Science & Technology (Part 1): July 2025 Current Affairs | Current Affairs & General Knowledge - CLAT PDF Download
Russia Jolted by Powerful 8.8-Magnitude Earthquake
 Why in News?
Why in News?
A powerful 8.8 magnitude earthquake struck off the coast of Russia’s Kamchatka Peninsula, leading to widespread tsunami warnings across the Pacific. The quake, centered 119 km southeast of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky at a shallow depth of 19.3 km, was initially reported as 8.0 but later upgraded. It was followed by a strong 6.9 aftershock. This marks the strongest global quake since Japan’s devastating 9.0 magnitude earthquake in March 2011 that triggered the Fukushima nuclear disaster.
Key Takeaways
- The Kamchatka earthquake is classified as a great earthquake, releasing immense energy.
- Each whole-number increase in magnitude corresponds to roughly 31.6 times more seismic energy.
- The region's seismic activity is due to tectonic plate movements, particularly subduction.
Additional Details
- Earthquake Magnitude: Refers to the measured energy released by an earthquake, while intensity describes the perceived shaking at specific locations.
- The Kamchatka Peninsula is one of the world's most earthquake-prone regions, having experienced several powerful quakes throughout history.
- Subduction Process: This geological process involves a denser tectonic plate sliding beneath a lighter one, leading to stress release and earthquakes.
- The Pacific Plate descends at a rate of approximately 86 mm per year, causing periodic massive earthquakes and tsunamis.
- The area is part of the Pacific Ocean’s Ring of Fire, known for its intense seismic and volcanic activity.
- More than 15 countries, including Russia and Japan, are affected by the Ring of Fire, which generates about 80% of major earthquakes globally.
The recent earthquake in Kamchatka exemplifies the ongoing tectonic activity in the region, highlighting the importance of understanding seismic risks and preparing for potential future events.
CRIB Blood Group Discovery
Why in News?
A new blood group named CRIB has been discovered in a woman from Kolar district in Karnataka, marking a historic finding as it is previously unidentified globally. This discovery was announced at the 35th Regional Congress of the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT) held in Milan, Italy.
Key Takeaways
- The CRIB blood group is part of the Cromer (CR) blood group system.
- CRIB stands for "Cromer" and "India, Bangalore," reflecting its origin.
- Identifying new antigens like CRIB enhances safety in blood transfusions.
Additional Details
- Cromer Blood Group System: This system includes 12 high-prevalence antigens and 3 low-prevalence antigens found on the decay-accelerating factor (DAF).
- Rare Blood Types: A rare blood type is defined as one that is present in only 0.1% of the population, which can complicate transfusions and surgeries if antibodies develop.
The identification of new blood groups and antigens is crucial for improving compatibility testing and donor matching in medical emergencies, thereby enhancing the overall safety of blood transfusions.
NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR)
Why in News?
The NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) is scheduled for launch from Sriharikota, India, utilizing the GSLV Mk-II launch vehicle.
Key Takeaways
- Launch Vehicle: GSLV Mk-II
- Launch Site: Sriharikota, India
- Mission Life: Planned for 3 years, with a design lifespan of over 5 years
- Orbit: Sun-synchronous polar orbit at an altitude of 747 km with an inclination of 98.4°
- Data Access: Free and near real-time data, with disaster maps provided in under 5 hours
Additional Details
- Objective: High-precision monitoring of Earth's surface changes, including tectonics, agriculture, ecosystems, ice, floods, and landslides.
- Hardware Contributions:
- NASA: L-band SAR, 12-meter antenna, avionics.
- ISRO: S-band SAR, satellite bus, launch services.
- Development Timeline:
- Initial Concept: 2007 (NASA); ISRO joined in 2012.
- Formal Agreement: 2014.
- Investment: NASA - ~$1.16 billion; ISRO - ~$90 million.
Key Features of NISAR
- What is Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR)?
- Operates day/night and in all weather conditions.
- Simulates a large radar antenna through motion.
- Pierces clouds, vegetation, and soil.
- Dual-Band SAR:
- L-band SAR (1.257 GHz): Provides deeper penetration, ideal for forests, tectonic shifts, and permafrost.
- S-band SAR (3.2 GHz): Focuses on surface details, aiding in agriculture, flood mapping, and biomass tracking.
- Radar Antenna: 12-meter deployable mesh reflector.
- Resolution: 3-10 m spatial; cm-level vertical resolution.
- Swath Width: 240 km.
- Imaging Frequency: Global land/ice coverage every 12 days, less frequent in polar zones.
- Data Output: Generates 80 TB/day, which is three times the capacity of current Earth observatories.
Applications and Impact
- Disaster Relief: Provides before-and-after imagery for effective planning.
- Climate Monitoring: Tracks glacier melt and forest degradation.
- Agriculture: Monitors crop health, rotation, and food security.
- Infrastructure: Detects land subsidence in areas such as dams and cities.
- Strategic Value: Represents one of the most powerful Earth-observing radar satellites, the first with dual SAR payload, and enhances the India-US space partnership.
The NISAR mission exemplifies a significant collaboration in space technology, combining resources from NASA and ISRO to achieve groundbreaking advancements in Earth observation and monitoring.
N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA)
Why in News?
The Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) has mandated that drug controllers across all States and Union Territories instruct manufacturers to monitor the levels of a potentially carcinogenic chemical known as N-Nitrosodimethylamine in antacid Ranitidine.
Key Takeaways
- NDMA is a volatile organic compound commonly found in the environment.
- It is classified as a probable human carcinogen based on animal research.
- Exposure to NDMA can occur through environmental sources and contaminated food or medications.
Additional Details
- N-Nitrosodimethylamine: NDMA is a yellow, odorless liquid that was historically used in the production of rocket fuel and is a byproduct of various industrial processes, including water chlorination.
- NDMA is formed when secondary or tertiary amines react with nitrite ions under acidic conditions.
- Common sources of NDMA exposure include processed foods like cured meats (especially bacon), beer, fish, cheese, and even some vegetables.
- People are typically exposed to small amounts of NDMA through their diet and the environment.
In summary, the presence of NDMA in medications like Ranitidine poses potential health risks, especially considering its classification as a probable carcinogen. Monitoring and regulation of this compound are crucial for public health safety.
What is Legionnaires' Disease?
Why in News?
Residents of Central Harlem, New York City, are being urged to take precautions due to recent cases of Legionnaires' disease, leading health authorities to initiate an urgent investigation.
Key Takeaways
- Legionnaires' disease is a serious lung infection caused by the bacterium Legionella.
- The disease is primarily transmitted through inhalation of contaminated water or soil.
- It is non-contagious and cannot be spread from person to person.
- Older adults and individuals with weakened immune systems are at greater risk.
Additional Details
- Transmission:Legionella bacteria are commonly found in freshwater environments like lakes and rivers, as well as in soil. Most infections occur when individuals breathe in contaminated aerosols from water sources.
- The disease is not spread through drinking contaminated water unless it is aspirated into the lungs.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include fever, chills, headaches, malaise, and muscle pain (myalgia). Untreated cases can be fatal.
- Treatment: Early treatment with antibiotics is usually effective. However, some patients may continue to experience health issues even after treatment.
In summary, Legionnaires' disease poses a serious health risk, particularly for vulnerable populations, and requires prompt medical attention to ensure effective treatment.
Deep-Brain Stimulation
Why in News?
Deep-Brain Stimulation (DBS) has gained attention as an innovative medical technique that has been employed by over 160,000 individuals globally to address specific neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Key Takeaways
- DBS involves the implantation of electrodes in targeted brain areas.
- The technique is primarily used for treating movement disorders.
- DBS can also be used for certain psychiatric conditions.
Additional Details
- What is Deep-Brain Stimulation? DBS is a medical procedure where electrodes are surgically implanted into specific regions of the brain to help treat various disorders. These electrodes are linked to a device, similar to a pacemaker, which is placed under the skin and delivers controlled electrical impulses to the brain.
- How does it work? The device sends mild electrical impulses to targeted brain regions, helping to correct abnormal brain activity or chemical imbalances. This is particularly effective for conditions where faulty electrical signals cause symptoms.
- Applications: DBS is most widely recognized for its effectiveness in movement disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, and dystonia, particularly for patients whose symptoms are unresponsive to medication. It has also been approved for treating obsessive-compulsive disorder and is being researched for conditions like severe depression and epilepsy.
- Advantages of DBS: One significant benefit of DBS is its reversible nature; if the device is turned off, the stimulation ceases, unlike traditional surgeries that destroy brain tissue. It is believed to help normalize disrupted brain circuits at both the cellular and network levels.
Overall, Deep-Brain Stimulation holds promise for enhancing the quality of life for individuals with challenging neurological and psychiatric disorders by providing a method to manage and alleviate symptoms effectively.
India’s First Hydrogen Train Coach: A Step Towards Green Railways
Why in News?
Indian Railways has achieved a significant milestone by successfully testing its first hydrogen-powered coach at the Integral Coach Factory (ICF) in Chennai. This initiative represents a crucial advance towards the launch of India’s inaugural hydrogen-powered train, supporting the nation's objectives of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing the use of renewable energy sources.
Key Takeaways
- The hydrogen train project is currently in the final testing stage before commercial rollout.
- Hydrogen, as a clean fuel, aims to reduce India’s dependence on fossil fuels.
- Only a few countries have embarked on similar hydrogen projects, most of which remain experimental.
Additional Details
- Hydrogen Train Project: Launched by Northern Railway in 2020-21, the project involves retrofitting two 1600 HorsePower (HP) diesel power cars into hydrogen fuel cell-powered units.
- The project includes establishing a hydrogen storage and fuelling facility at Jind, Haryana, with a capacity of 3,000 kg of hydrogen.
- The Research Design & Standards Organisation (RDSO) is overseeing the design, testing, and validation processes.
- The retrofitted train will have 10 coaches and can accommodate over 2,600 passengers, operating between Jind and Sonepat in Haryana with two daily round trips covering 356 km.
- Safety Measures: Given hydrogen's flammability, safety protocols include pressure relief valves, leak detection sensors, temperature monitors, and optimized ventilation systems. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) studies simulate worst-case leak scenarios.
- To ensure adherence to global safety standards, the German firm TUV-SUD has been appointed as an independent safety auditor, with engineering led by Medha Servo Drives at ICF Chennai.
- The hydrogen fuelling facility at Jind will have two storage sections: 2,320 kg at low pressure and 680 kg at high pressure, complying with the Petroleum Explosives Safety Organisation (PESO) standards.
- Supporting infrastructure, such as power supply lines and firefighting tanks, is being developed to optimize facility operations.
- The initiative is part of the “Hydrogen for Heritage” project, which plans to deploy 35 hydrogen-powered trains on heritage and hill routes, each costing around ₹80 crore, with an additional ₹70 crore allocated for infrastructure per route.
- Although the operational costs of hydrogen-powered trains are high, they are expected to decrease with advancements in scale and efficiency.
- Hydrogen's appeal lies in its zero carbon emissions, aligning with India's green energy aspirations.
- India's hydrogen initiatives extend beyond railways; in 2024, a hydrogen-fueled bus was presented to Bhutan’s Prime Minister, highlighting India's broader commitment to sustainable mobility.
This innovative step towards hydrogen-powered transportation reflects India's commitment to sustainable development and reducing carbon footprints in various sectors.
Novel Microscope Observes Molecular Motion
Why in News?
Scientists at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) have developed a groundbreaking microscope that allows for real-time observation of molecular movements at an incredibly small scale, over a century after Albert Einstein's explanation of Brownian motion.
Key Takeaways
- This microscope showcases molecular motion in real time.
- It operates at an angstrom-level resolution, enabling detailed observation.
- The technology captures hundreds of billions of frames per second.
Additional Details
- Brownian Motion: This refers to the random movement of tiny particles in a fluid caused by constant collisions with surrounding molecules, which supports the existence of atoms and molecules as explained by Einstein in 1905.
- Particle Behavior: Smaller particles exhibit faster and more erratic movements, while larger particles move more slowly.
- Caltech Microscope Features:
- Resolution: Angstrom-level (1 Å = 0.0000000001 m).
- Speed: Capable of capturing hundreds of billions of frames per second.
- Advantage: Provides wide-field, single-shot imaging without damaging the sample.
- How It Works:
- Fluorescent molecules in water are illuminated by ultrafast lasers.
- Scattered light is directed through a Digital Micromirror Device.
- Light is converted to electron patterns to reveal molecular size—faster changes indicate smaller molecules, while slower changes indicate larger ones.
This innovative microscope represents a significant advancement in the field of molecular biology and materials science, allowing researchers to observe and analyze molecular dynamics in unprecedented detail.
Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD)
Why in News?
Recently, the deaths of 16 chitals, or spotted deer, at the Rajiv Gandhi Zoological Park in Pune have been confirmed to be due to Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) following lab reports.
Key Takeaways
- FMD is a highly contagious viral disease affecting cloven-hoofed animals.
- It does not pose a threat to human health or food safety.
- The disease is transmitted through direct and indirect contact with infected animals.
Additional Details
- About Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD): FMD is caused by an aphthovirus from the family Picornaviridae and affects animals like cattle, sheep, goats, deer, and pigs. It is not related to the common childhood illness known as hand, foot, and mouth disease, which is caused by a different virus.
- Transmission: The virus spreads through direct contact with infected animals or indirectly via secretions (like milk and semen) and can also be carried by mechanical vectors such as people, vehicles, and even through air movement.
- Symptoms: FMD is characterized by symptoms such as fever, blister-like sores on the tongue and lips, lameness, and reluctance to eat. It can lead to severe production losses in livestock.
- Vaccination: Vaccines for FMD are available but need to be specific to the virus type causing the outbreak. There are seven known strains of the virus.
In conclusion, while the majority of infected animals can recover, FMD often leaves them weakened and can be fatal, especially in young animals. The disease remains a significant concern for livestock production and trade.
NISAR Satellite - A Landmark NASA-ISRO Collaboration for Earth Observation
Why in News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is preparing to launch the NISAR satellite from Sriharikota aboard a GSLV Mk-II rocket. This mission, which is a collaboration between NASA and ISRO, is set to take place on July 30 and is regarded as one of the most advanced Earth observation missions globally, with a budget of Rs. 12,000 crore and over a decade of development.
Key Takeaways
- NISAR is the first dual-band radar satellite for Earth observation.
- It combines NASA's radar technology with ISRO's engineering expertise.
- The satellite will monitor various environmental and disaster-related phenomena.
Additional Details
- Unique Features:NISAR is equipped with dual-frequency synthetic aperture radar (SAR), featuring:
- L-band radar (1.257 GHz): Suitable for penetrating dense forests and soil to assess subsurface movements.
- S-band radar (3.2 GHz): Optimized for surface-level observations, including crop growth and biomass estimates.
- Wide Coverage: The radar swath width is 240 km, with a spatial resolution of 3-10 meters, enabling precise tracking of phenomena such as land subsidence.
- Scientific Applications: NISAR supports research across six key themes, including solid Earth processes, ecosystems, and disaster response.
- India-Specific Enhancements: While NISAR will function globally, ISRO will operate the S-band radar over India to enhance applications in agriculture, forestry, and disaster management.
- Data Accessibility: NISAR will adopt an open-data policy, ensuring data availability typically within a few hours after acquisition.
In conclusion, NISAR represents a significant advancement in Earth observation technology, contributing to global scientific knowledge and supporting various applications critical for environmental monitoring and disaster response.
AI for India 2.0 Programme
Why in News?
The Minister of State (Independent Charge) for the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) recently updated the Rajya Sabha about the AI for India 2.0 Programme, which aims to enhance skill development in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML).
Key Takeaways
- The programme was launched in 2023 on the occasion of 'World Youth Skills Day'.
- It offers free online training in AI and ML with a focus on vernacular accessibility.
- Content is available in nine Indian languages, including Hindi, Telugu, and Kannada.
- The target audience includes college students, fresh graduates, and early-career professionals, particularly from rural and non-English-speaking backgrounds.
Additional Details
- Special Focus on Vernacular Languages: The programme emphasizes content delivery in local languages, thereby empowering youth and making tech education accessible.
- Collaboration: It is a joint initiative involving GUVI (Grab Ur Vernacular Imprint), an ed-tech company incubated by IIT Madras and IIM Ahmedabad, along with Skill India, aiming to promote education in vernacular languages.
- The programme is nationally accredited by NCVET and IIT Madras, ensuring the quality and recognition of the training provided.
This initiative represents a significant step towards equipping young individuals with cutting-edge skills in AI and ML, ultimately contributing to the growth of a skilled workforce in India.
What is Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD)?
Why in News?
The Pune district is currently facing the challenge of Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD), with more than 900 cattle reported as infected and new cases emerging daily. This situation poses a significant risk to the local milk supply.
Key Takeaways
- Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD): A highly infectious viral disease affecting cattle and water buffalo.
- Causative Agent: Caused by the lumpy skin disease virus (LSDV), a member of the Capripoxvirus genus.
- Transmission: Spread by blood-feeding insects and contaminated feeding and watering sources.
- Symptoms: High fever, enlarged lymph nodes, and multiple skin nodules.
- Treatment: No specific treatment; prevention through vaccination is crucial.
Additional Details
- Causative Agent: LSDV is not zoonotic, meaning it cannot be transmitted to humans. It is part of the Poxviridae family, which includes smallpox and monkeypox viruses.
- Endemic Regions: LSD is endemic in Africa and the Middle East, with increasing cases reported in Europe and Southeast Asia. It is especially prevalent during the wet summer and fall months, particularly in low-lying areas near water bodies.
- Economic Impact: The disease can lead to a temporary reduction in milk production, temporary or permanent sterility in bulls, damage to hides, and in severe cases, death.
- Transmission Details: Infected animals can shed the virus through oral and nasal secretions, contaminating common feeding and watering troughs, facilitating further spread.
- Supportive Care: Infected animals may receive supportive care, including antibiotics, painkillers, and wound care sprays to manage symptoms.
In summary, Lumpy Skin Disease poses a serious threat to cattle health and local economies, highlighting the importance of awareness and proactive vaccination strategies to mitigate its impact.
Winter Fog Experiment (WiFEX)
Why in News?
The Winter Fog Experiment (WiFEX) has achieved a significant milestone, marking ten years of extensive research focused on the dense winter fog in North India.
Key Takeaways
- Launched in winter 2015 at Indira Gandhi International Airport, New Delhi.
- Led by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology in collaboration with various governmental bodies.
- One of the few long-term experiments worldwide dedicated to studying fog phenomena.
Additional Details
- Objectives: The primary goals of WiFEX include enhancing the now-casting (next 6 hours) and forecasting capabilities for winter fog across different time and spatial scales.
- Impact: Aims to mitigate the adverse effects of fog on transportation, aviation, and the economy, as well as to reduce accidents caused by poor visibility.
- Methodology: Utilizes advanced instruments such as micrometeorology towers, ceilometers, and high-frequency sensors to gather comprehensive data on various atmospheric parameters, constructing a unique dataset that helps in understanding the formation and dissipation of dense fog.
- Forecasting Model: The insights gained have contributed to the creation of a high-resolution (3 km) probabilistic fog prediction model, recognized as one of the most sophisticated forecasting tools in the region.
The model has demonstrated over 85% accuracy in predicting the onset, density, duration, and clearance of very dense fog (visibility below 200 meters), thereby significantly improving operational forecasting capabilities.
AdFalciVax Vaccine
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) is in the process of developing a new malaria vaccine candidate named AdFalciVax, aimed specifically at combating the Plasmodium falciparum parasite.
Key Takeaways
- AdFalciVax is a recombinant vaccine, utilizing parts of genes to trigger an immune response.
- It is developed in collaboration with various research institutes and utilizes a safe, food-grade bacterium for production.
- The vaccine targets multiple stages of the malaria parasite lifecycle.
- It offers advantages over existing malaria vaccines in terms of cost-effectiveness and storage requirements.
Additional Details
- Recombinant Vaccine: This type of vaccine uses genetic engineering to insert specific parts of the malaria parasite's genes into a host cell, prompting the expression of target proteins that elicit an immune response.
- Collaboration: The development of AdFalciVax involves the Regional Medical Research Centre in Bhubaneswar (RMRCBB), the National Institute of Malaria Research (NIMR), and the Department of Biotechnology's National Institute of Immunology (DBT-NII).
- Production: The vaccine is produced using Lactococcus lactis, a safe, food-grade bacterium, which aids in the vaccine's safety profile.
- Dual-Stage Protection: Unlike existing vaccines that target only one stage of the parasite, AdFalciVax incorporates antigenic components that focus on both the pre-erythrocytic and sexual stages, aiming to enhance individual protection and reduce transmission through mosquitoes.
- Storage Benefits: The formulation of AdFalciVax remains potent for over nine months at room temperature, thus minimizing the challenges associated with cold chain logistics in vaccine distribution, especially in remote areas.
In conclusion, the AdFalciVax vaccine represents a promising advancement in malaria prevention, offering unique benefits and a dual-target approach to combat one of the world's most significant health challenges.
Chikungunya: A Growing Concern
Why in News?
The Ministry of Health in China has launched an emergency campaign to protect individuals at risk of Chikungunya fever, a mosquito-borne viral disease that is becoming increasingly prevalent.
Key Takeaways
- Chikungunya is caused by the Chikungunya Virus (CHIKV).
- Symptoms include fever and severe joint pain, often leading to misdiagnosis with diseases like dengue and Zika.
Additional Details
- Transmission: The disease is transmitted to humans through the bites of infected female mosquitoes, primarily Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. These mosquitoes can also carry other viruses such as dengue and Zika. Importantly, the infection is not contagious between humans.
- Symptoms: The onset of fever is abrupt, typically accompanied by joint pain. Other common symptoms include muscle pain, headache, nausea, fatigue, and rash. Severe joint pain may last for several days but can persist for months or even years. Serious complications are rare but can occur, particularly in elderly individuals and young children.
- Treatment: Currently, there is no vaccine or antiviral treatment available for Chikungunya. Management focuses on alleviating symptoms.
In summary, as Chikungunya cases rise, public health efforts are crucial to manage and mitigate the spread of this disease.
Gujarat’s Tribal Genome Sequencing Project
Why in News?
Gujarat has initiated India’s first Tribal Genome Sequencing Project aimed at mapping the genetic data of tribal communities, significantly contributing to the national Genome India Project (GIP).
Key Takeaways
- This project was announced in Gujarat’s 2025-26 budget and is set to span over 5 years under the Gujarat Biotechnology Research Centre (GBRC).
- The focus is on genome sequencing of tribal communities, which constitute approximately 15% of Gujarat’s population (around 1 crore individuals).
- The project aims to address the under-representation of tribal genetic data, which previously had only about 100 samples from Gujarat.
Additional Details
- Sample Size: The project will involve 4,158 individuals, including 378 trio families, to create a reference genome panel of 2,000 samples.
- Data Collection: Data will include blood, stool, genealogical, physiological, and lifestyle information.
- Precision Medicine Applications: The project will facilitate early detection of conditions such as sickle cell anemia, G6PD deficiency, and BRCA-linked cancers.
- Gene-Trait Mapping: It aims to explore genetic links to specific traits, including agility and archery skills.
- Genomic Sampling Protocol: The project will employ SNP genotyping to filter closely related samples and will conduct Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) on 2,000 diverse samples using Illumina NovaSeq 6000 technology.
- Data Security: The project will ensure privacy and anonymity through double encryption methods.
The Gujarat Tribal Genome Sequencing Project not only enhances the understanding of tribal genetics but also contributes to the broader objectives of the Genome India Project, which aims to map genetic diversity across the country.
About the Genome India Project (GIP)
- Initiation: Launched in January 2020 by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT).
- Structure: It is a multi-institutional consortium involving leading Indian research organizations.
- Objectives:
- Diversity Mapping: To decode genetic variation across the Indian population.
- Reference Panel: To build a Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP)-based haplotype database for Indian genomes.
- Biobank Creation: To establish DNA reserves for research and therapeutic development.
- Key Achievements:
- Sequenced 10,074 genomes from 99 ethnic groups.
- Data is securely stored at the Indian Biological Data Centre (IBDC) in Faridabad.
- Insights gained have revealed rare traits that aid in the development of affordable diagnostics and predictive tools.
This initiative not only enhances the understanding of India's genetic landscape but also provides valuable insights for global genomics research and its applications in healthcare.
INVICTUS: Europe’s New Hypersonic Research Initiative
Why in News?
The European Space Agency (ESA) has recently collaborated with the UK-based company Frazer-Nash to launch the INVICTUS research programme, aimed at advancing hypersonic technologies.
Key Takeaways
- INVICTUS focuses on developing technologies for reusable vehicles that can launch horizontally.
- The programme is financed through ESA’s General Support Technology Programme (GSTP) and the Technology Development Element (TDE).
- The research will involve a fully reusable experimental aerospace vehicle capable of flying at speeds of Mach 5 (five times the speed of sound).
- The vehicle aims to demonstrate critical technologies necessary for sustained hypersonic flight within the atmosphere.
Additional Details
- Vehicle Capabilities: The INVICTUS vehicle will be designed to be upgradable, allowing for the interchange of materials, software, and propulsion systems throughout various flight test campaigns.
- Technological Significance: The INVICTUS programme will validate the use of a hydrogen-fuelled precooled air-breathing propulsion system for both horizontal take-off and hypersonic flight.
- INVICTUS builds on previous technology advancements managed by ESA, providing opportunities for industry, agencies, and academia to test future hypersonic technologies in relevant environments.
Overall, the INVICTUS programme represents a significant step forward in hypersonic research, promising advancements that could shape the future of aerospace technology.
Piezo-Photocatalytic Water Filter
Why in News?
Indian scientists from INST Mohali, IIT-Dharwad, and IIT-Kharagpur have developed an innovative, cost-effective, and reusable water filter that effectively removes toxic industrial dyes through a process known as piezo-photocatalysis.
Key Takeaways
- The water filter utilizes a combination of sunlight and mechanical vibrations to function efficiently.
- It has shown promising results in laboratory tests, specifically in the removal of harmful dyes from water.
Additional Details
- Material Used: The filter is constructed using 3D-printed polylactic acid (PLA) sheets, which are biodegradable. These sheets are coated with bismuth ferrite (BFO) nanoparticles.
- Working Mechanism:The filter operates through two main processes:
- Photocatalysis: This process utilizes sunlight to decompose dye molecules.
- Piezoelectric Effect: It harnesses vibrations (such as ultrasound) to enable functioning even in the absence of light.
- Performance: The filter can be reused up to 5 times with only a 3% loss in efficiency. Laboratory tests have demonstrated a 99% removal rate for Congo Red dye and a 74% removal rate for Methylene Blue within 90 minutes.
- Significance: This technology is eco-friendly as it removes toxic dyes without the use of harmful chemicals or electricity.
- Cost-Effectiveness: It is a more affordable and safer alternative compared to traditional ozone or chemical-intensive treatment methods.
- Green Energy Use: The filter operates on renewable energy sources, utilizing sunlight and mechanical vibrations, thus requiring no external power supply.
- Policy Alignment: The development aligns with the goals of initiatives such as Namami Gange, Jal Nigam, and Aatmanirbhar Bharat.
- Scalability: This technology is ideally suited for deployment near textile treatment plants, promoting sustainable practices in water filtration.
This innovative approach offers a promising solution for water purification, addressing environmental concerns while supporting national initiatives aimed at sustainability.
Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO) and the Interstellar Comet C/2025 N1 (ATLAS)
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Indian astronomers have successfully captured images of the interstellar comet C/2025 N1 (ATLAS), also referred to as 3I/ATLAS, using the Himalayan Chandra Telescope (HCT) located at the Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO) in Hanle, Ladakh. This achievement highlights the capabilities of Indian astronomical research and the significance of the observatory's facilities.
Key Takeaways
- The Himalayan Chandra Telescope is a vital asset for astronomical research in India.
- The observatory is positioned at a high altitude, providing optimal conditions for observing celestial phenomena.
- Hanle is recognized as a Dark Sky Reserve, promoting the preservation of night sky quality.
Additional Details
- Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO): The IAO, also known as the Hanle Observatory, is situated in the Hanle Valley of Ladakh at an altitude of 4500 metres above sea level.
- Established: Inaugurated in 2001, the observatory is managed by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) based in Bengaluru.
- Geographical Features: The site is characterized by a dry, cold desert environment, minimal light pollution, and low atmospheric water vapour, making it ideal for astronomical observations.
- Infrastructure: The observatory houses a 2-meter aperture Himalayan Chandra Telescope (HCT), which is remotely operated from the Centre for Research and Education in Science and Technology (CREST) in Bengaluru. It is equipped with a solar power plant, satellite communication systems, and a liquid nitrogen plant for cooling detectors.
- Dark Sky Reserve: Hanle is designated as a Dark Sky Reserve by the International Dark-Sky Association, aimed at minimizing light pollution to preserve the quality of its night skies.
The successful imaging of comet C/2025 N1 (ATLAS) underscores the importance of the Indian Astronomical Observatory as a center for astronomical excellence and highlights the significant role of Indian scientists in the field of space exploration.
Solar EruptioN Integral Field Spectrograph
Why in News?
The Solar EruptioN Integral Field Spectrograph (SNIFS) is set to launch as part of a collaborative effort by NASA and international solar physicists from New Mexico. This mission aims to deepen our understanding of the solar atmosphere, particularly the complex chromosphere.
Key Takeaways
- SNIFS is designed to explore the dynamics and energetics of the solar chromosphere.
- It represents the first solar ultraviolet integral field spectrograph, combining imaging and spectrographic capabilities.
- The mission will observe real-time high-resolution data from both the chromosphere and the transition region of the Sun.
Additional Details
- Integral Field Spectrograph:This advanced technology merges two critical functions:
- Imagers: Capture extensive photos and videos, allowing for a broad view of light.
- Spectrographs: Analyze light by separating it into various wavelengths, helping identify elemental composition, temperature, and movement from a single location.
- Target Observation: The SNIFS mission will focus on the hydrogen Lyman-alpha line, which is the most intense line in the solar ultraviolet spectrum and a key diagnostic for assessing conditions in the upper chromosphere.
This innovative approach will enhance our comprehension of solar activities and their implications for space weather, contributing significantly to the field of solar physics.
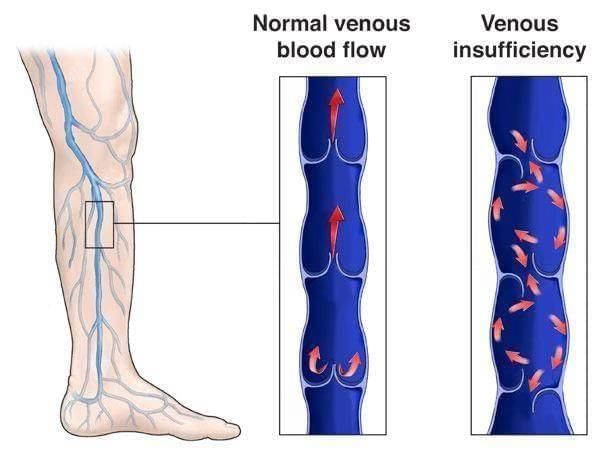
What is Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI)?
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, former US President Donald Trump has been diagnosed with Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI), a condition affecting blood flow in the legs.
Key Takeaways
- CVI occurs when leg veins struggle to return blood to the heart.
- It can lead to symptoms such as pain, swelling, and varicose veins.
- Risk factors include obesity, pregnancy, family history, and previous leg injuries.
Additional Details
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency: This condition arises when the valves in the leg veins do not function properly, causing blood to pool in the legs.
- The condition affects approximately 1 in 20 adults, with a higher prevalence among older individuals.
- Common symptoms include cramps, skin changes, and leg ulcers.
- Treatment options range from lifestyle changes such as regular exercise and weight management to more advanced methods like compression therapy and medication.
In summary, while CVI may not pose a serious health threat, it can significantly impact quality of life. Early intervention and treatment can help manage symptoms effectively.
What is a Protostar?
Why in News?
A recent discovery by a team of researchers at the IIST in Thiruvananthapuram has revealed the presence of radio emissions exhibiting circular polarization near a massive young protostar that is still in the process of formation, located approximately 4,500 light-years from Earth.
Key Takeaways
- A protostar is an early stage in the formation of a star.
- It consists of a large mass of gas and dust formed by the contraction of a giant molecular cloud in the interstellar medium.
- The protostar formation process can take anywhere from 100,000 to 10 million years, depending on the star's mass.
Additional Details
- Formation Process: The formation of a protostar begins with an increase in density in the molecular cloud core and concludes with the formation of a pre-main-sequence star.
- T-Tauri Stars: Pre-main-sequence stars that have similar mass to the Sun are classified as T-Tauri stars.
- Once hydrogen fusion ignites in the core, the star starts producing energy and transitions into a main sequence star.
- Protostars are typically enveloped in dust, which obstructs the light they emit, making them challenging to observe in the visible spectrum.
This discovery sheds light on the ongoing processes of star formation and helps enhance our understanding of the early stages of stellar evolution.
IIST Scientists Detected Circular Polarisation near Massive Protostar
Why in News?
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology (IIST) have successfully detected radio emissions exhibiting circular polarisation near a young massive protostar known as IRAS 18162-2048. This discovery holds significant implications for understanding star formation and the role of magnetic fields in the universe.
Key Takeaways
- The discovery provides the first direct evidence of magnetic fields originating from the protostar itself.
- Circular polarisation is a rare phenomenon that offers insights into the magnetic environment surrounding protostars.
- The magnetic field strength near IRAS 18162-2048 is estimated to be 100 times stronger than that of Earth's magnetic field.
Additional Details
- About Protostars: Protostars are early-stage stars that form through the gravitational collapse of dense regions in molecular clouds. They are in the accretion phase, actively gathering gas and dust but not yet undergoing sustained nuclear fusion.
- Jet Ejection: These stars emit bipolar jets, which are high-speed streams of particles often observed at their poles.
- Massive Protostars: Protostars like IRAS 18162-2048 are expected to evolve into stars with masses exceeding 8–10 times that of the Sun.
- Challenges in Observation: The protostar is heavily obscured by dense gas and dust, complicating traditional observational methods.
- Recent Observations: The detection of circular polarisation in radio waves indicates the presence of strong magnetic fields, reinforcing the theory that such fields contribute to jet formation in both stars and black holes.
This breakthrough not only enhances our understanding of protostellar jet dynamics but also paves the way for future studies on the role of magnetic fields in star formation processes.
|
98 videos|939 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Science & Technology (Part 1): July 2025 Current Affairs - Current Affairs & General Knowledge - CLAT
| 1. What is Legionnaires' Disease and what causes it? |  |
| 2. How does Deep-Brain Stimulation work and what conditions can it treat? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) mission? |  |
| 4. What are the implications of the discovery of N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA)? |  |
| 5. What is Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) and how does it affect livestock? |  |





















