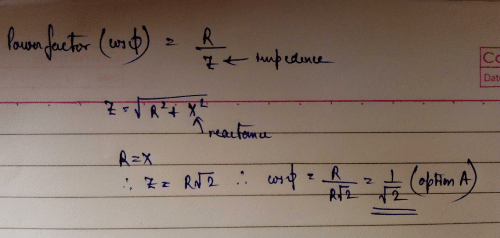All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of October Week 2 for NEET Exam
Find the total voltage applied in a series RLC circuit when i=3mA, VL=30V, VC=18V and R=1000 ohms.
13.95V
2 32.67V
3 6.67V
4 51V
2
3
4
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Explanation: Total voltage= VR+VL+VC.
VR=1000x3x10-3=3V.
Therefore, total voltage = 30+18+3=51V.
VR=1000x3x10-3=3V.
Therefore, total voltage = 30+18+3=51V.
Fossils are most commonly preserved in______.- a)Sedimentary rocks
- b)Igneous rocks
- c)Metamorphic rocks
- d)Any type of rock
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Fossils are most commonly preserved in______.
a)
Sedimentary rocks
b)
Igneous rocks
c)
Metamorphic rocks
d)
Any type of rock

|
Prerana M N answered |
Sedimentary rocks are mostly involved in forming fossils, owing to the way in which they are formed.
Mortality in babies is an example of ______- a)Stabilizing selection
- b)Directional selection
- c)Disruptive selection
- d)Abortion selection
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mortality in babies is an example of ______
a)
Stabilizing selection
b)
Directional selection
c)
Disruptive selection
d)
Abortion selection

|
EduRev NEET answered |
- Mortality in babies is an example of stabilizing selection.
- It is all depended on the baby’s birth weight.
- The optimum birth weight is 7.3 pounds which favor this selection.
- Newborn infants with less than 5.5 pounds and more than 10 pounds have the highest mortality rate.
Links between organisms that show branching pattern of evolutionary relationships are shown by- a)Phylogenetic trees
- b)Living fossils
- c)Comparative embryology
- d)Two fossil layers
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Links between organisms that show branching pattern of evolutionary relationships are shown by
a)
Phylogenetic trees
b)
Living fossils
c)
Comparative embryology
d)
Two fossil layers
|
|
Krithika Kumar answered |
Phylogenetic trees are diagrams that show the evolutionary relationships between different organisms. They are used to display the branching pattern of evolutionary relationships between organisms. The diagram looks like a tree with branches that represent different groups of organisms. These branches are called clades, and they represent groups of organisms that have descended from a common ancestor.
Phylogenetic trees are constructed based on a variety of data, including:
1. Morphological characteristics: The physical features of organisms, such as their shape, size, and structure.
2. Molecular data: DNA and RNA sequences are used to compare the genetic makeup of different organisms.
3. Fossil records: The study of fossils provides evidence of the evolutionary history of organisms.
Phylogenetic trees are an important tool for understanding the relationships between organisms and how they have evolved over time. They can be used to answer questions about the origins of different species and how they are related to one another.
In conclusion, phylogenetic trees are diagrams that show the branching pattern of evolutionary relationships between organisms. They are constructed based on a variety of data, including morphological characteristics, molecular data, and fossil records. They are an important tool for understanding the evolutionary history of organisms.
Phylogenetic trees are constructed based on a variety of data, including:
1. Morphological characteristics: The physical features of organisms, such as their shape, size, and structure.
2. Molecular data: DNA and RNA sequences are used to compare the genetic makeup of different organisms.
3. Fossil records: The study of fossils provides evidence of the evolutionary history of organisms.
Phylogenetic trees are an important tool for understanding the relationships between organisms and how they have evolved over time. They can be used to answer questions about the origins of different species and how they are related to one another.
In conclusion, phylogenetic trees are diagrams that show the branching pattern of evolutionary relationships between organisms. They are constructed based on a variety of data, including morphological characteristics, molecular data, and fossil records. They are an important tool for understanding the evolutionary history of organisms.
When an emf E = 7cos wt is applied across a circuit, the current is I = 5coswt. What is the power factor for the circuit?- a)infinite
- b)3/4
- c)zero
- d)1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When an emf E = 7cos wt is applied across a circuit, the current is I = 5coswt. What is the power factor for the circuit?
a)
infinite
b)
3/4
c)
zero
d)
1
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Since E and I are in the same phase.
Therefore, phase difference will be 0 and since power factor= cosx (where x= phase difference) and x =0
therefore, cos x or power factor will be =1
Therefore, phase difference will be 0 and since power factor= cosx (where x= phase difference) and x =0
therefore, cos x or power factor will be =1
Only One Option Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.Q. Which of the SN2 reaction is fastest?- a)
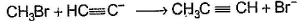
- b)
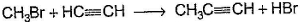
- c)
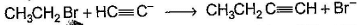
- d)
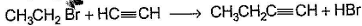
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Which of the SN2 reaction is fastest?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Monika Devi answered |
SN2 reaction means this will be applicable for primary or 1 degree carbon atom and attack by the reagent is forwarded so on doing mechanism we getted that CH3 carry + charge & Br get - charge so acetyl group that have negative charge goes on methyl group & Br react with electronic species
If the instantaneous current in a circuit is given by i = 2 cos (ωt + φ) A, the rms value of the current is
- a)√2 A
- b)2√2 A
- c)2 A
- d)0 A
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If the instantaneous current in a circuit is given by i = 2 cos (ωt + φ) A, the rms value of the current is
a)
√2 A
b)
2√2 A
c)
2 A
d)
0 A
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
i=2cost
=Imcost
So, Im=2amp
IRMS=Im/√2
=2/√2
=√2amp
=Imcost
So, Im=2amp
IRMS=Im/√2
=2/√2
=√2amp
Praying mantis is a good example of- a)Warning colouration
- b)Social insects
- c)Mullerianmimcry
- d)Camouflage
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Praying mantis is a good example of
a)
Warning colouration
b)
Social insects
c)
Mullerianmimcry
d)
Camouflage
|
|
Lakshmi Khanna answered |
< b="" />Camouflage< />
The correct answer for the given question is option 'D' - Camouflage. A praying mantis is a perfect example of an organism that uses camouflage as a defense mechanism. Camouflage refers to the ability of an organism to blend in with its surroundings, making it difficult for predators to detect or capture it. Praying mantises have evolved unique adaptations that allow them to effectively camouflage in their environment, making them highly successful predators themselves.
Adaptations for Camouflage
Praying mantises have several physical adaptations that help them camouflage effectively:
1. Body Shape: Praying mantises have an elongated body shape that resembles sticks or plant stems, allowing them to blend in with the surrounding vegetation. Their thin bodies and elongated legs further aid in mimicking plant structures.
2. Coloration: Praying mantises come in a range of colors including green, brown, and even pink. These colors help them match the color of their surroundings, whether it be leaves, twigs, or flowers. Some species can even change their coloration to match their environment.
3. Texture: The texture of a praying mantis' exoskeleton also contributes to its camouflage. The rough and uneven surface helps break up its outline, making it harder for predators to spot them.
Benefits of Camouflage
Camouflage provides several benefits to praying mantises, including:
1. Predator Avoidance: By blending in with their surroundings, praying mantises can avoid being detected by predators such as birds, lizards, and even other insects. This allows them to hide in plain sight and increases their chances of survival.
2. Ambush Predation: Praying mantises are ambush predators, relying on their camouflage to remain undetected by their prey. They patiently wait for unsuspecting insects to come within striking distance, using their cryptic coloration and immobility to remain hidden until the opportune moment.
3. Reproductive Success: Camouflage also plays a role in the reproductive success of praying mantises. Females, in particular, benefit from their camouflage as it allows them to hide from males after mating, reducing the risk of cannibalism.
In conclusion, the praying mantis is an excellent example of an organism that utilizes camouflage as a defense mechanism. Its unique adaptations in body shape, coloration, and texture allow it to blend seamlessly with its surroundings, providing benefits such as predator avoidance and successful predation.
The correct answer for the given question is option 'D' - Camouflage. A praying mantis is a perfect example of an organism that uses camouflage as a defense mechanism. Camouflage refers to the ability of an organism to blend in with its surroundings, making it difficult for predators to detect or capture it. Praying mantises have evolved unique adaptations that allow them to effectively camouflage in their environment, making them highly successful predators themselves.
Adaptations for Camouflage
Praying mantises have several physical adaptations that help them camouflage effectively:
1. Body Shape: Praying mantises have an elongated body shape that resembles sticks or plant stems, allowing them to blend in with the surrounding vegetation. Their thin bodies and elongated legs further aid in mimicking plant structures.
2. Coloration: Praying mantises come in a range of colors including green, brown, and even pink. These colors help them match the color of their surroundings, whether it be leaves, twigs, or flowers. Some species can even change their coloration to match their environment.
3. Texture: The texture of a praying mantis' exoskeleton also contributes to its camouflage. The rough and uneven surface helps break up its outline, making it harder for predators to spot them.
Benefits of Camouflage
Camouflage provides several benefits to praying mantises, including:
1. Predator Avoidance: By blending in with their surroundings, praying mantises can avoid being detected by predators such as birds, lizards, and even other insects. This allows them to hide in plain sight and increases their chances of survival.
2. Ambush Predation: Praying mantises are ambush predators, relying on their camouflage to remain undetected by their prey. They patiently wait for unsuspecting insects to come within striking distance, using their cryptic coloration and immobility to remain hidden until the opportune moment.
3. Reproductive Success: Camouflage also plays a role in the reproductive success of praying mantises. Females, in particular, benefit from their camouflage as it allows them to hide from males after mating, reducing the risk of cannibalism.
In conclusion, the praying mantis is an excellent example of an organism that utilizes camouflage as a defense mechanism. Its unique adaptations in body shape, coloration, and texture allow it to blend seamlessly with its surroundings, providing benefits such as predator avoidance and successful predation.
What is phase angle given R = 10, Z = 20- a)30°
- b)45°
- c)60°
- d)90°
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is phase angle given R = 10, Z = 20
a)
30°
b)
45°
c)
60°
d)
90°

|
Manvi Goyal answered |
Cos x (power factor) = R/Z
= 10/20
=1/2
x= 60
= 10/20
=1/2
x= 60
Find the true power given apparent power = 10 W and power factor = 0.5- a)0.5 W
- b)0.05 W
- c)5 W
- d)50 W
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the true power given apparent power = 10 W and power factor = 0.5
a)
0.5 W
b)
0.05 W
c)
5 W
d)
50 W

|
.mie. answered |
Ys.. C is correct opt... as ... true powr = apparent powr × powr factor.. here apparent power =10W and power factor=0.5 so true power =10×0.5 = 5W
Evolution of different species in a given area starting from a point and spreading to other geographical areas is known as- a)Migration
- b)Divergent evolution
- c)Adaptive radiation
- d)Natural selection
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Evolution of different species in a given area starting from a point and spreading to other geographical areas is known as
a)
Migration
b)
Divergent evolution
c)
Adaptive radiation
d)
Natural selection
|
|
Mansi Deshpande answered |
Adaptive Radiation:
Adaptive radiation is the evolution of different species in a given area starting from a point and spreading to other geographical areas. It is a type of divergent evolution that occurs when a single ancestral species evolves into many different species to adapt to different ecological niches. The term "adaptive radiation" was coined by the American evolutionary biologist Henry Fairfield Osborn in 1897.
Factors that contribute to adaptive radiation:
1. Ecological opportunity: When new habitats or resources become available, organisms can exploit them and evolve to fill new niches.
2. Morphological innovation: Morphological innovation can allow organisms to exploit new resources or habitats.
3. Competition: Competition for resources can drive organisms to evolve different adaptations, leading to adaptive radiation.
Examples of adaptive radiation:
1. Darwin's finches: The Galápagos Islands are home to a number of different finch species that evolved from a common ancestor. Each species has a specialized beak that allows it to feed on different types of food.
2. Hawaiian honeycreepers: The Hawaiian Islands are home to a diverse group of birds known as honeycreepers. These birds evolved from a single ancestral species and have adapted to different ecological niches on the islands.
3. Australian marsupials: Australia is home to a number of different marsupial species that evolved from a common ancestor. These marsupials have adapted to different ecological niches, such as the kangaroo, koala, and Tasmanian devil.
Conclusion:
Adaptive radiation is an important process in the evolution of new species. It allows organisms to adapt to new environments and resources and can lead to the development of new ecological niches. The study of adaptive radiation can provide insights into the mechanisms of evolution and the factors that contribute to biodiversity.
Adaptive radiation is the evolution of different species in a given area starting from a point and spreading to other geographical areas. It is a type of divergent evolution that occurs when a single ancestral species evolves into many different species to adapt to different ecological niches. The term "adaptive radiation" was coined by the American evolutionary biologist Henry Fairfield Osborn in 1897.
Factors that contribute to adaptive radiation:
1. Ecological opportunity: When new habitats or resources become available, organisms can exploit them and evolve to fill new niches.
2. Morphological innovation: Morphological innovation can allow organisms to exploit new resources or habitats.
3. Competition: Competition for resources can drive organisms to evolve different adaptations, leading to adaptive radiation.
Examples of adaptive radiation:
1. Darwin's finches: The Galápagos Islands are home to a number of different finch species that evolved from a common ancestor. Each species has a specialized beak that allows it to feed on different types of food.
2. Hawaiian honeycreepers: The Hawaiian Islands are home to a diverse group of birds known as honeycreepers. These birds evolved from a single ancestral species and have adapted to different ecological niches on the islands.
3. Australian marsupials: Australia is home to a number of different marsupial species that evolved from a common ancestor. These marsupials have adapted to different ecological niches, such as the kangaroo, koala, and Tasmanian devil.
Conclusion:
Adaptive radiation is an important process in the evolution of new species. It allows organisms to adapt to new environments and resources and can lead to the development of new ecological niches. The study of adaptive radiation can provide insights into the mechanisms of evolution and the factors that contribute to biodiversity.
One Integer Value Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 18-20) This section contains 3 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).Consider the following reaction,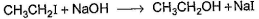 Q. The above reaction was started taking equal concentrations of ethyl iodide and NaOH. After 1.0 h, concentration of iodoethane is dropped to (1/3)rd of initial value. By what factor, the rate of reaction would have been decreased by the same time?
Q. The above reaction was started taking equal concentrations of ethyl iodide and NaOH. After 1.0 h, concentration of iodoethane is dropped to (1/3)rd of initial value. By what factor, the rate of reaction would have been decreased by the same time?
Correct answer is '9'. Can you explain this answer?
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 18-20) This section contains 3 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Consider the following reaction,
Q.
The above reaction was started taking equal concentrations of ethyl iodide and NaOH. After 1.0 h, concentration of iodoethane is dropped to (1/3)rd of initial value. By what factor, the rate of reaction would have been decreased by the same time?
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
Rate = A [C2H5I] [OH-] Rate is linear function of both alkyl halide and nucleophile concentration both will decrease by same factor. Hence, if after 1.0 h concentration of iodoethane decreases to 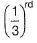 concentration of hydroxide will also decrease by the same factor and rate by
concentration of hydroxide will also decrease by the same factor and rate by 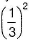 , i.e. by 9 times.
, i.e. by 9 times.
One or More than One Options Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 9-14) This section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.Q. In a SN2 reaction rate of reaction depends on- a)concentration of substrate
- b)concentration of nucleophile
- c)nature of leaving group
- d)number of lone pairs on donor atom
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 9-14) This section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
In a SN2 reaction rate of reaction depends on
a)
concentration of substrate
b)
concentration of nucleophile
c)
nature of leaving group
d)
number of lone pairs on donor atom

|
Arnab Chavan answered |
In a SN2 reaction, Rate = k[substrate] [nucleophile]
Hence, rate depends both on concentration of substrate as well as nucleophile. Rate of reaction also depends on nature of leaving group. A better leaving group gives lower activation energy hence, greater rate of reaction. Number of lone pair has no role to play in nucieophilicity hence reactivity.
Hence, rate depends both on concentration of substrate as well as nucleophile. Rate of reaction also depends on nature of leaving group. A better leaving group gives lower activation energy hence, greater rate of reaction. Number of lone pair has no role to play in nucieophilicity hence reactivity.
Which statement is true about SN2 mechanism?- a)The rate of reaction increases on increasing strength of the nucleophile
- b)The reaction is faster in polar aprotic solvents
- c)The rate of reaction increases as the leaving group ability increases
- d)Ali'of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which statement is true about SN2 mechanism?
a)
The rate of reaction increases on increasing strength of the nucleophile
b)
The reaction is faster in polar aprotic solvents
c)
The rate of reaction increases as the leaving group ability increases
d)
Ali'of the above

|
Arnab Chavan answered |
Stronger the nucleophile, faster the SN2 reaction. Polar aprotic solvent solvate cations, makes anionic nucleophile more available for reaction, hence faster reaction. A better leaving group lowers the activation energy increasing rate of SN2 reaction.
Which ape is closely related to the man?- a)Orangutan
- b)Chimpanzee
- c)Gibbon
- d)Gorilla
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which ape is closely related to the man?
a)
Orangutan
b)
Chimpanzee
c)
Gibbon
d)
Gorilla

|
Lead Academy answered |
- Chimpanzee is closely related to man. DNA content and DNA matching are the same in both.
- This similarity is more than 99% with chimpanzee whereas 94% with a gibbon.
Which theory explains the origin of universe?- a)Molecular theory
- b)Darwin theory
- c)Lamarck theory
- d)Big bang theory
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which theory explains the origin of universe?
a)
Molecular theory
b)
Darwin theory
c)
Lamarck theory
d)
Big bang theory

|
Nayanika Reddy answered |
Origin of universe is explained by big bang theory. According to this theory, whole universe was concentrated into single sphere. Due to same unknown region, there was explosion in it that forms different galaxies still moving away from each other.
The difference between Homo sapiens and the Homo erectus was ____.- a)Homo erectus was much smaller in size than Homo sapiens
- b)Homo sapiens originated in Africa while Homo erectus was in Asia
- c)Homo erectus stayed in Africa while Homo sapiens did not
- d)The size of their brain of Homo erectus was smaller to homo sapiens
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The difference between Homo sapiens and the Homo erectus was ____.
a)
Homo erectus was much smaller in size than Homo sapiens
b)
Homo sapiens originated in Africa while Homo erectus was in Asia
c)
Homo erectus stayed in Africa while Homo sapiens did not
d)
The size of their brain of Homo erectus was smaller to homo sapiens
|
|
Jhanvi Menon answered |
The correct answer is option 'D': The size of their brain of Homo erectus was smaller than that of Homo sapiens.
Explanation:
Homo sapiens and Homo erectus are two distinct species of hominins that lived during different periods of human evolution. There are several differences between these two species, but one of the most significant differences lies in the size of their brains.
1. Homo erectus:
- Homo erectus is an extinct species of hominin that lived from about 1.9 million years ago to about 143,000 years ago.
- They had a relatively larger cranial capacity compared to earlier hominins, but their brain size was still smaller than that of Homo sapiens.
- The average cranial capacity of Homo erectus was about 900 to 1100 cubic centimeters.
- Homo erectus is known for its robust physical features, including a thick skull, prominent brow ridges, and a long, low skull shape.
2. Homo sapiens:
- Homo sapiens, also known as anatomically modern humans, emerged around 300,000 years ago and are the only surviving species of hominins.
- They have a significantly larger brain size compared to Homo erectus.
- The average cranial capacity of Homo sapiens is about 1200 to 1600 cubic centimeters.
- Homo sapiens have a more rounded skull shape and less pronounced brow ridges compared to earlier hominins.
Importance of brain size:
- The size of the brain is often correlated with cognitive abilities, such as problem-solving, language, and complex social interactions.
- A larger brain size generally indicates a higher level of cognitive development and intelligence.
- The increase in brain size throughout human evolution is believed to be associated with the development of complex behaviors and cultural advancements.
In summary, the main difference between Homo sapiens and Homo erectus is that the size of the brain of Homo erectus was smaller compared to that of Homo sapiens.
Explanation:
Homo sapiens and Homo erectus are two distinct species of hominins that lived during different periods of human evolution. There are several differences between these two species, but one of the most significant differences lies in the size of their brains.
1. Homo erectus:
- Homo erectus is an extinct species of hominin that lived from about 1.9 million years ago to about 143,000 years ago.
- They had a relatively larger cranial capacity compared to earlier hominins, but their brain size was still smaller than that of Homo sapiens.
- The average cranial capacity of Homo erectus was about 900 to 1100 cubic centimeters.
- Homo erectus is known for its robust physical features, including a thick skull, prominent brow ridges, and a long, low skull shape.
2. Homo sapiens:
- Homo sapiens, also known as anatomically modern humans, emerged around 300,000 years ago and are the only surviving species of hominins.
- They have a significantly larger brain size compared to Homo erectus.
- The average cranial capacity of Homo sapiens is about 1200 to 1600 cubic centimeters.
- Homo sapiens have a more rounded skull shape and less pronounced brow ridges compared to earlier hominins.
Importance of brain size:
- The size of the brain is often correlated with cognitive abilities, such as problem-solving, language, and complex social interactions.
- A larger brain size generally indicates a higher level of cognitive development and intelligence.
- The increase in brain size throughout human evolution is believed to be associated with the development of complex behaviors and cultural advancements.
In summary, the main difference between Homo sapiens and Homo erectus is that the size of the brain of Homo erectus was smaller compared to that of Homo sapiens.
A correct statement about transition state of SN2 reaction is - a)the transition state proceeds and follow an unstable reaction intermediate
- b)the transition state will always have net negative charge
- c)existence of this state implies an exothermic reaction
- d)the single transition state represents the point of maximum free energy of the reaction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A correct statement about transition state of SN2 reaction is
a)
the transition state proceeds and follow an unstable reaction intermediate
b)
the transition state will always have net negative charge
c)
existence of this state implies an exothermic reaction
d)
the single transition state represents the point of maximum free energy of the reaction

|
Anuj Iyer answered |
SN2 reaction is a one step (concerted) reaction that involes a single transition state.
Consider the reaction given below.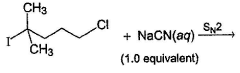 Q. The correct statement(s) applicable to the above reaction is/are
Q. The correct statement(s) applicable to the above reaction is/are- a)Cl- is substituted predominantly
- b) Cl- is a better leaving group
- c)substitution of I- in the above reaction required greater activation energy than for Cl-
- d)addition of some Nal catalyse the substitution reaction
Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the reaction given below.
Q.
The correct statement(s) applicable to the above reaction is/are
a)
Cl- is substituted predominantly
b)
Cl- is a better leaving group
c)
substitution of I- in the above reaction required greater activation energy than for Cl-
d)
addition of some Nal catalyse the substitution reaction

|
Prashanth Banerjee answered |
Steric hindrance plays the most important role in SN2 reaction. Hence, although Cl is poorer leaving group than I, Cl is substituted predominantly in the above reaction due to less steric hindrance at α-carbon. Addition of Nal replace Cl by I and substitution becomes easier.
The extinct human who lived 1,00,000 to 40,000 years ago, in Europe, Asia and parts of Africa, with short stature, heavy eye brows, retreating foreheads, large jaws with heavy teeth, stocky bodies, a lumbering gait and stooped posture was- a)Neanderthal human
- b)Ramapithecus
- c)Cro-Magnon human
- d)Homo habilis
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The extinct human who lived 1,00,000 to 40,000 years ago, in Europe, Asia and parts of Africa, with short stature, heavy eye brows, retreating foreheads, large jaws with heavy teeth, stocky bodies, a lumbering gait and stooped posture was
a)
Neanderthal human
b)
Ramapithecus
c)
Cro-Magnon human
d)
Homo habilis
|
|
Meghana Mehta answered |
The correct answer is option 'A' - Neanderthal human.
Explanation:
Neanderthals were a species of extinct humans who lived from approximately 100,000 to 40,000 years ago in Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa. They are known for their distinct physical features and characteristics.
Physical Features:
1. Short Stature: Neanderthals had a relatively short average height compared to modern humans, with males averaging around 5'5" and females around 5'1".
2. Heavy Eye Brows: They had prominent brow ridges and heavy eyebrows, giving them a unique facial appearance.
3. Retreating Foreheads: Neanderthals had low and sloping foreheads.
4. Large Jaws with Heavy Teeth: They had robust jaws and large teeth, which were adapted for a diet that included tough and coarse foods.
5. Stocky Bodies: Neanderthals had a robust and stocky body build, with strong bones and muscles.
6. Lumbering Gait and Stooped Posture: Due to their body structure, Neanderthals had a distinctive gait and posture, often described as stooped or hunched.
Differences from Modern Humans:
Despite some similarities to modern humans, Neanderthals had several distinct features that set them apart:
1. Cranial Capacity: Neanderthals had a larger cranial capacity than modern humans, suggesting a different pattern of brain development.
2. Tool Use: Neanderthals were skilled toolmakers and used a variety of stone tools for hunting and other activities.
3. Cultural Behavior: They had their own unique cultural behaviors, including burying their dead and creating symbolic objects.
4. Genetic Differences: Genetic studies have shown that Neanderthals interbred with early modern humans, and some individuals of non-African descent today carry a small percentage of Neanderthal DNA.
Conclusion:
Neanderthals were an extinct human species that lived in Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa. They had distinct physical features such as short stature, heavy eyebrows, retreating foreheads, large jaws with heavy teeth, stocky bodies, a lumbering gait, and a stooped posture. Neanderthals had their own unique cultural behaviors and interbred with early modern humans.
Explanation:
Neanderthals were a species of extinct humans who lived from approximately 100,000 to 40,000 years ago in Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa. They are known for their distinct physical features and characteristics.
Physical Features:
1. Short Stature: Neanderthals had a relatively short average height compared to modern humans, with males averaging around 5'5" and females around 5'1".
2. Heavy Eye Brows: They had prominent brow ridges and heavy eyebrows, giving them a unique facial appearance.
3. Retreating Foreheads: Neanderthals had low and sloping foreheads.
4. Large Jaws with Heavy Teeth: They had robust jaws and large teeth, which were adapted for a diet that included tough and coarse foods.
5. Stocky Bodies: Neanderthals had a robust and stocky body build, with strong bones and muscles.
6. Lumbering Gait and Stooped Posture: Due to their body structure, Neanderthals had a distinctive gait and posture, often described as stooped or hunched.
Differences from Modern Humans:
Despite some similarities to modern humans, Neanderthals had several distinct features that set them apart:
1. Cranial Capacity: Neanderthals had a larger cranial capacity than modern humans, suggesting a different pattern of brain development.
2. Tool Use: Neanderthals were skilled toolmakers and used a variety of stone tools for hunting and other activities.
3. Cultural Behavior: They had their own unique cultural behaviors, including burying their dead and creating symbolic objects.
4. Genetic Differences: Genetic studies have shown that Neanderthals interbred with early modern humans, and some individuals of non-African descent today carry a small percentage of Neanderthal DNA.
Conclusion:
Neanderthals were an extinct human species that lived in Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa. They had distinct physical features such as short stature, heavy eyebrows, retreating foreheads, large jaws with heavy teeth, stocky bodies, a lumbering gait, and a stooped posture. Neanderthals had their own unique cultural behaviors and interbred with early modern humans.
Which of the following is not a similarity between man and apes?
- a)Smaller head, less cranial capacity
- b)Erect posture
- c)none
- d)Grasping hands
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a similarity between man and apes?
a)
Smaller head, less cranial capacity
b)
Erect posture
c)
none
d)
Grasping hands

|
Lead Academy answered |
- Smaller head, less cranial capacity is not a similarity between man and apes.
- Actually, they had a larger head and more cranial capacity.
- The remaining options share similarities between man and apes.
Which fossil of the ape was known as the connecting link between apes and man?- a)Ramapithecus
- b)Dryopithecus
- c)Australopithecus
- d)Shivapithecus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which fossil of the ape was known as the connecting link between apes and man?
a)
Ramapithecus
b)
Dryopithecus
c)
Australopithecus
d)
Shivapithecus

|
Lead Academy answered |
- Australopithecus was known as the connecting link between apes and man.
- They had complete erect posture and showed bipedal locomotion.
- It was the first man to stand erect.
Lamarck theory of organic evolution is usually known as- a)Natural selection
- b)Inheritance of acquired characters
- c)Descent with change
- d)Continuity of germplasm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Lamarck theory of organic evolution is usually known as
a)
Natural selection
b)
Inheritance of acquired characters
c)
Descent with change
d)
Continuity of germplasm
|
|
Shathananda Varanasi answered |
Correct answer is B because, as you know, lamarck in his theory talked only about the inheritance of the acquired characters from the parents to progeny. He told that, giraffes has acquired the long neck from the ancestors in which the long neck was not present at the time of birth, but aquired during their course of development.
The power factor of an RL circuit 1/root2. If the frequency of a.c. is doubled, what will be the power factor?a)1/√7b)1/√5c)1/√3d)1/√11Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
X_L = ω L
Power factor of a RL A.C. Circuit is given by
p.f. = R /√[ R^2+ X_L^2]
= 1 /√[ 1 + (ω^2L^2/R^2) ] = 1/√2 given
=> ωL/R = 1
If frequency is doubled, then ωL/R becomes twice.
p.f. = 1/√[1 + 4] = 1/√5
A SN2 reaction involves back side attack of nucleophile at the α-carbon of substrate because- a)both nucleophile and leaving group are electron rich, nucleophilic attack occur from most distant position
- b)there is greater electron density on the back side of substrate
- c)there is not enough physical space in the front side from where leaving group leaves the substrate
- d)substrate possesses a hole in the backside
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
A SN2 reaction involves back side attack of nucleophile at the α-carbon of substrate because
a)
both nucleophile and leaving group are electron rich, nucleophilic attack occur from most distant position
b)
there is greater electron density on the back side of substrate
c)
there is not enough physical space in the front side from where leaving group leaves the substrate
d)
substrate possesses a hole in the backside

|
Anuj Iyer answered |
Both nucleophile and leaving group are electron rich species, nucleophile attacks from backside (most remote position) to have minimum repulsion with leaving group. Also, due to the presence of leaving group on front side there is less physical space for attack of nucleophile.
Consider the following compound,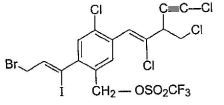 Q. If the above compound is treated with excess of NaCN(aq), how many CN- group would be incorporated by SN2 reaction?
Q. If the above compound is treated with excess of NaCN(aq), how many CN- group would be incorporated by SN2 reaction?
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following compound,
Q.
If the above compound is treated with excess of NaCN(aq), how many CN- group would be incorporated by SN2 reaction?
|
|
Ritika Sengupta answered |
Only the circled groups are substituted in SN2,
What is the correct increasing order of reactivity of the followings in SN2 reaction ?I. CH2 = CH — Br
II. CH2 = CH— I
III. CH3CH2CH2 — I
IV. CH3OCH2CH2 — I - a)I < II < III < IV
- b)III < II < I < IV
- c)II < III < IV < I
- d)II < I < III < IV
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the correct increasing order of reactivity of the followings in SN2 reaction ?
I. CH2 = CH — Br
II. CH2 = CH— I
III. CH3CH2CH2 — I
IV. CH3OCH2CH2 — I
II. CH2 = CH— I
III. CH3CH2CH2 — I
IV. CH3OCH2CH2 — I
a)
I < II < III < IV
b)
III < II < I < IV
c)
II < III < IV < I
d)
II < I < III < IV

|
Tejas Singh answered |
Allyl bromide (I) is most reactive among the given halides as pi bonds from allylic position stabilises the transition state. Vinyl iodide (II) is least reactive due to partial double bond character. Electron withdrawing inductive effect of CH3O- increases reactivity of (IV) over (III)
What is the average power/cycle in a capacitor?- a)0
- b)infinite
- c)E0L0 cos Ø
- d)E0L0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the average power/cycle in a capacitor?
a)
0
b)
infinite
c)
E0L0 cos Ø
d)
E0L0
|
|
Ankita Datta answered |
The average power consumed/cycle in an ideal capacitor is 0.
The average power consumed in an ideal capacitor is given as based on the instantaneous power which is supplied to the capacitor:
pc = iv= (im cos ωt)(vm sin ωt)
pc = imvm (cos ωt sin ωt)
pc=(imvm/2)sin2ωt
We know that sin ωt = 0
Therefore, average power = 0
The average power consumed in an ideal capacitor is given as based on the instantaneous power which is supplied to the capacitor:
pc = iv= (im cos ωt)(vm sin ωt)
pc = imvm (cos ωt sin ωt)
pc=(imvm/2)sin2ωt
We know that sin ωt = 0
Therefore, average power = 0
A type of natural selection in which more individuals acquire peripheral character value at both ends of distribution curve is- a)Directional selection
- b)Disruptive selection
- c)Balancing selection
- d)Stabilising selection
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A type of natural selection in which more individuals acquire peripheral character value at both ends of distribution curve is
a)
Directional selection
b)
Disruptive selection
c)
Balancing selection
d)
Stabilising selection

|
Bs Academy answered |
Natural selection can lead to stabilisation (in which more individuals acquire mean character value), directional change (more individuals acquire value other than the mean character value) or disruption (more individuals acquire peripheral character value at both ends of the distribution curve)
Human being belongs to the species of_____.- a)Homo erectus
- b)Hominidae
- c)Homo sapiens
- d)Homo habillis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Human being belongs to the species of_____.
a)
Homo erectus
b)
Hominidae
c)
Homo sapiens
d)
Homo habillis
|
|
Debolina Chopra answered |
Human being belongs to the species of Homo sapiens.
Homo sapiens is the scientific name for modern humans. The classification of humans as Homo sapiens is based on several factors, including physical characteristics, genetic similarities, and cultural attributes.
Here is a detailed explanation of why humans are classified as Homo sapiens:
1. Classification System:
- Humans are classified within the animal kingdom, specifically in the class Mammalia, order Primates, and family Hominidae.
- The family Hominidae includes great apes (orangutans, gorillas, and chimpanzees) and humans.
- Within the family Hominidae, humans are further classified into the genus Homo.
2. Genus Homo:
- The genus Homo includes several extinct species such as Homo habilis, Homo erectus, and Homo neanderthalensis, as well as the modern humans Homo sapiens.
- These species share common characteristics and evolutionary traits.
3. Homo sapiens:
- Homo sapiens is the only surviving species of the genus Homo.
- The term "sapiens" means "wise" or "intelligent" in Latin, reflecting the cognitive abilities and complex societies of modern humans.
- Homo sapiens have distinct physical features, including an upright posture, large brain size, and a highly developed capacity for language and abstract thinking.
- Humans also exhibit unique cultural and behavioral traits, such as the ability to use tools, create art, and engage in symbolic communication.
4. Genetic Similarities:
- Humans share a significant amount of their genetic material with other members of the Hominidae family, particularly with chimpanzees.
- DNA analysis has revealed a high degree of genetic similarity between humans and chimpanzees, supporting the classification of humans as part of the Hominidae family.
In conclusion, humans belong to the species Homo sapiens, which is a result of their unique physical characteristics, genetic similarities to other members of the Hominidae family, and distinctive cognitive and cultural attributes.
Homo sapiens is the scientific name for modern humans. The classification of humans as Homo sapiens is based on several factors, including physical characteristics, genetic similarities, and cultural attributes.
Here is a detailed explanation of why humans are classified as Homo sapiens:
1. Classification System:
- Humans are classified within the animal kingdom, specifically in the class Mammalia, order Primates, and family Hominidae.
- The family Hominidae includes great apes (orangutans, gorillas, and chimpanzees) and humans.
- Within the family Hominidae, humans are further classified into the genus Homo.
2. Genus Homo:
- The genus Homo includes several extinct species such as Homo habilis, Homo erectus, and Homo neanderthalensis, as well as the modern humans Homo sapiens.
- These species share common characteristics and evolutionary traits.
3. Homo sapiens:
- Homo sapiens is the only surviving species of the genus Homo.
- The term "sapiens" means "wise" or "intelligent" in Latin, reflecting the cognitive abilities and complex societies of modern humans.
- Homo sapiens have distinct physical features, including an upright posture, large brain size, and a highly developed capacity for language and abstract thinking.
- Humans also exhibit unique cultural and behavioral traits, such as the ability to use tools, create art, and engage in symbolic communication.
4. Genetic Similarities:
- Humans share a significant amount of their genetic material with other members of the Hominidae family, particularly with chimpanzees.
- DNA analysis has revealed a high degree of genetic similarity between humans and chimpanzees, supporting the classification of humans as part of the Hominidae family.
In conclusion, humans belong to the species Homo sapiens, which is a result of their unique physical characteristics, genetic similarities to other members of the Hominidae family, and distinctive cognitive and cultural attributes.
What is another name of human evolution?- a)Neogenesis
- b)Anthropogenesis
- c)Metagenesis
- d)Fossilizes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is another name of human evolution?
a)
Neogenesis
b)
Anthropogenesis
c)
Metagenesis
d)
Fossilizes

|
Stepway Academy answered |
- Human evolution or anthropogenesis is part of biological evolution which studies the emergence of Homo sapiens sapiens.
- They were the distinct species from other hominids, great apes and placental mammals.
1-chlorobutane is more reactive than 2-chloro-2-methyl propane in a SN2 reaction because- a)α-carbon is less crowded in 1-chlorobutane
- b)α-carbon is less electropositive in 1-chlorobutane
- c)electron donating inductive effect of three methyl group is greater in 2-chloro 2-methyl propane
- d)α-carbon is more electropositive in 1-chlorobutan
Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
1-chlorobutane is more reactive than 2-chloro-2-methyl propane in a SN2 reaction because
a)
α-carbon is less crowded in 1-chlorobutane
b)
α-carbon is less electropositive in 1-chlorobutane
c)
electron donating inductive effect of three methyl group is greater in 2-chloro 2-methyl propane
d)
α-carbon is more electropositive in 1-chlorobutan

|
Arnab Chavan answered |
As indicated in the given reaction, α-carbon is less hindered in 1- chloropropane. Also + I effect of three methyl groups in 2- chloro-2-methyl propane decreases electropositive character of α-carbon, decreases reactivity further in SN2 reaction.
The correct statement concerning a SN2 reaction is- a)the reaction mechanism involve atleast one reactive intermediate
- b)transition state is pentavalent
- c)product is formed after passing through several transition states
- d)nucleophile attacks from front side on which leaving group is present
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statement concerning a SN2 reaction is
a)
the reaction mechanism involve atleast one reactive intermediate
b)
transition state is pentavalent
c)
product is formed after passing through several transition states
d)
nucleophile attacks from front side on which leaving group is present

|
Subhankar Mukherjee answered |
The Correct Statement Concerning a SN2 Reaction
The correct statement concerning a SN2 (substitution nucleophilic bimolecular) reaction is option B - the transition state is pentavalent.
Explanation:
SN2 reactions are a type of nucleophilic substitution reaction in which a nucleophile replaces a leaving group in a molecule. This reaction involves the simultaneous bond-breaking of the leaving group and the bond-forming of the nucleophile.
In an SN2 reaction, the nucleophile attacks the electrophilic carbon atom (the carbon atom bonded to the leaving group) from the front side, opposite to the leaving group. This is known as front-side attack or backside attack.
Transition State:
During the SN2 reaction, there is a transition state in which the nucleophile is partially bonded to the carbon atom, and the leaving group is partially detached. This transition state is characterized by a pentavalent carbon atom, meaning it has five attached groups. The nucleophile, leaving group, and three other substituents attached to the carbon atom are all present in the transition state.
The pentavalent transition state is formed because the nucleophile starts forming a bond with the carbon atom before the leaving group completely detaches. This transition state is highly unstable and short-lived, and it represents the highest energy point along the reaction pathway.
Reactive Intermediate:
In an SN2 reaction, there is no formation of a reactive intermediate. The reaction occurs in a single step, where the nucleophile directly replaces the leaving group without the formation of any intermediate species.
Product Formation:
In SN2 reactions, the product is formed directly from the transition state without passing through several transition states. Once the nucleophile has fully bonded to the carbon atom, the leaving group completely detaches, and the product is formed.
To summarize, the correct statement concerning an SN2 reaction is that the transition state is pentavalent (option B). This transition state represents the highest energy point in the reaction, and the nucleophile attacks the carbon atom from the front side opposite to the leaving group. The reaction occurs in a single step without the formation of any reactive intermediate, and the product is formed directly from the transition state.
The correct statement concerning a SN2 (substitution nucleophilic bimolecular) reaction is option B - the transition state is pentavalent.
Explanation:
SN2 reactions are a type of nucleophilic substitution reaction in which a nucleophile replaces a leaving group in a molecule. This reaction involves the simultaneous bond-breaking of the leaving group and the bond-forming of the nucleophile.
In an SN2 reaction, the nucleophile attacks the electrophilic carbon atom (the carbon atom bonded to the leaving group) from the front side, opposite to the leaving group. This is known as front-side attack or backside attack.
Transition State:
During the SN2 reaction, there is a transition state in which the nucleophile is partially bonded to the carbon atom, and the leaving group is partially detached. This transition state is characterized by a pentavalent carbon atom, meaning it has five attached groups. The nucleophile, leaving group, and three other substituents attached to the carbon atom are all present in the transition state.
The pentavalent transition state is formed because the nucleophile starts forming a bond with the carbon atom before the leaving group completely detaches. This transition state is highly unstable and short-lived, and it represents the highest energy point along the reaction pathway.
Reactive Intermediate:
In an SN2 reaction, there is no formation of a reactive intermediate. The reaction occurs in a single step, where the nucleophile directly replaces the leaving group without the formation of any intermediate species.
Product Formation:
In SN2 reactions, the product is formed directly from the transition state without passing through several transition states. Once the nucleophile has fully bonded to the carbon atom, the leaving group completely detaches, and the product is formed.
To summarize, the correct statement concerning an SN2 reaction is that the transition state is pentavalent (option B). This transition state represents the highest energy point in the reaction, and the nucleophile attacks the carbon atom from the front side opposite to the leaving group. The reaction occurs in a single step without the formation of any reactive intermediate, and the product is formed directly from the transition state.
What is genetic equilibrium?- a)When all the alleles of a gene are present in a population in equal frequencies
- b)When the number of heterozygotes in a population are not equal to the number of either of the homozygote
- c)When the number of heterozygotes in a population are equal to the number of either of the homozygote
- d)When the frequency of particular genes or alleles remain constant in a population through generations
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is genetic equilibrium?
a)
When all the alleles of a gene are present in a population in equal frequencies
b)
When the number of heterozygotes in a population are not equal to the number of either of the homozygote
c)
When the number of heterozygotes in a population are equal to the number of either of the homozygote
d)
When the frequency of particular genes or alleles remain constant in a population through generations
|
|
Akash Nair answered |
Understanding Genetic Equilibrium
Genetic equilibrium, also known as Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, is a fundamental concept in population genetics. It describes a state in which the genetic composition of a population remains stable over time.
Key Characteristics of Genetic Equilibrium:
- Constant Allele Frequencies: In genetic equilibrium, the frequencies of alleles (alternative forms of a gene) in a population do not change from one generation to the next. This stability implies that the genetic variation remains constant.
- No Evolutionary Forces: For a population to achieve genetic equilibrium, it must be free from evolutionary influences such as natural selection, genetic drift, mutation, migration, and non-random mating. These factors can alter allele frequencies, leading to evolution.
- Mathematical Model: The Hardy-Weinberg principle provides a mathematical framework to predict genotype frequencies based on allele frequencies. It states that in a large, randomly mating population, the expected genotype frequencies can be calculated using the equation p² + 2pq + q² = 1, where p and q represent the frequencies of two alleles.
Importance of Genetic Equilibrium:
- Baseline for Comparison: Genetic equilibrium serves as a baseline to identify when a population is evolving. By comparing real populations to this model, scientists can detect changes in allele frequencies and understand evolutionary processes.
- Understanding Population Genetics: Studying genetic equilibrium helps in understanding the dynamics of genetic diversity, conservation biology, and the mechanisms of evolution.
In conclusion, option 'D' is correct because genetic equilibrium refers specifically to the condition where the frequency of particular genes or alleles remains constant in a population through generations, signifying no evolutionary change.
Genetic equilibrium, also known as Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, is a fundamental concept in population genetics. It describes a state in which the genetic composition of a population remains stable over time.
Key Characteristics of Genetic Equilibrium:
- Constant Allele Frequencies: In genetic equilibrium, the frequencies of alleles (alternative forms of a gene) in a population do not change from one generation to the next. This stability implies that the genetic variation remains constant.
- No Evolutionary Forces: For a population to achieve genetic equilibrium, it must be free from evolutionary influences such as natural selection, genetic drift, mutation, migration, and non-random mating. These factors can alter allele frequencies, leading to evolution.
- Mathematical Model: The Hardy-Weinberg principle provides a mathematical framework to predict genotype frequencies based on allele frequencies. It states that in a large, randomly mating population, the expected genotype frequencies can be calculated using the equation p² + 2pq + q² = 1, where p and q represent the frequencies of two alleles.
Importance of Genetic Equilibrium:
- Baseline for Comparison: Genetic equilibrium serves as a baseline to identify when a population is evolving. By comparing real populations to this model, scientists can detect changes in allele frequencies and understand evolutionary processes.
- Understanding Population Genetics: Studying genetic equilibrium helps in understanding the dynamics of genetic diversity, conservation biology, and the mechanisms of evolution.
In conclusion, option 'D' is correct because genetic equilibrium refers specifically to the condition where the frequency of particular genes or alleles remains constant in a population through generations, signifying no evolutionary change.
On Galapagos island, Darwin observed variation in beaks of birds (Darwin's finches) and he concluded:- a) Inter species variation
- b) Intraspecies variation
- c) Natural selection according to food
- d) Inheritance of acquired characters
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
On Galapagos island, Darwin observed variation in beaks of birds (Darwin's finches) and he concluded:
a)
Inter species variation
b)
Intraspecies variation
c)
Natural selection according to food
d)
Inheritance of acquired characters

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
- All the varieties, he conjectured, evolved on the island itself.
- From the original seed eating features, many other forms with altered beaks arose, enabling them to become insectivorous and vegetarian finches
The correct statement regarding a SN2 reaction is/are- a)reaction involving stronger bond formation to α-carbon occur at faster rate
- b)reaction shows kinetic isotopic effect
- c)substitution of
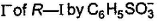 lower the activation energy of reaction
lower the activation energy of reaction - d)presence of electron withdrawing group in substrate increases reactivity
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statement regarding a SN2 reaction is/are
a)
reaction involving stronger bond formation to α-carbon occur at faster rate
b)
reaction shows kinetic isotopic effect
c)
substitution of 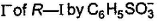 lower the activation energy of reaction
lower the activation energy of reaction
d)
presence of electron withdrawing group in substrate increases reactivity

|
Anuj Iyer answered |
Stronger bond formation at α-carbon affects the stability of product (thermodynamics) not the rate (kinetics) of reaction. Change of isotope at α-position or in halogens affect the rate, hence show kinetic isotopic effect. Presence of electron withdrawing group in substrate increases electrophilicity of α-carbon hence, increases its reactivity towards nucleophiles.
Under identical experimental condition, how many of the following substrate react at faster rate with aqueous NaOH than 2-bromobutane as substrate?
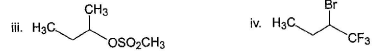



Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
Under identical experimental condition, how many of the following substrate react at faster rate with aqueous NaOH than 2-bromobutane as substrate?
|
|
Chirag Joshi answered |
Compounds (II), (III), (IV), (V), (VIII) and (X) react at faster rate than 2-bromobutane in SN2 reaction.
Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three Questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).PassageThe general mechanism of a SN2 reaction is as follows.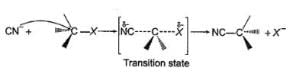 Factors that limit the rate of reaction are steric hindrance at α-cabron of substrate and strength of C—X bond. Any factor which stabilises transition state increases the rate of reaction.Q. Consider the following SN2 reaction,
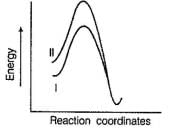
Factors that limit the rate of reaction are steric hindrance at α-cabron of substrate and strength of C—X bond. Any factor which stabilises transition state increases the rate of reaction.Q. Consider the following SN2 reaction, Which of the following energy diagram is correctly labelled?
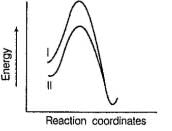
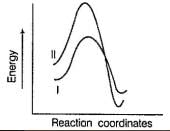
Which of the following energy diagram is correctly labelled?- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
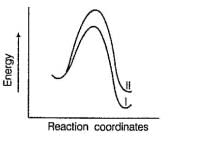
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three Questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
The general mechanism of a SN2 reaction is as follows.

Factors that limit the rate of reaction are steric hindrance at α-cabron of substrate and strength of C—X bond. Any factor which stabilises transition state increases the rate of reaction.
Q.
Consider the following SN2 reaction,

Which of the following energy diagram is correctly labelled?
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Tejas Singh answered |
Products are same in both reactions, hence same potential energies of products are shown. Also I- is better leaving group, has lower activation energy in SN2 reaction as indicated by curve-l in diagram.
This diagram represents which selection?
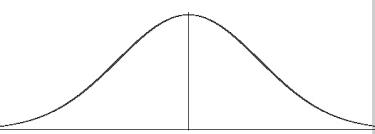
- a)Disruptive selection
- b)Stabilizing selection
- c)Directional selection
- d)Artificial selection
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
This diagram represents which selection?

a)
Disruptive selection
b)
Stabilizing selection
c)
Directional selection
d)
Artificial selection

|
EduRev NEET answered |
- This graph indicates stabilizing selection. As we can see, the peak gets higher and narrower.
- In this selection, most of the individuals acquire mean character value.
Consider the following SN2 reaction,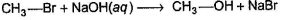 Q. Which of the following could increase the reactivity (rate) of reaction ?
Q. Which of the following could increase the reactivity (rate) of reaction ?- a)Increasing NaOH concentration
- b)Adding some Nal
- c)Replacing CHsBr by 14CH3— Br
- d) Using NaO18 H in place of NaOH
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following SN2 reaction,
Q.
Which of the following could increase the reactivity (rate) of reaction ?
a)
Increasing NaOH concentration
b)
Adding some Nal
c)
Replacing CHsBr by 14CH3— Br
d)
Using NaO18 H in place of NaOH

|
Anuj Iyer answered |
Increasing concentration of nucleophile (NaOH) increases the reactivity. Adding some Nal also catalyse reaction because of following equilibrium.
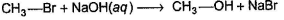
Now reaction occur with CH3I which has better leaving group. Heavier isotope forms stronger covalent bond. Hence, replacing CH3Br by 14CH3Br stabilises substrate, decreases rate whereas replacing NaOH by NaO18H stabilises transition state increases rate of reaction.
Now reaction occur with CH3I which has better leaving group. Heavier isotope forms stronger covalent bond. Hence, replacing CH3Br by 14CH3Br stabilises substrate, decreases rate whereas replacing NaOH by NaO18H stabilises transition state increases rate of reaction.
Chapter doubts & questions for October Week 2 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of October Week 2 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.