All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of August Week 3 for NEET Exam
A person standing on a rotating platform with his hands lowered outstretches his arms. The angular momentum of the person- a)becomes zero
- b)decreases
- c)remains constant
- d)inreases
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A person standing on a rotating platform with his hands lowered outstretches his arms. The angular momentum of the person
a)
becomes zero
b)
decreases
c)
remains constant
d)
inreases
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
Yes because there is absence of any external force or torque so angular momentum will remain constant
here outstretching the hands means internal forces are working.. so moment of inertia increases in this case and to make angular momentum constant when angular velocity decreases.
here outstretching the hands means internal forces are working.. so moment of inertia increases in this case and to make angular momentum constant when angular velocity decreases.
The mass of an electron is 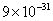 kg. It revolves around the nucleus of an atom in a circular orbit of radius 4.5 Å, with a speed of
kg. It revolves around the nucleus of an atom in a circular orbit of radius 4.5 Å, with a speed of 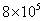 m/s. The angular momentum of electron is
m/s. The angular momentum of electron is- a)2.24 x 10-4 kgm2s-1
- b)3.24 x 10-34 kgm2s-1
- c)4.24 x10-34 kgm2s-1
- d)2.24 x 10-34 kgm2s-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The mass of an electron is 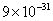 kg. It revolves around the nucleus of an atom in a circular orbit of radius 4.5 Å, with a speed of
kg. It revolves around the nucleus of an atom in a circular orbit of radius 4.5 Å, with a speed of 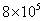 m/s. The angular momentum of electron is
m/s. The angular momentum of electron is
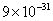 kg. It revolves around the nucleus of an atom in a circular orbit of radius 4.5 Å, with a speed of
kg. It revolves around the nucleus of an atom in a circular orbit of radius 4.5 Å, with a speed of 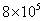 m/s. The angular momentum of electron is
m/s. The angular momentum of electron isa)
2.24 x 10-4 kgm2s-1
b)
3.24 x 10-34 kgm2s-1
c)
4.24 x10-34 kgm2s-1
d)
2.24 x 10-34 kgm2s-1
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
M=9x10-31Kg,r=4.5x10-10
V=8x105m/s
L=mvr
=9x10-31 x 4.5 x 10-10 x 8 x 105 = 3.24 x 10-34 kgm2s-1
V=8x105m/s
L=mvr
=9x10-31 x 4.5 x 10-10 x 8 x 105 = 3.24 x 10-34 kgm2s-1
The plant cell wall are made up of- a)Cellulose
- b)Starch
- c)Glycogen Bacteria
- d)Inulin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The plant cell wall are made up of
a)
Cellulose
b)
Starch
c)
Glycogen Bacteria
d)
Inulin

|
Srishti Sen answered |
Plant cell walls are made of cellulose. Paper made from plant pulp is cellulose.
The oils have- a)High melting point
- b)Low melting point
- c)Optimum melting point
- d)No melting point
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The oils have
a)
High melting point
b)
Low melting point
c)
Optimum melting point
d)
No melting point
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Oils have lower melting point (e.g., gingely oil) and hence remain as oil in winters.
A particle of mass 1 kg is fired from the origin of the co-ordinate axis-making angle 45 with the horizontal. After time t its position vector is 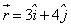 and velocity
and velocity 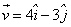 . What is the angular momentum of the particle at that instant?
. What is the angular momentum of the particle at that instant?- a)-25
- b)-7
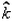
- c)25
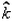
- d)7
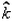
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle of mass 1 kg is fired from the origin of the co-ordinate axis-making angle 45 with the horizontal. After time t its position vector is 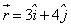 and velocity
and velocity 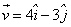 . What is the angular momentum of the particle at that instant?
. What is the angular momentum of the particle at that instant?
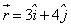 and velocity
and velocity 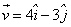 . What is the angular momentum of the particle at that instant?
. What is the angular momentum of the particle at that instant?a)
-25 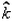
b)
-7 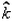
c)
25 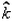
d)
7 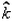
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
A uniform circular disc of radius 50 cm at rest is free to turn about an axis having perpendicular to its plane and passes through its centre. This situation can be shown by the figure given below:
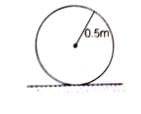
Therefore,

Therefore,
Angular acceleration = α = 2 rad/s2
Angular speed, ω = αt = 4 rad/s
Centripetal acceleration, ac = ω2r
42 x 0.5
=16 x 0.5
= 8m/s2
Linear acceleration at the end of 2 s is,
at = αt = 2 x 0.5 = 1 m/s2
Therefore, the net acceleration at the end of 2.0 sec is given by
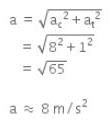
Which one is not a denaturing factor for protein?- a)High energy radiation
- b)High pressure
- c)Drastic change in pH
- d)High temperature
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is not a denaturing factor for protein?
a)
High energy radiation
b)
High pressure
c)
Drastic change in pH
d)
High temperature

|
Prasenjit Pillai answered |
Protein molecules get denatured due to high temperature, very high or low pH and high energy radiation but there is no effect due to high pressure.
kgm2s-1 is the unit of- a)force
- b)angular momentum
- c)tourqe
- d)moment of inertia
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
kgm2s-1 is the unit of
a)
force
b)
angular momentum
c)
tourqe
d)
moment of inertia
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
L = Iw
L is the angular momentum, I is the MOI and w is the rotational velocity.
[I] = [ML2T0], [w] = [M0L0T-1]
[L] = [MLT-1]
L is the angular momentum, I is the MOI and w is the rotational velocity.
[I] = [ML2T0], [w] = [M0L0T-1]
[L] = [MLT-1]
An earth satellite is moving around the earth in a circular orbit. In such case, what is conserved?- a)force
- b)velocity
- c)angular momentum
- d)linear momentum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An earth satellite is moving around the earth in a circular orbit. In such case, what is conserved?
a)
force
b)
velocity
c)
angular momentum
d)
linear momentum
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
An earth satellite is moving in a circular motion due to change in the direction of velocity. Its angular momentum about centre is conserved as there is no external force acting on the system.
The earth rotates about an axis passing through its north and south poles with a period of one day. If it is struck by meteorites, then- a)moment of inertia decreases and angular velocity increases
- b)moment of inertia decreases and angular velocity decreases
- c)moment of inertia increases and angular velocity decreases
- d)moment of inertia increases and angular velocity increases
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The earth rotates about an axis passing through its north and south poles with a period of one day. If it is struck by meteorites, then
a)
moment of inertia decreases and angular velocity increases
b)
moment of inertia decreases and angular velocity decreases
c)
moment of inertia increases and angular velocity decreases
d)
moment of inertia increases and angular velocity increases
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Because angular momentum remains constant as the moment of inertia is increasing here so the angular velocity will decrease.
Given,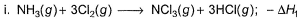
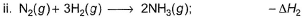
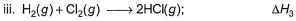
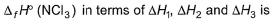
- a)
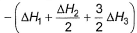
- b)
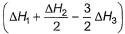
- c)
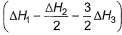
- d)
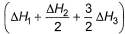
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Given,
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
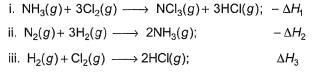
Applying i-ii/2-3/2iii
We get ∆fH of NCl3 in terms of ∆H1, ∆H2 and ∆H3
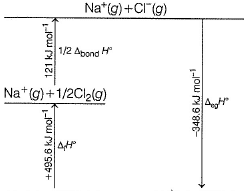
Following diagram represents Born-Haber cycle to determine lattice energy of NaCI(s). It is based on Hess’s law of constant heat summation. ΔlatticeH° of 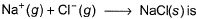
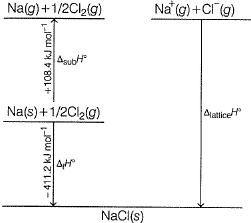
- a)-788 kJ mol-1
- b)+788 kJ mol-1
- c)-411.2 kJ mol-1
- d)+411.2 kJ mol-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Following diagram represents Born-Haber cycle to determine lattice energy of NaCI(s). It is based on Hess’s law of constant heat summation. ΔlatticeH° of
a)
-788 kJ mol-1
b)
+788 kJ mol-1
c)
-411.2 kJ mol-1
d)
+411.2 kJ mol-1
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
-411.2 = 108.4 + 495.6 + 121.0 - 348.6 + LE
=>LE= -411.2 - 108.4 - 495.6 - 121.0 +348.6
=> LE = -787.6 ~ -788 kJ mol-1
-411.2 = 108.4 + 495.6 + 121.0 - 348.6 + LE
=>LE= -411.2 - 108.4 - 495.6 - 121.0 +348.6
=> LE = -787.6 ~ -788 kJ mol-1
Direction (Q. Nos. 12-15) This section contains 4 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).Q. Based on (BE) values, ΔrH° of the following reaction 298 K is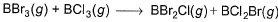
Correct answer is '0'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 12-15) This section contains 4 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. Based on (BE) values, ΔrH° of the following reaction 298 K is
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Let the BE value of B---Br bond be x and B---Cl bond be y
BE of BBr3 is 3x, BCl3=3y , BBr2Cl=2x+y ,BCl2Br=2y+x
then ∆Hr=Hr(products)-Hr(reactants)=(2x+y+2y+x) - (3x+3y)=0
BE of BBr3 is 3x, BCl3=3y , BBr2Cl=2x+y ,BCl2Br=2y+x
then ∆Hr=Hr(products)-Hr(reactants)=(2x+y+2y+x) - (3x+3y)=0
Given, HCI (g) → H (g) + Cl (g) at 298 K (say temperature T K),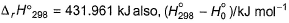 For
For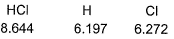 Q. Thus, for the given reaction
Q. Thus, for the given reaction 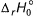 (at 0 K) is
(at 0 K) is- a)428.136 kJ
- b)-428.136 kJ
- c)431.961 kJ
- d)-431.961 kJ
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Given, HCI (g) → H (g) + Cl (g) at 298 K (say temperature T K),
For
Q. Thus, for the given reaction 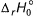 (at 0 K) is
(at 0 K) is
a)
428.136 kJ
b)
-428.136 kJ
c)
431.961 kJ
d)
-431.961 kJ

|
Infinity Academy answered |
Ho= Ho of product - Ho of reactant
so ho =(6.197 + 6.272 ) - 8.644
= 3.825
Ho298-Ho = 431.961 - 3.825=428.136532873
so ho =(6.197 + 6.272 ) - 8.644
= 3.825
Ho298-Ho = 431.961 - 3.825=428.136532873
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-7) This section contains 7 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Given,The enthalpies of elements in their standard states are taken as zero. The enthalpy of formation of a compound- a)is always negative
- b)is always positive
- c)may be positive or negative
- d)is never negative
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-7) This section contains 7 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Given,
The enthalpies of elements in their standard states are taken as zero. The enthalpy of formation of a compound
a)
is always negative
b)
is always positive
c)
may be positive or negative
d)
is never negative
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Depend on whether the formation of compounds is exothermic or endothermic.For exothermic reaction, enthalpy of formation would be negative and for endothermic,it is positive.
Direction (Q. Nos. 9 and 10) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given ptions (a),(b),(c),(d).Consider the following thermochemical equations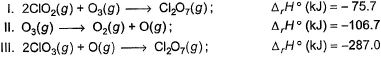
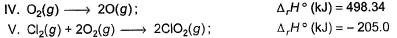
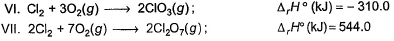 Q. ΔrH° of the following thermochemical reaction isCIO2 (g) + O (g) → CIO3 (g)
Q. ΔrH° of the following thermochemical reaction isCIO2 (g) + O (g) → CIO3 (g)- a)-197 kJ
- b)+197 kJ
- c)+312 kJ
- d)+212 kJ
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 9 and 10) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given ptions (a),(b),(c),(d).
Consider the following thermochemical equations
Q. ΔrH° of the following thermochemical reaction is
CIO2 (g) + O (g) → CIO3 (g)
a)
-197 kJ
b)
+197 kJ
c)
+312 kJ
d)
+212 kJ
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The question can be simply done by understanding that this reaction is endothermic so ∆H is negative.
Hence A is correct.
Heat of combustion of CH2CO(g) is - 981.1 kJ mol-1 and that of CH4 (g) is - 802.3 kJat 298 K. If 1247.0 kJ of heat is released in the following change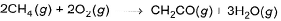 Q. How many moles of CH4(g)are used?
Q. How many moles of CH4(g)are used?
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
Heat of combustion of CH2CO(g) is - 981.1 kJ mol-1 and that of CH4 (g) is - 802.3 kJat 298 K. If 1247.0 kJ of heat is released in the following change
Q. How many moles of CH4(g)are used?
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
[2CH4 + 2O2 → CH2O + H2O]n
∆HC = n[-981.1-(-8023×2)]
1247 = n[-981.1+1604.6]
N[623.5] = 1247
N = 4
So, no of moles of CH4 = n×2 = 2×2 = 4
∆HC = n[-981.1-(-8023×2)]
1247 = n[-981.1+1604.6]
N[623.5] = 1247
N = 4
So, no of moles of CH4 = n×2 = 2×2 = 4
Angular momentum is equal to____.(All the symbols used have their usual meanings)- a)L = I2ω
- b)L = Iω
- c)L = ma
- d)L = I/α
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Angular momentum is equal to____.(All the symbols used have their usual meanings)
a)
L = I2ω
b)
L = Iω
c)
L = ma
d)
L = I/α
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Angular momentum is equal to L = Iω. It is the formula.
Assertion (A): Competitive inhibitors bind to the active site of an enzyme, preventing substrate binding. Reason (R): Competitive inhibition can be overcome by increasing the concentration of the substrate.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Competitive inhibitors bind to the active site of an enzyme, preventing substrate binding.
Reason (R): Competitive inhibition can be overcome by increasing the concentration of the substrate.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
- The Assertion is correct because competitive inhibitors indeed bind to the active site of an enzyme, which prevents the substrate from binding.
- The Reason is also correct as increasing the substrate concentration can outcompete the inhibitor for the active site, thereby restoring enzyme activity.
- Additionally, the Reason effectively explains the Assertion as it describes how competitive inhibition can be mitigated, confirming that both statements are true and that the Reason is the correct explanation for the Assertion.
The measured enthalpy change for burning of ketene (g) (CH2CO) is - 981.1 kJ mo-1 at 298 K ,CH2CO (g)+ 2O2(g) → 2CO2 (g) + H2O (g) and that of CH4 (g) is - 802.3 kJ mol-1 at 298 K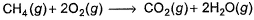 Thus, enthalpy change at 298 K for the following thermochemical reaction is
Thus, enthalpy change at 298 K for the following thermochemical reaction is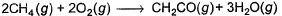
- a)-623.5 kJ
- b)+623.5 kJ
- c)-178.8 kJ
- d)+802.3 kJ
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The measured enthalpy change for burning of ketene (g) (CH2CO) is - 981.1 kJ mo-1 at 298 K ,CH2CO (g)+ 2O2(g) → 2CO2 (g) + H2O (g) and that of CH4 (g) is - 802.3 kJ mol-1 at 298 K
Thus, enthalpy change at 298 K for the following thermochemical reaction is
a)
-623.5 kJ
b)
+623.5 kJ
c)
-178.8 kJ
d)
+802.3 kJ
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
CH2CO (g)+ 2O2(g) → 2CO2 (g) + H2O (g) -(i)
CH4 (g)+ 2O2(g) → CO2 (g) + 2H2O (g) -(ii)
CH4 (g)+ 2O2(g) → CO2 (g) + 2H2O (g) -(ii)
On 2(ii)-(i)
2CH4 (g)+ 2O2(g) → CH2CO (g) + 3H2O (g) -(iii)
∆H(iii) = 2∆H(ii) - ∆H(i) = [2 (-802.3) -(-981.1)] -623.5 kJ mol-1
∆H(iii) = 2∆H(ii) - ∆H(i) = [2 (-802.3) -(-981.1)] -623.5 kJ mol-1
Consider the following reactions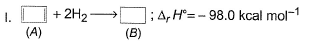
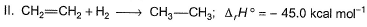 Q. What is the resonance energy (in kcal) of A?
Q. What is the resonance energy (in kcal) of A?
Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following reactions
Q. What is the resonance energy (in kcal) of A?
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Resonance energy = (Observed ∆H) - (Theoretical ∆H)
= (-98.0) - 2(-45.0)
= -8 kcal mol-1
So we have Resnance energy = 8
= (-98.0) - 2(-45.0)
= -8 kcal mol-1
So we have Resnance energy = 8
How many subunits are there in human adult haemoglobin?- a)4
- b)5
- c)3
- d)2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How many subunits are there in human adult haemoglobin?
a)
4
b)
5
c)
3
d)
2

|
Rajat Roy answered |
Proteins human haemoglobin consists of 4 subunits. Two of these are identical toeach other. Hence, two subunits of αα type and two subunits of ββ type together constitute the human haemoglobin (Hb).
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct option.Assertion: Both amino group and acidic group act as substituents on the same carbon called α-amino acids.Reason: Amino acids are inorganic compounds containing an amino group.- a)Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)Assertion is true but the reason is false.
- c)Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- d)Assertion is false but the reason is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct option.
Assertion: Both amino group and acidic group act as substituents on the same carbon called α-amino acids.
Reason: Amino acids are inorganic compounds containing an amino group.
a)
Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
Assertion is true but the reason is false.
c)
Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
d)
Assertion is false but the reason is true.

|
Lead Academy answered |
Amino acids are organic compounds containing an amino group and an acidic group as substituents on the same carbon, i.e. the α-carbon. Hence, they are called α-amino acids.
Which of the following statements regarding the catalytic cycle of enzyme action is/are correct?i. The substrate binds to the active site of the enzyme, fitting perfectly into it.ii. The enzyme changes shape to fit more tightly around the substrate after binding occurs.iii. The enzyme-product complex is formed when the active site breaks the chemical bonds of the substrate.iv. The enzyme remains permanently altered after releasing the products of the reaction.- a)ii and iii
- b)i and ii
- c)iii and iv
- d)i, ii, and iii
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements regarding the catalytic cycle of enzyme action is/are correct?
i. The substrate binds to the active site of the enzyme, fitting perfectly into it.
ii. The enzyme changes shape to fit more tightly around the substrate after binding occurs.
iii. The enzyme-product complex is formed when the active site breaks the chemical bonds of the substrate.
iv. The enzyme remains permanently altered after releasing the products of the reaction.
a)
ii and iii
b)
i and ii
c)
iii and iv
d)
i, ii, and iii
|
|
Ashish Dasgupta answered |
Understanding the Catalytic Cycle of Enzyme Action
Enzymes are biological catalysts that facilitate biochemical reactions. The statements provided pertain to the catalytic cycle of enzyme action, and the correct answer is option 'D' (i, ii, and iii). Let’s analyze each statement:
i. Substrate Binding
- The substrate binds to the active site of the enzyme, fitting perfectly into it.
- This statement is partially true; however, it is more accurate to say that the substrate does not always fit perfectly. The "induced fit" model suggests that the enzyme undergoes a conformational change to accommodate the substrate.
ii. Enzyme Conformational Change
- The enzyme changes shape to fit more tightly around the substrate after binding occurs.
- This is true and describes the induced fit model, wherein the binding of the substrate induces a change in the enzyme's shape, enhancing the interaction between enzyme and substrate.
iii. Formation of Enzyme-Product Complex
- The enzyme-product complex is formed when the active site breaks the chemical bonds of the substrate.
- This statement is correct. The enzyme catalyzes the reaction, lowering the activation energy and facilitating the breaking and formation of bonds, leading to the production of products.
iv. Permanent Alteration of the Enzyme
- The enzyme remains permanently altered after releasing the products of the reaction.
- This statement is incorrect. Enzymes typically return to their original state after the reaction, allowing them to participate in subsequent reactions.
Conclusion
The correct statements are ii and iii, affirming that the answer is option 'D' (i, ii, and iii are considered correct in context). Understanding these concepts is essential for grasping enzyme functionality in biochemical processes.
Enzymes are biological catalysts that facilitate biochemical reactions. The statements provided pertain to the catalytic cycle of enzyme action, and the correct answer is option 'D' (i, ii, and iii). Let’s analyze each statement:
i. Substrate Binding
- The substrate binds to the active site of the enzyme, fitting perfectly into it.
- This statement is partially true; however, it is more accurate to say that the substrate does not always fit perfectly. The "induced fit" model suggests that the enzyme undergoes a conformational change to accommodate the substrate.
ii. Enzyme Conformational Change
- The enzyme changes shape to fit more tightly around the substrate after binding occurs.
- This is true and describes the induced fit model, wherein the binding of the substrate induces a change in the enzyme's shape, enhancing the interaction between enzyme and substrate.
iii. Formation of Enzyme-Product Complex
- The enzyme-product complex is formed when the active site breaks the chemical bonds of the substrate.
- This statement is correct. The enzyme catalyzes the reaction, lowering the activation energy and facilitating the breaking and formation of bonds, leading to the production of products.
iv. Permanent Alteration of the Enzyme
- The enzyme remains permanently altered after releasing the products of the reaction.
- This statement is incorrect. Enzymes typically return to their original state after the reaction, allowing them to participate in subsequent reactions.
Conclusion
The correct statements are ii and iii, affirming that the answer is option 'D' (i, ii, and iii are considered correct in context). Understanding these concepts is essential for grasping enzyme functionality in biochemical processes.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?i. Lipids are generally water soluble and include simple fatty acids.ii. Fatty acids can be either saturated (without double bonds) or unsaturated (with one or more double bonds).iii. Glycerol is a simple sugar that can be esterified with fatty acids to form triglycerides.iv. Phospholipids are found in cell membranes and contain phosphorus.- a)ii and iv
- b)i and iii
- c)i, ii, and iv
- d)ii and iii
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. Lipids are generally water soluble and include simple fatty acids.
ii. Fatty acids can be either saturated (without double bonds) or unsaturated (with one or more double bonds).
iii. Glycerol is a simple sugar that can be esterified with fatty acids to form triglycerides.
iv. Phospholipids are found in cell membranes and contain phosphorus.
a)
ii and iv
b)
i and iii
c)
i, ii, and iv
d)
ii and iii

|
Top Rankers answered |
To determine the correct statements:
- Statement i is incorrect because lipids are generally water insoluble, not soluble.
- Statement ii is correct as it accurately describes the types of fatty acids.
- Statement iii is incorrect because glycerol is not a simple sugar; it is a trihydroxy alcohol (trihydroxy propane) that combines with fatty acids to form triglycerides.
- Statement iv is correct as phospholipids are indeed found in cell membranes and contain phosphorus.
Thus, the correct statements are ii and iv, making Option A the right choice.
The condition for free expansion of an ideal gas under adiabatic condition is
- a)q = 0, w = 0, ΔT = 0
- b)q ≠ 0, w = 0, ΔT = 0
- c)q = 0, w = 0, ΔT ≠ 0
- d)q = 0, w > 0, ΔT = 0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The condition for free expansion of an ideal gas under adiabatic condition is
a)
q = 0, w = 0, ΔT = 0
b)
q ≠ 0, w = 0, ΔT = 0
c)
q = 0, w = 0, ΔT ≠ 0
d)
q = 0, w > 0, ΔT = 0

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Explanation:
For free expansion of ideal gas,
Pext = 0
WpV = 0
For adiabatic process,
q = 0
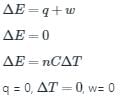
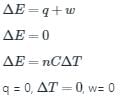
Conclusion:
Thus, the condition for free expansion of an ideal gas under adiabatic condition is q = 0, w = 0, ΔT = 0.
Direction (Q. Nos. 11) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.Q. For liquid water at 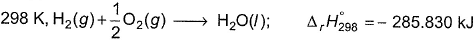
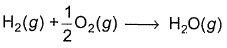
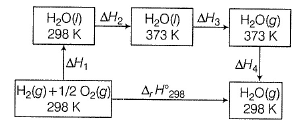
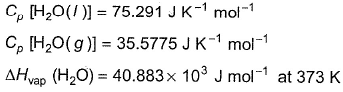 Compare the parameters ΔH1, ΔH2 ... in Column I with the corresponding values in kJ in Column II.
Compare the parameters ΔH1, ΔH2 ... in Column I with the corresponding values in kJ in Column II.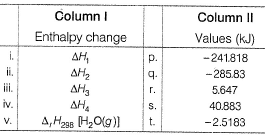

- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 11) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q. For liquid water at
Compare the parameters ΔH1, ΔH2 ... in Column I with the corresponding values in kJ in Column II.
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
∆H1=∆rH298=-285.83kJmol-¹
∆H²=Cp(liq)∆T=75.29×75 =5.64kJmol-¹
∆H³=∆Hvap =40.88kJmol-¹
∆H⁴=Cp(gas)∆T=35.57×(-75) =-2.5183kJmol-¹
∆H²=Cp(liq)∆T=75.29×75 =5.64kJmol-¹
∆H³=∆Hvap =40.88kJmol-¹
∆H⁴=Cp(gas)∆T=35.57×(-75) =-2.5183kJmol-¹
Which of the following pairs is incorrect?- a)Terpenoides: Abrin and Ricin
- b)Alkaloids: Morphine and Codeine
- c)Pigments: Carotenoids and Anthocyanins
- d)Drugs: Vinblastin and Curcumin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following pairs is incorrect?
a)
Terpenoides: Abrin and Ricin
b)
Alkaloids: Morphine and Codeine
c)
Pigments: Carotenoids and Anthocyanins
d)
Drugs: Vinblastin and Curcumin
|
|
Pooja Mukherjee answered |
Explanation of Incorrect Pair
The incorrect pair in the given options is:
Terpenoids: Abrin and Ricin
Understanding the Components
- Terpenoids:
- These are a large class of organic compounds produced by a variety of plants, particularly conifers.
- They are derived from isoprene units and are often responsible for the aromatic properties of many plants.
- Examples include menthol and limonene.
- Abrin and Ricin:
- Both are toxic proteins derived from specific plant seeds (Abrus precatorius for abrin and Ricinus communis for ricin).
- They are classified as lectins and not terpenoids, meaning they do not fit into the terpenoid category.
Correct Pairings
- Alkaloids: Morphine and Codeine:
- Alkaloids are nitrogen-containing compounds known for their pharmacological effects.
- Morphine and codeine are both derived from the opium poppy and exhibit analgesic properties.
- Pigments: Carotenoids and Anthocyanins:
- Both are pigments found in plants, carotenoids giving yellow to red hues, and anthocyanins providing red, purple, and blue colors.
- Drugs: Vinblastine and Curcumin:
- Vinblastine is a chemotherapy medication, while curcumin is a compound found in turmeric with anti-inflammatory properties.
Conclusion
The classification of abrin and ricin as terpenoids is incorrect, making option A the right answer. The other pairs accurately represent their respective categories.
The incorrect pair in the given options is:
Terpenoids: Abrin and Ricin
Understanding the Components
- Terpenoids:
- These are a large class of organic compounds produced by a variety of plants, particularly conifers.
- They are derived from isoprene units and are often responsible for the aromatic properties of many plants.
- Examples include menthol and limonene.
- Abrin and Ricin:
- Both are toxic proteins derived from specific plant seeds (Abrus precatorius for abrin and Ricinus communis for ricin).
- They are classified as lectins and not terpenoids, meaning they do not fit into the terpenoid category.
Correct Pairings
- Alkaloids: Morphine and Codeine:
- Alkaloids are nitrogen-containing compounds known for their pharmacological effects.
- Morphine and codeine are both derived from the opium poppy and exhibit analgesic properties.
- Pigments: Carotenoids and Anthocyanins:
- Both are pigments found in plants, carotenoids giving yellow to red hues, and anthocyanins providing red, purple, and blue colors.
- Drugs: Vinblastine and Curcumin:
- Vinblastine is a chemotherapy medication, while curcumin is a compound found in turmeric with anti-inflammatory properties.
Conclusion
The classification of abrin and ricin as terpenoids is incorrect, making option A the right answer. The other pairs accurately represent their respective categories.
Assertion (A): The acid insoluble fraction of biomolecules includes proteins, nucleic acids, polysaccharides, and lipids, which are all classified as macromolecules. Reason (R): Lipids, despite having lower molecular weights than 800 Da, are classified as macromolecules because they exhibit polymeric characteristics.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are false
- c)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- d)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): The acid insoluble fraction of biomolecules includes proteins, nucleic acids, polysaccharides, and lipids, which are all classified as macromolecules.
Reason (R): Lipids, despite having lower molecular weights than 800 Da, are classified as macromolecules because they exhibit polymeric characteristics.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are false
c)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
d)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
|
|
Sanaya Dey answered |
Understanding the Assertion and Reason
The question presents an Assertion (A) and a Reason (R) regarding the classification of biomolecules. Let’s analyze both statements for clarity.
Assertion (A)
- The acid insoluble fraction of biomolecules includes:
- Proteins
- Nucleic acids
- Polysaccharides
- Lipids
- These are all categorized as macromolecules due to their large size and complex structures.
Reason (R)
- Lipids are mentioned as having lower molecular weights than 800 Da.
- The classification of lipids as macromolecules is attributed to their polymeric characteristics.
Analysis of the Statements
- Assertion:
- True: All the mentioned biomolecules are indeed macromolecules, which are typically defined as large molecules composed of smaller structural units (monomers).
- Reason:
- True: While lipids can have molecular weights lower than 800 Da, they are classified as macromolecules because of their complex structures and functions in biological systems. However, lipids do not exhibit true polymeric characteristics like proteins and nucleic acids, which are formed from repeating monomer units.
Conclusion
- Both Assertion and Reason are true, but the Reason does not correctly explain the Assertion. Lipids are categorized as macromolecules based on their functional roles and structural complexity rather than their molecular weight or polymeric nature.
Thus, the correct answer is option C: Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
The question presents an Assertion (A) and a Reason (R) regarding the classification of biomolecules. Let’s analyze both statements for clarity.
Assertion (A)
- The acid insoluble fraction of biomolecules includes:
- Proteins
- Nucleic acids
- Polysaccharides
- Lipids
- These are all categorized as macromolecules due to their large size and complex structures.
Reason (R)
- Lipids are mentioned as having lower molecular weights than 800 Da.
- The classification of lipids as macromolecules is attributed to their polymeric characteristics.
Analysis of the Statements
- Assertion:
- True: All the mentioned biomolecules are indeed macromolecules, which are typically defined as large molecules composed of smaller structural units (monomers).
- Reason:
- True: While lipids can have molecular weights lower than 800 Da, they are classified as macromolecules because of their complex structures and functions in biological systems. However, lipids do not exhibit true polymeric characteristics like proteins and nucleic acids, which are formed from repeating monomer units.
Conclusion
- Both Assertion and Reason are true, but the Reason does not correctly explain the Assertion. Lipids are categorized as macromolecules based on their functional roles and structural complexity rather than their molecular weight or polymeric nature.
Thus, the correct answer is option C: Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
In case of a projectile, the angular momentum is minimum- a)at some location other than those mentioned above
- b)at the starting point
- c)at the highest point
- d)on return to the ground
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In case of a projectile, the angular momentum is minimum
a)
at some location other than those mentioned above
b)
at the starting point
c)
at the highest point
d)
on return to the ground

|
Imk Pathsala answered |
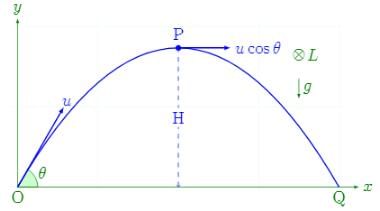
At the starting point of the projectile, the perpendicular distance from the point of rotation is zero as it's on the ground itself. Since one factor of the product is zero, the angular momentum at the starting point will be zero too.
Which of the following statements given above is/are correct?i. In the absence of any enzyme, the formation of H2CO3 is very slow, with about 200 molecules produced in an hour.ii. Carbonic anhydrase accelerates the reaction rate by approximately 10 million times, producing about 600,000 molecules of H2CO3 every second.iii. The metabolic pathway from glucose to pyruvic acid involves ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions.iv. Under anaerobic conditions in skeletal muscle, pyruvic acid is formed instead of lactic acid.- a)i and ii
- b) i, ii and iii
- c)i, iii and iv
- d)ii and iii
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements given above is/are correct?
i. In the absence of any enzyme, the formation of H2CO3 is very slow, with about 200 molecules produced in an hour.
ii. Carbonic anhydrase accelerates the reaction rate by approximately 10 million times, producing about 600,000 molecules of H2CO3 every second.
iii. The metabolic pathway from glucose to pyruvic acid involves ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
iv. Under anaerobic conditions in skeletal muscle, pyruvic acid is formed instead of lactic acid.
a)
i and ii
b)
i, ii and iii
c)
i, iii and iv
d)
ii and iii

|
Bs Academy answered |
To analyze the statements:
- Statement i is correct; it describes the slow reaction rate in the absence of an enzyme.
- Statement ii is also correct; it accurately describes the function of carbonic anhydrase and its dramatic acceleration of the reaction rate.
- Statement iii is accurate; it notes that the pathway from glucose to pyruvic acid consists of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
- Statement iv is incorrect; under anaerobic conditions, lactic acid is produced in skeletal muscle, not pyruvic acid.
Therefore, the correct answer, which includes statements i, ii and iii, is Option B.
Which of the following are aromatic amino acids?- a)Phenylalanine, tryptophan
- b)Serine, glutamic acid
- c)Alanine, glycine
- d)Lysine, valine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are aromatic amino acids?
a)
Phenylalanine, tryptophan
b)
Serine, glutamic acid
c)
Alanine, glycine
d)
Lysine, valine

|
Ashwini Khanna answered |
Based on number of amino and carboxyl groups, there are acidic (e.g., glutamic acid), basic (lysine) and neutral (valine) amino acids. Similarly, there are aromatic amino acids (tyrosine, phenylalanine, tryptophan).
What happens to enzymes at low temperature?- a)They get inactivated.
- b)They get over activated.
- c)They remain unaffected.
- d)They get denatured.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What happens to enzymes at low temperature?
a)
They get inactivated.
b)
They get over activated.
c)
They remain unaffected.
d)
They get denatured.
|
|
Prasenjit Khanna answered |
Effect of Low Temperature on Enzymes
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms. Temperature plays a crucial role in their activity.
1. Enzyme Activity at Low Temperatures
- At low temperatures, enzymes do not function optimally.
- Enzyme-catalyzed reactions typically slow down because molecular movement decreases.
2. Kinetic Energy Reduction
- Enzymes rely on kinetic energy to facilitate interactions with substrates.
- Lower temperatures result in reduced kinetic energy, leading to fewer effective collisions between enzymes and substrates.
3. Inactivation of Enzymes
- Although enzymes are not denatured at low temperatures, their activity can be significantly diminished.
- The result is a state of inactivation where the enzyme is present but not catalyzing reactions effectively.
4. Temperature and Reaction Rates
- The general rule is that for every 10°C decrease in temperature, the reaction rate can drop by about half.
- This is why many biological processes slow down during colder conditions.
5. Reversible Nature of Enzyme Inactivation
- It is important to note that this inactivation is often reversible.
- When temperatures rise back to optimal levels, enzyme activity can resume.
Conclusion
In summary, at low temperatures, enzymes can become inactivated due to reduced kinetic energy and decreased reaction rates. This impact is critical to understanding enzyme functionality, particularly in biological and biochemical contexts.
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms. Temperature plays a crucial role in their activity.
1. Enzyme Activity at Low Temperatures
- At low temperatures, enzymes do not function optimally.
- Enzyme-catalyzed reactions typically slow down because molecular movement decreases.
2. Kinetic Energy Reduction
- Enzymes rely on kinetic energy to facilitate interactions with substrates.
- Lower temperatures result in reduced kinetic energy, leading to fewer effective collisions between enzymes and substrates.
3. Inactivation of Enzymes
- Although enzymes are not denatured at low temperatures, their activity can be significantly diminished.
- The result is a state of inactivation where the enzyme is present but not catalyzing reactions effectively.
4. Temperature and Reaction Rates
- The general rule is that for every 10°C decrease in temperature, the reaction rate can drop by about half.
- This is why many biological processes slow down during colder conditions.
5. Reversible Nature of Enzyme Inactivation
- It is important to note that this inactivation is often reversible.
- When temperatures rise back to optimal levels, enzyme activity can resume.
Conclusion
In summary, at low temperatures, enzymes can become inactivated due to reduced kinetic energy and decreased reaction rates. This impact is critical to understanding enzyme functionality, particularly in biological and biochemical contexts.
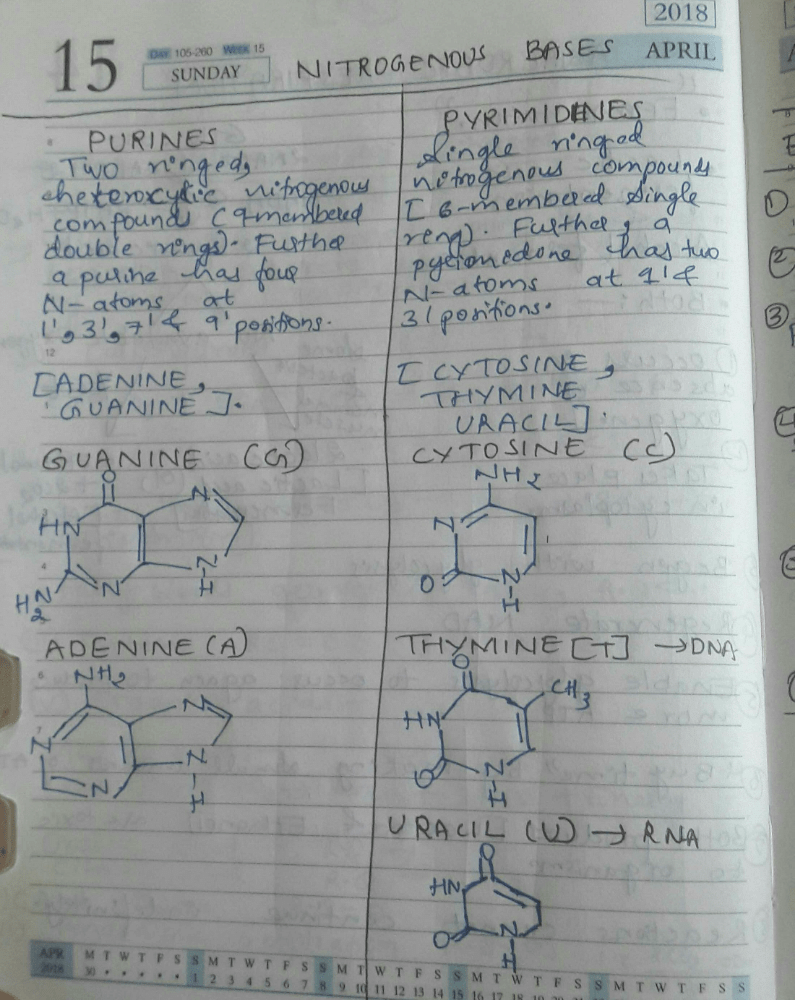
Which of the following nitrogenous base produces nucleoside only with ribose sugar?- a)Thymine
- b)Guanine
- c)Uracil
- d)Adenine
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following nitrogenous base produces nucleoside only with ribose sugar?
a)
Thymine
b)
Guanine
c)
Uracil
d)
Adenine

|
Ruchi Chakraborty answered |
Uracil nitrogenous base is produces nucleoside only with ribose sugar. This nucleoside is present only inside the RNA and absent in DNA.
Which of the following statements regarding nucleic acids is/are correct?i. Nucleic acids are comprised of polynucleotides that contain ribose or deoxyribose sugars.ii. The building blocks of nucleic acids are amino acids.iii. The nitrogenous bases adenine, guanine, uracil, cytosine, and thymine are found in nucleic acids.iv. DNA is a type of nucleic acid that contains ribose sugar.- a)A: i and iii
- b)B: ii and iv
- c)C: i, iii, and iv
- d)D: i, ii, and iii
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements regarding nucleic acids is/are correct?
i. Nucleic acids are comprised of polynucleotides that contain ribose or deoxyribose sugars.
ii. The building blocks of nucleic acids are amino acids.
iii. The nitrogenous bases adenine, guanine, uracil, cytosine, and thymine are found in nucleic acids.
iv. DNA is a type of nucleic acid that contains ribose sugar.
a)
A: i and iii
b)
B: ii and iv
c)
C: i, iii, and iv
d)
D: i, ii, and iii
|
|
Devanshi Banerjee answered |
Understanding Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids are fundamental biomolecules essential for all forms of life. Let’s analyze each statement individually to determine their correctness.
Statement i: Nucleic acids are comprised of polynucleotides that contain ribose or deoxyribose sugars.
- This statement is correct. Nucleic acids, such as RNA and DNA, are polymers (polynucleotides) made up of nucleotides, which include ribose (in RNA) and deoxyribose (in DNA) sugars.
Statement ii: The building blocks of nucleic acids are amino acids.
- This statement is incorrect. The building blocks of nucleic acids are nucleotides, not amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins.
Statement iii: The nitrogenous bases adenine, guanine, uracil, cytosine, and thymine are found in nucleic acids.
- This statement is correct. These nitrogenous bases are integral to nucleic acids. Adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine are found in DNA, while adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil are found in RNA.
Statement iv: DNA is a type of nucleic acid that contains ribose sugar.
- This statement is incorrect. DNA contains deoxyribose sugar, not ribose.
Conclusion
Based on the analysis:
- The correct statements are i and iii.
- Thus, the correct answer is option C: i, iii, and iv.
However, the provided answer option "A" is incorrect, as it states that only statements i and iii are correct. The answer should consider the analysis of all statements accurately.
Nucleic acids are fundamental biomolecules essential for all forms of life. Let’s analyze each statement individually to determine their correctness.
Statement i: Nucleic acids are comprised of polynucleotides that contain ribose or deoxyribose sugars.
- This statement is correct. Nucleic acids, such as RNA and DNA, are polymers (polynucleotides) made up of nucleotides, which include ribose (in RNA) and deoxyribose (in DNA) sugars.
Statement ii: The building blocks of nucleic acids are amino acids.
- This statement is incorrect. The building blocks of nucleic acids are nucleotides, not amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins.
Statement iii: The nitrogenous bases adenine, guanine, uracil, cytosine, and thymine are found in nucleic acids.
- This statement is correct. These nitrogenous bases are integral to nucleic acids. Adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine are found in DNA, while adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil are found in RNA.
Statement iv: DNA is a type of nucleic acid that contains ribose sugar.
- This statement is incorrect. DNA contains deoxyribose sugar, not ribose.
Conclusion
Based on the analysis:
- The correct statements are i and iii.
- Thus, the correct answer is option C: i, iii, and iv.
However, the provided answer option "A" is incorrect, as it states that only statements i and iii are correct. The answer should consider the analysis of all statements accurately.
Relation between torque and angular momentum is similar to the relation between- a)force and linear momentum
- b)energy and displacement
- c)acceleration and velocity
- d)mass and moment of inertia
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Relation between torque and angular momentum is similar to the relation between
a)
force and linear momentum
b)
energy and displacement
c)
acceleration and velocity
d)
mass and moment of inertia
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Torque is the rate of change of angular momentum.
Force in linear motion corresponds to Torque in rotary motion.
Thus, just as Newton’s second law can be written as F=dP/dtF for linear motion, it can be written as T=dL/dt for rotary motion.
Assertion (A): The formation of the enzyme-substrate complex is a transient phenomenon crucial for catalysis.
Reason (R): The transition state structure is the most stable state during the conversion of substrate to product.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion - c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): The formation of the enzyme-substrate complex is a transient phenomenon crucial for catalysis.
Reason (R): The transition state structure is the most stable state during the conversion of substrate to product.
Reason (R): The transition state structure is the most stable state during the conversion of substrate to product.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false

|
Infinity Academy answered |
Assertion (A): The formation of the enzyme-substrate complex is indeed a transient phenomenon and is crucial for catalysis, as it facilitates the reaction by bringing the substrate into proximity with the active site of the enzyme and lowering the activation energy. This is true.
Reason (R): The transition state structure is actually the least stable state, not the most stable state, during the conversion of substrate to product. The transition state is an intermediate, high-energy configuration that occurs before the substrate is converted into the product. This makes the Reason false.
Thus, the Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
Reason (R): The transition state structure is actually the least stable state, not the most stable state, during the conversion of substrate to product. The transition state is an intermediate, high-energy configuration that occurs before the substrate is converted into the product. This makes the Reason false.
Thus, the Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?i. Polysaccharides are composed of long chains of monosaccharides and can be classified as homopolymers or heteropolymers.ii. Cellulose is a homopolymer made only of glucose and forms complex helical structures.iii. Starch serves as an energy reserve in plants and can form helical structures that bind iodine, producing a blue color.iv. Glycogen, found in animals, is a linear polysaccharide that does not have branches.- a) ii and iv
- b) i and iii
- c) i, ii and iii
- d) iii and iv
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. Polysaccharides are composed of long chains of monosaccharides and can be classified as homopolymers or heteropolymers.
ii. Cellulose is a homopolymer made only of glucose and forms complex helical structures.
iii. Starch serves as an energy reserve in plants and can form helical structures that bind iodine, producing a blue color.
iv. Glycogen, found in animals, is a linear polysaccharide that does not have branches.
a)
ii and iv
b)
i and iii
c)
i, ii and iii
d)
iii and iv

|
EduRev NEET answered |
- Statement i is correct because polysaccharides can indeed be classified as homopolymers (like cellulose, which is made only of glucose) or heteropolymers (which contain different types of monosaccharides).
- Statement ii is incorrect; while cellulose is a homopolymer of glucose, it does not form complex helical structures. Instead, it has a linear structure that forms microfibrils.
- Statement iii is correct; starch serves as an energy reserve in plants and forms helical structures that can bind iodine, resulting in a blue complex.
- Statement iv is incorrect; glycogen is a highly branched polysaccharide, not linear, which allows for rapid mobilization of glucose when needed.
Thus, the correct statements are those in Option B: i and iii.
Proteins are polymers of amino acids that are connected by __________- a)Vanderwaal linkages
- b)Glycosidic linkage
- c)Phosphodiester linkage
- d)Peptide linkage
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Proteins are polymers of amino acids that are connected by __________
a)
Vanderwaal linkages
b)
Glycosidic linkage
c)
Phosphodiester linkage
d)
Peptide linkage

|
Ambition Institute answered |
- Proteins are polymers of amino acids undergo dehydration to form a peptide linkage.
- Dipeptides are formed by a single peptide bond and a tripeptide through two peptide bonds and so on.
Diborane is a potential rocket fuel which undergoes combustion according to the reaction,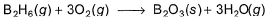 From the following data, enthalpy change for the combustion of diborane is
From the following data, enthalpy change for the combustion of diborane is
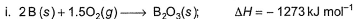
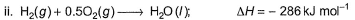

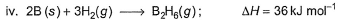
- a)-36 kJ mol-1
- b)-1237 kJ mol-1
- c)-2035 kJ mol-1
- d)-1639 kJ mol-1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Diborane is a potential rocket fuel which undergoes combustion according to the reaction,
From the following data, enthalpy change for the combustion of diborane is
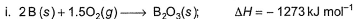
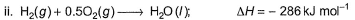

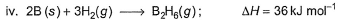
a)
-36 kJ mol-1
b)
-1237 kJ mol-1
c)
-2035 kJ mol-1
d)
-1639 kJ mol-1
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
On applying equation 1 + 3 times equation 2 minus equation 4 plus equation 3, we will get enthalpy change for the combustion of diborane.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?i. All amino acids contain an amino group and a carboxyl group attached to the same carbon atom.ii. There are only twenty types of amino acids that are found in proteins.iii. The R group in amino acids can vary and influences the properties of the amino acid.iv. Amino acids can only be classified as acidic or basic.- a) i, ii, and iii
- b) ii and iv
- c) i, iii, and iv
- d) i, ii, iii, and iv
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. All amino acids contain an amino group and a carboxyl group attached to the same carbon atom.
ii. There are only twenty types of amino acids that are found in proteins.
iii. The R group in amino acids can vary and influences the properties of the amino acid.
iv. Amino acids can only be classified as acidic or basic.
a)
i, ii, and iii
b)
ii and iv
c)
i, iii, and iv
d)
i, ii, iii, and iv

|
Bs Academy answered |
- Statement i is correct because all amino acids indeed have an amino group (-NH2) and a carboxyl group (-COOH) attached to the same α-carbon.
- Statement ii is also correct as there are exactly twenty standard amino acids that are incorporated into proteins.
- Statement iii is correct because the R group (side chain) varies among amino acids and determines their unique chemical properties.
- Statement iv is incorrect; while amino acids can be classified as acidic or basic, they can also be neutral and aromatic, making this statement false.
Thus, the correct statements are i, ii, and iii, leading to the answer being Option A.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?i. Enzymes require cofactors for catalytic activity, and the protein portion is known as the apoenzyme.ii. Prosthetic groups are loosely associated with the apoenzyme and can be easily removed.iii. Coenzymes are transiently associated with the apoenzyme and often derived from vitamins.iv. Metal ions serve as cofactors and are essential for the activity of certain enzymes.- a) i and ii
- b) iii and iv
- c) i, iii, and iv
- d) ii and iv
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. Enzymes require cofactors for catalytic activity, and the protein portion is known as the apoenzyme.
ii. Prosthetic groups are loosely associated with the apoenzyme and can be easily removed.
iii. Coenzymes are transiently associated with the apoenzyme and often derived from vitamins.
iv. Metal ions serve as cofactors and are essential for the activity of certain enzymes.
a)
i and ii
b)
iii and iv
c)
i, iii, and iv
d)
ii and iv

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
- Statement i is correct because enzymes do require cofactors to be catalytically active, and the protein part without the cofactor is indeed called the apoenzyme.
- Statement ii is incorrect; prosthetic groups are tightly bound to the apoenzyme, not loosely associated.
- Statement iii is correct because coenzymes are indeed transiently associated with the apoenzyme and are often derived from vitamins, such as NAD from niacin.
- Statement iv is correct as certain enzymes do require metal ions, which are essential for their catalytic activity, forming coordination bonds at the active site.
Thus, the correct combination of statements is i, iii, and iv, corresponding to Option C.
Tertiary structure of protein is formed by __________- a)Sulphide linkages between different amino acids
- b)Multiple chains of polypeptides held together by hydrogen bonds
- c)Peptide linkages between two amino acids
- d)Hydrogen bond formed by helical or pleated structure
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Tertiary structure of protein is formed by __________
a)
Sulphide linkages between different amino acids
b)
Multiple chains of polypeptides held together by hydrogen bonds
c)
Peptide linkages between two amino acids
d)
Hydrogen bond formed by helical or pleated structure

|
Bs Academy answered |
- Primary structure of protein is formed by peptide linkages between two amino acids.
- Secondary structure, i.e. α-Helix and β-Sheath, of protein is formed by hydrogen bonds.
- Tertiary structure of protein is formed by sulphide linkages between different amino acids Quaternary structure is formed when multiple chains of polypeptides held together by hydrogen bonds.
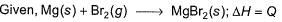
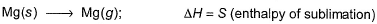
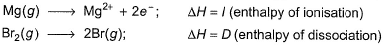
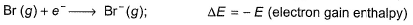
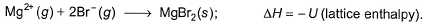 Thus,
Thus,- a)Q = S + I + D - E - U
- b)Q = S + 2I + D - E - U
- c)Q = S + 1 + D - 2E - U
- d)Q = S +1 + D - E + U
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Thus,
a)
Q = S + I + D - E - U
b)
Q = S + 2I + D - E - U
c)
Q = S + 1 + D - 2E - U
d)
Q = S +1 + D - E + U
|
|
Jhanvi Chakraborty answered |
Put the things we need as reactant on LHS the product on RHS. To do that, we will apply equation S+I+D-2E-U.
Which type of enzyme catalyzes the transfer of a group (other than hydrogen) between substrates?- a) Oxidoreductases
- b) Transferases
- c) Hydrolases
- d) Ligases
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of enzyme catalyzes the transfer of a group (other than hydrogen) between substrates?
a)
Oxidoreductases
b)
Transferases
c)
Hydrolases
d)
Ligases

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
Transferases are enzymes that facilitate the transfer of functional groups from one substrate to another, which is essential for various metabolic processes.
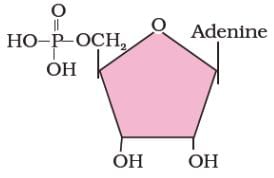
Identify the biomolecule shown in the structural diagram given below.
- a)Adenosine
- b)Adenylic acid
- c)d-Adenosine
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the biomolecule shown in the structural diagram given below.


a)
Adenosine
b)
Adenylic acid
c)
d-Adenosine
d)
None of these

|
EduRev NEET answered |
The given molecule is adenylic acid. It is a nucleotide found in RNA. It is an ester of phosphoric acid with the nucleoside adenosine. It consists of a phosphate group, a pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine.
Chapter doubts & questions for August Week 3 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of August Week 3 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup