All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of May Week 1 for NEET Exam
Direction (Q. Nos. 12 and 13) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given ptions (a),(b),(c),(d)A hypothetical electromagnetic wave is pictured here.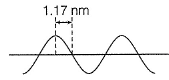 Q. Energy associated with this wave is
Q. Energy associated with this wave is- a)4.24 x 10-19J
- b)2.12 x 10-19J
- c)1.06 x 10-19J
- d)8.49 x 10-19J
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 12 and 13) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given ptions (a),(b),(c),(d)
A hypothetical electromagnetic wave is pictured here.
Q. Energy associated with this wave is
a)
4.24 x 10-19J
b)
2.12 x 10-19J
c)
1.06 x 10-19J
d)
8.49 x 10-19J
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
A to E makes one complete wave.
HIV attack :-- a)Epithelial cell
- b)Sex cell germinal cells
- c)B - lymphocytes
- d)T4 - lymphocytes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
HIV attack :-
a)
Epithelial cell
b)
Sex cell germinal cells
c)
B - lymphocytes
d)
T4 - lymphocytes
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta answered |
HIV attack and destroy T4 - lymphocytes also known as CD4 cells, are white blood cells that fight infection and play an important role in your immune system. If too many CD4 cells are lost, your immune system will have trouble fighting off infections. Even a minor infection such as cold can be much more severe because the body has difficulty responding to new infections.
Rain falls at a speed of 50m/s and a child walks on a straight road from east to west at a speed of 100m/s. To find the direction in which the child should hold the umbrella use- a)resultant speed of child and rain
- b)resultant speed of rain and child
- c)relative speed of rain with respect to child
- d)relative speed of child with respect to rain
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Rain falls at a speed of 50m/s and a child walks on a straight road from east to west at a speed of 100m/s. To find the direction in which the child should hold the umbrella use
a)
resultant speed of child and rain
b)
resultant speed of rain and child
c)
relative speed of rain with respect to child
d)
relative speed of child with respect to rain
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
The child should hold the umbrella in the direction at which the rain appears to fall on him, which is the direction of relative speed of rain with respect to the child.
The motion of a freely falling body is an example of:- a)uniformly accelerated motion
- b)non uniformly accelerated motion
- c)uniform motion
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The motion of a freely falling body is an example of:
a)
uniformly accelerated motion
b)
non uniformly accelerated motion
c)
uniform motion
d)
none of the above
|
|
Om Desai answered |
A freely falling body observes a constant downwards force of gravity which hence applies a constant downward acceleration upon the body.
Energy of a mole of radio wave photons with a frequency of 909 kHz is- a)6.02 x 10-28 J
- b)3.62 x 10-4 J
- c)1.00 x 10-4 J
- d)6.02 x 10-31 J
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Energy of a mole of radio wave photons with a frequency of 909 kHz is
a)
6.02 x 10-28 J
b)
3.62 x 10-4 J
c)
1.00 x 10-4 J
d)
6.02 x 10-31 J
|
|
Rajeev Nair answered |
E = N0hv
= 6.02 x 1023 x 6.62 x 10-34 Js x 909 x103 s-1
= 3.62 x 10-4 J
= 3.62 x 10-4 J
A body of mass 1kg and 10kg are dropped simultaneously from the top of a tower. The ratio of the time taken by them to reach the ground is- a)9.8:98
- b)1:1
- c)10:1
- d)1:10
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A body of mass 1kg and 10kg are dropped simultaneously from the top of a tower. The ratio of the time taken by them to reach the ground is
a)
9.8:98
b)
1:1
c)
10:1
d)
1:10
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
1:1, the time taken does not depend on the mass of the falling object.
The kinematic equation of motion v = u+at is not applicable if :- a)Displacement is not constant
- b)motion is non-uniform.
- c)acceleration is not constant
- d)velocity is not constant
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The kinematic equation of motion v = u+at is not applicable if :
a)
Displacement is not constant
b)
motion is non-uniform.
c)
acceleration is not constant
d)
velocity is not constant
|
|
Yash Ghoshal answered |
Explanation:
The kinematic equation of motion v = u + at is one of the four equations of motion which are used to describe the motion of an object under constant acceleration. The equation shows the relationship between the initial velocity (u), acceleration (a), time (t), and final velocity (v) of an object. However, this equation is not applicable if the acceleration is not constant.
Constant acceleration means that the rate of change of velocity is constant. If the acceleration is not constant, then the rate of change of velocity is changing, and the equation v = u + at does not hold true for the entire motion.
For example, if an object is moving in a circular path, its acceleration changes direction at every point, and hence, the acceleration is not constant. In this case, the kinematic equation cannot be used to describe the motion of the object.
Similarly, if an object is thrown vertically upwards, the acceleration of the object changes as it moves upwards and then downwards due to the force of gravity. Hence, the kinematic equation v = u + at cannot be used to describe the entire motion of the object.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the kinematic equation of motion v = u + at is not applicable if the acceleration is not constant, and the rate of change of velocity is changing. The equation is valid only for objects that are moving under constant acceleration. Hence, before using this equation to solve any problem, it is important to check whether the acceleration is constant or not.
The kinematic equation of motion v = u + at is one of the four equations of motion which are used to describe the motion of an object under constant acceleration. The equation shows the relationship between the initial velocity (u), acceleration (a), time (t), and final velocity (v) of an object. However, this equation is not applicable if the acceleration is not constant.
Constant acceleration means that the rate of change of velocity is constant. If the acceleration is not constant, then the rate of change of velocity is changing, and the equation v = u + at does not hold true for the entire motion.
For example, if an object is moving in a circular path, its acceleration changes direction at every point, and hence, the acceleration is not constant. In this case, the kinematic equation cannot be used to describe the motion of the object.
Similarly, if an object is thrown vertically upwards, the acceleration of the object changes as it moves upwards and then downwards due to the force of gravity. Hence, the kinematic equation v = u + at cannot be used to describe the entire motion of the object.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the kinematic equation of motion v = u + at is not applicable if the acceleration is not constant, and the rate of change of velocity is changing. The equation is valid only for objects that are moving under constant acceleration. Hence, before using this equation to solve any problem, it is important to check whether the acceleration is constant or not.
Interferons are synthesized in response to[CBSE-2001]- a)Mycoplasma
- b)Bacteria
- c)Viruses
- d)Fungi
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Interferons are synthesized in response to
[CBSE-2001]
a)
Mycoplasma
b)
Bacteria
c)
Viruses
d)
Fungi
|
|
Pragati Pillai answered |
**Interferons and their synthesis in response to viruses**
**Introduction:**
Interferons are a group of small proteins that play a crucial role in the immune response against viral infections. They are synthesized and released by host cells in response to viral invasion. Interferons act as signaling molecules, allowing cells to communicate with each other and coordinate their antiviral defenses.
**Synthesis of Interferons:**
Interferons are synthesized in response to viral infections by infected host cells. The synthesis of interferons is triggered by the detection of viral components or the activation of specific cellular pathways involved in antiviral defense.
**Viral Infections and Interferon Synthesis:**
When a virus infects a host cell, it releases its genetic material (either DNA or RNA) into the host cell. The viral genetic material is recognized by specific cellular sensors called pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), which are present in the host cell cytoplasm or on the cell surface.
**Activation of Cellular Pathways:**
The recognition of viral genetic material by PRRs activates specific cellular pathways, such as the Toll-like receptor (TLR) pathway or the retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I)-like receptor (RLR) pathway. These pathways lead to the activation of transcription factors, such as interferon regulatory factors (IRFs) and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB).
**Transcription and Translation of Interferons:**
The activated transcription factors bind to specific DNA sequences in the promoter regions of interferon genes, leading to their transcription. The transcribed interferon mRNA is then translated into interferon protein in the cytoplasm.
**Release and Action of Interferons:**
Once synthesized, interferons are released by the infected host cell and bind to specific receptors on neighboring cells. This binding activates a signaling cascade within the recipient cells, leading to the induction of antiviral defense mechanisms. These mechanisms include the upregulation of genes involved in the inhibition of viral replication and the activation of immune cells, such as natural killer (NK) cells and macrophages, to eliminate virus-infected cells.
**Conclusion:**
In summary, interferons are synthesized in response to viral infections. The detection of viral genetic material by cellular sensors triggers specific cellular pathways, leading to the synthesis and release of interferons. These interferons then act as signaling molecules, coordinating the immune response against viral infections.
**Introduction:**
Interferons are a group of small proteins that play a crucial role in the immune response against viral infections. They are synthesized and released by host cells in response to viral invasion. Interferons act as signaling molecules, allowing cells to communicate with each other and coordinate their antiviral defenses.
**Synthesis of Interferons:**
Interferons are synthesized in response to viral infections by infected host cells. The synthesis of interferons is triggered by the detection of viral components or the activation of specific cellular pathways involved in antiviral defense.
**Viral Infections and Interferon Synthesis:**
When a virus infects a host cell, it releases its genetic material (either DNA or RNA) into the host cell. The viral genetic material is recognized by specific cellular sensors called pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), which are present in the host cell cytoplasm or on the cell surface.
**Activation of Cellular Pathways:**
The recognition of viral genetic material by PRRs activates specific cellular pathways, such as the Toll-like receptor (TLR) pathway or the retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I)-like receptor (RLR) pathway. These pathways lead to the activation of transcription factors, such as interferon regulatory factors (IRFs) and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB).
**Transcription and Translation of Interferons:**
The activated transcription factors bind to specific DNA sequences in the promoter regions of interferon genes, leading to their transcription. The transcribed interferon mRNA is then translated into interferon protein in the cytoplasm.
**Release and Action of Interferons:**
Once synthesized, interferons are released by the infected host cell and bind to specific receptors on neighboring cells. This binding activates a signaling cascade within the recipient cells, leading to the induction of antiviral defense mechanisms. These mechanisms include the upregulation of genes involved in the inhibition of viral replication and the activation of immune cells, such as natural killer (NK) cells and macrophages, to eliminate virus-infected cells.
**Conclusion:**
In summary, interferons are synthesized in response to viral infections. The detection of viral genetic material by cellular sensors triggers specific cellular pathways, leading to the synthesis and release of interferons. These interferons then act as signaling molecules, coordinating the immune response against viral infections.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. FM radio broadcasts at 900 kHz. What wavelength does this corresponds to?- a)333 m
- b)3.03 x 10-3m
- c)330 m
- d)3300 m
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. FM radio broadcasts at 900 kHz. What wavelength does this corresponds to?
a)
333 m
b)
3.03 x 10-3m
c)
330 m
d)
3300 m
|
|
Soumya Mukherjee answered |
Understanding FM Radio Frequency and Wavelength
FM radio broadcasts at a frequency of 900 kHz. To find the corresponding wavelength, we can use the formula that relates frequency and wavelength in a vacuum:
Formula for Wavelength
Wavelength (λ) = Speed of Light (c) / Frequency (f)
Where:
- Speed of Light (c) ≈ 3 x 10^8 meters per second
- Frequency (f) = 900 kHz = 900,000 Hz (since 1 kHz = 1,000 Hz)
Calculating the Wavelength
Using the values:
- λ = (3 x 10^8 m/s) / (900,000 Hz)
- λ = (3 x 10^8) / (9 x 10^5)
- λ = 333.33 meters
Thus, the wavelength that corresponds to a frequency of 900 kHz is approximately 333 meters.
Conclusion
So, the correct answer to the question is:
- Option (a): 333 m
This calculation illustrates how the frequency of radio waves is inversely related to their wavelength; as frequency increases, wavelength decreases.
FM radio broadcasts at a frequency of 900 kHz. To find the corresponding wavelength, we can use the formula that relates frequency and wavelength in a vacuum:
Formula for Wavelength
Wavelength (λ) = Speed of Light (c) / Frequency (f)
Where:
- Speed of Light (c) ≈ 3 x 10^8 meters per second
- Frequency (f) = 900 kHz = 900,000 Hz (since 1 kHz = 1,000 Hz)
Calculating the Wavelength
Using the values:
- λ = (3 x 10^8 m/s) / (900,000 Hz)
- λ = (3 x 10^8) / (9 x 10^5)
- λ = 333.33 meters
Thus, the wavelength that corresponds to a frequency of 900 kHz is approximately 333 meters.
Conclusion
So, the correct answer to the question is:
- Option (a): 333 m
This calculation illustrates how the frequency of radio waves is inversely related to their wavelength; as frequency increases, wavelength decreases.
Bacteriophage is similar to a fungus & bacterium in having :-- a)RNA as the genetic material
- b)DNA as the genetic material
- c)Cell wall
- d)Similar in reproduction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Bacteriophage is similar to a fungus & bacterium in having :-
a)
RNA as the genetic material
b)
DNA as the genetic material
c)
Cell wall
d)
Similar in reproduction
|
|
Mission 2021 answered |
DNA and RNA are the genetic materials out of which DNA universally serves as the carrier of hereditary information from one generation to another in all the organisms except viruses. Among viruses, some carry DNA (either single or double stranded) as hereditary material while some have RNA (either single or double stranded) as hereditary material. But they never have both DNA and RNA. Bacteriophages are DNA viruses thus they resemble fungi in having DNA as herditary material.
A gas absorbs photon of wavelength 355 nm and emits at two wavelengths. If one of the emissions is at 680 nm, the other is at[AlEEE 2011]- a)1035nm
- b)325 nm
- c)743 nm
- d)518 nm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A gas absorbs photon of wavelength 355 nm and emits at two wavelengths. If one of the emissions is at 680 nm, the other is at
[AlEEE 2011]
a)
1035nm
b)
325 nm
c)
743 nm
d)
518 nm
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
1/λ = 1/λ1 + 1/λ2
1355 = 1680 + 1λ2
1/λ2 = (680 − 355/680 x 355)
⇒ λ2 = 743nm.
Which of the following quantity does not remain constant during the uniform circular motion?- a)linear momentum
- b)speed
- c)angular velocity
- d)angular acceleration
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following quantity does not remain constant during the uniform circular motion?
a)
linear momentum
b)
speed
c)
angular velocity
d)
angular acceleration
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
- Linear momentum is not constant but angular momentum is
- Speed has to be constant for “uniform” circular motion
- For obvious reasons ω is constant
- And the same goes for α
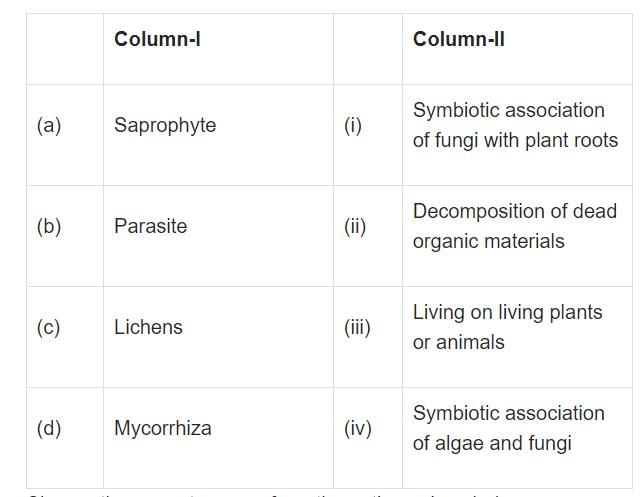
All given statements stand true with respect to Lichens, except
- a)Absence of lichens in any area indicates that the area is highly polluted with SO2.
- b)The algal component of lichen is known as mycobiont and the fungal component as phycobiont
- c)Body of lichens is made up of phycobionts only.
- d)Mycobiont partner of lichens is always heterotrophic.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
All given statements stand true with respect to Lichens, except
a)
Absence of lichens in any area indicates that the area is highly polluted with SO2.
b)
The algal component of lichen is known as mycobiont and the fungal component as phycobiont
c)
Body of lichens is made up of phycobionts only.
d)
Mycobiont partner of lichens is always heterotrophic.

|
Top Rankers answered |
(B) The correct answer is B: Mycobiont partner of lichens is always heterotrophic.
Here's the detailed explanation:
- Lichens are symbiotic organisms consisting of a fungus (mycobiont) and an alga or cyanobacterium (phycobiont).
- The mycobiont is the fungal partner in lichens and is typically heterotrophic, meaning it obtains organic carbon from the environment.
- The phycobiont, which can be an alga or a cyanobacterium, is autotrophic and provides the mycobiont with organic carbon through photosynthesis.
- This mutualistic relationship allows lichens to thrive in diverse environments by combining the strengths of both partners.
Here's the detailed explanation:
- Lichens are symbiotic organisms consisting of a fungus (mycobiont) and an alga or cyanobacterium (phycobiont).
- The mycobiont is the fungal partner in lichens and is typically heterotrophic, meaning it obtains organic carbon from the environment.
- The phycobiont, which can be an alga or a cyanobacterium, is autotrophic and provides the mycobiont with organic carbon through photosynthesis.
- This mutualistic relationship allows lichens to thrive in diverse environments by combining the strengths of both partners.
Which of the following pathogenic diseases could have symptoms like mosaic formation, leaf rolling and curling, yellowing and vein clearing, dwarfing, and stunted growth?- a)Viroid
- b)Viral
- c)Caused by prions
- d)Fungal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following pathogenic diseases could have symptoms like mosaic formation, leaf rolling and curling, yellowing and vein clearing, dwarfing, and stunted growth?
a)
Viroid
b)
Viral
c)
Caused by prions
d)
Fungal
|
|
Mahi Menon answered |
Understanding Viral Diseases in Plants
Viral infections in plants often lead to a range of symptoms that can significantly affect their health and growth. The symptoms you mentioned—mosaic formation, leaf rolling and curling, yellowing and vein clearing, dwarfing, and stunted growth—are characteristic of viral infections. Here's a detailed explanation:
Common Symptoms of Viral Infections:
- Mosaic Formation: This symptom appears as a patchy discoloration on leaves, resulting from uneven chlorophyll distribution caused by viral replication.
- Leaf Rolling and Curling: Viruses can disrupt normal cellular function, leading to abnormal growth patterns in leaves, resulting in curling or rolling.
- Yellowing and Vein Clearing: Viruses often interfere with the plant's ability to produce chlorophyll, causing yellowing. Vein clearing occurs when the virus affects the vascular tissues, leading to less chlorophyll around the veins.
- Dwarfing and Stunted Growth: Viral infections can impair the overall growth of the plant by affecting hormone balance and nutrient uptake, leading to reduced size and vigor.
Why Other Options are Less Likely:
- Viroids: These are smaller infectious agents that primarily affect plants but do not typically cause the wide range of symptoms seen in viral infections.
- Prions: These are misfolded proteins associated with diseases in animals, particularly in the nervous system, and are not known to infect plants.
- Fungal Infections: While they can cause some similar symptoms like stunted growth, they usually present different signs such as mold or fungal structures.
In conclusion, the symptoms listed are most indicative of a viral disease, making option 'B' the correct answer. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for diagnosing and managing plant health effectively.
Viral infections in plants often lead to a range of symptoms that can significantly affect their health and growth. The symptoms you mentioned—mosaic formation, leaf rolling and curling, yellowing and vein clearing, dwarfing, and stunted growth—are characteristic of viral infections. Here's a detailed explanation:
Common Symptoms of Viral Infections:
- Mosaic Formation: This symptom appears as a patchy discoloration on leaves, resulting from uneven chlorophyll distribution caused by viral replication.
- Leaf Rolling and Curling: Viruses can disrupt normal cellular function, leading to abnormal growth patterns in leaves, resulting in curling or rolling.
- Yellowing and Vein Clearing: Viruses often interfere with the plant's ability to produce chlorophyll, causing yellowing. Vein clearing occurs when the virus affects the vascular tissues, leading to less chlorophyll around the veins.
- Dwarfing and Stunted Growth: Viral infections can impair the overall growth of the plant by affecting hormone balance and nutrient uptake, leading to reduced size and vigor.
Why Other Options are Less Likely:
- Viroids: These are smaller infectious agents that primarily affect plants but do not typically cause the wide range of symptoms seen in viral infections.
- Prions: These are misfolded proteins associated with diseases in animals, particularly in the nervous system, and are not known to infect plants.
- Fungal Infections: While they can cause some similar symptoms like stunted growth, they usually present different signs such as mold or fungal structures.
In conclusion, the symptoms listed are most indicative of a viral disease, making option 'B' the correct answer. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for diagnosing and managing plant health effectively.
Identify the incorrect statement -- a)Some acellular organisms like viruses and viroids as well as the lichens are not included in the five kingdom system of classification
- b)The algal component is known as phycobiont and fungal component as mycobiont,
- c)The most notable diseases caused by prions are bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE)
- d)In Lichens , Algae provide shelter and absorb mineral nutrients and water for its partner.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the incorrect statement -
a)
Some acellular organisms like viruses and viroids as well as the lichens are not included in the five kingdom system of classification
b)
The algal component is known as phycobiont and fungal component as mycobiont,
c)
The most notable diseases caused by prions are bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE)
d)
In Lichens , Algae provide shelter and absorb mineral nutrients and water for its partner.

|
Lead Academy answered |
Statement (D) in incorrect as Algae prepare food for fungi and fungi provide shelter and absorb mineral nutrients and water for its partner.
Select the incorrect statement about cathode rays.- a)They travel from cathode to anode
- b)They travel in a straight line in the absence of an external electrical or magnetic field
- c)Their nature is independent of the materials of cathode
- d)Their nature is dependent on the nature of the gas present
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the incorrect statement about cathode rays.
a)
They travel from cathode to anode
b)
They travel in a straight line in the absence of an external electrical or magnetic field
c)
Their nature is independent of the materials of cathode
d)
Their nature is dependent on the nature of the gas present

|
Amrita Sarkar answered |
(a) Cathode rays travel from cathode (source) to anode. True
(b) In the absence of these fields, they are not deflected but in the presence of electrical field, they are deflected indicating that they are charged. Thus, True
(c) Their nature is independent of the material of cathode. True
(d) Their nature is independent of the nature of the gas.
Thus, given statement is false.
(b) In the absence of these fields, they are not deflected but in the presence of electrical field, they are deflected indicating that they are charged. Thus, True
(c) Their nature is independent of the material of cathode. True
(d) Their nature is independent of the nature of the gas.
Thus, given statement is false.
A uniform force of (3 i + j) N acts on a particle of mass 2 kg. Hence the particle is displaced from position (2 i + k) m to position ( 4 i + 3 j - k) m. The work done by the force on the particle is,- a)9 J
- b)6 J
- c)13 J
- d)15 J
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A uniform force of (3 i + j) N acts on a particle of mass 2 kg. Hence the particle is displaced from position (2 i + k) m to position ( 4 i + 3 j - k) m. The work done by the force on the particle is,
a)
9 J
b)
6 J
c)
13 J
d)
15 J
|
|
Ishan Ghosh answered |
Uniform force acting = 3i + j N
Displacement done = (4-2)i + 3j + (-1-1)k
= 2i + 3j -2k
Thus total work done = F.s (dot product here)
We get W = 3 x 2 + 1 x 3 + 0 x -2
= 9J
Displacement done = (4-2)i + 3j + (-1-1)k
= 2i + 3j -2k
Thus total work done = F.s (dot product here)
We get W = 3 x 2 + 1 x 3 + 0 x -2
= 9J
Which of the following is not correctly paired ?- a)Inert Crystals - Virus
- b)Free RNA - Viroids
- c)Normal protein - Prions
- d)Symbionts - Lichen
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not correctly paired ?
a)
Inert Crystals - Virus
b)
Free RNA - Viroids
c)
Normal protein - Prions
d)
Symbionts - Lichen
|
|
Pooja Desai answered |
Understanding Inert Crystals and Viruses
Inert crystals, like viruses, are non-living entities. Viruses are composed of genetic material (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat, and they require a host to replicate.
Free RNA and Viroids
Viroids are small, infectious RNA molecules that lack a protein coat. They are known to cause diseases in plants and consist solely of free RNA.
Normal Protein and Prions
Prions are misfolded proteins that can induce other normal proteins to misfold, leading to neurodegenerative diseases. Thus, this pairing is incorrect because a normal protein does not exhibit prion characteristics under normal conditions.
Symbionts and Lichens
Lichens are symbiotic associations between fungi and photosynthetic partners, typically algae or cyanobacteria. This pairing is correct as it reflects the mutualistic relationship present in lichens.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option 'C' because normal proteins do not behave like prions until they undergo misfolding. This distinction is crucial in understanding prion diseases, which are distinct from regular protein functions.
Inert crystals, like viruses, are non-living entities. Viruses are composed of genetic material (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat, and they require a host to replicate.
Free RNA and Viroids
Viroids are small, infectious RNA molecules that lack a protein coat. They are known to cause diseases in plants and consist solely of free RNA.
Normal Protein and Prions
Prions are misfolded proteins that can induce other normal proteins to misfold, leading to neurodegenerative diseases. Thus, this pairing is incorrect because a normal protein does not exhibit prion characteristics under normal conditions.
Symbionts and Lichens
Lichens are symbiotic associations between fungi and photosynthetic partners, typically algae or cyanobacteria. This pairing is correct as it reflects the mutualistic relationship present in lichens.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option 'C' because normal proteins do not behave like prions until they undergo misfolding. This distinction is crucial in understanding prion diseases, which are distinct from regular protein functions.
Select the correct statement -- a)Viriods are similar in size to viruses
- b)Lichens are examples of parasitism.
- c)Prions are different in size to viruses
- d)Prions are similar in size to viruses
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement -
a)
Viriods are similar in size to viruses
b)
Lichens are examples of parasitism.
c)
Prions are different in size to viruses
d)
Prions are similar in size to viruses
|
|
Nishtha Shah answered |
Understanding Prions and Viruses
Prions and viruses are both pathogenic entities, but they differ in many aspects, including their structure, replication methods, and the diseases they cause. However, when it comes to size, they are indeed similar.
Comparison of Sizes
- Prions: These are misfolded proteins that can induce other proteins to misfold, leading to neurodegenerative diseases. They are typically in the range of 10 to 100 nanometers in size.
- Viruses: Viruses are much more complex structures that include genetic material (DNA or RNA) enclosed in a protein coat. They range from about 20 to 300 nanometers.
Given that both prions and viruses fall within a similar size range, it can be said that they are comparable in size. Thus, the assertion that "Prions are similar in size to viruses" is accurate.
Reasons for the Correctness of Option D
- Size Overlap: Both prions and viruses measure in nanometers, making them comparable in size.
- Pathogenic Nature: While they behave differently biologically, their size allows them to interact with cellular structures similarly, which is crucial for their pathogenicity.
- Misconceptions: Often, prions are misunderstood due to their protein nature, but their size similarity to viruses is a key point of consideration in microbiology.
In conclusion, option 'D' accurately reflects the relationship in size between prions and viruses, reinforcing the idea that while they are fundamentally different entities, they share similarities in their dimensions.
Prions and viruses are both pathogenic entities, but they differ in many aspects, including their structure, replication methods, and the diseases they cause. However, when it comes to size, they are indeed similar.
Comparison of Sizes
- Prions: These are misfolded proteins that can induce other proteins to misfold, leading to neurodegenerative diseases. They are typically in the range of 10 to 100 nanometers in size.
- Viruses: Viruses are much more complex structures that include genetic material (DNA or RNA) enclosed in a protein coat. They range from about 20 to 300 nanometers.
Given that both prions and viruses fall within a similar size range, it can be said that they are comparable in size. Thus, the assertion that "Prions are similar in size to viruses" is accurate.
Reasons for the Correctness of Option D
- Size Overlap: Both prions and viruses measure in nanometers, making them comparable in size.
- Pathogenic Nature: While they behave differently biologically, their size allows them to interact with cellular structures similarly, which is crucial for their pathogenicity.
- Misconceptions: Often, prions are misunderstood due to their protein nature, but their size similarity to viruses is a key point of consideration in microbiology.
In conclusion, option 'D' accurately reflects the relationship in size between prions and viruses, reinforcing the idea that while they are fundamentally different entities, they share similarities in their dimensions.
Select the correct statement(s).
- a)The ideal body, which emits and absorbs all frequencies is called a black body
- b)The exact frequency distribution of the emitted radiation from a black body depends upon its temperature
- c)The radiation emitted goes from a lower frequency to higher frequency as the temperature increases
- d)In vacuum, all types of electromagnetic radiation travel at the same speed
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement(s).
a)
The ideal body, which emits and absorbs all frequencies is called a black body
b)
The exact frequency distribution of the emitted radiation from a black body depends upon its temperature
c)
The radiation emitted goes from a lower frequency to higher frequency as the temperature increases
d)
In vacuum, all types of electromagnetic radiation travel at the same speed

|
Sushant Khanna answered |
(a) Correct
(b) As temperature increases, distribution of frequency (and energy) increases. Thus, correct.
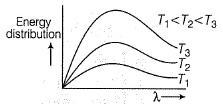
(c) As temperature increases, radiation emitted is shifted to lower wavelength, i.e. higher frequency. Correct
(d) All types of radiations have same speed 3 x 108 ms-1. Correct
(b) As temperature increases, distribution of frequency (and energy) increases. Thus, correct.
(c) As temperature increases, radiation emitted is shifted to lower wavelength, i.e. higher frequency. Correct
(d) All types of radiations have same speed 3 x 108 ms-1. Correct
Direction (Q. Nos. 15 and 16) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)Q. In Millikan’s experiment, static electric charge on the oil drops has been obtained by shining X-rays. If the static electric charge on the oil drop is -1.282x 10-18 C, calculate the number of electrons present on it.
Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 15 and 16) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q. In Millikan’s experiment, static electric charge on the oil drops has been obtained by shining X-rays. If the static electric charge on the oil drop is -1.282x 10-18 C, calculate the number of electrons present on it.

|
Manisha Mehta answered |
Charge on one electron = - 1.6022 x 10-19C
Let, number of electrons = N
Then total charge = - N x 1.6022 x 10-19C
Given, total charge = -1.282 x 10-18 C
Thus, - N x 1.6022 x 10-19 C = - 1. 282 x 10-18C
Let, number of electrons = N
Then total charge = - N x 1.6022 x 10-19C
Given, total charge = -1.282 x 10-18 C
Thus, - N x 1.6022 x 10-19 C = - 1. 282 x 10-18C
∴ N = 8
The angular velocity (in rad/s) of a body rotating at N r.p.m. is- a)π N/60
- b)2 π N/60
- c)π N/120
- d)π N/180
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The angular velocity (in rad/s) of a body rotating at N r.p.m. is
a)
π N/60
b)
2 π N/60
c)
π N/120
d)
π N/180
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
Angular velocity is defined as the rate of change of angular displacement with respect to time. It is usually expressed by a Greek letter ω (omega).
Mathematically, angular velocity,
ω =dθ/dt
If a body is rotating at the rate of N r.p.m. (revolutions per minute), then its angular velocity,
ω = 2πΝ / 60 rad/s
Which of the following conclusions could not be derived from Rutherford’s α-particle scattering experiment?- a)Electrons and nucleus are held together by electrostatic forces of attraction
- b)The radius of the atom is larger than that of the nucleus
- c)Most of the space in the atom is empty
- d)Electrons move in a circular path of fixed energy. Circular paths are called orbits
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following conclusions could not be derived from Rutherford’s α-particle scattering experiment?
a)
Electrons and nucleus are held together by electrostatic forces of attraction
b)
The radius of the atom is larger than that of the nucleus
c)
Most of the space in the atom is empty
d)
Electrons move in a circular path of fixed energy. Circular paths are called orbits

|
Dipika Choudhury answered |
(a) Electrons (-) and nucleus (+) are held togeather by electrostatic forces of attractions. Thus. true.
(b) Radius of the atom (= 10-10m) > radiue of the nucleus (10-15m). Thus true
(c) Most of the space is empty as given by radius of the nucleus and atom. Thus, true.
(d) As electron moves in a circular paith, it emits energy and ultimately false into nucleus. Thus, false.
(b) Radius of the atom (= 10-10m) > radiue of the nucleus (10-15m). Thus true
(c) Most of the space is empty as given by radius of the nucleus and atom. Thus, true.
(d) As electron moves in a circular paith, it emits energy and ultimately false into nucleus. Thus, false.
A hypothetical electromagnetic wave is pictured here. Q. A standing wave in a string 42 cm long has a total of six nodes (including those at the ends). Wavelength of the standing wave is
Q. A standing wave in a string 42 cm long has a total of six nodes (including those at the ends). Wavelength of the standing wave is- a)7.0 cm
- b)16.8 cm
- c)10.5 cm
- d)5.25 cm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A hypothetical electromagnetic wave is pictured here.
Q. A standing wave in a string 42 cm long has a total of six nodes (including those at the ends). Wavelength of the standing wave is
a)
7.0 cm
b)
16.8 cm
c)
10.5 cm
d)
5.25 cm

|
Ayush Joshi answered |
If there are 6 nodes, then there are 5 segments between nodes, and the wavelength of the underlying wave is 2 of those (because they look similar when they’re moving but if you freeze-frame, every second one is the opposite direction), so I make it 2*42/5 = 16.8 cm.
Direction (Q. Nos. 14) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct. Q. The colours of visible light are at different wavelength. Match the wavelengths in Column I with their colours in Column II.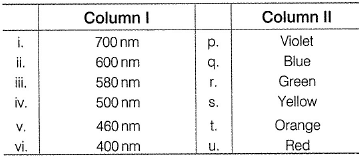
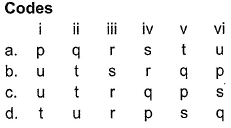
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 14) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q. The colours of visible light are at different wavelength. Match the wavelengths in Column I with their colours in Column II.
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Ishita Reddy answered |
Thus, (i)(700nm) Red (u)
(ii) (600 nm) - Orange (t)
(iii) (580 nm) - Yellow (s)
(iv) (500nm) - Green (r)
(v) (460 nm) - Blue (q)
(vi) (400 nm) - Violet (p)
(ii) (600 nm) - Orange (t)
(iii) (580 nm) - Yellow (s)
(iv) (500nm) - Green (r)
(v) (460 nm) - Blue (q)
(vi) (400 nm) - Violet (p)
Chapter doubts & questions for May Week 1 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of May Week 1 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.