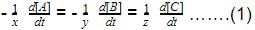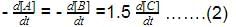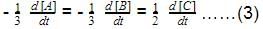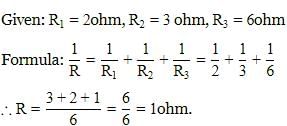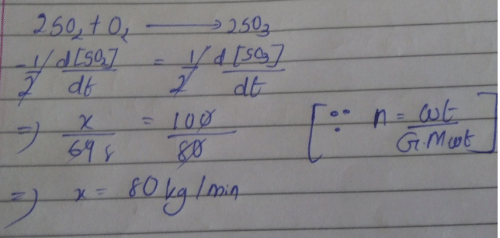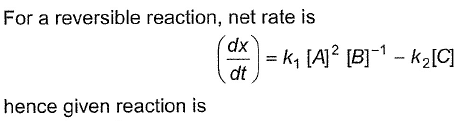All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of June Week 4 for NEET Exam
Direction (Q. Nos. 14 and 15) This section contains a passage describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d)
Passage
The decomposition of NO2 at 400 K proceeds at a of rate of 5.4 x 10 -5 mol L-1 s-1 when [NO2] = 0.01 mol-1
2 NO2(g) → 2NO(g ) + O2(g).
Q. What is the rate law when observed rate is 1.35 x 10-5 mol L-1 s-1 at [NO2] = 0.005 mol L-1?
- a)k[NO2]
- b)k[NO2]0
- c)k[NO2]3
- d)k[NO2]2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 14 and 15) This section contains a passage describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d)
Passage
The decomposition of NO2 at 400 K proceeds at a of rate of 5.4 x 10 -5 mol L-1 s-1 when [NO2] = 0.01 mol-1
2 NO2(g) → 2NO(g ) + O2(g).
Q. What is the rate law when observed rate is 1.35 x 10-5 mol L-1 s-1 at [NO2] = 0.005 mol L-1?
a)
k[NO2]
b)
k[NO2]0
c)
k[NO2]3
d)
k[NO2]2
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Given unit of rate = mol L-1 s-1
General formula for unit of rate = mol n-1 Ln-1 s -1
On equating,
1-n = 1 ⇒ n = 0
n-1 = -1 ⇒ n = 0
General formula for unit of rate = mol n-1 Ln-1 s -1
On equating,
1-n = 1 ⇒ n = 0
n-1 = -1 ⇒ n = 0
Hence, it is a zero order reaction.
The initial rates of reaction for the equation, 2A + B → Products.Products were determined under various initial concentrations of reactants. Thus, rate law is equal to
Thus, rate law is equal to- a)k[A][B]
- b)k[A][B]2
- c) k[A]
- d) k[B]
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The initial rates of reaction for the equation, 2A + B → Products.
Products were determined under various initial concentrations of reactants.
Thus, rate law is equal to
a)
k[A][B]
b)
k[A][B]2
c)
k[A]
d)
k[B]
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
Let order w.r.t. A = a, order w.r.t. B = b
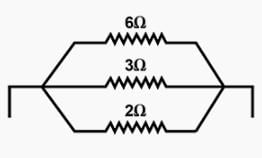
What is current I in the circuit as shown in figure?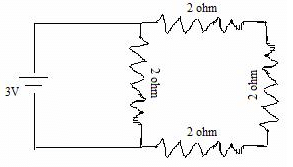
- a)1 A
- b)2.0 A
- c)1.2 A
- d)0.5 A
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is current I in the circuit as shown in figure?
a)
1 A
b)
2.0 A
c)
1.2 A
d)
0.5 A
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Three 2Ω resistors are in series. Their total resistance =6Ω. Now it is in parallel with 2Ω resistor, so total resistance,
1/R=1/2+1/6=3+1/6=4/6=2/3
R=3/2
∴I=RV=3/(3/2)=3×2/3=2A
1/R=1/2+1/6=3+1/6=4/6=2/3
R=3/2
∴I=RV=3/(3/2)=3×2/3=2A
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-13) This section contains multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctQ. In the following reaction, which has maximum rate w.r.t. rate of disappearance of NH3?4NH3 + 502 → 4NO + 6H2O- a)O2
- b)NO
- c)H2O
- d)Equal
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-13) This section contains multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
Q. In the following reaction, which has maximum rate w.r.t. rate of disappearance of NH3?
4NH3 + 502 → 4NO + 6H2O
a)
O2
b)
NO
c)
H2O
d)
Equal

|
Nabanita Basu answered |
Understanding the Reaction
The given reaction is:
4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O
This reaction involves the disappearance of ammonia (NH3) and the appearance of the products NO and H2O.
Rate of Reaction
The rate of a chemical reaction can be expressed in terms of the rate of disappearance of reactants or the rate of appearance of products.
Stoichiometry of the Reaction
- According to the stoichiometry:
- 4 moles of NH3 produce 4 moles of NO and 6 moles of H2O.
- The coefficients in the balanced equation indicate the relative rates of disappearance and appearance.
Rate of Disappearance
- The rate of disappearance of NH3 is given by:
Rate = - (1/4) * d[NH3]/dt
- The rates for O2, NO, and H2O can be expressed similarly:
- O2: Rate = - (1/5) * d[O2]/dt
- NO: Rate = (1/4) * d[NO]/dt
- H2O: Rate = (1/6) * d[H2O]/dt
Comparison of Rates
To find the maximum rate of disappearance, we can compare the rates derived from the balanced equation:
- NH3: - (1/4) (for every 1 mole of disappearance)
- O2: - (1/5) (for every 1 mole of disappearance)
- NO: (1/4) (for every 1 mole of appearance)
- H2O: (1/6) (for every 1 mole of appearance)
The fractions reveal how many moles of each substance are involved in the reaction. The lower the denominator, the higher the rate of disappearance or appearance.
Conclusion
- Among the reactants and products, H2O has the highest coefficient when considering the rate of disappearance of NH3.
- Therefore, the maximum rate of disappearance is related to H2O's formation.
Thus, the correct answer is option 'C' (H2O).
The given reaction is:
4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O
This reaction involves the disappearance of ammonia (NH3) and the appearance of the products NO and H2O.
Rate of Reaction
The rate of a chemical reaction can be expressed in terms of the rate of disappearance of reactants or the rate of appearance of products.
Stoichiometry of the Reaction
- According to the stoichiometry:
- 4 moles of NH3 produce 4 moles of NO and 6 moles of H2O.
- The coefficients in the balanced equation indicate the relative rates of disappearance and appearance.
Rate of Disappearance
- The rate of disappearance of NH3 is given by:
Rate = - (1/4) * d[NH3]/dt
- The rates for O2, NO, and H2O can be expressed similarly:
- O2: Rate = - (1/5) * d[O2]/dt
- NO: Rate = (1/4) * d[NO]/dt
- H2O: Rate = (1/6) * d[H2O]/dt
Comparison of Rates
To find the maximum rate of disappearance, we can compare the rates derived from the balanced equation:
- NH3: - (1/4) (for every 1 mole of disappearance)
- O2: - (1/5) (for every 1 mole of disappearance)
- NO: (1/4) (for every 1 mole of appearance)
- H2O: (1/6) (for every 1 mole of appearance)
The fractions reveal how many moles of each substance are involved in the reaction. The lower the denominator, the higher the rate of disappearance or appearance.
Conclusion
- Among the reactants and products, H2O has the highest coefficient when considering the rate of disappearance of NH3.
- Therefore, the maximum rate of disappearance is related to H2O's formation.
Thus, the correct answer is option 'C' (H2O).
Reaction kinetics deals with the study of- a)Rate of reaction
- b)Mechanism of reaction
- c)Factors which affects the rate of reaction
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Reaction kinetics deals with the study of
a)
Rate of reaction
b)
Mechanism of reaction
c)
Factors which affects the rate of reaction
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Reaction kinetics deals with the study of rate of reaction, their mechanism and the factors which affects the rate of reaction. It specifies all the general characteristics of a chemical reaction.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-13) This section contains multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctQ. In the following reaction, which has maximum rate w.r.t. rate of disappearance of NH3?4NH3 + 502 → 4NO + 6H2O- a)O2
- b)NO
- c)H2O
- d)Equal
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-13) This section contains multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
Q. In the following reaction, which has maximum rate w.r.t. rate of disappearance of NH3?
4NH3 + 502 → 4NO + 6H2O
a)
O2
b)
NO
c)
H2O
d)
Equal
|
|
Manoj Chauhan answered |
By stoichiometry of the reaction

similarly,
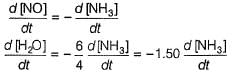
Direction (Q. Nos. 16-18) This section contains 3 questions. When worked out will result in one integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)In the following reaction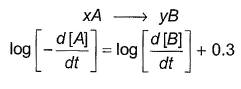 Q. Where negative sign indicates rate of disappearance of the reactant. What is the value of x/y ?
Q. Where negative sign indicates rate of disappearance of the reactant. What is the value of x/y ?- a)2
- b)4
- c)5
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 16-18) This section contains 3 questions. When worked out will result in one integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
In the following reaction
Q. Where negative sign indicates rate of disappearance of the reactant. What is the value of x/y ?
a)
2
b)
4
c)
5
d)
6
|
|
Praveen Reddy answered |
Three resistors of 4Ω, 12Ω , and 6Ω are connected in parallel. No. of 12Ω resistors required to be connected in parallel to reduce the total resistance to half of its original is- a)6
- b)3
- c)12
- d)2
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Three resistors of 4Ω, 12Ω , and 6Ω are connected in parallel. No. of 12Ω resistors required to be connected in parallel to reduce the total resistance to half of its original is
a)
6
b)
3
c)
12
d)
2

|
Sanchita Iyer answered |
Understanding Parallel Resistance
In a parallel circuit, the total resistance (R_total) is calculated using the formula:
1/R_total = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 + ...
For the given resistors:
- R1 = 4 ohms
- R2 = 12 ohms
- R3 = 6 ohms
Calculating the Original Total Resistance
Let's find the total resistance with the existing resistors.
- 1/R_total = 1/4 + 1/12 + 1/6
Finding a common denominator (which is 12):
- 1/R_total = 3/12 + 1/12 + 2/12 = 6/12
Thus,
- R_total = 2 ohms.
Target Resistance
We want to reduce the total resistance to half of its original value:
- Target Resistance = 2 ohms / 2 = 1 ohm.
Adding 12 Ohm Resistors
Let 'n' be the number of additional 12 ohm resistors needed in parallel to reach 1 ohm.
The new total resistance formula becomes:
1/R_new = 1/R_total + n/R2
Where R2 is 12 ohms:
1/R_new = 1/2 + n/12.
Setting R_new to 1 ohm gives:
1 = 1/2 + n/12.
Rearranging the equation:
1 - 1/2 = n/12
1/2 = n/12
Thus, n = 6.
Conclusion
To achieve a total resistance of 1 ohm, you need to connect 6 additional 12 ohm resistors in parallel. Hence, the correct answer is:
A) 6
In a parallel circuit, the total resistance (R_total) is calculated using the formula:
1/R_total = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 + ...
For the given resistors:
- R1 = 4 ohms
- R2 = 12 ohms
- R3 = 6 ohms
Calculating the Original Total Resistance
Let's find the total resistance with the existing resistors.
- 1/R_total = 1/4 + 1/12 + 1/6
Finding a common denominator (which is 12):
- 1/R_total = 3/12 + 1/12 + 2/12 = 6/12
Thus,
- R_total = 2 ohms.
Target Resistance
We want to reduce the total resistance to half of its original value:
- Target Resistance = 2 ohms / 2 = 1 ohm.
Adding 12 Ohm Resistors
Let 'n' be the number of additional 12 ohm resistors needed in parallel to reach 1 ohm.
The new total resistance formula becomes:
1/R_new = 1/R_total + n/R2
Where R2 is 12 ohms:
1/R_new = 1/2 + n/12.
Setting R_new to 1 ohm gives:
1 = 1/2 + n/12.
Rearranging the equation:
1 - 1/2 = n/12
1/2 = n/12
Thus, n = 6.
Conclusion
To achieve a total resistance of 1 ohm, you need to connect 6 additional 12 ohm resistors in parallel. Hence, the correct answer is:
A) 6
The reaction rate is defined as the rate at which the concentration of the reactants __________ with time or the concentration of products ___________ with time.- a)Increase, increase
- b)Decrease, decrease
- c)Decrease, increase
- d)Increase, decrease
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction rate is defined as the rate at which the concentration of the reactants __________ with time or the concentration of products ___________ with time.
a)
Increase, increase
b)
Decrease, decrease
c)
Decrease, increase
d)
Increase, decrease
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The reaction rate is defined as the rate at which the concentration of the reactants decreases with time or the concentration of products increases with time.
For the reaction,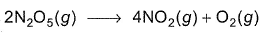
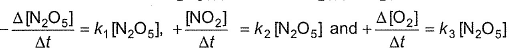 Thus,
Thus,- a)k1 = k2 = k3
- b)2k1 = k2 = 4k3
- c)2k1 = 4k2 = k3
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For the reaction,
Thus,
a)
k1 = k2 = k3
b)
2k1 = k2 = 4k3
c)
2k1 = 4k2 = k3
d)
None of these

|
Chetu Bola answered |
V hav a formula. I. E For a reaction aA-----bB+cC Rate of reaction is [A] /[t]. a AC to given, 1/2[N205]/[t]=k1[N205]/2------eq(1) 1/4[N02]/[t]=k2[N205]/4------eq(2) 1/1[02]/[t]=k3[02]------eq(3) On diving all d 3 equations, v get K1/2=k2/4=k3 Multiply vit 4 to all d ratios V get 2k1=k2=4k3
Which one of the following traits is only expressed in the presence of identical alleles?- a)Yellow seed
- b)Inflated pod
- c)Green pod
- d)Green seed
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Yellow seed
b)
Inflated pod
c)
Green pod
d)
Green seed

|
EduRev NEET answered |
In Mendelian genetics, traits like green seed color are recessive and are expressed only when the individual has two identical recessive alleles (yy). Hence, the green seed trait is only expressed in the presence of identical alleles.
In a plant, red fruit (R) is dominant over yellow fruit (r) and tallness (T) is dominant over shortness (t). If a plant with RRTT genotype is crossed with a plant that is rrtt, then:- a)25% will be tall with red fruit
- b)50% will be tall with red fruit
- c)75% will be tall with red fruit
- d)All of the offspring will be tall with red fruits
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
25% will be tall with red fruit
b)
50% will be tall with red fruit
c)
75% will be tall with red fruit
d)
All of the offspring will be tall with red fruits

|
EduRev NEET answered |
The RRTT plant will produce only gametes with RT, and the rrtt plant will produce gametes with rt. The resulting F1 generation will all have the genotype RrTt and will exhibit the dominant traits for both characteristics: tallness and red fruit. Therefore, all offspring will be tall with red fruit.
‘When two pairs of traits are combined in a hybrid, segregation of one pair of characters is independent of the other pair of characters’. This is the statement of:- a)Law of Dominance
- b)Law of Segregation
- c)Law of Independent Assortment
- d)Law of Linkage
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Law of Dominance
b)
Law of Segregation
c)
Law of Independent Assortment
d)
Law of Linkage
|
|
Tejas Kumar answered |
Understanding the Law of Independent Assortment
The statement "When two pairs of traits are combined in a hybrid, segregation of one pair of characters is independent of the other pair of characters" refers to the Law of Independent Assortment. This principle was formulated by Gregor Mendel based on his experiments with pea plants.
Key Points of the Law of Independent Assortment:
- Definition: The law states that alleles for different traits segregate independently during the formation of gametes. This means that the inheritance of one trait will not affect the inheritance of another trait.
- Mendel's Experiments: Mendel observed that when he crossed plants differing in two characteristics (like seed shape and seed color), the traits assorted independently into the offspring. For example, round seeds could be yellow or green independently of their shape.
- Genetic Variation: This law is crucial for genetic variation, as it allows for new combinations of traits in the offspring, contributing to diversity within a species.
- Dihybrid Crosses: In a typical dihybrid cross (involving two traits), the phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation (offspring) is 9:3:3:1, illustrating the independent assortment of traits.
Importance in Genetics:
- Predicting Offspring Traits: Understanding this law helps in predicting the probability of offspring inheriting particular combinations of traits.
- Basis for Genetic Research: The Law of Independent Assortment serves as a foundational concept in genetics, influencing studies related to heredity and genetic linkage.
In summary, the Law of Independent Assortment is fundamental in genetics, explaining how different traits are inherited independently of one another, thereby shaping the genetic makeup of future generations.
The statement "When two pairs of traits are combined in a hybrid, segregation of one pair of characters is independent of the other pair of characters" refers to the Law of Independent Assortment. This principle was formulated by Gregor Mendel based on his experiments with pea plants.
Key Points of the Law of Independent Assortment:
- Definition: The law states that alleles for different traits segregate independently during the formation of gametes. This means that the inheritance of one trait will not affect the inheritance of another trait.
- Mendel's Experiments: Mendel observed that when he crossed plants differing in two characteristics (like seed shape and seed color), the traits assorted independently into the offspring. For example, round seeds could be yellow or green independently of their shape.
- Genetic Variation: This law is crucial for genetic variation, as it allows for new combinations of traits in the offspring, contributing to diversity within a species.
- Dihybrid Crosses: In a typical dihybrid cross (involving two traits), the phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation (offspring) is 9:3:3:1, illustrating the independent assortment of traits.
Importance in Genetics:
- Predicting Offspring Traits: Understanding this law helps in predicting the probability of offspring inheriting particular combinations of traits.
- Basis for Genetic Research: The Law of Independent Assortment serves as a foundational concept in genetics, influencing studies related to heredity and genetic linkage.
In summary, the Law of Independent Assortment is fundamental in genetics, explaining how different traits are inherited independently of one another, thereby shaping the genetic makeup of future generations.
The decomposition of NO2 at 400 K proceeds at a of rate of 5.4 x 10 -5 mol L-1 s-1 when [NO2] = 0.01 mol-12 NO2(g) → 2NO(g ) + O2(g).Q. Rate constant of the reaction will be - a)0.54 L mol-1 s-1
- b)0.54 x 10-3 L mol-1 s-1
- c)5.4 s-1
- d)0.54s-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The decomposition of NO2 at 400 K proceeds at a of rate of 5.4 x 10 -5 mol L-1 s-1 when [NO2] = 0.01 mol-1
2 NO2(g) → 2NO(g ) + O2(g).
Q. Rate constant of the reaction will be
a)
0.54 L mol-1 s-1
b)
0.54 x 10-3 L mol-1 s-1
c)
5.4 s-1
d)
0.54s-1
|
|
Simran Patel answered |
Understanding the Reaction Rate
The given reaction is:
2 NO2(g) → 2 NO(g) + O2(g)
The rate of the reaction is expressed as:
Rate = - (1/2) d[NO2]/dt
Given:
- Rate = 5.4 x 10^-5 mol L^-1 s^-1
- [NO2] = 0.01 mol L^-1
Rate Law Expression
For this reaction, the rate law can be expressed as:
Rate = k [NO2]^n
Where:
- k = rate constant
- n = order of the reaction
Assuming the reaction is first-order with respect to NO2 (n = 1):
Calculating the Rate Constant (k)
1. Substitute the given values into the rate law:
- Rate = k [NO2]
- 5.4 x 10^-5 mol L^-1 s^-1 = k (0.01 mol L^-1)
2. Rearranging the equation to solve for k:
- k = (5.4 x 10^-5 mol L^-1 s^-1) / (0.01 mol L^-1)
- k = 5.4 x 10^-3 s^-1
3. Converting to appropriate units:
- Since k = 5.4 x 10^-3 s^-1 can also be expressed as:
- k = 0.54 x 10^-2 s^-1 = 0.54 L mol^-1 s^-1 (taking into account the units of rate and concentration)
Conclusion
Thus, the rate constant k is 0.54 L mol^-1 s^-1. The correct answer is option 'A'.
The given reaction is:
2 NO2(g) → 2 NO(g) + O2(g)
The rate of the reaction is expressed as:
Rate = - (1/2) d[NO2]/dt
Given:
- Rate = 5.4 x 10^-5 mol L^-1 s^-1
- [NO2] = 0.01 mol L^-1
Rate Law Expression
For this reaction, the rate law can be expressed as:
Rate = k [NO2]^n
Where:
- k = rate constant
- n = order of the reaction
Assuming the reaction is first-order with respect to NO2 (n = 1):
Calculating the Rate Constant (k)
1. Substitute the given values into the rate law:
- Rate = k [NO2]
- 5.4 x 10^-5 mol L^-1 s^-1 = k (0.01 mol L^-1)
2. Rearranging the equation to solve for k:
- k = (5.4 x 10^-5 mol L^-1 s^-1) / (0.01 mol L^-1)
- k = 5.4 x 10^-3 s^-1
3. Converting to appropriate units:
- Since k = 5.4 x 10^-3 s^-1 can also be expressed as:
- k = 0.54 x 10^-2 s^-1 = 0.54 L mol^-1 s^-1 (taking into account the units of rate and concentration)
Conclusion
Thus, the rate constant k is 0.54 L mol^-1 s^-1. The correct answer is option 'A'.
In a test cross involving F1 dihybrid flies, more parental-type offspring were produced than the recombinant-type offspring. This indicates:- a)Chromosomes failed to separate during meiosis
- b)The two genes are linked and present on the same chromosome
- c)Both of the characters are controlled by more than one gene
- d)The two genes are located on two different chromosomes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Chromosomes failed to separate during meiosis
b)
The two genes are linked and present on the same chromosome
c)
Both of the characters are controlled by more than one gene
d)
The two genes are located on two different chromosomes

|
EduRev NEET answered |
When more parental-type offspring are produced than recombinant-type offspring in a test cross, it indicates that the two genes are linked and present on the same chromosome. This linkage reduces the frequency of recombination between them.
In a certain polluted atm osphere containing O3 at a steady concentration of 2.0 x 10-6 M, the hourly production of O3 by all sources was estimated as 7.2 x 10-15 M. If the only mechanism for destruction of O3 in the second-order reaction is2O3 → 3O2then rate constant for destruction reaction, defined by the rate law for - Δ[O3]/Δf is x * 10-7 M-1 s-1 . What is the value of x?- a)5
- b)2
- c)7
- d)8
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a certain polluted atm osphere containing O3 at a steady concentration of 2.0 x 10-6 M, the hourly production of O3 by all sources was estimated as 7.2 x 10-15 M. If the only mechanism for destruction of O3 in the second-order reaction is
2O3 → 3O2
then rate constant for destruction reaction, defined by the rate law for - Δ[O3]/Δf is x * 10-7 M-1 s-1 . What is the value of x?
a)
5
b)
2
c)
7
d)
8

|
Janhavi Kaur answered |
In Mendel's experiments with garden pea, round seed shape (RR) was dominant over wrinkled seeds (rr), and yellow cotyledon (YY) was dominant over green cotyledon (yy). What are the expected phenotypes in the F2 generation of the cross RRYY x rryy?- a)Only round seeds with green cotyledons
- b)Only wrinkled seeds with yellow cotyledons
- c)Only wrinkled seeds with green cotyledons
- d)Round seeds with yellow cotyledons and wrinkled seeds with yellow cotyledons
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Only round seeds with green cotyledons
b)
Only wrinkled seeds with yellow cotyledons
c)
Only wrinkled seeds with green cotyledons
d)
Round seeds with yellow cotyledons and wrinkled seeds with yellow cotyledons
|
|
Ashutosh Malik answered |
Understanding the Parental Cross
In Mendel's experiments, we start with a parental cross of RRYY (homozygous round seeds with yellow cotyledons) and rryy (homozygous wrinkled seeds with green cotyledons).
F1 Generation Phenotype
The F1 generation from this cross will exhibit the following genotype:
- All offspring will be RrYy (heterozygous for both traits).
Since round (R) and yellow (Y) are dominant traits, all F1 plants will have round seeds and yellow cotyledons.
F2 Generation: The Next Step
When we self-fertilize the F1 generation (RrYy x RrYy), we can use a Punnett square to determine the phenotypes of the F2 generation:
Expected Genotypic Ratio
- The genotypes for the seed shape (R and r) will follow a 3:1 ratio:
- Round (RR, Rr): 3
- Wrinkled (rr): 1
- The genotypes for the cotyledon color (Y and y) will also follow a 3:1 ratio:
- Yellow (YY, Yy): 3
- Green (yy): 1
Combining Traits in F2 Generation
To find the combinations of phenotypes, we can pair the outcomes:
- Round seeds with yellow cotyledons (3/4 for seeds x 3/4 for color) = 9/16
- Round seeds with green cotyledons (3/4 for seeds x 1/4 for color) = 3/16
- Wrinkled seeds with yellow cotyledons (1/4 for seeds x 3/4 for color) = 3/16
- Wrinkled seeds with green cotyledons (1/4 for seeds x 1/4 for color) = 1/16
Conclusion
Thus, the phenotypes in the F2 generation will include:
- Round seeds with yellow cotyledons
- Wrinkled seeds with yellow cotyledons
- Round seeds with green cotyledons
- Wrinkled seeds with green cotyledons
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D': round seeds with yellow cotyledons and wrinkled seeds with yellow cotyledons.
In Mendel's experiments, we start with a parental cross of RRYY (homozygous round seeds with yellow cotyledons) and rryy (homozygous wrinkled seeds with green cotyledons).
F1 Generation Phenotype
The F1 generation from this cross will exhibit the following genotype:
- All offspring will be RrYy (heterozygous for both traits).
Since round (R) and yellow (Y) are dominant traits, all F1 plants will have round seeds and yellow cotyledons.
F2 Generation: The Next Step
When we self-fertilize the F1 generation (RrYy x RrYy), we can use a Punnett square to determine the phenotypes of the F2 generation:
Expected Genotypic Ratio
- The genotypes for the seed shape (R and r) will follow a 3:1 ratio:
- Round (RR, Rr): 3
- Wrinkled (rr): 1
- The genotypes for the cotyledon color (Y and y) will also follow a 3:1 ratio:
- Yellow (YY, Yy): 3
- Green (yy): 1
Combining Traits in F2 Generation
To find the combinations of phenotypes, we can pair the outcomes:
- Round seeds with yellow cotyledons (3/4 for seeds x 3/4 for color) = 9/16
- Round seeds with green cotyledons (3/4 for seeds x 1/4 for color) = 3/16
- Wrinkled seeds with yellow cotyledons (1/4 for seeds x 3/4 for color) = 3/16
- Wrinkled seeds with green cotyledons (1/4 for seeds x 1/4 for color) = 1/16
Conclusion
Thus, the phenotypes in the F2 generation will include:
- Round seeds with yellow cotyledons
- Wrinkled seeds with yellow cotyledons
- Round seeds with green cotyledons
- Wrinkled seeds with green cotyledons
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D': round seeds with yellow cotyledons and wrinkled seeds with yellow cotyledons.
Following reaction can take place in both directions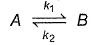
 For the forward reaction, rate varies with concentration of A as and for the backward reaction
For the forward reaction, rate varies with concentration of A as and for the backward reaction  Hence, net reaction rate is
Hence, net reaction rate is- a)= K1[A] - K2[B]
- b)= (K1 - K2[B])
- c)= (K1[A]-K2)
- d)= (k1-k2)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Following reaction can take place in both directions
For the forward reaction, rate varies with concentration of A as and for the backward reaction
Hence, net reaction rate is
a)
= K1[A] - K2[B]
b)
= (K1 - K2[B])
c)
= (K1[A]-K2)
d)
= (k1-k2)

|
Om Kumar answered |
Chapter doubts & questions for June Week 4 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of June Week 4 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.