planet's resources for future generations. This day should represent more than just a date; it must be a turning point for policy, people, and the planet.
- Earth Day highlights the ecological crisis and the essentials required for human survival: clean air, safe water, nourishing food, and natural resources.
- The planet is facing severe challenges due to overexploitation, leading to depletion and degradation of resources.
- India's sustainability initiatives aim to transition from rhetoric to responsibility through various climate commitments.
Additional Details
- Ecological Crisis: The planet cannot sustain humanity's greed-driven consumption. Issues such as deforestation, plastic pollution, air quality deterioration, declining groundwater, and erratic weather patterns are prevalent.
- Earth Day's Evolution: Since its inception in 1970, Earth Day has influenced global environmental policies but often gets reduced to symbolic actions rather than meaningful change.
- India's Sustainability Journey: Initiatives like the Panchamrit Pledge aim for significant climate commitments, including reaching 500GW of non-fossil energy capacity by 2030 and achieving net-zero emissions by 2070.
- Renewable Energy Focus: Solar energy is a cornerstone of India’s climate action, with initiatives like the International Solar Alliance and large solar parks enhancing renewable energy capacity.
- Legal Framework: The Environment Protection Act (1986) and newer regulations on e-waste and plastic management are expanding to meet contemporary environmental challenges.
In conclusion, Earth Day must evolve beyond mere symbolism. It should inspire actions such as mindful consumption, reducing plastic use, supporting green policies, and fostering a deeper connection with nature. Sustainability is no longer a choice; it is an existential imperative as there is no Planet B.
GS3/Environment
Cloudburst and Its Impact in Ramban District
 Why in News?
Why in News?
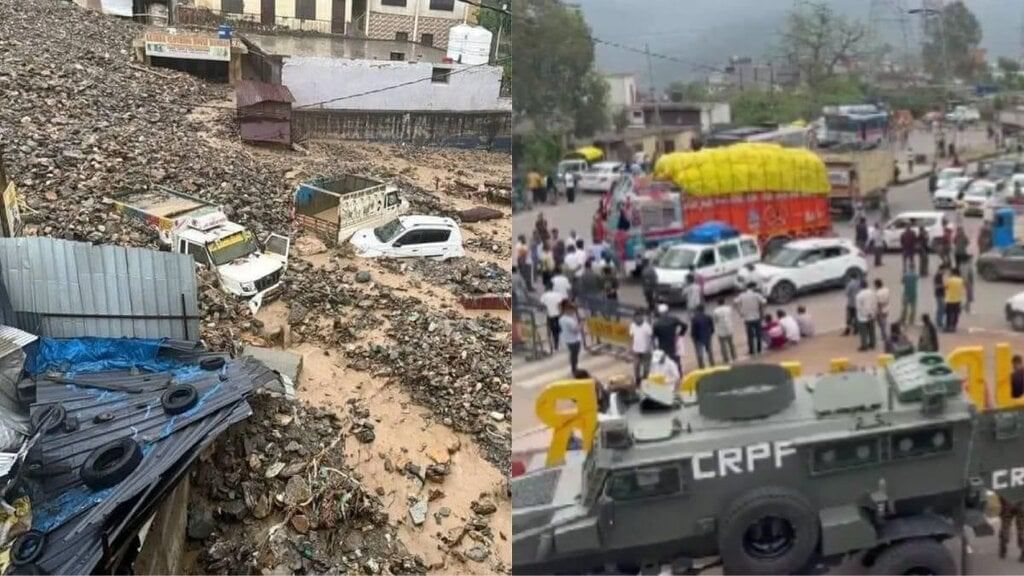
The Ramban district of Jammu and Kashmir has recently experienced devastating effects due to severe weather, characterized by torrential rainfall and hail. The India Meteorological Department (IMD) reported a remarkable 9 mm of rainfall in just 24 hours, which is a staggering 575% increase from the normal rainfall of 2.5 mm.
- A cloudburst is defined as a localized and extremely intense rainfall event.
- Such events often lead to severe consequences, including flash floods and landslides.
Additional Details
- What is a Cloudburst? A cloudburst is an intense rainfall event characterized by 10 cm or more rainfall within one hour over a small area of approximately 10 km × 10 km. Even 5 cm of rain in 30 minutes can qualify as a cloudburst.
- Cloudbursts are more common in mountainous regions due to a phenomenon known as orographic lift, where warm air ascends mountain slopes, expands, cools, and releases moisture as precipitation.
- The localized nature of cloudbursts makes them challenging to predict, leading to overwhelming drainage systems and resulting in flash floods and landslides.
Flash floods occur as a result of sudden and rapid inundation when excessive rainwater enters streams, drains, or rivers, often overwhelming natural drainage systems. They tend to be more frequent in areas with rocky terrain that absorbs little water, leading to increased surface runoff. Unlike riverine floods that cause long-term damage, flash floods are often more deadly, catching people off guard and leading to significant loss of life.
GS3/Environment
Arctic Amplification
Why in News?
The 2024 European State of the Climate Report reveals alarming trends in global and European temperatures, highlighting the phenomenon of Arctic amplification and its severe implications for climate and ecology.
- Europe has warmed nearly twice as fast as the global average, with a temperature increase of about 4°C.
- Arctic amplification is a critical phenomenon where temperature rises in polar regions exceed those in other parts of the world.
- Factors contributing to Arctic amplification include Ice-Albedo Feedback, Lapse Rate Feedback, Water Vapour Feedback, and Ocean Heat Transport.
Additional Details
- Arctic Amplification: This phenomenon describes the accelerated warming in the Arctic, driven by changes in the net radiation balance of the atmosphere, largely due to increased greenhouse gases such as CO₂ and methane.
- The global average temperature has risen by approximately 3°C since pre-industrial levels (1850-1900), with Europe exceeding this by crossing the critical 5°C threshold for the first time.
- Regional variations in Europe include the eastern part experiencing warmer and sunnier conditions, while western regions faced cloudier and wetter weather.
- Southeastern European countries like Bulgaria, Romania, Serbia, and Croatia recorded their longest heatwave in 2024, highlighting the extremes of climate change.
The findings underscore the urgent need for climate action, as the accelerated warming in Europe and the Arctic poses significant risks for ecosystems and human societies alike.
GS3/Environment
Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS)
Why in News?
The Surat Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS) has gained attention as it represents the world’s first market-based initiative specifically aimed at controlling particulate air pollution. Launched in 2019, this innovative scheme focuses on trading emissions related to particulate matter rather than carbon dioxide (CO₂). It marks a significant step in India's approach to environmental management, particularly for high-emission industries.
- The Surat ETS is the first of its kind globally designed to address particulate air pollution.
- It operates under a cap-and-trade system where emission permits can be traded among industries.
- This scheme specifically targets 342 high-emitting industries, primarily in the textile sector.
- Developed by the Gujarat Pollution Control Board (GPCB) in collaboration with various academic institutions.
Additional Details
- Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS): A regulatory tool that aims to reduce air pollution by creating economic incentives. Under this system, a cap is placed on total permissible emissions, and industries receive emission permits that can be bought or sold, facilitating the trading of pollution rights.
- Significance: The Surat ETS is particularly notable as it represents India’s first emissions market for any pollutant, focusing on industries that utilize solid and liquid fuels, such as coal, lignite, and diesel.
- The program encourages cleaner industries to sell their unused permits to more polluting units, thereby creating a financial incentive for pollution reduction.
Overall, the Surat ETS is a pioneering initiative that could serve as a model for other regions seeking to manage air pollution through market-based solutions.
GS3/Science and Technology
LEDA 1313424: The Bullseye Galaxy
 Why in News?
Why in News?
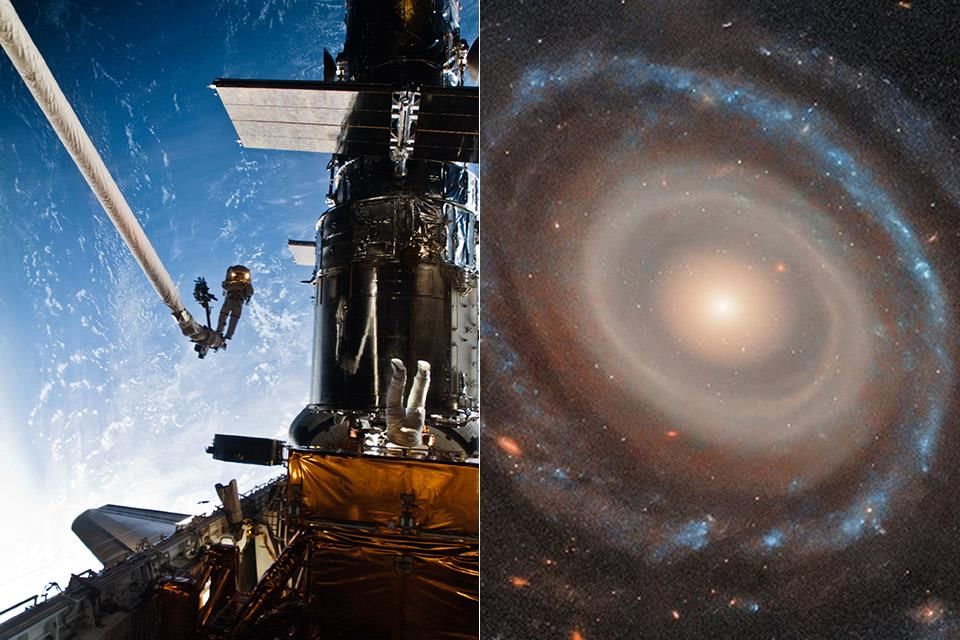
The recent discovery of the Bullseye Galaxy (LEDA 1313424) by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has garnered significant attention due to its unique structure. This galaxy features an unprecedented nine rings, offering new insights into galaxy evolution and the potential for evolving into a Giant Low Surface Brightness (GLSB) galaxy.
- The Bullseye Galaxy contains nine rings, far exceeding the typical 2 to 3 rings found in most ringed galaxies.
- The rings likely formed from a collision with a blue dwarf galaxy approximately 50 million years ago.
- This discovery enhances our understanding of galaxy interactions and the formation of multiple rings.
Additional Details
- Giant Low Surface Brightness (GLSB) Galaxies: These are large, diffuse galaxies characterized by low surface brightness and lower star counts, making them appear dimmer. They contain extensive hydrogen disks, which are essential for star formation, but their low hydrogen density limits star creation.
- GLSB galaxies are thought to hold substantial amounts of dark matter, impacting their mass distribution and challenging existing cosmological models due to their unique hydrogen content.
- The Bullseye Galaxy's extended disk and hydrogen content suggest it may evolve into a GLSB galaxy, providing insights into the formation of such galaxies and their distribution in the universe.
This discovery not only expands our knowledge of galaxy structures but also raises important questions about the dynamics of galaxies in the universe.
Consider the following phenomena:
- Light is affected by gravity.
- The Universe is constantly expanding.
- Matter warps its surrounding space-time.
Which of the above is/are the prediction/predictions of Albert Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity, often discussed in the media? Options: (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3
GS3/Defence & Security
Terror Attack on Tourists in J&K’s Pahalgam
 Why in News?
Why in News?
In a tragic incident, twenty-eight individuals, primarily tourists, lost their lives in a terrorist attack in the picturesque Baisaran Valley, located in Pahalgam, Anantnag district of Jammu and Kashmir. This marked the deadliest attack since the abrogation of Article 370 in 2019, with the remote and elevated terrain complicating rescue efforts. The Resistance Front, a proxy group backed by the ISI and affiliated with Lashkar-e-Taiba, has claimed responsibility for the assault.
- The attack is the most lethal since the abrogation of Article 370, highlighting ongoing security challenges in the region.
- Pahalgam, a favored hill station, is known for its natural beauty and trekking opportunities.
- The Resistance Front (TRF) is a militant group that emerged after the abrogation of Article 370 and has been active in targeting civilians.
Additional Details
- Pahalgam: A well-known hill station in Anantnag district, approximately 90 km from Srinagar International Airport, famous for its scenic beauty.
- Tourist Attractions:Pahalgam is renowned for sites such as:
- Amarnath Cave Temple - A significant Hindu shrine.
- Aru Wildlife Sanctuary - Home to diverse wildlife including brown bears and musk deer.
- Betaab Valley - Named after a popular Bollywood film.
- Tulian Lake - An attractive alpine lake ideal for trekkers.
- Baisaran - Often referred to as "Mini Switzerland," known for its stunning meadows and dense forests.
- The terrorist attack underscores a severe internal security challenge, affecting tourism and overall perceptions of safety in Jammu and Kashmir.
- The TRF has been linked to various attacks targeting tourists, minority communities, and migrant workers since its inception.
This attack not only disrupts the growing tourism sector, which was seen as a sign of normalcy post-Article 370, but also reignites fears of violence in the valley. The timing of the attack, coinciding with significant diplomatic visits, raises concerns about its implications for regional security and international relations.
GS3/Environment
Poás Volcano
Why in News?
The Poás Volcano, a prominent tourist destination in Costa Rica, has recently erupted, drawing attention due to its geological activity and environmental impact.
- Poás is one of Costa Rica's most active volcanoes, located within the Poás Volcano National Park.
- The volcano features a large main crater, measuring approximately 1.5 km in width and 300 meters deep.
- Recent volcanic activity has included ash-producing eruptions and increased gas emissions.
Additional Details
- Volcanic Characteristics: Poás is classified as a composite stratovolcano, with a complex structure formed by multiple eruptive centers. It covers a basal area of about 400 sq.km and rises to an elevation of 2,708 meters above sea level.
- Environmental Impact: Since 1989, the volcano has significantly increased gas emissions, leading to acid rain that has adversely affected flora in the park and nearby agricultural areas.
- This year, the crater lake has been drying up, contributing to ongoing eruptions and ash ejections.
The recent eruptions and environmental changes highlight the need for monitoring and understanding the impacts of volcanic activity on both the local ecosystem and human activities.
GS3/Science and Technology
Quantum Gravity Gradiometer (QGG)
Why in News?
Nasa scientists are exploring an innovative application of cold atom-based Quantum Gravity Gradiometers (QGGs) to monitor changes in the Earth's mass distribution, particularly in relation to climate change.
- The QGG will be deployed on a satellite to detect minute variations in gravitational forces.
- It employs atoms cooled to near absolute zero, allowing them to enter wave-like states.
- Lasers are used to manipulate these atoms, measuring phase shifts that correlate with gravitational forces.
Additional Details
- Detection Capability: The QGG can measure differences in acceleration as subtle as 10-15 m/s2 over a distance of just 1 meter.
- The instrument can assess the mass of large geological formations, such as the Himalayas, and monitor the movement of water, ice, and geological materials with high precision from low Earth orbit.
- Gravitational Variability: The gravitational force experienced at different locations on Earth varies due to the mass of nearby objects, with stronger gravitational pull near dense structures like mountain ranges compared to less dense areas like cities.
- Application: QGGs are sensitive instruments that measure how gravitational acceleration changes across different locations, which is useful in resource exploration, such as locating hydrocarbon deposits.
This advanced technology represents a significant step forward in our ability to measure and understand the Earth's gravitational field and its implications for climate science and resource management.
GS3/Economy
Sunrise Industries and India's Manufacturing Goals
Why in News?
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman has announced India's intention to boost the manufacturing sector's contribution to the GDP from 12% to 23% over the next two decades, leveraging the growth of sunrise sectors.
- India aims to significantly increase its manufacturing sector's share in GDP.
- Sunrise industries are critical for this growth due to their rapid development and innovation.
Additional Details
- Sunrise Industry:This term refers to sectors that are in a state of rapid growth and innovation, often characterized by high growth rates and numerous startups. Examples include:
- Alternative energy (highlighted in 2003 and 2007)
- Social media and cloud computing (emerged in 2011 and 2012)
- Blockchain technologies (developed from 2013 to 2017)
- Information technology and clean energy.
- As these industries evolve, they may lead to the decline of older sectors, commonly referred to as sunset industries.
- Life Cycle of a Sunrise Industry: Industries can transition from the sunrise phase to maturity and eventually into the sunset stage. An example is the compact disc industry, which thrived in the 1990s but declined due to the rise of digital media in the 21st century.
In summary, the focus on sunrise industries is pivotal for India’s ambitious manufacturing goals, promising both economic growth and technological advancement.
GS2/International Relations
Exploring India’s Potential in the Arctic Region
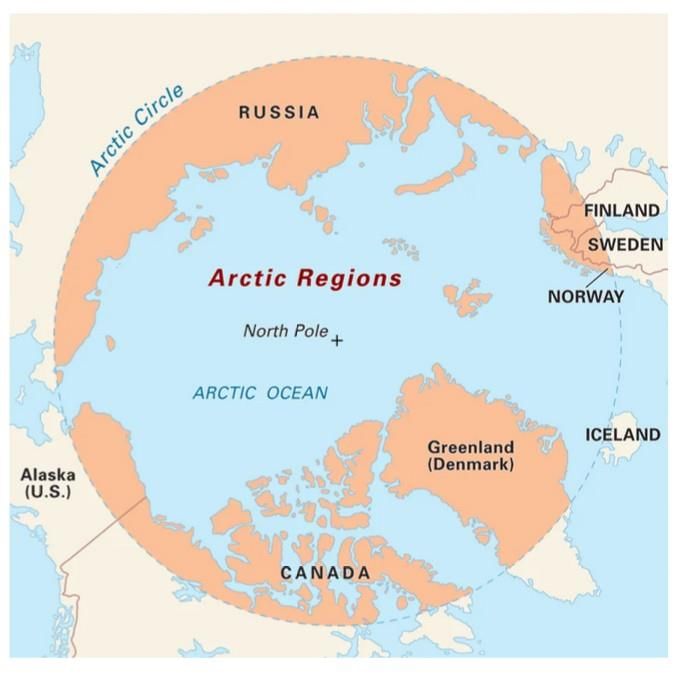 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Arctic region is undergoing significant transformations due to climate change, which is melting ice and altering global trade routes. This scenario presents India with an opportunity to engage strategically in the Arctic, necessitating an examination of its Arctic policy, the implications of the Northern Sea Route (NSR), and the diplomatic balancing act between Western nations and Russia.
- The Arctic is becoming a focal point for geopolitical competition as climate change accelerates ice melt.
- India's Arctic policy aims to enhance its economic and strategic interests through proactive engagement.
- The Northern Sea Route (NSR) offers a shorter trade pathway between Europe and Asia, presenting significant commercial benefits.
- India is investing in Arctic-ready infrastructure, evidenced by a $3 billion Maritime Development Fund announced in its 2025-26 Budget.
Additional Details
- Climate Change and Economic Opportunity: The NSR, which runs along the Russian Arctic coast, could drastically reduce shipping times and costs, making it a vital corridor for trade.
- India’s Early Engagement: Since signing the Svalbard Treaty in 1920, India has developed a presence in the Arctic with its research base, Himadri, and has focused on understanding climate impacts on national issues.
- Diplomatic Balancing Act: India must navigate its relationships with Russia, China, and Western nations to ensure its Arctic ambitions do not conflict with geopolitical tensions.
- Collaborating with like-minded countries like Japan and South Korea could enhance India's influence in Arctic governance.
India's ambitions in the Arctic signify a crucial intersection of commerce, climate considerations, and diplomacy. The potential of the NSR is immense, and to harness it, India must prioritize technological advancements and strategic discussions, potentially appointing a 'polar ambassador' to articulate its Arctic interests effectively.
GS3/Economy
Jwaneng Diamond Mine
 Why in News?
Why in News?
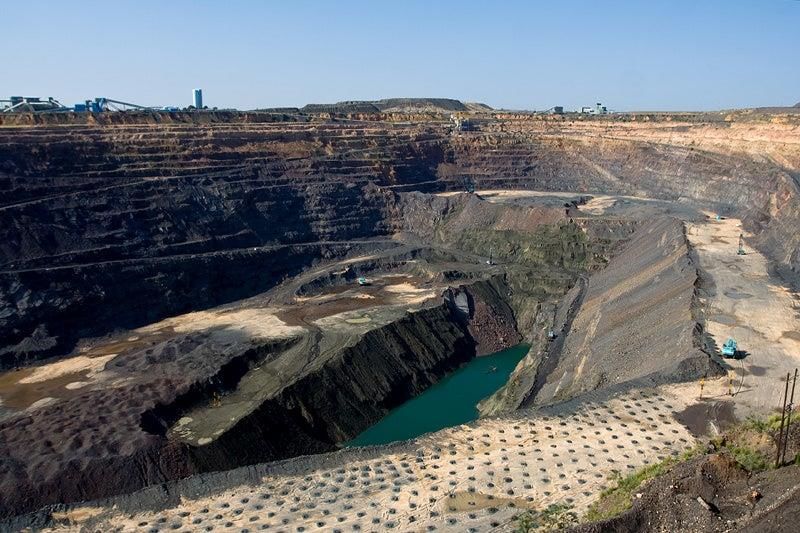
The Jwaneng Diamond Mine is recognized as the richest diamond mine in the world, with an estimated value of 1 billion euros. Its significant contributions to Botswana's economy and its advanced mining technology make it a notable topic of discussion.
- Located in Botswana, Jwaneng is often referred to as the "Prince of Mines."
- Operated by Debswana, a collaboration between De Beers and the Botswana government.
- In 2023, the mine produced 13.3 million carats of diamonds.
- Revenue generated by the mine has exceeded $96 billion since its inception.
Additional Details
- Geographical Significance: The mine is situated on the edge of the Kalahari Desert, approximately 170 km southwest of Gaborone, Botswana's capital. It is located within an ancient volcanic crater.
- Mining Technology: Jwaneng employs advanced mining techniques, including large drills and state-of-the-art processing technologies like X-ray and laser sorters to separate diamonds from rock.
- Environmental Standards: Jwaneng was the first mine in Botswana to receive ISO 14001 certification, highlighting its commitment to eco-friendly practices.
Overall, the Jwaneng Diamond Mine has not only solidified its status as a leading diamond producer but has also played a crucial role in shaping the economic landscape of Botswana.
|
55 videos|5389 docs|1141 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 23rd April 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the Bamiyan Buddhas and why are they significant? |  |
| 2. How does Earth Day promote sustainable stewardship? |  |
| 3. What are the effects of cloudbursts in the Ramban District? |  |
| 4. What is Arctic amplification and its implications? |  |
| 5. How does the Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS) work? |  |
















