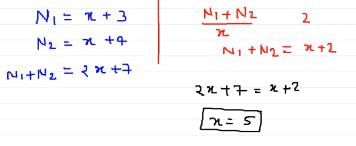All Exams >
CLAT >
Weekly Test for CLAT UG >
All Questions
All questions of Week 4 for CLAT Exam
PRINCIPLE: A gift comprising both existing and future property is void as to the latter.FACTS: X has a house which is owned by him. He contracted to purchase a plot of land adjacent to the said house but the sale (of the plot of land) in his favour is yet to be completed. He makes a gift of both the properties (house and land) to Y. Under the afore-mentioned circumstances, which of the following derivations is CORRECT?- a)Gift of both the properties is valid.
- b)Gift of both the properties is void.
- c)Gift of house is void, but the gift of the plot of land is valid.
- d)Gift of house is valid, but the gift of the plot of land is void.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
PRINCIPLE: A gift comprising both existing and future property is void as to the latter.
FACTS: X has a house which is owned by him. He contracted to purchase a plot of land adjacent to the said house but the sale (of the plot of land) in his favour is yet to be completed. He makes a gift of both the properties (house and land) to Y. Under the afore-mentioned circumstances, which of the following derivations is CORRECT?
a)
Gift of both the properties is valid.
b)
Gift of both the properties is void.
c)
Gift of house is void, but the gift of the plot of land is valid.
d)
Gift of house is valid, but the gift of the plot of land is void.
|
|
Aditya Ghosh answered |
Principle: A gift comprising both existing and future property is void as to the latter.
Facts: X has a house which is owned by him. He contracted to purchase a plot of land adjacent to the said house but the sale (of the plot of land) in his favour is yet to be completed. He makes a gift of both the properties (house and land) to Y.
Derivation:
The principle states that a gift comprising both existing and future property is void as to the latter. In this case, X has made a gift of both the properties, i.e. the house and the plot of land, to Y. However, the sale of the plot of land in X's favour is yet to be completed, which means that the plot of land is a future property. Therefore, the gift of the plot of land is void as per the principle.
However, the gift of the house is valid as it is an existing property and can be given as a gift. Thus, option D, i.e. the gift of house is valid, but the gift of the plot of land is void, is the correct answer.
Conclusion:
A gift comprising both existing and future property is void as to the latter. In this case, the gift of the house is valid, but the gift of the plot of land is void as the sale of the plot of land in X's favour is yet to be completed.
Facts: X has a house which is owned by him. He contracted to purchase a plot of land adjacent to the said house but the sale (of the plot of land) in his favour is yet to be completed. He makes a gift of both the properties (house and land) to Y.
Derivation:
The principle states that a gift comprising both existing and future property is void as to the latter. In this case, X has made a gift of both the properties, i.e. the house and the plot of land, to Y. However, the sale of the plot of land in X's favour is yet to be completed, which means that the plot of land is a future property. Therefore, the gift of the plot of land is void as per the principle.
However, the gift of the house is valid as it is an existing property and can be given as a gift. Thus, option D, i.e. the gift of house is valid, but the gift of the plot of land is void, is the correct answer.
Conclusion:
A gift comprising both existing and future property is void as to the latter. In this case, the gift of the house is valid, but the gift of the plot of land is void as the sale of the plot of land in X's favour is yet to be completed.
TANGIBLE- a)Ethereal
- b)Concrete
- c)Actual
- d)Solid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Ethereal
b)
Concrete
c)
Actual
d)
Solid
|
|
Meera Rana answered |
The antonym of TANGIBLE is Ethereal.
In a three digit number the digit in the unit’s place is twice the digit in the ten’s place and 1.5 times the digit in the hundred’s place. If the sum of all the three digits of the number is 13, what is the number?- a)356
- b)456
- c)436
- d)626
- e)516
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a three digit number the digit in the unit’s place is twice the digit in the ten’s place and 1.5 times the digit in the hundred’s place. If the sum of all the three digits of the number is 13, what is the number?
a)
356
b)
456
c)
436
d)
626
e)
516

|
Bank Exams India answered |
100a + 10b + c
c = 2b → b = c/2
c = 1.5a → a = c/1.5
c/1.5 + c/2 + c = 13
6.5c = 39
c = 6, b = 3, a = 4 ⇒ 436
c = 2b → b = c/2
c = 1.5a → a = c/1.5
c/1.5 + c/2 + c = 13
6.5c = 39
c = 6, b = 3, a = 4 ⇒ 436
PRINCIPLE: "Nobody shall unlawfully interfere with a person's use or enjoyment of land, or some right over, or in connection with it. The use or enjoyment, envisaged herein, should be normal and reasonable taking into account surrounding situation."
FACTS: Jeevan and Pavan were neighbours in a residential locality. Pavan started a typing class in a part of his house and his typing sound disturbed Jeevan who could not put up with any kind of continuous noise. He filed a suit against Pavan.
- a)Pavan is liable, because he should not have started typing class in his house
- b)Pavan is liable, because as a neighbour, he should have realised Jeevan's delicate nature
- c)None of these
- d)Pavan is not liable, because typing sound did not disturb anyone else other than Jeevan
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
PRINCIPLE: "Nobody shall unlawfully interfere with a person's use or enjoyment of land, or some right over, or in connection with it. The use or enjoyment, envisaged herein, should be normal and reasonable taking into account surrounding situation."
FACTS: Jeevan and Pavan were neighbours in a residential locality. Pavan started a typing class in a part of his house and his typing sound disturbed Jeevan who could not put up with any kind of continuous noise. He filed a suit against Pavan.
a)
Pavan is liable, because he should not have started typing class in his house
b)
Pavan is liable, because as a neighbour, he should have realised Jeevan's delicate nature
c)
None of these
d)
Pavan is not liable, because typing sound did not disturb anyone else other than Jeevan
|
|
Dia Mehta answered |
- Private Nuisance can be defined as "any continuous activity or state of affairs causing a substantial and unreasonable interference with a (claimant's) land or his use or enjoyment of that land".
- Private nuisance, unlike public nuisance, is only a tort, and damages for personal injuries are not recoverable.
Sum of three consecutive odd numbers & three consecutive even numbers together is 231. Difference between the smallest odd number and the smallest even number is 11. What is the sum of the largest even number and largest odd number?- a)71
- b)91
- c)101
- d)81
- e)Can not be determined
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Sum of three consecutive odd numbers & three consecutive even numbers together is 231. Difference between the smallest odd number and the smallest even number is 11. What is the sum of the largest even number and largest odd number?
a)
71
b)
91
c)
101
d)
81
e)
Can not be determined
|
|
Kendrika answered |
Let the three odd numbers be x, (x + 2), (x + 4) and
The three even numbers be (x + 11), (x + 13) and (x + 15)
Then,
⇔ x + (x + 2) + (x + 4) + (x + 11) + (x + 13) + (x + 15) = 231
⇔ 6x + 45 = 231
⇔ 6x = 186
⇔ x = 31
∴ Required sum :
= (x + 4) + (x + 15)
= 2x + 19
= 2 × 31 + 19
= 62 + 19
= 81
The three even numbers be (x + 11), (x + 13) and (x + 15)
Then,
⇔ x + (x + 2) + (x + 4) + (x + 11) + (x + 13) + (x + 15) = 231
⇔ 6x + 45 = 231
⇔ 6x = 186
⇔ x = 31
∴ Required sum :
= (x + 4) + (x + 15)
= 2x + 19
= 2 × 31 + 19
= 62 + 19
= 81
PRINCIPLE: In a civil action for defamation, truth of the defamatory matter is an absolute defence. However, the burden of proving truth is on the defendant; and he is liable if he does not successfully discharge this burden.FACTS: D, who was the editor of a local weekly, published a series of articles mentioning that P, who was a government servant, issued false certificates, accepted bribe, adopted corrupt and illegal means to mint money and was a “mischief monger”. P brought a civil action against D, who could not prove the facts published by him. Under the circumstances, which of the following derivations is CORRECT?- a)D would be liable, since he could not prove the facts published by him.
- b)D would not be liable as such an action could curtail the right of expression and speech of press.
- c)D would not be liable as media could publish anything.
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
PRINCIPLE: In a civil action for defamation, truth of the defamatory matter is an absolute defence. However, the burden of proving truth is on the defendant; and he is liable if he does not successfully discharge this burden.
FACTS: D, who was the editor of a local weekly, published a series of articles mentioning that P, who was a government servant, issued false certificates, accepted bribe, adopted corrupt and illegal means to mint money and was a “mischief monger”. P brought a civil action against D, who could not prove the facts published by him. Under the circumstances, which of the following derivations is CORRECT?
a)
D would be liable, since he could not prove the facts published by him.
b)
D would not be liable as such an action could curtail the right of expression and speech of press.
c)
D would not be liable as media could publish anything.
d)
None of the above.
|
|
Nishtha Pandey answered |
Facts shows that D was not able to prove all what he had published in the newspaper. Thus, he had used defamatory statement, performed maliciously to defame & harm to his reputation.
So, yes D would be liable, since he could not prove the facts published by him.
hope it helps!!!
So, yes D would be liable, since he could not prove the facts published by him.
hope it helps!!!
PRINCIPLE: Whoever, intending to take dishonestly any movable property out of the possession of any person without that person’s consent moves that property, such taking is said to commit theft.FACT: RAMU cuts down a tree on RINKU’S ground, with the intention of dishonestly taking the tree out of RINKU’S profession without RINKU’S consent. A could not take the tree away.- a)RAMU can be prosecuted for theft
- b)RAMU cannot be prosecuted for theft
- c)RAMU can be prosecuted for attempt to theft
- d)RAMU has neither committed theft nor attempt to commit theft
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
PRINCIPLE: Whoever, intending to take dishonestly any movable property out of the possession of any person without that person’s consent moves that property, such taking is said to commit theft.
FACT: RAMU cuts down a tree on RINKU’S ground, with the intention of dishonestly taking the tree out of RINKU’S profession without RINKU’S consent. A could not take the tree away.
a)
RAMU can be prosecuted for theft
b)
RAMU cannot be prosecuted for theft
c)
RAMU can be prosecuted for attempt to theft
d)
RAMU has neither committed theft nor attempt to commit theft
|
|
Faizan Khan answered |
Ramu will be prosecuted for theft, since he had theintention of taking away the tree after cutting it.
The principle clearly talks about the intention of taking away property.
The principle clearly talks about the intention of taking away property.
BRIEF- a)Limited
- b)Small
- c)Little
- d)Short
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
BRIEF
a)
Limited
b)
Small
c)
Little
d)
Short
|
|
Malavika Nambiar answered |
brief means for a small period of time.
EMBEZZLE- a)Misappropriate
- b)Balance
- c)Remunerate
- d)Clear
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Misappropriate
b)
Balance
c)
Remunerate
d)
Clear
|
|
Baishali Das answered |
Meaning of Embezzle: steal or misappropriate (money placed in one's trust or belonging to the organization for which one works).
PRINCIPLE: When an act, which would otherwise be an offence, is not that offence by reason of the youth, the want of maturity of understanding, the unsoundness of mind or the intoxication of the person doing that act, every person has the same right of private defence against that act, which he would have if the act were that offence. Nothing is an offence which is done in the exercise of the right of private defence.FACTS: A, under the influence of madness, attempts to kill B. B in order to save his life cause grievous hurt to A.- a)A has committed an offence
- b)A has not committed an offence
- c)B has committed an offence
- d)B has not committed any offence
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
PRINCIPLE: When an act, which would otherwise be an offence, is not that offence by reason of the youth, the want of maturity of understanding, the unsoundness of mind or the intoxication of the person doing that act, every person has the same right of private defence against that act, which he would have if the act were that offence. Nothing is an offence which is done in the exercise of the right of private defence.
FACTS: A, under the influence of madness, attempts to kill B. B in order to save his life cause grievous hurt to A.
a)
A has committed an offence
b)
A has not committed an offence
c)
B has committed an offence
d)
B has not committed any offence
|
|
Sharanya chauhan answered |
Principle: Private Defence
According to the principle, when an act, which would otherwise be an offence, is not that offence by reason of the unsoundness of mind of the person doing that act, every person has the same right of private defence against that act, which he would have if the act were that offence. Nothing is an offence which is done in the exercise of the right of private defence.
Facts: Attempt to Kill Under Influence of Madness
A, under the influence of madness, attempts to kill B. B, in order to save his life, causes grievous hurt to A.
Conclusion: B has not committed any offence
In this case, A was attempting to kill B under the influence of madness, which means he was not in a sound state of mind. As per the principle, nothing is an offence which is done in the exercise of the right of private defence. Therefore, B, in order to save his life, caused grievous hurt to A. This act is not an offence as B exercised his right to private defence.
Hence, the correct answer is option D, i.e., B has not committed any offence.
According to the principle, when an act, which would otherwise be an offence, is not that offence by reason of the unsoundness of mind of the person doing that act, every person has the same right of private defence against that act, which he would have if the act were that offence. Nothing is an offence which is done in the exercise of the right of private defence.
Facts: Attempt to Kill Under Influence of Madness
A, under the influence of madness, attempts to kill B. B, in order to save his life, causes grievous hurt to A.
Conclusion: B has not committed any offence
In this case, A was attempting to kill B under the influence of madness, which means he was not in a sound state of mind. As per the principle, nothing is an offence which is done in the exercise of the right of private defence. Therefore, B, in order to save his life, caused grievous hurt to A. This act is not an offence as B exercised his right to private defence.
Hence, the correct answer is option D, i.e., B has not committed any offence.
A throws water on B and the drop of the water falls on B. A committed- a)Battery
- b)assault
- c)no offence
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A throws water on B and the drop of the water falls on B. A committed
a)
Battery
b)
assault
c)
no offence
d)
none of the above

|
Udisha Mishra answered |
Battery means any using any physical force or a physical contact without any lawful justification. Here that drop is a medium and the act does not have any lawful justification. This it amount to battery.
A number when divided by 143 leaves 31 as remainder. What will be the remainder
when the same number is divided by 13 ?- a)0
- b)1
- c)3
- d)5
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A number when divided by 143 leaves 31 as remainder. What will be the remainder
when the same number is divided by 13 ?
when the same number is divided by 13 ?
a)
0
b)
1
c)
3
d)
5
e)
None of these

|
Abhishek answered |
Number is = x
x = divisor + remainder
x = 143 + 31
x = 174
when the same number is decided by 13
remainder= 174÷13
= 5 Ans.
x = divisor + remainder
x = 143 + 31
x = 174
when the same number is decided by 13
remainder= 174÷13
= 5 Ans.
The Railway authorities allowed a train to be over-crowded. In consequence, a legitimate passenger, Mr. X got his pocket picked. Choose appropriate answer-- a)Mr. X can sue the railway authorities for the loss suffered.
- b)Mr. X cannot sue because he had given his consent to travel in over-crowded train.
- c)Mr. X cannot sue the railway authorities because there was no infringement of legal right and mere fact that the loss was caused does not give to a cause of action.
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The Railway authorities allowed a train to be over-crowded. In consequence, a legitimate passenger, Mr. X got his pocket picked. Choose appropriate answer-
a)
Mr. X can sue the railway authorities for the loss suffered.
b)
Mr. X cannot sue because he had given his consent to travel in over-crowded train.
c)
Mr. X cannot sue the railway authorities because there was no infringement of legal right and mere fact that the loss was caused does not give to a cause of action.
d)
None of the above.
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
A cause of action is a set of facts that are used to justify claims or right to sue to obtain property or money or enforcement of a right against another party and since there is no infringement of legal rights of X, there is no cause of action arising against the Railway authority and hence he cannot sue them.
Principle - Violation of a legal right, with or without actual damage, gives rise to a tort. However, actual damage without violation of a legal right does not give rise to tortious liability.Facts – Ayush has a shop that offers printing, Xerox, and book binding services. In the shop, he also sells notebooks, stationery, printing inks, paper and other such items. He has a big board outside his shop displaying all the things he deals in, and this board is instrumental in attracting customers, who would otherwise be unaware that he sold such things. His shop is situated in a narrow street with several other stores. Rajesh owns a book store next to him, and he installs a display shelf with all the titles he sells, outside his shop in order to woo customers. This shelf obscures the view to Ayush‘s board, and there is a decrease in the number of customers who buy from him. Ayush decides to sue Rajesh and claim damages.- a)Ayush can get damages, as he has suffered damage. The display shelf of Rajesh obscured the view of Ayush‘s board, and Rajesh had no right to do that.
- b)Ayush can claim damages, but it is up to the court to grant them, as the loss suffered is not so substantial. The shelf did not entirely block the view to the board.
- c)Ayush cannot claim damages in this case, as his legal rights have not been violated by Rajesh in setting up a display shelf.
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Principle - Violation of a legal right, with or without actual damage, gives rise to a tort. However, actual damage without violation of a legal right does not give rise to tortious liability.
Facts – Ayush has a shop that offers printing, Xerox, and book binding services. In the shop, he also sells notebooks, stationery, printing inks, paper and other such items. He has a big board outside his shop displaying all the things he deals in, and this board is instrumental in attracting customers, who would otherwise be unaware that he sold such things. His shop is situated in a narrow street with several other stores. Rajesh owns a book store next to him, and he installs a display shelf with all the titles he sells, outside his shop in order to woo customers. This shelf obscures the view to Ayush‘s board, and there is a decrease in the number of customers who buy from him. Ayush decides to sue Rajesh and claim damages.
a)
Ayush can get damages, as he has suffered damage. The display shelf of Rajesh obscured the view of Ayush‘s board, and Rajesh had no right to do that.
b)
Ayush can claim damages, but it is up to the court to grant them, as the loss suffered is not so substantial. The shelf did not entirely block the view to the board.
c)
Ayush cannot claim damages in this case, as his legal rights have not been violated by Rajesh in setting up a display shelf.
d)
None of the above.

|
Aishwarya Rajput answered |
Ayush suffered damages tho... but his actual legal rights were not violated. According to principle violation of LEGAL RIGHTS brings tortious liability... so he cannot claim damages.
PRINCIPLE - Violation of a legal right, with or without actual damage, gives rise to a tort. However, actual damage without violation of a legal right does not give rise to tortious liability.
FACTS – Arpita was travelling to Ladakh for a business visit, while she was stopped by some police officers at a check post on the highway. They detained her on the pretext of her possessing illegal substances on her person, and restricted her from contacting anybody who might help her in the predicament. As a result of being detained, she was unable to fulfil the purpose of her visit, and the business deal was lost, causing losses to her company. When she was finally released, she wished to sue the police authorities for infringement on her fundamental rights to movement, speech and expression.
Q. Will she succeed in these claims?
- a)Arpita will succeed only in the claim for violation of her right to movement, as the loss she suffered was due to this.
- b)Arpita cannot sue for violation of her right to freedom of speech and expression, as she was eventually released and did not suffer any real harm.
- c)Both (a) and (b)
- d)Arpita will succeed in both claims as there has been a violation of her legal rights in both circumstances, and the police authorities will be liable.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
PRINCIPLE - Violation of a legal right, with or without actual damage, gives rise to a tort. However, actual damage without violation of a legal right does not give rise to tortious liability.
FACTS – Arpita was travelling to Ladakh for a business visit, while she was stopped by some police officers at a check post on the highway. They detained her on the pretext of her possessing illegal substances on her person, and restricted her from contacting anybody who might help her in the predicament. As a result of being detained, she was unable to fulfil the purpose of her visit, and the business deal was lost, causing losses to her company. When she was finally released, she wished to sue the police authorities for infringement on her fundamental rights to movement, speech and expression.
Q. Will she succeed in these claims?
Q. Will she succeed in these claims?
a)
Arpita will succeed only in the claim for violation of her right to movement, as the loss she suffered was due to this.
b)
Arpita cannot sue for violation of her right to freedom of speech and expression, as she was eventually released and did not suffer any real harm.
c)
Both (a) and (b)
d)
Arpita will succeed in both claims as there has been a violation of her legal rights in both circumstances, and the police authorities will be liable.
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
The above case is based on the legal doctrine of Injuria sine damnum which means injury of legal rights without damage. It basically states that infringement of an absolute private right without any actual loss or damage. Here, physical damages or actual loss means loss or damage in terms of health, money, etc.
CONSEQUENCES- a)Results
- b)Conclusions
- c)Difficulties
- d)Applications
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Results
b)
Conclusions
c)
Difficulties
d)
Applications
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
- Consequences are results of something that already had happened whereas conclusions are the final verdits of discussions or ideas.
- Results: something that happens because of something else; the final situation at the end of a series of actions
- Conclusions: an opinion that you reach after thinking about something carefully
- Difficulties: the state or condition of being difficult
- Applications: the action of putting something into operation.
The equation of a wave disturbance is given as :
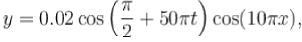 where X and y are in metres and f in seconds. Choose the wrong statement:
where X and y are in metres and f in seconds. Choose the wrong statement:- a)Node occurs at x = 0.15 m
- b)The wavelength is 0.2 m
- c)Antinode occurs at x = 0.3 m
- d)The speed of the constituent waves is 5 m/s
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The equation of a wave disturbance is given as :
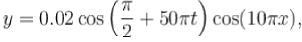 where X and y are in metres and f in seconds. Choose the wrong statement:
where X and y are in metres and f in seconds. Choose the wrong statement:
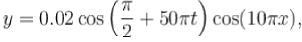 where X and y are in metres and f in seconds. Choose the wrong statement:
where X and y are in metres and f in seconds. Choose the wrong statement:a)
Node occurs at x = 0.15 m
b)
The wavelength is 0.2 m
c)
Antinode occurs at x = 0.3 m
d)
The speed of the constituent waves is 5 m/s

|
Ameya Rane answered |
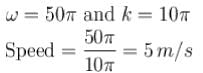
The correct answer is: The speed of the constituent waves is 5 m/s
The sum of two even numbers is six more than twice of the smaller number. If the difference between these two numbers is 6, If the larger number lies between 15 to 25 Which is the smaller number?
- a)16
- b)6
- c)24
- d)12
- e)Can not be determined
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The sum of two even numbers is six more than twice of the smaller number. If the difference between these two numbers is 6, If the larger number lies between 15 to 25 Which is the smaller number?
a)
16
b)
6
c)
24
d)
12
e)
Can not be determined
|
|
Kavya Saxena answered |
If 12 is smaller number then larger number is 18
Sum = (12+18) = 30
Twice of the smaller number = 24.
The sum of two even numbers is six more than twice of the smaller number.
Therefore Number 12 satisfy both the conditions.
Sum = (12+18) = 30
Twice of the smaller number = 24.
The sum of two even numbers is six more than twice of the smaller number.
Therefore Number 12 satisfy both the conditions.
‘X’ with a view to murdering ‘Y’ enters ‘Y’ bedroom at night when ‘Y’ is out of station. What is ‘X’ guilty of?- a)Murder
- b)house trespass
- c)attempt to murder
- d)no offence
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
‘X’ with a view to murdering ‘Y’ enters ‘Y’ bedroom at night when ‘Y’ is out of station. What is ‘X’ guilty of?
a)
Murder
b)
house trespass
c)
attempt to murder
d)
no offence
|
|
Dia Mehta answered |
Well as Y was away so murder or anything of that sort is impossible to happen, and as X went in with a view to murder Y he has committed trespass.
LAMENT- a)Complain
- b)Comment
- c)Condone
- d)Console
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Complain
b)
Comment
c)
Condone
d)
Console

|
Ankit Anchal answered |
No, Lament correct meaning is sorrow, grief
A certain number of two digits is three times the sum of its digits. If 45 is added to it, the digits are reversed. The number is _______
- a)16
- b)72
- c)63
- d)27
- e)Can not be determined
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A certain number of two digits is three times the sum of its digits. If 45 is added to it, the digits are reversed. The number is _______
a)
16
b)
72
c)
63
d)
27
e)
Can not be determined

|
KS Coaching Center answered |
A certain number of two digits is three times the sum of its digits only 27 satisfies this condition.
27 + 45 = 72
Therefore Ans is – 27
27 + 45 = 72
Therefore Ans is – 27
INDISCREET- a)Reliable
- b)Honest
- c)Prudent
- d)Stupid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Reliable
b)
Honest
c)
Prudent
d)
Stupid

|
Aspire Academy answered |
Indiscreet : Imprudent, unwise.
Reliable : Dependable.
Honest : Truthful, sincere.
Prudent : Wise, judicious.
Stupid : Unintelligent, ignorant.
Reliable : Dependable.
Honest : Truthful, sincere.
Prudent : Wise, judicious.
Stupid : Unintelligent, ignorant.
Antonym of Indiscreet is Prudent.
Principle – The master is liable for the wrongful acts of the servant done in the course of employment. Facts – Pradyuman is a mechanic working in the car mechanics shop owned by Abhjit. Pallavi wants her Audi A8 to be serviced and cleaned, as she is planning to go on a long drive soon. She drops off the car at the mechanic‘s, and asks Pradyuman to have it ready in two days. Pradyuman, while trying to drive the car to the jet-cleaning area, accidentally bumps it against the wall and a dent is created on the car door. When Pallavi comes to take her serviced car, she is livid at the condition in which it is returned to her, and wishes to sue for damages.- a)Only Pradyuman will be liable as he has caused the damage to the car.
- b)Both Pradyuman and Abhijit will be jointly liable.
- c)Abhijit will be liable to pay damages, as Pradhyuman is his servant and the damage was caused in the course of employment.
- d)Pallavi will not be entitled to claim damages as she should not have given her car to a small mechanic such as Abhijit.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Principle – The master is liable for the wrongful acts of the servant done in the course of employment.
Facts – Pradyuman is a mechanic working in the car mechanics shop owned by Abhjit. Pallavi wants her Audi A8 to be serviced and cleaned, as she is planning to go on a long drive soon. She drops off the car at the mechanic‘s, and asks Pradyuman to have it ready in two days. Pradyuman, while trying to drive the car to the jet-cleaning area, accidentally bumps it against the wall and a dent is created on the car door. When Pallavi comes to take her serviced car, she is livid at the condition in which it is returned to her, and wishes to sue for damages.
a)
Only Pradyuman will be liable as he has caused the damage to the car.
b)
Both Pradyuman and Abhijit will be jointly liable.
c)
Abhijit will be liable to pay damages, as Pradhyuman is his servant and the damage was caused in the course of employment.
d)
Pallavi will not be entitled to claim damages as she should not have given her car to a small mechanic such as Abhijit.

|
Nune. Triveni answered |
Answer is C. Applying the principle of Principal- Agent relationship. Principal is liable for any wrongs made by the servant or agent. So here it is very clear that the master is liable to pay on behalf of his servant Pradyuman. But later even master can also deduct the damages from the servant wages which is the other side of the case which is not relevant on the face of the question.
PRINCIPLE: A master is liable for the acts committed by his servant in the course of employment.FACT: Sanjay is a driver working in Brookebond and Co. One day, the Manager asked him to drop a customer at the airport and get back at the earliest. On his way back from the airport, he happened to see his fiancé Ruhina waiting for a bus to go home. He offered to drop her at home, which happened to be close to his office. She got into the car and soon thereafter; the car somersaulted due to negligence of Sanjay. Ruhina was thrown out of the car and suffered multiple injuries. She seeks compensation from Brookebond and Co.- a)Brookebond and Co., shall be liable, because Sanjay was in the course of employment at the time of accident
- b)Brookebond and Co., shall not be liable, Sanjay was not in the course of employment when he took Ruhina inside the car.
- c)Ruhina got into the car at her own risk, and therefore, she cannot sue anybody.
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
PRINCIPLE: A master is liable for the acts committed by his servant in the course of employment.
FACT: Sanjay is a driver working in Brookebond and Co. One day, the Manager asked him to drop a customer at the airport and get back at the earliest. On his way back from the airport, he happened to see his fiancé Ruhina waiting for a bus to go home. He offered to drop her at home, which happened to be close to his office. She got into the car and soon thereafter; the car somersaulted due to negligence of Sanjay. Ruhina was thrown out of the car and suffered multiple injuries. She seeks compensation from Brookebond and Co.
a)
Brookebond and Co., shall be liable, because Sanjay was in the course of employment at the time of accident
b)
Brookebond and Co., shall not be liable, Sanjay was not in the course of employment when he took Ruhina inside the car.
c)
Ruhina got into the car at her own risk, and therefore, she cannot sue anybody.
d)
None of the above.
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
- Vicarious liability can be defined as a legal doctrine that assigns liability for an injury to a person who did not cause the injury who has a particular relationship to the person who did act negligently. It can also be called imputed negligence.
- This doctrine arises under the common law doctrine of agency, respondeat superior, the responsibility of the superior for the acts of their subordinate or, in a broader sense, the responsibility of any third party that had the "right, ability or duty to control" the activities of a violator.
- Hence, in the above situation, since the act was not committed in the course of employment, Ruhina will not succeed.
PRINCIPLE: Everybody is under a legal obligation to take reasonable care to avoid and act or omission which he can take reasonable care to avoid and act or omission which he can foresee would injure his neighbour. The neighbour, for this purpose, is any person whom he should have in his mind as likely to be affected by his act.FACTS: Krishnan, while driving a car at high speed in a crowded road, knocked down a cyclist. The cyclist died on the spot with a lot of blood spilling around, Lakshmi, a pregnant woman passing by, suffered from a nervous shock, leading to abortion. Lakshmi filed a suit against Krishnan claiming damages.- a)Krishnan will be liable, because he owed a duty of reasonable care to everybody on the road including Lakshmi.
- b)Krishnan will not be liable, because he could not have foreseen Lakshmi suffering from nervous shock as a result of his act.
- c)Krishnan will be liable to Lakshmi because he failed to drive carefully.
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
PRINCIPLE: Everybody is under a legal obligation to take reasonable care to avoid and act or omission which he can take reasonable care to avoid and act or omission which he can foresee would injure his neighbour. The neighbour, for this purpose, is any person whom he should have in his mind as likely to be affected by his act.
FACTS: Krishnan, while driving a car at high speed in a crowded road, knocked down a cyclist. The cyclist died on the spot with a lot of blood spilling around, Lakshmi, a pregnant woman passing by, suffered from a nervous shock, leading to abortion. Lakshmi filed a suit against Krishnan claiming damages.
a)
Krishnan will be liable, because he owed a duty of reasonable care to everybody on the road including Lakshmi.
b)
Krishnan will not be liable, because he could not have foreseen Lakshmi suffering from nervous shock as a result of his act.
c)
Krishnan will be liable to Lakshmi because he failed to drive carefully.
d)
None of the above.
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
Remoteness of damage is inversely proportional to the amount of compensation and here Krishna is unable to see this consequences that is why laxmi is not entitled to compensation.
When a number is added to 20 percent of the second number, we get 150 percent of the second number. Find the ratio between the first and second number?- a)13:9
- b)12:10
- c)13:10
- d)17:10
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When a number is added to 20 percent of the second number, we get 150 percent of the second number. Find the ratio between the first and second number?
a)
13:9
b)
12:10
c)
13:10
d)
17:10
e)
None of these

|
Bank Exams India answered |
a + (20/100)*b = (150/100)*b
a:b = 13:10
a:b = 13:10
IRONIC- a)Inflexible
- b)Bitter
- c)Good-natured
- d)Disguisedly sarcastic
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Inflexible
b)
Bitter
c)
Good-natured
d)
Disguisedly sarcastic
|
|
Mainak Gupta answered |
The synonym of the word "ironic" is "disguisedly sarcastic".
Explanation:
The word "ironic" is an adjective that describes a situation or statement that is the opposite of what is expected or intended. It often involves a discrepancy between what is said and what is meant, leading to a sense of humor or mockery.
On the other hand, the phrase "disguisedly sarcastic" means that something is said or done with a hidden or subtle form of mocking or ridicule. It implies that the speaker or writer is expressing their thoughts in a way that is not immediately obvious but still conveys a sense of sarcasm.
To understand the similarity between these two terms, let's break down the meanings of both words:
- Ironic: This term refers to a situation in which the outcome is contrary to what was expected or intended. It often involves a humorous or satirical twist. For example, if someone who is always late for meetings becomes a time management expert, it would be considered ironic.
- Disguisedly sarcastic: This phrase implies that someone is expressing their thoughts or opinions in a way that is subtly mocking or ridiculing. It suggests that the sarcasm is not overt but rather concealed or disguised. For instance, if someone says, "Oh, great job! You really excelled at making a mess," it would be an example of disguised sarcasm.
Based on these definitions, we can see that both "ironic" and "disguisedly sarcastic" share a common thread of expressing a contradiction or mockery. In both cases, there is a gap between what is said or done and what is actually meant. Therefore, "disguisedly sarcastic" can be considered a synonym for "ironic".
Explanation:
The word "ironic" is an adjective that describes a situation or statement that is the opposite of what is expected or intended. It often involves a discrepancy between what is said and what is meant, leading to a sense of humor or mockery.
On the other hand, the phrase "disguisedly sarcastic" means that something is said or done with a hidden or subtle form of mocking or ridicule. It implies that the speaker or writer is expressing their thoughts in a way that is not immediately obvious but still conveys a sense of sarcasm.
To understand the similarity between these two terms, let's break down the meanings of both words:
- Ironic: This term refers to a situation in which the outcome is contrary to what was expected or intended. It often involves a humorous or satirical twist. For example, if someone who is always late for meetings becomes a time management expert, it would be considered ironic.
- Disguisedly sarcastic: This phrase implies that someone is expressing their thoughts or opinions in a way that is subtly mocking or ridiculing. It suggests that the sarcasm is not overt but rather concealed or disguised. For instance, if someone says, "Oh, great job! You really excelled at making a mess," it would be an example of disguised sarcasm.
Based on these definitions, we can see that both "ironic" and "disguisedly sarcastic" share a common thread of expressing a contradiction or mockery. In both cases, there is a gap between what is said or done and what is actually meant. Therefore, "disguisedly sarcastic" can be considered a synonym for "ironic".
Assertion (A): when you invite somebody to your house, you cannot sue him for trespass.Reason (R): one cannot enforce a right which one has voluntarily waived or abandonedCodes:- a)Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
- c)(A) is true (R) is wrong
- d)(A) is wrong (R) is wrong
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): when you invite somebody to your house, you cannot sue him for trespass.
Reason (R): one cannot enforce a right which one has voluntarily waived or abandoned
Codes:
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
c)
(A) is true (R) is wrong
d)
(A) is wrong (R) is wrong
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
A is the correct option.Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). If we take an example to prove the situation- if person A voluntarily invites person B in his house then person A can't sue B for trespass.
If the positions of the digits of a two digit number are interchanged, the number obtained is smaller than the original number by 27. If the digits of the number are in the ratio of 1:2, what is the original number?
- a)16
- b)32
- c)63
- d)48
- e)Can not be determined
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the positions of the digits of a two digit number are interchanged, the number obtained is smaller than the original number by 27. If the digits of the number are in the ratio of 1:2, what is the original number?
a)
16
b)
32
c)
63
d)
48
e)
Can not be determined

|
Divey Sethi answered |
original number – 10x + y
(10x + y) – (10y + x) = 27
9(x – y) = 27
x – y = 3
y/x = 1/2
x = 2y
y = 3, x = 6 →63
(10x + y) – (10y + x) = 27
9(x – y) = 27
x – y = 3
y/x = 1/2
x = 2y
y = 3, x = 6 →63
VENT- a)Opening
- b)Stodge
- c)End
- d)Past tense of go
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Opening
b)
Stodge
c)
End
d)
Past tense of go
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
- Meaning of vent: An opening that allows air, gas, or liquid to pass out of or into a confined space.
- Meaning of Opening: a space or gap that allows passage or access
- Meaning of Stodge: food that is heavy, filling, and high in carbohydrates
- Meaning of End: a final part of something, especially a period of time, an activity, or a story.
INDICT- a)Condemn
- b)Reprimand
- c)Accuse
- d)Allege
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Condemn
b)
Reprimand
c)
Accuse
d)
Allege

|
Sameer Rane answered |
To indict someone is to formally accuse them of a crime. A court jury can indict someone who has gone to trial and is found guilty of a crime. To accuse someone of something doesn't mean that they have broken the law, but simply that they have done something wrong.
PRINCIPLE: Interference with another’s goods in such a way as to deny the latter’s title to the goods amounts to conversion, and thus it is a civil wrong. It is an act intentionally done inconsistent with the owner’s right, though the doer may not know of, or intends to challenge the property or possession of the true owner.
FACTS: R went to a cycle-stand to park his bicycle. Seeing the stand fully occupied, he removed a few bicycles in order to rearrange a portion of the stand and make some space for his bicycle. He parked his bicycle properly, and put back all the bicycles except the one belonging to S. In fact, R was in a hurry, and therefore, he could not put back S’s bicycle. Somebody came on the way and took away S’s bicycle. The watchman of the stand did not take care of it assuming that the bicycle was not parked inside the stand. S filed a suit against R for conversion.
Q. Which of the following derivations is CORRECT?
- a)R could not be held liable for the negligence of the watchman.
- b)S would succeed because R’s act led to the stealing of his bicycle.
- c)S would not succeed because R did not take away the bicycle himself.
- d)S would not succeed because R’s intention was not bad.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
PRINCIPLE: Interference with another’s goods in such a way as to deny the latter’s title to the goods amounts to conversion, and thus it is a civil wrong. It is an act intentionally done inconsistent with the owner’s right, though the doer may not know of, or intends to challenge the property or possession of the true owner.
FACTS: R went to a cycle-stand to park his bicycle. Seeing the stand fully occupied, he removed a few bicycles in order to rearrange a portion of the stand and make some space for his bicycle. He parked his bicycle properly, and put back all the bicycles except the one belonging to S. In fact, R was in a hurry, and therefore, he could not put back S’s bicycle. Somebody came on the way and took away S’s bicycle. The watchman of the stand did not take care of it assuming that the bicycle was not parked inside the stand. S filed a suit against R for conversion.
Q. Which of the following derivations is CORRECT?
Q. Which of the following derivations is CORRECT?
a)
R could not be held liable for the negligence of the watchman.
b)
S would succeed because R’s act led to the stealing of his bicycle.
c)
S would not succeed because R did not take away the bicycle himself.
d)
S would not succeed because R’s intention was not bad.
|
|
Dia Mehta answered |
According to the principle given here it is clear that R had made interference with S’s property.
- Interference with another’s goods in such a way as to deny the latter’s title to the goods amounts to conversion, and thus it is a civil wrong.
- It is an act intentionally done inconsistent with the owner’s right, though the doer may not know of, or intends to challenge the property or possession of the true owner.
PRINCIPLE: Any direct physical interference with the goods in somebody’s possession without lawful justification is called trespass to goods.FACTS: A purchased a car from a person who had no little to it and had sent it to a garage for repair. X, believing, wrongly, that the car was his, removed it from the garage.- a)X can be held responsible for trespass to goods.
- b)X cannot be held responsible for trespass to good as he was under a wrong belief.
- c)X has not committed any wrong.
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
PRINCIPLE: Any direct physical interference with the goods in somebody’s possession without lawful justification is called trespass to goods.
FACTS: A purchased a car from a person who had no little to it and had sent it to a garage for repair. X, believing, wrongly, that the car was his, removed it from the garage.
a)
X can be held responsible for trespass to goods.
b)
X cannot be held responsible for trespass to good as he was under a wrong belief.
c)
X has not committed any wrong.
d)
None of the above.
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
It is clear from the principle,
- Any direct physical interference with the goods in somebody’s possession without lawful justification is called trespass to goods.
X, believing, wrongly, that the car was his, removed it from the garage. Wrong belief is not a remedy available in torts.
Sum of eight consecutive odd numbers is 656. Average of four consecutive even numbers is 87. What is the sum of the largest even number and largest odd number?- a)171
- b)191
- c)101
- d)181
- e)179
Correct answer is option 'E'. Can you explain this answer?
Sum of eight consecutive odd numbers is 656. Average of four consecutive even numbers is 87. What is the sum of the largest even number and largest odd number?
a)
171
b)
191
c)
101
d)
181
e)
179
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
odd numbers — x-8, x-6, x-4, x-2, x, x+2, x+4, x+6
x-8 + x-6 + x-4 + x-2 + x + x+2 + x+4 + x+6 = 656
8x – 8 =656
x = 83
Even numbers — y-2, y, y+2, y+4
4y + 4 = 87 * 4
y = 86
sum of the largest even number and odd number = 89 + 90 = 179
x-8 + x-6 + x-4 + x-2 + x + x+2 + x+4 + x+6 = 656
8x – 8 =656
x = 83
Even numbers — y-2, y, y+2, y+4
4y + 4 = 87 * 4
y = 86
sum of the largest even number and odd number = 89 + 90 = 179
A number is divided by 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6, reminder in each case is one. But the number is exactly divisible by 7. The number lies between 250 and 350, the sum of digits of the number will be
- a)4
- b)7
- c)6
- d)10
- e)Can not be determined
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A number is divided by 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6, reminder in each case is one. But the number is exactly divisible by 7. The number lies between 250 and 350, the sum of digits of the number will be
a)
4
b)
7
c)
6
d)
10
e)
Can not be determined
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
To solve this problem, we need to find a number that satisfies the following conditions:
- When divided by 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6, the remainder is 1.
- The number is divisible by 7.
- The number lies between 250 and 350.
Let's start by finding the least common multiple (LCM) of 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6, which is the smallest number divisible by all of these numbers.
LCM(2, 3, 4, 5, 6) = 60
We need to find a number of the form 7k, where k is an integer, that leaves a remainder of 1 when divided by 60. The numbers in this sequence can be expressed as 60n + 1, where n is an integer.
Now, let's find the first few numbers of the form 60n + 1 that are divisible by 7 and lie between 250 and 350:
- For n = 4: 60(4) + 1 = 241 (not divisible by 7)
- For n = 5: 60(5) + 1 = 301 (divisible by 7)
So, the number we're looking for is 301.
Now, let's find the sum of its digits: 3 + 0 + 1 = 4
Therefore, the sum of the digits of the number is 4.
Guess the correct Synonym of the following word:
CORPULENT
- a)Lean
- b)Gaunt
- c)Emaciated
- d)Obese
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Guess the correct Synonym of the following word:
CORPULENT
a)
Lean
b)
Gaunt
c)
Emaciated
d)
Obese

|
Ishani Rane answered |
CORPULENT means large of body. Obese means Obesity occurs over time when you eat more calories than you use. The balance between calories-in and calories-out differs for each person.
PRINCIPLE: A person has no legal remedy for an injury caused by an act to which he has consentedFACTS: R, a cricket enthusiast, purchases a ticket to watch a T20 match organized by the Indian Premier League (IPL). During the match, a ball struck for six hits R on his body and injures him. He sues IPL for compensation for the medical expenses. Which of the following derivations is CORRECT?- a)R should be compensated as he purchased the ticket to get entertainment and not get injured.
- b)R would fail in his action, as he voluntarily exposed himself to the risk.
- c)IPL would be liable as it did not ensure that the spectators were protected from the risk of such injuries.
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
PRINCIPLE: A person has no legal remedy for an injury caused by an act to which he has consented
FACTS: R, a cricket enthusiast, purchases a ticket to watch a T20 match organized by the Indian Premier League (IPL). During the match, a ball struck for six hits R on his body and injures him. He sues IPL for compensation for the medical expenses. Which of the following derivations is CORRECT?
a)
R should be compensated as he purchased the ticket to get entertainment and not get injured.
b)
R would fail in his action, as he voluntarily exposed himself to the risk.
c)
IPL would be liable as it did not ensure that the spectators were protected from the risk of such injuries.
d)
None of the above.
|
|
Tejaswini nayar answered |
Principle:
A person has no legal remedy for an injury caused by an act to which he has consented.
Facts:
R, a cricket enthusiast, purchases a ticket to watch a T20 match organized by the Indian Premier League (IPL). During the match, a ball struck for six hits R on his body and injures him. He sues IPL for compensation for the medical expenses.
Correct derivation:
The correct derivation is option 'B', i.e., R would fail in his action, as he voluntarily exposed himself to the risk.
Explanation:
When R purchased the ticket for the T20 match, he voluntarily exposed himself to the risk of getting hit by a ball. It is a well-known fact that cricket is a sport played with a hard ball, and there is always a risk of getting hit by a ball while watching the game. By purchasing a ticket and entering the stadium, R has impliedly consented to the risk of getting hit by a ball.
Therefore, R has no legal remedy for the injury caused by the ball hitting him as he had already consented to the risk while watching the match. IPL is not liable for the injury caused to R as it does not owe any duty of care to R in this case. IPL has taken all reasonable steps to ensure the safety of the spectators, and R had voluntarily exposed himself to the risk of getting hit by a ball.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, R cannot claim compensation from IPL for the injury caused by the ball hitting him as he had already consented to the risk by purchasing the ticket and entering the stadium. Therefore, option 'B' is the correct derivation in this case.
A person has no legal remedy for an injury caused by an act to which he has consented.
Facts:
R, a cricket enthusiast, purchases a ticket to watch a T20 match organized by the Indian Premier League (IPL). During the match, a ball struck for six hits R on his body and injures him. He sues IPL for compensation for the medical expenses.
Correct derivation:
The correct derivation is option 'B', i.e., R would fail in his action, as he voluntarily exposed himself to the risk.
Explanation:
When R purchased the ticket for the T20 match, he voluntarily exposed himself to the risk of getting hit by a ball. It is a well-known fact that cricket is a sport played with a hard ball, and there is always a risk of getting hit by a ball while watching the game. By purchasing a ticket and entering the stadium, R has impliedly consented to the risk of getting hit by a ball.
Therefore, R has no legal remedy for the injury caused by the ball hitting him as he had already consented to the risk while watching the match. IPL is not liable for the injury caused to R as it does not owe any duty of care to R in this case. IPL has taken all reasonable steps to ensure the safety of the spectators, and R had voluntarily exposed himself to the risk of getting hit by a ball.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, R cannot claim compensation from IPL for the injury caused by the ball hitting him as he had already consented to the risk by purchasing the ticket and entering the stadium. Therefore, option 'B' is the correct derivation in this case.
PRINCIPLE: Res ipsa loquitur, i.e., the thing speaks for itself.FACTS: Seema got herself operated for the removal of her uterus in the defendant’s hospital, as there was diagnosed to be a cyst in one of her ovaries. Due the negligence of the surgeon, who performed the operation, abdominal pack was left in her abdomen. The same was removed by a second surgery.- a)Surgeon cannot be held responsible because it is merely a human error
- b)Surgeon can be held responsible but Seema will have to prove in the court of law that the surgeon was grossly negligent
- c)Surgeon will be responsible and Seema need not to prove surgeon’s negligence because presence of abdominal pack in her abdomen is sufficient proof therefore
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
PRINCIPLE: Res ipsa loquitur, i.e., the thing speaks for itself.
FACTS: Seema got herself operated for the removal of her uterus in the defendant’s hospital, as there was diagnosed to be a cyst in one of her ovaries. Due the negligence of the surgeon, who performed the operation, abdominal pack was left in her abdomen. The same was removed by a second surgery.
a)
Surgeon cannot be held responsible because it is merely a human error
b)
Surgeon can be held responsible but Seema will have to prove in the court of law that the surgeon was grossly negligent
c)
Surgeon will be responsible and Seema need not to prove surgeon’s negligence because presence of abdominal pack in her abdomen is sufficient proof therefore
d)
None of the above
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
Surgeon left an abdominal pack in her abdomen which is a fact and it speaks for itself and hence sufficient enough for the case.
Two numbers such that the sum of twice the first number and thrice the second number is 100 and the sum of thrice the first number and twice the second number is 120. Which is larger number?- a)64
- b)72
- c)65
- d)32
- e)None of the Above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two numbers such that the sum of twice the first number and thrice the second number is 100 and the sum of thrice the first number and twice the second number is 120. Which is larger number?
a)
64
b)
72
c)
65
d)
32
e)
None of the Above
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
2x + 3y = 100 –(i)
3x + 2y = 120 –(ii)
By Solving eqn (i) and (ii)
x = 32, y = 12
3x + 2y = 120 –(ii)
By Solving eqn (i) and (ii)
x = 32, y = 12
INEBRIATE- a)Dreamy
- b)Stupefied
- c)Unsteady
- d)Drunken
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Dreamy
b)
Stupefied
c)
Unsteady
d)
Drunken

|
Dhruv Mehra answered |
When you want to use an impressive word to say that someone is drunk, go ahead and use inebriated. If you like, you can also use it to refer to someone who is intoxicated with substances other than alcohol, but at its heart, inebriated simply means tanked, blotto, stinko, drunk. In more recent years, it has taken on the sense of being particularly energized or zany and exhilarated with drunkenness, but still drunk.
PRINCIPLE: Trespass to land means direct interference with the possession of land without lawful justification. Trespass could be committed either by a person himself entering the land of another person or doing the same through some tangible object(s).FACTS: A throws some stones upon his neighbor’s (B’s) premises.Which of the following derivations is CORRECT?- a)A has committed trespass.
- b)A has not committed trespass, as he has not entered B’s premises.
- c)A has committed nuisance.
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
PRINCIPLE: Trespass to land means direct interference with the possession of land without lawful justification. Trespass could be committed either by a person himself entering the land of another person or doing the same through some tangible object(s).
FACTS: A throws some stones upon his neighbor’s (B’s) premises.Which of the following derivations is CORRECT?
a)
A has committed trespass.
b)
A has not committed trespass, as he has not entered B’s premises.
c)
A has committed nuisance.
d)
None of the above.

|
Nishant Upadhyay answered |
According to the principle "Trespass could be by entering the land himself or doing the same by tangible objects" Tangible objects are the objects which can be touched and throwing stuff like a stone is a tangible object. Hence A has committed trespass
Principle – Volenti non fit injuria - No remedy can be claimed for harm caused through voluntary consent.Facts – On a hot, sunny day, Avtar Singh, a traffic policeman wishes to take a break from his work on the Jangpura-Jayanagar junction. He sees a grocery store nearby, and decides to buy some refreshments. To get to the grocery store, he must cross the busy road first. While doing so, he sees that a child has suddenly jumped down from the pavement on the other side, and is attempting to cross the road, despite vehicles hurtling past at a high speed. On seeing an approaching car that the child does not seem to be aware of, Avtar lunges forward and pushes the child out of the way. However, the driver of the car, Mr. Takwani, is unable to stop the car in time and hits Avtar, who sustains serious injuries, including a torn ligament. This means that Avtar will not be able to perform his duties as a traffic policeman for at least six months. He wishes to sue Takwani and claim damages for his loss in income, but Takwani asserts that there was a green light, and he had committed no fault in driving at a reasonable speed. It was Avtar who had suddenly lunged forward, giving him no time to apply the brakes! Decide.- a)Avtar voluntarily lunged forward to save the child from being hit by the approaching car, fully aware that there were vehicles approaching at high speeds. Therefore, he cannot claim damages.
- b)Avtar had no option but to put himself in harm‘s way, and save the innocent child. Takwani should have been more careful while driving, and hence, he must pay damages for the harm suffered by Avtar.
- c)Avtar was being unnecessarily noble, his act was entirely voluntary, so he cannot claim any damages.
- d)Takwani was at fault, and must be prosecuted for rash and reckless driving.Ans. A
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Principle – Volenti non fit injuria - No remedy can be claimed for harm caused through voluntary consent.
Facts – On a hot, sunny day, Avtar Singh, a traffic policeman wishes to take a break from his work on the Jangpura-Jayanagar junction. He sees a grocery store nearby, and decides to buy some refreshments. To get to the grocery store, he must cross the busy road first. While doing so, he sees that a child has suddenly jumped down from the pavement on the other side, and is attempting to cross the road, despite vehicles hurtling past at a high speed. On seeing an approaching car that the child does not seem to be aware of, Avtar lunges forward and pushes the child out of the way. However, the driver of the car, Mr. Takwani, is unable to stop the car in time and hits Avtar, who sustains serious injuries, including a torn ligament. This means that Avtar will not be able to perform his duties as a traffic policeman for at least six months. He wishes to sue Takwani and claim damages for his loss in income, but Takwani asserts that there was a green light, and he had committed no fault in driving at a reasonable speed. It was Avtar who had suddenly lunged forward, giving him no time to apply the brakes! Decide.
a)
Avtar voluntarily lunged forward to save the child from being hit by the approaching car, fully aware that there were vehicles approaching at high speeds. Therefore, he cannot claim damages.
b)
Avtar had no option but to put himself in harm‘s way, and save the innocent child. Takwani should have been more careful while driving, and hence, he must pay damages for the harm suffered by Avtar.
c)
Avtar was being unnecessarily noble, his act was entirely voluntary, so he cannot claim any damages.
d)
Takwani was at fault, and must be prosecuted for rash and reckless driving.Ans. A

|
Nishant Upadhyay answered |
As simple as it is, Volenti Non Fit Injuria - No d... moreamages for harm caused by voluntary actions.Avtar jumped before the car by his own wish to save the child so he can't clam any damages whatsoever. There is no mention of Takwani being rash so option D and B are out.between option A and C, A is the better pick because it justifies the whole thing properly and unnecessarily noble is just not right in option C
CANNY- a)Obstinate
- b)Handsome
- c)Clever
- d)Stout
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Obstinate
b)
Handsome
c)
Clever
d)
Stout

|
Ishani Rane answered |
Canny : intelligent and showing good judgement especially in business or politics.
Stout: Fat
Handsome :attractive
Obstinate: refusing to change your opinion,behaviour...
So answer is clever.
WARRIOR- a)Soldier
- b)Sailor
- c)Pirate
- d)Spy
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Soldier
b)
Sailor
c)
Pirate
d)
Spy
|
|
Bhavya Singh answered |
Meaning of Warrior: a brave or experienced soldier or fighter.
Find out the Synonym of the following wordJEOPARDY- a)Safe
- b)Hunting
- c)Endangered
- d)Extinct
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find out the Synonym of the following word
JEOPARDY
a)
Safe
b)
Hunting
c)
Endangered
d)
Extinct
|
|
Meera Rana answered |
- Jeopardy means danger of loss, harm, or failure.
- Safe means free from danger; not able to be hurt
- Hunting means the act of following and killing wild animals or birds as a sport or for food
- Endangered means (used about animals, plants, etc.) in danger of disappearing from the world (becoming extinct)
- Extinct means (used about a type of animal, plant, etc.) no longer existing
CAPACIOUS- a)Limited
- b)Caring
- c)Foolish
- d)Changeable
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
CAPACIOUS
a)
Limited
b)
Caring
c)
Foolish
d)
Changeable
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
'Capacious' means large or extensive.
The correct antonym of the given word is option D, 'limited' which means restricted or insufficient.
Options A, B and C are incorrect because 'changeable' means uncertain or variable, 'foolish' means stupid and 'caring' means heeding or concerned.
The correct antonym of the given word is option D, 'limited' which means restricted or insufficient.
Options A, B and C are incorrect because 'changeable' means uncertain or variable, 'foolish' means stupid and 'caring' means heeding or concerned.
Principle - Violation of a legal right, with or without actual damage, gives rise to a tort. However, actual damage without violation of a legal right does not give rise to tortuous liability.Facts – Mr. Akhil lives in a locality that lies just off the main road, which supports heavy traffic and is one of the most important roads in his city. The street on which his house is located is, however, quiet and peaceful, and Akhil is pleased to live there. One day, some road repair works are undertaken on the main road, and as a result, the municipal authorities decide to divert the traffic through the street on which Akhil resides. Akhil is greatly disturbed and annoyed by the constant sound of the vehicles, honking, and traffic jams along the narrow street. He wishes to sue the municipal authorities for the nuisance caused by this diversion of traffic. Will he succeed?- a)Yes, Akhil will succeed, as his legal right to a peaceful environment is violated by the constant noise of the vehicles.
- b)Yes, Akhil will succeed, as his mental peace has been affected by the act of the municipal authorities.
- c)No, Akhil has no legal right to enjoy a peaceful street, so there has been no violation of a legal right, despite actual damage. So, he cannot succeed in a tortious claim.
- d)Facts are inadequate to decide.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Principle - Violation of a legal right, with or without actual damage, gives rise to a tort. However, actual damage without violation of a legal right does not give rise to tortuous liability.
Facts – Mr. Akhil lives in a locality that lies just off the main road, which supports heavy traffic and is one of the most important roads in his city. The street on which his house is located is, however, quiet and peaceful, and Akhil is pleased to live there. One day, some road repair works are undertaken on the main road, and as a result, the municipal authorities decide to divert the traffic through the street on which Akhil resides. Akhil is greatly disturbed and annoyed by the constant sound of the vehicles, honking, and traffic jams along the narrow street. He wishes to sue the municipal authorities for the nuisance caused by this diversion of traffic. Will he succeed?
a)
Yes, Akhil will succeed, as his legal right to a peaceful environment is violated by the constant noise of the vehicles.
b)
Yes, Akhil will succeed, as his mental peace has been affected by the act of the municipal authorities.
c)
No, Akhil has no legal right to enjoy a peaceful street, so there has been no violation of a legal right, despite actual damage. So, he cannot succeed in a tortious claim.
d)
Facts are inadequate to decide.
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
Violation of a legal right, with or without actual damage, gives rise to a tort. However, actual damage without violation of a legal right does not give rise to tortuous liability.
Akhil has no legal right to enjoy a peaceful street, so there has been no violation of a legal right, despite actual damage. So, he cannot succeed in a tortious claim.
Practice Quiz or MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) with solutions are available for Practice, which would help you prepare for "Antonyms" under Verbal Aptitude. You can practice these practice quizzes as per your speed and improvise the topic. The same topic is covered under various competitive examinations like - CAT, GMAT, Bank PO, SSC and other competitive examinations. Q. Select the antonym of the given following words:VICTORIOUS- a)Defeated
- b)Annexed
- c)Destroyed
- d)Vanquished
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Practice Quiz or MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) with solutions are available for Practice, which would help you prepare for "Antonyms" under Verbal Aptitude. You can practice these practice quizzes as per your speed and improvise the topic. The same topic is covered under various competitive examinations like - CAT, GMAT, Bank PO, SSC and other competitive examinations.
Q. Select the antonym of the given following words:
VICTORIOUS
a)
Defeated
b)
Annexed
c)
Destroyed
d)
Vanquished
|
|
Meera Rana answered |
Victorious is an antonym for defeated in beaten topic.
Chapter doubts & questions for Week 4 - Weekly Test for CLAT UG 2025 is part of CLAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the CLAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for CLAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Week 4 - Weekly Test for CLAT UG in English & Hindi are available as part of CLAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for CLAT Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup