UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 1st September 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Economy
India’s Economic Churn and the Nectar of Growth
Why in News?
The current economic scenario in India highlights a transformation shaped by crises, much like the mythological churning of the ocean, which resulted in the creation of nectar. India's history of economic challenges, from the 1991 liberalization to the recent digital surge prompted by the COVID-19 pandemic, demonstrates how adversity can catalyze resilience and growth.
Key Takeaways
- India's economy shows strong growth, with real GDP surging by 7.8% in Q1 FY 2025-26.
- Significant improvements in various sectors: manufacturing (7.7%), construction (7.6%), and services (9.3%).
- India is on track to become the world's third-largest economy by the end of the decade.
- 25 crore Indians have moved out of multidimensional poverty due to targeted interventions.
- India’s energy security and green transition are pivotal for future growth.
Additional Details
- Resilient Growth: The economy is characterized by broad-based growth across sectors, with nominal GDP increasing by 8.8%, driven by consumption and investment.
- Growth With Inclusion: The reduction in poverty is linked to the delivery of essential services such as universal bank accounts and health coverage.
- Energy Security: India is the third-largest energy consumer and is expanding its refining capacity, essential for meeting the projected doubling of energy demand by 2047.
- Green Transition: Ethanol blending has increased significantly, reflecting India's commitment to clean energy and its role in stabilizing global oil markets.
- Industrial and Digital Transformation: Initiatives like the Pradhan Mantri Gati Shakti are enhancing sectors such as semiconductors and renewable energy, supported by a robust digital economy.
In conclusion, independent forecasts suggest that by 2038, India could rank as the world’s second-largest economy in purchasing power parity terms, with a GDP exceeding $34 trillion. This trajectory hinges on continued reforms and the ability to harness clean energy, highlighting India's capacity to turn moments of doubt into opportunities for breakthroughs.
GS3/Environment
Collapse of Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC)
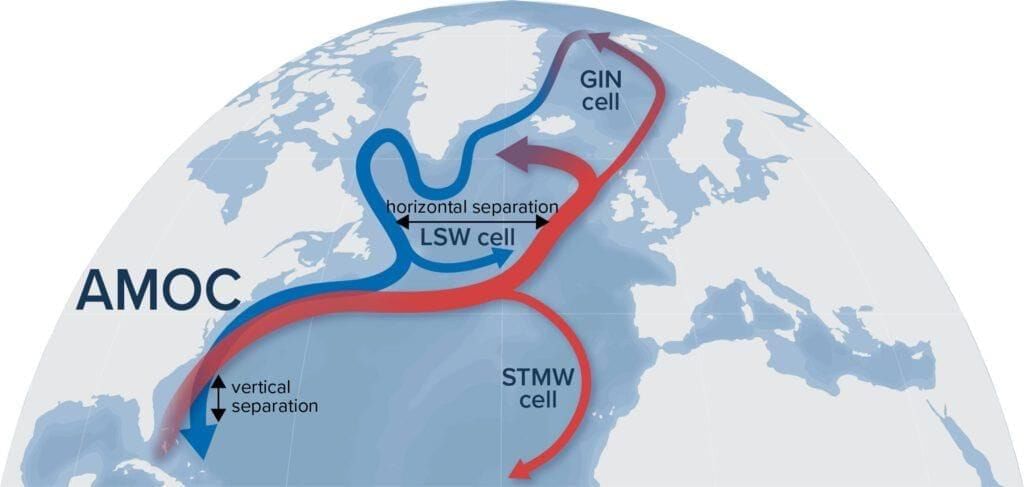 Why in News?
Why in News?
A recent study has indicated that the collapse of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) is now considered a plausible scenario, rather than a low-probability event.
Key Takeaways
- The AMOC is an extensive system of ocean currents, a crucial component of the thermohaline circulation (THC), often referred to as the global ocean conveyor belt.
- It plays a vital role in transporting warm tropical surface waters northward and returning cooler waters southward as deep currents.
Additional Details
- Function of AMOC: It distributes heat and nutrients across the world's oceans, contributing significantly to global climate regulation.
- Reasons for AMOC Slowdown:
- Melting ice sheets in Greenland and the Arctic are adding freshwater to the ocean, which lowers the density of seawater, hindering the sinking process that drives circulation.
- A 2019 study noted that increased rainfall in the Indian Ocean affects rainfall patterns in the Atlantic, which may temporarily enhance AMOC due to saltier water sinking more quickly.
- Climate models project a potential weakening of 34-45% in AMOC by the year 2100 if global warming continues unabated.
- Consequences of AMOC Collapse:
- Europe and the North Atlantic could experience significant cooling.
- There would likely be a reduction in rainfall across Europe.
- Changes in El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) patterns may occur, impacting global weather systems.
- Expansion of sea ice in the Greenland–Iceland–Norwegian seas is anticipated.
- A long-term shift in rainfall patterns toward the southern tropical Atlantic could lead to increased climate variability and regional extremes.
In summary, the potential collapse of AMOC poses serious implications for global climate stability, highlighting the urgency of addressing climate change.
Question for Consideration:
Consider the following factors:
- 1. Rotation of the Earth
- 2. Air pressure and wind
- 3. Density of ocean water
- 4. Revolution of the Earth
Which of the above factors influence the ocean currents?
- Options: (a) 1 and 2 Only (b) 1, 2 and 3* (c) 1 and 4 (d) 2, 3 and 4
GS3/Environment
Fireflies Emerge as Ecological Indicators
Why in News?
A recent study conducted in Tamil Nadu has documented various species of fireflies and emphasized their importance as ecological indicators of habitat health.
Key Takeaways
- Fireflies are bioluminescent beetles belonging to the family Lampyridae.
- They serve as indicators of ecological health, with their presence reflecting the state of the ecosystem.
- Fireflies are significantly impacted by environmental changes, including pesticide use and light pollution.
Additional Details
- Identity: Fireflies belong to the family Lampyridae and are not true flies.
- Life Cycle: The larvae live in soil or leaf litter, feeding on snails and worms. Adults emerge after rainfall and have a short lifespan focused on reproduction.
- Indian Species: Notable species include Abscondita chinensis, Luciola ovalis, Luciola nicolleri, Asymmetricata humeralis, and Pyrocoelia analis.
- Distribution: Fireflies are found in tropical and temperate regions, being most visible during humid monsoon nights.
- Bioluminescence: The glow is produced in an abdominal light organ using luciferin, luciferase, oxygen, and ATP.
- Light Nature: Their light is cold and efficient, with colors varying between green and yellow depending on the species.
- Courtship Function: Flashing serves as a mating signal, with males emitting species-specific codes that females respond to if correct.
- Sensitivity: Fireflies are highly sensitive to pesticides, habitat degradation, artificial lighting, and polluted water.
- Habitat Health Indicator: Large synchronized gatherings indicate intact ecosystems, while sparse populations suggest disturbances.
- Light Pollution Impact: Artificial light disrupts their flashing behavior, leading to decreased mating success.
- Local Evidences: Communities such as the Malasar and Irula have reported declines in firefly populations linked to pesticide exposure and polluted streams.
- Indicator Role: Fireflies act as proxy species for nocturnal biodiversity, signaling risks to other species like moths, bats, and amphibians.
Overall, fireflies play a critical role in indicating ecosystem health and their decline serves as a warning for environmental changes that could impact broader biodiversity.
GS2/Governance
NGO ‘Educate Girls’ Wins Ramon Magsaysay Award 2025
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Ramon Magsaysay Award for the year 2025 has been awarded to Educate Girls, an Indian NGO dedicated to promoting girls’ education in rural and underprivileged areas. This recognition highlights the significant impact of the organization in addressing educational challenges faced by girls in these regions.
Key Takeaways
- Educate Girls is the first Indian organization to receive the Ramon Magsaysay Award since its inception in 1958.
- Other notable recipients of the 2025 award include Shaahina Ali from Maldives, an environmental activist, and Fr. Flaviano Antonio L. Villanueva from the Philippines, a human rights defender.
Additional Details
- About Educate Girls: Originally founded as the Foundation to Educate Girls Globally, it is led by CEO Gayatri Nair Lobo. The organization aims to tackle gender inequality in education and uplift rural communities through girls’ schooling.
- Impact: Educate Girls operates in some of India’s most remote regions and employs community workers known as preraks and team balikas to enhance enrollment and retention of girls in schools. The initiative has created a ripple effect where educating girls leads to family upliftment and community strengthening.
- Ramon Magsaysay Award Overview: Often referred to as the "Nobel Prize of Asia," this award has been presented annually since its establishment in 1958 to honor individuals and organizations demonstrating integrity in governance, service, and idealism in democracy.
- Notable Indian Recipients: Previous Indian recipients of the award include Vinoba Bhave, Mother Teresa, and Satyajit Ray, among others. Educate Girls joins this prestigious list as the first Indian NGO to be honored.
This recognition underscores the vital role of NGOs like Educate Girls in transforming education and promoting gender equality, reflecting the broader commitment to social justice and empowerment in society.
GS1/History & Culture
Sankaradeva’s Vrindavani Vastra to be displayed in Assam
Why in News?
Assam is set to showcase the 16th-century Vrindavani Vastra in 2027, under an 18-month lease from the British Museum, secured by a sovereign guarantee.
Key Takeaways
- The Vrindavani Vastra is a significant cultural artifact from the 16th century.
- It was woven under the guidance of Srimanta Sankaradeva in Assam.
- The original piece is lost, but fragments are preserved in various museums.
- Plans are underway to bring it to Assam temporarily.
Additional Details
- Origin: The Vrindavani Vastra is a silk tapestry created in the 16th century in Taniguchi (Barpeta), Assam, under Srimanta Sankaradeva's guidance.
- Commission: This tapestry was commissioned by Cilarai, the brother of Koch king Naranarayana.
- Design & Content: It depicts various scenes from Krishna's childhood and Vrindavan leelas, including his birth, adventures, and the defeat of Kamsa, featuring multicolored silk with loom-embroidered captions.
- Current Status: The original piece is lost, but fragments are preserved in the British Museum, Victoria & Albert Museum (London), and Guimet Museum (Paris).
Who was Srimanta Sankaradeva (1449–1568)?
Srimanta Sankaradeva was an Assamese Vaishnavite saint, scholar, cultural reformer, and polymath.
- Religious Contribution: He founded the Ekasarana Dharma, a monotheistic Bhakti movement centered on Lord Krishna, rejecting idol worship, caste divisions, and Brahmanical orthodoxy.
- Motto: "Eka Deva, Eka Seva, Eka Biney Nahi Kewa" (One God, One Service, None Else).
- Influence: His teachings significantly influenced the Koch and Ahom kingdoms.
Cultural Contribution
- Founded Borgeet (devotional songs).
- Created Ankia Naat and Bhaona (religious theatre).
- Promoted the Sattriya dance, recognized as a classical dance of India.
- Developed Brajavali, a literary language.
Social Reform
- Considered the father of modern Assamese identity.
- Promoted equality, fraternity, and community cohesion.
- Ended regressive practices, such as human sacrifice.
Legacy
Srimanta Sankaradeva's legacy lies in his ability to combine art, devotion, and social reform, creating a unified cultural renaissance and being revered as one of Assam's greatest spiritual and cultural icons.
UPSC 2014
With reference to the famous Sattriya dance, consider the following statements:
- 1. Sattriya is a combination of music, dance, and drama.
- 2. It is a centuries-old living tradition of Vaishnavites of Assam.
- 3. It is based on classical Ragas and Talas of devotional songs composed by Tulsidas, Kabir, and Mirabai.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- Options: (a) 1 only (b) 1 and 2 only* (c) 2 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 only
GS3/Environment
Data Shows Seas Rising Faster Around Maldives, Lakshadweep Than Believed
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The issue of rising sea levels has gained significant attention due to its severe implications for ecosystems, economies, and human settlements, particularly for vulnerable island nations such as the Maldives and Lakshadweep. Recent research using coral microatolls indicates that sea levels in the Indian Ocean began rising rapidly as early as the 1950s, challenging previous assumptions based on satellite and tide-gauge data.
Key Takeaways
- Coral microatolls provide a natural record of sea-level changes.
- Sea-level rise in the Indian Ocean has been accelerating since the late 1950s.
- Vulnerable island nations face significant risks due to rising sea levels.
Additional Details
- Coral Microatolls: These are disk-shaped colonies of coral that stop growing upwards when they reach the lowest tide level, providing a natural record of sea-level changes over time. Research conducted at the Mahutigalaa reef in the Huvadhoo Atoll of the Maldives measured a Porites microatoll from 1930 to 2019, revealing a significant rise.
- Accelerated Sea-Level Rise:Data indicates a rise of 0.3 meters over the past 90 years, with varying rates of increase:
- 1930-1959: 1-1.84 mm/year
- 1960-1992: 2.76-4.12 mm/year
- 1990-2019: 3.91-4.87 mm/year
- Climate Variability: The growth patterns of corals were affected by climatic events such as El Niño and the Indian Ocean Dipole, highlighting the influence of climate variability on marine ecosystems.
- Regional Significance: The Indian Ocean is warming at a rate higher than the global average, which contributes to accelerated sea-level rise and highlights the need for better monitoring in this region.
- Adaptation Strategies: The findings stress the importance of understanding the timing and magnitude of sea-level rise for effective coastal planning and disaster preparedness.
The revelation that sea-level rise in the Maldives and Lakshadweep began decades earlier than previously thought serves as a crucial alert for policymakers and local communities. As the Indian Ocean continues to warm, proactive measures and international cooperation will be essential for the survival of low-lying nations facing existential threats.
GS2/Polity
India’s Federal Design and the Debate on J&K Statehood
Why in News?
The recent directive from the Supreme Court regarding the restoration of statehood for Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) has reignited discussions surrounding India’s federal structure and the delicate balance between Union authority and State autonomy. This comes in light of the Supreme Court's upholding of the abrogation of Article 370 in December 2023, which enabled significant changes to J&K’s status.
Key Takeaways
- The Supreme Court has mandated the Union Government to restore statehood and conduct Assembly elections in J&K.
- The delay in announcing a roadmap for restoration raises concerns about federalism and Union dominance.
Additional Details
- Constitutional Framework for State Formation:The Indian Constitution outlines three primary methods for the creation of States:
- Admission: Political entities like J&K joined India via the Instrument of Accession in 1947.
- Establishment: New territories were integrated after acquisition under international law, as seen with Goa and Sikkim.
- Reorganization: Involves Parliament altering boundaries, merging, dividing, or renaming existing States. However, it cannot permanently downgrade a State to a Union Territory, reinforcing India's federal principles.
- The Federal Character of India:India’s Constitution creates a Union of States, emphasizing indivisibility and a strong central authority, which includes:
- Indivisibility of the Union: States cannot secede, promoting unity.
- Bicameralism with Rajya Sabha: A permanent Upper House ensures ongoing State representation at the Union level.
- Basic Structure Doctrine: Federalism is recognized as part of the Constitution's core structure, protecting it from dilution.
- J&K and the Federal Debate: The Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act of 2019 transformed the State into two Union Territories. The Supreme Court upheld this change but emphasized the necessity for restoring J&K’s statehood.
- Importance of Restoring Statehood:
- Federal Integrity: Upholds India’s commitment to shared governance.
- Democratic Rights: Empowering an elected Assembly enhances representation and accountability.
- Balancing Power: Reducing the Lieutenant Governor's influence aligns governance with democratic federalism.
- Judicial Mandate: Following the Supreme Court’s directive strengthens constitutional trust.
- Political Stability: Restoration may alleviate regional alienation and bolster faith in India’s federal structure.
The ongoing debate emphasizes a crucial question for India: how to effectively balance national security considerations with the principles of federalism. The key to addressing this lies in respecting constitutional commitments while pragmatically responding to the realities on the ground.
GS3/Economy
India’s Fertiliser Shortage
 Why in News?
Why in News?
India has experienced an exceptional southwest monsoon this year, with rainfall from June to August exceeding the historical average by 6.1%. The distribution of rainfall has been favorable across regions, with notable increases in June (8.9%), July (4.8%), and August (5.5%). Additionally, May saw a remarkable 106.4% above-normal rain. Out of 36 meteorological subdivisions, 33 recorded normal rainfall, with deficits only in Bihar, Assam, Meghalaya, and Arunachal Pradesh. The timely rainfall has led to increased kharif sowing, particularly in rice and maize, driving up fertiliser demand.
Key Takeaways
- Fertiliser sales have surged due to favorable monsoon conditions.
- There is a rising demand for fertilisers amidst limited supply.
- The government needs to address policy lessons for better fertiliser management.
Additional Details
- Fertiliser Sales Surge: Sales of most fertilisers, including urea, single super phosphate (SSP), muriate of potash (MOP), and complex blends, recorded double-digit growth from April to July 2025 compared to the same period in 2024.
- Dip in DAP Sales: Diammonium phosphate (DAP) sales decreased by 12.8%, continuing a trend of supply shortages that have led farmers to substitute DAP with alternatives like SSP and the complex 20:20:0:13.
- 20:20:0:13 as a Major Player: This fertiliser has gained popularity due to its composition of 20% nitrogen, 20% phosphorus pentoxide, and 13% sulphur, making it a viable alternative to DAP.
- Supply Issues: Despite increased demand for fertilisers, domestic urea production fell from 102.1 lakh tonnes the previous year to 93.6 lakh tonnes, while DAP output remained unchanged at 13.7 lakh tonnes. Imports of both urea and DAP have also declined.
- Sharp Stock Depletion: As of August 1, 2025, urea stocks dropped to 37.2 lakh tonnes from 86.4 lakh tonnes the previous year, indicating a critical shortage.
- Peak Season Shortages: The supply crunch was most severe during July and August, which are peak consumption months for kharif crops. Reports indicated farmers waited for hours to secure urea, highlighting the urgency of the situation.
- Government Response: The government may have underestimated the fertiliser demand for kharif crops, especially for rice and maize, which require significant urea applications.
- Future Considerations: With kharif consumption peaking, attention must turn to ensuring sufficient fertiliser supplies for the upcoming rabi season, leveraging strong water availability.
- Import Trends: Falling imports of urea and DAP may change with improved relations between India and China, which could alleviate some supply issues.
In summary, the ongoing fertiliser shortage amid rising demand highlights the need for strategic planning and management to avoid future disruptions. The situation calls for a reassessment of fertiliser policies to ensure sustainability and adequate supply for farmers.
GS3/Environment
Green Credit Programme (GCP) - Revised Rules for Tree Plantation
Why in News?
The Union Environment Ministry has recently introduced a new methodology for awarding green credits under the Green Credit Programme (GCP), replacing the previous framework. This revision includes significant changes regarding eligibility, time frames, and the use of credits.
Key Takeaways
- The GCP was launched in November 2023 during the UN Climate Conference (COP28) in Dubai.
- The programme aims to promote voluntary environmental protection actions, including tree plantation and waste management.
- New rules shift focus from mere tree counting to emphasizing long-term plantation health and survival.
Additional Details
- Awarding of Credits: The previous methodology required a minimum density of 1,100 trees per hectare within two years. This was criticized for neglecting survival rates. The new methodology allows credits to be earned after five years of restoration activities on degraded land, focusing on vegetation status and survival rates.
- Tradability of Credits: Under the revised rules, tree plantation credits are non-tradable and non-transferable, except between a holding company and its subsidiaries.
- Permissible Uses of Green Credits: Credits can be exchanged for compensatory afforestation obligations or to meet corporate social responsibility requirements, but will cease after such exchanges.
- The credits may also be utilized for reporting under environmental, social, and governance (ESG) indicators.
The revised Green Credit Programme represents a significant shift from superficial tree-planting initiatives to a more sustainable approach focused on ecological restoration. This change is expected to enhance India's climate resilience, improve biodiversity, and bolster corporate accountability in environmental stewardship.
GS3/Science and Technology
Adi Vaani App: India’s First Tribal AI Translator
Why in News?
The Ministry of Tribal Affairs has recently launched the Beta Version of Adi Vaani, which is recognized as India’s first AI-based translator specifically designed for tribal languages. This initiative aims to empower tribal communities and preserve endangered languages.
Key Takeaways
- Launch of Adi Vaani in Beta Version (2025).
- Developed under the Janjatiya Gaurav Varsh initiative.
- Created by a collaboration of institutes including IIT Delhi, BITS Pilani, and IIIT Hyderabad.
- Focus on enhancing digital literacy and cultural identity among tribal communities.
Additional Details
- Translation Modes: The app supports various modes including Text-to-Text, Text-to-Speech, Speech-to-Text, and Speech-to-Speech.
- Languages (Beta): Currently includes Santali, Bhili, Mundari, and Gondi, with plans to add Kui and Garo.
- AI Models: Utilizes NLLB (No Language Left Behind) and IndicTrans2 models, specifically adapted for low-resource languages.
- Community-Driven Development: Data is collected and validated by local experts, ensuring relevance and accuracy.
- Toolkit Additions: Features OCR for digitizing manuscripts, bilingual dictionaries, and curated repositories to support language preservation.
Overall, Adi Vaani represents a significant step forward in utilizing technology to support tribal languages and cultures, positioning India as a leader in the field of AI for endangered languages.
UPSC 2020 Question
With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following?
- 1. Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- 2. Create meaningful short stories and songs
- 3. Disease diagnosis
- 4. Text-to-Speech Conversion
- 5. Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Options: (a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only (b) 1, 3 and 4 only* (c) 2, 4 and 5 only (d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
|
38 videos|5167 docs|1089 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 1st September 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the key factors contributing to India's economic growth? |  |
| 2. How does the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) affect global climate patterns? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of Sankaradeva’s Vrindavani Vastra in Indian culture? |  |
| 4. How does the Green Credit Programme (GCP) promote environmental sustainability? |  |
| 5. What challenges are faced by India regarding fertilizer shortage and its impact on agriculture? |  |
















