All Exams >
Class 10 >
Weekly Tests for Class 10 Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of April Week 2 for Class 10 Exam
The number of polynomials having zeroes as -2 and 5 is:- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)More than 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of polynomials having zeroes as -2 and 5 is:
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
More than 3

|
Kamna Science Academy answered |
The polynomials x2-3x-10, 2x2-6x-20, (1/2)x2-(3/2)x-5, 3x2-9x-30, have zeroes as -2 and 5.
If p(x) is a polynomial of degree one and p(a) = 0, then a is said to be:- a)Zero of p(x)
- b)Value of p(x)
- c)Constant of p(x)
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If p(x) is a polynomial of degree one and p(a) = 0, then a is said to be:
a)
Zero of p(x)
b)
Value of p(x)
c)
Constant of p(x)
d)
None of the above

|
Kds Coaching answered |
If p(x) is a polynomial of degree one, it can be written as:
p(x) = mx + c
where m and c are constants, and m ≠ 0.
Given that p(a) = 0, substituting x = a into p(x):
p(a) = m(a) + c = 0
This equation implies that a is a root or zero of the polynomial p(x), as it satisfies p(a) = 0.
Hence, the correct answer is:
A: Zero of p(x)
p(x) = mx + c
where m and c are constants, and m ≠ 0.
Given that p(a) = 0, substituting x = a into p(x):
p(a) = m(a) + c = 0
This equation implies that a is a root or zero of the polynomial p(x), as it satisfies p(a) = 0.
Hence, the correct answer is:
A: Zero of p(x)
Identify the substances that are oxidised and the substances that are reduced in the following reaction.Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe- a)Fe2O3
- b)Al
- c)Fe
- d)Both A and B
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the substances that are oxidised and the substances that are reduced in the following reaction.
Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe
a)
Fe2O3
b)
Al
c)
Fe
d)
Both A and B

|
Kds Coaching answered |
To identify the substances that are oxidized and reduced in the given reaction:
Reaction: Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe
- Oxidation involves the loss of electrons.
- Reduction involves the gain of electrons.
- Iron (Fe) in Fe₂O₃:
- In Fe₂O₃, iron is in the +3 oxidation state.
- In elemental Fe, the oxidation state is 0.
- Thus, Fe is reduced from +3 to 0.
- Aluminum (Al):
- In elemental Al, the oxidation state is 0.
- In Al₂O₃, aluminum is in the +3 oxidation state.
- Thus, Al is oxidized from 0 to +3.
Substances:
- Substance reduced: Fe₂O₃ (iron is reduced to Fe).
- Substance oxidized: Al (aluminum is oxidized to Al₂O₃).
Correct Answer: (d) Both A and B
Explanation: Fe₂O₃ is reduced, and Al is oxidized.
Explanation: Fe₂O₃ is reduced, and Al is oxidized.
A polynomial of degree n has:- a)Only one zero
- b)At least n zeroes
- c)More than n zeroes
- d)At most n zeroes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A polynomial of degree n has:
a)
Only one zero
b)
At least n zeroes
c)
More than n zeroes
d)
At most n zeroes
|
|
Anjali garg answered |
Understanding Polynomial Zeros
Polynomials are mathematical expressions that involve variables raised to whole number powers. The degree of a polynomial is defined as the highest power of the variable in the expression.
Key Concept: The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
- This theorem states that a polynomial of degree n has exactly n roots (or zeros) in the complex number system, counting multiplicities.
Option Analysis
- Option A: Only one zero
- This is not always true; a polynomial can have multiple zeros or none.
- Option B: At least n zeros
- While a polynomial has exactly n roots, some could be repeated (counted multiple times), but they don’t guarantee distinct zeros.
- Option C: More than n zeros
- This is incorrect. A polynomial of degree n cannot have more than n roots.
- Option D: At most n zeros
- This is the correct answer. A polynomial can have anywhere from 0 to n zeros. Zeros can be real or complex. For example:
- A quadratic polynomial (degree 2) can have 0, 1, or 2 real roots.
- A cubic polynomial (degree 3) can have 0, 1, 2, or 3 real roots.
Conclusion
In summary, a polynomial of degree n can have at most n zeros, which may include repeated roots and complex solutions. This is a fundamental principle in algebra that helps in understanding the behavior of polynomial functions.
Polynomials are mathematical expressions that involve variables raised to whole number powers. The degree of a polynomial is defined as the highest power of the variable in the expression.
Key Concept: The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
- This theorem states that a polynomial of degree n has exactly n roots (or zeros) in the complex number system, counting multiplicities.
Option Analysis
- Option A: Only one zero
- This is not always true; a polynomial can have multiple zeros or none.
- Option B: At least n zeros
- While a polynomial has exactly n roots, some could be repeated (counted multiple times), but they don’t guarantee distinct zeros.
- Option C: More than n zeros
- This is incorrect. A polynomial of degree n cannot have more than n roots.
- Option D: At most n zeros
- This is the correct answer. A polynomial can have anywhere from 0 to n zeros. Zeros can be real or complex. For example:
- A quadratic polynomial (degree 2) can have 0, 1, or 2 real roots.
- A cubic polynomial (degree 3) can have 0, 1, 2, or 3 real roots.
Conclusion
In summary, a polynomial of degree n can have at most n zeros, which may include repeated roots and complex solutions. This is a fundamental principle in algebra that helps in understanding the behavior of polynomial functions.
If one zero of the quadratic polynomial x2 + 3x + k is 2, then the value of k is- a)10
- b)–10
- c)5
- d)–5
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If one zero of the quadratic polynomial x2 + 3x + k is 2, then the value of k is
a)
10
b)
–10
c)
5
d)
–5
|
|
Sheetal jain answered |
Given Problem
We have the quadratic polynomial:
x² + 3x + k, where one of the zeros is 2. We need to find the value of k.
Understanding Zeros of a Polynomial
- A zero (root) of a polynomial is a value of x that makes the polynomial equal to zero.
- If 2 is a zero, we can substitute x = 2 into the polynomial and set it equal to zero.
Substituting the Zero
Let's substitute x = 2 into the polynomial:
- 2² + 3(2) + k = 0
Now, calculate:
- 4 + 6 + k = 0
Simplifying the Equation
- Combine the constants:
10 + k = 0
- Now, isolate k:
k = -10
Conclusion
The value of k that satisfies the condition that one zero of the polynomial is 2 is k = -10.
Thus, the correct answer is option 'B'.
We have the quadratic polynomial:
x² + 3x + k, where one of the zeros is 2. We need to find the value of k.
Understanding Zeros of a Polynomial
- A zero (root) of a polynomial is a value of x that makes the polynomial equal to zero.
- If 2 is a zero, we can substitute x = 2 into the polynomial and set it equal to zero.
Substituting the Zero
Let's substitute x = 2 into the polynomial:
- 2² + 3(2) + k = 0
Now, calculate:
- 4 + 6 + k = 0
Simplifying the Equation
- Combine the constants:
10 + k = 0
- Now, isolate k:
k = -10
Conclusion
The value of k that satisfies the condition that one zero of the polynomial is 2 is k = -10.
Thus, the correct answer is option 'B'.
The zeroes of x2– 2x – 8 are:- a)(2, -4)
- b)(4, -2)
- c)(-2, -2)
- d)(-4, -4)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The zeroes of x2– 2x – 8 are:
a)
(2, -4)
b)
(4, -2)
c)
(-2, -2)
d)
(-4, -4)

|
EduRev Class 10 answered |
x2 – 2x – 8 = x2 – 4x + 2x – 8
= x(x – 4) + 2(x – 4)
= (x - 4)(x + 2)
Therefore, x = 4, -2.
= x(x – 4) + 2(x – 4)
= (x - 4)(x + 2)
Therefore, x = 4, -2.
Identify the substance oxidised and the substance reduced in the following reactions.MnO2 + 4HCl —–> MnCl2 + 2H20 + Cl2- a)MnO2 is getting reduced and H20 is getting oxidised.
- b)MnO2 is getting reduced and HCl is getting oxidised.
- c)MnCl2 is getting reduced and HCl is getting oxidised.
- d)HCl is getting reduced and Cl2 is getting oxidised.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the substance oxidised and the substance reduced in the following reactions.
MnO2 + 4HCl —–> MnCl2 + 2H20 + Cl2
a)
MnO2 is getting reduced and H20 is getting oxidised.
b)
MnO2 is getting reduced and HCl is getting oxidised.
c)
MnCl2 is getting reduced and HCl is getting oxidised.
d)
HCl is getting reduced and Cl2 is getting oxidised.

|
EduRev Class 10 answered |
MnO2 is getting reduced and HCl is getting oxidised.
What is the substance gaining oxygen and being oxidized during the described reaction?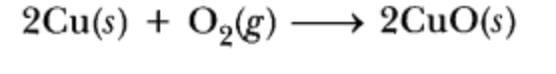
- a)Cu
- b)O
- c)CuO
- d)Not a redox reaction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the substance gaining oxygen and being oxidized during the described reaction?
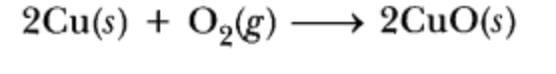
a)
Cu
b)
O
c)
CuO
d)
Not a redox reaction
|
|
Arnav raman answered |
Understanding the Reaction
The reaction given is:
2Cu(s) + O2(g) → 2CuO(s)
This equation describes a chemical reaction where copper (Cu) reacts with oxygen (O2) to form copper(II) oxide (CuO).
What is Oxidation?
In chemistry, oxidation refers to the process where a substance loses electrons or gains oxygen.
Identifying the Oxidized Substance
- In this reaction, copper (Cu) is the substance that is oxidized.
- Copper reacts with oxygen, and during this process, copper loses electrons and gains oxygen to form CuO.
Oxidation Process
- Copper (Cu) goes from an elemental state (0 oxidation state) to a compound state (oxidation state +2 in CuO).
- By gaining oxygen, Cu is effectively losing electrons, which is the hallmark of oxidation.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A', which indicates that copper (Cu) is the substance that is being oxidized in this reaction.
- Oxygen (O2) is actually being reduced in this process, as it gains electrons by reacting with copper.
In summary, the reaction showcases a redox process where copper is oxidized and oxygen is reduced, clearly identifying copper as the substance that gains oxygen and undergoes oxidation.
The reaction given is:
2Cu(s) + O2(g) → 2CuO(s)
This equation describes a chemical reaction where copper (Cu) reacts with oxygen (O2) to form copper(II) oxide (CuO).
What is Oxidation?
In chemistry, oxidation refers to the process where a substance loses electrons or gains oxygen.
Identifying the Oxidized Substance
- In this reaction, copper (Cu) is the substance that is oxidized.
- Copper reacts with oxygen, and during this process, copper loses electrons and gains oxygen to form CuO.
Oxidation Process
- Copper (Cu) goes from an elemental state (0 oxidation state) to a compound state (oxidation state +2 in CuO).
- By gaining oxygen, Cu is effectively losing electrons, which is the hallmark of oxidation.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A', which indicates that copper (Cu) is the substance that is being oxidized in this reaction.
- Oxygen (O2) is actually being reduced in this process, as it gains electrons by reacting with copper.
In summary, the reaction showcases a redox process where copper is oxidized and oxygen is reduced, clearly identifying copper as the substance that gains oxygen and undergoes oxidation.
What is a reduction reaction?- a)addition of hydrogen to a substance
- b)addition of oxygen to a substance
- c)removal of hydrogen from a substance
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is a reduction reaction?
a)
addition of hydrogen to a substance
b)
addition of oxygen to a substance
c)
removal of hydrogen from a substance
d)
none of the above

|
Kds Coaching answered |
In terms of hydrogen and oxygen:
Addition of hydrogen to a substance: Reduction
Removal of oxygen from a substance: Reduction
Therefore, option A, "addition of hydrogen to a substance," correctly defines a reduction reaction.
Identify the substance that is oxidised and reduced in the following reaction.

- a)CuO-reduced and Zn-oxidised
- b)Zn- reduced and CuO oxidised
- c)Cu- reduced and Zn-oxidised
- d)ZnO- reduced, Zn-oxidised
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the substance that is oxidised and reduced in the following reaction.


a)
CuO-reduced and Zn-oxidised
b)
Zn- reduced and CuO oxidised
c)
Cu- reduced and Zn-oxidised
d)
ZnO- reduced, Zn-oxidised

|
Nk Classes answered |
Zn is getting oxidised, CuO is getting reduced.
What is the quadratic polynomial whose sum and the product of zeroes is √2, 1/3 respectively?- a)3x2 - 3√2x +1
- b)3x2 + 3√2x +1
- c)3x2 + 3√2x -1
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the quadratic polynomial whose sum and the product of zeroes is √2, 1/3 respectively?
a)
3x2 - 3√2x +1
b)
3x2 + 3√2x +1
c)
3x2 + 3√2x -1
d)
None of the above

|
Gowri Mehta answered |
Understanding the Problem
To find the quadratic polynomial based on the given sum and product of its zeroes, we can use Vieta's formulas. For a quadratic polynomial in the form of ax² + bx + c, the relationships are:
- Sum of zeroes (α + β) = -b/a
- Product of zeroes (αβ) = c/a
In this case, we have:
- Sum of zeroes = √2
- Product of zeroes = 1/3
Formulating the Polynomial
1. Using Vieta's Formulas:
- From the sum of zeroes: α + β = √2
- Hence, -b/a = √2
- From the product of zeroes: αβ = 1/3
- Hence, c/a = 1/3
2. Choosing a Value for 'a':
- Let's choose a = 3 (to eliminate fractions easily).
- Then, -b/3 = √2 implies b = -3√2.
- For c, we have c/3 = 1/3, leading to c = 1.
Constructing the Polynomial
Now substituting the values of a, b, and c into the quadratic polynomial form:
- The polynomial becomes:
3x² - 3√2x + 1
Conclusion
The required quadratic polynomial is:
3x² - 3√2x + 1
Thus, the correct answer is option 'A'.
To find the quadratic polynomial based on the given sum and product of its zeroes, we can use Vieta's formulas. For a quadratic polynomial in the form of ax² + bx + c, the relationships are:
- Sum of zeroes (α + β) = -b/a
- Product of zeroes (αβ) = c/a
In this case, we have:
- Sum of zeroes = √2
- Product of zeroes = 1/3
Formulating the Polynomial
1. Using Vieta's Formulas:
- From the sum of zeroes: α + β = √2
- Hence, -b/a = √2
- From the product of zeroes: αβ = 1/3
- Hence, c/a = 1/3
2. Choosing a Value for 'a':
- Let's choose a = 3 (to eliminate fractions easily).
- Then, -b/3 = √2 implies b = -3√2.
- For c, we have c/3 = 1/3, leading to c = 1.
Constructing the Polynomial
Now substituting the values of a, b, and c into the quadratic polynomial form:
- The polynomial becomes:
3x² - 3√2x + 1
Conclusion
The required quadratic polynomial is:
3x² - 3√2x + 1
Thus, the correct answer is option 'A'.
The zeroes of the quadratic polynomial x2 + 99x + 127 are- a)both positive
- b)both negative
- c)one positive and one negative
- d)both equal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The zeroes of the quadratic polynomial x2 + 99x + 127 are
a)
both positive
b)
both negative
c)
one positive and one negative
d)
both equal

|
EduRev Class 10 answered |
Given quadratic polynomial is x2 + 99x + 127.
By comparing with the standard form, we get;
a = 1, b = 99 and c = 127
a > 0, b > 0 and c > 0
We know that in any quadratic polynomial, if all the coefficients have the same sign, then the zeroes of that polynomial will be negative.
Therefore, the zeroes of the given quadratic polynomial are negative.
Zeroes of p(x) = x2-27 are:- a)±9√3
- b)±3√3
- c)±7√3
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Zeroes of p(x) = x2-27 are:
a)
±9√3
b)
±3√3
c)
±7√3
d)
None of the above

|
Kds Coaching answered |
x2 - 27 = 0
x2 = 27
x = √27
x = ±3√3
If the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial ax2 + bx + c, c ≠ 0 are equal, then- a)c and b have opposite signs
- b)c and a have opposite signs
- c)c and b have same signs
- d)c and a have same signs
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial ax2 + bx + c, c ≠ 0 are equal, then
a)
c and b have opposite signs
b)
c and a have opposite signs
c)
c and b have same signs
d)
c and a have same signs

|
Nk Classes answered |
For equal roots, discriminant will be equal to zero.
b2 -4ac = 0
b2 = 4ac
ac = b2/4
ac > 0 (as square of any number cannot be negative)
Identify the substances that are oxidised in the following reactions.
2PbO + C → 2Pb + CO2- a)Pb
- b)C
- c)PbO
- d)CO2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the substances that are oxidised in the following reactions.
2PbO + C → 2Pb + CO2
2PbO + C → 2Pb + CO2
a)
Pb
b)
C
c)
PbO
d)
CO2

|
Kds Coaching answered |
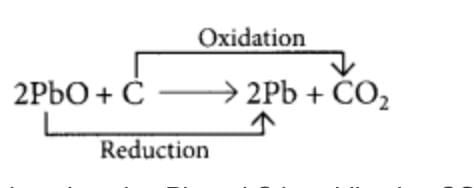
PbO is reduced to Pb and C is oxidised to CO2.
What is a oxidation reaction?- a)addition of hydrogen to a substance
- b)addition of oxygen to a substance
- c)removal of oxygen from a substance
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is a oxidation reaction?
a)
addition of hydrogen to a substance
b)
addition of oxygen to a substance
c)
removal of oxygen from a substance
d)
none of the above

|
Kds Coaching answered |
In terms of hydrogen and oxygen:
Addition of oxygen to a substance: Oxidation
Removal of hydrogen from a substance: Oxidation
Therefore, correct answer is option (b)
Chapter doubts & questions for April Week 2 - Weekly Tests for Class 10 Preparation 2025 is part of Class 10 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of April Week 2 - Weekly Tests for Class 10 Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 10 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









