All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of December Week 2 for NEET Exam
Read the following :
i. Blood vessels include arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood from heart to body parts and veins bring back blood from body parts to heart.
ii. The blood vessel which carry blood from heart to lungs is pulmonary artery and it carries oxygenated blood.- a)Statement ii) is correct and i) is wrong.
- b)both are correct
- c)Statement ii) is wrong and i) is correct.
- d)both are wrong
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following :
i. Blood vessels include arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood from heart to body parts and veins bring back blood from body parts to heart.
ii. The blood vessel which carry blood from heart to lungs is pulmonary artery and it carries oxygenated blood.
i. Blood vessels include arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood from heart to body parts and veins bring back blood from body parts to heart.
ii. The blood vessel which carry blood from heart to lungs is pulmonary artery and it carries oxygenated blood.
a)
Statement ii) is correct and i) is wrong.
b)
both are correct
c)
Statement ii) is wrong and i) is correct.
d)
both are wrong
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
- The arteries carry blood from the heart to all over body parts. Hence, statement (i) is correct.
- The vessels which carry blood from the heart to the lungs is the pulmonary artery but it carries deoxygenated blood. Hence, statement (ii) is correct.
Which wall would allow the flow of thermal energy between systems A and B to achieve thermal equilibrium?
- a)Diathermic wall
- b)Adiabatic wall
- c)Diadiabatic wall
- d)Thermal wall
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which wall would allow the flow of thermal energy between systems A and B to achieve thermal equilibrium?

a)
Diathermic wall
b)
Adiabatic wall
c)
Diadiabatic wall
d)
Thermal wall
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Wall that permits *heat" to flow through them,such as engine block is called diathermic wall.
wall Perfectly insulating ball that doesn't allow the flow heat to them are called adiabatic walls.
wall Perfectly insulating ball that doesn't allow the flow heat to them are called adiabatic walls.
The specialised patch of modified heart muscles from where contraction initiates, is/are :- a)Pacesetter of heart
- b)both SAN and AVN together
- c)Pacemaker of heart
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The specialised patch of modified heart muscles from where contraction initiates, is/are :
a)
Pacesetter of heart
b)
both SAN and AVN together
c)
Pacemaker of heart
d)
none of these
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
- The nodal musculature has the ability to generate action potentials without any external stimuli.
- The number of action potentials that could be generated in a minute varies at different parts of the nodal system.
- The SAN can generate the maximum number of action potentials and is responsible for initiating and maintaining the rhythmic contractile activity of the heart.
- Therefore, it is called the pacemaker.
Which is true about conformers of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane?Which is true about conformers of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane?
a) The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
b) In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
c) In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
d) The most stable conformer is non-polar - a)The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
- b)In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
- c)In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
- d)The most stable conformer is non-polar
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is true about conformers of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane?
Which is true about conformers of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane?
a) The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
b) In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
c) In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
d) The most stable conformer is non-polar
a) The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
b) In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
c) In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
d) The most stable conformer is non-polar
a)
The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
b)
In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
c)
In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
d)
The most stable conformer is non-polar
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The correct answer is option D
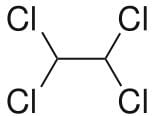
This molecule is non-polar two Cl atoms in one carbon atom cancel the polarity other two Cl atoms on the next carbon.
Also all the Cl atoms are at max distance from each other so max. Stability due to less repulsion between Cl atoms. Dihedral angle between H and Cl is 60°

This molecule is non-polar two Cl atoms in one carbon atom cancel the polarity other two Cl atoms on the next carbon.
Also all the Cl atoms are at max distance from each other so max. Stability due to less repulsion between Cl atoms. Dihedral angle between H and Cl is 60°
In the systemic circulation, blood vessel that carries blood from the intestine to liver is named :- a)Hepatic portal arch
- b)none of these
- c)Hepatic portal artery
- d)Hepatic portal vein
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the systemic circulation, blood vessel that carries blood from the intestine to liver is named :
a)
Hepatic portal arch
b)
none of these
c)
Hepatic portal artery
d)
Hepatic portal vein
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
Lienal vein is an old term for splenic vein. The portal vein or hepatic portal vein is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents.
The internal energy and the work done by a system decreases by same amount then- a)The temperature must decrease
- b)The process must be adiabatic
- c)The process must be isothermal
- d)both a and b
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The internal energy and the work done by a system decreases by same amount then
a)
The temperature must decrease
b)
The process must be adiabatic
c)
The process must be isothermal
d)
both a and b
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The internal energy of a system decreases by the same amount as the work done by the system.
Change in internal energy=work done+heat exchange
change in internal energy=work done if process has no heat exchange, i.e. it's adiabatic and the temperature must decrease
Change in internal energy=work done+heat exchange
change in internal energy=work done if process has no heat exchange, i.e. it's adiabatic and the temperature must decrease
Rh incompatibility develops when :- a)foetus is Rh-ve and father is Rh+ve
- b)foetus is Rh+ve and mother is Rh-ve
- c)foetus is Rh-ve and mother is Rh+ve
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rh incompatibility develops when :
a)
foetus is Rh-ve and father is Rh+ve
b)
foetus is Rh+ve and mother is Rh-ve
c)
foetus is Rh-ve and mother is Rh+ve
d)
None of these

|
Bhargavi Choudhury answered |
A special case of Rh incompatibility (mismatching) has been observed between the Rh-veblood of a pregnant mother with Rh+ve blood of the foetus.
Which of the following statements doesn’t hold true for blood clotting cascade?
i. Ruptured platelets release thromboplastin.
ii. Prothrombinis converted into thrombin in the presence of vitamin K and Na+ions.
iii. Fibrinogen is converted into fibrin through enzymatic action of thrombin in the presence of Ca++ions
iv. Fibrin makes clot via process of polymerisation.- a)only statement i) and iv) are wrong
- b)only statement ii) and iii) are wrong
- c)all statements are wrong
- d)only statement iv) is wrong
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements doesn’t hold true for blood clotting cascade?
i. Ruptured platelets release thromboplastin.
ii. Prothrombinis converted into thrombin in the presence of vitamin K and Na+ions.
iii. Fibrinogen is converted into fibrin through enzymatic action of thrombin in the presence of Ca++ions
iv. Fibrin makes clot via process of polymerisation.
i. Ruptured platelets release thromboplastin.
ii. Prothrombinis converted into thrombin in the presence of vitamin K and Na+ions.
iii. Fibrinogen is converted into fibrin through enzymatic action of thrombin in the presence of Ca++ions
iv. Fibrin makes clot via process of polymerisation.
a)
only statement i) and iv) are wrong
b)
only statement ii) and iii) are wrong
c)
all statements are wrong
d)
only statement iv) is wrong

|
Prakash Gharte answered |
Second statement is wrong because prothrombin is converted into thrombin in the presence of enzyme thrombokinase and Ca++ ions and third statement is right
First law of thermodynamics tells us:- a)the nature of the process taking place
- b)the direction in which a given process can take place
- c)to what extent the process takes place
- d)that heat supplied is used to carry out the process
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
First law of thermodynamics tells us:
a)
the nature of the process taking place
b)
the direction in which a given process can take place
c)
to what extent the process takes place
d)
that heat supplied is used to carry out the process
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
First law of thermodynamics is based on law of conservation of energy i.e. energy supplied to a system has to be used in raising the internal energy of the system. So heat supplied is used to carry out the process.
∆U = Q + W.
∆U = Q + W.
The Zeroth law leads to the concept of- a)temprature
- b)heat
- c)internal energy
- d)work
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Zeroth law leads to the concept of
a)
temprature
b)
heat
c)
internal energy
d)
work
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Zeroth law states that if two thermodynamic systems are each in thermal equilibrium with a third one, then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other. Thus as it deals with thermal equilibrium it is very clear that it is a concept of temperature.
Which is not true regarding conformers of ethane?- a)Theoretically infinite conformers exist
- b)Staggered conformer has lower torsional strain than eclipsed one
- c)Increasing temperature increases the percentage of eclipsed conformer
- d)By precise experimental setup, staggered conformer can be separated out of system
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is not true regarding conformers of ethane?
a)
Theoretically infinite conformers exist
b)
Staggered conformer has lower torsional strain than eclipsed one
c)
Increasing temperature increases the percentage of eclipsed conformer
d)
By precise experimental setup, staggered conformer can be separated out of system
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
The correct answer is Option D.
Although conformers differ in potential energy and stability, the difference is so small that it does not allow their practical separation.
Although conformers differ in potential energy and stability, the difference is so small that it does not allow their practical separation.
The First Law of Thermodynamics states that:- a)ΔQ - W = ΔU
- b)ΔQ - ΔW = U
- c)ΔQ - ΔU = ΔW
- d)Q - W = U
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The First Law of Thermodynamics states that:
a)
ΔQ - W = ΔU
b)
ΔQ - ΔW = U
c)
ΔQ - ΔU = ΔW
d)
Q - W = U
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy of an isolated system is constant. Energy can be transformed from one form to another, but can neither be created nor destroyed.
According to this law, some of the heat given to system is used to change the internal energy while the rest in doing work by the system. Mathematically,
ΔQ=ΔU+ΔW
where,
ΔQ = Heat supplied to the system
ΔW= Work done by the system.
ΔU = Change in the internal energy of the system.
If Q is positive, then there is a net heat transfer into the system, if W is positive, then there is work done by the system. So positive Q adds energy to the system and positive W takes energy from the system.
It can also be represented as ΔU=ΔQ-ΔW
We can say that internal energy tends to increase when heat is given to the system and vice versa.
Which of the following statement is true for a thermodynamical system where ∆U is the increase in internal energy and ∆W work done respectively?- a)∆U = ∆W in isothermal process
- b)∆U = ∆W in a adiabatic process
- c)∆U= -∆W in case of ideal gas
- d)∆U= -∆W in an adiabatic process
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is true for a thermodynamical system where ∆U is the increase in internal energy and ∆W work done respectively?
a)
∆U = ∆W in isothermal process
b)
∆U = ∆W in a adiabatic process
c)
∆U= -∆W in case of ideal gas
d)
∆U= -∆W in an adiabatic process
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
∆ U = ∆ Q - ∆ W
In an adiabatic process ∆Q is zero, therefore
∆ U = - ∆ W
In an adiabatic process ∆Q is zero, therefore
∆ U = - ∆ W
Which of the following correctly ranks the cycloalkanes in order of increasing ring strain per methylene group? - a)Cyclopropane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopentane < Cyclohexane
- b)Cyclohexane < Cyclopentane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopropane
- c)Cyclohexane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopentane < Cyclopropane
- d)Cyclopropane < Cyclopentane < Cyclobutane < Cyclohexane
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following correctly ranks the cycloalkanes in order of increasing ring strain per methylene group?
a)
Cyclopropane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopentane < Cyclohexane
b)
Cyclohexane < Cyclopentane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopropane
c)
Cyclohexane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopentane < Cyclopropane
d)
Cyclopropane < Cyclopentane < Cyclobutane < Cyclohexane
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
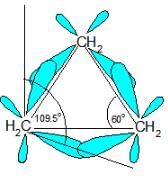
The C-C-C bond angles in cyclopropane (60o) and cyclobutane (90o) are much different than the ideal bond angle of 109.5o.This bond angle causes cyclopropane and cyclobutane to have a high ring strain. However, molecules, such as cyclohexane and cyclopentane, would have a much lower ring strain because the bond angle between the carbons is much closer to 109.5o.

The C-C-C bond angles in cyclopropane (60o) and cyclobutane (90o) are much different than the ideal bond angle of 109.5o.This bond angle causes cyclopropane and cyclobutane to have a high ring strain. However, molecules, such as cyclohexane and cyclopentane, would have a much lower ring strain because the bond angle between the carbons is much closer to 109.5o.
Which,of the following correctly lists the conformations of cyclohexane in order of increasing potential energies?- a)Chair < Boat < Twist boat < Half-chair
- b)Half-chair < Boat < Twist boat < Chair
- c)Chair < Twist boat < Half-chair < Boat
- d)Chair < Twist boat < Boat < Half-chair
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which,of the following correctly lists the conformations of cyclohexane in order of increasing potential energies?
a)
Chair < Boat < Twist boat < Half-chair
b)
Half-chair < Boat < Twist boat < Chair
c)
Chair < Twist boat < Half-chair < Boat
d)
Chair < Twist boat < Boat < Half-chair
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Correct answer is option D
Chair >Twist boat > Boat > Half-chair
above is the stability order of
the conformed.
Stability is inversely proportional to potential energy.
the conformed.
Stability is inversely proportional to potential energy.
Suppose we have a box filled with gas and a piston is also attached at the top of the box.What are the ways of changing the state of gas (and hence its internal energy)? Answer could be more than one choice.- a)Bring box in contact with a body with higher temperature
- b)Move the box so that it has kinetic energy
- c)Pushing the piston down so as to do work on the system
- d)both a and c
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Suppose we have a box filled with gas and a piston is also attached at the top of the box.What are the ways of changing the state of gas (and hence its internal energy)? Answer could be more than one choice.
a)
Bring box in contact with a body with higher temperature
b)
Move the box so that it has kinetic energy
c)
Pushing the piston down so as to do work on the system
d)
both a and c
|
|
Shail Majumdar answered |
**Explanation:**
To understand why the correct answer is option 'D', let's analyze each option one by one:
**a) Bring box in contact with a body with higher temperature:**
When a box filled with gas is brought in contact with a body at a higher temperature, heat flows from the higher temperature body to the gas inside the box. This increases the temperature and hence the internal energy of the gas. Therefore, this option is valid for changing the state of the gas.
**b) Move the box so that it has kinetic energy:**
Moving the box so that it has kinetic energy does not directly change the state of the gas. It only changes the position and motion of the box. However, if the box is connected to the piston, and the piston is not fixed, the kinetic energy of the box can be transferred to the gas by pushing the piston down. This will do work on the system and change the state of the gas. Therefore, this option indirectly allows for changing the state of the gas.
**c) Pushing the piston down so as to do work on the system:**
Pushing the piston down compresses the gas inside the box, reducing its volume. This work is done on the system, and as a result, the internal energy of the gas increases. Therefore, this option is valid for changing the state of the gas.
**d) Both a and c:**
From the explanations above, it is clear that both options a and c allow for changing the state of the gas. Bringing the box in contact with a body at a higher temperature increases the internal energy of the gas, and pushing the piston down to do work on the system also increases the internal energy of the gas. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - both a and c.
By using both options a and c, we can effectively change the state of the gas by increasing its internal energy through heat transfer and work done on the system.
To understand why the correct answer is option 'D', let's analyze each option one by one:
**a) Bring box in contact with a body with higher temperature:**
When a box filled with gas is brought in contact with a body at a higher temperature, heat flows from the higher temperature body to the gas inside the box. This increases the temperature and hence the internal energy of the gas. Therefore, this option is valid for changing the state of the gas.
**b) Move the box so that it has kinetic energy:**
Moving the box so that it has kinetic energy does not directly change the state of the gas. It only changes the position and motion of the box. However, if the box is connected to the piston, and the piston is not fixed, the kinetic energy of the box can be transferred to the gas by pushing the piston down. This will do work on the system and change the state of the gas. Therefore, this option indirectly allows for changing the state of the gas.
**c) Pushing the piston down so as to do work on the system:**
Pushing the piston down compresses the gas inside the box, reducing its volume. This work is done on the system, and as a result, the internal energy of the gas increases. Therefore, this option is valid for changing the state of the gas.
**d) Both a and c:**
From the explanations above, it is clear that both options a and c allow for changing the state of the gas. Bringing the box in contact with a body at a higher temperature increases the internal energy of the gas, and pushing the piston down to do work on the system also increases the internal energy of the gas. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - both a and c.
By using both options a and c, we can effectively change the state of the gas by increasing its internal energy through heat transfer and work done on the system.
Hot coffee in a thermos flask is shaken vigorously, considering it as a system which of the statement is not true?- a)Temperature of the system rises
- b)Internal energy of the coffee increased
- c)Heat energy has been added to coffee
- d)Work is done on the system
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Hot coffee in a thermos flask is shaken vigorously, considering it as a system which of the statement is not true?
a)
Temperature of the system rises
b)
Internal energy of the coffee increased
c)
Heat energy has been added to coffee
d)
Work is done on the system
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
No, heat is not transferred as the flask is insulated from the surroundings ∴dQ=0
Internal energy of a system increases by 60 J when 140 Jof heat is added to the gaseous system. The amount of work done would be:- a)80 J
- b)100 J
- c)200 J
- d)140 J
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Internal energy of a system increases by 60 J when 140 Jof heat is added to the gaseous system. The amount of work done would be:
a)
80 J
b)
100 J
c)
200 J
d)
140 J
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
We know that dq = dU + dW
And as dU = 60 and dq = 140J
We get dW = 140 - 60 = 80J
And as dU = 60 and dq = 140J
We get dW = 140 - 60 = 80J
Which structure separates the right and left atria of the heart?- a)Interventricular septum
- b)Interatrial septum
- c)Atrio-ventricular septum
- d)Pericardium
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which structure separates the right and left atria of the heart?
a)
Interventricular septum
b)
Interatrial septum
c)
Atrio-ventricular septum
d)
Pericardium
|
|
Anisha Dey answered |
Interatrial Septum
The structure that separates the right and left atria of the heart is called the interatrial septum. This septum is a wall of tissue that divides the upper chambers of the heart, allowing for the separation of deoxygenated blood (in the right atrium) from oxygenated blood (in the left atrium).
Function
- The interatrial septum plays a crucial role in preventing the mixing of oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood in the heart.
- It ensures that blood flows in a unidirectional manner through the heart, allowing for proper circulation throughout the body.
Composition
- The interatrial septum is made up of various structures including the septum primum, septum secundum, and the foramen ovale (which is a hole present in fetal hearts that allows blood to bypass the lungs).
Development
- During fetal development, the interatrial septum undergoes changes to allow for the proper functioning of the heart after birth. The closure of the foramen ovale is one such crucial step in the development of the interatrial septum.
Clinical Relevance
- Certain congenital heart defects, such as atrial septal defects (ASDs), can occur when there is an abnormal opening in the interatrial septum. This can lead to mixing of blood between the atria and affect heart function.
In summary, the interatrial septum is an important anatomical structure in the heart that ensures proper circulation of blood by separating the right and left atria.
The structure that separates the right and left atria of the heart is called the interatrial septum. This septum is a wall of tissue that divides the upper chambers of the heart, allowing for the separation of deoxygenated blood (in the right atrium) from oxygenated blood (in the left atrium).
Function
- The interatrial septum plays a crucial role in preventing the mixing of oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood in the heart.
- It ensures that blood flows in a unidirectional manner through the heart, allowing for proper circulation throughout the body.
Composition
- The interatrial septum is made up of various structures including the septum primum, septum secundum, and the foramen ovale (which is a hole present in fetal hearts that allows blood to bypass the lungs).
Development
- During fetal development, the interatrial septum undergoes changes to allow for the proper functioning of the heart after birth. The closure of the foramen ovale is one such crucial step in the development of the interatrial septum.
Clinical Relevance
- Certain congenital heart defects, such as atrial septal defects (ASDs), can occur when there is an abnormal opening in the interatrial septum. This can lead to mixing of blood between the atria and affect heart function.
In summary, the interatrial septum is an important anatomical structure in the heart that ensures proper circulation of blood by separating the right and left atria.
Assertion (A): Coronary artery disease is primarily caused by a buildup of calcium, fat, cholesterol, and fibrous tissues in the arteries.Reason (R): This accumulation leads to the narrowing of the arterial lumen, which reduces blood flow to the heart muscle.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Coronary artery disease is primarily caused by a buildup of calcium, fat, cholesterol, and fibrous tissues in the arteries.
Reason (R): This accumulation leads to the narrowing of the arterial lumen, which reduces blood flow to the heart muscle.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false

|
Bs Academy answered |
- Assertion Analysis: The assertion is true as coronary artery disease (CAD) is indeed caused by the buildup of substances such as calcium, fat, and cholesterol in the arterial walls.
- Reason Analysis: The reason is also true because the described accumulation does lead to the narrowing of the arteries, which is a key characteristic of CAD.
- Explanation Relation: The reason directly explains the assertion as it describes the process through which CAD occurs. Thus, both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason accurately explains the assertion.
Line in NCERT: "Coronary Artery Disease, often referred to as atherosclerosis, affects the vessels that supply blood to the heart muscle. It is caused by deposits of calcium, fat, cholesterol and fibrous tissues, which makes the lumen of arteries narrower."
In which organisms is an open circulatory system typically found?- a) Arthropods and molluscs
- b) Vertebrates
- c) Annelids and chordates
- d) Fishes and amphibians
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In which organisms is an open circulatory system typically found?
a)
Arthropods and molluscs
b)
Vertebrates
c)
Annelids and chordates
d)
Fishes and amphibians
|
|
Sagnik Jain answered |
Open Circulatory System Overview
An open circulatory system is a type of circulatory system where blood is not always contained within blood vessels. Instead, the blood, or hemolymph, bathes the organs directly in a body cavity known as a hemocoel.
Organisms with Open Circulatory Systems
- Arthropods: This group includes insects, arachnids, and crustaceans. In these organisms, the heart pumps hemolymph into the hemocoel, where it circulates freely around the tissues and organs. The low pressure of this system makes it suitable for small-bodied animals that do not require rapid blood circulation.
- Molluscs: Many molluscs, such as snails and clams, also possess an open circulatory system. Their hearts pump hemolymph into sinuses, where it directly contacts the organs. While cephalopods (like squids and octopuses) have a closed circulatory system, most other molluscs utilize the open type.
Comparison with Other Organisms
- Vertebrates: These organisms have a closed circulatory system where blood circulates within vessels, ensuring efficient transport of oxygen and nutrients, which is crucial for their larger and more complex body structures.
- Annelids and Chordates: Annelids (like earthworms) possess a closed circulatory system, while chordates (including mammals, birds, reptiles) have evolved a more complex closed system.
- Fishes and Amphibians: Both groups have a closed circulatory system. Fishes have a two-chambered heart, while amphibians usually possess a three-chambered heart, allowing for more efficient oxygenation of blood.
Conclusion
In summary, open circulatory systems are characteristic of arthropods and many molluscs, making option 'A' the correct answer. This system suits the physiological needs of these organisms by allowing sufficient nutrient and gas exchange while conserving energy.
An open circulatory system is a type of circulatory system where blood is not always contained within blood vessels. Instead, the blood, or hemolymph, bathes the organs directly in a body cavity known as a hemocoel.
Organisms with Open Circulatory Systems
- Arthropods: This group includes insects, arachnids, and crustaceans. In these organisms, the heart pumps hemolymph into the hemocoel, where it circulates freely around the tissues and organs. The low pressure of this system makes it suitable for small-bodied animals that do not require rapid blood circulation.
- Molluscs: Many molluscs, such as snails and clams, also possess an open circulatory system. Their hearts pump hemolymph into sinuses, where it directly contacts the organs. While cephalopods (like squids and octopuses) have a closed circulatory system, most other molluscs utilize the open type.
Comparison with Other Organisms
- Vertebrates: These organisms have a closed circulatory system where blood circulates within vessels, ensuring efficient transport of oxygen and nutrients, which is crucial for their larger and more complex body structures.
- Annelids and Chordates: Annelids (like earthworms) possess a closed circulatory system, while chordates (including mammals, birds, reptiles) have evolved a more complex closed system.
- Fishes and Amphibians: Both groups have a closed circulatory system. Fishes have a two-chambered heart, while amphibians usually possess a three-chambered heart, allowing for more efficient oxygenation of blood.
Conclusion
In summary, open circulatory systems are characteristic of arthropods and many molluscs, making option 'A' the correct answer. This system suits the physiological needs of these organisms by allowing sufficient nutrient and gas exchange while conserving energy.
What is the primary cause of coronary artery disease (CAD)?- a)Excessive contraction of the heart muscle
- b)Infections in the heart muscle
- c)Deposits of calcium, fat, cholesterol, and fibrous tissues in the arteries
- d)Overproduction of adrenal medullary hormones affecting the heart
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Excessive contraction of the heart muscle
b)
Infections in the heart muscle
c)
Deposits of calcium, fat, cholesterol, and fibrous tissues in the arteries
d)
Overproduction of adrenal medullary hormones affecting the heart

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is primarily caused by the buildup of deposits such as calcium, fat, cholesterol, and fibrous tissues within the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle. This buildup leads to the narrowing of the arterial lumen, which can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of heart attack and other cardiac complications. This process is often referred to as atherosclerosis and is the leading cause of CAD.
The first law of thermodynamics1. Is a restatement of the principle of conservation of energy as applied to heat energy
2. Is the basis for the definition of internal energy
3. Is basis for the definition of temperature
4. asserts the impossibility of achieving an absolute zero temperature.- a)1 and 2
- b)only 1
- c)1 and 3
- d)1,2 and 4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The first law of thermodynamics
1. Is a restatement of the principle of conservation of energy as applied to heat energy
2. Is the basis for the definition of internal energy
3. Is basis for the definition of temperature
4. asserts the impossibility of achieving an absolute zero temperature.
2. Is the basis for the definition of internal energy
3. Is basis for the definition of temperature
4. asserts the impossibility of achieving an absolute zero temperature.
a)
1 and 2
b)
only 1
c)
1 and 3
d)
1,2 and 4
|
|
Stuti Joshi answered |
The change is internal energy if the system is equal to the difference between the heat added to the system and work done by the system.


Where does the atrioventricular bundle (AV bundle) emerge from after passing through the atrioventricular septa?- a) Left atrium
- b) Interventricular septum
- c) Right ventricle
- d) Pulmonary artery
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Where does the atrioventricular bundle (AV bundle) emerge from after passing through the atrioventricular septa?
a)
Left atrium
b)
Interventricular septum
c)
Right ventricle
d)
Pulmonary artery

|
Top Rankers answered |
The atrioventricular bundle (AV bundle) is a bundle of nodal fibers that continues from the atrioventricular node (AVN) and passes through the atrioventricular septa. It emerges on the top of the interventricular septum, where it immediately divides into a right and left bundle. These branches further propagate into minute fibers throughout the ventricular musculature of the respective sides, playing a crucial role in coordinating the electrical impulses that regulate the contraction of the ventricles.
Which type of heart structure is present in amphibians and reptiles, except crocodiles?- a) 2-chambered heart with an atrium and a ventricle
- b) 3-chambered heart with two atria and a single ventricle
- c) 4-chambered heart with two atria and two ventricles
- d) 5-chambered heart with multiple atria and ventricles
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of heart structure is present in amphibians and reptiles, except crocodiles?
a)
2-chambered heart with an atrium and a ventricle
b)
3-chambered heart with two atria and a single ventricle
c)
4-chambered heart with two atria and two ventricles
d)
5-chambered heart with multiple atria and ventricles

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
Amphibians and reptiles, except crocodiles, possess a 3-chambered heart with two atria and a single ventricle. This heart structure allows for a degree of separation between oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, although there is some mixing in the single ventricle before circulation. This setup contrasts with the more efficient 4-chambered heart found in crocodiles, birds, and mammals.
Line in NCERT: "Amphibians and the reptiles (except crocodiles) have a 3-chambered heart with two atria and a single ventricle."
Which of the following cycloalkanes exhibits the greatest molar heat of combustion per —CH2 — group?- a)Methylcyclobutane
- b)Cyclopentane
- c)Cyclobutane
- d)Cyclopropane
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following cycloalkanes exhibits the greatest molar heat of combustion per —CH2 — group?
a)
Methylcyclobutane
b)
Cyclopentane
c)
Cyclobutane
d)
Cyclopropane

|
Nishanth Verma answered |
Cyclopropane is a cycloalkane molecule with the molecular formula C3H6, consisting of three carbon atoms linked to each other to form a ring, with each carbon atom bearing two hydrogen atoms resulting in D3h molecular symmetry. The small size of the ring creates substantial ring strain in the structure.
The correct statement concerning conformers of 1,2-dichloroethane is- a)it's gauche conformer has higher potential energy than an eclipsed conformer in which H—Cl atoms are eclipsing
- b)syn-periplanar conformer is most stable
- c)increasing temperature decreases dipole moment of 1,2-dichloroethane
- d)the two gauche conformers are enantiomers
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statement concerning conformers of 1,2-dichloroethane is
a)
it's gauche conformer has higher potential energy than an eclipsed conformer in which H—Cl atoms are eclipsing
b)
syn-periplanar conformer is most stable
c)
increasing temperature decreases dipole moment of 1,2-dichloroethane
d)
the two gauche conformers are enantiomers
|
|
Rishabh Malhotra answered |
Option D is correct answer
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.The molecular formula C5H12 contains how many isomeric alkanes?- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
The molecular formula C5H12 contains how many isomeric alkanes?
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4

|
Jay Chakraborty answered |
n-pentane, 2-ethylpropane, and 2-methylbutane are the 3 isomeric alkanes of C5H12 (pentane).
What is the primary role of thrombin in the blood coagulation process?- a) It converts fibrinogen into fibrin.
- b) It activates prothrombin.
- c) It initiates the cascade reaction of clotting factors.
- d) It releases calcium ions into the bloodstream.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary role of thrombin in the blood coagulation process?
a)
It converts fibrinogen into fibrin.
b)
It activates prothrombin.
c)
It initiates the cascade reaction of clotting factors.
d)
It releases calcium ions into the bloodstream.

|
Bs Academy answered |
Thrombin plays a crucial role in the coagulation process by converting fibrinogen, an inactive plasma protein, into fibrin, which forms the meshwork that constitutes a blood clot. This conversion is essential for the formation of a stable clot that traps blood cells and prevents further bleeding. An interesting fact about thrombin is that it not only aids in clot formation but also has roles in wound healing and inflammation, showcasing its importance beyond just coagulation.
What is the primary function of the sympathetic nerves in regulating cardiac activity?- a)They decrease the rate of the heart beat and the speed of conduction of action potentials.
- b)They increase the rate of the heart beat and the strength of ventricular contractions.
- c)They regulate blood pressure by decreasing the cardiac output.
- d)They directly control the deposition of calcium and cholesterol in coronary arteries.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
They decrease the rate of the heart beat and the speed of conduction of action potentials.
b)
They increase the rate of the heart beat and the strength of ventricular contractions.
c)
They regulate blood pressure by decreasing the cardiac output.
d)
They directly control the deposition of calcium and cholesterol in coronary arteries.
|
|
Pankaj Dasgupta answered |
Primary Function of Sympathetic Nerves
The sympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in regulating cardiac activity, especially during times of stress or physical exertion. Its primary function is to prepare the body for "fight or flight" responses.
Key Points:
- Increased Heart Rate:
Sympathetic nerves release neurotransmitters, primarily norepinephrine, which bind to beta-adrenergic receptors in the heart. This action leads to an increase in the heart rate (chronotropy).
- Enhanced Ventricular Contractions:
The sympathetic stimulation also strengthens the contractions of the ventricular muscles (inotropy). This means that each heartbeat pumps a greater volume of blood, increasing the efficiency of the heart.
- Improved Conduction Velocity:
Sympathetic activation accelerates the conduction of electrical impulses through the heart's conduction system, particularly in the atrioventricular (AV) node, which further supports the increased heart rate.
- Overall Cardiac Output:
The combination of increased heart rate and stronger contractions significantly boosts cardiac output, which is essential during physical activities or stress responses.
Conclusion:
Option 'B' is correct because the primary function of the sympathetic nerves in regulating cardiac activity is to increase both the rate of the heart beat and the strength of ventricular contractions. This mechanism is vital for meeting the body's heightened demand for oxygen and nutrients during periods of stress or exertion.
The sympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in regulating cardiac activity, especially during times of stress or physical exertion. Its primary function is to prepare the body for "fight or flight" responses.
Key Points:
- Increased Heart Rate:
Sympathetic nerves release neurotransmitters, primarily norepinephrine, which bind to beta-adrenergic receptors in the heart. This action leads to an increase in the heart rate (chronotropy).
- Enhanced Ventricular Contractions:
The sympathetic stimulation also strengthens the contractions of the ventricular muscles (inotropy). This means that each heartbeat pumps a greater volume of blood, increasing the efficiency of the heart.
- Improved Conduction Velocity:
Sympathetic activation accelerates the conduction of electrical impulses through the heart's conduction system, particularly in the atrioventricular (AV) node, which further supports the increased heart rate.
- Overall Cardiac Output:
The combination of increased heart rate and stronger contractions significantly boosts cardiac output, which is essential during physical activities or stress responses.
Conclusion:
Option 'B' is correct because the primary function of the sympathetic nerves in regulating cardiac activity is to increase both the rate of the heart beat and the strength of ventricular contractions. This mechanism is vital for meeting the body's heightened demand for oxygen and nutrients during periods of stress or exertion.
What distinguishes the circulatory pathways in birds and mammals from those in fishes and amphibians?
- a)Presence of a single circulation system
- b)Double circulation system
- c)Mixing of deoxygenated and oxygenated blood in the heart
- d)3-chambered heart structure
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What distinguishes the circulatory pathways in birds and mammals from those in fishes and amphibians?
a)
Presence of a single circulation system
b)
Double circulation system
c)
Mixing of deoxygenated and oxygenated blood in the heart
d)
3-chambered heart structure

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Birds and mammals have a double circulation system, where oxygenated and deoxygenated blood are kept separate throughout circulation. This setup allows for more efficient delivery of oxygen to the body tissues. In contrast, fishes and amphibians have systems that involve mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in the heart, leading to less efficient transport of oxygen.
What is relationship between the following Fischer Projections?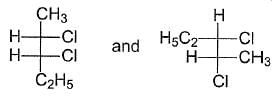
- a)Enantiomers
- b)Conformers
- c)Diastereomers
- d)Structural Isomers
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is relationship between the following Fischer Projections?
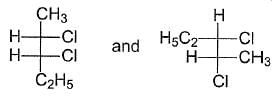
a)
Enantiomers
b)
Conformers
c)
Diastereomers
d)
Structural Isomers

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
The Fischer Projections represent different types of stereoisomers. Here’s a breakdown of their relationships:
- Enantiomers: These are mirror images of each other and are not superimposable.
- Conformers: These are different spatial orientations of the same molecule, resulting from rotation around single bonds.
- Diastereomers: These are stereoisomers that are not mirror images of one another. They have different physical properties.
- Structural Isomers: These differ in the connectivity of their atoms, leading to different compounds.
The correct relationship for the given Fischer Projections is diastereomers.
The structure below are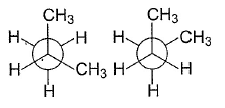
- a)not isomers
- b)conformers
- c)enantiomers
- d)structural isomers
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The structure below are
a)
not isomers
b)
conformers
c)
enantiomers
d)
structural isomers

|
Msb Srinivas answered |
The methyl group shifts from one carbon to another.they are positional isomers i.e a type of structural isomers
The given figure shows schematic plan of blood circulation in humans with labels A to D. Identify the labels and select the correct option.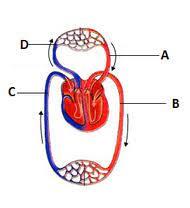
- a)C - Pulmonary artery
- b) D - Dorsal aorta
- c)A - Pulmonary vein
- d)B - Vena cava
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The given figure shows schematic plan of blood circulation in humans with labels A to D. Identify the labels and select the correct option.
a)
C - Pulmonary artery
b)
D - Dorsal aorta
c)
A - Pulmonary vein
d)
B - Vena cava

|
Bs Academy answered |
A- Pulmonary vein
B- Dorsal aorta
C- Vena cava
D- Pulmonary artery
B- Dorsal aorta
C- Vena cava
D- Pulmonary artery
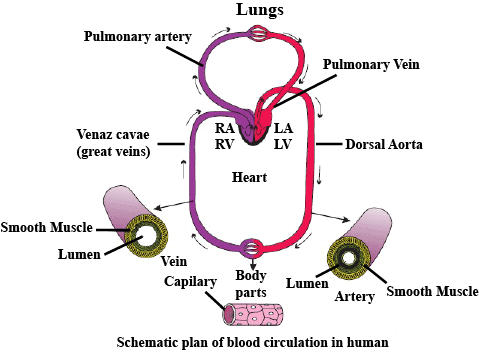
Line in NCERT: "Pulmonary artery" "Pulmonary Vein" "Dorsal aorta" "Vena cava"
Chapter doubts & questions for December Week 2 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of December Week 2 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









