All Exams >
CLAT >
4 Months Preparation Course for CLAT UG >
All Questions
All questions of Physics for CLAT Exam
The equation of a wave disturbance is given as :
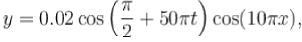 where X and y are in metres and f in seconds. Choose the wrong statement:
where X and y are in metres and f in seconds. Choose the wrong statement:- a)Node occurs at x = 0.15 m
- b)The wavelength is 0.2 m
- c)Antinode occurs at x = 0.3 m
- d)The speed of the constituent waves is 5 m/s
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The equation of a wave disturbance is given as :
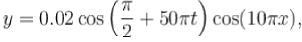 where X and y are in metres and f in seconds. Choose the wrong statement:
where X and y are in metres and f in seconds. Choose the wrong statement:
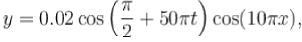 where X and y are in metres and f in seconds. Choose the wrong statement:
where X and y are in metres and f in seconds. Choose the wrong statement:a)
Node occurs at x = 0.15 m
b)
The wavelength is 0.2 m
c)
Antinode occurs at x = 0.3 m
d)
The speed of the constituent waves is 5 m/s

|
Ameya Rane answered |
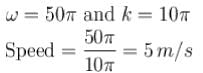
The correct answer is: The speed of the constituent waves is 5 m/s
Consider the following statements about a computer named “ Greenware” .
1. ‘Greenware’ is completely free of both hazardous PVC (Polyvinylchloride) and BFR (brominated flame-retardants).
2. Manufacturing of ‘Greenware’ can be a special action like replacing all standard light bulbs with CFLs or a more general application to live more ecologically.Q. Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a)1 only
- b)2 only
- c)Both 1 and 2
- d)Neither 1 nor 2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements about a computer named “ Greenware” .
1. ‘Greenware’ is completely free of both hazardous PVC (Polyvinylchloride) and BFR (brominated flame-retardants).
2. Manufacturing of ‘Greenware’ can be a special action like replacing all standard light bulbs with CFLs or a more general application to live more ecologically.
1. ‘Greenware’ is completely free of both hazardous PVC (Polyvinylchloride) and BFR (brominated flame-retardants).
2. Manufacturing of ‘Greenware’ can be a special action like replacing all standard light bulbs with CFLs or a more general application to live more ecologically.
Q. Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 only
b)
2 only
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
Neither 1 nor 2

|
Sounak Basu answered |
‘Greenware’ is completely free of both hazardous PVC and BFR and its manufacturing can be a special action like replacing all standard light bulbs with CFLs or a more general application to live more ecologically.
When a body falls from an aeroplane, there is increase in its –
- a)Acceleration
- b)Mass
- c)Kinetic energy
- d)Potential energy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When a body falls from an aeroplane, there is increase in its –
a)
Acceleration
b)
Mass
c)
Kinetic energy
d)
Potential energy
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
- The energy possessed by a body by its motion is called kinetic energy.
- K.E = ½ × mv2 where, m = mass, v = velocity, K.E = kinetic energy.
- Potential Energy is possessed by its position or configuration.
- When a body falls from an aeroplane its velocity increases, so it's kinetic energy increases (K.E = ½ × mv2).
Correct option is C. Kinetic Energy
A computer cookie is a small text file placed on computers by a website. Which among the following can be the use of cookie?
1. Cookies can carry viruses.
2. Cookies can be used to maintain data.
3. Cookies can be used to track internet user’s web browsing.
4. Cookies can install malware on the host computer. - a)1 and 2 only
- b)2 and 3 only
- c)3 and 4 only
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A computer cookie is a small text file placed on computers by a website. Which among the following can be the use of cookie?
1. Cookies can carry viruses.
2. Cookies can be used to maintain data.
3. Cookies can be used to track internet user’s web browsing.
4. Cookies can install malware on the host computer.
1. Cookies can carry viruses.
2. Cookies can be used to maintain data.
3. Cookies can be used to track internet user’s web browsing.
4. Cookies can install malware on the host computer.
a)
1 and 2 only
b)
2 and 3 only
c)
3 and 4 only
d)
All the above
|
|
Mayank Joshi answered |
Activity.
4. Cookies can personalize website content.
5. Cookies can store login information.
6. Cookies can improve website performance.
The correct options are 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6. Cookies are not capable of carrying viruses.
4. Cookies can personalize website content.
5. Cookies can store login information.
6. Cookies can improve website performance.
The correct options are 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6. Cookies are not capable of carrying viruses.
What is a keyboard used in a computer for?- a)To input text and numbers and send commands to the computer.
- b)To create new keys to use with your computer.
- c)To open the computer up.
- d)To create pictures and images and send them to your computer.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is a keyboard used in a computer for?
a)
To input text and numbers and send commands to the computer.
b)
To create new keys to use with your computer.
c)
To open the computer up.
d)
To create pictures and images and send them to your computer.

|
Saptarshi Malik answered |
A computer keyboard, a typewriter–style device having a particular arrangement of buttons or keys, is a main input device. It inputs text, numbers and sends commands to the computer.
Consider the following statements:
Assertion (A): Space Based Solar Power (SBSP) is considered to be made a national goal.
Reason (R): Supply of SBSP is 99% uninterrupted throughout the year, besides the enormity of energy availability.
Q. Select the correct answers from the codes given below:- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
Assertion (A): Space Based Solar Power (SBSP) is considered to be made a national goal.
Reason (R): Supply of SBSP is 99% uninterrupted throughout the year, besides the enormity of energy availability.
Q. Select the correct answers from the codes given below:
Assertion (A): Space Based Solar Power (SBSP) is considered to be made a national goal.
Reason (R): Supply of SBSP is 99% uninterrupted throughout the year, besides the enormity of energy availability.
Q. Select the correct answers from the codes given below:
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.

|
Ipsita Bajaj answered |
Space based solar power (SBSP) is considered to be made a national goal, because its supply is 99% uninterrupted throughout the year, besides the enormity of energy availability.
The frequency changes by 10% as the source approaches a stationary observer with constant speed vs. What would be the percentage change in frequency as the source recedes the observer with the same speed ? Given, that vs « v ( v = speed of sound in air)- a)16.7%
- b)8.5%
- c)14.3%
- d)20%
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The frequency changes by 10% as the source approaches a stationary observer with constant speed vs. What would be the percentage change in frequency as the source recedes the observer with the same speed ? Given, that vs « v ( v = speed of sound in air)
a)
16.7%
b)
8.5%
c)
14.3%
d)
20%
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
A team of scientists at NASA with the European Space Agency are working to probe dark energy or the existence of dark matter. Consider the following statements in this regard.
1. Dark matter is called so because it does not interact with light.
2. Dark matter interacts with ordinary matter through gravity and binds galaxies together like an invisible glue.
3. While dark matter pulls matter together, dark energy pushes the universe apart at ever increasing speed. 4. Dark matters are potentially effective in many dignostic devices such as PET scanners.Q. Which of the statements given above are correct?- a)1, 2 and 3 only
- b)2, 3 and 4 only
- c)1, 3 and 4 only
- d)1, 2, 3 and 4.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A team of scientists at NASA with the European Space Agency are working to probe dark energy or the existence of dark matter. Consider the following statements in this regard.
1. Dark matter is called so because it does not interact with light.
2. Dark matter interacts with ordinary matter through gravity and binds galaxies together like an invisible glue.
3. While dark matter pulls matter together, dark energy pushes the universe apart at ever increasing speed. 4. Dark matters are potentially effective in many dignostic devices such as PET scanners.
1. Dark matter is called so because it does not interact with light.
2. Dark matter interacts with ordinary matter through gravity and binds galaxies together like an invisible glue.
3. While dark matter pulls matter together, dark energy pushes the universe apart at ever increasing speed. 4. Dark matters are potentially effective in many dignostic devices such as PET scanners.
Q. Which of the statements given above are correct?
a)
1, 2 and 3 only
b)
2, 3 and 4 only
c)
1, 3 and 4 only
d)
1, 2, 3 and 4.

|
Saptarshi Malik answered |
Dark matter is a type of matter hypothesized in astronomy and cosmilogy to account for a large part of the mass that appears missing from the universe, it does not interact with light. It is also hypothesized that it interacts with ordinary matter through gravity and binds galaxies, and it pushes the universe apart.
A war of succession was fought among the sons of Shahjahan in 1657-58 A.D. Who were they?- a)Kam Baksh, Murad, Dara, Aurangzeb
- b)Aurangzeb, Dara, Shuja, Kam Baksh
- c)Dara, Aurangzeb, Murad, Shuja
- d)Dara, Kamran, Aurangzeb, Murad
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A war of succession was fought among the sons of Shahjahan in 1657-58 A.D. Who were they?
a)
Kam Baksh, Murad, Dara, Aurangzeb
b)
Aurangzeb, Dara, Shuja, Kam Baksh
c)
Dara, Aurangzeb, Murad, Shuja
d)
Dara, Kamran, Aurangzeb, Murad
|
|
Deepak Kapoor answered |
The sons of Shahjahan who fought in the war of succession in 1657-58 A.D. were Dara Shikoh, Shuja, Aurangzeb, and Murad. These four brothers were all contenders for the Mughal throne after Shahjahan's illness and eventual death in 1657. The war of succession lasted for over a year and ultimately resulted in Aurangzeb's victory and his ascension to the Mughal throne.
Consider the following statements with respect to Intelligent Flight Control System (IFCS):
1. It is developed by NASA
2. It is used in NF-15B aircraft
3. The IFCS Generation-I flight was first tested in 2003.
4. An artificial neural network is used in this control sytem.Q. Which of the following statement codes are correct?- a)1 and 2 only
- b)2, 3 and 4 only
- c)1, 2, 3 and 4
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements with respect to Intelligent Flight Control System (IFCS):
1. It is developed by NASA
2. It is used in NF-15B aircraft
3. The IFCS Generation-I flight was first tested in 2003.
4. An artificial neural network is used in this control sytem.
1. It is developed by NASA
2. It is used in NF-15B aircraft
3. The IFCS Generation-I flight was first tested in 2003.
4. An artificial neural network is used in this control sytem.
Q. Which of the following statement codes are correct?
a)
1 and 2 only
b)
2, 3 and 4 only
c)
1, 2, 3 and 4
d)
None of these
|
|
Diya Singh answered |
Statement Analysis:
Let's analyze each statement one by one:
Statement 1: It is developed by NASA.
Statement 2: It is used in NF-15B aircraft.
Statement 3: The IFCS Generation-I flight was first tested in 2003.
Statement 4: An artificial neural network is used in this control system.
Explanation:
Statement 1: It is developed by NASA.
The Intelligent Flight Control System (IFCS) is not specifically developed by NASA. It is a general term used to describe advanced flight control systems that incorporate intelligent algorithms and technologies.
Therefore, statement 1 is incorrect.
Statement 2: It is used in NF-15B aircraft.
The NF-15B aircraft is a modified version of the F-15B Eagle aircraft used for research and development purposes. It has been used by NASA and other organizations for various flight experiments and testing. While it is possible that an Intelligent Flight Control System (IFCS) could be used in the NF-15B aircraft, the statement does not provide enough information to confirm this.
Therefore, statement 2 is ambiguous and cannot be determined as correct or incorrect.
Statement 3: The IFCS Generation-I flight was first tested in 2003.
The statement mentions the testing of the IFCS Generation-I flight in 2003. However, there is no specific information available to confirm or refute this claim. Without any supporting evidence, we cannot determine the accuracy of this statement.
Therefore, statement 3 is ambiguous and cannot be determined as correct or incorrect.
Statement 4: An artificial neural network is used in this control system.
An artificial neural network (ANN) is a type of computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks. ANNs have been widely used in various fields, including aerospace engineering, for tasks such as control systems, pattern recognition, and optimization. It is possible that an ANN could be used in an Intelligent Flight Control System (IFCS) to enhance its capabilities and performance.
Therefore, statement 4 is plausible and could be correct.
Conclusion:
Based on the analysis, statement 1 is incorrect, statement 2 and 3 are ambiguous, and statement 4 is plausible. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C' - 1, 2, 3, and 4.
Let's analyze each statement one by one:
Statement 1: It is developed by NASA.
Statement 2: It is used in NF-15B aircraft.
Statement 3: The IFCS Generation-I flight was first tested in 2003.
Statement 4: An artificial neural network is used in this control system.
Explanation:
Statement 1: It is developed by NASA.
The Intelligent Flight Control System (IFCS) is not specifically developed by NASA. It is a general term used to describe advanced flight control systems that incorporate intelligent algorithms and technologies.
Therefore, statement 1 is incorrect.
Statement 2: It is used in NF-15B aircraft.
The NF-15B aircraft is a modified version of the F-15B Eagle aircraft used for research and development purposes. It has been used by NASA and other organizations for various flight experiments and testing. While it is possible that an Intelligent Flight Control System (IFCS) could be used in the NF-15B aircraft, the statement does not provide enough information to confirm this.
Therefore, statement 2 is ambiguous and cannot be determined as correct or incorrect.
Statement 3: The IFCS Generation-I flight was first tested in 2003.
The statement mentions the testing of the IFCS Generation-I flight in 2003. However, there is no specific information available to confirm or refute this claim. Without any supporting evidence, we cannot determine the accuracy of this statement.
Therefore, statement 3 is ambiguous and cannot be determined as correct or incorrect.
Statement 4: An artificial neural network is used in this control system.
An artificial neural network (ANN) is a type of computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks. ANNs have been widely used in various fields, including aerospace engineering, for tasks such as control systems, pattern recognition, and optimization. It is possible that an ANN could be used in an Intelligent Flight Control System (IFCS) to enhance its capabilities and performance.
Therefore, statement 4 is plausible and could be correct.
Conclusion:
Based on the analysis, statement 1 is incorrect, statement 2 and 3 are ambiguous, and statement 4 is plausible. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C' - 1, 2, 3, and 4.
ISRO space vision 2025 includes:
1. Satellite based communication and navigation systems mainly for rural connectivity.
2. Space science mission for better understanding of solar system and universe.
3. Reusable Launch Vehicles Technology demonstrator mission leading to Two-stageTo-orbit-(TSTO).
4. Planetary explorations to Mars and Venus. Which of the above statements is/are correct?- a)1 and 2
- b)2 and 4
- c)1, 2 and 3
- d)2, 3 and 4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
ISRO space vision 2025 includes:
1. Satellite based communication and navigation systems mainly for rural connectivity.
2. Space science mission for better understanding of solar system and universe.
3. Reusable Launch Vehicles Technology demonstrator mission leading to Two-stageTo-orbit-(TSTO).
4. Planetary explorations to Mars and Venus. Which of the above statements is/are correct?
1. Satellite based communication and navigation systems mainly for rural connectivity.
2. Space science mission for better understanding of solar system and universe.
3. Reusable Launch Vehicles Technology demonstrator mission leading to Two-stageTo-orbit-(TSTO).
4. Planetary explorations to Mars and Venus. Which of the above statements is/are correct?
a)
1 and 2
b)
2 and 4
c)
1, 2 and 3
d)
2, 3 and 4

|
Arnab Saha answered |
ISRO space vision 2025 includes satellite based communication and navigation systems mainly for rural connectivity.
A standing wave is maintained in a homogeneous string of cross-sectional area a and density p. It is formed by superposition of two waves travelling in opposite directions given by the equation.

The total mechanical energy confined between the sections corresponding to the adjacent antinodes is :- a)
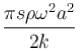
- b)
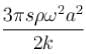
- c)
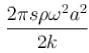
- d)
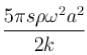
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A standing wave is maintained in a homogeneous string of cross-sectional area a and density p. It is formed by superposition of two waves travelling in opposite directions given by the equation.

The total mechanical energy confined between the sections corresponding to the adjacent antinodes is :

The total mechanical energy confined between the sections corresponding to the adjacent antinodes is :
a)
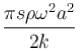
b)
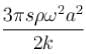
c)
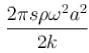
d)
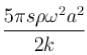

|
Lekshmi Deshpande answered |
Distance between two adjacent antinodes is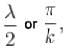
Volume of string between two adjacent antinodes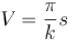
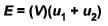
Here, u is the energy density (energy per unit volume) which is equal to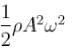
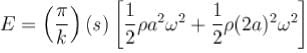
The correct answer is :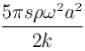
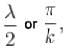
Volume of string between two adjacent antinodes
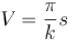
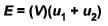
Here, u is the energy density (energy per unit volume) which is equal to
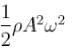
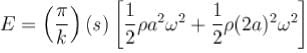
The correct answer is :
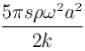
Orbital decay, a process of prolonged reduction in the attitude of a Satellite’s Orbit is caused by which of the following reasons?
1. Atmospheric drag
2. Tides
3. Gravitational pull Correct - a)1 only
- b)3 only
- c)1 and 3 only
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Orbital decay, a process of prolonged reduction in the attitude of a Satellite’s Orbit is caused by which of the following reasons?
1. Atmospheric drag
2. Tides
3. Gravitational pull Correct
1. Atmospheric drag
2. Tides
3. Gravitational pull Correct
a)
1 only
b)
3 only
c)
1 and 3 only
d)
1, 2 and 3

|
Surbhi Basu answered |
Orbital decay, a process of prolonged reduction in the altitude of a satellite’s orbit is caused due to atmospheric drag, tides and gravitational pull.
Consider the following statements with respect to the new Remote Sensing Data Policy:
1. Agencies other than ISRO can also be nodal agencies for remote sensing.
2. All remote sensing imagery and data up to one meter resolution will be made freely available.
3. The old 2001 policy mandated that ISRO could release only data up to 6.8 resolutions.Q. Which of the statements given above are correct?- a)1 and 2 only
- b)1 and 3 only
- c)2 and 3 only
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements with respect to the new Remote Sensing Data Policy:
1. Agencies other than ISRO can also be nodal agencies for remote sensing.
2. All remote sensing imagery and data up to one meter resolution will be made freely available.
3. The old 2001 policy mandated that ISRO could release only data up to 6.8 resolutions.
1. Agencies other than ISRO can also be nodal agencies for remote sensing.
2. All remote sensing imagery and data up to one meter resolution will be made freely available.
3. The old 2001 policy mandated that ISRO could release only data up to 6.8 resolutions.
Q. Which of the statements given above are correct?
a)
1 and 2 only
b)
1 and 3 only
c)
2 and 3 only
d)
1, 2 and 3

|
Akshita Datta answered |
The old 2001 policy mandated that ISRO could release only data upto 5.8 meter resolution.
What is the difference between present Wi – Fi technology and super Wi – Fi?
1. Present Wi – Fi technology supports 802.11 b/g/n standard while new super Wi – Fi will support 802.11 ad standard.
2. Super Wi – Fi can send data upto the length of 1 – 2 GB and eventually there would be no log in the speed.
3. The new super Wi – Fi would function at the speed of 7 gigabytes per second, much more than the speed of ordinary Wi – Fi.
Q. Select the correct answer using the codes given below:- a)1 and 2 only
- b)2 and 3 only
- c)1 and 3 only
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the difference between present Wi – Fi technology and super Wi – Fi?
1. Present Wi – Fi technology supports 802.11 b/g/n standard while new super Wi – Fi will support 802.11 ad standard.
2. Super Wi – Fi can send data upto the length of 1 – 2 GB and eventually there would be no log in the speed.
3. The new super Wi – Fi would function at the speed of 7 gigabytes per second, much more than the speed of ordinary Wi – Fi.
Q. Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
1. Present Wi – Fi technology supports 802.11 b/g/n standard while new super Wi – Fi will support 802.11 ad standard.
2. Super Wi – Fi can send data upto the length of 1 – 2 GB and eventually there would be no log in the speed.
3. The new super Wi – Fi would function at the speed of 7 gigabytes per second, much more than the speed of ordinary Wi – Fi.
Q. Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
a)
1 and 2 only
b)
2 and 3 only
c)
1 and 3 only
d)
1, 2 and 3

|
Milan Jain answered |
New Super Wi-Fi will support 802.11 ad standard, it can send data upto the length of 1-2 GB and would function at the speed of 7 gigabits per second.
The angular velocity depends upon the rate of change of the _______. - a)Angular Distance
- b)Angular acceleration
- c)Angular Displacement
- d)torque
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The angular velocity depends upon the rate of change of the _______.
a)
Angular Distance
b)
Angular acceleration
c)
Angular Displacement
d)
torque
|
|
Eshaan Kapoor answered |
The angular velocity is defined as the rate of change of angular displacement and is a vector quantity which specifies the angular speed of an object and the axis about which the object is rotating.
Ultra violet radiations of the Sun do not reach the earth because, earth's atmosphere is surrounded by –- a)Carbon dioxide
- b)Ammonia
- c)Chlorine
- d)Ozone
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Ultra violet radiations of the Sun do not reach the earth because, earth's atmosphere is surrounded by –
a)
Carbon dioxide
b)
Ammonia
c)
Chlorine
d)
Ozone
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
The ozone layer absorbs 97-99% of the Sun's medium-frequency ultraviolet light (from about 200 nm to 315 nm wavelength), which potentially damages exposed life forms on Earth. Ozone is formed from dioxygen by the action of ultraviolet light and also atmospheric electrical discharges, and is present in low concentrations throughout the Earth's atmosphere. In total, ozone makes up only 0.6 parts per million of the atmosphere.
The mass and energy equivalent to 1 a.m.u. respectively are -- a)1.67 x 10−27 g, 9.30 MeV
- b)1.67 x 10−27kg, 930 MeV
- c)1.67 x 10−27kg, 1 MeV
- d)1.67 x 10−34 kg, 1 MeV
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The mass and energy equivalent to 1 a.m.u. respectively are -
a)
1.67 x 10−27 g, 9.30 MeV
b)
1.67 x 10−27kg, 930 MeV
c)
1.67 x 10−27kg, 1 MeV
d)
1.67 x 10−34 kg, 1 MeV
|
|
Dia Mehta answered |
The mass and energy equivalent to 1 a.m.u. respectively are 1.67 x 10−27kg, 930 MeV.
Good conductor of electricity is –- a)dry air
- b)paper
- c)kerosene
- d)graphite
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Good conductor of electricity is –
a)
dry air
b)
paper
c)
kerosene
d)
graphite
|
|
Eshaan Kapoor answered |
Graphite has a tendency to behave very much like a metal because the carbon molecules arrange themselves into a lattice structure. The crystal lattice is the same orientation that metal forms, and it allows the free-movement of electrons, making it a good electrical conductor. The characteristics possesses by the graphite for conduction is far better than the dry air paper and kerosene and that's what makes it a good conductor.
String 1 has twice the length, twice the radius, twice the tension and twice the density of another string 2. The relation between the fundamental frequencies of 1 and 2 is :- a)f1 = f2
- b)f1 = 2f2
- c)f2 = 4f1
- d)f1 = 4f2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
String 1 has twice the length, twice the radius, twice the tension and twice the density of another string 2. The relation between the fundamental frequencies of 1 and 2 is :
a)
f1 = f2
b)
f1 = 2f2
c)
f
2
= 4f1
d)
f1 = 4f2

|
Anisha Pillai answered |
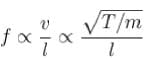
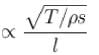
(m = mass per unit length =pS)
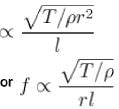
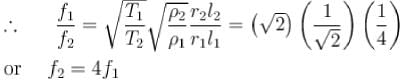
The correct answer is: f2 = 4f1
A heavy rope is suspended from a rigid support. A wave pulse is set up at the lower end, then :- a)the pulse will travel with decreasing speed
- b)the pulse will travel with increasing speed
- c)the pulse will travel with uniform speed
- d)the pulse cannot travel through the rope
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A heavy rope is suspended from a rigid support. A wave pulse is set up at the lower end, then :
a)
the pulse will travel with decreasing speed
b)
the pulse will travel with increasing speed
c)
the pulse will travel with uniform speed
d)
the pulse cannot travel through the rope
|
|
Lavanya Joshi answered |
Explanation:
When a wave pulse is set up at the lower end of a heavy rope suspended from a rigid support, the pulse will travel with increasing speed. This can be understood by considering the properties of wave propagation and the behavior of a heavy rope.
Wave Propagation:
When a wave travels through a medium, it transfers energy without transporting matter. The speed of a wave depends on the properties of the medium through which it travels. In the case of a heavy rope, the speed of the wave pulse depends on the tension in the rope and the mass per unit length of the rope.
Behavior of a Heavy Rope:
In a heavy rope, the tension is greater at the top and decreases towards the bottom due to the weight of the rope. The mass per unit length of the rope is also greater at the top and decreases towards the bottom.
Explanation of Option B:
The wave pulse in the heavy rope will travel with increasing speed because of the decreasing tension and mass per unit length towards the bottom of the rope. Here is a detailed explanation:
1. At the lower end of the rope, where the wave pulse is set up, the tension and mass per unit length are relatively smaller compared to the top of the rope.
2. As the wave pulse travels upwards, it encounters regions of higher tension and mass per unit length.
3. Due to the higher tension and mass per unit length, the wave pulse experiences a greater resistance to motion, causing it to slow down initially.
4. However, as the wave pulse moves further up, it encounters regions of lower tension and mass per unit length.
5. The lower tension and mass per unit length result in less resistance to motion, allowing the wave pulse to accelerate.
6. Therefore, the wave pulse travels with increasing speed as it moves towards the top of the rope.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the wave pulse will travel with increasing speed in a heavy rope suspended from a rigid support. This is due to the variation in tension and mass per unit length along the length of the rope.
When a wave pulse is set up at the lower end of a heavy rope suspended from a rigid support, the pulse will travel with increasing speed. This can be understood by considering the properties of wave propagation and the behavior of a heavy rope.
Wave Propagation:
When a wave travels through a medium, it transfers energy without transporting matter. The speed of a wave depends on the properties of the medium through which it travels. In the case of a heavy rope, the speed of the wave pulse depends on the tension in the rope and the mass per unit length of the rope.
Behavior of a Heavy Rope:
In a heavy rope, the tension is greater at the top and decreases towards the bottom due to the weight of the rope. The mass per unit length of the rope is also greater at the top and decreases towards the bottom.
Explanation of Option B:
The wave pulse in the heavy rope will travel with increasing speed because of the decreasing tension and mass per unit length towards the bottom of the rope. Here is a detailed explanation:
1. At the lower end of the rope, where the wave pulse is set up, the tension and mass per unit length are relatively smaller compared to the top of the rope.
2. As the wave pulse travels upwards, it encounters regions of higher tension and mass per unit length.
3. Due to the higher tension and mass per unit length, the wave pulse experiences a greater resistance to motion, causing it to slow down initially.
4. However, as the wave pulse moves further up, it encounters regions of lower tension and mass per unit length.
5. The lower tension and mass per unit length result in less resistance to motion, allowing the wave pulse to accelerate.
6. Therefore, the wave pulse travels with increasing speed as it moves towards the top of the rope.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the wave pulse will travel with increasing speed in a heavy rope suspended from a rigid support. This is due to the variation in tension and mass per unit length along the length of the rope.
Which one of the following is not correctly matched?- a)Akash — A medium range multi-target missile
- b)Nag — An anti-tank missile
- c)Pinaka — A multi-barrel rocket launcher weapon system
- d)Trishul — A short range surface to surface missile
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not correctly matched?
a)
Akash — A medium range multi-target missile
b)
Nag — An anti-tank missile
c)
Pinaka — A multi-barrel rocket launcher weapon system
d)
Trishul — A short range surface to surface missile

|
Madhurima Chauhan answered |
Akash is a medium–range mobile surface–to– air missile. Nag is an antitank missile by DRDO. Pinaka is a multiple rocket launcher produced for Indian Army by DRDO while Trishul is a missile system of a short range surface to–air missile as a part of the Integrated Guided Missile Development Program.
What is the maximum value of deforming force up to which a material shows elastic property and above which the material loses it?- a)Elasticity
- b)Strain
- c)Elastic Limit
- d)Stress
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the maximum value of deforming force up to which a material shows elastic property and above which the material loses it?
a)
Elasticity
b)
Strain
c)
Elastic Limit
d)
Stress
|
|
Dia Mehta answered |
The Maximum Extent to which a solid may be stretched without permanent alteration of size or shape.
Light year is the unit of -- a)Frequency
- b)Distance
- c)Energy
- d)Power
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Light year is the unit of -
a)
Frequency
b)
Distance
c)
Energy
d)
Power
|
|
Garima patil answered |
**Explanation:**
The correct answer is option **B) Distance**.
A light-year is a unit of distance used in astronomy to measure large distances in space. It is defined as the distance that light travels in one year in a vacuum. Since light travels at a constant speed of approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (or about 186,282 miles per second), the distance covered by light in one year is immense.
To better understand the concept of a light-year, let's break down the distance calculation and the significance of using this unit in astronomy:
**Definition of a Light-Year:**
- A light-year is the distance that light travels in one year.
- Light travels at a speed of about 299,792 kilometers per second (or about 186,282 miles per second).
- Therefore, in one year, light can travel about 9.46 trillion kilometers (or about 5.88 trillion miles).
**Importance of Light-Years in Astronomy:**
- The vast distances between celestial objects in space make it impractical to use conventional units like kilometers or miles.
- Astronomers use light-years to measure the distances between stars, galaxies, and other objects in the universe.
- Light-years allow us to comprehend the enormous scale of the universe and the time it takes for light to travel across such vast distances.
**Examples of Light-Years:**
- The nearest star to Earth, Proxima Centauri, is approximately 4.24 light-years away.
- The Andromeda Galaxy, our closest neighboring galaxy, is about 2.537 million light-years away.
- The observable universe is estimated to be about 93 billion light-years in diameter.
In conclusion, a light-year is a unit of distance used in astronomy to measure the vast distances between celestial objects. It represents the distance that light travels in one year and is an essential tool for understanding the scale and size of the universe.
The correct answer is option **B) Distance**.
A light-year is a unit of distance used in astronomy to measure large distances in space. It is defined as the distance that light travels in one year in a vacuum. Since light travels at a constant speed of approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (or about 186,282 miles per second), the distance covered by light in one year is immense.
To better understand the concept of a light-year, let's break down the distance calculation and the significance of using this unit in astronomy:
**Definition of a Light-Year:**
- A light-year is the distance that light travels in one year.
- Light travels at a speed of about 299,792 kilometers per second (or about 186,282 miles per second).
- Therefore, in one year, light can travel about 9.46 trillion kilometers (or about 5.88 trillion miles).
**Importance of Light-Years in Astronomy:**
- The vast distances between celestial objects in space make it impractical to use conventional units like kilometers or miles.
- Astronomers use light-years to measure the distances between stars, galaxies, and other objects in the universe.
- Light-years allow us to comprehend the enormous scale of the universe and the time it takes for light to travel across such vast distances.
**Examples of Light-Years:**
- The nearest star to Earth, Proxima Centauri, is approximately 4.24 light-years away.
- The Andromeda Galaxy, our closest neighboring galaxy, is about 2.537 million light-years away.
- The observable universe is estimated to be about 93 billion light-years in diameter.
In conclusion, a light-year is a unit of distance used in astronomy to measure the vast distances between celestial objects. It represents the distance that light travels in one year and is an essential tool for understanding the scale and size of the universe.
"Curie" is unit of : - a)Radioactivity
- b)Temperature
- c)Heat
- d)Energy
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
"Curie" is unit of :
a)
Radioactivity
b)
Temperature
c)
Heat
d)
Energy
|
|
Dia Mehta answered |
Curie, in physics, unit of activity of a quantity of a radioactive substance, named in honour of the French physicist Marie Curie. One curie (1 Ci) is equal to 3.7 x 1010 Becquerel (Bq). Radioactivity refers to the particles which are emitted from nuclei as a result of nuclear instability.
Which of the following statements is correct regarding the SKA telescope?
1. At present, it has 36 antennas with diameter of 12 meters each and it is placed at the remote Murchison Radio Astronomy Observatory
2. The radio waves generated from this telescope can provide details of the cosmos far away and the gases that resulted in the formation of any particular star.
Q. Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
- a)1 only
- b)2 only
- c)Neither 1 nor 2
- d)Both 1 and 2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is correct regarding the SKA telescope?
1. At present, it has 36 antennas with diameter of 12 meters each and it is placed at the remote Murchison Radio Astronomy Observatory
2. The radio waves generated from this telescope can provide details of the cosmos far away and the gases that resulted in the formation of any particular star.
Q. Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
1. At present, it has 36 antennas with diameter of 12 meters each and it is placed at the remote Murchison Radio Astronomy Observatory
2. The radio waves generated from this telescope can provide details of the cosmos far away and the gases that resulted in the formation of any particular star.
Q. Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
a)
1 only
b)
2 only
c)
Neither 1 nor 2
d)
Both 1 and 2

|
Shreya Mishra answered |
Statement 2 is correct: Yes, radio telescopes can provide details about the cosmos and the gases that formed stars.
Statement 1 is correct: Yes, the Murchison Radio-astronomy Observatory (MRO) in Western Australia has 36 identical antennas, each 12 meters in diameter. These antennas are part of the Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder (ASKAP), which is a single astronomical interferometer with a total collecting area of around 4,000 square meters.
Both 1 and 2 are correct.
Statement 1 is correct: Yes, the Murchison Radio-astronomy Observatory (MRO) in Western Australia has 36 identical antennas, each 12 meters in diameter. These antennas are part of the Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder (ASKAP), which is a single astronomical interferometer with a total collecting area of around 4,000 square meters.
Both 1 and 2 are correct.
Which of the following is optical illusion? - a)Rainbow
- b)Earthshine
- c)Halo
- d)Mirage
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is optical illusion?
a)
Rainbow
b)
Earthshine
c)
Halo
d)
Mirage
|
|
Sonia patil answered |
Explanation:
A mirage is an optical illusion that occurs due to the bending of light rays. It is a phenomenon where distant objects appear to be shimmering, distorted, or displaced from their actual position. The correct answer is option 'D' because a mirage fits the description of an optical illusion.
Definition of a Mirage:
A mirage is a phenomenon that occurs when light rays bend due to the variation in air temperature. It usually happens in hot, desert-like environments where the ground is significantly heated. The bending of light causes an apparent displacement of objects, creating the illusion of water or reflections.
Causes of Mirage:
1. Temperature Gradient: Mirages occur due to the temperature gradient in the air. The air close to the ground is hotter than the air higher up. This temperature difference causes the light rays to bend as they pass through the layers of air with varying densities.
2. Total Internal Reflection: When light travels from one medium to another, it bends or refracts. In the case of a mirage, the temperature gradient causes the light rays to bend more than usual, leading to total internal reflection. This reflection creates the illusion of water or a shiny surface.
Types of Mirage:
1. Inferior Mirage: An inferior mirage is the most common type of mirage. It occurs when the air close to the ground is hotter than the air above. This causes the light rays to bend upwards, creating an image of objects below the actual position.
2. Superior Mirage: A superior mirage occurs when the air close to the ground is colder than the air above. In this case, the light rays bend downwards, creating an image of objects above their actual position. Superior mirages are often seen in cold Arctic regions.
Characteristics of a Mirage:
1. Shimmering Effect: Mirages create a shimmering effect, making the reflected image appear unstable or wavering.
2. Displacement: Mirages can displace the position of objects, making them appear higher or lower than their actual location.
3. Illusion of Water: One of the common characteristics of a mirage is the illusion of water. Due to the bending of light, distant objects may appear as if they are reflecting off a water surface.
4. Distance: Mirages often occur at a distance, particularly in desert areas where the ground is heated.
In conclusion, a mirage is an optical illusion that occurs due to the bending of light rays caused by a temperature gradient in the air. It creates the illusion of shimmering, displaced, or distorted objects, often resembling water or reflections.
A mirage is an optical illusion that occurs due to the bending of light rays. It is a phenomenon where distant objects appear to be shimmering, distorted, or displaced from their actual position. The correct answer is option 'D' because a mirage fits the description of an optical illusion.
Definition of a Mirage:
A mirage is a phenomenon that occurs when light rays bend due to the variation in air temperature. It usually happens in hot, desert-like environments where the ground is significantly heated. The bending of light causes an apparent displacement of objects, creating the illusion of water or reflections.
Causes of Mirage:
1. Temperature Gradient: Mirages occur due to the temperature gradient in the air. The air close to the ground is hotter than the air higher up. This temperature difference causes the light rays to bend as they pass through the layers of air with varying densities.
2. Total Internal Reflection: When light travels from one medium to another, it bends or refracts. In the case of a mirage, the temperature gradient causes the light rays to bend more than usual, leading to total internal reflection. This reflection creates the illusion of water or a shiny surface.
Types of Mirage:
1. Inferior Mirage: An inferior mirage is the most common type of mirage. It occurs when the air close to the ground is hotter than the air above. This causes the light rays to bend upwards, creating an image of objects below the actual position.
2. Superior Mirage: A superior mirage occurs when the air close to the ground is colder than the air above. In this case, the light rays bend downwards, creating an image of objects above their actual position. Superior mirages are often seen in cold Arctic regions.
Characteristics of a Mirage:
1. Shimmering Effect: Mirages create a shimmering effect, making the reflected image appear unstable or wavering.
2. Displacement: Mirages can displace the position of objects, making them appear higher or lower than their actual location.
3. Illusion of Water: One of the common characteristics of a mirage is the illusion of water. Due to the bending of light, distant objects may appear as if they are reflecting off a water surface.
4. Distance: Mirages often occur at a distance, particularly in desert areas where the ground is heated.
In conclusion, a mirage is an optical illusion that occurs due to the bending of light rays caused by a temperature gradient in the air. It creates the illusion of shimmering, displaced, or distorted objects, often resembling water or reflections.
Which among the following is not a characteristic of transition metals? - a)Tendency to gain electrons
- b)Low electro negativity
- c)Low ionization energy
- d)Malleability
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is not a characteristic of transition metals?
a)
Tendency to gain electrons
b)
Low electro negativity
c)
Low ionization energy
d)
Malleability
|
|
Sonakshi kulkarni answered |
Transition Metals Characteristics:
Transition metals have several unique characteristics that set them apart from other elements in the periodic table. One of the key characteristics of transition metals is their tendency to gain electrons. However, this is not a characteristic of transition metals. Let's explore the other characteristics in detail:
Low Electronegativity:
- Transition metals generally have low electronegativity compared to other elements. This means they have a lower tendency to attract electrons towards themselves in a chemical bond.
Low Ionization Energy:
- Transition metals have relatively low ionization energy, which is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. This characteristic makes transition metals more likely to form positive ions.
Malleability:
- Transition metals are known for their malleability, which is the ability to be hammered or pressed into thin sheets without breaking. This property is due to the presence of delocalized electrons in the metal's structure.
Tendency to Gain Electrons:
- Unlike nonmetals, transition metals do not have a strong tendency to gain electrons. Instead, they typically lose electrons to form positively charged ions, which is a key characteristic of transition metals.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'A' - Tendency to gain electrons is not a characteristic of transition metals. Transition metals are known for their low electronegativity, low ionization energy, and malleability, making them unique elements in the periodic table.
Transition metals have several unique characteristics that set them apart from other elements in the periodic table. One of the key characteristics of transition metals is their tendency to gain electrons. However, this is not a characteristic of transition metals. Let's explore the other characteristics in detail:
Low Electronegativity:
- Transition metals generally have low electronegativity compared to other elements. This means they have a lower tendency to attract electrons towards themselves in a chemical bond.
Low Ionization Energy:
- Transition metals have relatively low ionization energy, which is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. This characteristic makes transition metals more likely to form positive ions.
Malleability:
- Transition metals are known for their malleability, which is the ability to be hammered or pressed into thin sheets without breaking. This property is due to the presence of delocalized electrons in the metal's structure.
Tendency to Gain Electrons:
- Unlike nonmetals, transition metals do not have a strong tendency to gain electrons. Instead, they typically lose electrons to form positively charged ions, which is a key characteristic of transition metals.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'A' - Tendency to gain electrons is not a characteristic of transition metals. Transition metals are known for their low electronegativity, low ionization energy, and malleability, making them unique elements in the periodic table.
In a refrigerator, the cooling system should always be –- a)at the top
- b)at the bottom
- c)at the middle
- d)can be anywhere
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a refrigerator, the cooling system should always be –
a)
at the top
b)
at the bottom
c)
at the middle
d)
can be anywhere
|
|
Dia Mehta answered |
The compressor is the motor (or engine) of the cooling system. It is normally at the bottom of the refrigerator in the back. The compressor runs whenever the refrigerator thermostat calls for cooling.
Consider the following statements:
1. European Space Agency (ESA) has joined the NASA’s Euclid Mission to be launched in 2020.
2. Euclid Mission is a space telescope designed to investigate the cosmological mysteries of dark matter and dark energy.Q. Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a)1 only
- b)2 only
- c)Both 1 and 2
- d)Neither 1 nor 2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. European Space Agency (ESA) has joined the NASA’s Euclid Mission to be launched in 2020.
2. Euclid Mission is a space telescope designed to investigate the cosmological mysteries of dark matter and dark energy.
1. European Space Agency (ESA) has joined the NASA’s Euclid Mission to be launched in 2020.
2. Euclid Mission is a space telescope designed to investigate the cosmological mysteries of dark matter and dark energy.
Q. Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 only
b)
2 only
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
Neither 1 nor 2

|
Shreya Mishra answered |
NASA has joined the European space Agency’s (ESA’) Euclid mission, a telescope designed to investigate the cosmological mysteries of dark matter and dark energy. Euclid is a medium –class (“M–class”) mission and is part of ESA’s “Cosmic Vision”, 2015–2025 scientific program.
The new version of advanced television, beyond the high definition television is 4 K television. Consider the following statements in this regard?
1. The basic principle of 4K TV is Near Field Communication (NFC).
2. The term 4K refers to the horizontal resolution of the images, which are all on the order of 4,000 pixels. 3. If the screen is too big then the HD gives the blurred images because the resolution of the images and pixels are limited.Q. Which of the statements given above are correct?- a)1 and 2 only
- b)2 and 3 only
- c)1 and 3 only
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The new version of advanced television, beyond the high definition television is 4 K television. Consider the following statements in this regard?
1. The basic principle of 4K TV is Near Field Communication (NFC).
2. The term 4K refers to the horizontal resolution of the images, which are all on the order of 4,000 pixels. 3. If the screen is too big then the HD gives the blurred images because the resolution of the images and pixels are limited.
1. The basic principle of 4K TV is Near Field Communication (NFC).
2. The term 4K refers to the horizontal resolution of the images, which are all on the order of 4,000 pixels. 3. If the screen is too big then the HD gives the blurred images because the resolution of the images and pixels are limited.
Q. Which of the statements given above are correct?
a)
1 and 2 only
b)
2 and 3 only
c)
1 and 3 only
d)
1, 2 and 3

|
Anirudh Joshi answered |
4K TV is an Ultra high definition television. UHDTV, has horizontal resolution on the order of 4,000 pixels. Since its screen is too big the HD gives blurred images.
A device which is used to limit the current in an electrical circuit is called a -- a)Grid
- b)Fuse
- c)Hub
- d)Conductor
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A device which is used to limit the current in an electrical circuit is called a -
a)
Grid
b)
Fuse
c)
Hub
d)
Conductor
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
A fuse places a limit on the amount of current that can be drawn by an electric circuit by opening (blowing or melting) when the current exceeds a preset limit. This protects the circuit and the surroundings from fire or damage in the case of an overload or short circuit.
A train is moving with a constant speed along a circular track. The engine o f the train emits a sound of frequency f. The frequency heard by the guard at rear end of the train :- a)is equal to f
- b)is greater than f
- c)is less than f
- d)may be greater than, less than or equal to f depending on the factors like speed of train, length of train and radius of circular track
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A train is moving with a constant speed along a circular track. The engine o f the train emits a sound of frequency f. The frequency heard by the guard at rear end of the train :
a)
is equal to f
b)
is greater than f
c)
is less than f
d)
may be greater than, less than or equal to f depending on the factors like speed of train, length of train and radius of circular track

|
Aryan Gupta answered |
Let v be the speed of sound and u the speed of train.
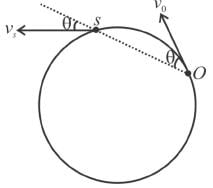
Then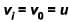
and
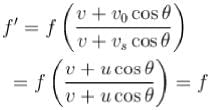
The correct answer is: is equal to f

Then
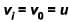
and
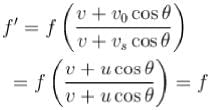
The correct answer is: is equal to f
The method of protecting iron from rusting, by coating a thin layer of Zinc is called -- a)Galvanizing
- b)rancidity
- c)Alloy
- d)Pulverizing
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The method of protecting iron from rusting, by coating a thin layer of Zinc is called -
a)
Galvanizing
b)
rancidity
c)
Alloy
d)
Pulverizing
|
|
Ishani khanna answered |
Galvanizing: Protecting Iron from Rusting
Galvanizing is the method of protecting iron from rusting by coating it with a thin layer of zinc. It is a widely used technique to prevent corrosion and extend the lifespan of iron and steel objects. Let's delve into the details of galvanizing and why it is an effective method of protection.
1. What is Galvanizing?
Galvanizing is a process in which a layer of zinc is applied to the surface of iron or steel to create a protective barrier. The zinc coating acts as a sacrificial anode, meaning it corrodes instead of the iron or steel beneath it. This sacrificial action ensures that the iron or steel remains protected from rusting.
2. How is Galvanizing done?
The galvanizing process involves several steps:
2.1 Surface Preparation:
The surface of the iron or steel object is cleaned to remove any dirt, grease, or oxide layers. This step is crucial as it ensures proper adhesion of the zinc coating.
2.2 Immersion in a Zinc Bath:
The cleaned iron or steel object is immersed in a bath of molten zinc at a temperature of around 450°C. The object is carefully dipped into the bath, allowing the zinc to adhere to its surface.
2.3 Metallurgical Reaction:
During immersion, a metallurgical reaction occurs between the iron or steel and the molten zinc. This reaction forms a series of zinc-iron alloy layers on the surface of the object.
2.4 Cooling and Finishing:
After the object is removed from the zinc bath, it is allowed to cool, allowing the zinc coating to solidify and adhere firmly to the iron or steel surface. The galvanized object is then typically inspected for any defects or imperfections.
3. Advantages of Galvanizing:
Galvanizing offers several advantages as a method of protecting iron from rusting:
3.1 Corrosion Resistance:
The zinc coating provides excellent corrosion resistance to the iron or steel object, preventing rust formation even in harsh environments.
3.2 Longevity:
Galvanized objects have a longer lifespan compared to bare iron or steel. The zinc coating acts as a durable protective layer, extending the life of the object.
3.3 Cost-Effective:
Galvanizing is a cost-effective method of protection as it requires minimal maintenance. The initial investment in galvanizing pays off in terms of reduced repair and replacement costs.
3.4 Aesthetic Appeal:
Galvanized objects have a visually appealing silver-gray finish that is often desirable in architectural and decorative applications.
4. Applications of Galvanizing:
Galvanizing is widely used in various industries and applications, including:
- Construction: Galvanized steel is used in roofing, fencing, structural components, and other construction applications.
- Automotive: Galvanized parts are used in automobile manufacturing to enhance corrosion resistance.
- Agriculture: Galvanized equipment and structures are commonly used in farming and agricultural settings.
- Electrical: Galvanized electrical conduits and cable trays provide protection against corrosion.
In conclusion, galvanizing is a highly effective method of protecting iron from rusting by coating it with a thin layer of zinc. This process creates a barrier that prevents the iron
Galvanizing is the method of protecting iron from rusting by coating it with a thin layer of zinc. It is a widely used technique to prevent corrosion and extend the lifespan of iron and steel objects. Let's delve into the details of galvanizing and why it is an effective method of protection.
1. What is Galvanizing?
Galvanizing is a process in which a layer of zinc is applied to the surface of iron or steel to create a protective barrier. The zinc coating acts as a sacrificial anode, meaning it corrodes instead of the iron or steel beneath it. This sacrificial action ensures that the iron or steel remains protected from rusting.
2. How is Galvanizing done?
The galvanizing process involves several steps:
2.1 Surface Preparation:
The surface of the iron or steel object is cleaned to remove any dirt, grease, or oxide layers. This step is crucial as it ensures proper adhesion of the zinc coating.
2.2 Immersion in a Zinc Bath:
The cleaned iron or steel object is immersed in a bath of molten zinc at a temperature of around 450°C. The object is carefully dipped into the bath, allowing the zinc to adhere to its surface.
2.3 Metallurgical Reaction:
During immersion, a metallurgical reaction occurs between the iron or steel and the molten zinc. This reaction forms a series of zinc-iron alloy layers on the surface of the object.
2.4 Cooling and Finishing:
After the object is removed from the zinc bath, it is allowed to cool, allowing the zinc coating to solidify and adhere firmly to the iron or steel surface. The galvanized object is then typically inspected for any defects or imperfections.
3. Advantages of Galvanizing:
Galvanizing offers several advantages as a method of protecting iron from rusting:
3.1 Corrosion Resistance:
The zinc coating provides excellent corrosion resistance to the iron or steel object, preventing rust formation even in harsh environments.
3.2 Longevity:
Galvanized objects have a longer lifespan compared to bare iron or steel. The zinc coating acts as a durable protective layer, extending the life of the object.
3.3 Cost-Effective:
Galvanizing is a cost-effective method of protection as it requires minimal maintenance. The initial investment in galvanizing pays off in terms of reduced repair and replacement costs.
3.4 Aesthetic Appeal:
Galvanized objects have a visually appealing silver-gray finish that is often desirable in architectural and decorative applications.
4. Applications of Galvanizing:
Galvanizing is widely used in various industries and applications, including:
- Construction: Galvanized steel is used in roofing, fencing, structural components, and other construction applications.
- Automotive: Galvanized parts are used in automobile manufacturing to enhance corrosion resistance.
- Agriculture: Galvanized equipment and structures are commonly used in farming and agricultural settings.
- Electrical: Galvanized electrical conduits and cable trays provide protection against corrosion.
In conclusion, galvanizing is a highly effective method of protecting iron from rusting by coating it with a thin layer of zinc. This process creates a barrier that prevents the iron
This scientist gave the law- ‘Properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number.’ This property of the fundamental importance of atomic number was discovered by- a)Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner
- b)John Newlands
- c)Dmitri lvanovich Mendeléev
- d)Henry Moseley
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
This scientist gave the law- ‘Properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number.’ This property of the fundamental importance of atomic number was discovered by
a)
Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner
b)
John Newlands
c)
Dmitri lvanovich Mendeléev
d)
Henry Moseley
|
|
Eshaan Kapoor answered |
In 1913, Henry Moseley showed that the atomic number of an element is a more fundamental property than its atomic mass as described below.
Consider the following statements about Dhanush missile and select the correct answer:
1. Dhanush missile is an indigenously developed naval version of the Prithvi short range ballistic missile.
2. It is a single stage missile and was developed by the DRDO and it uses liquid propellant.
3. It has a strike range of up to 350 km and can carry 500 kg of conventional warheads only. - a)1 and 2 only
- b)1 and 3 only
- c)2 and 3 only
- d)all the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements about Dhanush missile and select the correct answer:
1. Dhanush missile is an indigenously developed naval version of the Prithvi short range ballistic missile.
2. It is a single stage missile and was developed by the DRDO and it uses liquid propellant.
3. It has a strike range of up to 350 km and can carry 500 kg of conventional warheads only.
1. Dhanush missile is an indigenously developed naval version of the Prithvi short range ballistic missile.
2. It is a single stage missile and was developed by the DRDO and it uses liquid propellant.
3. It has a strike range of up to 350 km and can carry 500 kg of conventional warheads only.
a)
1 and 2 only
b)
1 and 3 only
c)
2 and 3 only
d)
all the above
|
|
Nisha Chavan answered |
Explanation:
The correct answer is option 'A' which states that statements 1 and 2 are correct.
Statement 1: Dhanush missile is an indigenously developed naval version of the Prithvi short-range ballistic missile.
The first statement is correct. Dhanush missile is indeed an indigenously developed naval version of the Prithvi short-range ballistic missile. The Prithvi missile series was developed by the Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO) of India, and the naval version of the missile is known as Dhanush. Dhanush is specifically designed for use by the Indian Navy and is capable of being launched from naval ships.
Statement 2: It is a single-stage missile and was developed by the DRDO, and it uses liquid propellant.
The second statement is also correct. Dhanush missile is a single-stage missile that was developed by the DRDO. It uses liquid propellant, which is a type of rocket propellant in liquid form. Liquid propellants are commonly used in missiles as they provide high energy density and are easier to handle and control during the launch.
Statement 3: It has a strike range of up to 350 km and can carry 500 kg of conventional warheads only.
The third statement is incorrect. Dhanush missile has a strike range of about 350 km, but it is capable of carrying different types of warheads, including both conventional and nuclear warheads. It has a payload capacity of around 500 kg, which allows for various types of warheads to be carried depending on the mission requirements.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' as statements 1 and 2 are correct.
The correct answer is option 'A' which states that statements 1 and 2 are correct.
Statement 1: Dhanush missile is an indigenously developed naval version of the Prithvi short-range ballistic missile.
The first statement is correct. Dhanush missile is indeed an indigenously developed naval version of the Prithvi short-range ballistic missile. The Prithvi missile series was developed by the Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO) of India, and the naval version of the missile is known as Dhanush. Dhanush is specifically designed for use by the Indian Navy and is capable of being launched from naval ships.
Statement 2: It is a single-stage missile and was developed by the DRDO, and it uses liquid propellant.
The second statement is also correct. Dhanush missile is a single-stage missile that was developed by the DRDO. It uses liquid propellant, which is a type of rocket propellant in liquid form. Liquid propellants are commonly used in missiles as they provide high energy density and are easier to handle and control during the launch.
Statement 3: It has a strike range of up to 350 km and can carry 500 kg of conventional warheads only.
The third statement is incorrect. Dhanush missile has a strike range of about 350 km, but it is capable of carrying different types of warheads, including both conventional and nuclear warheads. It has a payload capacity of around 500 kg, which allows for various types of warheads to be carried depending on the mission requirements.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' as statements 1 and 2 are correct.
Q.48) Speed of sound is the greatest in : - a)Water
- b)Air
- c)Glass
- d)Glycerine
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Q.48) Speed of sound is the greatest in :
a)
Water
b)
Air
c)
Glass
d)
Glycerine
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
Sound travels faster in liquids and non-porous solids than it does in air. It travels about 4.3 times as fast in water (1,484 m/s), and nearly 15 times as fast in iron (5,120 m/s), than in air at 20 degrees Celsius.
Energy that is produced commercially from coal is called –- a)Light energy
- b)Kinetic energy
- c)Thermal energy
- d)Potential energy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Energy that is produced commercially from coal is called –
a)
Light energy
b)
Kinetic energy
c)
Thermal energy
d)
Potential energy
|
|
Dia Mehta answered |
Thermal enemy, but in most cases coal is used for electricity. The steel industry uses coal (or coke rather) in blast furnaces. Thermal energy is the part of the total internal energy of a thermodynamic system or sample of matter that results in the system temperature. This quantity may be difficult to determine or even meaningless unless the system has attained its temperature only through heating, and not been subjected to work input or output, or any other energy-changing processes.
Nuclear reactors used to produce electricity are based on –- a)Nuclear fission
- b)Nuclear fusion
- c)Cold fusion
- d)Superconductivity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Nuclear reactors used to produce electricity are based on –
a)
Nuclear fission
b)
Nuclear fusion
c)
Cold fusion
d)
Superconductivity
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
A nuclear reactor is a device to initiate and control a sustained nuclear chain reaction. Most commonly they are used for generating electricity and for the propulsion of ships. Usually heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid (water or gas), which runs through turbines that power either ship's propellers or generators.
Laser is a device to produce -- a)a beam of white light
- b)coherent light
- c)microwaves
- d)X-rays
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Laser is a device to produce -
a)
a beam of white light
b)
coherent light
c)
microwaves
d)
X-rays
|
|
Sonakshi nambiar answered |
Understanding Laser Technology
Lasers are specialized devices that produce a specific type of light known as coherent light. Let's delve into why option 'B' is the correct answer.
What is Coherent Light?
- Coherent light consists of waves that are in phase with each other, meaning their peaks and troughs align perfectly.
- This results in a concentrated beam of light that can travel long distances without spreading out significantly.
Characteristics of Laser Light
- Monochromatic: Laser light is typically of a single wavelength, which means it appears as one color. This characteristic is essential in applications like laser surgery and optical communication.
- Highly Directional: Unlike ordinary light sources, lasers emit light in a narrow beam. This directionality allows for precise targeting, making lasers useful in various fields, including medicine and industry.
- High Intensity: The coherent nature of laser light means that it can achieve much higher intensities compared to regular light sources, allowing for powerful applications like cutting and engraving.
Why Not Other Options?
- A) Beam of White Light: White light is composed of multiple wavelengths and is not coherent.
- C) Microwaves: While microwaves are a form of electromagnetic radiation, they do not fall under the category of laser light.
- D) X-rays: X-ray production involves different mechanisms and does not produce coherent light as lasers do.
Conclusion
In summary, lasers are designed to produce coherent light, characterized by its monochromatic, directional, and intense properties, making option 'B' the correct answer. Understanding these features is crucial for grasping how lasers are utilized in various scientific and practical applications.
Lasers are specialized devices that produce a specific type of light known as coherent light. Let's delve into why option 'B' is the correct answer.
What is Coherent Light?
- Coherent light consists of waves that are in phase with each other, meaning their peaks and troughs align perfectly.
- This results in a concentrated beam of light that can travel long distances without spreading out significantly.
Characteristics of Laser Light
- Monochromatic: Laser light is typically of a single wavelength, which means it appears as one color. This characteristic is essential in applications like laser surgery and optical communication.
- Highly Directional: Unlike ordinary light sources, lasers emit light in a narrow beam. This directionality allows for precise targeting, making lasers useful in various fields, including medicine and industry.
- High Intensity: The coherent nature of laser light means that it can achieve much higher intensities compared to regular light sources, allowing for powerful applications like cutting and engraving.
Why Not Other Options?
- A) Beam of White Light: White light is composed of multiple wavelengths and is not coherent.
- C) Microwaves: While microwaves are a form of electromagnetic radiation, they do not fall under the category of laser light.
- D) X-rays: X-ray production involves different mechanisms and does not produce coherent light as lasers do.
Conclusion
In summary, lasers are designed to produce coherent light, characterized by its monochromatic, directional, and intense properties, making option 'B' the correct answer. Understanding these features is crucial for grasping how lasers are utilized in various scientific and practical applications.
Eclipses occur due to which optical phenomena? - a)Reflection
- b)Refraction
- c)Rectilinear propagation
- d)Diffraction
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Eclipses occur due to which optical phenomena?
a)
Reflection
b)
Refraction
c)
Rectilinear propagation
d)
Diffraction
|
|
Pallavi nair answered |
Eclipses occur due to Rectilinear Propagation.
Explanation:
Eclipses are fascinating astronomical events that occur when one celestial body passes through the shadow of another celestial body. They can be categorized into two types: solar eclipses and lunar eclipses.
1. Solar Eclipses:
Solar eclipses occur when the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth, casting its shadow on a portion of the Earth's surface. During a solar eclipse, the moon blocks the direct sunlight from reaching certain areas on the Earth.
- Shadow Formation:
The shadow of the Moon consists of two parts: the umbra and the penumbra. The umbra is the darkest part of the shadow, where the Moon completely blocks the sunlight. The penumbra is a lighter shadow where only a portion of the sunlight is blocked.
- Path of Totality:
The path of totality refers to the region on the Earth's surface where the Moon completely covers the Sun, resulting in a total solar eclipse. Only the observers within this narrow path can witness the complete blocking of the Sun. Outside this path, the observers witness a partial solar eclipse where only a portion of the Sun is obscured.
2. Lunar Eclipses:
Lunar eclipses occur when the Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon, casting its shadow on the Moon. During a lunar eclipse, the Earth blocks the sunlight from directly reaching the Moon.
- Shadow Formation:
Similar to solar eclipses, the Earth's shadow also consists of two parts: the umbra and the penumbra. The umbra is the region where the Earth completely blocks the sunlight, and the penumbra is the region where only a portion of the sunlight is blocked.
- Types of Lunar Eclipses:
There are three types of lunar eclipses: total lunar eclipses, partial lunar eclipses, and penumbral lunar eclipses. A total lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes through the Earth's umbra, resulting in the complete darkening of the Moon. A partial lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes partially through the Earth's umbra. A penumbral lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes only through the Earth's penumbra, resulting in a subtle darkening of the Moon.
In conclusion, eclipses occur due to the optical phenomenon of rectilinear propagation. During a solar eclipse, the Moon's shadow is cast on the Earth, and during a lunar eclipse, the Earth's shadow is cast on the Moon. These phenomena are a result of the straight-line propagation of light, where the light rays travel in straight lines until they encounter an obstacle (in this case, the Moon or the Earth), causing an eclipse to occur.
Explanation:
Eclipses are fascinating astronomical events that occur when one celestial body passes through the shadow of another celestial body. They can be categorized into two types: solar eclipses and lunar eclipses.
1. Solar Eclipses:
Solar eclipses occur when the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth, casting its shadow on a portion of the Earth's surface. During a solar eclipse, the moon blocks the direct sunlight from reaching certain areas on the Earth.
- Shadow Formation:
The shadow of the Moon consists of two parts: the umbra and the penumbra. The umbra is the darkest part of the shadow, where the Moon completely blocks the sunlight. The penumbra is a lighter shadow where only a portion of the sunlight is blocked.
- Path of Totality:
The path of totality refers to the region on the Earth's surface where the Moon completely covers the Sun, resulting in a total solar eclipse. Only the observers within this narrow path can witness the complete blocking of the Sun. Outside this path, the observers witness a partial solar eclipse where only a portion of the Sun is obscured.
2. Lunar Eclipses:
Lunar eclipses occur when the Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon, casting its shadow on the Moon. During a lunar eclipse, the Earth blocks the sunlight from directly reaching the Moon.
- Shadow Formation:
Similar to solar eclipses, the Earth's shadow also consists of two parts: the umbra and the penumbra. The umbra is the region where the Earth completely blocks the sunlight, and the penumbra is the region where only a portion of the sunlight is blocked.
- Types of Lunar Eclipses:
There are three types of lunar eclipses: total lunar eclipses, partial lunar eclipses, and penumbral lunar eclipses. A total lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes through the Earth's umbra, resulting in the complete darkening of the Moon. A partial lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes partially through the Earth's umbra. A penumbral lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes only through the Earth's penumbra, resulting in a subtle darkening of the Moon.
In conclusion, eclipses occur due to the optical phenomenon of rectilinear propagation. During a solar eclipse, the Moon's shadow is cast on the Earth, and during a lunar eclipse, the Earth's shadow is cast on the Moon. These phenomena are a result of the straight-line propagation of light, where the light rays travel in straight lines until they encounter an obstacle (in this case, the Moon or the Earth), causing an eclipse to occur.
Pycnometer is an instrument used to measure the –- a)Density
- b)Intensity of solar radiation
- c)Intensity of earthquake
- d)High temperatures
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Pycnometer is an instrument used to measure the –
a)
Density
b)
Intensity of solar radiation
c)
Intensity of earthquake
d)
High temperatures
|
|
Sonia das answered |
Explanation:
Density Measurement:
- Pycnometer is an instrument used to measure the density of liquids or solids.
- It is a small glass bottle with a stopper that has a capillary tube attached to it.
- The pycnometer is weighed empty and then filled with the substance whose density is to be measured.
- The weight of the filled pycnometer is then recorded.
- By knowing the weight of the substance and the volume of the pycnometer, the density can be calculated using the formula: Density = Mass/Volume.
Other Options:
- Intensity of solar radiation is measured using instruments like pyranometer or radiometer.
- Intensity of earthquakes is measured using seismometers and seismographs.
- High temperatures are measured using thermometers or pyrometers.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A', as pycnometer is specifically designed for measuring density.
Density Measurement:
- Pycnometer is an instrument used to measure the density of liquids or solids.
- It is a small glass bottle with a stopper that has a capillary tube attached to it.
- The pycnometer is weighed empty and then filled with the substance whose density is to be measured.
- The weight of the filled pycnometer is then recorded.
- By knowing the weight of the substance and the volume of the pycnometer, the density can be calculated using the formula: Density = Mass/Volume.
Other Options:
- Intensity of solar radiation is measured using instruments like pyranometer or radiometer.
- Intensity of earthquakes is measured using seismometers and seismographs.
- High temperatures are measured using thermometers or pyrometers.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A', as pycnometer is specifically designed for measuring density.
Multiple Independent Re-entry Vehicles (MIRVs) are used in Agni-V missile made by DRDO, consider the following statements in regard to MIRVs.
1. Under it, each missile will be capable of carrying 2-10 separate nuclear warheads.
2. Under it, each warhead can be assigned to a different target.
3. Under it, two or more warheads can be assigned to the same target.Q. Which of the following statements is/are correct?- a)1 only
- b)2 only
- c)2 and 3 only
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Multiple Independent Re-entry Vehicles (MIRVs) are used in Agni-V missile made by DRDO, consider the following statements in regard to MIRVs.
1. Under it, each missile will be capable of carrying 2-10 separate nuclear warheads.
2. Under it, each warhead can be assigned to a different target.
3. Under it, two or more warheads can be assigned to the same target.
1. Under it, each missile will be capable of carrying 2-10 separate nuclear warheads.
2. Under it, each warhead can be assigned to a different target.
3. Under it, two or more warheads can be assigned to the same target.
Q. Which of the following statements is/are correct?
a)
1 only
b)
2 only
c)
2 and 3 only
d)
1, 2 and 3
|
|
Debolina Yadav answered |
Explanation:
1. Each missile capable of carrying multiple warheads:
- MIRVs are designed to carry multiple independently targetable re-entry vehicles (MIRVs), which means that each missile can carry 2-10 separate nuclear warheads.
- This capability allows a single missile to target multiple locations or to overwhelm a missile defense system by releasing multiple warheads.
2. Warheads can be assigned to different targets:
- One of the key features of MIRVs is that each warhead can be assigned to a different target.
- This increases the flexibility and effectiveness of the missile system, as it can strike multiple targets simultaneously.
3. Multiple warheads can be assigned to the same target:
- While each warhead can be assigned to a different target, it is also possible for two or more warheads to be assigned to the same target.
- This redundancy ensures a higher probability of successful target destruction, even in the face of potential missile defense systems.
Therefore, all three statements are correct, making option 'D' the correct answer.
Tape recorder should not be kept near one of the following things –- a)Clock
- b)Magnet
- c)Electrical switchboard
- d)Radio
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Tape recorder should not be kept near one of the following things –
a)
Clock
b)
Magnet
c)
Electrical switchboard
d)
Radio
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
The cassette tape contains a magnetic strip wound around two spools. Tiny magnetic particles are randomly scattered throughout the tape. A tape recorder should not be kept near a magnet as the latter can cause the magnetic material to be pushed and pulled out of place. Rearranging the magnetic particles erases the sound.
Two rods, one of copper and other of steel, experience the same up thrust when placed in water. Thus, both have –- a)equal volume
- b)equal weight
- c)equal density
- d)equal mass
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two rods, one of copper and other of steel, experience the same up thrust when placed in water. Thus, both have –
a)
equal volume
b)
equal weight
c)
equal density
d)
equal mass
|
|
Dia Mehta answered |
When a body is placed in water, the upthrust or buoyant force acting on it depends upon the following factors: (1) Volume of the body submerged in the liquid - (V), or volume of the liquid displaced - (V); (ft) Density of the liquid - (d); and (Hi) Acceleration due to gravity In-line.
Minimum numbers of unequal vectors which can give zero resultant are -- a)Two
- b)Three
- c)Four
- d)More than four
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Minimum numbers of unequal vectors which can give zero resultant are -
a)
Two
b)
Three
c)
Four
d)
More than four
|
|
Stuti nayar answered |
Explanation:
When two vectors are added, they can either give zero or a resultant vector. However, when three or more vectors are added, they can never give zero as the resultant vector. Let's understand why:
Two vectors:
When two vectors are added, they can either give zero or a resultant vector. If the two vectors are of the same magnitude and opposite in direction, they will give a resultant vector of zero. For example, if two forces of 5 N each are applied in opposite directions, they will cancel out each other and the net force will be zero.
Three vectors:
When three vectors are added, they can never give zero as the resultant vector. The reason is that three vectors can form a triangle, and the sum of any two sides of a triangle is always greater than the third side. Therefore, there will always be a resultant vector when three vectors are added.
Four or more vectors:
When four or more vectors are added, they can never give zero as the resultant vector. The reason is that four or more vectors can form a polygon, and the sum of any two sides of a polygon is always greater than the third side. Therefore, there will always be a resultant vector when four or more vectors are added.
Therefore, the minimum number of unequal vectors which can give zero resultant are two.
When two vectors are added, they can either give zero or a resultant vector. However, when three or more vectors are added, they can never give zero as the resultant vector. Let's understand why:
Two vectors:
When two vectors are added, they can either give zero or a resultant vector. If the two vectors are of the same magnitude and opposite in direction, they will give a resultant vector of zero. For example, if two forces of 5 N each are applied in opposite directions, they will cancel out each other and the net force will be zero.
Three vectors:
When three vectors are added, they can never give zero as the resultant vector. The reason is that three vectors can form a triangle, and the sum of any two sides of a triangle is always greater than the third side. Therefore, there will always be a resultant vector when three vectors are added.
Four or more vectors:
When four or more vectors are added, they can never give zero as the resultant vector. The reason is that four or more vectors can form a polygon, and the sum of any two sides of a polygon is always greater than the third side. Therefore, there will always be a resultant vector when four or more vectors are added.
Therefore, the minimum number of unequal vectors which can give zero resultant are two.
Water is not suitable as a calorimetric substance because it –- a)has high specific heat
- b)is a good conductor
- c)has high boiling point
- d)low latent heat of vaporization
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Water is not suitable as a calorimetric substance because it –
a)
has high specific heat
b)
is a good conductor
c)
has high boiling point
d)
low latent heat of vaporization
|
|
Eshaan Kapoor answered |
The specific heat of water is higher than all other common substances. Hence, water is used for heating purposes (as in hot water bottles) and for cooling purposes (as in radiators of cars). Off all the liquids, mercury has the lowest specific heat due to which it is used as a thermometric liquid.
Gamma rays have greatest similarity with –- a)α-rays
- b)β-rays
- c)X-rays
- d)U.V.-rays
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Gamma rays have greatest similarity with –
a)
α-rays
b)
β-rays
c)
X-rays
d)
U.V.-rays
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
Gamma radiation, also known as gamma rays or hyphenated as gamma-rays and denoted as y, is electromagnetic radiation of high frequency and therefore high energy. Gamma rays are ionizing radiation and are thus biologically hazardous. They are classically produced by the decay from high energy states of atomic nuclei (gamma decay), but are also created by other processes.
What is found in frequency modulation? - a)Fixed frequency
- b)Fixed dimension
- c)Change in frequency and dimension
- d)Change in dimension only
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is found in frequency modulation?
a)
Fixed frequency
b)
Fixed dimension
c)
Change in frequency and dimension
d)
Change in dimension only
|
|
Eshaan Kapoor answered |
Frequency modulation (FM) conveys information over a carrier wave by varying its instantaneous frequency. This contrasts with amplitude modulation, in which the amplitude of the carrier is varied while its frequency remains constant. Frequency modulation is also used in telemetry, radar, seismic prospecting and newborn EEG seizure monitoring.
Consider the following statements:
1. Nirbhaya is a subsonic cruise missile being developed by DRDO.
2. The air version of Brahmos has been successfully test-fired recently.
3. Brahmos-II will be hypersonic cruise missile with target range of more than 300 km.Q. Which of the above statements is/are not true?- a)1 and 2 only
- b)2 and 3 only
- c)all of the above
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. Nirbhaya is a subsonic cruise missile being developed by DRDO.
2. The air version of Brahmos has been successfully test-fired recently.
3. Brahmos-II will be hypersonic cruise missile with target range of more than 300 km.
1. Nirbhaya is a subsonic cruise missile being developed by DRDO.
2. The air version of Brahmos has been successfully test-fired recently.
3. Brahmos-II will be hypersonic cruise missile with target range of more than 300 km.
Q. Which of the above statements is/are not true?
a)
1 and 2 only
b)
2 and 3 only
c)
all of the above
d)
none of these

|
सिद्धि शिशोदिया answered |
Ans.no.b
Chapter doubts & questions for Physics - 4 Months Preparation Course for CLAT UG 2025 is part of CLAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the CLAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for CLAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Physics - 4 Months Preparation Course for CLAT UG in English & Hindi are available as part of CLAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for CLAT Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









