UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 27th April 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Defence & Security
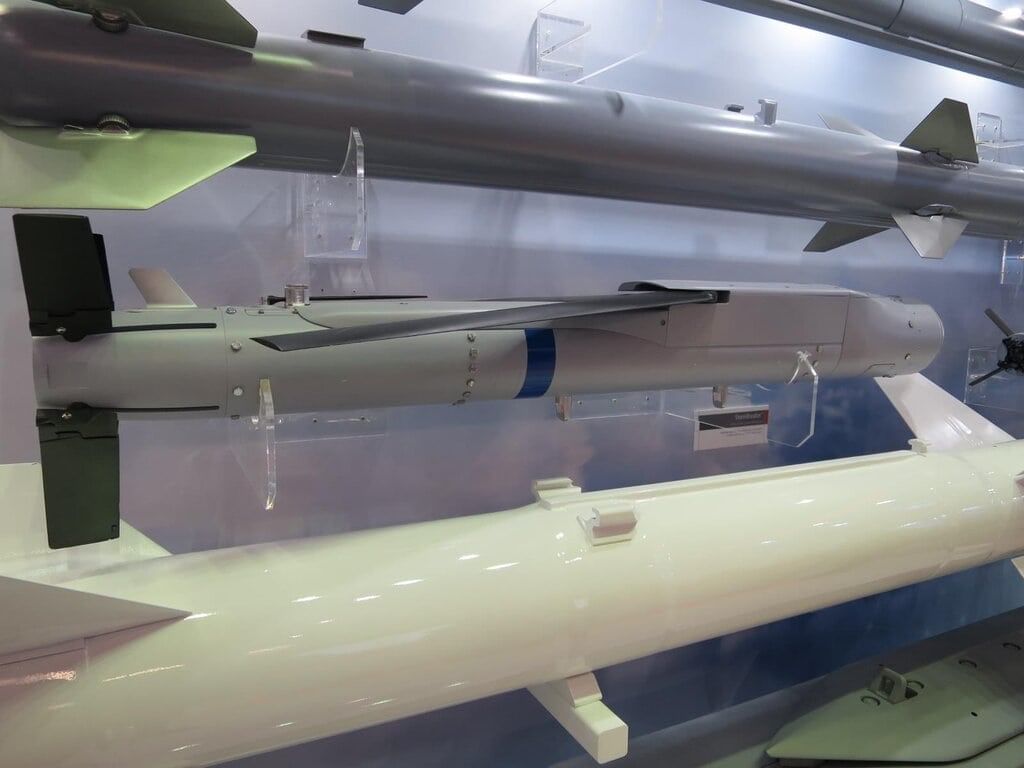
What is the StormBreaker Glide Bomb?
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The StormBreaker glide bomb has been reported to be in use by US fighter jets during combat operations against the Houthis, which forms part of a broader bombing campaign targeting Iran-backed rebel forces.
- The StormBreaker, also known as the GBU-53/B or Small Diameter Bomb II (SDB-II), is an American precision-guided glide bomb.
- It is developed by Raytheon for all-weather precision strikes against various targets.
Additional Details
- Specifications: The StormBreaker weighs 93 kg, measures 1.76 meters in length, and has a diameter between 15 to 18 cm.
- Guidance System: It features a multi-mode guidance system, combining millimeter-wave radar, uncooled infrared imaging, and a digital semi-active laser for enhanced targeting accuracy.
- Navigation: Equipped with a GPS/INS navigation system, it allows for real-time in-flight target updates, which increases its adaptability during missions.
- TacNet Data Link: This technology supports weapon-to-weapon collaboration, facilitating Automatic Target Recognition (ATR) to identify and engage tracked or wheeled vehicles.
- Warhead: The StormBreaker has a multi-effects warhead that combines blast, fragmentation, and shaped charge modes, ensuring effectiveness against a variety of targets.
- Range: It can strike moving targets at a distance of up to 45 miles and stationary targets at a maximum range of 69 miles.
Recent reports suggest a StormBreaker may have landed intact in Yemen, raising concerns about the potential for this advanced weapon to fall into the wrong hands.
GS2/International Relations
What is the United Nations High Seas Treaty?
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Delegates recently convened at the first session of the Preparatory Commission meeting in New York, two years after the adoption of the High Seas Treaty, to establish the necessary rules for its implementation and prepare for the first Conference of Parties (COP1).
- The treaty, formally known as the Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) Agreement, is the first international treaty aimed at protecting oceans beyond national boundaries.
- It is legally binding and focuses on the sustainable use of marine biological diversity through international cooperation.
- The treaty is expected to enter into force 120 days after 60 countries have ratified it.
Additional Details
- Objectives: The treaty contains 75 articles designed to protect and responsibly use marine environments, maintain the integrity of ocean ecosystems, and conserve marine biodiversity. It aims to designate 30% of the oceans as protected areas by 2030, as pledged during the UN biodiversity conference in 2022.
- Marine Protected Areas (MPAs): It provides a legal framework for establishing MPAs to safeguard wildlife and manage genetic resources from the high seas.
- The treaty mandates environmental assessments to evaluate commercial activities, such as deep-sea mining, to mitigate potential damage.
- It establishes a Conference of Parties (CoP) that will meet periodically to hold member states accountable for governance and biodiversity issues.
- Signatories are required to share ocean resources fairly, prohibiting claims of sovereign rights over resources found in the high seas.
- The treaty promotes an inclusive, ecosystem-centric approach that utilizes traditional and scientific knowledge to minimize environmental impacts.
The high seas refer to ocean areas beyond national jurisdiction, starting at the edge of countries' exclusive economic zones, which extend up to 370 km (200 nautical miles) from coastlines. Covering more than 60% of the world's oceans, these waters are often unregulated and susceptible to exploitation, making the treaty a significant step towards sustainable ocean governance.
GS3/Science and Technology
No Phenotype Data Details in GenomeIndia's Proposal Call
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) has raised concerns among researchers across India by initiating a proposal call for 'Translational Research using GenomeIndia data' without providing essential information regarding the available phenotype data.
- The GenomeIndia project has collected data from over 20,000 individuals across 83 population groups.
- Preliminary findings related to genetic data were published in the journal Nature Genetics on April 8, 2025.
Additional Details
- Types of Phenotype Data Collected:The phenotype data collected encompasses a range of anthropometric measurements:
- Height
- Weight
- Hip circumference
- Waist circumference
- Blood pressure
- Blood Sample Analysis:From the blood samples, various health indicators were assessed, including:
- Complete blood counts
- Biochemical data
- Glucose levels
- Lipid profiles
- Liver function tests
- Kidney function tests
- About 'Phenome India' Project: Launched on December 7, 2023, by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), this initiative aims to create India-specific risk prediction models for cardio-metabolic diseases such as diabetes, liver diseases, and cardiac diseases.
- This is India's first comprehensive longitudinal health monitoring study focusing on cardio-metabolic health, involving around 10,000 participants from 17 states and 24 cities.
- The data collected includes clinical questionnaires, lifestyle and dietary habits, anthropometric measurements, imaging and scanning data, and extensive biochemical and molecular data.
- This study is vital for understanding how India's ethnic diversity and lifestyle patterns impact the incidence of cardio-metabolic disorders.
- The CSIR is promoting a Predictive, Personalised, Participatory, and Preventive (P4) healthcare model tailored to Indian genetic and phenotypic profiles.
The lack of detailed phenotype data in the GenomeIndia proposal has highlighted the need for transparency to facilitate effective research and enhance the understanding of genetic contributions to health outcomes in diverse populations.
GS3/Science and Technology
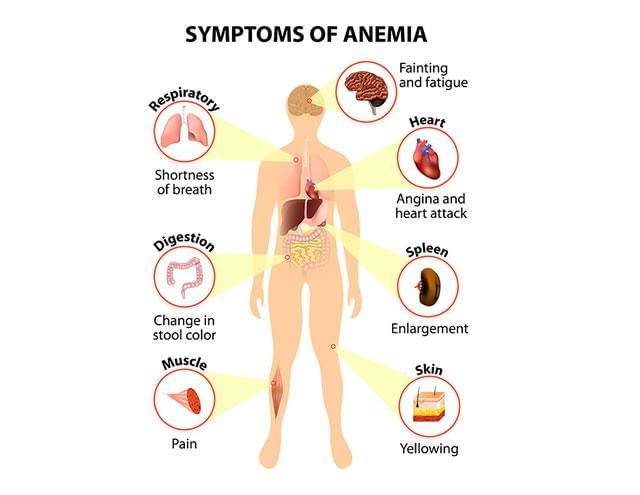
Key Facts About Anaemia
 Why in News?
Why in News?
A recent study in the UK has highlighted a significant concern regarding anaemia during pregnancy, linking it to a 47% increased risk of heart conditions in newborns.
- Anaemia is characterized by a deficiency of healthy red blood cells or hemoglobin.
- Hemoglobin is crucial for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the body’s organs.
- Symptoms of anaemia include tiredness, weakness, and shortness of breath.
Additional Details
- Anaemia Types: There are various forms of anaemia, each with distinct causes. Some types are inherited, while others can develop over a person's lifetime.
- Statistics: According to the WHO, approximately 40% of children aged 6-59 months, 37% of pregnant women, and 30% of women aged 15-49 globally are affected by anaemia.
- Severity: Anaemia can be categorized as short-term or long-term and can range from mild to severe, with severe cases posing life-threatening risks.
- Common Type: Iron-deficiency anaemia is a prevalent form, often resulting from insufficient iron intake, absorption issues, or blood loss.
- Treatment Options: Treatment may include dietary changes, supplements, or medical procedures to manage or prevent anaemia.
In summary, understanding anaemia, its implications during pregnancy, and the importance of adequate iron levels can help mitigate health risks for both mothers and their children.
GS1/Geography
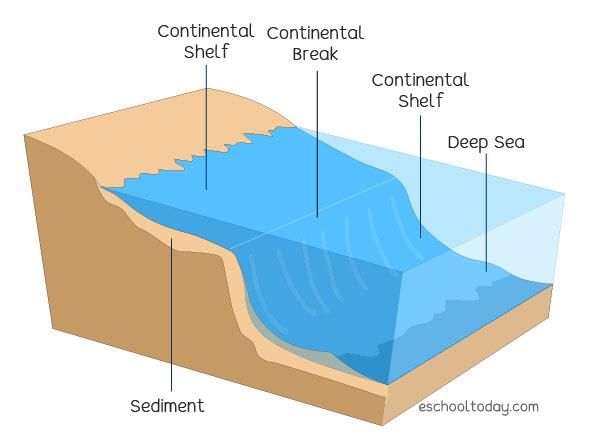
Key Facts about Continental Shelf
 Why in News?
Why in News?
India has recently expanded its claim in the Central Arabian Sea regarding its ‘extended continental shelf’ by nearly 10,000 sq.km. This modification comes as India seeks to resolve a long-standing maritime boundary dispute with Pakistan.
- The continental shelf is an extension of a coastal State's land territory into the ocean.
- Continental shelves typically feature shallow waters, rich in biodiversity due to sunlight penetration.
- Countries can claim an extended continental shelf beyond 200 nautical miles if supported by scientific evidence.
Additional Details
- Continental Shelf: The continental shelf is the submerged border of a continent, extending from the coastline to the shelf break, where the ocean depth increases significantly.
- Formation: Over millions of years, continental shelves have formed from organic and inorganic materials. Sediments carried by rivers accumulate at the edges of continents, contributing to the structure.
- Ecological Significance: Continental shelves are vital ecosystems, hosting a wide variety of marine life, including microscopic organisms and large kelp forests. They serve as essential feeding grounds for various sea creatures.
- Extended Continental Shelf: Under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), coastal nations can claim rights to their continental shelf for resource exploration and exploitation beyond the standard 200 nautical miles, provided they can prove the area connects to their landmass.
In conclusion, the continental shelf is not only significant for its ecological role but also for its geopolitical implications, especially as nations seek to expand their maritime territories for economic benefits.
GS3/Economy
Frequent Downtimes in UPI Services
 Why in News?
Why in News?
In March and April, the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) system experienced three significant outages, disrupting payment services on popular applications such as GPay and PhonePe. A primary reason for these outages was individual banks overwhelming the National Payments Corporation of India’s (NPCI) systems by sending excessive transaction status check requests.
- UPI outages caused disruptions in major payment applications.
- Excessive transaction requests from banks led to NPCI system overloads.
Additional Details
- How UPI Works: UPI operates on the Immediate Payment Service (IMPS) architecture. Banks must join the UPI system and enable users to link their bank accounts via a mobile number on Payment Service Provider (PSP) apps like PhonePe or GPay. Almost all public and private banks participate in this network.
- Interoperability: UPI is designed for interoperability, allowing users to access their bank accounts through any UPI-enabled app and register on multiple apps simultaneously.
- Role of NPCI: Although UPI is perceived as a peer-to-peer system, nearly all transactions are routed through NPCI, which encrypts user PINs and forwards payment information to the payer’s bank for transaction processing.
- Single Point of Failure: NPCI's essential role in encryption and transaction routing means that any downtime at NPCI can lead to complete disruption of UPI services, as banks cannot process transactions independently.
- Cause of Outages: Recent outages were attributed to individual banks sending excessive “check transaction” requests to NPCI, stressing the system's single point of failure.
- Introduction of UPI Lite: To mitigate downtime, NPCI launched UPI Lite, allowing users to make small payments (up to ₹2,000) without entering a PIN. However, these transactions still require NPCI for device verification.
- Impact on Bank Incentives: Banks have limited opportunities to collect transaction fees, as they incur costs without being able to charge a Merchant Discount Rate (MDR). This lack of financial incentive affects their motivation to maintain uptime standards, leading to more frequent outages.
- Comparison with Card Networks: Commercial card networks like MasterCard and Visa experience fewer downtimes due to better monitoring and enforceable service level agreements (SLAs).
- Government’s Incentive Programme: To address these issues, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) initiated an incentive program to reward banks for good performance and penalize those with poor uptime.
The frequent downtimes in UPI services underline the challenges faced in maintaining robust payment infrastructure in India. The ongoing reliance on NPCI as a central point for transaction processing emphasizes the need for a more resilient system to ensure uninterrupted financial services.
GS2/International Relations
India Expands its Extended Continental Shelf Claim in the Arabian Sea
Why in News?
India has recently expanded its Extended Continental Shelf (ECS) claim by nearly 10,000 square kilometers in the Central Arabian Sea. This move includes modifications to earlier claims to mitigate a long-standing maritime boundary dispute with Pakistan. The revised submissions were made in April 2025 to the United Nations' Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf (CLCS)
- India's ECS claim has been expanded by 10,000 sq km.
- Modifications were made to avoid disputes with Pakistan.
- Submissions to the CLCS occurred in April 2025.
Additional Details
- Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ): Coastal nations have exclusive rights to resources such as fishing and mining up to 200 nautical miles from their baselines. Additional claims can be made if scientifically proven to be a natural extension of their landmass to the CLCS.
- India’s Current Oceanic Claims: India's territorial sea extends for 12 nautical miles, and the EEZ spans 200 nautical miles. The new ECS extension adds approximately 1.2 million square kilometers to India's existing 2 million square kilometers EEZ, equating the total seabed area to nearly India's land area of 3.274 million square kilometers.
- Dispute with Pakistan and Sir Creek Issue: In 2021, Pakistan raised objections over a 100 nautical mile overlap near the disputed Sir Creek region, leading to the CLCS rejecting India's full claim in March 2023.
- India's Strategic Response: On April 3, 2025, India submitted two partial claims focused on safeguarding uncontested regions, thereby strengthening its position in the valuable Central Arabian Sea area.
- Overlap with Other Countries: India’s claims also face scrutiny from Oman, Myanmar, and Sri Lanka, although agreements exist with Oman that prevent disputes. New consultations regarding claims in the Bay of Bengal and Indian Ocean will commence later this year.
This expansion of India's ECS claim reflects its strategic interests in the Arabian Sea and underscores the importance of maritime boundaries in international relations. The technical contributions from institutions like the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR, Goa) have been crucial in determining the extents of these claims.
GS2/International Relations
Line of Control (LoC)
Why in News?
Recent reports indicate that Pakistan has violated the ceasefire along the Line of Control (LoC) in the Kashmir Valley, prompting a response from the Indian army to the unprovoked firing.
- The LoC serves as the de facto military boundary between India and Pakistan in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Established after the 1947-48 India-Pakistan war, it is a ceasefire line and not an international boundary.
- The LoC was redefined from the Ceasefire Line (CFL) to the Line of Control following the Simla Agreement in 1972.
- The total length of the LoC is approximately 740 kilometers.
- Frequent skirmishes occur due to the heavy militarization of the area.
Additional Details
- Geographical Scope: The LoC extends from the Ladakh region in the north to the Poonch district in the south.
- On the Indian side, the LoC includes parts of Jammu and Kashmir as well as Ladakh, while on the Pakistani side, it encompasses Pakistan Occupied Kashmir (POK), Gilgit, and Baltistan.
- This boundary is distinct from the International Border (IB), which is the officially recognized border between India and Pakistan in other regions.
The ongoing tensions along the Line of Control highlight the fragile security situation in the region, necessitating vigilance and appropriate responses from both nations.
GS3/Defence & Security
Recent Explosion at Shahid Rajaee Port in Iran
 Why in News?
Why in News?
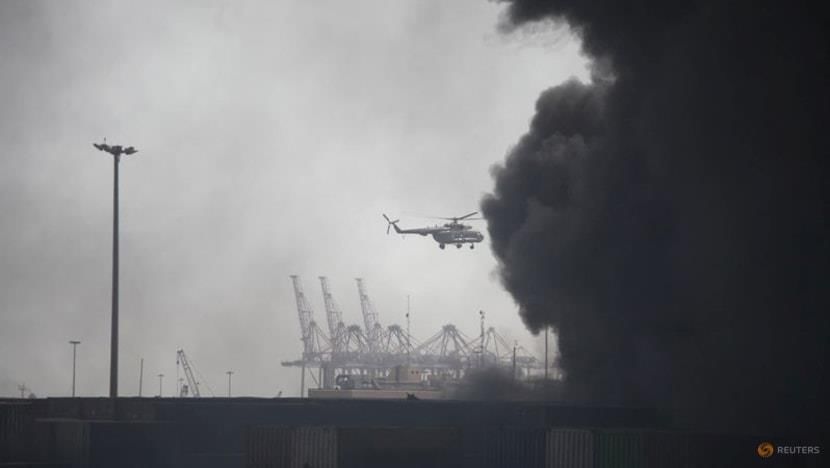
A massive explosion occurred at Shahid Rajaee Port, located near Bandar Abbas in southern Iran, leading to tragic consequences including 18 deaths and around 800 injuries. This incident underscores the ongoing challenges related to safety and security in critical infrastructure within the region.
- The explosion at Shahid Rajaee Port resulted in significant casualties and injuries.
- Iran is strategically located with multiple land and maritime borders, influencing regional dynamics.
Additional Details
- Geographical Significance: Iran is a prominent country in West Asia, bordered by Armenia, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan to the north, and Afghanistan, Pakistan to the east, with Iraq and Turkey to the west and northwest, respectively.
- Maritime Borders: Iran has significant maritime borders with countries such as Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, and Saudi Arabia, and is adjacent to the Caspian Sea to the north and the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman to the south.
- Natural Resources: Iran is rich in natural resources, including oil, natural gas, coal, and various minerals like copper, iron ore, and zinc.
- Strategic Importance of Shahid Rajaee Port: This port is crucial due to its proximity to the Strait of Hormuz, a key global oil trade passage, making it vital for energy security.
The explosion at Shahid Rajaee Port not only highlights the safety issues within such critical facilities but also emphasizes Iran's strategic role in global energy markets. Continued focus on infrastructure safety and regional stability remains essential.
GS3/Science and Technology
What is a 3D Microscope?
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian Army's Department of Ophthalmology at Army Hospital (Research and Referral) in New Delhi has achieved a significant milestone by performing Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (MIGS) utilizing a 3D Microscope for the first time.
- A 3D Microscope enhances visualization by providing depth information in images.
- It is particularly beneficial for complex eye surgeries and offers improved surgical outcomes.
Additional Details
- Microscope: A microscope is a device that magnifies small objects, making them visible by bending (refracting) light rays through curved lenses. The most common type is the optical microscope, which focuses visible light through lenses to create enlarged images.
- 3D Imaging: Unlike traditional 2D microscopes that produce flat images, 3D microscopes utilize advanced optical, electron, or computational techniques to capture and reconstruct three-dimensional data, allowing for detailed visualization of the topography, volume, and internal structures of samples.
- Features of the 3D Microscope: This microscope employs advanced three-dimensional visualization technology, aiding in complex eye surgeries for conditions such as squint, cataracts, corneal diseases, glaucoma, and retinal disorders.
- Special Equipment: Surgeons use specialized 3D polarization glasses along with a 55-inch 4K ultra-HD display during procedures.
- Key Advantages:
- Reduced surgical time and lower complication rates compared to conventional techniques.
- Decreased endoilluminator power requirements, minimizing photo-toxicity risks.
- Facilitates surgeries in complex and rare cases.
This innovative technology represents a significant advancement in surgical techniques, particularly in the field of ophthalmology, enhancing the precision and effectiveness of surgical interventions.
GS3/Environment
Mahuadanr Wolf Sanctuary: India’s First Wolf Sanctuary
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Mahuadanr Wolf Sanctuary, located in the Latehar district of Jharkhand, is notable for being India's first and only sanctuary dedicated to the conservation of wolves. It plays a vital role in protecting the endangered Indian grey wolf population.
- The sanctuary covers approximately 63 square kilometers and was established in 1976.
- It is part of the larger Palamau Tiger Reserve, contributing to regional biodiversity.
- Wildlife in the sanctuary includes species such as spotted deer, wild boar, hyenas, and bears.
Additional Details
- Indian Grey Wolf (Canis lupus pallipes): This subspecies is found across Southwest Asia and the Indian subcontinent. It typically inhabits scrublands, grasslands, and semi-arid agroecosystems, thriving in warmer temperatures.
- Unlike other wolf subspecies, the Indian grey wolf tends to form smaller packs and exhibits less vocal behavior, primarily hunting at night from dusk until dawn.
- Conservation Status: The Indian grey wolf is classified as Endangered on the IUCN Red List, with an estimated population of 2,000 to 3,000 individuals. It is listed in Appendix I of CITES, indicating the highest level of international protection, and is included under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 in India, ensuring maximum legal protection.
The Mahuadanr Wolf Sanctuary serves as a crucial habitat for the Indian grey wolf and is instrumental in conservation efforts aimed at sustaining this often-misunderstood carnivore.
|
55 videos|5389 docs|1141 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 27th April 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the StormBreaker Glide Bomb and how does it operate? |  |
| 2. What is the United Nations High Seas Treaty and its significance? |  |
| 3. What are the key facts about anemia and its impact on health? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the Continental Shelf in international law? |  |
| 5. What are the reasons for frequent downtimes in UPI services in India? |  |
















