UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 9th May 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Defence & Security
INS Vikrant: India’s Indigenously Designed Aircraft Carrier
Source: Deccan Herald
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Indian Navy has deployed its latest and most advanced naval asset, the INS Vikrant, to the Arabian Sea amid rising tensions with Pakistan following its recent aerial incursions into Indian airspace.
Key Takeaways
- INS Vikrant is India's first homegrown aircraft carrier, commissioned in 2022.
- It has a significant indigenous content of 76%, enhancing India's defense capabilities.
- India joins an elite group of nations capable of designing and constructing aircraft carriers.
Additional Details
- Dimensions: The aircraft carrier measures 262 metres in length and 62 metres in width, featuring 14 decks, equivalent to a 14-storey building.
- Capacity: It can accommodate over 1,500 personnel and has a full-load displacement of 43,000 tonnes.
- Power and Speed: INS Vikrant is powered by four gas turbines that generate a total of 88 MW, allowing it to reach a maximum speed of 28 knots.
- Endurance: The carrier can operate independently for 45 days and cover a distance of 8,600 miles (13,890 kilometres).
- Air Wing: It supports an air wing of 30 aircraft, including MIG-29K fighter jets, Kamov-31 helicopters, MH-60R multi-role helicopters, and indigenously produced Advanced Light Helicopters (ALH) and Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) (Navy).
- Aircraft Operations: Utilizing a Short Take-Off but Arrested Landing (STOBAR) system, INS Vikrant features a ski-jump for launching aircraft and 'arrester wires' for their recovery.
In summary, the commissioning of INS Vikrant not only bolsters India's naval capabilities but also signifies its growing prowess in indigenous defense manufacturing, enhancing its strategic posture in the region.
GS3/Science and Technology
What is Thalassaemia?
Source: Money Control
Why in News?
World Thalassaemia Day is commemorated on May 8 each year to enhance public awareness and encourage action regarding this genetic disorder, which impacts millions globally.
Key Takeaways
- Thalassaemia is an inherited blood disorder that results in reduced levels of hemoglobin in the body.
- Hemoglobin is essential for red blood cells to transport oxygen throughout the body.
- Insufficient hemoglobin or red blood cells can lead to anemia, causing fatigue and weakness.
- The disorder is caused by gene mutations inherited from one or both parents.
Additional Details
- Types of Thalassaemia: The type of thalassaemia a person has depends on the specific gene mutations inherited.
- Symptoms:Thalassaemia can lead to mild or severe anemia along with other complications over time, such as iron overload. Common symptoms include:
- Trouble breathing
- Feeling cold
- Pale skin
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Treatments:
- Blood Transfusions: Regular blood transfusions are essential for treating and preventing anemia, particularly in severe cases where transfusions may be required monthly.
- Chelation Therapy: This treatment uses medication to remove excess iron that accumulates from frequent blood transfusions.
- Bone Marrow Transplant: The only potential cure for thalassaemia involves a stem cell or bone marrow transplant, though this procedure is infrequent due to associated risks.
Thalassaemia is a significant health issue that requires awareness, understanding, and appropriate medical interventions to manage effectively.
GS3/Defence & Security
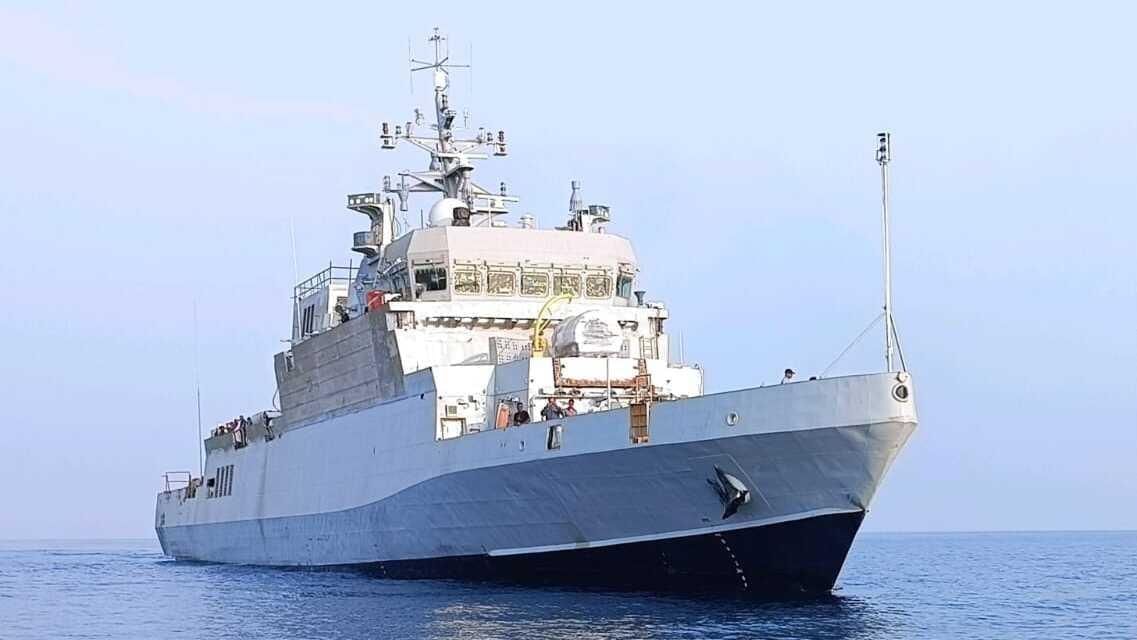
Delivery of 'Arnala' - First Anti Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft to the Indian Navy
Source: Economic Times
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The delivery of 'Arnala' marks a significant milestone in India's naval capabilities, representing the first of eight indigenously produced Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Crafts (ASW SWCs) designed to enhance the Indian Navy's operational effectiveness in coastal regions.
Key Takeaways
- 'Arnala' is designed and constructed by Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata, and built at L&T Shipyard, Kattupalli, under a Public-Private Partnership (PPP).
- The ship adheres to the Indian Register of Shipping (IRS) classification rules, showcasing India's commitment to domestic naval architecture standards.
- 'Arnala' is named after the historic Arnala Fort, symbolizing India's maritime heritage.
- The vessel is 77 meters long and is the largest Indian Naval warship powered by a Diesel Engine-Waterjet propulsion system.
Additional Details
- Primary Roles:The key functions of 'Arnala' include:
- Underwater surveillance in coastal zones.
- Search and Rescue (SAR) operations.
- Low Intensity Maritime Operations (LIMO).
- Coastal Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW) operations.
- Advanced mine-laying capabilities.
- The induction of such ASW SWCs significantly boosts India's shallow water anti-submarine warfare capacity, which is crucial for maritime security in littoral zones.
- Over 80% of the components used in 'Arnala' are sourced indigenously, reflecting a major step towards achieving 'Aatmanirbhar Bharat' in defence manufacturing.
The launch of 'Arnala' not only enhances India's naval capabilities but also underscores the successful collaboration between public and private sectors in the country's defence manufacturing ecosystem.
GS3/Science and Technology
Lead-to-Gold Transmutation
Source: Science Direct
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The ALICE detector at CERN has made a groundbreaking discovery by confirming the transmutation of lead into gold through nuclear processes at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC).
Key Takeaways
- Experimental verification of lead-to-gold transmutation at CERN.
- Chrysopoeia, the ancient alchemical pursuit, has been scientifically explored.
- Utilization of high-energy collisions to create gold nuclei.
Additional Details
- Chrysopoeia: This term refers to the ancient alchemists' quest to convert base metals into gold, which was thought possible due to the similar densities of lead and gold. Modern chemistry clarifies that these are distinct elements and cannot be transformed through chemical means.
- Mechanism of Transmutation: Gold nuclei (Au-203) are formed by ejecting three protons and two neutrons from lead nuclei (Pb-208) during ultra-peripheral collisions at the LHC. These collisions create strong electromagnetic fields as lead nuclei, containing 82 protons, travel at 99.9993% of the speed of light, compressing the field into a fleeting photon pulse. This process, known as electromagnetic dissociation, triggers internal nuclear oscillations, leading to the release of protons and neutrons.
- Role of ALICE Detector and ZDC: The ALICE detector employs Zero Degree Calorimeters (ZDCs) to identify photon-nucleus interactions and detect the ejection of protons, which correlates to the formation of lead, thallium, and mercury, respectively. This represents the first systematic detection of gold creation at the LHC, facilitated by ALICE’s precision in capturing high-energy low-particle events.
- About the Large Hadron Collider (LHC): The LHC is the world's largest and most powerful particle accelerator, located on the Franco-Swiss border near Geneva. It spans 27 kilometers and is designed to investigate fundamental particles and validate the predictions of the Standard Model by colliding two beams of hadrons (usually protons or lead nuclei) at nearly the speed of light.
- About CERN: Established in 1954, CERN (European Organization for Nuclear Research) is Europe’s first joint scientific endeavor post-World War II. It has 23 member states and 10 associate members, including India. CERN focuses on high-energy particle physics research and houses the LHC and its associated detectors.
This discovery not only sheds light on historical alchemical aspirations but also advances our understanding of nuclear physics, demonstrating the potential for transforming one element into another under extreme conditions.
GS3/Defence & Security
What are HAROP Drones?
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Indian armed forces have recently utilized Israeli-made Harop drones to conduct precision strikes targeting air defense systems in Pakistan as part of their ongoing 'Operation Sindoor'.
Key Takeaways
- The Harop drone is developed by the MBT Missiles Division of Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI).
- It is classified as a loitering munition, designed for both reconnaissance and attack.
- These drones can autonomously identify and strike hostile targets, such as radar systems and missile launchers.
Additional Details
- Loitering Munition: Harop drones are engineered to hover for up to nine hours, identifying and destroying targets by crashing into them with an explosive payload.
- Operational Capabilities:
- Equipped with electro-optical (EO) or infrared (IR) seekers for tracking static and mobile threats.
- Offers a man-in-the-loop control mode, enabling human oversight and final decision-making before impact.
- Includes an abort capability, allowing for mission cancellation mid-flight to prevent collateral damage.
- Specifications:
- Wingspan: 3 meters
- Length: 2.5 meters
- Maximum Speed: 417 km/h
- Operational Range: 200 km
- Flight Endurance: Over 6 hours
- Service Ceiling: Approximately 15,000 feet
- Warhead: 16 kg high-explosive
- Accuracy: Circular Error Probable (CEP) of under one meter
- The Harop can loiter over hostile areas, strike from various angles, and operate effectively in GPS-denied environments due to its resistance to satellite jamming.
The Harop drone has been in operation for over a decade, showcasing its effectiveness as a precision strike weapon in modern warfare.
GS3/Defence & Security
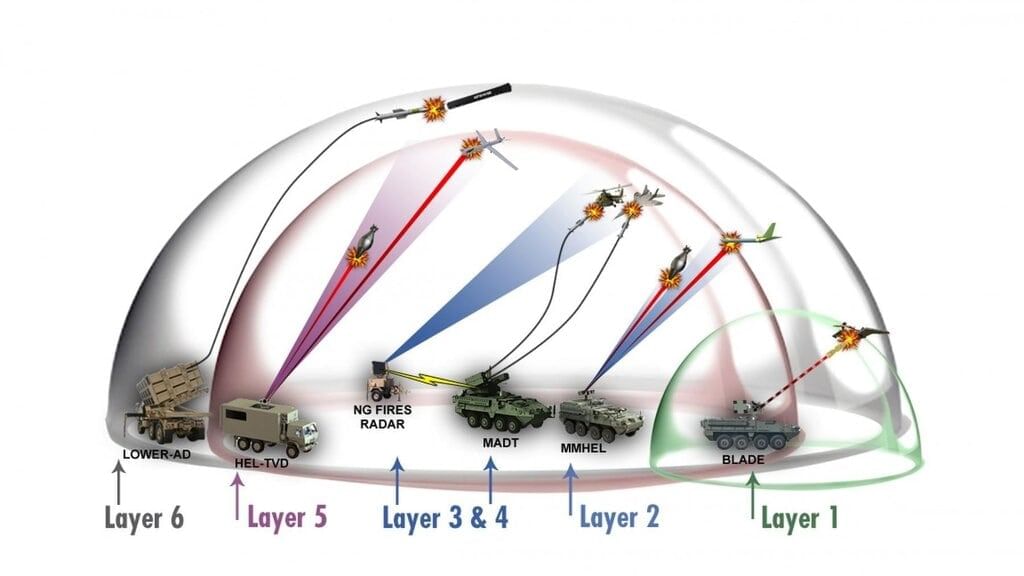
Working of Air Defence Systems
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
India successfully countered coordinated attacks from Pakistan, targeting multiple Pakistani air defence systems and reportedly neutralizing one in Lahore. The Indian Army confirmed that its response was proportional to Pakistan's actions in both domain and intensity.
Key Takeaways
- Air defence systems play a vital role in modern warfare by protecting against enemy aerial strikes.
- Neutralizing air defence systems significantly increases a nation's vulnerability to aerial attacks.
Additional Details
- Air Defence System Operations: The primary objective is to eliminate aerial threats such as enemy fighter aircraft, drones, and missiles.
- Components of an Air Defence System:A robust air defence system integrates various components:
- Radars
- Control centres
- Defensive fighter aircraft
- Ground-based missile and artillery units
- Electronic warfare tools
- Key Operations of Air Defence:
- Detection: Utilizes radars (and sometimes satellites) to identify incoming threats by emitting electromagnetic waves.
- Tracking: Continuous monitoring of threats through radar and other sensors to avoid friendly fire.
- C3 Role: A strong Command, Control, and Communication system is crucial for effective decision-making during engagements.
- Fighter Aircraft (Interceptors):
- Purpose: To engage and neutralize enemy aircraft before they can strike.
- Capabilities: Includes fast scramble, rapid climb, and agile combat; examples include MiG-21 Bison, MiG-29, Su-30MKI, HAL Tejas, and Dassault Rafale.
- Surface-to-Air Missiles (SAMs):These are the primary weapons in modern air defence systems, categorized into:
- Heavy Long-Range SAMs (e.g., S-400)
- Medium-Range SAMs (e.g., Akash, Barak)
- Short-Range (MANPADS) for low-altitude threats.
- Electronic Warfare (EW): This involves neutralizing threats without physical destruction by manipulating the electromagnetic spectrum, including jamming enemy systems.
On May 8, the Indian Air Force (IAF) activated its Integrated Counter-UAS Grid and successfully intercepted a coordinated attack by Pakistan involving drones and missiles targeting 15 Indian military bases and cities.
Key Air Defence Systems Deployed
- S-400 Triumf: Deployed on the northern border; three squadrons received from Russia.
- Barak 8 MRSAM: A medium-range system developed jointly with Israel.
- S-125 Pechora: A legacy Russian system still in active use.
Debris from intercepted drones and missiles is currently being collected as part of the ongoing assessment of the situation.
HAROP: A Modern Loitering Munition
- Definition: HAROP loiters near the target area before crashing into it with an explosive payload.
- Features: Known as "suicide drones" or "kamikaze drones," they are equipped with nose-mounted cameras for precision targeting.
- Capabilities: Effective against high-value targets and can be launched from both land and naval platforms.
This comprehensive overview underscores the critical importance of air defence systems in maintaining national security and responding effectively to aerial threats.
GS2/International Relations
Chile and India Sign Terms of Reference for Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement
Source: AIR
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, India and Chile formalized the Terms of Reference (ToR) to initiate discussions for a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA), marking a significant step in enhancing bilateral trade relations.
Key Takeaways
- Chile is a long, narrow country located in South America.
- It shares borders with Peru and Bolivia to the north, Argentina to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west.
Geographical Overview
- Andes Mountains: The world's longest continental mountain range.
- Atacama Desert: The driest non-polar desert in the world.
- Loa River: Chile’s longest river, measuring approximately 440 km.
- Ojos del Salado: The world’s highest active volcano and the second highest peak in South America at 6,880 m.
- Chile is prone to frequent earthquakes and tsunamis because of its location on the Pacific Ring of Fire.
Economic Resources
- Chile is the world's largest producer of copper.
- It is part of the "Lithium Triangle" along with Argentina and Bolivia, holding over 75% of global lithium reserves found under salt flats.
- Other significant resources include molybdenum, iron ore, timber, hydropower, and precious metals.
This agreement is expected to strengthen economic ties between the two nations, enhancing trade and investment opportunities, while also providing a platform for cooperation in various sectors.
GS3/Environment
India's Participation in the 20th Session of the United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF20)
Source: PIB
 Why in News?
Why in News?
India recently took an active role in the 20th Session of the United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF20), which convened at the United Nations Headquarters in New York, highlighting its commitment to global forest conservation efforts.
Key Takeaways
- The UNFF was established in 2000 by the UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) to promote sustainable forest management and conservation.
- India is a founding member of the UNFF and continues to influence global forest policy.
- The Indian delegation reported significant achievements in forest conservation and reaffirmed its commitment to the United Nations Strategic Plan for Forests (UNSPF) 2017–2030.
Additional Details
- Forest Cover: India has seen a steady increase in forest and tree cover, now accounting for 17% of its geographical area, as per the latest India State of Forest Report.
- Key National Initiatives:
- Aravalli Green Wall project for land restoration.
- 86% increase in mangrove cover over the past decade.
- Afforestation efforts covering over 1.55 lakh hectares.
- Green India Mission involving the planting of 4 billion seedlings.
- Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam (Plant4Mother) campaign.
- International Big Cat Alliance: India invited all UN Member States to join this platform aimed at protecting seven big cat species through collaborative research and capacity-building.
- Studies presented focused on quantifying ecosystem services such as carbon sequestration, water provisioning, and biodiversity conservation, utilizing tools like the System of Environmental-Economic Accounting (SEEA) and the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MEA).
India's engagement in UNFF20 underscores its proactive approach towards forest conservation and sustainable management, aligning with international efforts to combat climate change and promote biodiversity.
GS2/International Relations
Caution and Optimism: On India’s FTA with the United Kingdom
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?
India and the United Kingdom recently finalized a significant Free Trade Agreement (FTA), announced by Prime Minister Narendra Modi and U.K. Prime Minister Keir Starmer. This agreement allows 99% of Indian exports to the U.K. to enter without incurring import duties.
Key Takeaways
- Zero-duty access for 99% of Indian exports enhances competitiveness in the U.K. market.
- Exemption from social security contributions for Indian workers in the U.K. boosts net salaries.
- Facilitated movement of professionals and investors to promote service sector growth.
Additional Details
- Zero-Duty Access: This provision allows Indian sectors such as gems and jewellery, apparel, and engineering goods to compete more effectively in the U.K., making these products more appealing to British consumers.
- Social Security Relief: Indian IT professionals on temporary assignments will benefit from higher take-home pay due to exemptions from social security contributions for up to three years.
- Boost to Services Trade: The FTA promotes easier mobility for professionals, which may lead to increased foreign direct investment (FDI) in sectors like consultancy and startups.
Stakeholder Optimism
- Engineering Goods Sector: Anticipates a surge in exports, projecting a near doubling of engineering exports to the U.K. to $7.55 billion by 2029-30.
- Apparel and Textile Industry: Gains a competitive edge with zero-duty access, enhancing market share against competitors like Bangladesh and Vietnam.
- Gems and Jewellery Sector: Welcomes duty-free access for high-value items, boosting profitability.
- IT and Professional Services: Benefits from easier mobility and qualifications recognition, reducing visa friction.
- Indian Employers: Save on costs when hiring Indian talent in the U.K. due to the social security exemption.
Concerns from Farmers
- Threat from Imported Agricultural Products: Reduced tariffs on U.K. agricultural exports like lamb and salmon may negatively impact local farmers.
- Low-Income Conditions: Farmers fear increased competition could worsen their financial stability, as many depend on traditional farming.
- Lack of Protective Mechanisms: The FTA does not provide safeguards for farmers against sudden import surges.
Influence on Future Trade Agreements
- Negotiation Template: The India-U.K. FTA may serve as a model for future trade negotiations with the EU and the U.S.
- Precedent for Sensitive Sector Concessions: Concessions made in this FTA may lead to similar demands in future agreements.
- Pressure on Domestic Policy: Opening markets may create pressure on India's manufacturing sector and trade policies in upcoming FTAs.
Way Forward
- Safeguarding Vulnerable Sectors: Implement protective clauses to shield farmers and MSMEs, such as phased liberalization and review mechanisms.
- Strengthening Domestic Competitiveness: Enhance manufacturing capacity and support R&D to fully leverage new market opportunities.
In conclusion, while the India-U.K. FTA presents significant opportunities for various sectors, it also raises concerns, particularly for farmers. The agreement's implications may extend to future trade deals, necessitating careful consideration of domestic policies to protect vulnerable sectors.
GS3/Environment
Finance Ministry Unveils Draft Climate Taxonomy Document
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Finance Ministry of India has introduced a draft document titled ‘Framework of India’s Climate Finance Taxonomy.’ This document aims to steer investments towards clean energy and climate-resilient infrastructure, providing clear definitions and criteria to identify environmentally sustainable projects.
Key Takeaways
- The taxonomy classifies economic activities as sustainable or transitional.
- It encourages the adoption of climate-friendly technologies.
- It aims to prevent greenwashing, which is the misleading practice of overstating environmental efforts.
- The framework supports India's goals of achieving Net Zero emissions by 2070 and a developed nation by 2047.
Additional Details
- Greenwashing: This refers to the deceptive practice of making unverified or exaggerated claims about environmental initiatives, misrepresenting actual progress on climate change.
- The taxonomy serves as a crucial tool for investors and banks to identify credible green investments, thereby supporting India's position in global climate negotiations.
- It addresses international disputes where developed nations often overstate their contributions to climate finance initiatives in developing countries.
Categories of Climate Activities
- Climate Supportive: Activities that directly reduce greenhouse gas emissions or enhance climate resilience.
- Climate Transition: Activities aimed at reducing emissions in hard-to-abate sectors such as iron, steel, and cement.
Key Sectors Covered
- Power generation
- Buildings and infrastructure
- Mobility/transport
- Agriculture and food systems
- Water security and resource management
Massive Scale-Up in Power Generation Capacity
- Target Capacity: Increase installed power capacity from 470.4 GW (February 2025) to 777.14 GW by 2049.
- Technology Focus:Prioritize investment in Advanced Ultra Super Critical (AUSC) thermal power plants, which offer 46% efficiency compared to:
- Subcritical: ~38%
- Supercritical: ~41–42%
- Goal: To achieve higher efficiency and lower emissions in thermal energy generation.
Climate Adaptation Investment Requirement
- Total Investment Needed: According to India’s Initial Adaptation Communication to the UN (December 2023), an estimated ₹56.68 trillion (approximately USD 648.5 billion) is required by 2030 based on 2023-24 prices.
- This funding will support adaptation actions in sectors such as forestry, fisheries, infrastructure, water resources, and ecosystems to mitigate the adverse impacts of climate change.
This draft climate taxonomy framework represents a pivotal step towards aligning investments with India's climate goals while ensuring transparency and accountability in environmental initiatives.
GS2/International Relations
Indo-Pacific Logistics Network (IPLN)
Source: AIR
Why in News?
The Quad partners recently gathered at the Asia-Pacific Center for Security Studies in Honolulu, Hawaii, to conduct a Tabletop Exercise, marking the initiation of the Quad Indo-Pacific Logistics Network (IPLN).
Key Takeaways
- The IPLN pilot project was launched during the fourth Quad Leaders’ Summit in September 2024.
- IPLN aims to enhance logistics collaboration among Quad partners for more efficient civilian disaster response in the Indo-Pacific region.
- This initiative complements existing partnerships and efforts in the region.
- IPLN highlights the Quad's commitment to a free and open Indo-Pacific and strengthens practical cooperation to tackle regional challenges.
Additional Details
- Quad: The Quadrilateral Security Dialogue, known as the Quad, comprises four nations: the United States, Australia, India, and Japan. It was established in response to the 2004 tsunami in the Indian Ocean region to coordinate humanitarian assistance.
- Historical Context: The first official meeting of Quad representatives occurred in May 2007 during the ASEAN Regional Forum summit in the Philippines. After a decade-long hiatus, they reconvened in November 2017 to discuss issues like connectivity, maritime security, and counter-terrorism.
- Since 2021, the Quad leaders have met annually to promote regional stability across South Asia, Southeast Asia, and the Pacific.
- Objectives: The core goals of the Quad include upholding a rules-based global order, ensuring freedom of navigation, and fostering a liberal trading system. This coalition also seeks to provide alternative debt financing options for nations within the Indo-Pacific.
- The Quad is perceived as a strategic alliance aimed at countering Chinese influence in the region.
The establishment of the IPLN signifies a significant step in enhancing regional cooperation for disaster response and reflects the Quad's broader strategy of maintaining stability and security in the Indo-Pacific.
GS3/Science and Technology
Kosmos 482 Mission
Source: BBC
 Why in News?
Why in News?
A 500-kg piece of a Soviet spacecraft, part of the Kosmos 482 mission launched in 1972, is expected to crash back to Earth.
Key Takeaways
- Kosmos 482 was launched on March 31, 1972, as part of the Venera Program aimed at exploring Venus.
- The mission's primary objectives included studying Venus's atmosphere and surface.
- It showcased technological and scientific superiority during the Cold War era.
Additional Details
- Kosmos 482:A Soviet space probe equipped with instruments to measure:
- Temperature
- Pressure
- Wind speed
- Atmospheric gases
- Rock composition
- The mission was significant due to speculation about potential life beneath Venus's thick clouds and its strategic importance in space exploration rivalry.
- During the period from 1961 to 1984, a total of 28 missions were launched toward Venus, with 13 probes entering its atmosphere and 10 landing, although they could only operate for 23 minutes to 2 hours due to harsh surface conditions.
The Kosmos 482 mission remains a pivotal part of space exploration history, illustrating the intense competition of the Cold War and the quest to understand our neighboring planet, Venus.
|
44 videos|5271 docs|1113 tests
|





















