All Exams >
JEE >
6 Months Preparation for JEE >
All Questions
All questions of Surface Chemistry for JEE Exam
The name aquadag is given to the colloidal sol of:- a)Copper in water
- b)platinum in water
- c)graphite in water
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The name aquadag is given to the colloidal sol of:
a)
Copper in water
b)
platinum in water
c)
graphite in water
d)
none of the above

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
The correct answer is Option C.
Aquadag is the name of a water-based colloidal graphite coating which is a colloidal solution of graphite in water.
During the adsorption of Krypton on activated charcoal at low temperature - a)ΔH < 0 and ΔS < 0
- b)ΔH > 0 and ΔS < 0
- c)ΔH > 0 and ΔS > 0
- d)ΔH < 0 and ΔS > 0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During the adsorption of Krypton on activated charcoal at low temperature
a)
ΔH < 0 and ΔS < 0
b)
ΔH > 0 and ΔS < 0
c)
ΔH > 0 and ΔS > 0
d)
ΔH < 0 and ΔS > 0
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Correct answer is option A
During the adsorption of krypton on activated charcoal at low temperature.
ΔH<0 and ΔS<0.
Since adsorption is an exothermic process, the enthalpy change is negative. Heat is given out during the process.
The krypton gas adsorbed on activated charcoal is more ordered than unadsorbed krypton gas. Hence, the process occurs with a decrease in entropy.
In other words, the entropy change is negative for the process.
During the adsorption of krypton on activated charcoal at low temperature.
ΔH<0 and ΔS<0.
Since adsorption is an exothermic process, the enthalpy change is negative. Heat is given out during the process.
The krypton gas adsorbed on activated charcoal is more ordered than unadsorbed krypton gas. Hence, the process occurs with a decrease in entropy.
In other words, the entropy change is negative for the process.
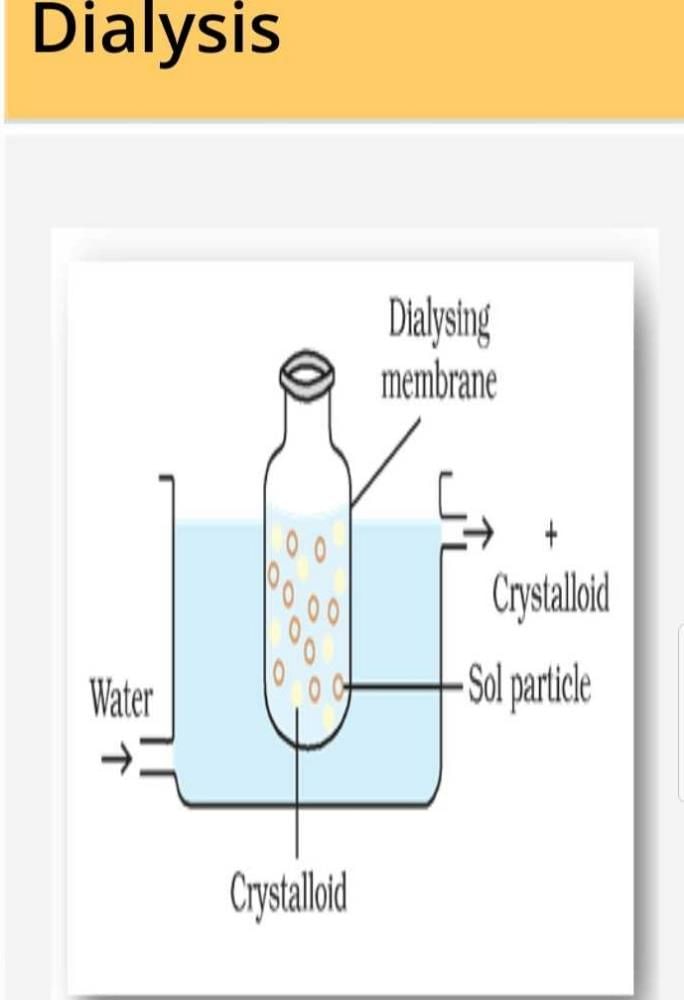
Blood is purified by:- a)Dialysis
- b)Filtration
- c)Coagulation
- d)Electro-osmosis
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Blood is purified by:
a)
Dialysis
b)
Filtration
c)
Coagulation
d)
Electro-osmosis
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Healthy kidneys clean your blood and remove extra fluid in the form of urine. They also make substances that keep your body healthy. Dialysis replaces some of these functions when your kidneys no longer work.
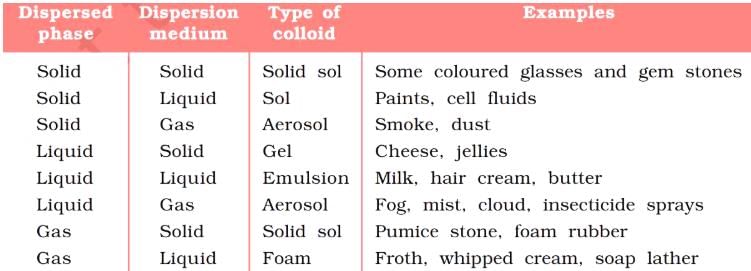
An example of colloid in which both phase and medium are solid is?- a)milk
- b)cheese
- c)cake
- d)marble
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An example of colloid in which both phase and medium are solid is?
a)
milk
b)
cheese
c)
cake
d)
marble

|
Ashu Bhardwaj answered |
Cake batter an emulsion ,cheese a gel ,solid in liquid malai,milk emulsion, so marble is left
Which one of the following is not applicable to chemisorption ?- a)Its heat of adsorption is high
- b)It takes place at high temperature
- c)It is reversible
- d)It forms mono-molecular layers
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not applicable to chemisorption ?
a)
Its heat of adsorption is high
b)
It takes place at high temperature
c)
It is reversible
d)
It forms mono-molecular layers
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Chemisorption is irreversible in nature because in chemisorption there are strong covalent bond are formed which do not brake easily to separate the reactants because of this it has high heat of adsorption, takes place at high temperatures and forms monolayers.
Which one of the following is lyophilic colloid ?- a)Milk
- b)Gum
- c)Fog
- d)Blood
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is lyophilic colloid ?
a)
Milk
b)
Gum
c)
Fog
d)
Blood
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Colloidal sols formed by mixing substances in a suitable dispersion medium are called lyophilic sols. These are quite stable. They are also known as reversible sols because the dispersion medium can be separated from the colloid by means of physical methods like evaporation. For e.g. gum, gelatin, starch, rubber etc.
Rotation at high speed makes the colloid settle down and the impurities remain in solution. What is this process called?- a)Ultra centrifugation
- b)Ultrafiltration
- c)Dialysis
- d)Mechanical dispersion
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Rotation at high speed makes the colloid settle down and the impurities remain in solution. What is this process called?
a)
Ultra centrifugation
b)
Ultrafiltration
c)
Dialysis
d)
Mechanical dispersion
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
The ultracentrifuge is a centrifuge optimized for spinning a rotor at very high speeds, capable of generating acceleration as high as 1 000 000 g (approx. 9 800 km/s2). There are two kinds of ultracentrifuges, the preparative and the analytical ultracentrifuge.
Which of the following statements about physical adsorption is not correct ?- a)It is usually monolayer
- b)It is reversible in nature
- c)It involves van der Weals interactions between adsorbent and adsorbate
- d)It involves small value of adsorption
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about physical adsorption is not correct ?
a)
It is usually monolayer
b)
It is reversible in nature
c)
It involves van der Weals interactions between adsorbent and adsorbate
d)
It involves small value of adsorption
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Physical adsorption is a multilayer phenomenon
A dispersion of AgCl in water is:- a)hydrophobic sol
- b)an emulsion
- c)an aerosol
- d)hydrophilic colloid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A dispersion of AgCl in water is:
a)
hydrophobic sol
b)
an emulsion
c)
an aerosol
d)
hydrophilic colloid
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
AgCl beinga covalent molecule is insoluble in water and hence hydrophobic.
Depending upon the nature of interaction between the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium, colloidal sols are divided in how many categories?- a)1
- b)2
- c)6
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Depending upon the nature of interaction between the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium, colloidal sols are divided in how many categories?
a)
1
b)
2
c)
6
d)
4
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Depending upon the nature of interaction between the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium, colloidal sols are divided into two categories, namely, lyophilic and lyophobic:
1. Lyophilic colloids: The colloidal solution in which the particles of the dispersed phase have a greater affinity for the dispersion medium are called lyophilic colloids. The common example of lyophilic colloids are glue, gelatin, starch, protein, rubber, etc.
2. Lyophobic colloids: The colloidal solutions in which the particles of the dispersed phase have no affinity or love rather have hatred for the dispersion medium are called lyophobic colloids.
Statement-1 : All colloidal dispersions give very low osmotic pressure and show very small freezing point depression or boiling pointelevation. Statement-2 : Tydall effect is due to scattering of light from the surface of colloidal particles.- a)Statement-2 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
- b)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1.
- c)Statement-2 is True, Statement-2 is False.
- d)Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement-1 : All colloidal dispersions give very low osmotic pressure and show very small freezing point depression or boiling pointelevation.
Statement-2 : Tydall effect is due to scattering of light from the surface of colloidal particles.
a)
Statement-2 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
b)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1.
c)
Statement-2 is True, Statement-2 is False.
d)
Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
The Tyndall effect is seen due to light scattering by particles in a colloid or particles in a fine suspension. So, solution particles show the Tyndall effect due to the scattering of light and scattering is directly proportional to the size of sol particles.
Also, colloidal particles have a high molar mass so, their mole fraction is very less causing low colligative properties and hence, all colloidal dispersion give very low osmotic pressure and show very small freezing point depression or boiling point elevation.
Also, colloidal particles have a high molar mass so, their mole fraction is very less causing low colligative properties and hence, all colloidal dispersion give very low osmotic pressure and show very small freezing point depression or boiling point elevation.
Which gas will be adsorbed on a solid to greater extent.- a)A gas having non polar molecule
- b)A gas having highest critical temperature (Tc)
- c)A gas having lowest critical temperature.
- d)A gas having highest critical pressure.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which gas will be adsorbed on a solid to greater extent.
a)
A gas having non polar molecule
b)
A gas having highest critical temperature (Tc)
c)
A gas having lowest critical temperature.
d)
A gas having highest critical pressure.
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
A gas with high critical temperature has high vander waal force due to which they are more easily liquefiable & hence more easily adsorb as adsorption decreases their energy
When do particles aggregate to form micelles?- a)below craft temperature
- b)below CMC
- c)low concentration
- d)high concentration and above craft temperature
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When do particles aggregate to form micelles?
a)
below craft temperature
b)
below CMC
c)
low concentration
d)
high concentration and above craft temperature
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option D.
In high concentration, particles aggregate to form micelles; it happens above Tk called kraft’s temperature and critical micelle concentration (CMC). If the concentration is low and it forms a true solution.
In high concentration, particles aggregate to form micelles; it happens above Tk called kraft’s temperature and critical micelle concentration (CMC). If the concentration is low and it forms a true solution.
100 mL of a colloidal solution is completely precipitated by addition of 5 mL of 1 M Nacl solution . Calculate the coagulation value of Nacl . - a)200
- b)100
- c)50
- d)25
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
100 mL of a colloidal solution is completely precipitated by addition of 5 mL of 1 M Nacl solution . Calculate the coagulation value of Nacl .
a)
200
b)
100
c)
50
d)
25
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Coagulation value is the millimoles of an electrolyte that must be added to 1 L of a colloidal solution for complete coagulation .Therefore , 5 mL of 1 M NaCl = 1/1000 X 5=0.005 OR 5 m moles .
100 mL of a colloidal solution require NaCl for complete coagulation = 50 m moles
Therefore , Coagulation value of NaCl = 50
The formation of micelles takes places above a particular temperature, called as:- a)CMC
- b)Kraft temperature
- c)Boiling point
- d)Specific temperature
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The formation of micelles takes places above a particular temperature, called as:
a)
CMC
b)
Kraft temperature
c)
Boiling point
d)
Specific temperature

|
Syed Hussain answered |
Above this concentration only the surfactants form micelles and micelle formation takes place. To reach this concentration, a temperature is required which is called Critical Micelle temperature or Kraft temperature
Fog is a colloidal system of- a)Gas in liquid
- b)Liquid in gas
- c)Gas in gas
- d)Gas in solid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Fog is a colloidal system of
a)
Gas in liquid
b)
Liquid in gas
c)
Gas in gas
d)
Gas in solid

|
Sankar Chakraborty answered |
The actual dispersed liquid is a colloid of which there are many examples. Any colloid consisting of a solid dispersed in a gas is called a smoke. A liquid dispersed in a gas is referred to as a fog. So it appears that fog is an example of a colloid of tiny particles of water vapor and air.
When a graph is plotted between log x/m and log p, it is straight line With an angle 45° and intercept 0.3010 on y-axis. If initial pressure is 0.3 atm, what will be the amount of gas adsorbed per gm of adsorbent : - a)0.4
- b)0.6
- c)0.8
- d)0.1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When a graph is plotted between log x/m and log p, it is straight line With an angle 45° and intercept 0.3010 on y-axis. If initial pressure is 0.3 atm, what will be the amount of gas adsorbed per gm of adsorbent :
a)
0.4
b)
0.6
c)
0.8
d)
0.1

|
Top Rankers answered |




Select correct statement (s) : - a)hydrophilic colloid is a colloid in which there is a strong attraction between the dispersed phase and water
- b)hydrophobic colloid is a colloid in which there is a lack of attraction between the dispersed phase and water
- c)hydrophobic soils are often formed when a solid crystallises rapidly from a chemical reaction or a supersaturated solution
- d)all of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select correct statement (s) :
a)
hydrophilic colloid is a colloid in which there is a strong attraction between the dispersed phase and water
b)
hydrophobic colloid is a colloid in which there is a lack of attraction between the dispersed phase and water
c)
hydrophobic soils are often formed when a solid crystallises rapidly from a chemical reaction or a supersaturated solution
d)
all of the above
|
|
Bad Star answered |
Hydrophilic colloids: These are water-loving colloids. The colloid particles are attracted to the water. They are also known as reversible sols. Examples include Agar, gelatin, pectin, etc
Hydrophobic colloids: These are the opposite in nature to hydrophilic colloids. The colloid particles are repelled by water. They are also called irreversible sols. Examples include Gold sols, clay particles, etc
therefore than can easily form supersaturated solution
Hydrophobic colloids: These are the opposite in nature to hydrophilic colloids. The colloid particles are repelled by water. They are also called irreversible sols. Examples include Gold sols, clay particles, etc
therefore than can easily form supersaturated solution
Statement-1 : The Brownian movement is due to the bombardment of collodial particles by the molecules of dispersion medium which are in the constant motion like molecules in a gas.Statement-2 :Brownian movement provides a visible proof of the random kinetic motion of molecules in a liquid. - a)Statement-2 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
- b)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1.
- c)Statement-2 is True, Statement-2 is False.
- d)Statement-2 is False, Statement-2 is True.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement-1 : The Brownian movement is due to the bombardment of collodial particles by the molecules of dispersion medium which are in the constant motion like molecules in a gas.
Statement-2 :Brownian movement provides a visible proof of the random kinetic motion of molecules in a liquid.
a)
Statement-2 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
b)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1.
c)
Statement-2 is True, Statement-2 is False.
d)
Statement-2 is False, Statement-2 is True.
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
The correct answer is option B
Reason for statement 1 will be the movement is due to the uneven bombardment of the colloidal particles in the dispersion medium.
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1.
Reason for statement 1 will be the movement is due to the uneven bombardment of the colloidal particles in the dispersion medium.
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1.
Smoke precipitator works on the principle of- a)Distribution law
- b)Neutralization of charge on colloids
- c)Le-Chaterliers principle
- d)Addition of electrolytes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Smoke precipitator works on the principle of
a)
Distribution law
b)
Neutralization of charge on colloids
c)
Le-Chaterliers principle
d)
Addition of electrolytes
|
|
Gowri Menon answered |
Neutralization of charge on colloid as per hardy shulze rule.
Colloidal solution are classified on the basis of- a)Molecules size
- b)Organic or inorganic
- c)Surface tension value
- d)PH value
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Colloidal solution are classified on the basis of
a)
Molecules size
b)
Organic or inorganic
c)
Surface tension value
d)
PH value
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Molecular size for colloidal range in 1nm–1000 nm.
Gold number of haemoglobin is 0.03. Hence, 100 mL of gold sol will require haemoglobin so that gold is not coagulated by 10 mL of 10% NaCl solution: - a)0.03 mg
- b)30 mg
- c)0.30 mg
- d)3 mg
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Gold number of haemoglobin is 0.03. Hence, 100 mL of gold sol will require haemoglobin so that gold is not coagulated by 10 mL of 10% NaCl solution:
a)
0.03 mg
b)
30 mg
c)
0.30 mg
d)
3 mg
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The correct answer is a.
Given : gold number =0.03
Given : gold number =0.03
Gold sol volume =100ml,
Let the amount of haemoglobin required be x mg
Since we all know that gold number is the amount in milligrams required to prevent the coagulation of 10 ml of gold sol by 1 ml of 10% NaCl.
x/100�10 = gold number
x/100�10=0.03
x=0.03 mg
Colloids can be purified by- a)Condensation
- b)Peptization
- c)Coagulation
- d)Dialysis
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Colloids can be purified by
a)
Condensation
b)
Peptization
c)
Coagulation
d)
Dialysis

|
Mumtaj Ali answered |
Colloids can be purified by 3 methods mainly-- dialysis, electrodialysis and ultrafiltration.
Given below are a few electrolytes, indicates which one among them will bring about the coagulation of a gold sol. quickest and in the least of concentration ?- a)NaCl
- b)MgSO4
- c)Al2(SO4)3
- d)K4[Fe(CN)6]
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Given below are a few electrolytes, indicates which one among them will bring about the coagulation of a gold sol. quickest and in the least of concentration ?
a)
NaCl
b)
MgSO4
c)
Al2(SO4)3
d)
K4[Fe(CN)6]

|
Juhi Deshpande answered |
As per Hardy shulze rule coagulation power a +ve charge which is maximum in Al3+.
At the critical micelle concentration (CMC) the surfacent molecules- a)Decompose
- b)Dissociate
- c)Associate
- d)Become completely soluble
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
At the critical micelle concentration (CMC) the surfacent molecules
a)
Decompose
b)
Dissociate
c)
Associate
d)
Become completely soluble
|
|
Lakshya Agnihotri answered |
There are many answers based upon different reasoning but if there would be a direct answer then it would have been like
AT CMC micelle formation takes place...
option a ,b ,d does not say about the formation of micelle but option c says associativity which means formation of micelle.... thus it can be your direct answer.
AT CMC micelle formation takes place...
option a ,b ,d does not say about the formation of micelle but option c says associativity which means formation of micelle.... thus it can be your direct answer.
The volume of gases NH3, CO2 and CH4 adsorbed by one gram of charcoal at 298 K are in- a)CH4 > CO2 > NH3
- b)NH3 > CH4 > CO2
- c)NH3 > CO2 > CH4
- d)CO2 > NH3 > CH4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The volume of gases NH3, CO2 and CH4 adsorbed by one gram of charcoal at 298 K are in
a)
CH4 > CO2 > NH3
b)
NH3 > CH4 > CO2
c)
NH3 > CO2 > CH4
d)
CO2 > NH3 > CH4
|
|
Navya Banerjee answered |
>b)CO2 >NH3
This is because the adsorption of gases on charcoal is dependent on the size and shape of the gas molecule, as well as the nature of the charcoal surface. In general, smaller molecules are more easily adsorbed than larger ones, and polar molecules are more easily adsorbed than nonpolar ones.
NH3 is a polar molecule, but it is larger than CO2 and CH4, so it is less easily adsorbed. CO2 is a small nonpolar molecule, so it is more easily adsorbed than NH3 but less easily adsorbed than CH4. CH4 is the smallest and most nonpolar of the three gases, so it is the most easily adsorbed.
Therefore, the correct order of gas adsorption is CH4 > CO2 > NH3.
This is because the adsorption of gases on charcoal is dependent on the size and shape of the gas molecule, as well as the nature of the charcoal surface. In general, smaller molecules are more easily adsorbed than larger ones, and polar molecules are more easily adsorbed than nonpolar ones.
NH3 is a polar molecule, but it is larger than CO2 and CH4, so it is less easily adsorbed. CO2 is a small nonpolar molecule, so it is more easily adsorbed than NH3 but less easily adsorbed than CH4. CH4 is the smallest and most nonpolar of the three gases, so it is the most easily adsorbed.
Therefore, the correct order of gas adsorption is CH4 > CO2 > NH3.
Finally divided catalyst has greater surface area and has greater catalytic activity then the compact solid. If a total surface area of 6291456 cm is required for adsorption of gaseous reaction in a catalysed reaction, then how many splits should be made of cube exactly 1 cm in length. - a)60
- b)80
- c)20
- d)22
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Finally divided catalyst has greater surface area and has greater catalytic activity then the compact solid. If a total surface area of 6291456 cm is required for adsorption of gaseous reaction in a catalysed reaction, then how many splits should be made of cube exactly 1 cm in length.
a)
60
b)
80
c)
20
d)
22
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
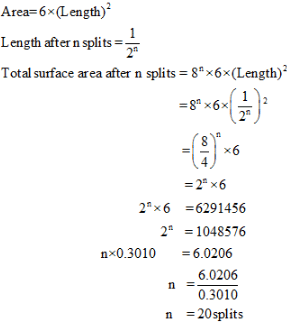
At CIVIC, the surfactant molecules : - a)Decomposes
- b)Become completely soluble
- c)Associate
- d)Dissociate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
At CIVIC, the surfactant molecules :
a)
Decomposes
b)
Become completely soluble
c)
Associate
d)
Dissociate
|
|
Diksha Vidyarthi answered |
I think it's a misprint.. it must be cmc-critical micelles concentration and at cmc molecules associate., formation of aggregates
Statement-1: In the coagulation of negatively charged arsenic sulphide soil, the coagulating power decreases in the order, Al3+ > Ba2+ > Na+. Statement-2 : Generally greater the valence of coagulating ion, the greater is its power of coagulation.- a)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
- b)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1.
- c)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is False.
- d)Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement-1: In the coagulation of negatively charged arsenic sulphide soil, the coagulating power decreases in the order, Al3+ > Ba2+ > Na+.
Statement-2 : Generally greater the valence of coagulating ion, the greater is its power of coagulation.
a)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
b)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1.
c)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is False.
d)
Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True

|
Thedot Starry answered |
Both the statements are correct. this is hardy schulze rule given in ncert chemistry surface chemistry
Which one of the following statements is correct: - a)Brownian movement is more pronounced for smaller particles than for bigger ones
- b)Sols of metal sulphides are lyophilic
- c)Schulze-Hardy law states, the bigger the size of the ion, the greater is its coagulating power
- d)Onewould expect charcoal to adsorb chlorine more strongly than hydrogen sulphide
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is correct:
a)
Brownian movement is more pronounced for smaller particles than for bigger ones
b)
Sols of metal sulphides are lyophilic
c)
Schulze-Hardy law states, the bigger the size of the ion, the greater is its coagulating power
d)
Onewould expect charcoal to adsorb chlorine more strongly than hydrogen sulphide
|
|
Nisha Kulkarni answered |
Brownian Movement:
• Brownian movement is the random movement of particles suspended in a fluid due to collisions with molecules of the surrounding medium.
• The magnitude of Brownian movement is directly proportional to the size of the particle.
• Hence, the smaller the particle, the more pronounced is the Brownian movement.
Sols of Metal Sulphides:
• A sol is a colloidal solution in which the dispersed phase is a solid and the dispersion medium is a liquid.
• Lyophilic sols are those in which the dispersed phase has a strong affinity for the dispersion medium.
• Metal sulphides are usually lyophobic, i.e., they have a weak affinity for the dispersion medium.
• Hence, option 'B' is incorrect.
Schulze-Hardy Law:
• Schulze-Hardy law states that the greater the size of the ion, the greater is its coagulating power.
• Coagulation is the process of settling down of colloidal particles under the influence of some external agency.
• The law holds good for ions of the same charge and for the same concentration of the electrolyte.
• Hence, option 'C' is incorrect.
Adsorption:
• Adsorption is the process of accumulation of a substance at the surface of a solid or a liquid.
• The strength of adsorption depends on the nature of the adsorbent and the adsorbate.
• Charcoal is a good adsorbent for many substances, including chlorine and hydrogen sulphide.
• However, the strength of adsorption depends on the nature of the adsorbate.
• Hence, option 'D' is incorrect.
Conclusion:
• Option 'A' is correct as the Brownian movement is more pronounced for smaller particles than for bigger ones.
• Brownian movement is the random movement of particles suspended in a fluid due to collisions with molecules of the surrounding medium.
• The magnitude of Brownian movement is directly proportional to the size of the particle.
• Hence, the smaller the particle, the more pronounced is the Brownian movement.
Sols of Metal Sulphides:
• A sol is a colloidal solution in which the dispersed phase is a solid and the dispersion medium is a liquid.
• Lyophilic sols are those in which the dispersed phase has a strong affinity for the dispersion medium.
• Metal sulphides are usually lyophobic, i.e., they have a weak affinity for the dispersion medium.
• Hence, option 'B' is incorrect.
Schulze-Hardy Law:
• Schulze-Hardy law states that the greater the size of the ion, the greater is its coagulating power.
• Coagulation is the process of settling down of colloidal particles under the influence of some external agency.
• The law holds good for ions of the same charge and for the same concentration of the electrolyte.
• Hence, option 'C' is incorrect.
Adsorption:
• Adsorption is the process of accumulation of a substance at the surface of a solid or a liquid.
• The strength of adsorption depends on the nature of the adsorbent and the adsorbate.
• Charcoal is a good adsorbent for many substances, including chlorine and hydrogen sulphide.
• However, the strength of adsorption depends on the nature of the adsorbate.
• Hence, option 'D' is incorrect.
Conclusion:
• Option 'A' is correct as the Brownian movement is more pronounced for smaller particles than for bigger ones.
Colloidal particles in a sol. can be coagulated by- a)Heating
- b)Adding an electrolyte
- c)Adding oppositely charged sol
- d)Any of the above methods
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Colloidal particles in a sol. can be coagulated by
a)
Heating
b)
Adding an electrolyte
c)
Adding oppositely charged sol
d)
Any of the above methods
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
The correct answer is option D
Stability of the lyophobic sols is due to presence of charge on colloidal particles. If charge is removed, particles come together and settle down. Spontaneous destabilization of solution is ageing and destabilization of solution by artificial means is called coagulation.
Methods of coagulation are as follows:
1. Boiling
2. Dialysis
3. Addition of electrolytes
4. Mixing two oppositely charged sols
5. Electrophoresis
Methods of coagulation are as follows:
1. Boiling
2. Dialysis
3. Addition of electrolytes
4. Mixing two oppositely charged sols
5. Electrophoresis
As2S3 sol is- a)Positive colloid
- b)Negative colloid
- c)Neutral colloid
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
As2S3 sol is
a)
Positive colloid
b)
Negative colloid
c)
Neutral colloid
d)
None of the above
|
|
Aarav Sharma answered |
As we know As₂S₃ is a negatively charged solution .
In this solution the negative charge is due to adsorption of S�⁻ ion .
For Example-
For the coagulation of the As₂S₃(Which is negatively charged solution) , We need positively charged solution ,So the most flocculating solution will be AlCl₃ because Al has 3⁺ charge on it.
The nature of bonding forces in adsorptiona)Purely... more physical such as Van Der Waal's forcesb)Purely chemicalc)Both chemical and physical alwaysd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Gopal Sengupta answered |
Vander waal force is responsible for adsorption.
Which one of following statement is not correct in respect of lyophilic sols ?- a)There is a considerable interaction between the dispersed phase and dispersion medium
- b)These are quite stable and are not easily coagulated
- c)They carry charge
- d)The particle are hydrated
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of following statement is not correct in respect of lyophilic sols ?
a)
There is a considerable interaction between the dispersed phase and dispersion medium
b)
These are quite stable and are not easily coagulated
c)
They carry charge
d)
The particle are hydrated
|
|
Navya Banerjee answered |
Lyophilic sols are also known as reversible sols because they can be prepared by simply mixing the dispersed phase with the dispersion medium without any chemical reaction. Here, we will discuss the given statement and why option 'C' is not correct.
Statement Analysis:
a) There is a considerable interaction between the dispersed phase and dispersion medium:
- Lyophilic sols have a strong interaction between the dispersed phase and dispersion medium due to the formation of a solvation layer around each particle.
- The solvation layer is formed due to the adsorption of the solvent molecules on the surface of the dispersed phase.
b) These are quite stable and are not easily coagulated:
- Lyophilic sols are quite stable and can be stored for a longer period of time without any coagulation.
- This stability is due to the strong interaction between the dispersed phase and dispersion medium.
c) They carry charge:
- This statement is not correct as lyophilic sols do not carry any charge on their particles.
- They are different from lyophobic sols, which carry a charge due to the adsorption of ions on the surface of the particles.
d) The particles are hydrated:
- Lyophilic sols have a high degree of solvation due to the formation of a solvation layer around each particle.
- This solvation layer contains the solvent molecules that are adsorbed on the surface of the particle.
Conclusion:
- Option 'C' is not correct as lyophilic sols do not carry any charge on their particles.
- Lyophilic sols have a strong interaction between the dispersed phase and dispersion medium, which makes them stable and not easily coagulated.
- The particles in lyophilic sols are hydrated due to the formation of a solvation layer around each particle.
Statement Analysis:
a) There is a considerable interaction between the dispersed phase and dispersion medium:
- Lyophilic sols have a strong interaction between the dispersed phase and dispersion medium due to the formation of a solvation layer around each particle.
- The solvation layer is formed due to the adsorption of the solvent molecules on the surface of the dispersed phase.
b) These are quite stable and are not easily coagulated:
- Lyophilic sols are quite stable and can be stored for a longer period of time without any coagulation.
- This stability is due to the strong interaction between the dispersed phase and dispersion medium.
c) They carry charge:
- This statement is not correct as lyophilic sols do not carry any charge on their particles.
- They are different from lyophobic sols, which carry a charge due to the adsorption of ions on the surface of the particles.
d) The particles are hydrated:
- Lyophilic sols have a high degree of solvation due to the formation of a solvation layer around each particle.
- This solvation layer contains the solvent molecules that are adsorbed on the surface of the particle.
Conclusion:
- Option 'C' is not correct as lyophilic sols do not carry any charge on their particles.
- Lyophilic sols have a strong interaction between the dispersed phase and dispersion medium, which makes them stable and not easily coagulated.
- The particles in lyophilic sols are hydrated due to the formation of a solvation layer around each particle.
Milk is an example of- a)Emulsion
- b)Suspension
- c)Foam
- d)Sol.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Milk is an example of
a)
Emulsion
b)
Suspension
c)
Foam
d)
Sol.
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Milk is emulsion (butter fat dispersed in water).
Foam rubber is an example of which type of colloid?
- a)solid sol
- b)foam
- c)solid foam
- d)sol
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Foam rubber is an example of which type of colloid?
a)
solid sol
b)
foam
c)
solid foam
d)
sol
|
|
Shraddha Choudhury answered |
Foam is a dispersion of a gas in a liquid (liquid foams) or in a solid (solid foams). Foam rubber is gas dispersed in rubber.
Gold number of a lyophilic sol is such property that: - a)the larger its value, the greater is the peptising power
- b)the lower its value, the greater is the peptising power
- c)the lower its value, the greater is the protecting power
- d)the larger its value, the greater is the protecting power
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Gold number of a lyophilic sol is such property that:
a)
the larger its value, the greater is the peptising power
b)
the lower its value, the greater is the peptising power
c)
the lower its value, the greater is the protecting power
d)
the larger its value, the greater is the protecting power
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
Gold numbers are defined as the minimum amount of protective colloid in milligrams which prevents a colour change from red to violet of 10 ml gold sol by the addition of 1 ml of 10% NaCl solution. More is the gold number, less is the protective power of lyophilic colloid since it means that amount required is more.
Which of the following is a lyophobic colloid ?- a)Gelatin
- b)Sulphur
- c)Starch
- d)Gum arabic
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a lyophobic colloid ?
a)
Gelatin
b)
Sulphur
c)
Starch
d)
Gum arabic
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Gelation, starch & gum are organic in nature & hence lyophilic in nature but S8 is inorganic in nature & hence lyophobic in nature
All colloids- a)Are suspensions of one phase in another
- b)Are two-phase systems
- c)Contain only water soluble particles
- d)Are true solutions
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
All colloids
a)
Are suspensions of one phase in another
b)
Are two-phase systems
c)
Contain only water soluble particles
d)
Are true solutions

|
Nidhi Nambiar answered |
Introduction:
Colloids are a type of mixture that consist of two phases: a dispersed phase and a continuous phase. The dispersed phase consists of small particles or droplets that are dispersed throughout the continuous phase. Colloids are different from solutions because the particles in colloids are larger and do not dissolve completely in the continuous phase.
Explanation:
b) Are two-phase systems:
Colloids are two-phase systems because they consist of two distinct phases - the dispersed phase and the continuous phase. The dispersed phase contains the particles or droplets that are dispersed throughout the continuous phase. The continuous phase is the medium in which the dispersed phase is dispersed. Examples of colloids include milk, mayonnaise, and fog. In milk, for example, fat globules are dispersed throughout the water-based continuous phase.
a) Are suspensions of one phase in another:
This statement is incorrect. Colloids are not suspensions of one phase in another. Suspensions are heterogeneous mixtures in which solid particles are dispersed in a liquid or gas. In suspensions, the particles are larger and can settle over time. In colloids, the particles are smaller and remain dispersed throughout the continuous phase due to the repulsive forces between them.
c) Contain only water-soluble particles:
This statement is incorrect. Colloids can contain particles that are soluble or insoluble in the continuous phase. For example, in an oil-in-water emulsion, the oil droplets are insoluble in water but are dispersed throughout it. Similarly, in a gelatin colloid, the gelatin particles are soluble in water but form a gel-like structure.
d) Are true solutions:
This statement is incorrect. Colloids are not true solutions. True solutions are homogeneous mixtures in which the solute particles are completely dissolved in the solvent. In colloids, the dispersed phase consists of particles that are larger and do not dissolve completely in the continuous phase. The particles in colloids can be seen under a microscope and can scatter light, giving colloids their characteristic opaqueness or translucence.
Conclusion:
In summary, colloids are two-phase systems consisting of a dispersed phase and a continuous phase. They are not suspensions of one phase in another, do not necessarily contain only water-soluble particles, and are not true solutions. Colloids have unique properties and can be found in various everyday substances.
Colloids are a type of mixture that consist of two phases: a dispersed phase and a continuous phase. The dispersed phase consists of small particles or droplets that are dispersed throughout the continuous phase. Colloids are different from solutions because the particles in colloids are larger and do not dissolve completely in the continuous phase.
Explanation:
b) Are two-phase systems:
Colloids are two-phase systems because they consist of two distinct phases - the dispersed phase and the continuous phase. The dispersed phase contains the particles or droplets that are dispersed throughout the continuous phase. The continuous phase is the medium in which the dispersed phase is dispersed. Examples of colloids include milk, mayonnaise, and fog. In milk, for example, fat globules are dispersed throughout the water-based continuous phase.
a) Are suspensions of one phase in another:
This statement is incorrect. Colloids are not suspensions of one phase in another. Suspensions are heterogeneous mixtures in which solid particles are dispersed in a liquid or gas. In suspensions, the particles are larger and can settle over time. In colloids, the particles are smaller and remain dispersed throughout the continuous phase due to the repulsive forces between them.
c) Contain only water-soluble particles:
This statement is incorrect. Colloids can contain particles that are soluble or insoluble in the continuous phase. For example, in an oil-in-water emulsion, the oil droplets are insoluble in water but are dispersed throughout it. Similarly, in a gelatin colloid, the gelatin particles are soluble in water but form a gel-like structure.
d) Are true solutions:
This statement is incorrect. Colloids are not true solutions. True solutions are homogeneous mixtures in which the solute particles are completely dissolved in the solvent. In colloids, the dispersed phase consists of particles that are larger and do not dissolve completely in the continuous phase. The particles in colloids can be seen under a microscope and can scatter light, giving colloids their characteristic opaqueness or translucence.
Conclusion:
In summary, colloids are two-phase systems consisting of a dispersed phase and a continuous phase. They are not suspensions of one phase in another, do not necessarily contain only water-soluble particles, and are not true solutions. Colloids have unique properties and can be found in various everyday substances.
Assertion: Isoelectric point is pHpH at which colloidal can move towards either of electrode.
Reason: At isoelectric point coolidal particles becomes electrically netural .- a)If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
- b)If assertion is false but reason is true.
- c)If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
- d)If assertion is true but reason is false.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion: Isoelectric point is pHpH at which colloidal can move towards either of electrode.
Reason: At isoelectric point coolidal particles becomes electrically netural .
Reason: At isoelectric point coolidal particles becomes electrically netural .
a)
If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
b)
If assertion is false but reason is true.
c)
If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
d)
If assertion is true but reason is false.
|
|
Sreemoyee Choudhury answered |
At isoelectric point, colloid particles will not move towards either of electrodse because they will come chargeless .
When a colloidal solution is observed under ultramicroscope, we can see- a)Light scattered by colloidal particle
- b)Size of the colloidal particle
- c)Shape of the colloidal particle
- d)Relative size of the colloidal particle
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When a colloidal solution is observed under ultramicroscope, we can see
a)
Light scattered by colloidal particle
b)
Size of the colloidal particle
c)
Shape of the colloidal particle
d)
Relative size of the colloidal particle
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Ultra–microscope is based on tyndall effect which is based on scattering of light.
Which method is used for preparation of metal sols?- a)Electrical disintegration
- b)Ultra centrifugation
- c)Dialysis
- d)Ultrafiltration
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which method is used for preparation of metal sols?
a)
Electrical disintegration
b)
Ultra centrifugation
c)
Dialysis
d)
Ultrafiltration
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
Metal sols are prepared by making electrode of the metals and immersed in dispersion medium and electric arc is struck. This process involves dispersion and condensation.
Alums purify muddy water by- a)Dialysis
- b)Absorption
- c)Coagulation
- d)Forming true solution
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Alums purify muddy water by
a)
Dialysis
b)
Absorption
c)
Coagulation
d)
Forming true solution
|
|
Ayush Kumar Jha answered |
Mud water contains charged colloidal particles which is neutralized by adding alum
The minimum concentration of an electrolyte required to cause coagulation of a sol. is called- a)Flocculation value
- b)Gold number
- c)Protective value
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The minimum concentration of an electrolyte required to cause coagulation of a sol. is called
a)
Flocculation value
b)
Gold number
c)
Protective value
d)
None of these

|
Ansari Adnan answered |
“The minimum concentration of an electrolyte which is required to cause the coagulation or flocculation of a sol is known as flocculation value.” “The number of millimoles of an electrolyte required to bring about the coagulation of one litre of a colloidal solution is called its flocculation value.”
Size of colloidal particles may range from - a)1 to 1000 nm
- b)10 to 100 pm
- c)1 to 1001.1M
- d)1 to 10 mm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Size of colloidal particles may range from
a)
1 to 1000 nm
b)
10 to 100 pm
c)
1 to 1001.1M
d)
1 to 10 mm
|
|
Preethi Kulkarni answered |
Size of colloidal particles may range from 1 to 1000 nm.
Colloidal particles are particles that are intermediate in size between true solutions and suspensions. They are larger than individual molecules but smaller than visible particles. The size of colloidal particles plays a crucial role in determining their properties and behavior. Let's explore why the correct answer is option 'A' and understand the range of colloidal particle sizes.
Definition of Colloidal Particles:
Colloidal particles are defined as particles that range in size from 1 to 1000 nanometers (nm). These particles are typically composed of clusters of atoms or molecules and are dispersed in a continuous medium, such as a liquid or gas. The size range of colloidal particles is important because it allows them to exhibit unique properties and behavior due to their large surface area-to-volume ratio.
Key Points:
- Colloidal particles range in size from 1 to 1000 nm.
- They are larger than individual molecules but smaller than visible particles.
- Colloidal particles are composed of clusters of atoms or molecules.
- They are dispersed in a continuous medium, such as a liquid or gas.
- The size range of colloidal particles allows them to exhibit unique properties.
Importance of Colloidal Particle Size:
The size of colloidal particles is crucial as it directly impacts their stability, optical properties, and reactivity. The small size of colloidal particles gives them a large surface area, which leads to increased interactions with their surrounding medium and enhanced reactivity. Additionally, the size of colloidal particles affects their ability to scatter light, making them useful in various applications such as inks, paints, and pharmaceutical formulations.
Applications of Colloidal Particles:
Colloidal particles find applications in various fields due to their unique properties. Some common applications include:
1. Medicine and Healthcare: Colloidal particles are used in drug delivery systems, where the small size allows for easy absorption and targeted delivery of medications.
2. Food Industry: Colloidal particles are used as stabilizers, emulsifiers, and thickeners in food products to improve texture and stability.
3. Environmental Remediation: Colloidal particles can be used to remove pollutants from water and soil through processes such as adsorption and coagulation.
4. Nanotechnology: Colloidal particles are used as building blocks for the fabrication of nanomaterials with tailored properties.
In conclusion, the correct answer to the question is option 'A' as the size of colloidal particles typically ranges from 1 to 1000 nm. The size range is significant in determining the unique properties and applications of colloidal particles in various fields.
Colloidal particles are particles that are intermediate in size between true solutions and suspensions. They are larger than individual molecules but smaller than visible particles. The size of colloidal particles plays a crucial role in determining their properties and behavior. Let's explore why the correct answer is option 'A' and understand the range of colloidal particle sizes.
Definition of Colloidal Particles:
Colloidal particles are defined as particles that range in size from 1 to 1000 nanometers (nm). These particles are typically composed of clusters of atoms or molecules and are dispersed in a continuous medium, such as a liquid or gas. The size range of colloidal particles is important because it allows them to exhibit unique properties and behavior due to their large surface area-to-volume ratio.
Key Points:
- Colloidal particles range in size from 1 to 1000 nm.
- They are larger than individual molecules but smaller than visible particles.
- Colloidal particles are composed of clusters of atoms or molecules.
- They are dispersed in a continuous medium, such as a liquid or gas.
- The size range of colloidal particles allows them to exhibit unique properties.
Importance of Colloidal Particle Size:
The size of colloidal particles is crucial as it directly impacts their stability, optical properties, and reactivity. The small size of colloidal particles gives them a large surface area, which leads to increased interactions with their surrounding medium and enhanced reactivity. Additionally, the size of colloidal particles affects their ability to scatter light, making them useful in various applications such as inks, paints, and pharmaceutical formulations.
Applications of Colloidal Particles:
Colloidal particles find applications in various fields due to their unique properties. Some common applications include:
1. Medicine and Healthcare: Colloidal particles are used in drug delivery systems, where the small size allows for easy absorption and targeted delivery of medications.
2. Food Industry: Colloidal particles are used as stabilizers, emulsifiers, and thickeners in food products to improve texture and stability.
3. Environmental Remediation: Colloidal particles can be used to remove pollutants from water and soil through processes such as adsorption and coagulation.
4. Nanotechnology: Colloidal particles are used as building blocks for the fabrication of nanomaterials with tailored properties.
In conclusion, the correct answer to the question is option 'A' as the size of colloidal particles typically ranges from 1 to 1000 nm. The size range is significant in determining the unique properties and applications of colloidal particles in various fields.
Which of the following factors affects the adsorption of a gas on solid ?- a)Tc(cirtical temp.)
- b)Temperature of gas
- c)Pressure of gas
- d)All of them
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following factors affects the adsorption of a gas on solid ?
a)
Tc(cirtical temp.)
b)
Temperature of gas
c)
Pressure of gas
d)
All of them
|
|
Arka Das answered |
Extent of adsorption increase with increase in critical temperature
Chapter doubts & questions for Surface Chemistry - 6 Months Preparation for JEE 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Surface Chemistry - 6 Months Preparation for JEE in English & Hindi are available as part of JEE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily