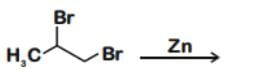All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of January Week 3 for NEET Exam
Out of the following compounds , which will be have a zero dipole moment.- a)1,1 - dichloroethylene
- b)cis-1,2-dichlorethylene
- c)trans-1,2-dichlorethylene
- d)none of these.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Out of the following compounds , which will be have a zero dipole moment.
a)
1,1 - dichloroethylene
b)
cis-1,2-dichlorethylene
c)
trans-1,2-dichlorethylene
d)
none of these.
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
In case of trans-1,2-dichloroethylene
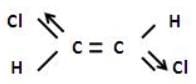
The net dipole moment is zero but in case of cis -1,2 -dicholorethylene.
There is some resultant dipole moment.
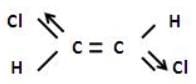
The net dipole moment is zero but in case of cis -1,2 -dicholorethylene.
There is some resultant dipole moment.
Which among these is not a structural isomer of the compound C4H8?- a)But-1-ene
- b)But-2-ene
- c)But-3-ene
- d)2-methylpropene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among these is not a structural isomer of the compound C4H8?
a)
But-1-ene
b)
But-2-ene
c)
But-3-ene
d)
2-methylpropene

|
Saqib Shabir answered |
The answer is c. But-3-ene. But-3-ene is not a structural isomer of C4H8 because it is the same molecule as But-1-ene, just numbered differently. The structural isomers of C4H8 are But-1-ene, But-2-ene, and 2-methylpropene. But-1-ene and But-2-ene are position isomers, differing in the position of the double bond. 2-methylpropene is a branched isomer. But-3-ene is not a distinct isomer because the numbering of the carbon chain starts from the end closest to the double bond, making it identical to But-1-ene.
During vigorous exercise :
i. lactic acid accumulates in muscle cells to meet its energy needs immediately.
ii. lactic acid is formed by anaerobic respiration hence oxygen consumption by muscles is reduced.
iii. This reduction in oxygen consumption is called oxygen debt of muscle.
Which of the following statement is Correct ?
- a)only statement ii) and iii) are correct.
- b)only statement i) and ii) are correct.
- c)only statement i) is correct.
- d)all statements are correct.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During vigorous exercise :
i. lactic acid accumulates in muscle cells to meet its energy needs immediately.
ii. lactic acid is formed by anaerobic respiration hence oxygen consumption by muscles is reduced.
iii. This reduction in oxygen consumption is called oxygen debt of muscle.
Which of the following statement is Correct ?
i. lactic acid accumulates in muscle cells to meet its energy needs immediately.
ii. lactic acid is formed by anaerobic respiration hence oxygen consumption by muscles is reduced.
iii. This reduction in oxygen consumption is called oxygen debt of muscle.
Which of the following statement is Correct ?
a)
only statement ii) and iii) are correct.
b)
only statement i) and ii) are correct.
c)
only statement i) is correct.
d)
all statements are correct.

|
Prisha Singh answered |
During vigorous exercise, lactic acid accumulates in muscles cells to meet the energy requirement of muscle cell. Lactic acid is formed due to insufficient availability of oxygen.
How many degrees of freedom do non linear triatomic gas molecules has?- a)two
- b)six
- c)three
- d)five
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many degrees of freedom do non linear triatomic gas molecules has?
a)
two
b)
six
c)
three
d)
five
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
A triatomic nonlinear gaseous atom has 6 degrees of freedom, that are 3 in all transrational directions and three rotational barriers in all the three axises.
Each pectoral girdle :
i. has 2 pairs of bones, a pair of clavicle and a pair of scapula.
ii. scapula contains expanded process and glenoid cavity, the latter is for articulation of the head of humerus.
- a)Both are correct
- b)Statement i) is wrong and ii) is correct.
- c)both are wrong
- d)Statement i) is correct and ii) is wrong.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Each pectoral girdle :
i. has 2 pairs of bones, a pair of clavicle and a pair of scapula.
ii. scapula contains expanded process and glenoid cavity, the latter is for articulation of the head of humerus.
i. has 2 pairs of bones, a pair of clavicle and a pair of scapula.
ii. scapula contains expanded process and glenoid cavity, the latter is for articulation of the head of humerus.
a)
Both are correct
b)
Statement i) is wrong and ii) is correct.
c)
both are wrong
d)
Statement i) is correct and ii) is wrong.

|
Vaibhav Basu answered |
Statement 1: Each pectoral girdle has two pairs of bones: a pair of clavicles and a pair of scapulae. The pectoral girdle, also known as the shoulder girdle, is a skeletal structure that connects the upper limb to the axial skeleton.
Statement 2: The head of the humerus bone articulates with the glenoid cavity of the pectoral girdle.
Hence both are correct.
Statement 2: The head of the humerus bone articulates with the glenoid cavity of the pectoral girdle.
Hence both are correct.
Which of the following compounds react most readily with Br2(g)?
- a) C2H2
- b) C3H6
- c)C2H4
- d)C4H10
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compounds react most readily with Br2(g)?
a)
C2H2
b)
C3H6
c)
C2H4
d)
C4H10
|
|
Siddharth Iyer answered |
The compound that reacts most readily with Br(g) is C3H6. Here's why:
Explanation:
When a compound reacts with Br(g), it undergoes a substitution reaction called bromination. In this reaction, a Br atom replaces a hydrogen atom in the compound. The reactivity of a compound towards bromination depends on its structure and the stability of the resulting product.
Comparing the compounds:
Let's compare the given compounds and analyze their structures to determine which one is most reactive towards bromination.
a) C2H2:
C2H2 is an alkyne with a triple bond between two carbon atoms. This triple bond is very strong and stable, making it difficult for Br(g) to break it and substitute a hydrogen atom. Therefore, C2H2 is less reactive towards bromination.
b) C3H6:
C3H6 is an alkene with a double bond between two carbon atoms. The double bond is weaker and less stable than a triple bond. Therefore, it is easier for Br(g) to break the double bond and substitute a hydrogen atom. This makes C3H6 more reactive towards bromination compared to C2H2.
c) C2H4:
C2H4 is also an alkene with a double bond between two carbon atoms, similar to C3H6. It has the same structure as C3H6, but it has fewer carbon atoms. Since the number of carbon atoms does not significantly affect the reactivity towards bromination, C2H4 is also reactive towards bromination, but less reactive compared to C3H6.
d) C4H10:
C4H10 is an alkane with only single bonds between carbon atoms. Alkanes are generally less reactive towards bromination because the single bonds are strong and stable. Breaking a single bond to substitute a hydrogen atom is more difficult for Br(g) compared to breaking a double or triple bond. Therefore, C4H10 is the least reactive towards bromination among the given compounds.
Conclusion:
Based on the structural analysis and the stability of the bonds, C3H6 is the most reactive compound towards bromination among the given options.
Explanation:
When a compound reacts with Br(g), it undergoes a substitution reaction called bromination. In this reaction, a Br atom replaces a hydrogen atom in the compound. The reactivity of a compound towards bromination depends on its structure and the stability of the resulting product.
Comparing the compounds:
Let's compare the given compounds and analyze their structures to determine which one is most reactive towards bromination.
a) C2H2:
C2H2 is an alkyne with a triple bond between two carbon atoms. This triple bond is very strong and stable, making it difficult for Br(g) to break it and substitute a hydrogen atom. Therefore, C2H2 is less reactive towards bromination.
b) C3H6:
C3H6 is an alkene with a double bond between two carbon atoms. The double bond is weaker and less stable than a triple bond. Therefore, it is easier for Br(g) to break the double bond and substitute a hydrogen atom. This makes C3H6 more reactive towards bromination compared to C2H2.
c) C2H4:
C2H4 is also an alkene with a double bond between two carbon atoms, similar to C3H6. It has the same structure as C3H6, but it has fewer carbon atoms. Since the number of carbon atoms does not significantly affect the reactivity towards bromination, C2H4 is also reactive towards bromination, but less reactive compared to C3H6.
d) C4H10:
C4H10 is an alkane with only single bonds between carbon atoms. Alkanes are generally less reactive towards bromination because the single bonds are strong and stable. Breaking a single bond to substitute a hydrogen atom is more difficult for Br(g) compared to breaking a double or triple bond. Therefore, C4H10 is the least reactive towards bromination among the given compounds.
Conclusion:
Based on the structural analysis and the stability of the bonds, C3H6 is the most reactive compound towards bromination among the given options.
Read the following statements about muscle contraction in humans :
i. chemical energy is converted into mechanical energy during muscle contraction and the chemical is a neurotransmitter.
ii. a neurotransmitter acetylcholine at motor end plate converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
iii. in a contracted muscle, volume remains the same.
iv. a contracted muscle becomes shorter and thicker.
- a)only iv) is correct.
- b)only i), iii) and iv) are correct.
- c)only i) and iv) are correct.
- d)only ii), iii) and iv) are correct.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements about muscle contraction in humans :
i. chemical energy is converted into mechanical energy during muscle contraction and the chemical is a neurotransmitter.
ii. a neurotransmitter acetylcholine at motor end plate converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
iii. in a contracted muscle, volume remains the same.
iv. a contracted muscle becomes shorter and thicker.
i. chemical energy is converted into mechanical energy during muscle contraction and the chemical is a neurotransmitter.
ii. a neurotransmitter acetylcholine at motor end plate converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
iii. in a contracted muscle, volume remains the same.
iv. a contracted muscle becomes shorter and thicker.
a)
only iv) is correct.
b)
only i), iii) and iv) are correct.
c)
only i) and iv) are correct.
d)
only ii), iii) and iv) are correct.
|
|
Akash Khanna answered |
Explanation:
Muscle contraction is a complex process that involves the conversion of chemical energy into mechanical energy. Let's analyze each statement to understand why option 'B' is the correct answer.
i. Chemical energy is converted into mechanical energy during muscle contraction, and the chemical is a neurotransmitter.
During muscle contraction, chemical energy stored in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is converted into mechanical energy. ATP is the primary energy source for muscle contraction. The release of a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine initiates the process of muscle contraction by transmitting the electrical signal from the nervous system to the muscle fibers.
ii. A neurotransmitter acetylcholine at the motor end plate converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
This statement is incorrect. Acetylcholine released at the motor end plate does not directly convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. It acts as a chemical messenger that binds to receptors on the muscle fibers, triggering a series of events that lead to muscle contraction. The electrical energy from the nerve impulse is converted into a chemical signal (acetylcholine) which then initiates the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, leading to muscle contraction.
iii. In a contracted muscle, volume remains the same.
This statement is incorrect. During muscle contraction, the volume of the muscle decreases. As the muscle fibers generate force, they pull on the tendons, causing the muscle to shorten. This shortening leads to a decrease in muscle volume.
iv. A contracted muscle becomes shorter and thicker.
This statement is correct. When a muscle contracts, it becomes shorter and thicker. The individual muscle fibers slide past each other, causing the overlapping actin and myosin filaments to shorten. This sliding filament mechanism is responsible for muscle contraction. As the muscle fibers shorten, the muscle as a whole becomes thicker.
Based on the explanations above, we can conclude that only statements i), iii), and iv) are correct. Hence, the correct answer is option 'B' - only i), iii), and iv) are correct.
Muscle contraction is a complex process that involves the conversion of chemical energy into mechanical energy. Let's analyze each statement to understand why option 'B' is the correct answer.
i. Chemical energy is converted into mechanical energy during muscle contraction, and the chemical is a neurotransmitter.
During muscle contraction, chemical energy stored in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is converted into mechanical energy. ATP is the primary energy source for muscle contraction. The release of a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine initiates the process of muscle contraction by transmitting the electrical signal from the nervous system to the muscle fibers.
ii. A neurotransmitter acetylcholine at the motor end plate converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
This statement is incorrect. Acetylcholine released at the motor end plate does not directly convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. It acts as a chemical messenger that binds to receptors on the muscle fibers, triggering a series of events that lead to muscle contraction. The electrical energy from the nerve impulse is converted into a chemical signal (acetylcholine) which then initiates the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, leading to muscle contraction.
iii. In a contracted muscle, volume remains the same.
This statement is incorrect. During muscle contraction, the volume of the muscle decreases. As the muscle fibers generate force, they pull on the tendons, causing the muscle to shorten. This shortening leads to a decrease in muscle volume.
iv. A contracted muscle becomes shorter and thicker.
This statement is correct. When a muscle contracts, it becomes shorter and thicker. The individual muscle fibers slide past each other, causing the overlapping actin and myosin filaments to shorten. This sliding filament mechanism is responsible for muscle contraction. As the muscle fibers shorten, the muscle as a whole becomes thicker.
Based on the explanations above, we can conclude that only statements i), iii), and iv) are correct. Hence, the correct answer is option 'B' - only i), iii), and iv) are correct.
The degree of freedom for tri atomic gas is:- a)6
- b)4
- c)5
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The degree of freedom for tri atomic gas is:
a)
6
b)
4
c)
5
d)
3
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Degrees of freedom are the ways in which a molecule of the gas can execute motion.
So in case of triatomic gas molecule:
1. It can translate (move) in all 3 dimensions, which accounts for 3 degrees of freedom (since there are 3 dimensions in which it could translate (move)).
2. This molecule can also revolve with Moment of Inertia ≠ 0 around all three axes, x, y, and z, which accounts for another 3 degrees of freedom (since there are 3 axes of rotation).
So in case of triatomic gas molecule:
1. It can translate (move) in all 3 dimensions, which accounts for 3 degrees of freedom (since there are 3 dimensions in which it could translate (move)).
2. This molecule can also revolve with Moment of Inertia ≠ 0 around all three axes, x, y, and z, which accounts for another 3 degrees of freedom (since there are 3 axes of rotation).
If a gas has n degree of freedom, ratio of principal specific heats of the gas is- a)1+ 2/n
- b)2n
- c)1 - 2/n
- d)-2n
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If a gas has n degree of freedom, ratio of principal specific heats of the gas is
a)
1+ 2/n
b)
2n
c)
1 - 2/n
d)
-2n
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Let us consider 1 mole of an ideal gas at kelvin temperature T. It has N molecules (Avogadro's number). The internal energy of an ideal gas is entirely kinetic. The average KE per molecule of a ideal gas is ½ nkT (k is boltzman constant), where n is degree of freedom. Therefore, the internal energy of one mole of a gas would be
E=N(1/2nKT)=1/2nRT (∵k=R/N)
Now, Cv=dE/dT=n/2 R
and Cp=n/2 R+R=(n/2+1)R
Cp/ Cv =(n/2+1)R/n/2=(1+2/n)
E=N(1/2nKT)=1/2nRT (∵k=R/N)
Now, Cv=dE/dT=n/2 R
and Cp=n/2 R+R=(n/2+1)R
Cp/ Cv =(n/2+1)R/n/2=(1+2/n)
The average distance a molecule can travel without colliding is called- a)Average distance
- b)Mean free path
- c)Mean drift
- d)Mean distance
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The average distance a molecule can travel without colliding is called
a)
Average distance
b)
Mean free path
c)
Mean drift
d)
Mean distance
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
Mean free path is the average distance between the two successive collisions. Inside the gas there are several molecules which are randomly moving and colliding with each other. The distance which a particular gas molecule travels without colliding is known as mean free path.
The property which doesn’t belong to muscle fibres is :- a)conductivity
- b)Excitability
- c)Contractility
- d)elasticity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The property which doesn’t belong to muscle fibres is :
a)
conductivity
b)
Excitability
c)
Contractility
d)
elasticity

|
Rajeev Sharma answered |
Muscle fibres have properties of excitability, elasticity and contractility but conductivity is not present in muscles fibers. These fibres help in movement of different body parts.
Myasthenia gravis leads to fatigue and weakness. It is not :- a)neuromuscular disease
- b)causing paralysis of respiratory muscles
- c)autoimmune disorder
- d)affecting heart muscles
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Myasthenia gravis leads to fatigue and weakness. It is not :
a)
neuromuscular disease
b)
causing paralysis of respiratory muscles
c)
autoimmune disorder
d)
affecting heart muscles

|
Akshat Chavan answered |
Myasthenia gravis is an auto immune disorder affecting neuromuscular junction leading to fatigue, weakening and paralysis of skeletal muscle.
Assertion (A): Red fibres in muscles have a high content of myoglobin, which contributes to their reddish appearance.Reason (R): These fibres primarily rely on anaerobic metabolism for energy production.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Red fibres in muscles have a high content of myoglobin, which contributes to their reddish appearance.
Reason (R): These fibres primarily rely on anaerobic metabolism for energy production.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false
|
|
Shanaya Sengupta answered |
Understanding the Assertion and Reason
The question revolves around the characteristics of muscle fibres, specifically red fibres, and their energy metabolism.
Assertion (A) Explained
- Red fibres, or slow-twitch fibres, are indeed rich in myoglobin, a protein that binds oxygen.
- This myoglobin content gives these fibres their reddish appearance, as it contains heme, which is responsible for the red color.
Reason (R) Explained
- The statement that red fibres primarily rely on anaerobic metabolism is incorrect.
- In reality, red fibres are adapted for aerobic metabolism, utilizing oxygen to generate energy efficiently over prolonged periods.
Conclusion
- Since Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false, the correct answer is option 'C'.
- The reason does not provide a correct explanation for the assertion, as red fibres do not primarily rely on anaerobic metabolism; they are more suited for endurance activities that require sustained energy through aerobic processes.
Key Takeaways
- Red fibres = High myoglobin content = Reddish appearance.
- Red fibres predominantly utilize aerobic metabolism, not anaerobic.
- The disconnection between the assertion and the reason confirms that option 'C' is indeed correct.
The question revolves around the characteristics of muscle fibres, specifically red fibres, and their energy metabolism.
Assertion (A) Explained
- Red fibres, or slow-twitch fibres, are indeed rich in myoglobin, a protein that binds oxygen.
- This myoglobin content gives these fibres their reddish appearance, as it contains heme, which is responsible for the red color.
Reason (R) Explained
- The statement that red fibres primarily rely on anaerobic metabolism is incorrect.
- In reality, red fibres are adapted for aerobic metabolism, utilizing oxygen to generate energy efficiently over prolonged periods.
Conclusion
- Since Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false, the correct answer is option 'C'.
- The reason does not provide a correct explanation for the assertion, as red fibres do not primarily rely on anaerobic metabolism; they are more suited for endurance activities that require sustained energy through aerobic processes.
Key Takeaways
- Red fibres = High myoglobin content = Reddish appearance.
- Red fibres predominantly utilize aerobic metabolism, not anaerobic.
- The disconnection between the assertion and the reason confirms that option 'C' is indeed correct.
When propene reacts with HBr in the presence of peroxide, it gives rise to
- a)Allyl bromide
- b)Isopropyl bromide
- c) n-propyl bromide
- d)3-bromopropane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When propene reacts with HBr in the presence of peroxide, it gives rise to
a)
Allyl bromide
b)
Isopropyl bromide
c)
n-propyl bromide
d)
3-bromopropane
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Explanation of the Reaction of Propene with HBr in the Presence of Peroxide
The reaction of propene with hydrogen bromide in the presence of peroxide follows the rule of anti-Markovnikov addition. This rule states that the hydrogen (H) from HBr will add to the carbon with the most hydrogen atoms already attached, and the bromine (Br) will add to the other carbon. Peroxide promotes this anti-Markovnikov addition.
In the case of propene (CH3-CH=CH2), the hydrogen from HBr will add to the terminal carbon, which already has two hydrogens. The bromine will add to the middle carbon.
Here are the steps of the reaction:
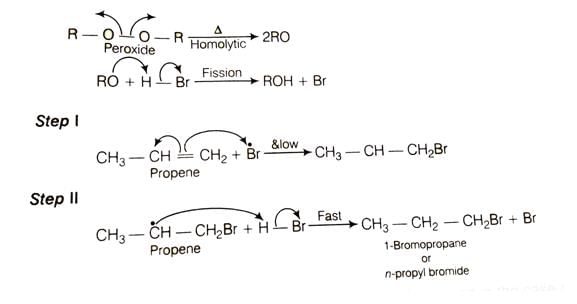
The reaction of propene with hydrogen bromide in the presence of peroxide follows the rule of anti-Markovnikov addition. This rule states that the hydrogen (H) from HBr will add to the carbon with the most hydrogen atoms already attached, and the bromine (Br) will add to the other carbon. Peroxide promotes this anti-Markovnikov addition.
In the case of propene (CH3-CH=CH2), the hydrogen from HBr will add to the terminal carbon, which already has two hydrogens. The bromine will add to the middle carbon.
Here are the steps of the reaction:

Look at the following figure of movement of the thin filaments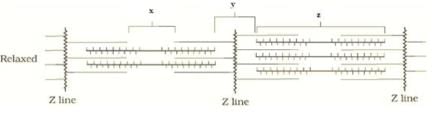 The label x, y, and z are respectively
The label x, y, and z are respectively- a)H zone, A band and I band
- b)I band, H zone, A band
- c)I band, A band, H zone
- d)H zone, I band, A band
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Look at the following figure of movement of the thin filaments

The label x, y, and z are respectively
a)
H zone, A band and I band
b)
I band, H zone, A band
c)
I band, A band, H zone
d)
H zone, I band, A band

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
The label x is H-zone, y is I band and z is A band.
Select the incorrect statement regarding alkenes.- a)In alkenes, the carbons are connected by pi bonds
- b)Alkenes have almost same physical properties as that of the alkanes
- c)Alkenes are less reactive than alkanes
- d)Alkenes undergo polymerization reaction
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the incorrect statement regarding alkenes.
a)
In alkenes, the carbons are connected by pi bonds
b)
Alkenes have almost same physical properties as that of the alkanes
c)
Alkenes are less reactive than alkanes
d)
Alkenes undergo polymerization reaction

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Alkenes are not less reactive than alkanes, indeed they are very reactive compared with them due to the presence of C=C.
Ethylene on reaction with bromine forms which among the following product?- a)BrH2C=CH2Br
- b)BrH2C-CH2Br
- c)Br2HC=CHBr2
- d)Br2HC-CHBr2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Ethylene on reaction with bromine forms which among the following product?
a)
BrH2C=CH2Br
b)
BrH2C-CH2Br
c)
Br2HC=CHBr2
d)
Br2HC-CHBr2

|
Lead Academy answered |
The above reaction between Ethene and bromine is known as electrophilic halogenation reaction and the products usually formed are ethylene dihalides.
1calorie = ?
- a)4148 Joules
- b)414.8 Joules
- c)4.8 Joules
- d)4.184 Joules
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
1calorie = ?
a)
4148 Joules
b)
414.8 Joules
c)
4.8 Joules
d)
4.184 Joules

|
Pragati Nair answered |
Explanation:
The conversion factor between calories and joules is as follows:
1 calorie = 4.184 joules
Therefore, to convert calories to joules, we need to multiply the number of calories by the conversion factor.
Step-by-Step Solution:
To convert 1 calorie to joules, we will use the conversion factor of 4.184 joules per calorie.
1 calorie * 4.184 joules/calorie = 4.184 joules
Therefore, 1 calorie is equal to 4.184 joules.
Answer:
The correct answer is option D: 4.148 Joules.
The conversion factor between calories and joules is as follows:
1 calorie = 4.184 joules
Therefore, to convert calories to joules, we need to multiply the number of calories by the conversion factor.
Step-by-Step Solution:
To convert 1 calorie to joules, we will use the conversion factor of 4.184 joules per calorie.
1 calorie * 4.184 joules/calorie = 4.184 joules
Therefore, 1 calorie is equal to 4.184 joules.
Answer:
The correct answer is option D: 4.148 Joules.
The mean free path is the ____________- a)average distance covered by a molecule between two successive collisions
- b)length of the container that contains the gas
- c)mean of the square of the average distance between two successive collisions
- d)square of the average distance between two successive collisions
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The mean free path is the ____________
a)
average distance covered by a molecule between two successive collisions
b)
length of the container that contains the gas
c)
mean of the square of the average distance between two successive collisions
d)
square of the average distance between two successive collisions
|
|
Anushka Das answered |
Mean Free Path
The mean free path is a concept used in physics to describe the average distance traveled by a molecule or particle between two successive collisions. It is an important parameter in the study of gas behavior and is particularly relevant in the kinetic theory of gases.
Definition
The mean free path can be defined as the average distance covered by a molecule between two successive collisions. It represents the average distance a molecule travels before it interacts with another molecule or particle in a gas.
Explanation
To understand why the correct answer is option 'A', let's consider the behavior of gas molecules in a container. The gas molecules are in constant motion, moving in straight lines until they collide with other molecules or the walls of the container.
Each time a molecule collides with another molecule or the walls, its direction and velocity may change. The time it takes for a molecule to collide again depends on its speed and the density of the gas. Molecules with higher speeds will collide more frequently, while molecules in a denser gas will also collide more frequently.
The mean free path is an average value, calculated by considering the total distance covered by all the molecules in a gas and dividing it by the total number of collisions. Since the molecules move in random directions, the actual path of each molecule may be different.
Importance
The mean free path is a fundamental parameter in the kinetic theory of gases and is used to characterize the behavior of gas molecules. It provides valuable information about the average distance traveled by molecules, which is important for understanding diffusion, heat conduction, and other transport phenomena in gases.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the mean free path is the average distance covered by a molecule between two successive collisions. It is an important parameter in the study of gas behavior and helps to describe the motion and interactions of gas molecules. Option 'A' is the correct answer because it accurately defines the mean free path.
The mean free path is a concept used in physics to describe the average distance traveled by a molecule or particle between two successive collisions. It is an important parameter in the study of gas behavior and is particularly relevant in the kinetic theory of gases.
Definition
The mean free path can be defined as the average distance covered by a molecule between two successive collisions. It represents the average distance a molecule travels before it interacts with another molecule or particle in a gas.
Explanation
To understand why the correct answer is option 'A', let's consider the behavior of gas molecules in a container. The gas molecules are in constant motion, moving in straight lines until they collide with other molecules or the walls of the container.
Each time a molecule collides with another molecule or the walls, its direction and velocity may change. The time it takes for a molecule to collide again depends on its speed and the density of the gas. Molecules with higher speeds will collide more frequently, while molecules in a denser gas will also collide more frequently.
The mean free path is an average value, calculated by considering the total distance covered by all the molecules in a gas and dividing it by the total number of collisions. Since the molecules move in random directions, the actual path of each molecule may be different.
Importance
The mean free path is a fundamental parameter in the kinetic theory of gases and is used to characterize the behavior of gas molecules. It provides valuable information about the average distance traveled by molecules, which is important for understanding diffusion, heat conduction, and other transport phenomena in gases.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the mean free path is the average distance covered by a molecule between two successive collisions. It is an important parameter in the study of gas behavior and helps to describe the motion and interactions of gas molecules. Option 'A' is the correct answer because it accurately defines the mean free path.
How many regions is the vertebral column divided into?- a)6
- b)5
- c)7
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many regions is the vertebral column divided into?
a)
6
b)
5
c)
7
d)
4

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Humans possess 26 vertebrae in the vertebral column. These vertebrae are divided into five different regions, namely the cervical (7), thoracic (12), lumbar (5), sacral (1-fused) and coccygeal (1-fused) regions.
On which of the following factors, does the average kinetic energy of gas molecules depend?- a)Pressure
- b)Velocity of gas molecules
- c)Absolute temperature
- d)Volume of the gas
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
On which of the following factors, does the average kinetic energy of gas molecules depend?
a)
Pressure
b)
Velocity of gas molecules
c)
Absolute temperature
d)
Volume of the gas
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
The average K.E. of a gas molecules depends only on the absolute temperature of the gas and is directly proportional to it.
Identify the one which shows E-Z mechanism?- a)2-methylpent-2-ene
- b)3-methylpent-2-ene
- c)Methyl-3-pent-2-ene
- d)2,3-methylpentene
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the one which shows E-Z mechanism?
a)
2-methylpent-2-ene
b)
3-methylpent-2-ene
c)
Methyl-3-pent-2-ene
d)
2,3-methylpentene

|
Lead Academy answered |
In ‘z’ mechanism, the compounds with higher priority will be located opposite to each other of the double bond, in ‘E’ mechanism the compounds with high priority will be located in z corners and hence 3-methylpent-2-ene is the one which shows E-Z mechanism in which the priority group is CH3 and CH2CH3.
Which disorder is caused due to wild contractions in muscles? Tetany Muscular dystrophy Gout Arthritis Tetany is caused due to rapid spasms (wild contractions) in muscle due to low Ca++ inbody fluid.- a)Arthritis
- b)Muscular dystrophy
- c)Tetany
- d)Gout
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which disorder is caused due to wild contractions in muscles? Tetany Muscular dystrophy Gout Arthritis Tetany is caused due to rapid spasms (wild contractions) in muscle due to low Ca++ inbody fluid.
a)
Arthritis
b)
Muscular dystrophy
c)
Tetany
d)
Gout

|
Rohan Unni answered |
Tetany is caused due to rapid spasms (wild contractions) in muscle due to low Ca++ inbody fluid.
In the following two graphs :
i.first graph shows: twitch→→ summation→→ etanus →→ fatigue.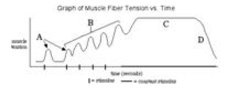 ii. second graph shows: incomplete and complete tetanus.
ii. second graph shows: incomplete and complete tetanus. 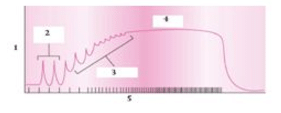
- a)Statement ii) is wrong and i) is correct..
- b)both statements are correct.
- c)Statement i) is correct and ii) is wrong.
- d)both statements are wrong.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following two graphs :
i.first graph shows: twitch→→ summation→→ etanus →→ fatigue.
i.first graph shows: twitch→→ summation→→ etanus →→ fatigue.
ii. second graph shows: incomplete and complete tetanus.
a)
Statement ii) is wrong and i) is correct..
b)
both statements are correct.
c)
Statement i) is correct and ii) is wrong.
d)
both statements are wrong.

|
Krish Khanna answered |
Graph 1 shows muscle fiber tension with time. Which occurs in order as : twitch→→summation→→tetanus→→fatigue. Graph 2 shows complete and incomplete tetanus. Tetanus is also known as lockjaw, which is a infection characterized by muscle spasm.
O2 is a __________ molecule , and has __________ translational degrees of freedom- a)Monatomic , three
- b)Diatomic , three
- c)Monatomic , one
- d)Diatomic , one
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
O2 is a __________ molecule , and has __________ translational degrees of freedom
a)
Monatomic , three
b)
Diatomic , three
c)
Monatomic , one
d)
Diatomic , one

|
Anshu Joshi answered |
Explanation:
Oxygen gas (O2) is a diatomic molecule, meaning it consists of two oxygen atoms bonded together. Each oxygen atom has 6 valence electrons, and when they bond together, they share two pairs of electrons, forming a double bond. This double bond is what holds the two oxygen atoms together in the O2 molecule.
Translational degrees of freedom:
Translational degrees of freedom refer to the number of independent ways a molecule can move in space. In other words, it refers to the number of ways a molecule can move and translate as a whole.
For a diatomic molecule like O2, there are three translational degrees of freedom because the molecule can move in three independent directions in space: x, y, and z. These translational degrees of freedom correspond to the movement of the center of mass of the molecule.
Options:
Let's analyze each option given:
a) Monatomic, three: This option is incorrect because O2 is a diatomic molecule, not monatomic. Monatomic molecules consist of single atoms and have three translational degrees of freedom.
b) Diatomic, three: This option is correct. O2 is a diatomic molecule, and it indeed has three translational degrees of freedom.
c) Monatomic, one: This option is incorrect because O2 is a diatomic molecule, not monatomic. Monatomic molecules consist of single atoms and have one translational degree of freedom.
d) Diatomic, one: This option is incorrect. O2 is a diatomic molecule and has three translational degrees of freedom, not one.
Conclusion:
Based on the explanation above, the correct answer is option B, "Diatomic, three." O2 is a diatomic molecule, and it has three translational degrees of freedom.
Oxygen gas (O2) is a diatomic molecule, meaning it consists of two oxygen atoms bonded together. Each oxygen atom has 6 valence electrons, and when they bond together, they share two pairs of electrons, forming a double bond. This double bond is what holds the two oxygen atoms together in the O2 molecule.
Translational degrees of freedom:
Translational degrees of freedom refer to the number of independent ways a molecule can move in space. In other words, it refers to the number of ways a molecule can move and translate as a whole.
For a diatomic molecule like O2, there are three translational degrees of freedom because the molecule can move in three independent directions in space: x, y, and z. These translational degrees of freedom correspond to the movement of the center of mass of the molecule.
Options:
Let's analyze each option given:
a) Monatomic, three: This option is incorrect because O2 is a diatomic molecule, not monatomic. Monatomic molecules consist of single atoms and have three translational degrees of freedom.
b) Diatomic, three: This option is correct. O2 is a diatomic molecule, and it indeed has three translational degrees of freedom.
c) Monatomic, one: This option is incorrect because O2 is a diatomic molecule, not monatomic. Monatomic molecules consist of single atoms and have one translational degree of freedom.
d) Diatomic, one: This option is incorrect. O2 is a diatomic molecule and has three translational degrees of freedom, not one.
Conclusion:
Based on the explanation above, the correct answer is option B, "Diatomic, three." O2 is a diatomic molecule, and it has three translational degrees of freedom.
The degree of freedom for diatomic gas is:- a)4
- b)6
- c)5
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The degree of freedom for diatomic gas is:
a)
4
b)
6
c)
5
d)
3
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
Like a diatomic molecule, a linear triatomic molecule has three translational and only two accessible rotational degrees of freedom. For Monoatomic Gas degree of freedom is 3, while for Diatomic Gas is it 5, and for Triatomic Gas it is
What is law of equipartition of energy?- a)The total energy is unequally distributed in all possible energy modes, with each mode having an average energy equal to 2kBT. This is known as the law of equipartition of energy.
- b)The total energy is unequally distributed in all possible energy modes, with each mode having an average energy equal to ½ kBT. This is known as the law of equipartition of energy.
- c)The total energy is equally distributed in all possible energy modes, with each mode having an average energy equal to ½ kBT. This is known as the law of equipartition of energy.
- d)The total energy is equally distributed in all possible energy modes, with each mode having an average energy equal to kBT. This is known as the law of equipartition of energy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is law of equipartition of energy?
a)
The total energy is unequally distributed in all possible energy modes, with each mode having an average energy equal to 2kBT. This is known as the law of equipartition of energy.
b)
The total energy is unequally distributed in all possible energy modes, with each mode having an average energy equal to ½ kBT. This is known as the law of equipartition of energy.
c)
The total energy is equally distributed in all possible energy modes, with each mode having an average energy equal to ½ kBT. This is known as the law of equipartition of energy.
d)
The total energy is equally distributed in all possible energy modes, with each mode having an average energy equal to kBT. This is known as the law of equipartition of energy
|
|
Tanishq Tiwari answered |
The total energy is equally distributed in all possible energy modes, with each mode having an average energy equal to ½ kBT. This is known as the law of equipartition of energy.
Ethylene bromide on treatment with Zn gives- a)Alkyne
- b)Alkene
- c)Alkane
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Ethylene bromide on treatment with Zn gives
a)
Alkyne
b)
Alkene
c)
Alkane
d)
All of the above
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Reaction of Ethylene Bromide with Zinc
Ethylene bromide, also known as 1,2-dibromoethane, is a halogenated hydrocarbon. When it is treated with zinc, an alkene is formed as a result. This reaction can be detailed as follows:
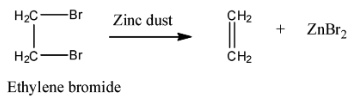
Why not Alkyne or Alkane?
An alkyne would require the removal of two pairs of hydrogen and bromine atoms, which does not occur in this reaction. An alkane would not have any double bonds, and the reaction with zinc specifically creates a double bond.
In conclusion, the correct answer is B: Alkene, because the reaction of ethylene bromide with zinc results in the formation of an alkene, specifically ethene. You can learn more about organic chemistry reactions on the EduRev platform.
Ethylene bromide, also known as 1,2-dibromoethane, is a halogenated hydrocarbon. When it is treated with zinc, an alkene is formed as a result. This reaction can be detailed as follows:

Why not Alkyne or Alkane?
An alkyne would require the removal of two pairs of hydrogen and bromine atoms, which does not occur in this reaction. An alkane would not have any double bonds, and the reaction with zinc specifically creates a double bond.
In conclusion, the correct answer is B: Alkene, because the reaction of ethylene bromide with zinc results in the formation of an alkene, specifically ethene. You can learn more about organic chemistry reactions on the EduRev platform.
Match the following bones and their synonyms :

- a)a)-ii, b)-iii, c)-i, d)-iv
- b)a)-iii, b)-ii, c)-iv, d)-ii
- c)a)-iv, b)-ii, c)-iii, d)-i
- d)a)-v, b)-ii, c)-iii, d)-iv
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following bones and their synonyms :


a)
a)-ii, b)-iii, c)-i, d)-iv
b)
a)-iii, b)-ii, c)-iv, d)-ii
c)
a)-iv, b)-ii, c)-iii, d)-i
d)
a)-v, b)-ii, c)-iii, d)-iv
|
|
Unknown answered |
Kneebone is also known as patella or knee cap it is a seasamoid bone which is basically a cartilage and later get ossified into bone clavicle is also known as collar bone it is of s shape it is the favorite question of anatomy 1st year it is also called as beauty bone....
immovable joints are sutures which are +nt in our skull or cranium...
immovable joints are sutures which are +nt in our skull or cranium...
The diagram given below represnts the histology of a striped muscle. Label the parts A,B,C,D,E and F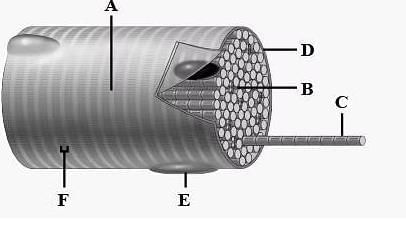
- a)A - Sarcoplasm, B - Nucleus, C - Sarcolemina, D - Myofibril, E - Dark band, F - Light band
- b)A - Sarcolemma. B - Nucleus, C - Dark band, D - Light band, E - Sarcoplasm, F -Myofibril
- c)A - Sarcoplasm, B - Light band, C - Myofibril, D - Sarcolemma, E - Nucleus, F - Dark band
- d)A - Light band, B - Sarcoplasm, C - Myofibril, D - Sarcolemma, E - Nucleus, F - Dark band
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The diagram given below represnts the histology of a striped muscle. Label the parts A,B,C,D,E and F

a)
A - Sarcoplasm, B - Nucleus, C - Sarcolemina, D - Myofibril, E - Dark band, F - Light band
b)
A - Sarcolemma. B - Nucleus, C - Dark band, D - Light band, E - Sarcoplasm, F -Myofibril
c)
A - Sarcoplasm, B - Light band, C - Myofibril, D - Sarcolemma, E - Nucleus, F - Dark band
d)
A - Light band, B - Sarcoplasm, C - Myofibril, D - Sarcolemma, E - Nucleus, F - Dark band

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
- A: Light band present on the myofibril is called I-band or isotropic band. It consists of only actin filaments.
- B: Sarcoplasm is enclosed by sarcolemma which contains many nuclei.
- C: Myofibril is made up of two types of myofilaments which are thick and thin.
- D: Sarcolemma is the plasma membrane of muscle fibre.
- E: Nucleus
- F: Dark band present on the myofibril is called A-band or anisotropic band.
So, the correct answer is 'A- light band, B- sarcoplasm, C- myofibril, D- sarcolemma, E- nucleus, F- dark band'.
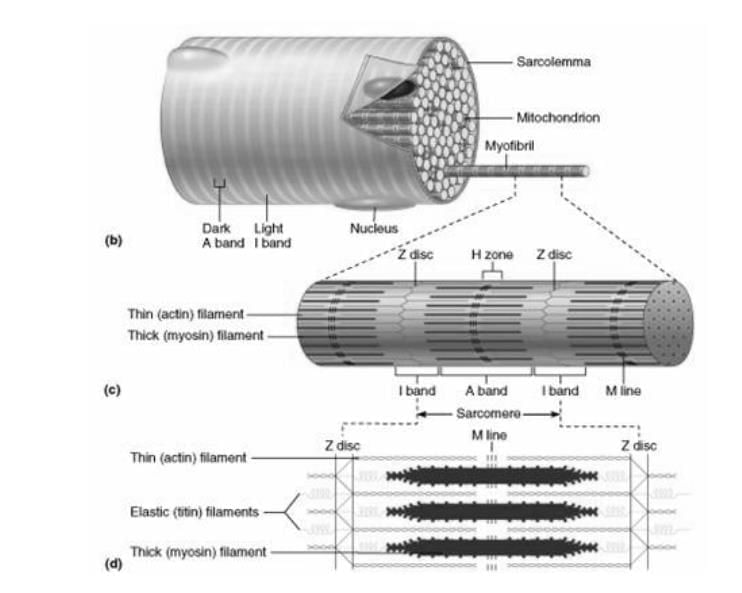
Topic in NCERT: Myofibrils
Line in NCERT: "each myofibril has alternate dark and light bands on it."
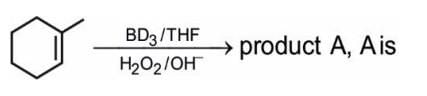
- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
A Aravind answered |
It is a type of HYDROBORATION OXIDATION REACTION (alcohol and phenol and ether chapter )
1.
2-Methylcyclohexene reacts with (BD3)2 to form a intermediate compound
2.
In which the deturium deficient site the deterium will go and attach
3.
And the peroxide will give a OH- and it will attach to the next to the deturium attach (it a kind of anti markowiffs rule)
Which of the following is not a part of hip bone?- a)Pubis
- b)tibia
- c)Ilium
- d)Ischium
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a part of hip bone?
a)
Pubis
b)
tibia
c)
Ilium
d)
Ischium

|
Rohan Unni answered |
Hip bone or pelvic girdle consists of two coxal bones. Each coxal bone is formed by the fusion of three bones- ilium, ischium and pubis
Polymerisation of actin monomers involves ATP hydrolysis as shown in the following figure : [choose the correct one]- a)
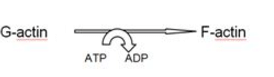
- b)
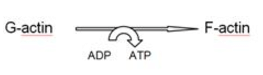
- c)
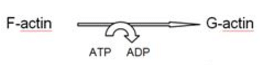
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Polymerisation of actin monomers involves ATP hydrolysis as shown in the following figure : [choose the correct one]
a)
b)
c)
d)
none

|
Rohan Unni answered |
Each ‘F’ actin is a polymer of monomeric ‘G’ (Globular) actins.
Chapter doubts & questions for January Week 3 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of January Week 3 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup