All Exams >
NEET >
1 Year Dropper Course for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Redox Reactions for NEET Exam
Which is chlorate (I) ion?
a) 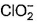
b)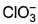
c)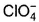
d)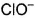
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
- ClO3- : A very reactive inorganic anion.
- The term chlorate can also be used to describe any compound containing the chlorate ion, normally chlorate salts.
- Example: Potassium chlorate, KClO3
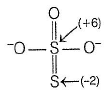
The difference in the oxidation number of the two types of sulphur atoms in Na2S4O6 is .........[HTJEE2011]
Correct answer is '7'. Can you explain this answer?
The difference in the oxidation number of the two types of sulphur atoms in Na2S4O6 is .........
[HTJEE2011]
|
|
Hrishikesh Sengupta answered |
Difference in oxidation number = 6 - (-1) = 7
Which of the following is not an example of redox reaction?- a)BaCl2 + H2SO4 ⎯→ BaSO4 + 2HCl
- b)Fe2O3 + 3CO ⎯→ 2Fe + 3CO2
- c)2K + F2 ⎯→ 2KF
- d)CuO + H2 ⎯→ Cu + H2O
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an example of redox reaction?
a)
BaCl2 + H2SO4 ⎯→ BaSO4 + 2HCl
b)
Fe2O3 + 3CO ⎯→ 2Fe + 3CO2
c)
2K + F2 ⎯→ 2KF
d)
CuO + H2 ⎯→ Cu + H2O
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
a) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2HCl is not a redox reaction, as there is no change in the oxidation state of any element.
It is an example of double displacement reactions.
It is an example of double displacement reactions.
The oxidation half reaction for following reaction is
Fe2+(aq) + Cr2O72-(aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + Cr3+(aq)- a)Fe3+(aq) → Fe2+ (aq)
- b)Cr2O72-(aq) → Cr3+(aq)
- c)Cr3+(aq) → Cr2O72-(aq)
- d)Fe2+ (aq) → Fe3+(aq)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxidation half reaction for following reaction is
Fe2+(aq) + Cr2O72-(aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + Cr3+(aq)
Fe2+(aq) + Cr2O72-(aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + Cr3+(aq)
a)
Fe3+(aq) → Fe2+ (aq)
b)
Cr2O72-(aq) → Cr3+(aq)
c)
Cr3+(aq) → Cr2O72-(aq)
d)
Fe2+ (aq) → Fe3+(aq)
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Oxidation half reaction for a reaction is that reaction which gives us the reactant and product formed after the oxidation of the reactant. In this case Fe+2 oxidizes itself to Fe+3 and so the oxidation of Fe+2 is oxidation half reaction. Option d correct.
In the following reaction, 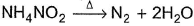 , oxidation number of
, oxidation number of- a)N changes from -2 to +2
- b)N changes from -2 to 0
- c)N in
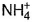 changes from -3 to 0 and that in
changes from -3 to 0 and that in 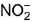 changes from +3 to 0
changes from +3 to 0 - d)N does not change
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following reaction, 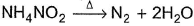 , oxidation number of
, oxidation number of
a)
N changes from -2 to +2
b)
N changes from -2 to 0
c)
N in 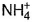 changes from -3 to 0 and that in
changes from -3 to 0 and that in 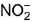 changes from +3 to 0
changes from +3 to 0
d)
N does not change

|
Learners Habitat answered |
In NH4NO2, the oxidation number of N in NH4+ is -3, and of N in NO2- is +3.
Oxidation numbers of P in PO4−3, of S in SO42− and that of Cr in Cr2O72− are respectively,- a) +5, +6 and +6
- b)+3, +6 and +5
- c)+5, +3 and +6
- d)-3, +6 and +6
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxidation numbers of P in PO4−3, of S in SO42− and that of Cr in Cr2O72− are respectively,
a)
+5, +6 and +6
b)
+3, +6 and +5
c)
+5, +3 and +6
d)
-3, +6 and +6
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
The correct answer is option A
(I) xPO43− ⇒ x + 4 × (−2) = −3
⇒x = −3 + 8 = +5
⇒x = +5
Oxidation number of P = +5
(II) xSO42− ⇒ x + 4 × (−2) = −2
⇒x = −2 + 8
⇒x = +6
Oxidation number of S=+6
(III) xCr2O72− ⇒2x + 7 × (−2) = −2
⇒2x =−2+14
⇒2x=12
⇒x= 12/2 = +6
(I) xPO43− ⇒ x + 4 × (−2) = −3
⇒x = −3 + 8 = +5
⇒x = +5
Oxidation number of P = +5
(II) xSO42− ⇒ x + 4 × (−2) = −2
⇒x = −2 + 8
⇒x = +6
Oxidation number of S=+6
(III) xCr2O72− ⇒2x + 7 × (−2) = −2
⇒2x =−2+14
⇒2x=12
⇒x= 12/2 = +6
Direction (Q. Nos. 17) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
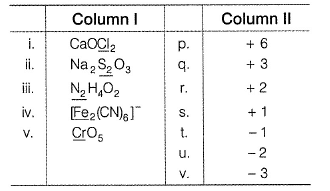
Match the compounds/ions having underlined atoms of different oxidation number (in Column I) with values (in Column II).


- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 17) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Match the compounds/ions having underlined atoms of different oxidation number (in Column I) with values (in Column II).


a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
(i) CaOCI2 has
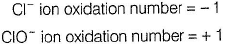
Oxidation number = + 6
Oxidation number = - 2
(ii) → (p,u)
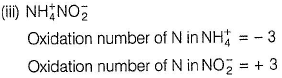
(iii) → (q.v)
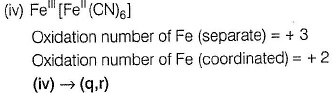
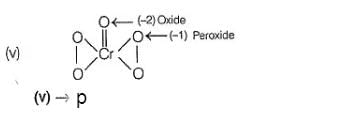
Oxidation number = + 6
Oxidation number = - 2
(ii) → (p,u)
(iii) → (q.v)

Oxidation number of 1/2 is assigned to oxygen atom in- a)superoxides
- b)when oxygen is bonded to fluorine
- c)when oxygen is bonded to metals
- d)peroxidesperoxides
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxidation number of 1/2 is assigned to oxygen atom in
a)
superoxides
b)
when oxygen is bonded to fluorine
c)
when oxygen is bonded to metals
d)
peroxidesperoxides
|
|
Arka Desai answered |
The oxidation number is a concept used in chemistry to keep track of the distribution of electrons in a compound or molecule. It is a measure of the charge that an atom would have if all the shared electrons were assigned to the more electronegative atom in a bond.
In the case of oxygen, its most common oxidation number is -2. However, in certain compounds, such as superoxides and peroxides, the oxidation number of oxygen deviates from -2.
Oxidation number of 1/2 is assigned to the oxygen atom in superoxides. Superoxides are a class of compounds that contain the superoxide ion, O2-. In this ion, each oxygen atom has an oxidation number of -1/2. This is because the oxygen-oxygen bond in the superoxide ion is a single bond with a bond order of 1/2. Therefore, each oxygen atom is assigned an oxidation number of -1/2 to account for the distribution of electrons in the bond.
In the case of peroxides, such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), the oxidation number of oxygen is -1. In peroxides, the oxygen-oxygen bond is a single bond with a bond order of 1. Each oxygen atom is assigned an oxidation number of -1 to account for the distribution of electrons in the bond.
When oxygen is bonded to fluorine, the oxidation number of oxygen is -1. Fluorine is the most electronegative element, and therefore, it attracts the shared electrons in the bond more strongly than oxygen. As a result, oxygen is assigned an oxidation number of -1 to account for the unequal distribution of electrons in the bond.
When oxygen is bonded to metals, the oxidation number of oxygen is typically -2. However, there are some exceptions to this rule, such as in certain metal peroxides or superoxides, where the oxidation number of oxygen deviates from -2.
In summary, the oxidation number of 1/2 is assigned to the oxygen atom in superoxides, where the oxygen-oxygen bond is a single bond with a bond order of 1/2. In other compounds, such as peroxides, fluorides, and most metal oxides, the oxidation number of oxygen is typically -1 or -2.
In the case of oxygen, its most common oxidation number is -2. However, in certain compounds, such as superoxides and peroxides, the oxidation number of oxygen deviates from -2.
Oxidation number of 1/2 is assigned to the oxygen atom in superoxides. Superoxides are a class of compounds that contain the superoxide ion, O2-. In this ion, each oxygen atom has an oxidation number of -1/2. This is because the oxygen-oxygen bond in the superoxide ion is a single bond with a bond order of 1/2. Therefore, each oxygen atom is assigned an oxidation number of -1/2 to account for the distribution of electrons in the bond.
In the case of peroxides, such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), the oxidation number of oxygen is -1. In peroxides, the oxygen-oxygen bond is a single bond with a bond order of 1. Each oxygen atom is assigned an oxidation number of -1 to account for the distribution of electrons in the bond.
When oxygen is bonded to fluorine, the oxidation number of oxygen is -1. Fluorine is the most electronegative element, and therefore, it attracts the shared electrons in the bond more strongly than oxygen. As a result, oxygen is assigned an oxidation number of -1 to account for the unequal distribution of electrons in the bond.
When oxygen is bonded to metals, the oxidation number of oxygen is typically -2. However, there are some exceptions to this rule, such as in certain metal peroxides or superoxides, where the oxidation number of oxygen deviates from -2.
In summary, the oxidation number of 1/2 is assigned to the oxygen atom in superoxides, where the oxygen-oxygen bond is a single bond with a bond order of 1/2. In other compounds, such as peroxides, fluorides, and most metal oxides, the oxidation number of oxygen is typically -1 or -2.
Hydrogen is prepared from H2O by adding- a)Ag, which acts as reducing agent
- b)Ca, which acts as reducing agent
- c)Au, which acts as oxidising agent
- d)AI, which acts as oxidising agent
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen is prepared from H2O by adding
a)
Ag, which acts as reducing agent
b)
Ca, which acts as reducing agent
c)
Au, which acts as oxidising agent
d)
AI, which acts as oxidising agent
|
|
Saumya Dey answered |
Preparation of Hydrogen from Water
- Hydrogen gas can be prepared from water by using a reducing agent, which reduces water to hydrogen gas and also gets oxidized in the process.
- Calcium (Ca) is a good reducing agent and can be used to prepare hydrogen gas from water.
- When calcium is added to water, it reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
- The chemical equation for the reaction is:
Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2
- Calcium has a strong affinity for oxygen and readily reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide, liberating hydrogen gas.
- This reaction is exothermic and produces a considerable amount of heat, which can be used to heat water or other substances.
- The liberated hydrogen gas can be collected by upward displacement of air or by using a gas syringe or gas jar.
- The purity of hydrogen gas prepared by this method is relatively low, as it may contain impurities like calcium hydroxide, unreacted water, and other gases like nitrogen and oxygen.
- Therefore, additional purification steps may be required to obtain pure hydrogen gas.
Advantages of using Calcium as a reducing agent
- Calcium is a readily available and inexpensive reducing agent.
- It reacts readily with water, producing a large amount of hydrogen gas.
- The reaction is exothermic and produces heat, which can be utilized in other processes.
- Calcium is a relatively safe reducing agent, as it does not react violently with water or other substances.
- The by-products of the reaction, calcium hydroxide, and hydrogen gas, are non-toxic and can be disposed of safely.
- Hydrogen gas can be prepared from water by using a reducing agent, which reduces water to hydrogen gas and also gets oxidized in the process.
- Calcium (Ca) is a good reducing agent and can be used to prepare hydrogen gas from water.
- When calcium is added to water, it reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
- The chemical equation for the reaction is:
Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2
- Calcium has a strong affinity for oxygen and readily reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide, liberating hydrogen gas.
- This reaction is exothermic and produces a considerable amount of heat, which can be used to heat water or other substances.
- The liberated hydrogen gas can be collected by upward displacement of air or by using a gas syringe or gas jar.
- The purity of hydrogen gas prepared by this method is relatively low, as it may contain impurities like calcium hydroxide, unreacted water, and other gases like nitrogen and oxygen.
- Therefore, additional purification steps may be required to obtain pure hydrogen gas.
Advantages of using Calcium as a reducing agent
- Calcium is a readily available and inexpensive reducing agent.
- It reacts readily with water, producing a large amount of hydrogen gas.
- The reaction is exothermic and produces heat, which can be utilized in other processes.
- Calcium is a relatively safe reducing agent, as it does not react violently with water or other substances.
- The by-products of the reaction, calcium hydroxide, and hydrogen gas, are non-toxic and can be disposed of safely.
The complex [Fe(H2O)5NO]2+ is formed in the ring-test for nitrate ion 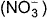 when freshly prepared FeSO4 solution is added to aqueous solution of
when freshly prepared FeSO4 solution is added to aqueous solution of 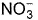 followed by the addition of conc. H2SO4. NO exists as NO+ (nitrosyl).Q. Magnetic moment
followed by the addition of conc. H2SO4. NO exists as NO+ (nitrosyl).Q. Magnetic moment 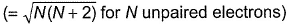 of Fe in the ring is
of Fe in the ring is - a)zero BM
- b)
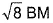
- c)
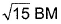
- d)
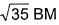
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The complex [Fe(H2O)5NO]2+ is formed in the ring-test for nitrate ion 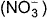 when freshly prepared FeSO4 solution is added to aqueous solution of
when freshly prepared FeSO4 solution is added to aqueous solution of 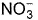 followed by the addition of conc. H2SO4. NO exists as NO+ (nitrosyl).
followed by the addition of conc. H2SO4. NO exists as NO+ (nitrosyl).
Q. Magnetic moment 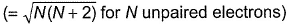 of Fe in the ring is
of Fe in the ring is
a)
zero BM
b)
c)
d)

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
Fe2+ is added asFeSO4
Fe+ is formed by charge transfer from NO to Fe2+
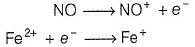
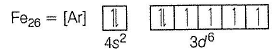
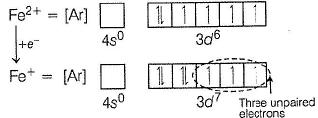
Fe+ has three unpaired electrons (N).
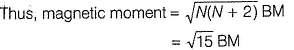
Fe+ is formed by charge transfer from NO to Fe2+
Fe+ has three unpaired electrons (N).
Oxidation numbers of P in PO43– , of S in SO42– and that of Cr in Cr2O72– are respectively [2009]- a)+ 3, + 6 and + 5
- b)+ 5, + 3 and + 6
- c)– 3, + 6 and + 6
- d)+ 5, + 6 and + 6
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxidation numbers of P in PO43– , of S in SO42– and that of Cr in Cr2O72– are respectively [2009]
a)
+ 3, + 6 and + 5
b)
+ 5, + 3 and + 6
c)
– 3, + 6 and + 6
d)
+ 5, + 6 and + 6
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
(i) Sum of oxidation states of all atoms = charge of ion.
(ii) oxidation number of oxygen = -2
Let the oxidation state of P in PO43- is x.
PO43-
x + 4 (-2) = - 3
x-8 = - 3
x = +5
Let the oxidation state of S in SO42- is y
y + 4(-2) = -2
y-8 = - 2
y = +6
Let the oxidation state of Cr in Cr2O72- is z.
2 x z+7(-2) = -2
2z-14 = - 2
z=+6
Hence, oxidation state of P, S and Cr are +5, +6 and +6
(ii) oxidation number of oxygen = -2
Let the oxidation state of P in PO43- is x.
PO43-
x + 4 (-2) = - 3
x-8 = - 3
x = +5
Let the oxidation state of S in SO42- is y
y + 4(-2) = -2
y-8 = - 2
y = +6
Let the oxidation state of Cr in Cr2O72- is z.
2 x z+7(-2) = -2
2z-14 = - 2
z=+6
Hence, oxidation state of P, S and Cr are +5, +6 and +6
I− reduces IO3- and I2 and itself oxidised to I2 in acidic medium. Thus, final reaction is- a)
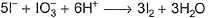
- b)
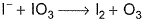
- c)
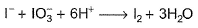
- d)None of the above is correct
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
I− reduces IO3- and I2 and itself oxidised to I2 in acidic medium. Thus, final reaction is
a)
b)
c)
d)
None of the above is correct
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
To balance oxidation number, cross-multiply by change in oxidation number
For the redox reactionMnO4– + C2O42- + H+ → Mn2+ + CO2 + H2O
The correct coefficients of the reactants for the balanced reaction are:- a)MnO4– C2O42- H+ 16 5 2
- b)MnO4– C2O42- H+ 2 16 5
- c)MnO4– C2O42- H+ 2 5 16
- d)MnO4– C2O42- H+ 5 16 2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For the redox reaction
MnO4– + C2O42- + H+ → Mn2+ + CO2 + H2O
The correct coefficients of the reactants for the balanced reaction are:
The correct coefficients of the reactants for the balanced reaction are:
a)
MnO4– C2O42- H+ 16 5 2
b)
MnO4– C2O42- H+ 2 16 5
c)
MnO4– C2O42- H+ 2 5 16
d)
MnO4– C2O42- H+ 5 16 2
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
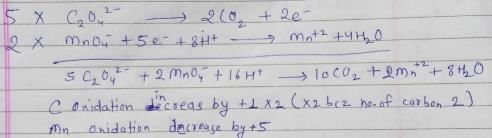
The loss of electron is termed as [1995]- a)oxidation
- b)reduction
- c)combustion
- d)neutralization
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The loss of electron is termed as [1995]
a)
oxidation
b)
reduction
c)
combustion
d)
neutralization

|
Mahesh Saini answered |
Losing of electron is called oxidation,
Direction (Q. Nos. 13 and 14) This section contains 2 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.Q. Which of the following species has/have oxidation number of the metal as + 6 ?- a)
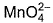
- b)
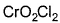
- c)
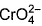
- d)
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 13 and 14) This section contains 2 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q. Which of the following species has/have oxidation number of the metal as + 6 ?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
To balance the oxygen atom in the given reaction in acidic medium
Cr2O72- (aq) → Cr3+(aq) we- a)Add water (H2O) on right side
- b)Add water (H2O) on left side
- c)Add O on right side
- d)Add O on left side
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
To balance the oxygen atom in the given reaction in acidic medium
Cr2O72- (aq) → Cr3+(aq) we
Cr2O72- (aq) → Cr3+(aq) we
a)
Add water (H2O) on right side
b)
Add water (H2O) on left side
c)
Add O on right side
d)
Add O on left side

|
Supriya Senapati answered |
Yes because right side is deficient of oxygen.
Assign oxidation number to P in NaH2PO4- a)+6
- b)+1
- c)+4
- d)5.0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Assign oxidation number to P in NaH2PO4
a)
+6
b)
+1
c)
+4
d)
5.0

|
Raksha Nambiar answered |
Oxidation state of P in NaH2PO4
Which of the following involves a redox reaction?- a)Reaction of H2SO4 with NaOH
- b)Production of ozone from oxygen in the atmosphere by lightning
- c)Production of nitrogen oxides from nitrogen and oxygen in the atmosphere by lightning
- d)Evaporation of water
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following involves a redox reaction?
a)
Reaction of H2SO4 with NaOH
b)
Production of ozone from oxygen in the atmosphere by lightning
c)
Production of nitrogen oxides from nitrogen and oxygen in the atmosphere by lightning
d)
Evaporation of water
|
|
Rocky Handsome answered |
•The 1st reaction is acid base reaction which does not involve either oxidation or reduction.
•O3 formation from O2 does not involve either oxidation or reduction.
•Nitrogen oxides from N2 and O2 involves oxidation of nitrogen and reduction of oxygen.
For example, N2 + O2---> NO2.
• Evaporation of H2O is a physical change and is not a chemical change.
Hence answer is C.
•O3 formation from O2 does not involve either oxidation or reduction.
•Nitrogen oxides from N2 and O2 involves oxidation of nitrogen and reduction of oxygen.
For example, N2 + O2---> NO2.
• Evaporation of H2O is a physical change and is not a chemical change.
Hence answer is C.
Select the set of compounds with oxidation-reduction duality.- a)Cl2, H3PO4, HCHO, HNO2
- b)Cl2, H3PO3, C6H5CHO, H2O2
- c)Br2, H3PO2, CH3CHO, H3PO4
- d)CrO2Cl2, KMnO4, SO3, CO2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the set of compounds with oxidation-reduction duality.
a)
Cl2, H3PO4, HCHO, HNO2
b)
Cl2, H3PO3, C6H5CHO, H2O2
c)
Br2, H3PO2, CH3CHO, H3PO4
d)
CrO2Cl2, KMnO4, SO3, CO2
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Com pounds having oxidising and reducing nature in given reaction are said to have oxidation-reduction duality. Such compounds are said to undergo disproportionation reaction.
(This is called Cannizzaro reaction.)
Note Such compounds have O.N. of the affected atoms intermediate of oxidation part and reduction part
In which of the following reactions, there is no change in valency ? [1994]- a)4 KClO3 —→ 3KClO4 + KCl
- b)SO2 + 2H2S —→ 2H2O + 3S
- c)BaO2 + H2SO4 —→ BaSO4 + H2O2
- d)3 BaO + O2 —→ 2 BaO2.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following reactions, there is no change in valency ? [1994]
a)
4 KClO3 —→ 3KClO4 + KCl
b)
SO2 + 2H2S —→ 2H2O + 3S
c)
BaO2 + H2SO4 —→ BaSO4 + H2O2
d)
3 BaO + O2 —→ 2 BaO2.

|
Maheshwar Saini answered |
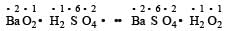
In this reaction, none of the elements undergoes a change in oxidation number or valency.
The oxidation number of oxygen in most compounds is- a)-3
- b)1
- c)4
- d)-2.0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxidation number of oxygen in most compounds is
a)
-3
b)
1
c)
4
d)
-2.0
|
|
Niharika Nair answered |
Oxidation number of oxygen in most compounds is -2.
Explanation:
- Oxidation number is the number assigned to an atom to indicate its degree of oxidation or loss/gain of electrons.
- Oxygen is a highly electronegative element, meaning it has a strong tendency to attract electrons.
- In most compounds, oxygen has an oxidation number of -2 because it tends to gain electrons to achieve a stable octet configuration (8 valence electrons).
- For example, in water (H2O), each hydrogen atom has an oxidation number of +1 and the oxygen atom has an oxidation number of -2, which balances out the charge to zero.
- There are some exceptions to this rule, such as in peroxides where oxygen has an oxidation number of -1, and in compounds with more electronegative elements where oxygen may have a positive oxidation number.
- Overall, the oxidation number of oxygen in most compounds is -2.
Explanation:
- Oxidation number is the number assigned to an atom to indicate its degree of oxidation or loss/gain of electrons.
- Oxygen is a highly electronegative element, meaning it has a strong tendency to attract electrons.
- In most compounds, oxygen has an oxidation number of -2 because it tends to gain electrons to achieve a stable octet configuration (8 valence electrons).
- For example, in water (H2O), each hydrogen atom has an oxidation number of +1 and the oxygen atom has an oxidation number of -2, which balances out the charge to zero.
- There are some exceptions to this rule, such as in peroxides where oxygen has an oxidation number of -1, and in compounds with more electronegative elements where oxygen may have a positive oxidation number.
- Overall, the oxidation number of oxygen in most compounds is -2.
The oxidation number of chromium in potassium dichromate is [1995]- a)+ 6
- b)– 5
- c)– 2
- d)+ 2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxidation number of chromium in potassium dichromate is [1995]
a)
+ 6
b)
– 5
c)
– 2
d)
+ 2

|
Ayush Sengupta answered |
Let x = oxidation no. of Cr in K2Cr2O7.
∴ (2 × 1) + (2 × x) + 7 (– 2) = 0
or 2 + 2x – 14 = 0 or x = + 6.
∴ (2 × 1) + (2 × x) + 7 (– 2) = 0
or 2 + 2x – 14 = 0 or x = + 6.
A mixture of potassium chlorate, oxalic acid and sulphuric acid is heated. During the reaction which element undergoes maximum change in the oxidation number ? [2012]- a)S
- b)H
- c)Cl
- d)C
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A mixture of potassium chlorate, oxalic acid and sulphuric acid is heated. During the reaction which element undergoes maximum change in the oxidation number ? [2012]
a)
S
b)
H
c)
Cl
d)
C

|
Ayush Sengupta answered |
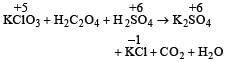
i.e. maximum change in oxidation number is observed in Cl (+5 to –1).
Phosphorus has the oxidation state of + 3 in- a)Phosphorous acid [1994]
- b)Orthophosphoric acid
- c)Hypophosphorous acid
- d)Metaphosphoric acid.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Phosphorus has the oxidation state of + 3 in
a)
Phosphorous acid [1994]
b)
Orthophosphoric acid
c)
Hypophosphorous acid
d)
Metaphosphoric acid.

|
Sushant Goyal answered |
O.N. of P in H3PO3 (phosphorous acid) 3 × 1 + x + 3 × (– 2) = 0 or x = + 3 In orthophosphoric acid (H3PO4) O.N. of P is + 5, in hypophosphorous acid (H3PO2) it is + 1 while in metaphosphoric acid (HPO3), it is + 5,
In this method, the two half equations are balanced separately and then added together to give balanced equation- a)Reluctant method
- b)Oxidizing agent method
- c)Reducing agent method
- d)Half reaction method
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In this method, the two half equations are balanced separately and then added together to give balanced equation
a)
Reluctant method
b)
Oxidizing agent method
c)
Reducing agent method
d)
Half reaction method
|
|
Kavita Joshi answered |
In the ion-electron method (also called the half-reaction method), the redox equation is separated into two half-equations - one for oxidation and one for reduction. Each of these half-reactions is balanced separately and then combined to give the balanced redox equation.
In which of the following reactions oxidation number of chromium has been affected?- a)
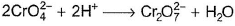
- b)
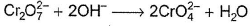
- c)
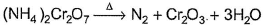
- d)

Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following reactions oxidation number of chromium has been affected?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Sankar Bose answered |
Oxidation number of Cr changes from +6 to +3.
Intensity of blue colour increases gradually when _________________- a)copper rod is dipped in silver nitrate solution
- b)silver rod is dipped in copper nitrate solution
- c)zinc rod is dipped in silver solution
- d)copper rod is dipped in zinc rod solution
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Intensity of blue colour increases gradually when _________________
a)
copper rod is dipped in silver nitrate solution
b)
silver rod is dipped in copper nitrate solution
c)
zinc rod is dipped in silver solution
d)
copper rod is dipped in zinc rod solution

|
EduRev NEET answered |
When a copper rod is dipped in silver nitrate solution, a redox reaction occurs between Copper and an aqueous solution of silver nitrate.
- So the intensity of blue colour increases gradually as silver deposits on the rod.
Reduction is defined in terms ofI. electronation and hydrogenation
II. deelectronation and gain of oxygen
III. increase in oxidation number
IV. decrease in oxidation numberSelect the correct terms- a)I and IV
- b)I and III
- c)II and II
- d)I and II
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Reduction is defined in terms of
I. electronation and hydrogenation
II. deelectronation and gain of oxygen
III. increase in oxidation number
IV. decrease in oxidation number
II. deelectronation and gain of oxygen
III. increase in oxidation number
IV. decrease in oxidation number
Select the correct terms
a)
I and IV
b)
I and III
c)
II and II
d)
I and II
|
|
Siddharth Mehra answered |
Reduction is defined in terms of electronation and hydrogenation
Reduction is a chemical process that involves the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation number. It can be defined in terms of two main reactions: electronation and hydrogenation.
I. Electronation:
- Electronation refers to the process of gaining electrons. In a reduction reaction, a molecule, ion, or atom accepts one or more electrons, resulting in a more negative charge.
- For example, in the reaction: X + e- -> X-, the atom X gains an electron, and its oxidation number decreases. This is a reduction reaction.
II. Hydrogenation:
- Hydrogenation is a specific type of reduction reaction where hydrogen atoms are added to a molecule.
- During hydrogenation, the molecule gains hydrogen atoms, and its oxidation number decreases. This is a reduction reaction.
- For example, in the reaction: X + H2 -> XH2, the molecule X gains hydrogen atoms, and its oxidation number decreases. This is a reduction reaction.
III. Increase in oxidation number:
- Increase in oxidation number is not associated with reduction but with oxidation.
- In oxidation, the oxidation number of an atom, ion, or molecule increases, indicating the loss of electrons.
- Reduction, on the other hand, involves the gain of electrons, resulting in a decrease in oxidation number.
IV. Decrease in oxidation number:
- Decrease in oxidation number is directly associated with reduction.
- Reduction reactions involve the gain of electrons, leading to a decrease in oxidation number.
- For example, if the oxidation number of an atom changes from +2 to 0, it has undergone reduction because its oxidation number has decreased.
Conclusion:
Based on the definitions of reduction and the given options, the correct terms that define reduction are I. electronation and IV. decrease in oxidation number. These two terms accurately describe the process of reduction, where electrons are gained and the oxidation number decreases. Therefore, option A. (I and IV) is the correct answer.
Reduction is a chemical process that involves the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation number. It can be defined in terms of two main reactions: electronation and hydrogenation.
I. Electronation:
- Electronation refers to the process of gaining electrons. In a reduction reaction, a molecule, ion, or atom accepts one or more electrons, resulting in a more negative charge.
- For example, in the reaction: X + e- -> X-, the atom X gains an electron, and its oxidation number decreases. This is a reduction reaction.
II. Hydrogenation:
- Hydrogenation is a specific type of reduction reaction where hydrogen atoms are added to a molecule.
- During hydrogenation, the molecule gains hydrogen atoms, and its oxidation number decreases. This is a reduction reaction.
- For example, in the reaction: X + H2 -> XH2, the molecule X gains hydrogen atoms, and its oxidation number decreases. This is a reduction reaction.
III. Increase in oxidation number:
- Increase in oxidation number is not associated with reduction but with oxidation.
- In oxidation, the oxidation number of an atom, ion, or molecule increases, indicating the loss of electrons.
- Reduction, on the other hand, involves the gain of electrons, resulting in a decrease in oxidation number.
IV. Decrease in oxidation number:
- Decrease in oxidation number is directly associated with reduction.
- Reduction reactions involve the gain of electrons, leading to a decrease in oxidation number.
- For example, if the oxidation number of an atom changes from +2 to 0, it has undergone reduction because its oxidation number has decreased.
Conclusion:
Based on the definitions of reduction and the given options, the correct terms that define reduction are I. electronation and IV. decrease in oxidation number. These two terms accurately describe the process of reduction, where electrons are gained and the oxidation number decreases. Therefore, option A. (I and IV) is the correct answer.
The more positive the value of E0, the greater is the tendency of the species to get reduced. Using the standard electrode potential of redox couples given below find out which of the following is the strongest oxidising agent. E0values : Fe3 + / Fe2+ = +0.77; I2(s)/l- = +0.54; cu2+/ Cu = +0.34; Ag+ / Ag = +0.80V- a)Ag+
- b)Fe3+
- c)I2 (s)
- d)Cu2+
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The more positive the value of E0, the greater is the tendency of the species to get reduced. Using the standard electrode potential of redox couples given below find out which of the following is the strongest oxidising agent.
E0values : Fe3 + / Fe2+ = +0.77; I2(s)/l- = +0.54; cu2+/ Cu = +0.34; Ag+ / Ag = +0.80V
a)
Ag+
b)
Fe3+
c)
I2 (s)
d)
Cu2+

|
Mansi Mukherjee answered |
Oxidation number of H is not always +1 . It can be -1 , 0.
Consider the elements: Cs, Ne, I and F. Identify the element(s) that exhibits only negative oxidation state- a)F
- b)I
- c)s
- d)Cs and F
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the elements: Cs, Ne, I and F. Identify the element(s) that exhibits only negative oxidation state
a)
F
b)
I
c)
s
d)
Cs and F

|
Sinjini Datta answered |
F has negative oxidation state as it is very electro negative.
When Cl2 gas reacts with hot and concentrated sodium hydroxide solution, the oxidation number of chlorine changes from : [2012]- a)zero to +1 and zero to –5
- b)zero to –1 and zero to +5
- c)zero to –1 and zero to +3
- d)zero to +1 and zero to –3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When Cl2 gas reacts with hot and concentrated sodium hydroxide solution, the oxidation number of chlorine changes from : [2012]
a)
zero to +1 and zero to –5
b)
zero to –1 and zero to +5
c)
zero to –1 and zero to +3
d)
zero to +1 and zero to –3

|
Arnab Iyer answered |
On reaction with hot and concentrated alkali a mixture of chloride and chlorate is formed
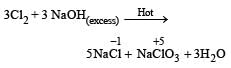
The correct order of N-compounds in its decreasing order of oxidation states is- a)HNO3, NO, N2, NH4Cl
- b)HNO3, NO, NH4Cl, N2
- c)HNO3, NH4Cl, NO, N2
- d)NH4Cl, N2, NO, HN03
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of N-compounds in its decreasing order of oxidation states is
a)
HNO3, NO, N2, NH4Cl
b)
HNO3, NO, NH4Cl, N2
c)
HNO3, NH4Cl, NO, N2
d)
NH4Cl, N2, NO, HN03

|
Infinity Academy answered |
To determine the decreasing order of oxidation states of nitrogen in the given compounds, we need to find the oxidation state of nitrogen in each compound:
- HNO3 (Nitric acid): Oxidation state of nitrogen: +5
- NO (Nitric oxide): Oxidation state of nitrogen: +2
- N2 (Dinitrogen): Oxidation state of nitrogen: 0
- NH4Cl (Ammonium chloride): Oxidation state of nitrogen: -3
Now, let's arrange these compounds in decreasing order of oxidation states:
- HNO3: +5
- NO: +2
- N2: 0
- NH4Cl: -3
So, the correct order in decreasing oxidation state is:
HNO3, NO, N2, NH4Cl
The process in which the strength of an unknown solution is calculated using a known standard solution.- a)Titration
- b)Oxidation
- c)Reduction
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The process in which the strength of an unknown solution is calculated using a known standard solution.
a)
Titration
b)
Oxidation
c)
Reduction
d)
None of these
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
A titration is a technique used to work out the concentration of an unknown solution based on its chemical reaction with a solution of known concentration. The process usually involves adding the known solution (the titrant) to a known quantity of the unknown solution (the analyte) until the reaction is complete.
Which of the following is true as per metal activity series?- a)Zn>Cu>Ag
- b)Zn<Cu<Ag
- c)Zn>Ag>Cu
- d)Zn<Ag<Cu
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is true as per metal activity series?
a)
Zn>Cu>Ag
b)
Zn<Cu<Ag
c)
Zn>Ag>Cu
d)
Zn<Ag<Cu

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Metal activity series or electrochemical series is a series in the decreasing order of metals which are active during a chemical reaction comparatively with each other.
- Here, Zinc’s activity is greater than Copper’s activity and Copper’s activity is greater than that of silver.
When a zinc rod is kept in a copper nitrate solution what happens?- a)zinc is deposited on copper
- b)copper is deposited in the beaker
- c)zinc is deposited in the beaker
- d)copper is deposited on zinc
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When a zinc rod is kept in a copper nitrate solution what happens?
a)
zinc is deposited on copper
b)
copper is deposited in the beaker
c)
zinc is deposited in the beaker
d)
copper is deposited on zinc

|
EduRev NEET answered |
When zinc is placed in copper nitrate solution the intensity of the blue colour is produced and copper iron is deposited on zinc.
- This is a Redox reaction between zinc and an aqueous solution of copper nitrate occurring in a beaker.
The oxidation number of phosphorus in pyrophosphoric acid is [1999]- a)+3
- b)+1
- c)+4
- d)+5
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxidation number of phosphorus in pyrophosphoric acid is [1999]
a)
+3
b)
+1
c)
+4
d)
+5

|
Naveen Menon answered |
Pyrophosphoric acid H4P2O7
Let oxidation state of phosphorus is x(4 × 1 + (– 2) × 7 + 2 x) = 0
∴ 2x = 10 or x = +5
Let oxidation state of phosphorus is x(4 × 1 + (– 2) × 7 + 2 x) = 0
∴ 2x = 10 or x = +5
The oxidation states of sulphur in the anions SO32–, S2O42– and S2O62– follow the order [2003]- a)
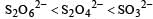
- b)
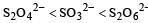
- c)
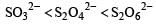
- d)
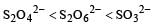
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxidation states of sulphur in the anions SO32–, S2O42– and S2O62– follow the order [2003]
a)
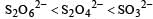
b)
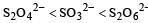
c)
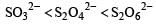
d)
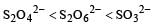
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
The correct answer is option B
Oxidation state of S2O42−
2(x) + 4(−2) = −2
2x = 8 − 2
2x = 6
x = 3
Oxidation state of SO32−
x + 3(−2) = −2
x = 6 − 2
x = 4
Oxidation state of S2O62−
2(x) + 6(−2) = −2
2x = 12 − 2
2x = 10
x = 5
So the oxidation state of sulphur in the anions S2O42−, S2O42− and S2O62− follows the order.S2O42− < SO32− < S2O62−.
Oxidation state of S2O42−
2(x) + 4(−2) = −2
2x = 8 − 2
2x = 6
x = 3
Oxidation state of SO32−
x + 3(−2) = −2
x = 6 − 2
x = 4
Oxidation state of S2O62−
2(x) + 6(−2) = −2
2x = 12 − 2
2x = 10
x = 5
So the oxidation state of sulphur in the anions S2O42−, S2O42− and S2O62− follows the order.S2O42− < SO32− < S2O62−.
The oxide, which cannot act as a reducing agent, is[1995]- a)NO2
- b)SO2
- c)CO2
- d)ClO2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxide, which cannot act as a reducing agent, is[1995]
a)
NO2
b)
SO2
c)
CO2
d)
ClO2
|
|
Keerthana Datta answered |
Explanation:
Reducing Agent:
A reducing agent is a substance that donates electrons to another chemical species in a redox reaction. It itself gets oxidized in the process.
Oxides:
Oxides are compounds that contain oxygen as an anion.
Identifying the Correct Answer:
To determine which oxide cannot act as a reducing agent, we need to consider the oxidation states of the elements present in each oxide. In general, nonmetals tend to gain electrons (get reduced) and act as oxidizing agents, while metals tend to lose electrons (get oxidized) and act as reducing agents.
Oxides Given:
a) NO2 - Nitrogen has an oxidation state of +4 in NO2, and it can be reduced to lower oxidation states, making it a potential reducing agent.
b) SO2 - Sulfur has an oxidation state of +4 in SO2, and it can be reduced to lower oxidation states, making it a potential reducing agent.
c) CO2 - Carbon has an oxidation state of +4 in CO2, and it cannot be further reduced as it already has the lowest common oxidation state for carbon, making it unable to act as a reducing agent.
d) ClO2 - Chlorine has an oxidation state of +4 in ClO2, and it can be reduced to lower oxidation states, making it a potential reducing agent.
Correct Answer:
The oxide that cannot act as a reducing agent is CO2 because carbon already has the lowest common oxidation state in this compound and cannot be further reduced.
Reducing Agent:
A reducing agent is a substance that donates electrons to another chemical species in a redox reaction. It itself gets oxidized in the process.
Oxides:
Oxides are compounds that contain oxygen as an anion.
Identifying the Correct Answer:
To determine which oxide cannot act as a reducing agent, we need to consider the oxidation states of the elements present in each oxide. In general, nonmetals tend to gain electrons (get reduced) and act as oxidizing agents, while metals tend to lose electrons (get oxidized) and act as reducing agents.
Oxides Given:
a) NO2 - Nitrogen has an oxidation state of +4 in NO2, and it can be reduced to lower oxidation states, making it a potential reducing agent.
b) SO2 - Sulfur has an oxidation state of +4 in SO2, and it can be reduced to lower oxidation states, making it a potential reducing agent.
c) CO2 - Carbon has an oxidation state of +4 in CO2, and it cannot be further reduced as it already has the lowest common oxidation state for carbon, making it unable to act as a reducing agent.
d) ClO2 - Chlorine has an oxidation state of +4 in ClO2, and it can be reduced to lower oxidation states, making it a potential reducing agent.
Correct Answer:
The oxide that cannot act as a reducing agent is CO2 because carbon already has the lowest common oxidation state in this compound and cannot be further reduced.
A metal in a compound can be displaced by another metal in the uncombined state. Which metal is a better reducing agent in such a case?
- a)Better reducing agent is the one that looses more electrons
- b)Better reducing agent is the one that looses less electrons
- c)Both are same in reducing capacity
- d)The reduced metal is a better reducing agent than the reducing metal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A metal in a compound can be displaced by another metal in the uncombined state. Which metal is a better reducing agent in such a case?
a)
Better reducing agent is the one that looses more electrons
b)
Better reducing agent is the one that looses less electrons
c)
Both are same in reducing capacity
d)
The reduced metal is a better reducing agent than the reducing metal

|
Bhavana Chavan answered |
Concept of Reducing Agent:
A reducing agent is a substance that loses or "donates" an electron to another substance in a redox chemical reaction. Therefore, a good reducing agent is the one that gets oxidized easily, or in other words, the one that can easily lose electrons.
Characteristics of a Good Reducing Agent:
A reducing agent is a substance that loses or "donates" an electron to another substance in a redox chemical reaction. Therefore, a good reducing agent is the one that gets oxidized easily, or in other words, the one that can easily lose electrons.
Characteristics of a Good Reducing Agent:
- Electron Loss: A better reducing agent is the one that loses more electrons. This is because by losing electrons, the reducing agent gets oxidized and in turn reduces the other substance. This is the basic principle of a redox reaction.
- Reactivity: The reactivity of the metal also determines its capacity as a reducing agent. Metals that are high in the reactivity series are good reducing agents. This is because they can easily lose electrons and get oxidized.
- Stability: Metals that are less stable are better reducing agents because they can easily lose electrons to attain a stable state.
Hence, Option A is the correct answer - a better reducing agent is the one that loses more electrons.
Consider the following experimental facts,I. When Cl2 gas is passed into Kl solution containing CHCI3, violet colour appears in CHCI3 layer.
II. When Cl2 gas is passed into KBr solution containing CHCI3, orange colour appears in CHCI3 layer.
III. When Cl2 gas is passed into a solution containing KBr, Kl and KCI, containing CHCI3, violet colour appears in CHCI3 layer.Select the correct experimental facts.- a)I and II
- b)I and III
- c)III Only
- d)II and III
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following experimental facts,
I. When Cl2 gas is passed into Kl solution containing CHCI3, violet colour appears in CHCI3 layer.
II. When Cl2 gas is passed into KBr solution containing CHCI3, orange colour appears in CHCI3 layer.
III. When Cl2 gas is passed into a solution containing KBr, Kl and KCI, containing CHCI3, violet colour appears in CHCI3 layer.
II. When Cl2 gas is passed into KBr solution containing CHCI3, orange colour appears in CHCI3 layer.
III. When Cl2 gas is passed into a solution containing KBr, Kl and KCI, containing CHCI3, violet colour appears in CHCI3 layer.
Select the correct experimental facts.
a)
I and II
b)
I and III
c)
III Only
d)
II and III
|
|
Poulomi Singh answered |
Oxidising power of F2 > CI2 > Br2 > l2
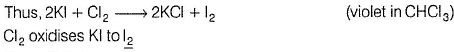
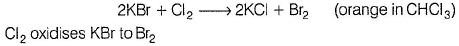
Thus, (II) is true.
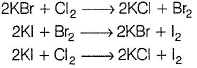
In experiment (III), orange colour of Br2 does not appear, as it also oxidises Kl to l2. Hence , only violet colour appears in CHCI3 layer. Thus, (III) is also true.
Thus, (II) is true.
In experiment (III), orange colour of Br2 does not appear, as it also oxidises Kl to l2. Hence , only violet colour appears in CHCI3 layer. Thus, (III) is also true.
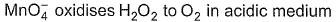
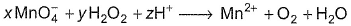 Coefficient x, y and z are respectively
Coefficient x, y and z are respectively

- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Coefficient x, y and z are respectively

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Cross -multiply by change in oxidation number and balance H by H+ ions.
Thus, x = 2, y = 5 and z = 6
The highest value of oxidation number changes from 1 to 7- a)in the atoms of transition elements
- b)the first three groups
- c)In alkaline earth metals
- d)across the third period in the periodic table
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The highest value of oxidation number changes from 1 to 7
a)
in the atoms of transition elements
b)
the first three groups
c)
In alkaline earth metals
d)
across the third period in the periodic table

|
Sai Mishra answered |
the highest value of oxidation number changes from 1 to 7.
In the reaction of metallic cobalt placed in nickel sulphate solution, therein is a competition for release of electrons At equilibrium, chemical tests reveal that both Ni+2 (aq) and Co+2 (aq) are present at moderate concentrations. The result is that:
- a)Only one reactant and one product is greatly favoured.
- b)Only [Co(s) and Ni+2 (aq)] are favoured
- c)Only Co+2 (aq) and Ni (s)] are favoured
- d)neither the reactants nor the products [are greatly favoured.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the reaction of metallic cobalt placed in nickel sulphate solution, therein is a competition for release of electrons At equilibrium, chemical tests reveal that both Ni+2 (aq) and Co+2 (aq) are present at moderate concentrations. The result is that:
a)
Only one reactant and one product is greatly favoured.
b)
Only [Co(s) and Ni+2 (aq)] are favoured
c)
Only Co+2 (aq) and Ni (s)] are favoured
d)
neither the reactants nor the products [are greatly favoured.

|
Arya Reddy answered |
The reaction of metallic cobalt in a nickel sulfate solution involves a competition for the release of electrons. This means that the cobalt metal can react with the nickel ions in the solution, or the nickel can deposit on the cobalt metal.
At equilibrium, the reaction has balanced out with no net change in the concentration of the reactants and products. The fact that both Ni+2 (aq) and Co+2 (aq) are present at moderate concentrations at equilibrium signifies that neither forward nor reverse reactions are greatly favoured.
- A: This option is incorrect because both reactants and products are present in moderate concentrations, indicating that neither is greatly favoured.
- B: This statement is not correct either. Even though Co (s) and Ni+2 (aq) are part of the reaction, the fact that Co+2 (aq) is also present at moderate concentrations shows that they are not the only favoured species.
- C: This option is also incorrect. Even though Co+2 (aq) and Ni (s) are part of the reaction, the fact that Ni+2 (aq) is also present at moderate concentrations shows that they are not the only favoured species.
- D: This is the correct answer. When a reaction is at equilibrium, it means that the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction. Therefore, neither the reactants nor the products are greatly favoured. In other words, the concentrations of the reactants and products remain constant over time
The oxidation number of an element in a compound is evaluated on the basis of certain rules. Which of the following rules is not correct in this respect?- a)The algebraic sum of all the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero.
- b)In all its compounds, the oxidation number of fluorine is – 1.
- c)An element in the free or the uncombined state bears oxidation number zero.
- d)The oxidation number of hydrogen is always +1.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxidation number of an element in a compound is evaluated on the basis of certain rules. Which of the following rules is not correct in this respect?
a)
The algebraic sum of all the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero.
b)
In all its compounds, the oxidation number of fluorine is – 1.
c)
An element in the free or the uncombined state bears oxidation number zero.
d)
The oxidation number of hydrogen is always +1.

|
Ishani Mehta answered |
as oxygen is more electronegative than Cl,Br and I. So they have positive oxidation state.
Chapter doubts & questions for Redox Reactions - 1 Year Dropper Course for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Redox Reactions - 1 Year Dropper Course for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
1 Year Dropper Course for NEET
503 videos|1698 docs|628 tests
|