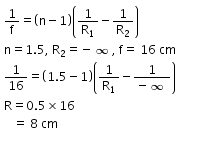All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of December Week 1 for NEET Exam
Heterocysts that take part in nitrogen fixation occur in- a)Nostoc
- b)Polysiphonia
- c)Ulothrix
- d)Fucus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Heterocysts that take part in nitrogen fixation occur in
a)
Nostoc
b)
Polysiphonia
c)
Ulothrix
d)
Fucus
|
|
Mubeena Akhter answered |
Heterocysts contain nitrogenase enzyme which helps to carry out nitrogen fixation.Nostoc show symbiotic association with corralloid roots of cycas and carries out nitrogen fixation.
Phenol is acidic due to resonance stabilization of its conjugate base :- a)O-H
- b)Benzyl alcohol
- c)Alkoxide ion
- d)Phenoxide ion
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Phenol is acidic due to resonance stabilization of its conjugate base :
a)
O-H
b)
Benzyl alcohol
c)
Alkoxide ion
d)
Phenoxide ion
|
|
Rishika Patel answered |
Polarity of Phenol
Phenol, also known as benzenol or carbolic acid, is an aromatic compound that consists of a benzene ring bonded to a hydroxyl group (-OH). The presence of the hydroxyl group makes phenol a polar molecule because oxygen is more electronegative than carbon and hydrogen.
Acidity of Phenol
Phenol is considered an acid because it can donate a proton (H+) and form a conjugate base. The acidity of phenol is attributed to resonance stabilization of its conjugate base, the phenoxide ion.
Resonance Stabilization of Phenoxide Ion
When phenol loses a proton, it forms the phenoxide ion (C6H5O-). The phenoxide ion is resonance stabilized, which means that the negative charge can be delocalized over the entire ring system through resonance structures.
Resonance Structures of Phenoxide Ion
The resonance structures of the phenoxide ion can be represented as follows:
1. In the first resonance structure, the lone pair on the oxygen atom forms a double bond with carbon, while the negative charge is located on the oxygen atom.
2. In the second resonance structure, the lone pair on the oxygen atom forms a double bond with one of the carbon atoms in the ring, while the negative charge is located on that carbon atom.
3. In the third resonance structure, the lone pair on the oxygen atom forms a double bond with another carbon atom in the ring, while the negative charge is located on that carbon atom.
The resonance structures demonstrate that the negative charge of the phenoxide ion is delocalized over the entire ring system, resulting in stability.
Comparison with Other Options
a) O-H: The O-H bond in phenol is the source of acidity, but it does not explain the resonance stabilization of the conjugate base.
b) Benzyl alcohol: While benzyl alcohol also has an -OH group, it lacks the aromatic ring required for resonance stabilization of the conjugate base.
c) Alkoxide ion: Alkoxide ions are formed when an alcohol loses a proton, but they do not have the same resonance stabilization as the phenoxide ion.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'D' (Phenoxide ion) because the resonance stabilization of the phenoxide ion is responsible for the acidity of phenol. The delocalization of the negative charge over the aromatic ring system increases the stability of the conjugate base, making phenol acidic.
Phenol, also known as benzenol or carbolic acid, is an aromatic compound that consists of a benzene ring bonded to a hydroxyl group (-OH). The presence of the hydroxyl group makes phenol a polar molecule because oxygen is more electronegative than carbon and hydrogen.
Acidity of Phenol
Phenol is considered an acid because it can donate a proton (H+) and form a conjugate base. The acidity of phenol is attributed to resonance stabilization of its conjugate base, the phenoxide ion.
Resonance Stabilization of Phenoxide Ion
When phenol loses a proton, it forms the phenoxide ion (C6H5O-). The phenoxide ion is resonance stabilized, which means that the negative charge can be delocalized over the entire ring system through resonance structures.
Resonance Structures of Phenoxide Ion
The resonance structures of the phenoxide ion can be represented as follows:
1. In the first resonance structure, the lone pair on the oxygen atom forms a double bond with carbon, while the negative charge is located on the oxygen atom.
2. In the second resonance structure, the lone pair on the oxygen atom forms a double bond with one of the carbon atoms in the ring, while the negative charge is located on that carbon atom.
3. In the third resonance structure, the lone pair on the oxygen atom forms a double bond with another carbon atom in the ring, while the negative charge is located on that carbon atom.
The resonance structures demonstrate that the negative charge of the phenoxide ion is delocalized over the entire ring system, resulting in stability.
Comparison with Other Options
a) O-H: The O-H bond in phenol is the source of acidity, but it does not explain the resonance stabilization of the conjugate base.
b) Benzyl alcohol: While benzyl alcohol also has an -OH group, it lacks the aromatic ring required for resonance stabilization of the conjugate base.
c) Alkoxide ion: Alkoxide ions are formed when an alcohol loses a proton, but they do not have the same resonance stabilization as the phenoxide ion.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'D' (Phenoxide ion) because the resonance stabilization of the phenoxide ion is responsible for the acidity of phenol. The delocalization of the negative charge over the aromatic ring system increases the stability of the conjugate base, making phenol acidic.
Identify the alcohol or phenol having a stronger acidic nature from the following.- a)CH3CH2OH
- b)C6H5OH
- c)CH3CHOHCH2CH3
- d)CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the alcohol or phenol having a stronger acidic nature from the following.
a)
CH3CH2OH
b)
C6H5OH
c)
CH3CHOHCH2CH3
d)
CH3CH2CH2CH2OH

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
- Phenol (C₆H₅OH) is more acidic than typical alcohols.
- This is due to the resonance stabilization of the phenoxide ion formed when phenol loses a hydrogen ion (H⁺).
- The negative charge on the oxygen atom in phenoxide ion is delocalized over the aromatic ring, increasing stability and acidity.
- In contrast, alcohols like ethanol (CH₃CH₂OH) do not have such resonance stabilization, making them less acidic.
- Therefore, phenol is the strongest acid among the given options.
- This is due to the resonance stabilization of the phenoxide ion formed when phenol loses a hydrogen ion (H⁺).
- The negative charge on the oxygen atom in phenoxide ion is delocalized over the aromatic ring, increasing stability and acidity.
- In contrast, alcohols like ethanol (CH₃CH₂OH) do not have such resonance stabilization, making them less acidic.
- Therefore, phenol is the strongest acid among the given options.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The acidity of phenols is due to
- A:
Oxidation process
- B:
Resonance stabilization of its ions.
- C:
Hybridisation
- D:
Presence of O-H group
The answer is b.
The acidity of phenols is due to
Oxidation process
Resonance stabilization of its ions.
Hybridisation
Presence of O-H group
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
The acidity of phenols is due to its ability to lose hydrogen ion to form phenoxide ions. In a phenol molecule, the sp2hybridised carbon atom of benzene ring attached directly to the hydroxyl group acts as an electron withdrawing group. This sp2 hybridized carbon atom of benzene ring attached directly to the hydroxyl group has higher electronegativity in comparison to hydroxyl group. Due to the higher electronegativity of this carbon atom in comparison to the hydroxyl group attached, electron density decreases on oxygen atom. The decrease in electron density increases the polarity of O-H bond and results in the increase in ionization of phenols. Thus, the phenoxide ion is formed. The phenoxide ion formed is stabilized by the delocalization of negative charge due to the resonance in benzene ring. Phenoxide ion has greater stability than phenols, as in case of phenol charge separation takes place during resonance.The resonance structures of phenoxide ions explain the delocalization of negative charge. In case of substituted phenols, acidity of phenols increases in the presence of electron withdrawing group. This is due to the stability of the phenoxide ion generated. The acidity of phenols further increases if these groups are attached at ortho and para positions. This is due to the fact that the negative charge in phenoxide ion is mainly delocalized at ortho and para positions of the attached benzene ring. On the other hand, the acidity of phenols decreases in presence of electron donating groups as they prohibit the formation of phenoxide ion.
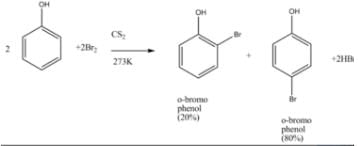
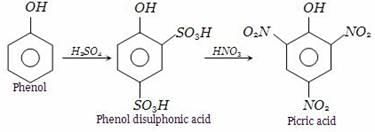
We can obtain picric acid from phenol by:- a)Sulphonation of phenol
- b)By Reimer Tiemann reaction
- c)Nitration of phenol
- d)Halogenation of phenol
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
We can obtain picric acid from phenol by:
a)
Sulphonation of phenol
b)
By Reimer Tiemann reaction
c)
Nitration of phenol
d)
Halogenation of phenol
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
Phenol heated with sulphuric acid gives phenol disulphonic acid, which further on reaction with nitric acid forms picric acid (2,4,6-trinitrophenol).
IUPAC name of m-cresol is ___________.- a)3-methylphenol
- b)3-chlorophenol
- c) 3-methoxyphenol
- d)benzene-1,3-diol
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
IUPAC name of m-cresol is ___________.
a)
3-methylphenol
b)
3-chlorophenol
c)
3-methoxyphenol
d)
benzene-1,3-diol
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Meta-Cresol, also 3-methylphenol, is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4(OH). It is a colourless, viscous liquid that is used as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals. It is a derivative of phenol and is an isomer of p-cresol and o-cresol.
Phenols do not respond to which of these tests?- a)Schiff’s reagent test
- b)FeCl3 test
- c)Br2 water test
- d)Litmus test
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Phenols do not respond to which of these tests?
a)
Schiff’s reagent test
b)
FeCl3 test
c)
Br2 water test
d)
Litmus test
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Phenols respond to all the above mentioned tests except Schiff’s reagent test, which is shown by aldehydes.
Phenol on treatment with Phthalic anhydride gives:- a)Phenolphthalein
- b)Salicylaldehyde
- c)Phthalic acid
- d)Salicylic acid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Phenol on treatment with Phthalic anhydride gives:
a)
Phenolphthalein
b)
Salicylaldehyde
c)
Phthalic acid
d)
Salicylic acid

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The correct answer is option A
Phenolphthalein gives pink colour with alkali.
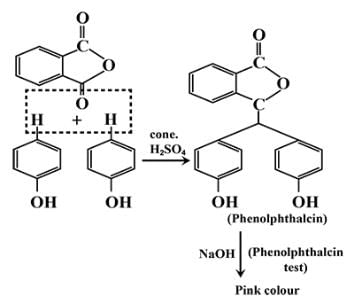
Phenolphthalein gives pink colour with alkali.

If R1 and R2 are the radii of curvature of a double convex lens, which of the following will have the largest power?- a)R1 = 10 cm and R2 = ∞
- b)R1 = R2 = 5 cm
- c)R1 = ∞ and R2 = 10 cm
- d)R1 = R2 = 10 cm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If R1 and R2 are the radii of curvature of a double convex lens, which of the following will have the largest power?
a)
R1 = 10 cm and R2 = ∞
b)
R1 = R2 = 5 cm
c)
R1 = ∞ and R2 = 10 cm
d)
R1 = R2 = 10 cm
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Using the lens maker’s formula we get
p= (μ−1) (1/R1+1/R2)
As we can clearly see, when R1= R2= 5cm then the maximum power is achieved.
p= (μ−1) (1/R1+1/R2)
As we can clearly see, when R1= R2= 5cm then the maximum power is achieved.
A convex lens produces a real image m times the size of the object. What is the distance of the object from the lens?- a)(m + 1)f
- b)
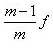
- c)(m – 1)f
- d)
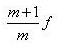
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A convex lens produces a real image m times the size of the object. What is the distance of the object from the lens?
a)
(m + 1)f
b)
c)
(m – 1)f
d)
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
M=−ϑ /u =−m/1
ϑ=−mu
(1/ϑ)−(1/u)=1/f
1/mu+1/u=−1/f
(1+m)/xu=−1/f
u= (1+m)f/(m)
ϑ=−mu
(1/ϑ)−(1/u)=1/f
1/mu+1/u=−1/f
(1+m)/xu=−1/f
u= (1+m)f/(m)
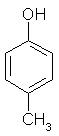
Which of the following is obtained as a major product in Friedel-Craft’s alkylation of phenol ?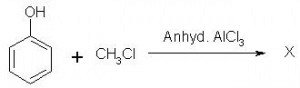
- a)
- b)
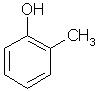
- c)
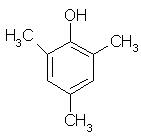
- d)
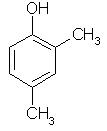
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is obtained as a major product in Friedel-Craft’s alkylation of phenol ?
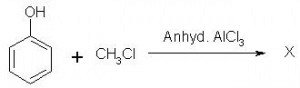
a)
b)
c)

d)

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
The correct answer is option A
P-methyl phenol is the major product.
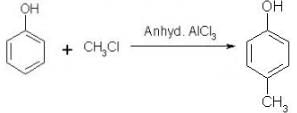
P-methyl phenol is the major product.

The residue left after methane production from cattle dung is- a)Used as manure
- b)Buried in landfills
- c)Used in civil construction
- d)Burnt
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The residue left after methane production from cattle dung is
a)
Used as manure
b)
Buried in landfills
c)
Used in civil construction
d)
Burnt
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
The raw material for biogas production is excreta (dung) of cattle. The biogas plant consists of a concrete tank (10-15 feet deep) in which bio-wastes are collected and slurry of dung is fed. A floating cover is placed over the slurry, which keeps on rising as the gas is produced in the tank due to the microbial activity. Methano bacterium in the dung act on the bio-wastes to produce bio-gas. The gas produced is supplied to nearby houses by an outlet. Through another outlet, the spent slurry is removed to be used as manure.
A convergent lens made of crown glass (refractive index 1.5) has focal length 20cm in air. If it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.60, its focal length will be:- a)100cm
- b)160cm
- c)-80cm
- d)-160cm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A convergent lens made of crown glass (refractive index 1.5) has focal length 20cm in air. If it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.60, its focal length will be:
a)
100cm
b)
160cm
c)
-80cm
d)
-160cm
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
When the lens is in air, we have (from lens maker's equation), 1/20 = [(1.5/1) - 1) (1/R1- 1/R2).
We are not bothered about the signs of R1 and R2 since they are unknown quantities.
Even though we know that the convergent lens will become divergent in the denser medium, we write lens maker's equation without bothering about the sign of its unknown focal length in the liquid. If if is the focal length in the liquid, we can write,
1/f = ((1.5/1.6) - 1) (1/R1 - 1/R2).
Dividing the first equation by the second, we obtain f/20 = 0.5x1.6/(-0.1) from which f = -160 cm
If two thin lenses of power p1 and p2 are held in contact then the power of the combination will be- a)p1 +p2
- b)p12 +p22
- c)p1 -p2
- d)(p1 +p2)1/2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If two thin lenses of power p1 and p2 are held in contact then the power of the combination will be
a)
p1 +p2
b)
p12 +p22
c)
p1 -p2
d)
(p1 +p2)1/2
|
|
Raghavendra Rane answered |
Explanation:
When two thin lenses of power p1 and p2 are held in contact, the power of the combination can be calculated using the lens formula:
1/f = 1/f1 + 1/f2
where f is the focal length of the combination lens, f1 is the focal length of the first lens, and f2 is the focal length of the second lens.
Using the relation p = 1/f, we get:
p = p1 + p2
This means that the power of the combination lens is equal to the sum of the powers of the individual lenses.
Therefore, the correct option is 'A' i.e. p1p2.
Summary:
When two thin lenses are held in contact, the power of the combination is equal to the sum of the powers of the individual lenses.
When two thin lenses of power p1 and p2 are held in contact, the power of the combination can be calculated using the lens formula:
1/f = 1/f1 + 1/f2
where f is the focal length of the combination lens, f1 is the focal length of the first lens, and f2 is the focal length of the second lens.
Using the relation p = 1/f, we get:
p = p1 + p2
This means that the power of the combination lens is equal to the sum of the powers of the individual lenses.
Therefore, the correct option is 'A' i.e. p1p2.
Summary:
When two thin lenses are held in contact, the power of the combination is equal to the sum of the powers of the individual lenses.
What is the unit of power of lens?- a)Centimetre
- b)Dioptre
- c)Metres
- d)Radians
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the unit of power of lens?
a)
Centimetre
b)
Dioptre
c)
Metres
d)
Radians
|
|
Sandy Naaz answered |
Dioptre is unit of power..
1 dioptre =- a)1m-9
- b)1m-2
- c)1m-6
- d)1m-1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
1 dioptre =
a)
1m-9
b)
1m-2
c)
1m-6
d)
1m-1
|
|
Anand Kumar answered |
Power=1/focal length
unit of power is dioptre or m^-1
unit of power is dioptre or m^-1
A concave lens of glass, refractive index 1.5, has both surfaces of same radius of curvature R. On immersion in a medium of refractive index 1.75, it will behave as a:- a)convergent lens of focal length 3.5R
- b)divergent lens of focal length 3.5R
- c)divergent lens of focal length 3.0R
- d)convergent lens of focal length 3.0R
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A concave lens of glass, refractive index 1.5, has both surfaces of same radius of curvature R. On immersion in a medium of refractive index 1.75, it will behave as a:
a)
convergent lens of focal length 3.5R
b)
divergent lens of focal length 3.5R
c)
divergent lens of focal length 3.0R
d)
convergent lens of focal length 3.0R
|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |

A double convex thin lens made of glass of refractive index 1.6 has radii of curvature 15 cm each. The focal length of this lens when immersed in a fluid of refractive index 1.63 is
- a)– 407 cm
- b)125 cm
- c)25 cm
- d)+ 250 cm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A double convex thin lens made of glass of refractive index 1.6 has radii of curvature 15 cm each. The focal length of this lens when immersed in a fluid of refractive index 1.63 is
a)
– 407 cm
b)
125 cm
c)
25 cm
d)
+ 250 cm
|
|
Rajesh Khatri answered |
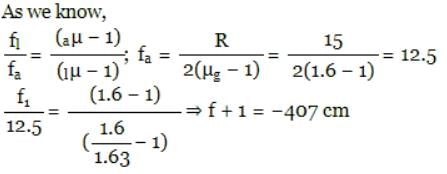
One of the constituents of baking powder is sodium hydrogencarbonate, the other constituent is- a)hydrochloric acid
- b)tartaric acid
- c)acetic acid
- d)sulphuric acid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the constituents of baking powder is sodium hydrogencarbonate, the other constituent is
a)
hydrochloric acid
b)
tartaric acid
c)
acetic acid
d)
sulphuric acid
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
(b) Baking powder is a mixture of baking soda NaHCO3,(sodium hydrogen carbonate)and a mild edible acid such as tartaric acid. When baking powder mixes with water (form a king cake or bread), sodium hydrogen carbonate reacts with tartaric acid to evolve carbon dioxide gas.
Select the correct group of biocontrol agents:- a)Nostoc, Azospirillum, Nucleopolyhedrovirus
- b)Bacillus thuringiensis, Tobacco mosaic virus, Aphids
- c)Trichoderma, Baculovirus, Bacillus thuringiensis
- d)Oscillatoria, Rhizobium, Trichoderma
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct group of biocontrol agents:
a)
Nostoc, Azospirillum, Nucleopolyhedrovirus
b)
Bacillus thuringiensis, Tobacco mosaic virus, Aphids
c)
Trichoderma, Baculovirus, Bacillus thuringiensis
d)
Oscillatoria, Rhizobium, Trichoderma

|
Lead Academy answered |
Biocontrol agents are organisms used to control pests or pathogens biologically.
Trichoderma is a fungus used against plant pathogens.
Baculovirus (like Nucleopolyhedrovirus) is used to target insect pests.
Bacillus thuringiensis is a bacterium producing toxins effective against insects.
Hence, Option C correctly lists known biocontrol agents.
Trichoderma is a fungus used against plant pathogens.
Baculovirus (like Nucleopolyhedrovirus) is used to target insect pests.
Bacillus thuringiensis is a bacterium producing toxins effective against insects.
Hence, Option C correctly lists known biocontrol agents.
If two thin lenses of focal length f1 and f2 are held in contact then the focal length of the combination will be - a)

- b)

- c)

- d)none
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If two thin lenses of focal length f1 and f2 are held in contact then the focal length of the combination will be
a)
b)
c)
d)
none
|
|
Khushi Pandey answered |
Option C is correct as..
1/f = 1/f1 + 1/f2
and,
P = P1 + P2
1/f = 1/f1 + 1/f2
and,
P = P1 + P2
Identify the incorrectly matched pair:- a)Baculoviruses – Species specific, broad spectrum insecticides
- b)Trichoderma – Free living fungi common in root ecosystems
- c)Ladybird – Biocontrol of aphids
- d)Organic farming – Pests kept at manageable levels rather than completely eradicated
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Baculoviruses – Species specific, broad spectrum insecticides
b)
Trichoderma – Free living fungi common in root ecosystems
c)
Ladybird – Biocontrol of aphids
d)
Organic farming – Pests kept at manageable levels rather than completely eradicated

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Baculoviruses are indeed species-specific but not broad-spectrum insecticides; they are narrow-spectrum, targeting specific insect pests. Hence, Option A is incorrectly matched.
Chapter doubts & questions for December Week 1 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of December Week 1 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup