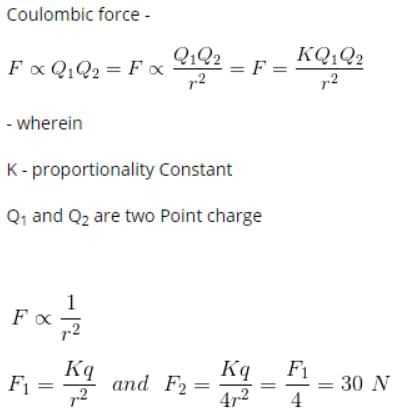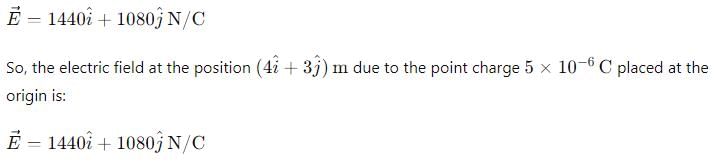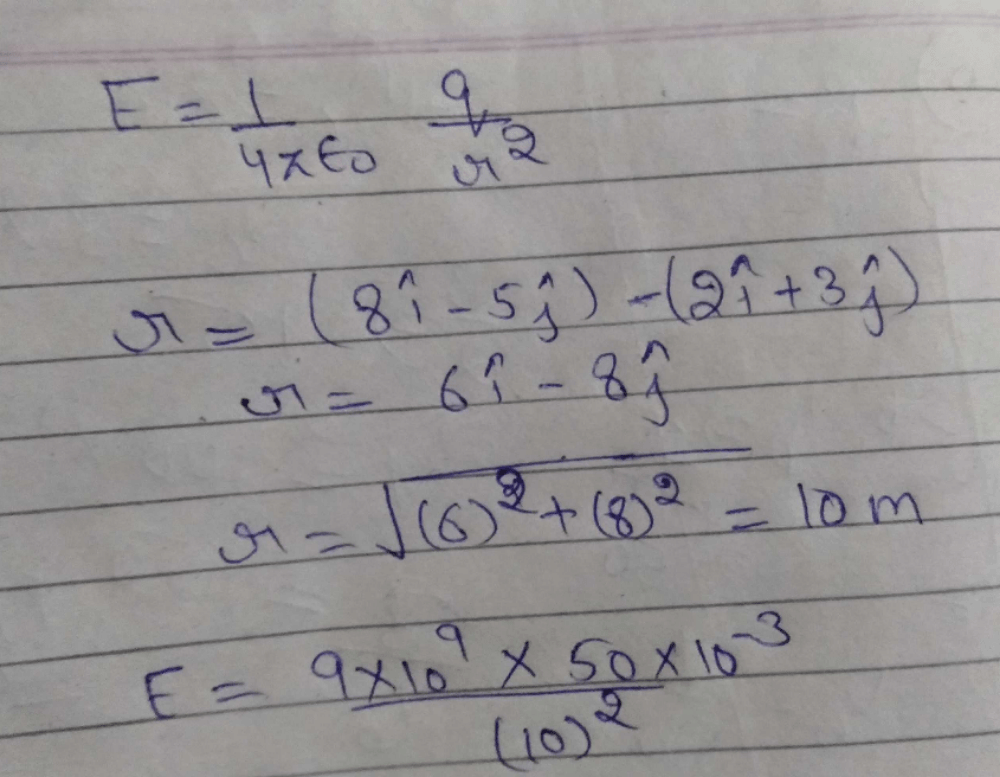All questions of Electrostatic Force for Grade 9 Exam
Six charges are placed at the corner of a regular hexagon as shown. If an electron is placed at its centre O, force on it will be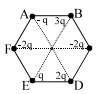
- a)Zero
- b)Along OF
- c)Along OC
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Six charges are placed at the corner of a regular hexagon as shown. If an electron is placed at its centre O, force on it will be
a)
Zero
b)
Along OF
c)
Along OC
d)
None of these

|
Dr Manju Sen answered |
The charges will be balanced by their counterparts on the opposite side. So, eventually the charges remaining will be 2q and b and 3q on D.
Since the charge distribution is asymmetrical, the net force on charge would be skewed towards D.
Since the charge distribution is asymmetrical, the net force on charge would be skewed towards D.
The electric field inside a dielectric decreases, when it is placed in an external electric field. This happens due to- a)Electrostatic shielding
- b)Polarization
- c)Electrostatic repulsion between atoms
- d)Electrostatic attraction between atoms
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The electric field inside a dielectric decreases, when it is placed in an external electric field. This happens due to
a)
Electrostatic shielding
b)
Polarization
c)
Electrostatic repulsion between atoms
d)
Electrostatic attraction between atoms

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The external electric field polarizes the dielectric and an electric field is produced.
The net electric field inside the dielectric decreases due to polarization.
The net electric field inside the dielectric decreases due to polarization.
The amount of work done in moving a charge from one point to another along an equipotential line or surface charge is- a)Zero
- b)Infinity
- c)One
- d)Two
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The amount of work done in moving a charge from one point to another along an equipotential line or surface charge is
a)
Zero
b)
Infinity
c)
One
d)
Two
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Since Potential difference between two points in equipotential surfaces is zero, the work done between two points in equipotential surface is also zero.
1 microfarad is equal to- a)10-6F
- b)10-12F
- c)10-15F
- d)10-9F
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
1 microfarad is equal to
a)
10-6F
b)
10-12F
c)
10-15F
d)
10-9F
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The microfarad (symbolized µF) is a unit of capacitance, equivalent to 0.000001 (10 to the -6th power) farad.
A particle of mass m and charge Q is placed in an electric field E which varies with time t ass E = E0 sinwt. It will undergo simple harmonic motion of amplitude- a)
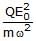
- b)
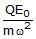
- c)
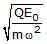
- d)
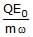
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle of mass m and charge Q is placed in an electric field E which varies with time t ass E = E0 sinwt. It will undergo simple harmonic motion of amplitude
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Due to verifying electric field, it experiences an verifying force :-
F=QE=QE0sinωt
at maximum amplitude A, it experience a maximum force of:-
Fmax=QE0
also, Restoring force in SHM is given by: - F=mω2x
for amplitude, x=A OR,
mω2A=QE0
⇒A= QE0/mω2
F=QE=QE0sinωt
at maximum amplitude A, it experience a maximum force of:-
Fmax=QE0
also, Restoring force in SHM is given by: - F=mω2x
for amplitude, x=A OR,
mω2A=QE0
⇒A= QE0/mω2
The polarized dielectric is equivalent to- a)non-zero volume charge density
- b)one charged surface with induced surface charge density
- c)two charged surfaces with induced surface charge densities
- d)zero surface charge density
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The polarized dielectric is equivalent to
a)
non-zero volume charge density
b)
one charged surface with induced surface charge density
c)
two charged surfaces with induced surface charge densities
d)
zero surface charge density

|
Learners Habitat answered |
A polarized dielectric is equivalent to two charged surfaces with induced charges (polarization charges).
The electrostatic potential energy between two charges q1 and q2 separated by a distance by r is given by- a)
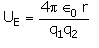
- b)
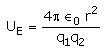
- c)
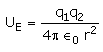
- d)
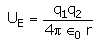
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The electrostatic potential energy between two charges q1 and q2 separated by a distance by r is given by
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Khushi Mittal answered |
Energy = force × distance U=Kq1q2/r^2 × r U=Kq1q2/r
Two charges 4q and q are placed 30 cm. apart. At what point the value of electric field will be zero- a)10 cm. away from q and between the charge
- b)10 cm. away from 4q and out side the line joining them.
- c)20 cm. away from 4q and between the charge
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Two charges 4q and q are placed 30 cm. apart. At what point the value of electric field will be zero
a)
10 cm. away from q and between the charge
b)
10 cm. away from 4q and out side the line joining them.
c)
20 cm. away from 4q and between the charge
d)
none
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Where E=0 this point is called neutral point.
it is the point where electric field of both charge is same
we know tha t E=kQ/r^2
here k=1/4pi€
for 4q charge
let at ''a'' distance we get E=0 which is from q charge
so distance from 4q of 'a' point is 30-a
electric field by 4q charge on a is
E=k4q/(30-a)^2
electric field by q charge on a point
E=kq/a^2
both electric field are equal so put them equal
k4q/(30-a)^2=kq/a^2
solve this we get
4a^2=(30-a)^2
2a=30-a
3a=30
a=10
so at a distance 10cm from charge q we get E=0
distance from 4q charge 30-10=20cm.
it is the point where electric field of both charge is same
we know tha t E=kQ/r^2
here k=1/4pi€
for 4q charge
let at ''a'' distance we get E=0 which is from q charge
so distance from 4q of 'a' point is 30-a
electric field by 4q charge on a is
E=k4q/(30-a)^2
electric field by q charge on a point
E=kq/a^2
both electric field are equal so put them equal
k4q/(30-a)^2=kq/a^2
solve this we get
4a^2=(30-a)^2
2a=30-a
3a=30
a=10
so at a distance 10cm from charge q we get E=0
distance from 4q charge 30-10=20cm.
A certain charge Q is divided at first into two parts, (q) and (Q-q). Later on the charges are placed at a certain distance. If the force of interaction between the two charges is maximum then- a)(Q/q) = (4/1)
- b)(Q/q) = (2/1)
- c)(Q/q) = (3/1)
- d)(Q/q) = (5/1)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A certain charge Q is divided at first into two parts, (q) and (Q-q). Later on the charges are placed at a certain distance. If the force of interaction between the two charges is maximum then
a)
(Q/q) = (4/1)
b)
(Q/q) = (2/1)
c)
(Q/q) = (3/1)
d)
(Q/q) = (5/1)
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The force between q & Q-q is given by :-
F = kq(Q-q)/r²
As it is given that force between these two is Maximum....so it will be max. when dF/dq is zero
i.e, dF/dq = {k(Q-2q)}/r² = 0
so, Q = 2q
Q/q = 2/1
F = kq(Q-q)/r²
As it is given that force between these two is Maximum....so it will be max. when dF/dq is zero
i.e, dF/dq = {k(Q-2q)}/r² = 0
so, Q = 2q
Q/q = 2/1
Which one of the following statement regarding electrostatics is wrong ?- a)Charge is quantized
- b)Charge is conserved
- c)There is an electric field near an isolated charge at rest
- d)A stationary charge produces both electric and magnetic fields
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statement regarding electrostatics is wrong ?
a)
Charge is quantized
b)
Charge is conserved
c)
There is an electric field near an isolated charge at rest
d)
A stationary charge produces both electric and magnetic fields
|
|
Nandita Ahuja answered |
Explanation:
Electrostatics is the study of electric charges at rest. It deals with the electric forces between charges, the electric field and potential, and the distribution of charges on conductors.
a) Charge is quantized:
The charge on a body or a particle is always a multiple of the elementary charge (1.6 × 10^-19 C). This means that charge is quantized, and we cannot have a fraction of an elementary charge. This is known as the law of conservation of charge.
b) Charge is conserved:
The total charge in a closed system is always conserved. This means that the net charge of a system cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be transferred from one object to another.
c) There is an electric field near an isolated charge at rest:
An isolated charged object creates an electric field around it. This electric field is a vector field that exerts a force on other charged objects in the vicinity of the charged object. The electric field is proportional to the charge and inversely proportional to the distance from the charged object.
d) A stationary charge produces both electric and magnetic fields:
This statement is incorrect. A stationary charge produces only an electric field, not a magnetic field. However, a moving charge produces both electric and magnetic fields.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct option is (d), which is wrong.
Electrostatics is the study of electric charges at rest. It deals with the electric forces between charges, the electric field and potential, and the distribution of charges on conductors.
a) Charge is quantized:
The charge on a body or a particle is always a multiple of the elementary charge (1.6 × 10^-19 C). This means that charge is quantized, and we cannot have a fraction of an elementary charge. This is known as the law of conservation of charge.
b) Charge is conserved:
The total charge in a closed system is always conserved. This means that the net charge of a system cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be transferred from one object to another.
c) There is an electric field near an isolated charge at rest:
An isolated charged object creates an electric field around it. This electric field is a vector field that exerts a force on other charged objects in the vicinity of the charged object. The electric field is proportional to the charge and inversely proportional to the distance from the charged object.
d) A stationary charge produces both electric and magnetic fields:
This statement is incorrect. A stationary charge produces only an electric field, not a magnetic field. However, a moving charge produces both electric and magnetic fields.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct option is (d), which is wrong.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A small circular ring has a uniform charge distribution. On a far-off axial point distance x from the centre of the ring, the electric field is proportional to
- A:
x-1
- B:
x-3/2
- C:
x-2
- D:
x5/4
The answer is C.
A small circular ring has a uniform charge distribution. On a far-off axial point distance x from the centre of the ring, the electric field is proportional to
x-1
x-3/2
x-2
x5/4
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Electric field due to a charged ring in given by: -
at point p
∣E∣= KQx /(R2+x2)3/2 Q =λ(2πr)
at a large distance, x≫R, so :- R2+x2≃x2
⇒∣E∣= K&x/(x2)3/2=KQ/x2=Eαx−2
so at a large distance, the ring behaves as a point particle.
at point p
∣E∣= KQx /(R2+x2)3/2 Q =λ(2πr)
at a large distance, x≫R, so :- R2+x2≃x2
⇒∣E∣= K&x/(x2)3/2=KQ/x2=Eαx−2
so at a large distance, the ring behaves as a point particle.
A charged particle of charge q and mass m is released from rest in an uniform electric field E. Neglecting the effect of gravity, the kinetic energy of the charged particle after time 't' seconds is- a)
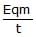
- b)
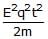
- c)
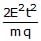
- d)
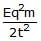
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A charged particle of charge q and mass m is released from rest in an uniform electric field E. Neglecting the effect of gravity, the kinetic energy of the charged particle after time 't' seconds is
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
Force on particle=F=qE
Hence, acceleration of particle=a=F/m=qE/m
Initial speed=u=0
Hence, final velocity=v=u+at=qEt/m
Kinetic energy=K=(1/2)mv2=(1/2)m(qEt/m)2
⟹K=E2q2t2/2m
Hence, acceleration of particle=a=F/m=qE/m
Initial speed=u=0
Hence, final velocity=v=u+at=qEt/m
Kinetic energy=K=(1/2)mv2=(1/2)m(qEt/m)2
⟹K=E2q2t2/2m
The dipole moment per unit volume is called- a)Polarization
- b)Surface charge density
- c)Linear charge density
- d)Volume charge density
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The dipole moment per unit volume is called
a)
Polarization
b)
Surface charge density
c)
Linear charge density
d)
Volume charge density
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The electric dipole moment per unit volume is called polarization or polarization density (vector p).
It is always directed from negative charge to positive charge.
If there are N atoms per unit volume than
vector p = N (vector p)
where p is the electric dipole moment of individual atom.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is
- A:
Zero
- B:
Infinity
- C:
Nonzero finite
- D:
None of the above
The answer is a.
The potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is
Zero
Infinity
Nonzero finite
None of the above

|
.mie. answered |
Answer is 0 as there are no other sources of electrostatic potential .... against which an external agent must do work.... in moving the point charge.... from infinity to its final location.... therefore correct opt is A
In bringing an electron towards another electron, the electrostatic potential energy of the system- a)becomes zero
- b)decreases
- c)remains same
- d)increases
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In bringing an electron towards another electron, the electrostatic potential energy of the system
a)
becomes zero
b)
decreases
c)
remains same
d)
increases
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The electron has negative charge. When an electron is bringing towards another electron, then due to same negative charge repulsive force is produced between them. So, to bring them closer a work is done against this repulsive force. This work is stored in the form of electrostatic potential energy. Thus, electrostatic potential energy of system increases.
Alternative: Electrostatic potential energy of system of two electrons
U=[1/4πε0][(−e)(−e)/r] = [1/4πε0](e^2/r)
Thus, as r decreases, potential energy U increases.
If a unit charge is taken from one part to another part over an equipotential surface, then what is the change in electrostatic potential energy of the charge?- a)10 J
- b)100 J
- c)1 J
- d)0 J
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If a unit charge is taken from one part to another part over an equipotential surface, then what is the change in electrostatic potential energy of the charge?
a)
10 J
b)
100 J
c)
1 J
d)
0 J

|
Utsav Srivastava answered |
Equipotential surface means the potential on every. point on that surface is constant. it means the change in potential on equipotential surface is zero we know that... ( electrostatic potential energy = change in potential × charge.)... ... according to this electrostatic potential energy is zero
Two identical positive charges are fixed on the y-axis, at equal distances from the origin O. A particle with a negative charge starts on the x-axis at a large distance from O, moves along the +x-axis, passes through O and moves far away from O. Its acceleration a is taken as positive along its direction of motion. The particle's acceleration a is plotted against its x-coordinate. Which of the following best represents the plot ?- a)
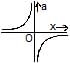
- b)
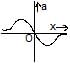
- c)
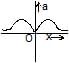
- d)
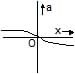
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two identical positive charges are fixed on the y-axis, at equal distances from the origin O. A particle with a negative charge starts on the x-axis at a large distance from O, moves along the +x-axis, passes through O and moves far away from O. Its acceleration a is taken as positive along its direction of motion. The particle's acceleration a is plotted against its x-coordinate. Which of the following best represents the plot ?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
New Words answered |
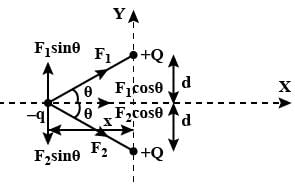
Consider the attached free body diagram for the given scenario.
From coulomb's law,
∣F1∣=∣F2∣= qQ /4πεor2
In y-direction, forces cancel, Fy=0
In x-direction, forces add up. Also, it is directed in +ve x direction if the position of −q is along −ve x axis and in −ve x direction if the position of −q is along +ve x axis.
Hence,
Fx=2qQcosθ i /4πεor2 ∀ x<0
Fx=2qQcosθ i /4πεor2 ∀ x≥0
But cosθ =x/r
r= √x2+d2
Substituting in force equation, we get
Fx=2qQx i /4πεo( x2+d2)3/2 ∀ x<0
Fx=2qQx i /4πεo( x2+d2)3/2 ∀ x≥0
Now, a=F/m by Newton's second law. It is positive when x is negative and negative when x is positive. This is satisfied only in option (B).
When a conductor is placed in an electric field; its free charge carriers adjust itself in order to oppose the electric field. This happen until- a)Both the fields cancel out each other
- b)Induced field become more than external field
- c)External field reach the maximum value
- d)Induced field reach the maximum value
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When a conductor is placed in an electric field; its free charge carriers adjust itself in order to oppose the electric field. This happen until
a)
Both the fields cancel out each other
b)
Induced field become more than external field
c)
External field reach the maximum value
d)
Induced field reach the maximum value
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
- When an external electric field is applied to the conductor, the free electrons in the conductor move in an opposite direction to that of the applied electric field.
- This movement of electrons induces another electric field inside the conductor which opposes the original external electric field.
- This continues until the induced electric field cancels out the external field.
The potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is
- a)Zero
- b)Infinity
- c)Non zero finite
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is
a)
Zero
b)
Infinity
c)
Non zero finite
d)
None of the above
|
|
Sahil Menon answered |
Explanation:
Potential energy is the energy possessed by a system due to the positions of its constituents. In the case of a system containing only one point charge, there is no other charge present to interact with it. Hence, the potential energy of such a system is zero.
To understand this concept, let us consider the formula for the potential energy of a system of two point charges:
U = kq1q2/r
where U is the potential energy, k is the Coulomb constant, q1 and q2 are the charges of the two point charges, and r is the distance between them.
When we have only one point charge in the system, q1 or q2 becomes zero. If we consider q1 to be zero, then the formula becomes:
U = kq1q2/r = 0
Therefore, the potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is zero.
In summary, the potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is zero because there is no other charge present to interact with it.
Potential energy is the energy possessed by a system due to the positions of its constituents. In the case of a system containing only one point charge, there is no other charge present to interact with it. Hence, the potential energy of such a system is zero.
To understand this concept, let us consider the formula for the potential energy of a system of two point charges:
U = kq1q2/r
where U is the potential energy, k is the Coulomb constant, q1 and q2 are the charges of the two point charges, and r is the distance between them.
When we have only one point charge in the system, q1 or q2 becomes zero. If we consider q1 to be zero, then the formula becomes:
U = kq1q2/r = 0
Therefore, the potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is zero.
In summary, the potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is zero because there is no other charge present to interact with it.
Which of the following statements is not true for polar molecules?- a)permanent dipole moment
- b)examples are oxygen and hydrogen molecules
- c)the centres of positive and negative charges are separated
- d)examples are HCl or water molecules
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not true for polar molecules?
a)
permanent dipole moment
b)
examples are oxygen and hydrogen molecules
c)
the centres of positive and negative charges are separated
d)
examples are HCl or water molecules
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
- Polar molecules occur when two atoms do not share electrons equally in a covalent bond.
- The oxygen side of the molecule has a slight negative charge, while the side with the hydrogen atoms has a slight positive charge.
- Ethanol is polar because the oxygen atoms attract electrons because of their higher electronegativity than other atoms in the molecule.
Two identical point charges are placed at a separation of l.P is a point on the line joining the charges, at a distance x from any one charge. The field at P is E. E is plotted against x for values of x from close to zero to slightly less than l. Which of the following best represents the resulting curve ?- a)
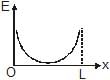
- b)
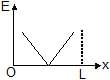
- c)
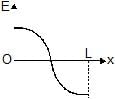
- d)
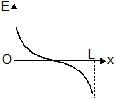
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two identical point charges are placed at a separation of l.P is a point on the line joining the charges, at a distance x from any one charge. The field at P is E. E is plotted against x for values of x from close to zero to slightly less than l. Which of the following best represents the resulting curve ?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Imk Pathsala answered |

At point P,
E=E1−E2 rightward
⟹E=(kq/x2)−(kq/(l−x)2) where k=1/4πϵo
⟹E=kq (l(l−2x)/x2(l−x)2)
From graph we can see that it can't be straight line and E=0 at x=l/2
At x=0 ,,E→∞ and at x=l, E→−∞
Hence, from the shown graphs the correct answer is (D).
If Q =2 coloumb and force on it is F=100 newtons , Then the value of field intensity will be- a)100 N/C
- b)50 N/C
- c)200 N/C
- d)10 N/C
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If Q =2 coloumb and force on it is F=100 newtons , Then the value of field intensity will be
a)
100 N/C
b)
50 N/C
c)
200 N/C
d)
10 N/C
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Electric force on a charge q placed in a region o electric field intensity is E and it is given by F = qE.
In this case, F = 100 N and q = 2 C.
So, E=F/q=100N/2C=50 N/C.
Hence, the value of field intensity will be 50 N/C.
In this case, F = 100 N and q = 2 C.
So, E=F/q=100N/2C=50 N/C.
Hence, the value of field intensity will be 50 N/C.
The dielectric Constant of a metal is- a)infinite
- b)zero
- c)equal to one
- d)less than one
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The dielectric Constant of a metal is
a)
infinite
b)
zero
c)
equal to one
d)
less than one
|
|
Nabanita Sen answered |
An electric field (E) is generated both inside the metal and outer (plates) which are equal in magnitude but opposite, making the net resultant field (Er) in the metal to be zero. Hence, the derived dielectric constant (K) of the metal is (E/Er = E/0) which is infinity. This is why the dielectric constant is infinity.
Electric potential is a -- a)Vector quantity
- b)Scalar quantity
- c) Neither vector Nor scalar
- d)Fictious quantity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Electric potential is a -
a)
Vector quantity
b)
Scalar quantity
c)
Neither vector Nor scalar
d)
Fictious quantity
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Electric potential is a pure Scalar quantity, The reason is as follows.
The Electric Potential is defined as the amount of work-done per unit positive charge to bring from infinity to that point under the influence of the primary charge only.
U=W/q
And work done is defined as the dot product of force and displacement which is a scalar quantity.
W=F.S
Thus Electric potential is a scalar quantity.
The Electric Potential is defined as the amount of work-done per unit positive charge to bring from infinity to that point under the influence of the primary charge only.
U=W/q
And work done is defined as the dot product of force and displacement which is a scalar quantity.
W=F.S
Thus Electric potential is a scalar quantity.
The direction (q) of at point P due to uniformly charged finite rod will be -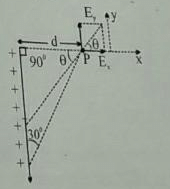
- a)At angle 30° from x-axis
- b)45° from x-axis
- c)60° from x-axis
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The direction (q) of at point P due to uniformly charged finite rod will be -
a)
At angle 30° from x-axis
b)
45° from x-axis
c)
60° from x-axis
d)
None of these

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
The angle suspended by the finite line charge at P=60°
So, the resultant electric field due to line charge will be at 60/2⇒30° since we can assume the charge concentrated at the centre of finite line charge.
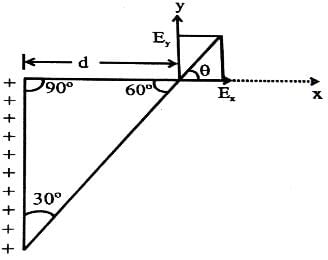
So, the resultant electric field due to line charge will be at 60/2⇒30° since we can assume the charge concentrated at the centre of finite line charge.

Four equal but like charge are placed at four corners of a square. The electric field intensity at the center of the square due to any one charge is E, then the resultant electric field intensity at centre of square will be- a)Zero
- b)4E
- c)E
- d)1/2E
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Four equal but like charge are placed at four corners of a square. The electric field intensity at the center of the square due to any one charge is E, then the resultant electric field intensity at centre of square will be
a)
Zero
b)
4E
c)
E
d)
1/2E
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
As the components of electric field intensity at diagonal are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, thus the intensity of electric field will be zero.
Hence the correct answer would be option A.
Hence the correct answer would be option A.
Two small balls having equal positive charge Q (Coulomb) on each are suspended by two insulating strings of equal length 'L' metre, from a hook fixed to a stand. The whole set up is taken in a satellite in to space where there is no gravity (state of weight lessness) Then the angle (q) between the two strings is- a)0º
- b)90º
- c)180º
- d)0º < q < 180º
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Two small balls having equal positive charge Q (Coulomb) on each are suspended by two insulating strings of equal length 'L' metre, from a hook fixed to a stand. The whole set up is taken in a satellite in to space where there is no gravity (state of weight lessness) Then the angle (q) between the two strings is
a)
0º
b)
90º
c)
180º
d)
0º < q < 180º
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
There is a condition of weightlessness in a satellite.
Therefore, mg=0
Due to electrostatic force of repulsion between the balls, the string would become horizontal.
Therefore, angle between the string =180
Therefore, mg=0
Due to electrostatic force of repulsion between the balls, the string would become horizontal.
Therefore, angle between the string =180
The extent of polarization depends on- a)Kinetic energy of bound charges
- b)Dipole potential energy
- c)Dipole potential energy and thermal energy
- d)Thermal energy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The extent of polarization depends on
a)
Kinetic energy of bound charges
b)
Dipole potential energy
c)
Dipole potential energy and thermal energy
d)
Thermal energy
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
Two factors on which the extent of polarization depends are:
The potential energy of dipoles in the external field which tends to align the dipole with in the field.
Thermal energy of the agitation which tends to randomize the alignment of the dipole.
A charge q = 1.0 C moves distance of 1.5 m in the direction of a uniform electric field E of magnitude 2.0 N/C. Find its change in electrostatic potential energy.- a)2 J
- b)3 J
- c)4 J
- d)1 J
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A charge q = 1.0 C moves distance of 1.5 m in the direction of a uniform electric field E of magnitude 2.0 N/C. Find its change in electrostatic potential energy.
a)
2 J
b)
3 J
c)
4 J
d)
1 J

|
Anchal Maurya answered |
Force (F)=E•q=2×1=2,. Energy (E)=F•d=2×1.5=3 joule
Negative mutual potential energy corresponds to attraction between two charges- a)False
- b)True
- c)Can’t predict
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Negative mutual potential energy corresponds to attraction between two charges
a)
False
b)
True
c)
Can’t predict
d)
None of the above

|
Soham Rastogi answered |
The formula for electric potential energy of system of 2 charges is (kq1q2)/r, if the result comes out to be negative,one of the charges has to be negative and one has to be positive, because there can be no other case in which it comes out to be negative. Since opposite charges attract each other,hence the answer is True.
An electric dipole is placed at an angle of 30° with an electric field intensity 2 × 105 N/C. It experiences a torque equal to 4 N m. The charge on the dipole, if the dipole length is 2 cm, is
- a)8 mC
- b)2 mC
- c)5 mC
- d)7 μC
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An electric dipole is placed at an angle of 30° with an electric field intensity 2 × 105 N/C. It experiences a torque equal to 4 N m. The charge on the dipole, if the dipole length is 2 cm, is
a)
8 mC
b)
2 mC
c)
5 mC
d)
7 μC
|
|
Srestha Chopra answered |
° with an electric field of magnitude 500 N/C. The dipole moment is 2 C.m. Find the torque experienced by the dipole.
The torque experienced by an electric dipole in an electric field is given by the formula:
τ = p E sinθ
where τ is the torque, p is the dipole moment, E is the electric field, and θ is the angle between the dipole moment and the electric field.
Substituting the given values, we get:
τ = (2 C.m) × (500 N/C) × sin30°
τ = (2 C.m) × (500 N/C) × 0.5
τ = 500 N.m
Therefore, the torque experienced by the dipole is 500 N.m.
The torque experienced by an electric dipole in an electric field is given by the formula:
τ = p E sinθ
where τ is the torque, p is the dipole moment, E is the electric field, and θ is the angle between the dipole moment and the electric field.
Substituting the given values, we get:
τ = (2 C.m) × (500 N/C) × sin30°
τ = (2 C.m) × (500 N/C) × 0.5
τ = 500 N.m
Therefore, the torque experienced by the dipole is 500 N.m.
When the distance between two charged particle is halved, the force between them becomes- a)One fourth
- b)One half
- c)Double
- d)Four times
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When the distance between two charged particle is halved, the force between them becomes
a)
One fourth
b)
One half
c)
Double
d)
Four times
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
The force between the two charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Hence, if distance between charges is halved (charges remaining kept constant), the force between the two charges is quadrupled.
If mass of the electron = 9.1 × 10_31 Kg. Charge on the electron = 1.6 × 10_19coulomb and g = 9.8 m/s2. Then the intensity of the electric field required to balance the weight of an electron is- a)5.6 × 10-9 N/C
- b)5.6 × 10-11 N/C
- c)5.6 × 10-8 N/C
- d) 5.6 × 10-7 N/C
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If mass of the electron = 9.1 × 10_31 Kg. Charge on the electron = 1.6 × 10_19coulomb and g = 9.8 m/s2. Then the intensity of the electric field required to balance the weight of an electron is
a)
5.6 × 10-9 N/C
b)
5.6 × 10-11 N/C
c)
5.6 × 10-8 N/C
d)
5.6 × 10-7 N/C
|
|
Deepak Kapoor answered |
We know that, qE=mg
So,E=mg/q
E=9.1x10-31x9.8x1019/1.6
E=9.1x9.8x10-12/1.6
E=5.6x10-11
So,E=mg/q
E=9.1x10-31x9.8x1019/1.6
E=9.1x9.8x10-12/1.6
E=5.6x10-11
The charge per unit length of the four quadrant of the ring is 2l, _2l, l and _l respectively. The electric field at the centre is - 
- a)–
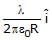
- b)
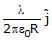
- c)
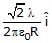
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The charge per unit length of the four quadrant of the ring is 2l, _2l, l and _l respectively. The electric field at the centre is -
a)
– 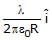
b)
c)
d)
None

|
Sidharth Gupta answered |
Divide in 4 1/4 rings and use result 2Klemda/r in both x and y axis and add by vector rule hope you do calculation own ur own
Two point charges in air at a distance of 20 cm. from each other interact with a certain force. At what distance from each other should these charges be placed in oil of relative permittivity 5 to obtain the same force of interaction
- a)8.94 × 10-2 m
- b)0.894 × 10-2 m
- c)89.4 × 10-2 m
- d)8.94 × 102 m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two point charges in air at a distance of 20 cm. from each other interact with a certain force. At what distance from each other should these charges be placed in oil of relative permittivity 5 to obtain the same force of interaction
a)
8.94 × 10-2 m
b)
0.894 × 10-2 m
c)
89.4 × 10-2 m
d)
8.94 × 102 m
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
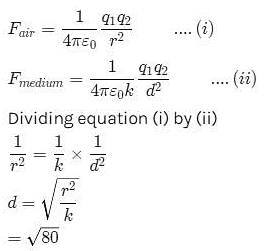
d=8.94 cm or
d=8.94x10-2
d=8.94x10-2
The displacement of charges inside the dielectric stops when- a)the external field becomes maximum
- b)the external force on the charges of the molecules is balanced by the force due to internal fields
- c)the internal force on the charges of the molecules is balanced by the forces due to the internal fields
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The displacement of charges inside the dielectric stops when
a)
the external field becomes maximum
b)
the external force on the charges of the molecules is balanced by the force due to internal fields
c)
the internal force on the charges of the molecules is balanced by the forces due to the internal fields
d)
none of the above
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
The displacement of charges inside the dielectric stops when the external force on the charges of the molecules is balanced by the force due to internal fields.
A uniformly polarized dielectric amounts to induced ______ charge density but no ______charge density.- a)volume, surface
- b)surface, volume
- c)volume, line
- d)line, volume
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A uniformly polarized dielectric amounts to induced ______ charge density but no ______charge density.
a)
volume, surface
b)
surface, volume
c)
volume, line
d)
line, volume
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
As charges are separated on the surface of the dielectric but not in its interior volume.
Two similar charge of +Q , as shown in figure are placed at A and B. _q charge is placed at point C midway between A and B. _q charge will oscillate if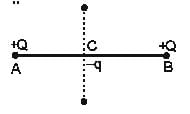
- a)It is moved towards A
- b)It is moved towards B
- c)It is moved upwards AB
- d)Distance between A and B is reduced
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two similar charge of +Q , as shown in figure are placed at A and B. _q charge is placed at point C midway between A and B. _q charge will oscillate if
a)
It is moved towards A
b)
It is moved towards B
c)
It is moved upwards AB
d)
Distance between A and B is reduced
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The answer should be c, b'cuz if it moves perpendicularly to the line joining a and b then only it will oscillate.
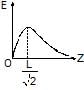
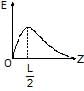
Four equal positive charges are fixed at the vertices of a square of side L. Z-axis is perpendicular to the plane of the square. The point z = 0 is the point where the diagonals of the square intersect each other. The plot of electric field due to the four charges, as one moves on the z-axis.
- a)

- b)
- c)

- d)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Four equal positive charges are fixed at the vertices of a square of side L. Z-axis is perpendicular to the plane of the square. The point z = 0 is the point where the diagonals of the square intersect each other. The plot of electric field due to the four charges, as one moves on the z-axis.
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Imk Pathsala answered |

Can you explain the answer of this question below:Two similar charge of +Q , as shown in figure are placed at A and B. _q charge is placed at point C midway between A and B. _q charge will oscillate if

- A:
It is moved towards A
- B:
It is moved towards B
- C:
It is moved upwards AB
- D:
Distance between A and B is reduced
The answer is a.
Two similar charge of +Q , as shown in figure are placed at A and B. _q charge is placed at point C midway between A and B. _q charge will oscillate if
It is moved towards A
It is moved towards B
It is moved upwards AB
Distance between A and B is reduced
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
When -q is displaced left or right of the force is increased so -q move towards that force hence will not perform SHM but when its displaced to AB it will perform SHM because it will return to its mean position.
A nonconducting ring of radius R has uniformly distributed positive charge Q. A small part of the ring, of length d, is removed (d<<R). The electric field at the centre of the ring will now be- a)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R3
- b)directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R2
- c)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R3
- d)directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R2.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A nonconducting ring of radius R has uniformly distributed positive charge Q. A small part of the ring, of length d, is removed (d<<R). The electric field at the centre of the ring will now be
a)
directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R3
b)
directed towards the gap, inversely proportional to R2
c)
directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R3
d)
directed away from the gap, inversely proportional to R2.
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Please refer to the figure below..
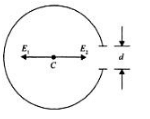
Initially the charge on the ring was 'Q' and we now have removed a section of the ring of length 'd', as shown above.
Now, the charge in the removed section will be
q = Q.(d/2πR)
it stems from the fact that the (linear) charge density remains the same in both the ring and the removed section [q/d = Q/2πR]
The electric field at the center would be zero as it gets cancelled out. After removing the section we have to fields being developed; E1 and E2.
Here,
E1 is the electric field due to the removed section
and
E2 is the electric field due to the remaining ring
Now, for the net electric field at the center to be zero,
E1 = E2
or
E2 = kq/R^2
so, [ q = Q.(d/2πR)]
E2 = kQd / 2πR^3
thus,
electric field is directed towards the gap and is proportional to R^3, so
correct answer - option (a)
Positive mutual potential energy of a system containing two charges corresponds to- a)Repulsion
- b)Attraction
- c)Can’t predict
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Positive mutual potential energy of a system containing two charges corresponds to
a)
Repulsion
b)
Attraction
c)
Can’t predict
d)
None of the above
|
|
Kiran Khanna answered |
Explanation:
The mutual potential energy of a system containing two charges is given by,
U = (1/4πε0) * (q1q2/r)
where q1 and q2 are the magnitudes of the charges, r is the distance between them, and ε0 is the permittivity of free space.
If the charges are of the same sign, i.e., both positive or both negative, then the product q1q2 is positive. As a result, the mutual potential energy U will also be positive. This means that the charges will experience a repulsive force, and will tend to move away from each other.
On the other hand, if the charges are of opposite sign, i.e., one positive and the other negative, then the product q1q2 will be negative. As a result, the mutual potential energy U will also be negative. This means that the charges will experience an attractive force, and will tend to move towards each other.
Therefore, we can conclude that a positive mutual potential energy of a system containing two charges corresponds to repulsion between the charges.
The mutual potential energy of a system containing two charges is given by,
U = (1/4πε0) * (q1q2/r)
where q1 and q2 are the magnitudes of the charges, r is the distance between them, and ε0 is the permittivity of free space.
If the charges are of the same sign, i.e., both positive or both negative, then the product q1q2 is positive. As a result, the mutual potential energy U will also be positive. This means that the charges will experience a repulsive force, and will tend to move away from each other.
On the other hand, if the charges are of opposite sign, i.e., one positive and the other negative, then the product q1q2 will be negative. As a result, the mutual potential energy U will also be negative. This means that the charges will experience an attractive force, and will tend to move towards each other.
Therefore, we can conclude that a positive mutual potential energy of a system containing two charges corresponds to repulsion between the charges.
Chapter doubts & questions for Electrostatic Force - Physics 2025 is part of Grade 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Electrostatic Force - Physics in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Physics
307 videos|482 docs|202 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily