All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of June Week 3 for NEET Exam
Specific resistance of a conductor increases with- a)Increase in cross-section and decrease in length
- b)Increase in cross-section
- c)Decrease in cross-section
- d)Increase in temperature
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Specific resistance of a conductor increases with
a)
Increase in cross-section and decrease in length
b)
Increase in cross-section
c)
Decrease in cross-section
d)
Increase in temperature
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
Therefore resistance increases with the length. When cross sectional area increases the space of the elctrons to travel increases(simply explained). Therefore less amount of obstacles for the current. Therefore when area increases the resistance decreases.
If the potential difference V applied on a conductor is doubled, the drift velocity of electrons will become- a)vd
- b)2vd
- c)4vd
- d)
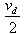
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the potential difference V applied on a conductor is doubled, the drift velocity of electrons will become
a)
vd
b)
2vd
c)
4vd
d)

|
EduRev JEE answered |
Drift velocity is directly proportional to potential difference.
Drift velocity is defined as the average velocity with which free electrons get drifted towards the positive end of the conductor under the influence of an external electric field.
Drift velocity is given by
vd= eEτ/ m
But, E=V/l
(if l is length of the conductor and V is constant potential difference applied across the ends of the conductor)
∴vd= eVτ/ml
⇒vd∝V
So, when the potential difference is doubled the drift velocity will be doubled.
Note - Current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the drift velocity.
Drift velocity is defined as the average velocity with which free electrons get drifted towards the positive end of the conductor under the influence of an external electric field.
Drift velocity is given by
vd= eEτ/ m
But, E=V/l
(if l is length of the conductor and V is constant potential difference applied across the ends of the conductor)
∴vd= eVτ/ml
⇒vd∝V
So, when the potential difference is doubled the drift velocity will be doubled.
Note - Current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the drift velocity.
On heating a conductor its resistance- a)depends on type of metal
- b)remains constant
- c)increases
- d)decreases
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
On heating a conductor its resistance
a)
depends on type of metal
b)
remains constant
c)
increases
d)
decreases
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
The resistance increases as the temperature of a metallic conductor increase, so the resistance is directly proportional to the temperature. When we increase the temperature the amplitude of vibration of atoms increases as a result of which the number of collision among the electrons and atom increases, and hence resistances increases.
A carbon resistor is marked in green, red, and orange bands. The approximate resistance of the resistor is
- a)52 x 103 Ω
- b)25000 Ω
- c)5 x 102 Ω
- d)5 x 104 Ω
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A carbon resistor is marked in green, red, and orange bands. The approximate resistance of the resistor is
a)
52 x 103 Ω
b)
25000 Ω
c)
5 x 102 Ω
d)
5 x 104 Ω
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
To determine the resistance of a carbon resistor based on the color bands, we need to refer to the standard resistor color code. The colors represent digits and multipliers as follows:
- Green: 5
- Red: 2
- Orange: Multiplier of 10^3 (1,000)
Given the color bands: Green, Red, Orange
The resistance value is calculated as follows:
- First digit: Green = 5
- Second digit: Red = 2
- Multiplier: Orange = 10^3 (1,000)
So the resistance is:
Resistance=(52)×10^3 ohms=52,000 ohms=52 kilo-ohms
Answer: The approximate resistance of the resistor is 52 kΩ.
Manganin and constantan have a low temperature coefficient of resistivity which means that- a)their resistance values change very little with temperature
- b)their resistance values only change at low temperatures
- c)their resistance values change greatly with temperature
- d)their resistance values do not change with temperature
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Manganin and constantan have a low temperature coefficient of resistivity which means that
a)
their resistance values change very little with temperature
b)
their resistance values only change at low temperatures
c)
their resistance values change greatly with temperature
d)
their resistance values do not change with temperature
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
The semiconductors and insulating material are having negative temperature coefficient of resistance. Therefore, the resistance of semiconductors and insulators decrease with rise in temperature. Alloys, such as manganin, constantan etc. are having very low and positive temperature coefficient of resistance.
Two special characteristics of the element of an electric heater:- a)low resistivity and high melting point
- b)low resistivity and low melting point
- c)high resistivity and low melting point
- d)high resistivity and high melting point
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two special characteristics of the element of an electric heater:
a)
low resistivity and high melting point
b)
low resistivity and low melting point
c)
high resistivity and low melting point
d)
high resistivity and high melting point

|
Samiksha Narwade answered |
Electric heater is device to heat water.... So when it have high melting pt. it we sustain heat nd won't melt....nd resistance means to oppose heat... So it should have high resistivity to heat water without getting damage....HOPE THIS WILL HELP YOU....!
The dimension of the temperature coefficient of resistivity is- a)(temperature.ohm)-1
- b)same as temperature.ohm
- c)same as (temperature)-1
- d)same as (temperature)2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The dimension of the temperature coefficient of resistivity is
a)
(temperature.ohm)-1
b)
same as temperature.ohm
c)
same as (temperature)-1
d)
same as (temperature)2
|
|
Ameya Pillai answered |
Temperature Coefficient of Resistivity
The temperature coefficient of resistivity is defined as the change in the electrical resistance of a material per unit change in temperature. It is denoted by the symbol α and has units of inverse temperature (K^-1) or reciprocal temperature (1/T).
Effect of Temperature on Electrical Resistance
When the temperature of a conductor increases, its electrical resistance also increases. This is due to the fact that as the temperature increases, the atoms in the conductor vibrate more vigorously, which results in more collisions between the electrons and the atoms. This increase in collisions leads to an increase in the resistance of the conductor.
Formula for Temperature Coefficient of Resistivity
The temperature coefficient of resistivity is given by the formula:
α = (1/ρ) x (dρ/dT)
where ρ is the resistivity of the material and dρ/dT is the rate of change of the resistivity with temperature.
Dimension of Temperature Coefficient of Resistivity
The dimension of the temperature coefficient of resistivity is the same as that of reciprocal temperature or (temperature)^-1. This can be seen from the formula for the temperature coefficient of resistivity:
α = (1/ρ) x (dρ/dT)
where ρ has units of ohm-meters (Ω.m) and dρ/dT has units of ohm-meters per Kelvin (Ω.m/K). Thus, the units of α are K^-1 or 1/T.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the temperature coefficient of resistivity is a measure of how the electrical resistance of a material changes with temperature. It has units of inverse temperature or reciprocal temperature, and its dimension is the same as that of (temperature)^-1.
The temperature coefficient of resistivity is defined as the change in the electrical resistance of a material per unit change in temperature. It is denoted by the symbol α and has units of inverse temperature (K^-1) or reciprocal temperature (1/T).
Effect of Temperature on Electrical Resistance
When the temperature of a conductor increases, its electrical resistance also increases. This is due to the fact that as the temperature increases, the atoms in the conductor vibrate more vigorously, which results in more collisions between the electrons and the atoms. This increase in collisions leads to an increase in the resistance of the conductor.
Formula for Temperature Coefficient of Resistivity
The temperature coefficient of resistivity is given by the formula:
α = (1/ρ) x (dρ/dT)
where ρ is the resistivity of the material and dρ/dT is the rate of change of the resistivity with temperature.
Dimension of Temperature Coefficient of Resistivity
The dimension of the temperature coefficient of resistivity is the same as that of reciprocal temperature or (temperature)^-1. This can be seen from the formula for the temperature coefficient of resistivity:
α = (1/ρ) x (dρ/dT)
where ρ has units of ohm-meters (Ω.m) and dρ/dT has units of ohm-meters per Kelvin (Ω.m/K). Thus, the units of α are K^-1 or 1/T.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the temperature coefficient of resistivity is a measure of how the electrical resistance of a material changes with temperature. It has units of inverse temperature or reciprocal temperature, and its dimension is the same as that of (temperature)^-1.
The rate law for a reaction between the substances A and 8 is given byrate = k[A]n [B]mIf concentration of A is doubled and that of 8 is halved, the new rate as compared to the earlier rate would be - a)
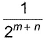
- b)(m + n)
- c)(n - m)
- d)2(n-m)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The rate law for a reaction between the substances A and 8 is given by
rate = k[A]n [B]m
If concentration of A is doubled and that of 8 is halved, the new rate as compared to the earlier rate would be
a)
b)
(m + n)
c)
(n - m)
d)
2(n-m)

|
Top Rankers answered |
Resistors can be wire bound or carbon resistors. Wire bound resistors are generally made of- a)Aluminium
- b)Carbon
- c)Copper
- d)Manganin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Resistors can be wire bound or carbon resistors. Wire bound resistors are generally made of
a)
Aluminium
b)
Carbon
c)
Copper
d)
Manganin
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
The wire material has a high resistivity, and is usually made of an alloy such as Nickel-chromium (Nichrome) or a copper-nickel-manganese alloy called Manganin. Common core materials include ceramic, plastic and glass. Wire wound resistors are the oldest type of resistors that are still manufactured today.
A steady current flows in a metallic conductor of non-uniform cross-section. The quantity/quantities constant along the length of the conductor is/are- a)Current and drift speed
- b)Current, electric field and drift velocity
- c)Speed only
- d)Current only.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A steady current flows in a metallic conductor of non-uniform cross-section. The quantity/quantities constant along the length of the conductor is/are
a)
Current and drift speed
b)
Current, electric field and drift velocity
c)
Speed only
d)
Current only.
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Steady current implies current is uniform across the cross-section.
Since current is constant, current per unit area and hence drift velocity are not constant.
J = nevd = σE
The above relation shows that nothing apart from the current is constant.
With green pods as a dominant trait over yellow, which of the following crosses will result in all progeny having yellow pods?- a)Homozygous green and homozygous yellow
- b)Heterozygous green and heterozygous green
- c)Homozygous yellow and homozygous yellow
- d)Homozygous green and homozygous green
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
With green pods as a dominant trait over yellow, which of the following crosses will result in all progeny having yellow pods?
a)
Homozygous green and homozygous yellow
b)
Heterozygous green and heterozygous green
c)
Homozygous yellow and homozygous yellow
d)
Homozygous green and homozygous green
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Yellow being recessive will express only when both alleles are present. That occurs only when both parents can contribute an allele encoding for the yellow pod. For all progeny to have yellow pods, both parents have to be homozygous for yellow pods.
The pure line round-seeded pea plant was crossed with a wrinkled-seeded pea plant. The F1 generation is ____ and it can be explained by _____.- a)Wrinkled : Law of segregation
- b)Round : Law of dominance
- c)Round : Co-dominance
- d)Wrinkled : Law of dominance
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Wrinkled : Law of segregation
b)
Round : Law of dominance
c)
Round : Co-dominance
d)
Wrinkled : Law of dominance

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The F1 generation from crossing a pure line round-seeded pea plant with a wrinkled-seeded pea plant will be round-seeded. This can be explained by the Law of Dominance, where round seeds are dominant over wrinkled seeds.
For the reaction,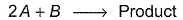 The half-life period was independent of concentration of B. On doubling the concentration A, rate increases two times. Thus, unit of rate constant for this reaction is
The half-life period was independent of concentration of B. On doubling the concentration A, rate increases two times. Thus, unit of rate constant for this reaction is- a)L mol-1s-1
- b)mol L-1s-1
- c)unitless
- d)S-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For the reaction,
The half-life period was independent of concentration of B. On doubling the concentration A, rate increases two times. Thus, unit of rate constant for this reaction is
a)
L mol-1s-1
b)
mol L-1s-1
c)
unitless
d)
S-1
|
|
Shanaya Choudhary answered |
I apologize, but your question about the reaction is incomplete. Could you provide more information or detail about the reaction you are referring to?
The rate equation for the reaction,2A + B → Cis found to be, rate = k[A] [B]Q. The correct statement in relation to this reaction is that the- a)unit of k must be s-1
- b)t1/2 is constant
- c)rate of formation of C is half of the rate of disappearance of A
- d)value of k is independent of the initial concentration of A and 8
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The rate equation for the reaction,
2A + B → C
is found to be, rate = k[A] [B]
Q. The correct statement in relation to this reaction is that the
a)
unit of k must be s-1
b)
t1/2 is constant
c)
rate of formation of C is half of the rate of disappearance of A
d)
value of k is independent of the initial concentration of A and 8

|
Amar Jain answered |
Rate = k (A)[B]
The given reaction is first order in A and first order is B.
Thus, total order = 2
Thus, total order = 2
(a) Unit of k = cone 1 - n time -1 = conc-1 time-1 Thus, (a) is false.
(b)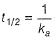 of second-order reaction, thus (b) is false.
of second-order reaction, thus (b) is false.
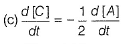
(b)
Thus, (c) is correct.
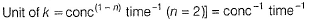
Thus, value of k is dependent on the concentration of A and B. Thus, (d) is false.
Thus, value of k is dependent on the concentration of A and B. Thus, (d) is false.
The type of materials whose resistivity is affected on adding the impurity is known as- a)Semiconductor
- b)Insulator
- c)Iron alloys
- d)Conductor
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The type of materials whose resistivity is affected on adding the impurity is known as
a)
Semiconductor
b)
Insulator
c)
Iron alloys
d)
Conductor
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Semiconductor - A material that is neither a good conductor of electricity nor a good insulator, but has properties of electrical conductivity somewhere between the two. Silicon and germanium are good semiconductor materials.
Direction (Q. No. 14) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.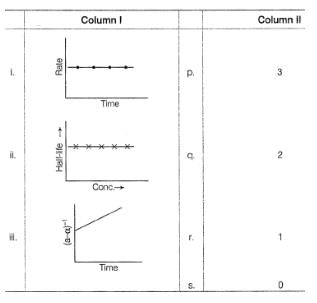

- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. No. 14) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Harsh Singhal answered |
For 2nd graph half live is cons.on increasing conc.so it is of 1st order
for 1st graph rate remains cons.with time means independent on conc.so it is of 0 order
so ans.is c
for 1st graph rate remains cons.with time means independent on conc.so it is of 0 order
so ans.is c
For a reaction, time of 75% reaction is thrice of time of 50% reaction. Thus, order of the reaction is- a)0
- b)1
- c)2
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
For a reaction, time of 75% reaction is thrice of time of 50% reaction. Thus, order of the reaction is
a)
0
b)
1
c)
2
d)
3
|
|
Anuj Unni answered |
For n th order reaction (n > 1)
This equation is true, if n = 2
The average time that elapses between two successive collisions of an electron is called- a)Drift velocity
- b)Free time
- c)Relaxation time
- d)Collision time
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The average time that elapses between two successive collisions of an electron is called
a)
Drift velocity
b)
Free time
c)
Relaxation time
d)
Collision time
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Relaxation time is the time interval between two successive collisions of electrons in a conductor, when current flows.
I = nave --> n->no. of free electrons a->area of conductor v->drift velocity e->charge of electron
but v=(eE/m)T--> E-> field m->mass of electron T->Relaxation time
From this, you can find expression of relaxation time.Field is V/length and V=IR.From this you can modify the expression in terms of resistivity.
Mobility of charge carriers in a conductor is given by- a)(charge of an electron).drift velocity/ electric field
- b)drift velocity/ electric field
- c)mass of an electron.(drift velocity/ electric field)
- d)(drift velocity)(electric field)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Mobility of charge carriers in a conductor is given by
a)
(charge of an electron).drift velocity/ electric field
b)
drift velocity/ electric field
c)
mass of an electron.(drift velocity/ electric field)
d)
(drift velocity)(electric field)
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Drift velocity of charge carriers in a conductor depend upon two factors, one is the intensity of applied electric field across the conductor and other is one property of the conductor called Mobility of Charge Carrier. In other words, for applied same electric field, on different metallic conductors there will be different drift velocities of electrons. These drift velocities of electrons depend upon a typical property of conductor called mobility of charge carrier.
What are the possible phenotypes that can be observed after self-crossing violet flowered pea plants?- a)All violet
- b)All white
- c)25% violet and 75% white
- d)25% white and 75% violet
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What are the possible phenotypes that can be observed after self-crossing violet flowered pea plants?
a)
All violet
b)
All white
c)
25% violet and 75% white
d)
25% white and 75% violet
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Violet is dominant over white. Self-crossing of violet flowered plants will produce 25% recessive plants, which will have white-flowers.
A plant that exhibits two alleles for only one trait is called ________- a)monohybrid
- b)dihybrid
- c)monogamous
- d)digamous
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A plant that exhibits two alleles for only one trait is called ________
a)
monohybrid
b)
dihybrid
c)
monogamous
d)
digamous
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Monohybrid refers to a hybrid that differs at only one gene. Thus, a plant that exhibits two alleles for one trait is a monohybrid.
What is the process of removal of anthers termed?- a)Demasculation
- b)Emasculation
- c)Remasculation
- d)Masculation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the process of removal of anthers termed?
a)
Demasculation
b)
Emasculation
c)
Remasculation
d)
Masculation
|
|
Dipanjan Choudhary answered |
The correct answer is option 'B', Emasculation.
Emasculation refers to the process of removing the anthers from a flower to prevent self-pollination and facilitate controlled cross-pollination. This technique is commonly used in plant breeding programs to produce hybrid plants with desired traits.
Here is a detailed explanation of the process of emasculation:
1. Purpose of Emasculation:
- Emasculation is performed to prevent self-pollination, where the pollen from the anthers of the same flower or plant is transferred to the stigma, leading to the production of self-pollinated seeds.
- By removing the anthers, the flower can be protected from self-pollination and allow for controlled pollination to introduce pollen from a different plant with desired traits.
2. Tools Required:
- Sterilized forceps or tweezers: These are used to carefully pluck the anthers from the flower without damaging the stigma or other reproductive structures.
- Sterilized scalpel or razor blade: This may be required to make precise cuts or remove unwanted parts of the flower during the emasculation process.
3. Procedure:
- Choose flowers that are at the right stage of development for emasculation. The flowers should be at the stage where the anthers are mature and ready to release pollen but the stigma is not receptive yet.
- Carefully remove the petals and sepals to expose the reproductive structures of the flower.
- Use sterilized forceps or tweezers to gently remove the anthers. Be cautious not to damage the stigma or other important parts of the flower.
- After emasculation, it is important to discard the removed anthers properly to prevent accidental pollination.
- It is also important to ensure that the stigma is not damaged during the emasculation process as it is the receptive part of the flower where pollen will be introduced later.
4. Importance of Emasculation:
- Emasculation is crucial in plant breeding programs to produce hybrid plants with desirable traits. By preventing self-pollination, breeders can control the pollination process and introduce pollen from a different plant to achieve specific genetic combinations.
- This technique allows breeders to create plants with improved characteristics such as disease resistance, increased yield, or better quality.
In conclusion, emasculation is the process of removing the anthers from a flower to prevent self-pollination and facilitate controlled cross-pollination. It is an important technique used in plant breeding programs to produce hybrid plants with desired traits.
Emasculation refers to the process of removing the anthers from a flower to prevent self-pollination and facilitate controlled cross-pollination. This technique is commonly used in plant breeding programs to produce hybrid plants with desired traits.
Here is a detailed explanation of the process of emasculation:
1. Purpose of Emasculation:
- Emasculation is performed to prevent self-pollination, where the pollen from the anthers of the same flower or plant is transferred to the stigma, leading to the production of self-pollinated seeds.
- By removing the anthers, the flower can be protected from self-pollination and allow for controlled pollination to introduce pollen from a different plant with desired traits.
2. Tools Required:
- Sterilized forceps or tweezers: These are used to carefully pluck the anthers from the flower without damaging the stigma or other reproductive structures.
- Sterilized scalpel or razor blade: This may be required to make precise cuts or remove unwanted parts of the flower during the emasculation process.
3. Procedure:
- Choose flowers that are at the right stage of development for emasculation. The flowers should be at the stage where the anthers are mature and ready to release pollen but the stigma is not receptive yet.
- Carefully remove the petals and sepals to expose the reproductive structures of the flower.
- Use sterilized forceps or tweezers to gently remove the anthers. Be cautious not to damage the stigma or other important parts of the flower.
- After emasculation, it is important to discard the removed anthers properly to prevent accidental pollination.
- It is also important to ensure that the stigma is not damaged during the emasculation process as it is the receptive part of the flower where pollen will be introduced later.
4. Importance of Emasculation:
- Emasculation is crucial in plant breeding programs to produce hybrid plants with desirable traits. By preventing self-pollination, breeders can control the pollination process and introduce pollen from a different plant to achieve specific genetic combinations.
- This technique allows breeders to create plants with improved characteristics such as disease resistance, increased yield, or better quality.
In conclusion, emasculation is the process of removing the anthers from a flower to prevent self-pollination and facilitate controlled cross-pollination. It is an important technique used in plant breeding programs to produce hybrid plants with desired traits.
Passage IIIA reaction between substances A and B is represented as: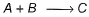 Observations on the rate of this reaction are obtained as :
Observations on the rate of this reaction are obtained as :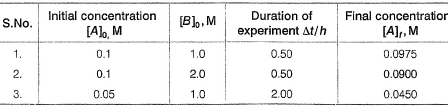 Q.Rate constant of the overall reaction is
Q.Rate constant of the overall reaction is- a)5.0 * 10-2 M-1 h-1
- b)5.0 * 10-2 M-2 h-1
- c)5.0 * 10-2 h-1
- d)5.0 * 10-2 mh-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage III
A reaction between substances A and B is represented as:
Observations on the rate of this reaction are obtained as :
Q.
Rate constant of the overall reaction is
a)
5.0 * 10-2 M-1 h-1
b)
5.0 * 10-2 M-2 h-1
c)
5.0 * 10-2 h-1
d)
5.0 * 10-2 mh-1
|
|
Sahil Rathod answered |
I am in standard 11 not 12
For semiconductors, the major factor affecting the value of resistivity when temperature changes is- a)n: the number of free electrons per unit volume
- b)e: the charge of an electron
- c)m: the mass of an electron
- d)τ:average time between collisions
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For semiconductors, the major factor affecting the value of resistivity when temperature changes is
a)
n: the number of free electrons per unit volume
b)
e: the charge of an electron
c)
m: the mass of an electron
d)
τ:average time between collisions

|
Divey Sethi answered |
n increases with temperature and this increase more than compensates any decrease in relaxation time. Hence, for semiconductors resistivity decreases with the increase in temperature.
The presence of two different alleles at a particular locus results in _________- a)Homozygosity
- b)Heterozygosity
- c)Hemizygosity
- d)Nullizygosity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The presence of two different alleles at a particular locus results in _________
a)
Homozygosity
b)
Heterozygosity
c)
Hemizygosity
d)
Nullizygosity
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Heterozygosity refers to different alleles present at a given locus. This is the condition that is of interest to the study of genetics. It can be used to test the nature of an allele.
During meiosis, what happens to the parental alleles?- a)They segregate
- b)They undergo repair
- c)They undergo breakage
- d)They replicate
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During meiosis, what happens to the parental alleles?
a)
They segregate
b)
They undergo repair
c)
They undergo breakage
d)
They replicate
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Based on his studies on pea plants, he observed that the parental recessive traits were observed again only in the F2 progeny without any form of blending in F1 generation. This points out that the factors segregate or separate during the process of meiosis.
Conversion of temperature into electric voltage is done with- a)thermometer
- b)resistor
- c)thermistor
- d)rheostat
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Conversion of temperature into electric voltage is done with
a)
thermometer
b)
resistor
c)
thermistor
d)
rheostat
|
|
Harsh Desai answered |
To convert temperature to voltage we can do a precise measurement of the temperature in a room. A NTC resistor or a thermistor
It is used as a sensor that has a strong temperature dependence.
It is used as a sensor that has a strong temperature dependence.
Which one of the following cannot be explained on the basis of Mendel's Law of Dominance?- a)The discrete unit controlling a particular character is called a factor
- b)Out of one pair of factors one is dominant, and the other is recessive
- c)Alleles do not show any blendings and both the characters recover as such in F2 generation.
- d)Factors occur in pairs
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
The discrete unit controlling a particular character is called a factor
b)
Out of one pair of factors one is dominant, and the other is recessive
c)
Alleles do not show any blendings and both the characters recover as such in F2 generation.
d)
Factors occur in pairs

|
Infinity Academy answered |
Mendel's Law of Dominance states that in a pair of alleles, one may mask the expression of the other. The third option (C) cannot be explained by this law because the Law of Dominance does not address the concept of blending or recovery of both characters in the F2 generation. Instead, it focuses on how dominant traits mask recessive traits, and the characters appear as distinct and separate in the F2 generation.
give the remaining questions
ChatGPT
give the remaining questions
ChatGPT
What process needs to be avoided for carrying of efficient crosses?- a)Self-pollination
- b)Fertilization
- c)Development of embryo
- d)Pollen tube development
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What process needs to be avoided for carrying of efficient crosses?
a)
Self-pollination
b)
Fertilization
c)
Development of embryo
d)
Pollen tube development
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Self-pollination leads to fertilization by the pollen from the same flower. A cross desires pollination and fertilization by pollen from a different plant. Hence self-pollination needs to be avoided.
Which of the following was not observed in F2 progeny of true-breeding tall and dwarf plants?- a)Homozygous tall plants
- b)Heterozygous tall plants
- c)Homozygous dwarf plants
- d)Heterozygous dwarf plants
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following was not observed in F2 progeny of true-breeding tall and dwarf plants?
a)
Homozygous tall plants
b)
Heterozygous tall plants
c)
Homozygous dwarf plants
d)
Heterozygous dwarf plants
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The F2 progeny has both dwarf and tall plants. 25% of them are homozygous tall, 50% are heterozygous tall, and 25% are homozygous dwarf. Dwarfness is a recessive trait and thus cannot be expressed in the heterozygous state.
If in the fermentation of sugar in an enzymatic solution that is 0.12 M, the concentration of sugar is reduced to 0.06 M in 10 h and to 0.03 M in 20 h. Thus, order of the reaction is - a)3
- b)2
- c)1
- d)0
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If in the fermentation of sugar in an enzymatic solution that is 0.12 M, the concentration of sugar is reduced to 0.06 M in 10 h and to 0.03 M in 20 h. Thus, order of the reaction is
a)
3
b)
2
c)
1
d)
0

|
Ashish Nambiar answered |

We find that, t75 = 2 x t50
Thus, given reaction is of first-order.
Kinetics of the following reaction,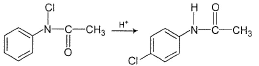 can be studied by
can be studied by- a)measurement of pH
- b)titration with hypo after adding Kl
- c)titration with AgNO3 solution
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Kinetics of the following reaction,
can be studied by
a)
measurement of pH
b)
titration with hypo after adding Kl
c)
titration with AgNO3 solution
d)
All of the above

|
Aditya Sen answered |
Cl-atom attached to N-atom, is an oxidising agent and can oxidise Kl to l2.
l2 can be titrated using hypo in iodometric titration.
Cl-atom attached to benzene nucleus is not an oxidising agent.
What does F in “F1 progeny” stand for?- a)Filial
- b)Fillial
- c)Filum
- d)Filler
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What does F in “F1 progeny” stand for?
a)
Filial
b)
Fillial
c)
Filum
d)
Filler
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta answered |
In basic terminology, the F1 generation is the first generation of offspring produced by a set of parents. The 'F' in F1 stands for 'filial.
If F2 dwarf plants were self-pollinated, then the genotype of F3 & F4 plants is:- a)TT and Tt
- b)tt and tt
- c)tt and Tt
- d)Tt and Tt
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
TT and Tt
b)
tt and tt
c)
tt and Tt
d)
Tt and Tt

|
Stepway Academy answered |
If F2 dwarf plants (genotype tt) are self-pollinated, all the offspring (F3 and F4) will also be dwarf with the genotype tt.
For the simple reaction,A → BWhen [A] was changed from 0.502 mol dm-3 to 1.004 mol dm-3 half-life dropped from 52 s to 26 s at 300 K. Thus, order of the reaction is - a)0
- b)1
- c)2
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For the simple reaction,
A → B
When [A] was changed from 0.502 mol dm-3 to 1.004 mol dm-3 half-life dropped from 52 s to 26 s at 300 K. Thus, order of the reaction is
a)
0
b)
1
c)
2
d)
3

|
Ashwini Chakraborty answered |
For nth order reaction,
(T50 ) is t1 ,at [A] = a1 and is t2 at [A] = a2
∴ 

(2) = (2)n-1
∴ n - 1 = 1, n = 2
Resistance of a conductor depends on- a)length
- b)length, area of cross-section, nature of material, temperature of conductor
- c)length and area of cross-section
- d)length, area of cross-section, nature of material
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Resistance of a conductor depends on
a)
length
b)
length, area of cross-section, nature of material, temperature of conductor
c)
length and area of cross-section
d)
length, area of cross-section, nature of material
|
|
Ashwini Shah answered |
The resistance of a conductor depends on thickness (cross sectional area of the wire), length and temperature.
Resistivity is defined as the measure of the resisting power of a specified material to the flow of an electric current.
R=ρ(I/A)
where R = Resistance of the conductor
ρ = Resistivity of the conductor
l = length of the conductor
A = Area of cross section
i.e., ρ=R (A/l)
Resistivity is defined as the measure of the resisting power of a specified material to the flow of an electric current.
R=ρ(I/A)
where R = Resistance of the conductor
ρ = Resistivity of the conductor
l = length of the conductor
A = Area of cross section
i.e., ρ=R (A/l)
The standard resistance coil are made of “manganin” because- a)Temperature coefficient of resistance remain constant
- b)Temperature coefficient of resistance is very low
- c)Temperature coefficient of resistance is very high
- d)Temperature coefficient of resistance is moderate
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The standard resistance coil are made of “manganin” because
a)
Temperature coefficient of resistance remain constant
b)
Temperature coefficient of resistance is very low
c)
Temperature coefficient of resistance is very high
d)
Temperature coefficient of resistance is moderate

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Answer :- b
Temperature coefficient of resistance is very low
For manganin, the temp coefficient of resistance is very low, and its resistivity is quite large. Due to which the resistance of the manganin wire remains almost unchanged with change in temperature. It is due to this fact; the wire of the manganin is used for making standard resistance coil.
A cross between tall and dwarf plants was performed, and 120 offspring were produced in which 90 plants were tall and 30 were dwarf. Find out the genotype of their parents.- a)Tt and TT
- b) Tt and Tt
- c) TT and tt
- d)tt and tt
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A cross between tall and dwarf plants was performed, and 120 offspring were produced in which 90 plants were tall and 30 were dwarf. Find out the genotype of their parents.
a)
Tt and TT
b)
Tt and Tt
c)
TT and tt
d)
tt and tt

|
Top Rankers answered |
The ratio of tall to dwarf plants in the offspring (90:30) indicates a 3:1 phenotypic ratio typical of a cross between two heterozygous tall plants (Tt x Tt). Thus, the parents must have been Tt and Tt.
What should be the phenotype of a cross between violet and white-flowered true-breeding garden pea plants?- a)Violet
- b)White
- c)Pink
- d)Red
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What should be the phenotype of a cross between violet and white-flowered true-breeding garden pea plants?
a)
Violet
b)
White
c)
Pink
d)
Red
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Violet is the dominant factor over white in pea flowers. Hence violet can express even in the presence of white. The cross of violet true-breeding and white true-breeding pea plants will produce all heterozygous offsprings. Thus, all of them will have violet flowers.
Direction (Q. Nos. 15-20) This section contains 3 paragraphs, each describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Six questions related to the paragraphs have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).Passage I Peroxy acetyl nitrite 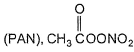 is an air pollutant, as it decomposes into radicals :
is an air pollutant, as it decomposes into radicals :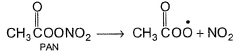 A sample of polluted air is analysed for its PAN content which is reported as molecules per litre of air at 298 K.
A sample of polluted air is analysed for its PAN content which is reported as molecules per litre of air at 298 K.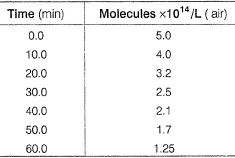 Q.Determine the order of the PAN decomposition
Q.Determine the order of the PAN decomposition- a)0
- b)1
- c)2
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 15-20) This section contains 3 paragraphs, each describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Six questions related to the paragraphs have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage I
Peroxy acetyl nitrite 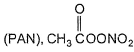 is an air pollutant, as it decomposes into radicals :
is an air pollutant, as it decomposes into radicals :
A sample of polluted air is analysed for its PAN content which is reported as molecules per litre of air at 298 K.
Q.
Determine the order of the PAN decomposition
a)
0
b)
1
c)
2
d)
3

|
Malavika Shah answered |
Time ; [PAN]
0 min 5.0 x 1014 molecules L-1
30 min 2.5 x 1014 molecules L-1
60 min 1.25 x 1014 molecules L-1
At 30 min, 50% reaction takes place.
At 60 min, 75% reaction takes place.
At 30 min, 50% reaction takes place.
At 60 min, 75% reaction takes place.
Thus, T75 = 2 x T50
it is valid for first order reaction. Thus, order = 1
For first order reactions, T50 = 0.693/k
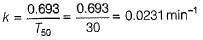
For nth order reaction, Graphs between log (rate) and log[A0] are of the type ([A0] is the initial concentration)
Graphs between log (rate) and log[A0] are of the type ([A0] is the initial concentration)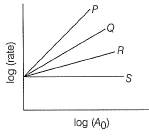 Lines P, Q, R and S are for the order
Lines P, Q, R and S are for the order 
- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For nth order reaction,
Graphs between log (rate) and log[A0] are of the type ([A0] is the initial concentration)
Lines P, Q, R and S are for the order
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Malavika Shah answered |
n = order of the reaction =slope of the line
Larger the value of the slope of the line, larger the order.
Thus, P = 3, Q = 2, R = 1, S = 0.
Passage IIH The reaction between nitric oxide (NO) and hydrogen (H2)has been investigated by measuring the initial rate of decrease of pressure in known mixture of gases. The following results were obtained at 1000 K.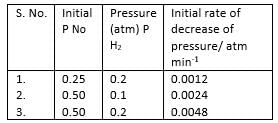 Q. Overall order of the reaction is
Q. Overall order of the reaction is- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)0
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage II
H The reaction between nitric oxide (NO) and hydrogen (H2)has been investigated by measuring the initial rate of decrease of pressure in known mixture of gases. The following results were obtained at 1000 K.

Q.
Overall order of the reaction is
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
0

|
Aditya Sen answered |
-dp/dt = k(PNO)a (PH2)b
0.0012 = k(0.25)a(0.2)b
0.0024 = k(0.50)a(0.1)b
0.0048 = k(0.50)a(0.2)b
From Eqs. (i) and (iii), we get
4 = (2)a
∴ (2)2 = (2)a
∴ a = 2
Thus w.r.t. No, order = 2
From Eqs.)ii) and (iii), we get
2 = (2)b
(2)1 = (2)b
∴ b = 1
Thus, w.r.t. H2, order = 1
Thus, w.r.t. H2, order = 1
Total order = 3
From Eq. (i),
0.0012 = k(0.25)2(0.2)1 = k (0.25)2(0.2)
∴ k = 0.0012/(0.25)2(0.02) = 0.096 atm-2 min-1
Passage IIIA reaction between substances A and B is represented as:A+B → CObservations on the rate of this reaction are obtained as :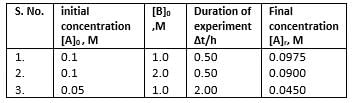 Q.
Q.
Order of the reaction w.r.t. A and B respectively are- a)1,1
- b)1,2
- c)2,1
- d)2,2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage III
A reaction between substances A and B is represented as:
A+B → C
Observations on the rate of this reaction are obtained as :

Q.
Order of the reaction w.r.t. A and B respectively are
Order of the reaction w.r.t. A and B respectively are
a)
1,1
b)
1,2
c)
2,1
d)
2,2

|
Dishani Kulkarni answered |
where, a == order w.r.t. A, 6 = order w.r.t. B
(i) 5.0 x 10-3 = k[0.1]a[1.0]b
(ii) 2.0 x 1-2 = k [0.1]a[2.0]b
(iii) 2.5 x 10-3 = k [0.05]a[1.0]b
From Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get
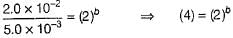
Order w.r.t.A = 1
From Eq. (ii), 5.0x10-3 = K(0.1)(1.0)2
∴ k = 5.0 x 10-2M-2h-1
For the following reaction,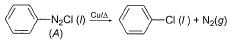 Variation of T50 with [A] is shown
Variation of T50 with [A] is shown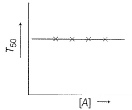 Q.After 10 min volume of N2 (g) is 10 L and after complete reaction, volume of N2 (g) is 50 L. Thus, T50 is
Q.After 10 min volume of N2 (g) is 10 L and after complete reaction, volume of N2 (g) is 50 L. Thus, T50 is- a)10 min
- b)20 min
- c)31 min
- d)41 min
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For the following reaction,
Variation of T50 with [A] is shown
Q.
After 10 min volume of N2 (g) is 10 L and after complete reaction, volume of N2 (g) is 50 L. Thus, T50 is
a)
10 min
b)
20 min
c)
31 min
d)
41 min

|
Dishani Kulkarni answered |
T50 is independent of concentration of [A], Thus, it follows first order kinetics.
When a conductor is placed in an electric field, the force experienced by its electrons will be- a)
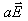
- b)
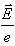
- c)
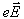 in direction
in direction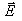
- d)
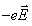 in opposite direction of
in opposite direction of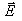
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When a conductor is placed in an electric field, the force experienced by its electrons will be
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Sahana Savalagi answered |
Answer is (d) because the direction that positive test charges are pushed. Thus, these negatively charged electrons move in the direction opposite the electric field.
Passage IIH The reaction between nitric oxide (NO) and hydrogen (H2)has been investigated by measuring the initial rate of decrease of pressure in known mixture of gases. The following results were obtained at 1000 K. Q.Rate constant of the overall reaction is
Q.Rate constant of the overall reaction is- a)0.0048 atm-2min-1
- b)0.0012 atm-1min-1
- c)0.0096 atm-2min-1
- d)0.0096 atm-1min-1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage II
H The reaction between nitric oxide (NO) and hydrogen (H2)has been investigated by measuring the initial rate of decrease of pressure in known mixture of gases. The following results were obtained at 1000 K.

Q.
Rate constant of the overall reaction is
a)
0.0048 atm-2min-1
b)
0.0012 atm-1min-1
c)
0.0096 atm-2min-1
d)
0.0096 atm-1min-1

|
Kavya Das answered |
0.0012 = k(0.25)2(0.2)1 = k(0.25)2(0.2)
∴ k = 0.0012/(0.25)2 (0.2) = 0.096 atm-2 min-1
In 1900 Mendel’s work was rediscovered by:- a)Korana, Nirenberg and Mathei
- b)De Vries, Correns and von Tschermak
- c)Avery, McCleod and McCarty
- d)Watson, Crick and Wilkins
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Korana, Nirenberg and Mathei
b)
De Vries, Correns and von Tschermak
c)
Avery, McCleod and McCarty
d)
Watson, Crick and Wilkins

|
Infinity Academy answered |
Mendel’s work was rediscovered in 1900 by De Vries, Correns, and von Tschermak. They independently found Mendel’s principles of inheritance, which had been overlooked and forgotten after their original publication.
nA → Product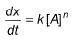 For the reaction, rate constant and rate of the reaction are equal, then on doubling the concentration of A, rate becomes,
For the reaction, rate constant and rate of the reaction are equal, then on doubling the concentration of A, rate becomes,- a)doubled
- b)four times
- c)halved
- d)constant
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
nA → Product
For the reaction, rate constant and rate of the reaction are equal, then on doubling the concentration of A, rate becomes,
a)
doubled
b)
four times
c)
halved
d)
constant

|
Kavya Das answered |
Thus, order = zero Rate is independent of concentration of A.
Thus, rate remains constant.
Chapter doubts & questions for June Week 3 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of June Week 3 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.













