NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Ethylene bromide on treatment with Zn givesa)...
Start Learning for Free
Ethylene bromide on treatment with Zn gives
- a)Alkyne
- b)Alkene
- c)Alkane
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Ethylene bromide on treatment with Zn givesa)Alkyneb)Alkenec)Alkaned)A...
Reaction of Ethylene Bromide with Zinc
Ethylene bromide, also known as 1,2-dibromoethane, is a halogenated hydrocarbon. When it is treated with zinc, an alkene is formed as a result. This reaction can be detailed as follows:
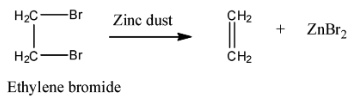
Why not Alkyne or Alkane?
An alkyne would require the removal of two pairs of hydrogen and bromine atoms, which does not occur in this reaction. An alkane would not have any double bonds, and the reaction with zinc specifically creates a double bond.
In conclusion, the correct answer is B: Alkene, because the reaction of ethylene bromide with zinc results in the formation of an alkene, specifically ethene. You can learn more about organic chemistry reactions on the EduRev platform.
Ethylene bromide, also known as 1,2-dibromoethane, is a halogenated hydrocarbon. When it is treated with zinc, an alkene is formed as a result. This reaction can be detailed as follows:

Why not Alkyne or Alkane?
An alkyne would require the removal of two pairs of hydrogen and bromine atoms, which does not occur in this reaction. An alkane would not have any double bonds, and the reaction with zinc specifically creates a double bond.
In conclusion, the correct answer is B: Alkene, because the reaction of ethylene bromide with zinc results in the formation of an alkene, specifically ethene. You can learn more about organic chemistry reactions on the EduRev platform.
Community Answer
Ethylene bromide on treatment with Zn givesa)Alkyneb)Alkenec)Alkaned)A...
Ethylene bromide (C2H4Br2) can undergo a reaction with zinc (Zn) to give an alkene.
The reaction between ethylene bromide and zinc is known as the dehalogenation reaction. In this reaction, the zinc metal acts as a reducing agent by donating electrons to the halogen atom (bromine) present in ethylene bromide. This results in the removal of the bromine atom from the molecule, leading to the formation of an alkene.
Here is the detailed explanation of the reaction:
1. Electrophilic addition of ethylene bromide: Ethylene bromide is an alkyl halide, and it can undergo electrophilic addition reactions. In the presence of a strong reducing agent like zinc, the bromine atom becomes the electrophile and attacks the double bond of ethylene. This leads to the formation of a cyclic intermediate with a positive charge on one of the carbon atoms.
2. Reduction by zinc: Zinc metal donates electrons to the cyclic intermediate, reducing the positive charge on the carbon atom. This results in the formation of a radical intermediate.
3. Elimination of bromine: The radical intermediate formed undergoes a rearrangement, leading to the elimination of the bromine atom. This results in the formation of an alkene. The double bond is formed between the two carbon atoms that were originally bonded to the bromine atom.
The reaction can be represented as follows:
C2H4Br2 + Zn → C2H4 + ZnBr2
In this reaction, ethylene bromide (C2H4Br2) reacts with zinc (Zn) to give ethylene (C2H4) and zinc bromide (ZnBr2). Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - Alkene.
It is important to note that the reaction conditions and the choice of reducing agent can influence the outcome of the reaction. In this specific case, the reaction between ethylene bromide and zinc results in the formation of an alkene. However, different alkyl halides and reducing agents can lead to the formation of other organic compounds such as alkanes or alkynes.
The reaction between ethylene bromide and zinc is known as the dehalogenation reaction. In this reaction, the zinc metal acts as a reducing agent by donating electrons to the halogen atom (bromine) present in ethylene bromide. This results in the removal of the bromine atom from the molecule, leading to the formation of an alkene.
Here is the detailed explanation of the reaction:
1. Electrophilic addition of ethylene bromide: Ethylene bromide is an alkyl halide, and it can undergo electrophilic addition reactions. In the presence of a strong reducing agent like zinc, the bromine atom becomes the electrophile and attacks the double bond of ethylene. This leads to the formation of a cyclic intermediate with a positive charge on one of the carbon atoms.
2. Reduction by zinc: Zinc metal donates electrons to the cyclic intermediate, reducing the positive charge on the carbon atom. This results in the formation of a radical intermediate.
3. Elimination of bromine: The radical intermediate formed undergoes a rearrangement, leading to the elimination of the bromine atom. This results in the formation of an alkene. The double bond is formed between the two carbon atoms that were originally bonded to the bromine atom.
The reaction can be represented as follows:
C2H4Br2 + Zn → C2H4 + ZnBr2
In this reaction, ethylene bromide (C2H4Br2) reacts with zinc (Zn) to give ethylene (C2H4) and zinc bromide (ZnBr2). Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - Alkene.
It is important to note that the reaction conditions and the choice of reducing agent can influence the outcome of the reaction. In this specific case, the reaction between ethylene bromide and zinc results in the formation of an alkene. However, different alkyl halides and reducing agents can lead to the formation of other organic compounds such as alkanes or alkynes.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Question Description
Ethylene bromide on treatment with Zn givesa)Alkyneb)Alkenec)Alkaned)All of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Ethylene bromide on treatment with Zn givesa)Alkyneb)Alkenec)Alkaned)All of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Ethylene bromide on treatment with Zn givesa)Alkyneb)Alkenec)Alkaned)All of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Ethylene bromide on treatment with Zn givesa)Alkyneb)Alkenec)Alkaned)All of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Ethylene bromide on treatment with Zn givesa)Alkyneb)Alkenec)Alkaned)All of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Ethylene bromide on treatment with Zn givesa)Alkyneb)Alkenec)Alkaned)All of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Ethylene bromide on treatment with Zn givesa)Alkyneb)Alkenec)Alkaned)All of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Ethylene bromide on treatment with Zn givesa)Alkyneb)Alkenec)Alkaned)All of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Ethylene bromide on treatment with Zn givesa)Alkyneb)Alkenec)Alkaned)All of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Ethylene bromide on treatment with Zn givesa)Alkyneb)Alkenec)Alkaned)All of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Ethylene bromide on treatment with Zn givesa)Alkyneb)Alkenec)Alkaned)All of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Ethylene bromide on treatment with Zn givesa)Alkyneb)Alkenec)Alkaned)All of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























