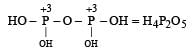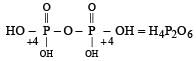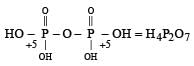All Exams >
NEET >
1 Year Dropper Course for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of p-Block Elements for NEET Exam
The correct statements among the given are
- a)Antimony belongs to 15th group and 5th period
- b)electron gain enthalpy of P > N > S > O
- c)Minimum and maximum oxidation number of phosphorus is -3 and +6
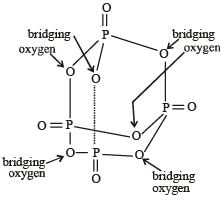
- d)Fluoroapatite, formula is Ca6(PO4)6 CaF2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statements among the given are
a)
Antimony belongs to 15th group and 5th period
b)
electron gain enthalpy of P > N > S > O
c)
Minimum and maximum oxidation number of phosphorus is -3 and +6
d)
Fluoroapatite, formula is Ca6(PO4)6 CaF2

|
Divey Sethi answered |
Option A: Group 5A (or VA) of the periodic table are the pnictogens: the nonmetals nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P), the metalloids arsenic (As) and antimony (Sb), and the metal bismuth (Bi).
Option B: The electron gain enthalpy of P< N< S< O.
Option C: Minimum and maximum oxidation number of phosphorus are -3 and +5 respectively.
Option D: Fluorapatite is a phosphate mineral with the formula Ca5(PO4)3F .
Option B: The electron gain enthalpy of P< N< S< O.
Option C: Minimum and maximum oxidation number of phosphorus are -3 and +5 respectively.
Option D: Fluorapatite is a phosphate mineral with the formula Ca5(PO4)3F .
Hence, option A is correct.
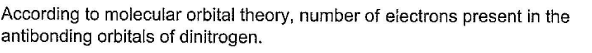
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Subhankar Choudhary answered |
Molecular Orbital Theory and Antibonding Orbitals in Nitrogen
Molecular orbital theory (MOT) is a theoretical model that describes the behavior of electrons in molecules based on the principles of quantum mechanics. It is used to explain and predict the properties of molecules, including their electronic and magnetic properties, bond lengths, bond angles, and so on.
In MOT, the electrons in a molecule are treated as waves that are described by molecular orbitals (MOs), which are mathematical functions that represent the probability of finding an electron at a given point in space. These MOs are formed by combining the atomic orbitals of the atoms in the molecule.
Antibonding orbitals are MOs that have a higher energy than the atomic orbitals from which they are formed. When electrons occupy these orbitals, they weaken the bond between the atoms in the molecule, making it more likely to break apart.
Nitrogen has five valence electrons, which are represented by the atomic orbitals s and p. In the molecule N2, these atomic orbitals combine to form five MOs: two bonding MOs, two antibonding MOs, and one nonbonding MO.
The two bonding MOs are lower in energy than the atomic orbitals from which they are formed, and they help to hold the two nitrogen atoms together. The nonbonding MO is filled with two electrons, which are shared equally between the two nitrogen atoms and do not contribute to the bond strength.
The two antibonding MOs are higher in energy than the atomic orbitals from which they are formed, and they weaken the bond between the two nitrogen atoms. When all five valence electrons are placed into the MOs, there are four electrons in the antibonding MOs and one electron in the nonbonding MO.
Therefore, according to molecular orbital theory, there are four electrons present in the antibonding orbitals of nitrogen.
Molecular orbital theory (MOT) is a theoretical model that describes the behavior of electrons in molecules based on the principles of quantum mechanics. It is used to explain and predict the properties of molecules, including their electronic and magnetic properties, bond lengths, bond angles, and so on.
In MOT, the electrons in a molecule are treated as waves that are described by molecular orbitals (MOs), which are mathematical functions that represent the probability of finding an electron at a given point in space. These MOs are formed by combining the atomic orbitals of the atoms in the molecule.
Antibonding orbitals are MOs that have a higher energy than the atomic orbitals from which they are formed. When electrons occupy these orbitals, they weaken the bond between the atoms in the molecule, making it more likely to break apart.
Nitrogen has five valence electrons, which are represented by the atomic orbitals s and p. In the molecule N2, these atomic orbitals combine to form five MOs: two bonding MOs, two antibonding MOs, and one nonbonding MO.
The two bonding MOs are lower in energy than the atomic orbitals from which they are formed, and they help to hold the two nitrogen atoms together. The nonbonding MO is filled with two electrons, which are shared equally between the two nitrogen atoms and do not contribute to the bond strength.
The two antibonding MOs are higher in energy than the atomic orbitals from which they are formed, and they weaken the bond between the two nitrogen atoms. When all five valence electrons are placed into the MOs, there are four electrons in the antibonding MOs and one electron in the nonbonding MO.
Therefore, according to molecular orbital theory, there are four electrons present in the antibonding orbitals of nitrogen.
Hot conc. H2SO4 acts as moderately strong oxidising agent. It oxidises both metals and nonmetals. Which of the following element is oxidised by conc. H2SO4 into two gaseous products?- a) Cu
- b)S
- c)C
- d)zn
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Hot conc. H2SO4 acts as moderately strong oxidising agent. It oxidises both metals and nonmetals. Which of the following element is oxidised by conc. H2SO4 into two gaseous products?
a)
Cu
b)
S
c)
C
d)
zn
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
C element is oxidised by conc. H2SO4 into two gaseous products.
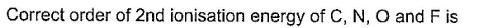
- a)
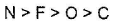
- b)
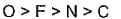
- c)
- d)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
The second ionization energy refers to the energy required to remove the electron from the corresponding monovalent cation of the respective atom.
It is expected to increase from left to right in the periodic table with the decrease in atomic size.
Since the Oxygen atom gets a stable electronic configuration, 2s22p3 after removing one electron, the O+ shows greater ionization energy than F+ as well as N+.
Thus, correct order will be: O > F > N > C
In the third period of the periodic table the element having smallest size is - a)Na
- b)CI
- c)Ar
- d)Si
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the third period of the periodic table the element having smallest size is
a)
Na
b)
CI
c)
Ar
d)
Si
|
|
Aarav Sharma answered |
The third period contains eight elements: sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, and argon.
In a period from left to right atomic size decreases due to Increase in nuclear charge.
but the noble gases are bigger than the halogens as they have octet and sort of repulsion occurs in the shells.
so the smallest element in a period is the halogen.so chlorine Cl is the smallest.
Which is the strongest acid in the following : [NEET 2013]- a)HClO3
- b)HClO4
- c)H2SO3
- d)H2SO4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the strongest acid in the following : [NEET 2013]
a)
HClO3
b)
HClO4
c)
H2SO3
d)
H2SO4

|
Surbhi Das answered |
HClO4 is the strongest acid amongst all because the oxidation state or Cl is maximum (+7).
A brown ring is formed in the ring test for NO3– ion. It is due to the formation of- a)[Fe(H2O)5 (NO)]2+
- b) FeSO4.NO2
- c)[Fe(H2O)4(NO)2]2+
- d)FeSO4.HNO3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A brown ring is formed in the ring test for NO3– ion. It is due to the formation of
a)
[Fe(H2O)5 (NO)]2+
b)
FeSO4.NO2
c)
[Fe(H2O)4(NO)2]2+
d)
FeSO4.HNO3

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
When freshly prepared solution of FeSO4 is added in a solution containing NO3– ion, it leads to formation of a brown coloured complex. This is known as brown ring test of nitrate.
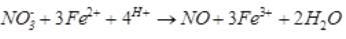
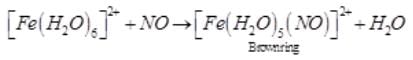
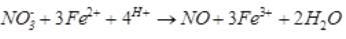
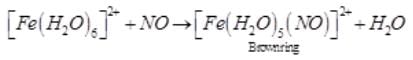

- a)
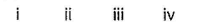

- b)
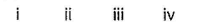

- c)
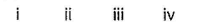
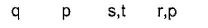
- d)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
(i) Nitrogen is a non-metal.
(ii) Phosphorus is a non-metal.
(iii) Arsenic is a metalloid and shows Sublimation.
(iv) Bismuth is metal and shows the Inert pair effect.
(ii) Phosphorus is a non-metal.
(iii) Arsenic is a metalloid and shows Sublimation.
(iv) Bismuth is metal and shows the Inert pair effect.
Hence, option A is correct.
Which of the following is a polar molecule ? [NEET 2013]- a)SF4
- b)SiF4
- c)XeF4
- d)BF3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a polar molecule ? [NEET 2013]
a)
SF4
b)
SiF4
c)
XeF4
d)
BF3

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
SF4 has 4 bond pairs and 1 lone pair of electrons, sp3d hybridisation leads to irregular shape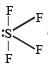 and resultant
and resultant
 and resultant
and resultantμ ≠ 0.
Among the following compounds, the number of compounds which have oxidation states of S is +4 ?PbS, SO2, SF6, Na2S2O3, H2SO3
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following compounds, the number of compounds which have oxidation states of S is +4 ?
PbS, SO2, SF6, Na2S2O3, H2SO3
|
|
Shreya Singh answered |
SO2...x+2(-2)=0.x=4..H2SO3.2(1)+x+3(-2)=0.2+x-6=0.-4+x=0.x=4...
- a)
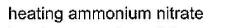
- b)

- c)

- d)
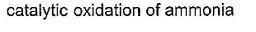
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Gauri Datta answered |
Oxidation of ammonia with CuO produces nitrogen gas and water vapor. This reaction is represented as:
2NH3 + 3CuO → 3Cu + N2 + 3H2O
The gaseous chemical produced in this reaction is nitrogen gas (N2), which is also obtained by reacting excess ammonia with chlorine. This reaction is represented as:
2NH3 + Cl2 → N2 + 2HCl
Explanation:
- Ammonium nitrate: Heating ammonium nitrate results in the decomposition of ammonium nitrate into nitrogen gas, water vapor, and oxygen gas. The reaction is represented as:
NH4NO3 → N2 + 2H2O + O2
- Potassium dichromate: Heating potassium dichromate results in the production of oxygen gas and potassium chromate. The reaction is represented as:
4K2Cr2O7 → 4K2CrO4 + 3O2
- Catalytic oxidation of ammonia: Catalytic oxidation of ammonia involves the use of a catalyst (such as platinum or palladium) to oxidize ammonia to nitrogen gas and water vapor. The reaction is represented as:
4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O
2NO + O2 → 2NO2
4NO2 + O2 → 2N2O5
N2O5 → N2 + 2.5O2
- Reacting excess ammonia with chlorine: This reaction involves the reaction of excess ammonia with chlorine gas to produce nitrogen gas and hydrochloric acid. The reaction is represented as:
2NH3 + Cl2 → N2 + 2HCl
Therefore, option B, reacting excess ammonia with chlorine, is the correct answer.
2NH3 + 3CuO → 3Cu + N2 + 3H2O
The gaseous chemical produced in this reaction is nitrogen gas (N2), which is also obtained by reacting excess ammonia with chlorine. This reaction is represented as:
2NH3 + Cl2 → N2 + 2HCl
Explanation:
- Ammonium nitrate: Heating ammonium nitrate results in the decomposition of ammonium nitrate into nitrogen gas, water vapor, and oxygen gas. The reaction is represented as:
NH4NO3 → N2 + 2H2O + O2
- Potassium dichromate: Heating potassium dichromate results in the production of oxygen gas and potassium chromate. The reaction is represented as:
4K2Cr2O7 → 4K2CrO4 + 3O2
- Catalytic oxidation of ammonia: Catalytic oxidation of ammonia involves the use of a catalyst (such as platinum or palladium) to oxidize ammonia to nitrogen gas and water vapor. The reaction is represented as:
4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O
2NO + O2 → 2NO2
4NO2 + O2 → 2N2O5
N2O5 → N2 + 2.5O2
- Reacting excess ammonia with chlorine: This reaction involves the reaction of excess ammonia with chlorine gas to produce nitrogen gas and hydrochloric acid. The reaction is represented as:
2NH3 + Cl2 → N2 + 2HCl
Therefore, option B, reacting excess ammonia with chlorine, is the correct answer.
In the MOT of F2 molecule, number of electrons occupying antibonding orbitals are
Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?
In the MOT of F2 molecule, number of electrons occupying antibonding orbitals are
|
|
Nandita Ahuja answered |
Fluorine atom have 2+7 electrons so an F2 molecule contain 18 electrons.
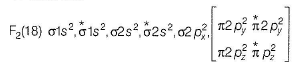
Hence, 8 electrons occupy the antibonding orbitals.
Hence, 8 electrons occupy the antibonding orbitals.
The correct statements among the following are
- a)Bond lengths in O2 ,
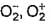 are 121 , 134, 149 pm
are 121 , 134, 149 pm
- b)Ozone is stronger oxidising agent than dioxygen
- c)O2 acts as reducing agent when it reacts with powerful oxidising agents like PtF6
- d)Ozone is much more stable than oxygen
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statements among the following are
a)
Bond lengths in O2 , 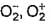 are 121 , 134, 149 pm
are 121 , 134, 149 pm
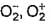 are 121 , 134, 149 pm
are 121 , 134, 149 pmb)
Ozone is stronger oxidising agent than dioxygen
c)
O2 acts as reducing agent when it reacts with powerful oxidising agents like PtF6
d)
Ozone is much more stable than oxygen

|
Srishti Kaur answered |
The correct option is Option A, B and C.
Bond length is inversely proportional to bond order. O2+ has the highest bond order among these three, so it should have the shortest bond length.
Ozone is a powerful oxidizing agent as compared to oxygen. This is due to the unstable nature of ozone and the nascent oxygen that is released during the reaction.
O2 when gas makes others like H2 gas to lose electrons, therefore, O2 gas is an oxidizing agent and H2 when gas loses electrons in redox reaction, therefore H2 gas is a reducing agent.
Oxygen is more stable than ozone. On heating, ozone readily dissociates and forms oxygen and free radicals of oxygen known as nascent oxygen which take part in reaction, thus ozone is more reactive than oxygen
Which of the following molecular species has unpaired electron(s) ?- a)N2
- b)O2
- c)NO+
- d)CN-
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following molecular species has unpaired electron(s) ?
a)
N2
b)
O2
c)
NO+
d)
CN-
|
|
Priya Chavan answered |
One or More than One Options Correct Type
This section contains 5 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
- a)

- b)
- c)
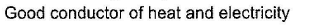
- d)
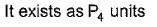
Correct answer is 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
This section contains 5 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
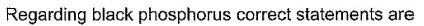
This section contains 5 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Rahul Desai answered |
(a.c) Being goad conductor of neat and elecnicky, black phosphorus is a most stabte allotrope of phosphorus
Which of the following statement is incorrect ?- a)SRP values of halogens F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
- b)Bond dissociation enthalpy of Br2 > F2 > Cl2 > I2
- c)Boiling points of I2 > Br2 > Cl2 > F2
- d)Reducing power of I- > Br- > Cl- > F-
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is incorrect ?
a)
SRP values of halogens F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
b)
Bond dissociation enthalpy of Br2 > F2 > Cl2 > I2
c)
Boiling points of I2 > Br2 > Cl2 > F2
d)
Reducing power of I- > Br- > Cl- > F-
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
The correct order of bond dissociation enthalpy is
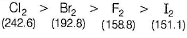
Which of the following is thermally the most stable?- a)H2Te
- b)H2S
- c)H2O
- d)H2Se
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is thermally the most stable?
a)
H2Te
b)
H2S
c)
H2O
d)
H2Se

|
Ujwal Patel answered |
Stability of hydrides decreases down the group so most stable is H2O
Direction (Q. Nos. 8-12) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.Q. Which of the following can act as dehydrating agent ?- a)P4O10
- b)POCI3
- c)Cone.H2SO4
- d)P4O6
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 8-12) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
Which of the following can act as dehydrating agent ?
a)
P4O10
b)
POCI3
c)
Cone.H2SO4
d)
P4O6

|
Keshav Bhatheja answered |
Conc h2so4 is a very good dehydrating agent as extract h2o from reaction very easily...by breaking into hso4- and h+ and the rest of two i dont know i think we have to learn them
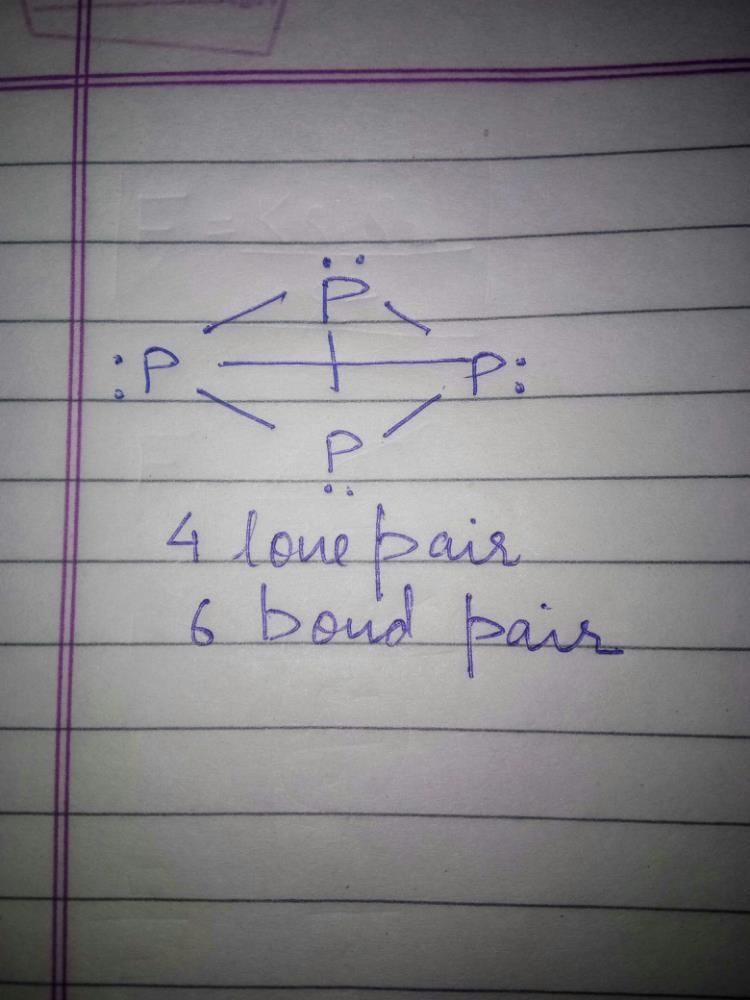
The number of P – O bonds and lone pairs of electron present in P4O6 molecule respectively - a)12 and 4
- b)8 and 8
- c)12 and 16
- d)12 and 12
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of P – O bonds and lone pairs of electron present in P4O6 molecule respectively
a)
12 and 4
b)
8 and 8
c)
12 and 16
d)
12 and 12

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
Number of P – O bonds = 12
Number of pair of electron = 16
Number of pair of electron = 16
When chlorine reacts with hot, cone. NaOH, the products formed are- a)NaCI
- b)NaOCI
- c)NaCIO3
- d)HCI
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
When chlorine reacts with hot, cone. NaOH, the products formed are
a)
NaCI
b)
NaOCI
c)
NaCIO3
d)
HCI

|
Anupama Nair answered |
When Cl2 reacts with hot and concentrated NaOH, then....6NaOH+3Cl2→5NaCl +NaClO3+3H2O...When Cl2 reacts with cold and dilute NaOH then ...2NaOH+Cl2→NaCl+NaOCl+H2O
Statement Type
This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct anser from the codes given below

- a)

- b)

- c)
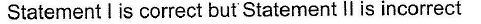
- d)
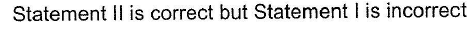
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement Type
This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct anser from the codes given below

This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct anser from the codes given below
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Pranjal Pillai answered |
P — P single bond in P4 molecule is much weaker
(213 kJ mol-1) than N ≡ N triple bond (941.4 kJ mol-1) in N2.
Among the following which is the strongest oxidising agent? [2009]- a)Br2
- b)I2
- c)Cl2
- d)F2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following which is the strongest oxidising agent? [2009]
a)
Br2
b)
I2
c)
Cl2
d)
F2

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
Standard reduction potential of halogens are positive and decreases from fluorine to iodine. Therefore halogens act as strong oxidising agent and their oxidising power decreases from fluorine to iodine.
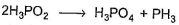 in this equivalent weight of the acid in the reactant side is obtained by dividing molecular weight with
in this equivalent weight of the acid in the reactant side is obtained by dividing molecular weight with
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Abc Bcd answered |
Because there are two molecules of acid in balanced equation.
Which of the following is the strongest Lewis base?
- a)NBr3
- b)NF3
- c)NCl3
- d)NI3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the strongest Lewis base?
a)
NBr3
b)
NF3
c)
NCl3
d)
NI3
|
|
Shanaya Choudhary answered |
Correct Answer :- D
- Lewis bases need to be able to donate electrons. Fluorine is the most electronegative element in the halogens followed by chlorine, bromine and iodine.
- Due to fluorine being strongly electronegative, it draws the electron density towards itself which makes it difficult for nitrogen atom to donate its lone pair of electrons. So, NF is the least basic. This trend follows the strength of electronegativity of the halides.
- Since iodine is least electronegative, it is the most basic trihalide of nitrogen.
So, we have the trend, in decreasing order of basic strength:
NF3 < NCl3 < NBr3 < NI3
The total number of positive oxidation states shown by fluorine is
Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer?
The total number of positive oxidation states shown by fluorine is
|
|
Puja Gupta answered |
Fluorine is an element that belongs to the halogen group in the periodic table. It has an atomic number of 9, and its electron configuration is 1s^2 2s^2 2p^5. Fluorine is highly electronegative, meaning it has a strong tendency to attract electrons towards itself when it forms chemical bonds. This property is due to its relatively small atomic size and high effective nuclear charge.
Fluorine has a total of 7 valence electrons, which are electrons in its outermost energy level (2s^2 2p^5). In order to achieve a stable electron configuration, fluorine tends to gain one electron to complete its octet. By gaining one electron, fluorine achieves a stable electron configuration similar to the nearest noble gas, neon (1s^2 2s^2 2p^6).
Fluorine's strong electronegativity and its tendency to gain electrons result in it having only one common oxidation state, which is -1. In this oxidation state, fluorine gains one electron to achieve a stable configuration of 1s^2 2s^2 2p^6. This oxidation state is commonly observed in compounds where fluorine acts as an anion, such as in the compound sodium fluoride (NaF). In NaF, fluorine gains an electron from sodium to form the F- ion.
It is important to note that although fluorine is highly electronegative and tends to gain electrons, it does not have the capability to lose electrons easily and form positive oxidation states. This is because fluorine's valence shell is almost full, and losing electrons would require a significant amount of energy.
In conclusion, fluorine has only one common oxidation state, which is -1. This is due to its strong electronegativity and its tendency to gain one electron to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Fluorine has a total of 7 valence electrons, which are electrons in its outermost energy level (2s^2 2p^5). In order to achieve a stable electron configuration, fluorine tends to gain one electron to complete its octet. By gaining one electron, fluorine achieves a stable electron configuration similar to the nearest noble gas, neon (1s^2 2s^2 2p^6).
Fluorine's strong electronegativity and its tendency to gain electrons result in it having only one common oxidation state, which is -1. In this oxidation state, fluorine gains one electron to achieve a stable configuration of 1s^2 2s^2 2p^6. This oxidation state is commonly observed in compounds where fluorine acts as an anion, such as in the compound sodium fluoride (NaF). In NaF, fluorine gains an electron from sodium to form the F- ion.
It is important to note that although fluorine is highly electronegative and tends to gain electrons, it does not have the capability to lose electrons easily and form positive oxidation states. This is because fluorine's valence shell is almost full, and losing electrons would require a significant amount of energy.
In conclusion, fluorine has only one common oxidation state, which is -1. This is due to its strong electronegativity and its tendency to gain one electron to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Number of chemical species having negative oxidation state for nitrogen among NF3, NCI3, NH2OH, NH3,CH3NH2, NH-2, L13N, N20, HCN, HNC, NO-2
Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of chemical species having negative oxidation state for nitrogen among
NF3, NCI3, NH2OH, NH3,CH3NH2, NH-2, L13N, N20, HCN, HNC, NO-2

|
Keerthana Mehta answered |
(8) Except in 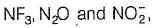 in all others N has negative oxidation states
in all others N has negative oxidation states
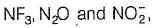 in all others N has negative oxidation states
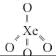
in all others N has negative oxidation statesWhich of the following statements is not correct about XeF2?
- a)It can be obtained by direct reaction between F2 and Xe at high pressure
- b)XeF2 undergoes alkaline hydrolysis to give O2 and Xe
- c)XeF2 is a powerful reducing agent
- d)XeF2 contains two bond pairs and three lone pairs
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not correct about XeF2?
a)
It can be obtained by direct reaction between F2 and Xe at high pressure
b)
XeF2 undergoes alkaline hydrolysis to give O2 and Xe
c)
XeF2 is a powerful reducing agent
d)
XeF2 contains two bond pairs and three lone pairs
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
XeF2 is obtained by direct reaction of Xe and F2 at high pressure. It undergoes alkali hydrolysis to produce Xe and O2. XeF2 is a powerful reducing agent where Xe+2 can change to +6 state.
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, each describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraphs have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).PassageSulphur and the rest of the elements of 16th group are less electronegative than oxygen. They can acquire ns2np6 by sharing two electrons with the atoms of other elements and thus, exhibit +2 oxidation state in their compounds, in addition to this, atoms have vacant d-orbitals in their valence shell due to which electrons I can be promoted from the s- and p-orbitals of the same shell. As a result, they can show +4 and +6 oxidation states. The oxidation states of elements never exceed +6.Q.Oxidation states of sulphur in H2S2O7 and H2S2O8 respectively are- a)+ 6 and + 7
- b)+ 6 and + 6
- c)+ 5 and + 6
- d)+ 5 and + 7
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, each describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraphs have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
Sulphur and the rest of the elements of 16th group are less electronegative than oxygen. They can acquire ns2np6 by sharing two electrons with the atoms of other elements and thus, exhibit +2 oxidation state in their compounds, in addition to this, atoms have vacant d-orbitals in their valence shell due to which electrons I can be promoted from the s- and p-orbitals of the same shell. As a result, they can show +4 and +6 oxidation states. The oxidation states of elements never exceed +6.
Q.
Oxidation states of sulphur in H2S2O7 and H2S2O8 respectively are
a)
+ 6 and + 7
b)
+ 6 and + 6
c)
+ 5 and + 6
d)
+ 5 and + 7
|
|
Om Desai answered |
H2S2O7 has no peroxy bond while H2S2O8 has one peroxy bond.
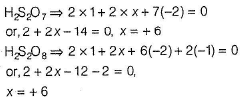
Which has lowest bond energy (single bond)?- a)O—H
- b)O—O
- c)S—H
- d)S—S
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which has lowest bond energy (single bond)?
a)
O—H
b)
O—O
c)
S—H
d)
S—S
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Sulfur atoms are larger than oxygen atoms.
Pi bonds are formed by overlapping of two parallel p orbitals. The further the distance between atoms, the lesser the overlapping and weaker the bond.
But sigma bonds in case of Oxygen and Nitrogen are not strong enough because you are bringing two very small atoms (with large no. of electrons in the outer shell) too close which makes the sigma bond comparatively unstable than that of S-S bond where sigma bond is more stable due to lesser electro static repulsion of non-bonding electrons.
Ozone can be detected by using- a)Silver
- b)Sodium
- c)Mercury
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Ozone can be detected by using
a)
Silver
b)
Sodium
c)
Mercury
d)
None of these

|
Aarya Dasgupta answered |
Ozone is detected by using Hg.
At what temperature white phosphorous changes to red phosphorous?- a)300° C
- b)450° C
- c)50° C
- d)400° C
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
At what temperature white phosphorous changes to red phosphorous?
a)
300° C
b)
450° C
c)
50° C
d)
400° C
|
|
Ananya Singh answered |
According to NCERT, red phosphorus is obtained by heating white phosphorus at 573 K in an inert atmosphere for several days. In degree celius, temperature = 300⁰ C (573K - 273).
Which are correct statements ?
- a)The melting point of antimony is higher than bismuth
- b)Ionisation energy of C < O < N
- c)In 15th group, all show allotropy except bismuth and nitrogen
- d)Maximum covalency of nitrogen and Phosphorus are 4 and 5 respectively
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which are correct statements ?
a)
The melting point of antimony is higher than bismuth
b)
Ionisation energy of C < O < N
c)
In 15th group, all show allotropy except bismuth and nitrogen
d)
Maximum covalency of nitrogen and Phosphorus are 4 and 5 respectively
|
|
Om Desai answered |
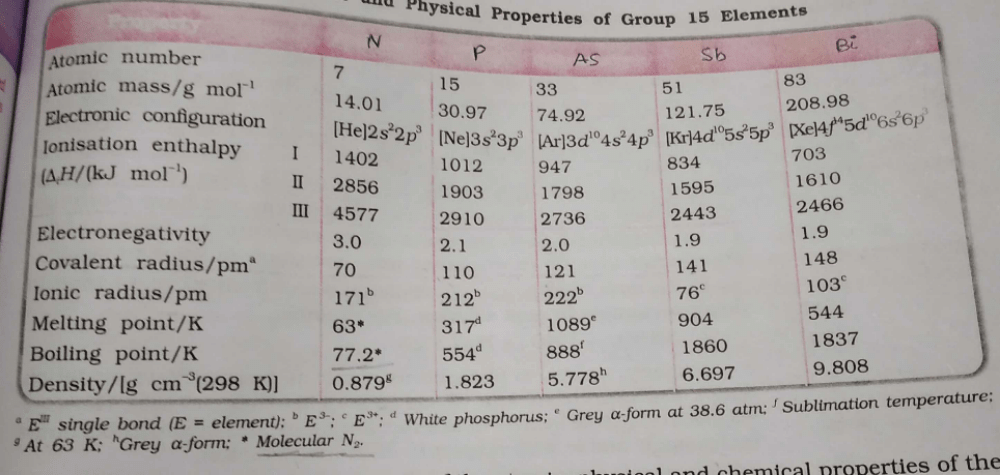
Option A: Bismuth has 6 electron shells, whereas Antimony has 5 electron shells. Because of this, the attractive force between two Bismuth atoms is less due to electron shielding, resulting in bismuth possessing a lower boiling point than antimony.
Option B: In a period of moving from left to right, the ionization energy increases. Since N has a table half-filled 2p subshell which requires large energy.
Thus, the correct order of ionization energy is C < O < N.
Option C: Except N and Bi, all the group 15 elements exhibits allotropy. The allotropes of phosphorous are rather complex but essentially, there are three allotropic forms known as white, red, and black phosphorous.
Option D: Maximum covalency of N & P are 4 and 5.
Option B: In a period of moving from left to right, the ionization energy increases. Since N has a table half-filled 2p subshell which requires large energy.
Thus, the correct order of ionization energy is C < O < N.
Option C: Except N and Bi, all the group 15 elements exhibits allotropy. The allotropes of phosphorous are rather complex but essentially, there are three allotropic forms known as white, red, and black phosphorous.
Option D: Maximum covalency of N & P are 4 and 5.
Hence, option A,B,C,D is correct.
Which is the correct order w.r.t the given property? - a)N > P > As > Sb > Bi (Atomic mass)
- b)N > P > As > Sb = Bi (Electronegativity)
- c)N > P > As > Sb = Bi (Covalent radii)
- d)N = P > As > Sb > Bi (Density)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the correct order w.r.t the given property?
a)
N > P > As > Sb > Bi (Atomic mass)
b)
N > P > As > Sb = Bi (Electronegativity)
c)
N > P > As > Sb = Bi (Covalent radii)
d)
N = P > As > Sb > Bi (Density)
|
|
Roshni Desai answered |
I'm sorry, but the question is incomplete. Please provide more information about the property being referred to.
In the all oxyacids of phosphorus, each phosphorus atom is in sp3-hybridised state. All these acids contain P—OH bonds, the hydrogen atom of which are ionisable imparting acidic nature to the compound. The ‘ous’ acids (oxidation state of P is + 1 or + 3) also have P—H bonds in which hydrogens are not ionisable.
The presence of P—H bonds in these acids imparts reducing properties. The structure of some oxyacids are drawn below: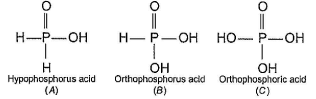
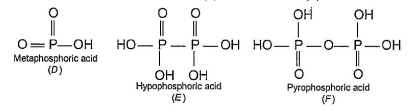 Q. Which of the acids show reducing properties?
Q. Which of the acids show reducing properties?- a)A and C
- b)A and B
- c)A , B and D
- d)C, D, E and F
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the all oxyacids of phosphorus, each phosphorus atom is in sp3-hybridised state. All these acids contain P—OH bonds, the hydrogen atom of which are ionisable imparting acidic nature to the compound. The ‘ous’ acids (oxidation state of P is + 1 or + 3) also have P—H bonds in which hydrogens are not ionisable.
The presence of P—H bonds in these acids imparts reducing properties. The structure of some oxyacids are drawn below:
The presence of P—H bonds in these acids imparts reducing properties. The structure of some oxyacids are drawn below:
Q.
Which of the acids show reducing properties?
a)
A and C
b)
A and B
c)
A , B and D
d)
C, D, E and F

|
Kirti Choudhary answered |
Reducing property is due to P...H bond
Harmful UV radiations emitted from the sun are prevented from reaching the earth by the presence of ozone in the- a)mesosphere
- b)thermosphere
- c)stratosphere
- d)troposphere
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Harmful UV radiations emitted from the sun are prevented from reaching the earth by the presence of ozone in the
a)
mesosphere
b)
thermosphere
c)
stratosphere
d)
troposphere

|
Pooja Pillai answered |
Stratosphere layer strongly absorb harmful UV-radiations (λ. 255 nm).
Which of the following is the most basic oxide?- a)Sb2O3
- b)Bi2O3 [2006]
- c)SeO2
- d)Al2O3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the most basic oxide?
a)
Sb2O3
b)
Bi2O3 [2006]
c)
SeO2
d)
Al2O3

|
Nilotpal Gupta answered |
More the oxidation state of the central atom (metal) more is its acidity. Hence SeO2 (O. S. of Se = +4) is acidic. Further for a given O.S., the basic character of the oxides increases with the increasing size of the central atom.
Thus Al2O3 and Sb2O3 are amphoteric and Bi2O3 is basic.
Thus Al2O3 and Sb2O3 are amphoteric and Bi2O3 is basic.
Noble gases do not react with other elements because [1994]- a)They are mono atomic
- b)They are found in abundance
- c)The size of their atoms is very small
- d)They are completely paired up and stable electron shells
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Noble gases do not react with other elements because [1994]
a)
They are mono atomic
b)
They are found in abundance
c)
The size of their atoms is very small
d)
They are completely paired up and stable electron shells

|
Abhishek Desai answered |
On account of highly stable ns2 np6 configuration in the valence shell. These elements have no tendency either to lose gain or share electrons with atoms of other elements i.e., their combining capacity or valency is zero. Further all the orbitals in the atoms of these elements are doubly occupied i.e electrons are not available for sharing.
Which of the following is not a use of noble gases?- a)Argon is widely used for filling incandescent electric bulbs
- b)Neon is used in safety devices for protecting electrical instruments
- c)Radon is used in radiotherapy of cancer
- d)Helium is filled in tubes of cycles and scooters tyres
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a use of noble gases?
a)
Argon is widely used for filling incandescent electric bulbs
b)
Neon is used in safety devices for protecting electrical instruments
c)
Radon is used in radiotherapy of cancer
d)
Helium is filled in tubes of cycles and scooters tyres
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Helium is used in filling tubes of aeroplane tyres.
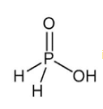 is the structure of
is the structure of- a)Phosphorous acid
- b)Hypophosphorus Acid
- c)Phosphoric acid
- d)Pyrophosphoric acid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Phosphorous acid
b)
Hypophosphorus Acid
c)
Phosphoric acid
d)
Pyrophosphoric acid
|
|
Baby Ghosh answered |
Of course..this is a structure of hypo phosphorus acid. It is a mineral acid with formula H4P2O6.In hypophosphorus acid,the phosphorus bonds are identical and joined with p-p bond .there is also joined oxygen and hydrogen bonds as the structure follows.
Chapter doubts & questions for p-Block Elements - 1 Year Dropper Course for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of p-Block Elements - 1 Year Dropper Course for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily