UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 28th May 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS1/Geography
Bow Echo Storms
Source: Indian Express
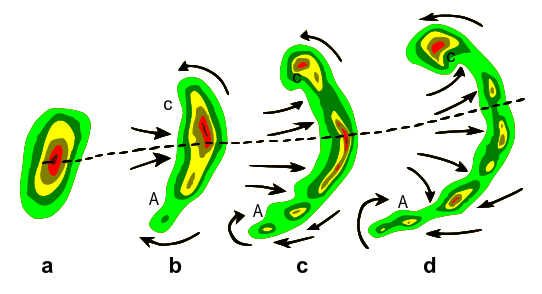 Why in News?
Why in News?
New Delhi recently experienced a significant thunderstorm with wind speeds reaching up to 100 km/h, which resulted in the formation of a bow echo—a distinct crescent-shaped pattern visible on weather radar.
Key Takeaways
- A bow echo is a storm pattern that looks like a curved bow, resembling an archer's bow.
- It typically forms within a mesoscale convective system (MCS), which consists of a large group of organized thunderstorms.
- The term "bow echo" was first introduced by meteorologist Ted Fujita, known for developing the Fujita scale for measuring tornado intensity.
Additional Details
- How It Forms: A bow echo forms when heavy rainfall causes cool air to sink and spread out near the ground. This cool air creates a gust front that pushes warm, moist air upward, leading to the development of new storms. A rear inflow jet, which consists of strong mid-level winds, propels the storm forward, creating a bow shape.
- Size and Duration: Bow echoes typically span between 20 to 200 km and can last anywhere from 3 to 6 hours.
- Wind Strength: These storm patterns can generate straight-line winds exceeding 100 km/h, similar to those observed in the recent storm in Delhi.
- Derechos: In extreme cases, bow echoes may evolve into derechos, which are extensive and long-lasting windstorms.
- Impacts: Bow echoes can lead to damaging winds that knock down trees and power lines, as well as cause structural damage to buildings. They can also produce brief tornadoes at the edges of the storm and generate intense short-lived wind blasts known as microbursts and downbursts, which can cause localized destruction.
Overall, understanding bow echo storms is crucial for meteorological safety and preparedness, especially in regions prone to severe weather events.
Question:
During a thunderstorm, the thunder in the skies is produced by the:
- 1. Meeting of cumulonimbus clouds in the sky
- 2. Lightning that separates the nimbus clouds
- 3. Violent upward movement of air and water particles
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
- (a) 1 only
- (b) 2 and 3
- (c) 1 and 3
- (d) None of the above produces the thunder
GS3/Economy
Free Trade Agreements and Indian Agriculture: Prospects and Pitfalls
Source: Research Gate
Why in News?
Between 2013-14 and 2024-25, India’s agricultural exports have experienced modest growth of slightly over 20%, increasing from $43.3 billion to $51.9 billion. However, agricultural imports have surged by 148% during the same period, rising from $15.5 billion to a record $38.5 billion. This significant increase in imports has resulted in a drastic reduction of India’s farm trade surplus, which fell from $27.7 billion to $13.4 billion.
In 2024-25, agricultural exports rose by 6.4%, surpassing the stagnation in overall export growth, while import growth was markedly higher at 17.2%, compared to a 6.2% increase in total merchandise imports. These developments occur as India is negotiating Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with the US and EU, both advocating for lower tariffs and greater access to Indian agricultural markets.
Key Takeaways
- India's agricultural trade surplus has significantly decreased.
- FTAs with the US and EU could alter tariff structures and market access.
- Export growth varies across different agricultural sectors.
Additional Details
- Marine Products: India’s top agricultural export, which saw earnings decline from $8.1 billion in 2022-23 to $7.4 billion in the following two years. Major markets include the US (35%), China (20%), and EU (15%). Concern: Rising US tariffs on frozen shrimp could further affect competitiveness.
- Rice Exports: Achieved record highs with combined basmati (6.1 mt) and non-basmati (14.1 mt) rice exports reaching $12.5 billion in 2024-25, primarily targeting markets in West Asia and Africa.
- Growth in Other Segments: Record-high exports noted in spices (especially chilli, cumin, turmeric), tobacco, coffee, and fruits & vegetables, while wheat and sugar exports are currently restricted due to domestic shortages.
- Cotton Collapse: Once a major exporter, India has now become a net importer of cotton, having seen exports decline dramatically.
- Buffalo Meat: Recovered to $4 billion in 2024-25, but still below previous levels.
India witnessed a significant rise in both spice exports and imports in 2024-25, maintaining its status as a leading exporter of non-traditional spices while becoming a net importer of traditional spices like pepper and cardamom.
Imports Overview
- Edible Oils and Pulses: These remain India's top agricultural imports, with pulses imports hitting a record $5.5 billion in 2024-25 due to domestic production challenges.
- Natural Rubber: Production has declined while consumption has surged, leading to higher import needs.
- Other Notable Imports: This includes fruits, dry fruits (like almonds, walnuts), and alcoholic beverages, which are expected to increase under new trade agreements.
The anticipated signing of FTAs with the US, EU, and UK may lead to increased imports of dry fruits, wines, and spirits. Additionally, potential pressure from the US for lower import duties and relaxed restrictions on genetically modified crops could significantly impact India's agricultural trade balance, potentially reducing the current surplus.
GS3/Defence & Security
India’s AMCA Stealth Jet Project Approved: A Leap Towards Indigenous Air Power
Source: Economic Times
Why in News?
The Defence Minister Rajnath Singh has given approval for the execution model of the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) Programme, marking a significant step in India's pursuit of self-reliant defence capabilities.
Key Takeaways
- The AMCA project aims to develop a fifth-generation stealth fighter jet.
- Five prototypes will be produced with a budget exceeding 15,000 crore.
- Delivery of the first operational unit is targeted for 2035.
Additional Details
- Features and Capabilities:The AMCA is designed as a twin-engine, 25-tonne aircraft featuring advanced stealth characteristics. Key aspects include:
- Internal weapons bays for reduced radar visibility.
- Super cruise capability for sustained supersonic flight.
- AI-assisted electronic pilot for enhanced decision-making.
- Integrated Vehicle Health Management for predictive maintenance.
- Strategic Significance: The AMCA project supports India’s 'Atmanirbhar Bharat' initiative by boosting indigenous defence production and positioning India among nations with advanced aerial combat technologies.
- Global Comparison: Compared to existing fifth-generation fighters like the F-35 (USA) and Sukhoi Su-57 (Russia), the AMCA aims for a balance between stealth and operational capability tailored to Indian defense needs.
- Challenges Ahead: A major hurdle in the AMCA program is engine development, which involves a joint venture with a foreign OEM to create a next-gen engine that meets specific thrust and stealth requirements.
The AMCA programme signifies a transformative leap in India’s air power, moving from older generations of aircraft to cutting-edge technology that enhances operational readiness across various combat scenarios.
GS1/Indian Society
India’s New Urban Worry — Rising Overnutrition
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
India is undergoing a significant shift in its public health landscape, transitioning from historical battles against undernutrition and infectious diseases to facing a growing epidemic of noncommunicable diseases (NCDs), primarily driven by lifestyle factors. Recent statistics from Hyderabad’s IT sector indicate that a staggering 84% of employees are affected by Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD), highlighting the urgent need to address the rising incidence of NCDs among urban populations.
Key Takeaways
- India's nutritional crisis features both undernutrition and rising obesity rates.
- Low- and middle-income countries bear a disproportionate burden of NCDs.
- Urban lifestyles contribute significantly to obesity and related health issues.
Additional Details
- Paradox of Malnutrition: India faces a dual challenge of persistent hunger in rural areas alongside increasing obesity in urban centers, with NCDs responsible for 74% of global deaths in 2019.
- Urbanisation and Lifestyle Shifts: The rapid urbanization, particularly in tech hubs like Hyderabad and Bengaluru, has led to sedentary jobs and diets high in ultra-processed foods.
- Public Health Indicators: Despite improvements in healthcare access, only 16% of hypertensive individuals have controlled blood pressure, and less than 10% of young diabetics achieve glycaemic control.
- Regulatory Shortfalls: Current consumer awareness efforts, such as the Eat Right India initiative, lack effective enforcement and face opposition from the food industry.
- Global Lessons: Learning from Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030, India could implement stronger regulations, such as calorie labeling and taxes on unhealthy foods.
In conclusion, India's urban health crisis, marked by poor nutrition and insufficient regulatory frameworks, demands immediate attention. With projections suggesting that nearly 450 million Indians could be overweight or obese by 2050, a comprehensive, multisectoral approach focusing on prevention and robust regulation is essential to tackle this impending health crisis.
GS2/International Relations
The Silver Jubilee of a Strategic Partnership
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?
This month marks 25 years of the Indo-German Strategic Partnership, celebrating a key milestone in their growing ties, shared goals, and long-standing cooperation across defence, economy, and sustainability.
Key Takeaways
- Strengthened bilateral relationship based on shared democratic values.
- Economic complementarity and collaboration on global peace initiatives.
- Germany's significant investment in India, enhancing job creation and educational exchange.
Additional Details
- Peace: Both countries share a vision for a peaceful, stable, and rules-based world, supported by regular Intergovernmental Consultations that strengthen political ties and cooperation.
- Prosperity: Focuses on economic growth, job creation, and improving quality of life, with over 2,000 German companies operating in India, creating more than 750,000 jobs.
- People-to-People Ties: Cultural and educational exchanges deepen bilateral relations, with over 50,000 Indian students studying in Germany, making them the largest foreign student group there.
- Future of the Planet (Green Development): Cooperation on climate change and renewable energy, exemplified by Germany’s €10 billion Indo-German Green and Sustainable Development Partnership supporting solar and wind projects in Gujarat.
- Technology and Innovation Collaboration: Joint scientific research and integration in high-tech industries, including Indian researchers in top German institutions and the operation of the Delhi-Meerut Rapid Rail by Deutsche Bahn.
The Indo-German relationship demonstrates a transformation from transactional engagement to a strategic, transformational alliance, with significant cooperation in various sectors. The future of this partnership looks promising, emphasizing deeper strategic and technological collaboration to address global challenges.
GS2/International Relations
As the U.S. Withdraws, China Expands Its Soft Power
Source: The Week
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The U.S. has been retreating from key international commitments under President Trump, notably withdrawing from the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Paris Agreement. Concurrently, China has been enhancing its global influence by providing financial aid and increasing investments around the world.
Key Takeaways
- The U.S. has accused the WHO of bias towards China and mismanagement during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- China is increasing its financial contributions to the WHO and expanding its global investments.
- China's stance on bilateral lending has made it the largest creditor globally.
- India's soft power is strong but faces challenges that need addressing.
Additional Details
- Perceived Bias and Mismanagement: The U.S. criticized the WHO for being biased towards China and mishandling the COVID-19 response. For example, President Trump claimed that the WHO did not hold China accountable during the early outbreak.
- Disproportionate Financial Burden: The U.S. stated it was unfairly contributing about 20% of the WHO's funding, compared to China's much smaller contribution until recently.
- Increased Financial Contributions to Global Institutions: China has pledged an additional $500 million to the WHO over five years, raising its assessed contribution from 6.5% in 2015-16 to 15% in 2024-25.
- Expansion of Bilateral Lending: China's share in global bilateral sovereign debt has increased from 1% in 2003 to 26% in 2023, making it the largest global lender.
- India's Cultural Influence: India's cultural exports, such as yoga and Bollywood, enhance its global soft power, but internal challenges affect its international image.
In conclusion, as the U.S. retreats from its global roles, China is actively stepping in to fill the void, enhancing its influence through strategic investments and financial support. Meanwhile, India must leverage its cultural strengths while addressing domestic issues to improve its standing in the global arena.
GS2/International Relations
Trump’s Crypto Diplomacy and Pakistan’s Digital Pivot - Strategic Implications for India
Source: Business World
 Why in News?
Why in News?
A significant geopolitical and technological shift is occurring with the cryptocurrency diplomacy between Pakistan and World Liberty Financial Inc (WLFI), a firm linked to the Trump family. This development coincides with Trump's renewed engagement with Pakistan during his second administration and an aggressive push for U.S. leadership in the crypto sector.
Key Takeaways
- MoU signed between WLFI and Pakistan Crypto Council aims to utilize blockchain for various financial initiatives.
- Concerns exist regarding the fragile state of Pakistan's economy and the potential misuse of cryptocurrencies.
- Trump's administration has shifted towards a pro-crypto stance, reversing previous skepticism.
- India faces new security and regulatory challenges in light of Pakistan's crypto developments.
Additional Details
- MoU Objectives:The Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) aims to:
- Enhance financial inclusion through blockchain technology.
- Monetize untapped national assets, particularly rare earth minerals.
- Introduce stablecoins for trade and remittances.
- Position Pakistan as a regional crypto hub.
- Trump’s Crypto Agenda:Following his re-election, Trump initiated several executive orders to promote cryptocurrency, including:
- Established a National Blockchain Innovation Strategy.
- Banned Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC).
- Created a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve to consolidate digital assets.
- India's Crypto Landscape: India has over 100 million crypto users and a market worth approximately $7 billion, yet lacks a clear regulatory framework. Recent Supreme Court interventions highlighted inconsistencies in taxing crypto without regulations, raising economic and national security concerns.
The rise of Trump’s crypto diplomacy and Pakistan’s digital alignment necessitate urgent policy introspection in India. Developing a comprehensive national crypto strategy is crucial to address security, economic, and geopolitical dimensions and to prevent a repeat of past strategic oversights.
GS1/Geography
Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO)
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
Recently, Mumbai experienced heavy monsoon rains two weeks earlier than expected due to a strong Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO), a significant weather pattern that enhances rainfall in the region.
Key Takeaways
- The MJO is a moving weather system that includes clouds, wind, rain, and pressure.
- It travels eastward around the tropics, completing a full cycle every 30 to 60 days.
Additional Details
- Discovery: The MJO was identified in the 1970s by meteorologists Roland Madden and Paul Julian.
- Two Phases:
- Enhanced convective phase: This phase is associated with heavy rain, storms, and increased cloudiness.
- Suppressed convective phase: This phase leads to dry and clear weather.
- Global Pattern: The MJO's phases are interconnected—when one area experiences rain, another might have dry conditions.
- MJO vs ENSO: Unlike El Niño, which lasts for months, the MJO changes every few weeks, impacting short-term weather patterns.
- Wider Impact: The MJO affects monsoons, cyclones, jet streams, and overall weather in both tropical and non-tropical regions. Its movement is classified into 8 phases, indicating where rain or dry weather may occur.
MJO and the Early Monsoon of 2025
- Early Monsoon Trigger: The early arrival of the monsoon in May 2025 was primarily due to a highly active MJO.
- IMD Observation: The India Meteorological Department noted that the MJO was in Phase 4 with high amplitude, which significantly influenced Indian rainfall.
- Rapid Monsoon Progress: The MJO facilitated the movement of extra moisture and clouds from the Indian Ocean, allowing the monsoon to transition from Kerala to Maharashtra in just two days.
- Other Contributing Factors:
- A strong cross-equatorial flow brought warm, moist air from the south.
- A low-pressure system in the Arabian Sea contributed to pre-monsoon rains in Mumbai.
- Record Rainfall: This combination of factors resulted in Mumbai experiencing its wettest May in over 100 years.
This event highlights the profound impact that tropical systems like the MJO can have on altering monsoon timing and rainfall patterns in India.
UPSC 2017
With reference to the ‘Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)’ sometimes mentioned in the news while forecasting the Indian monsoon, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- 1. The IOD phenomenon is characterized by a difference in sea surface temperature between the tropical Western Indian Ocean and the tropical Eastern Pacific Ocean.
- 2. An IOD phenomenon can influence an El Niño’s impact on the monsoon.
Options: (a) 1 only (b) 2 only* (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2
GS3/Environment
Conservation of Dugongs
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
May 28 is recognized annually as World Dugong Day, highlighting the need for conservation efforts regarding this unique marine mammal.
Key Takeaways
- Dugongs are herbivorous marine mammals, commonly referred to as sea cows.
- India's dugong population has drastically declined, now estimated at only 200 individuals.
Additional Details
- Species Info: The scientific name for dugongs is Dugong dugon. They are closely related to manatees and exclusively inhabit saltwater environments.
- Habitat: Dugongs thrive in shallow coastal waters, particularly found in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, the Gulf of Mannar, Palk Bay, and the Gulf of Kutch.
- Diet and Role: Their diet consists mainly of seagrass species, including Cymodocea, Halophila, Thalassia, and Halodule. As they graze, they aerate the seabed, earning them the title of "farmers of the sea."
- Lifespan and Behaviour: Dugongs can live for up to 70 years and are typically solitary or found in mother-calf pairs.
- Reproduction: Female dugongs reach maturity between 9 and 10 years and give birth every 3 to 5 years, leading to a slow population growth rate of about 5% annually.
- Conservation Concern: The population decline of dugongs in India raises significant conservation issues due to their limited numbers and shrinking habitat.
- Conservation Efforts in India:
- IUCN Status: Globally categorized as 'Vulnerable' and 'Regionally Endangered' in India.
- Legal Protection: Dugongs are safeguarded under Schedule I of the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972.
- Global Agreements: India became a member of the Convention on Migratory Species in 1983 and signed the Dugong Conservation MoU in 2008.
- Dugong Reserve: In 2022, India launched its first Dugong Conservation Reserve in Palk Bay, Tamil Nadu, encompassing 448.3 sq. km.
With reference to 'dugong', a mammal found in India, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- 1. It is a herbivorous marine animal.
- 2. It is found along the entire coast of India.
- 3. It is given legal protection under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972.
Options: (a) 1 and 2 (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 * (d) 3 only
In summary, the conservation of dugongs is critical not only for their survival but also for maintaining the ecological balance of their habitat.
GS3/Economy
Energy Efficiency Initiatives in India
Source: PIB
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Amid rising power deficits due to urbanization and climate pressures, India's UJALA scheme exemplifies the significant impact of energy efficiency, resulting in savings of $10 billion and 9,500 MW of power, thereby emphasizing the importance of efficiency over mere capacity expansion.
Key Takeaways
- India's peak power demand reached 250 GW in 2023-24, making it the third-largest power consumer globally.
- The power deficit increased from 0.69% in FY20 to approximately 5% in FY24.
- The UJALA scheme has distributed over 37 crore LED bulbs, significantly reducing power consumption.
Additional Details
- Peak Power Demand Challenges: Rapid urbanization and rising temperatures have led to increased electricity demand, particularly from cooling appliances.
- Slow Power Generation Expansion: The development of new power plants, especially coal-based, is capital and time-intensive, failing to keep up with demand.
- UJALA Scheme: Launched in 2015, this flagship program promotes energy-efficient lighting solutions, distributing LED bulbs and tube lights at affordable prices.
- Impact of UJALA: By improving lighting efficiency, UJALA has reduced peak power demand by over 1,500 MW and avoided the necessity to build 9,500 MW of new capacity, equivalent to 19 new coal-fired plants.
- Cost and Emission Reductions: The scheme has lowered the price of LED bulbs from ₹500 to ₹70, enhancing accessibility and contributing to a significant reduction in CO₂ emissions.
- Importance of Energy Efficiency: Enhancing energy efficiency is critical to bridging the gap between demand and supply, delaying the need for new fossil fuel-based power plants and supporting climate goals.
In conclusion, as India copes with increasing power demand and climate challenges, enhancing energy efficiency through initiatives like the UJALA scheme presents a practical solution. This approach not only addresses immediate energy needs but also supports long-term sustainability and cost-effectiveness in the energy sector.
GS3/Economy
Kumbakonam Vetrilai Betel Leaf Receives GI Tag
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
The Kumbakonam Vetrilai, commonly known as betel leaf or paan leaf, has recently been awarded the prestigious Geographical Indication (GI) tag by the Government of India. This recognition highlights the unique qualities and cultural significance of this product originating from the Kumbakonam region.
Key Takeaways
- The Kumbakonam Vetrilai is cultivated primarily in the Thanjavur region of Tamil Nadu.
- This betel leaf is noted for its heart-shaped leaves that vary in color from dark to light green.
- It plays a vital role in South Asian cuisine, especially as a key ingredient in paan, a popular post-meal chew.
- The first-year yield of the leaves is referred to as maaruvethalai, which are known for their durability and shelf life.
Additional Details
- Cultivation: Kumbakonam Vetrilai is grown in areas such as Kumbakonam, Thiruvaiyaru, Papanasam, Thiruvidaimarudur, and Rajagiri, benefiting from the fertile soil of the Cauvery basin.
- Harvesting Process: Farmers engage in a labor-intensive process, hand-picking the leaves from early morning until late night to ensure quality.
- Cultural Relevance: The leaf is integral to the traditional practice of chewing paan, enhancing its popularity in South Asian culture.
The GI tag is valid for a duration of 10 years and can be renewed, protecting the unique identity and reputation of Kumbakonam Vetrilai. This recognition not only supports local farmers but also promotes the cultural heritage associated with this product.
Back2Basics: Geographical Indication (GI) Tag
- A GI is a sign used on products that originate from a specific geographical location and possess qualities or a reputation tied to that origin.
- The nodal agency responsible for GI registration in India is the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- The GI system in India is governed by the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999, which came into effect in September 2003.
- GIs are defined under Article 22 (1) of the WTO Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Agreement.
In conclusion, the recognition of Kumbakonam Vetrilai with a GI tag not only enhances its marketability but also preserves the cultural identity of this cherished product.
|
51 videos|5377 docs|1138 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 28th May 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are Bow Echo Storms and how do they form? |  |
| 2. How do Free Trade Agreements impact Indian agriculture? |  |
| 3. What advancements are expected from India's AMCA Stealth Jet Project? |  |
| 4. What are the health implications of rising overnutrition in urban India? |  |
| 5. How is China's soft power expanding as the U.S. withdraws from global engagements? |  |
















