UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 1st May 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Economy
Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) in IndiaWhy in News?
In April 2025, Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) made headlines by becoming net buyers of Indian equities for the first time in four months, with an impressive inflow of ₹4,223 crore.
- FIIs are a subset of Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) and include large institutional entities such as mutual funds, pension funds, insurance companies, and hedge funds.
- FIIs typically take a strategic approach to investments in foreign markets, contributing long-term capital to emerging economies.
- Rapid outflows of FII investments can create instability in domestic markets, necessitating regulatory oversight.
Additional Details
- Regulatory Framework: FIIs in India are governed by various regulations, including the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999, SEBI (Foreign Portfolio Investors) Regulations, and the oversight of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) which monitors sectoral investment limits.
- Investment Ceilings: FIIs may invest up to 10% in any single Indian company, with a cumulative limit of 24% for all FIIs, NRIs, and PIOs combined. Eligible FII entities include university funds, charitable endowments, and trusts with at least a five-year operational track record.
- FIIs are also allowed to invest in unlisted securities and utilize their proprietary funds.
The recent increase in FII participation is largely attributed to the softening of the U.S. Dollar Index, which has fallen from 104-105 to around 99-100, thus enhancing the relative strength of the Indian rupee. Additionally, the RBI's accommodative stance on macroeconomic stability has further encouraged investments, particularly in sectors such as banking, financial services, and insurance (BFSI). However, it is noteworthy that FIIs have reduced their exposure to the IT sector due to concerns regarding a potential U.S. recession and its implications for technology earnings.
GS3/Environment
Vembanad Lake Rejuvenation Project
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Vembanad Lake Rejuvenation Project, initiated by the Alappuzha District Administration, is modeled after the Namami Gange Programme. A comprehensive five-year plan costing ₹188.25 crore has been proposed to the Kerala Chief Minister, with potential adjustments based on studies conducted by the Centre for Water Resources Development and Management (CWRDM).
- Formation of eight subcommittees across various sectors, including agriculture, fisheries, and disaster management.
- Significant reduction in the lake's surface area, with a 27% decrease noted from 1917 to 1990.
- Recent cleanup efforts have successfully removed 72 tonnes of plastic waste and large amounts of water hyacinth.
Additional Details
- Vembanad Lake: It is the longest lake in India and the largest in Kerala, stretching approximately 5 km in length and covering around 2,033 square kilometers.
- Geographical Significance: The lake spans three districts: Alappuzha, Kottayam, and Ernakulam, and is fed by six major rivers, including Meenachil and Pamba.
- Tourism and Ecology: Vembanad Lake hosts the Kumarakom Bird Sanctuary and is a key part of Kerala's backwater tourism, with annual events like the Nehru Trophy Snake Boat Race.
- Environmental Status: The lake is a Ramsar site, recognized in 2002 for its ecological importance, encompassing vital islands like Pathiramanal and Perumbalam.
The rejuvenation efforts aim to restore the ecological balance of Vembanad Lake, ensuring its sustainability for future generations while enhancing its role in local tourism and biodiversity.
GS2/International Relations
The Impact of Suspending a Water Treaty
Why in News?
The Indian government has recently suspended the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT) of 1960, a pivotal agreement with Pakistan, in response to the killing of 26 tourists in Jammu and Kashmir. This decision, made by India's Cabinet Committee on Security, represents a significant escalation in India's stance against Pakistan, particularly concerning allegations of cross-border terrorism.
- India's suspension of the IWT signals a potential termination of a long-standing water-sharing agreement.
- The treaty, established in 1960, does not allow for unilateral withdrawal without mutual consent.
- Legal complexities arise due to India's non-signature of the Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties.
- Pakistan plans to challenge India's decision in international legal forums.
Additional Details
- Legal Constraints: The IWT, brokered by the World Bank, includes Article XII (4), which states it remains in force unless terminated by mutual agreement. This limits India's ability to unilaterally withdraw.
- Potential Consequences: India's suspension could lead to strategic control over water flows, potentially causing artificial droughts or floods in Pakistan, which relies heavily on these rivers for agriculture and drinking water.
- Infrastructure Challenges: India has only developed a fraction of its permitted irrigation potential under the treaty, and while it has made progress on eastern rivers, the western rivers face significant infrastructural limitations.
- Geopolitical Risks: This move may set a precedent that could affect India's relations with other neighbors, including China and those involved in the Ganga Water Treaty.
In conclusion, India's suspension of the Indus Waters Treaty is a bold assertion of strategic sovereignty but poses significant legal, infrastructural, and geopolitical challenges. The long-term water security in the region may depend on collaborative management rather than unilateral actions.
GS3/Defence & Security
National Security Advisory Board Revamped
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Union government has recently restructured the National Security Advisory Board (NSAB), appointing former RAW chief Alok Joshi as its new chairman, alongside six other members. This restructuring is significant amidst escalating tensions between India and Pakistan, particularly following a recent terror attack in Pahalgam.
- The NSAB plays a crucial role within India’s three-tier national security structure.
- It provides essential inputs on strategic and security-related issues.
- The board brings together experts from various fields to shape national security policies.
Additional Details
- Need for NSAB: The NSAB aims to deliver a broad-based perspective on national security challenges, incorporating innovative insights from outside the government structure.
- Legal Mandate: The NSAB has no statutory or constitutional status, operating under the National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS) as an advisory and non-binding body. Its recommendations, while not enforceable, are influential.
- Composition: The board is chaired by a former senior official and consists of 7 members from diverse fields such as diplomacy, military, and academia. Members are appointed by the Prime Minister’s Office or upon the recommendation of the National Security Advisor.
- Functions and Responsibilities: The NSAB provides policy recommendations to the National Security Council (NSC), offers strategic guidance on threats, and focuses on research and independent analysis to support government decision-making.
- Current Agenda: The NSAB's agenda includes strategies for neighbourhood relations, border management, maritime security, internal security, strategic industries, and technology.
The recent reconstitution of the NSAB, with Alok Joshi as chairman and a diverse panel of experts, reflects the government's commitment to addressing complex security challenges effectively.
GS3/Environment
Red-Crowned Roofed Turtle
Why in News?
The endangered Red-Crowned Roofed Turtle (Batagur kachuga) has successfully returned to the Ganga River after an absence of thirty years, marking a significant achievement in biodiversity conservation.
- The Red-Crowned Roofed Turtle is a species endemic to South Asia.
- It is currently listed as Critically Endangered by the IUCN.
- National Chambal River Gharial Sanctuary hosts a substantial population of this turtle in India.
Additional Details
- Scientific Classification: The Red-Crowned Roofed Turtle is scientifically known as Batagur kachuga.
- Distribution: This species is native to India, Bangladesh, and Nepal, and was historically widespread in the Ganga River.
- Physical Features: It is a medium-sized turtle that can grow up to 56 cm in length and weigh up to 25 kg. Males are generally smaller than females, reaching only half the length of their female counterparts. They possess a reddish-orange head, a black crown, and a greenish-brown carapace with yellowish patterns. Their plastron is yellow with black markings, and they have a broad head with strong jaws and webbed feet.
- Diet: The Red-Crowned Roofed Turtle is omnivorous, feeding on a variety of plants and animals.
- Conservation Status: It is classified as Critically Endangered by the IUCN, is listed under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972, and is included in Appendix II of CITES.
The successful return of the Red-Crowned Roofed Turtle to its natural habitat is a hopeful sign for conservation efforts aimed at protecting endangered species and restoring biodiversity in aquatic ecosystems.
GS3/Science and Technology
Cosmic Clumpiness and the S8 Tension
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recent research highlights the significance of understanding the "clumpiness" of matter, quantified by Sigma-8 (S8) Tension, which may provide crucial insights into the universe's structure and complexity.
- S8 measures the distribution of matter throughout the universe, indicating how "clumpy" or evenly dispersed it is.
- High S8 tension signifies matter is clustered in specific areas, while low S8 indicates a more uniform distribution.
- Conflicting measurements of S8 have raised questions regarding our comprehension of the universe.
Additional Details
- S8: This measurement helps scientists study the arrangement of matter, including dark matter, which is invisible yet constitutes most of the universe.
- Implications for the ΛCDM Model: The ΛCDM model describes the universe's structure, mainly composed of dark energy. Discrepancies in S8 could suggest gaps in our understanding of dark energy or dark matter.
- Possible Implications:
- Revised Theories: Adjustments to our universe model may be necessary due to conflicting S8 values.
- Re-thinking Dark Energy: If S8 measurements diverge from predictions, the behavior of dark energy may need reevaluation.
- New Discoveries: The S8 tension might indicate undiscovered forces or particles affecting matter behavior.
- Better Observations: Enhanced telescopes and surveys, such as the Rubin Legacy Survey, could clarify the reasons behind the conflicting S8 measurements.
In summary, the ongoing research into S8 tension could reshape our understanding of the universe and its fundamental components.
[UPSC 2015]
In the context of modern scientific research, consider the following statements about 'IceCube', a particle detector located at the South Pole, which was recently in the news:
- (1) It is the world’s largest neutrino detector, encompassing a cubic km of ice.
- (2) It is a powerful telescope to search for dark matter.
- (3) It is buried deep in the ice.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- Options: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3*
GS2/Polity
Supreme Court Declares Digital Access a Fundamental Right Under Article 21
 Why in News?
Why in News?
In a significant ruling, the Supreme Court of India has declared that access to digital resources is a core component of the fundamental right to life and liberty, as outlined in the Constitution. This judgment reinforces the obligation of the State to address the digital divide, which includes improving infrastructure, skills, and accessible content, thereby ensuring inclusive digital access for all citizens.
- The right to digital access is now recognized as an intrinsic part of the right to life and liberty under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- The judgment emphasizes the need for inclusive policies to bridge the digital divide affecting marginalized groups in society.
- Specific directions were issued to revise KYC norms to accommodate the needs of individuals with disabilities.
Additional Details
- Relevant Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 21: Protects the right to life and dignity.
- Article 14: Ensures the right to equality.
- Article 15: Prohibits discrimination on various grounds.
- Article 38 (DPSP): Mandates the State to promote welfare and reduce inequalities.
- Digital Access as a Constitutional Right: The court ruled that digital access is essential for governance, education, healthcare, and economic opportunities in today’s digital landscape.
- The principle of substantive equality was highlighted, indicating that policies must cater to diverse needs rather than applying a one-size-fits-all approach.
- Addressing the digital divide is deemed a constitutional responsibility, crucial for upholding dignity and equality in public life.
This landmark judgment sets a precedent for future policies and governance related to digital rights, ensuring that all citizens, particularly those from vulnerable and historically marginalized communities, have equitable access to digital technologies and services.
GS3/Science and Technology
Global Antibiotic Research & Development Partnership (GARDP)
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recent research conducted by the Global Antibiotic Research and Development Partnership (GARDP) has highlighted a concerning trend: many multidrug-resistant infections in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), particularly in India, are inadequately treated due to significant gaps in access to appropriate antibiotics.
- GARDP's Mission: A not-for-profit organization focused on developing new antibiotic treatments for drug-resistant bacterial infections.
- Public Health Focus: Prioritizes public health needs in antibiotic development to tackle the immediate antimicrobial resistance (AMR) crisis.
- Founding: Established in 2018 by the World Health Organization (WHO) and Drugs for Neglected Diseases initiative (DNDi) in Geneva, Switzerland.
Additional Details
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): A critical global health challenge that threatens to render existing antibiotics ineffective.
- Collaborative Approach: GARDP brings together public and private entities to expedite the development and accessibility of new antibiotics.
- Global Action Plan: GARDP aims to fulfill the objectives laid out in the Global Action Plan on AMR, established in 2015, which emphasizes the urgent need for new antibiotic initiatives.
In conclusion, GARDP plays a vital role in addressing the urgent need for effective antibiotic treatments, ensuring that vulnerable populations gain access to life-saving medications, thus safeguarding public health for future generations.
GS3/Science and Technology
S8 Tension in Cosmology
Why in News?
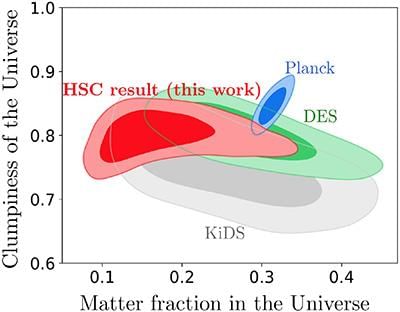
The Subaru Telescope in Hawaii, utilizing the Hyper Suprime-Cam, has conducted a comprehensive deep sky survey, reporting an S8 value of 0.747. This finding aligns with previous estimates obtained through gravitational lensing methods.
- The S8 value is a critical parameter in cosmology that quantifies the clustering of matter in the universe.
- There exists a tension in the values of S8 derived from different cosmological measurements, challenging the standard cosmological model.
Additional Details
- S8 (Sigma Eight): This parameter measures the "clumpiness" of matter across a scale of approximately 26 million light-years, indicating the density of matter, both visible and dark, in various regions of the cosmos.
- The universe began with the Big Bang about 13.8 billion years ago, characterized by a highly uniform state, as evidenced by the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB). Over time, small density fluctuations (about 1 in 100,000) evolved into the galaxies and structures we observe today.
- S8 tension:This term describes the discrepancy between S8 values obtained from different methods:
- CMB measurements: These provide a higher estimate of S8.
- Cosmic shear/lensing surveys: These yield a lower estimate, suggesting less clustering of matter than expected.
- The CMB consists of photons that are remnants from the Big Bang, and scientists have analyzed it to understand the universe's expansion, estimated at approximately 68 kilometers per second per megaparsec (km/s/Mpc).
- Cosmic Shear & Gravitational Lensing: This phenomenon involves distortions in galaxy shapes caused by gravitational lensing from intervening matter, which helps map dark matter distribution and provides insights into S8.
The lower S8 value from lensing indicates a discrepancy in the expected clumpiness of the universe, presenting challenges to the ΛCDM (Lambda Cold Dark Matter) model, which is the prevailing cosmological framework.
GS2/Governance
India’s Shame, the Trap of Bonded Labour
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Every year on May 1, International Labour Day is observed globally to honour workers' rights and the dignity of labour. Yet, for millions in India, this day serves as a grim reminder of their continued entrapment in bonded and forced labour, a form of modern-day slavery that strips individuals of their basic freedoms and human dignity. The harrowing stories of survivors like Mukesh Adivasi and K. Thenmozhi underscore the systemic exploitation that persists despite decades of legal prohibition and policy pledges.
- Mukesh Adivasi was trafficked over 1,400 kilometres to Karnataka for bonded labour on a sugarcane farm.
- K. Thenmozhi, a 13-year-old girl, was forced into bondage at a brick kiln due to her family's poverty.
- Despite legal frameworks, the eradication of bonded labour remains largely unfulfilled.
Additional Details
- Personal Stories of Entrapment:
- Mukesh Adivasi, a victim of bonded labour, worked under brutal conditions and endured severe abuse.
- K. Thenmozhi's family was driven into bondage for a small advance, leading to a life of hard labour and abuse.
- Structural Causes: The persistence of bonded labour is linked to socio-economic factors such as poverty, illiteracy, and caste-based discrimination.
- The Indian government has set ambitious goals to rehabilitate bonded labourers but has achieved only a fraction of the targets.
In conclusion, while International Labour Day should be a celebration of workers’ contributions and rights, in India it serves as a reminder of unfulfilled promises and deep systemic injustices. The persistence of bonded and forced labour demands more than token policy responses; it requires genuine political will, robust enforcement of labour laws, and social mobilisation. Until India confronts and dismantles the structures that sustain this exploitation, its economic progress will remain tainted by the suffering of its most vulnerable citizens.
GS2/International Relations
From a Rules-Based World to Shambolic Disorder
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The world is increasingly facing uncertainty and instability in various domains, a trend that predates the Trump administration. This situation has prompted leaders across government, business, and strategic sectors to brace for challenging times ahead.
- Geopolitical tensions are rising due to authoritarian leadership.
- Protectionism and trade wars are disrupting global economic stability.
- Technological advancements are creating new vulnerabilities in national security.
- Regional conflicts and military expansion are escalating tensions in critical areas.
- The resurgence of terrorism poses fresh security challenges.
Additional Details
- Leader-led Disruption and Geopolitical Tensions: Authoritarian figures like Xi Jinping, Vladimir Putin, and Donald Trump are significantly altering the landscape of global politics. For instance, Russia's invasion of Ukraine and the U.S. trade wars under Trump have strained longstanding international alliances.
- Rise of Protectionism and Trade Wars: Economic nationalism has led to tariff barriers that disrupt global trade. Trump's trade war with China notably reduced U.S. GDP growth and complicated global supply chains.
- Technological Disruption and Cyber Threats: Rapid advancements in technology, coupled with cyber threats, are destabilizing national security and job markets. The lack of governance frameworks for disruptive technologies has heightened digital vulnerabilities.
- Regional Conflicts and Expanding Military Influence: Ongoing conflicts in regions such as West Asia, along with military expansions, are creating instability. Notable examples include Israel’s military actions in Gaza and tensions in Syria.
- Resurgence of Terrorism and Non-State Actors: Groups like ISIS are re-emerging in regions such as Africa and South Asia, presenting new security challenges, as evidenced by recent attacks in Kashmir and increasing IS activities in Mozambique and Congo.
As the geopolitical landscape shifts, the U.S., once viewed as a bastion of democratic stability, is now perceived as deeply divided, with implications for its global standing.
U.S. Domestic Challenges
- Deepening Political Polarization: Internal ideological divisions have intensified, undermining national unity, particularly highlighted by the Capitol Hill riots in January 2021.
- Transactional Foreign Policy Approach: A self-serving foreign policy has led to fractured alliances, especially through Trump's tariff wars and criticisms of NATO allies.
- Targeting of Educational and Immigration Systems: Policies limiting foreign students threaten the U.S.'s soft power and economic contributions significantly, with restrictions on student visas under Trump estimated to impact $40 billion.
- Economic Protectionism and Declining Global Trade Role: The shift towards protectionist policies has diminished U.S. leadership in global economic governance, contributing to a decline in GDP growth.
China's Strategic Advances
- Expanding Influence through the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI): China is investing in infrastructure projects to create economic dependencies, such as the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), enhancing its political leverage in South Asia.
- Exploiting U.S. Retreat: With the U.S. stepping back from global leadership, China is consolidating its position, particularly evident in its role in the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP).
- Enhancing Military and Naval Presence: China is strengthening its military presence in vital maritime regions, including its controversial activities in the South China Sea.
- Strengthening Bilateral and Multilateral Ties: China is forging strategic alliances with neighboring countries to counterbalance U.S. influence, enhancing its dominance in the region.
- Leveraging the China-India Rivalry: China is exploiting tensions between India and neighboring countries to expand its influence and shift regional power dynamics in its favor.
Implications for India
- Strategic Encirclement and Security Concerns: China's growing presence in the region poses a strategic threat to India, exemplified by developments like the Hambantota Port in Sri Lanka, which aligns with a "String of Pearls" strategy.
- Economic Competition and Trade Imbalance: China's dominance in trade frameworks challenges Indian manufacturing and trade sovereignty. India's decision to opt out of RCEP stemmed from fears of detrimental impacts from cheap Chinese imports.
- Border Tensions and Military Confrontation: Ongoing disputes along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) are escalating military expenditures and diplomatic tensions, as highlighted by the 2020 Galwan Valley clash.
Way Forward for India
- Strengthen Strategic Partnerships: India should enhance ties with like-minded nations through forums such as Quad and ASEAN, particularly in defense and technology sectors.
- Boost Domestic Capabilities and Connectivity: Accelerating infrastructure development and self-reliant manufacturing initiatives like Atmanirbhar Bharat can help mitigate Chinese influence, exemplified by projects like the Chabahar Port.
Mains PYQ
[UPSC 2021] “The USA is facing an existential threat in the form of a China that is much more challenging than the erstwhile Soviet Union.” Explain.
This reflects a significant shift in the global power balance, presenting a formidable challenge to the international order historically dominated by the U.S. post-Cold War.
GS2/Polity
What is Notice to Air Mission (NOTAM)?
 Why in News?
Why in News?
India has recently issued a Notice to Air Mission (NOTAM) which has resulted in the closure of its airspace for all Pakistan-registered, operated, or leased aircraft, including airlines and military flights. This decision highlights the importance of NOTAMs in aviation safety and operational awareness.
- NOTAM stands for Notice to Air Mission, previously known as Notice to Airmen.
- It provides crucial information regarding aeronautical facilities, services, and hazards that affect flight operations.
Additional Details
- Purpose of NOTAM: NOTAMs are issued to inform pilots and relevant personnel about significant changes in airspace, airports, or equipment that could impact aircraft operations.
- Reasons for Issuing NOTAMs:
- Hazards such as air shows, parachute jumps, and other special flight activities.
- Flight operations involving important individuals, such as heads of state.
- Closed runways or taxiways that may affect flight routes.
- Unserviceable navigational aids that pilots rely on for safe navigation.
- Military exercises that impose temporary airspace restrictions.
- Unserviceable lights on tall structures that could pose a hazard.
- Temporary obstacles erected near airfields, such as cranes.
- NOTAMs are encoded for brevity but are designed to be clear enough for users to understand the associated hazards.
- They are communicated through the fastest means available to ensure timely delivery to all relevant parties.
It is essential for pilots to review NOTAMs prior to their flights, as failing to do so can jeopardize their safety and that of others. NOTAMs are accessible through various online platforms, ensuring that pilots can make informed decisions based on the most current information available.
|
55 videos|5389 docs|1141 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 1st May 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) and their role in the Indian economy? |  |
| 2. What are the key features of the Vembanad Lake Rejuvenation Project? |  |
| 3. How does the suspension of a water treaty impact India and its neighboring countries? |  |
| 4. What are the implications of the Supreme Court declaring digital access a fundamental right under Article 21? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges associated with bonded labour in India, and what measures can be taken to address them? |  |
















