All Exams >
NEET >
1 Year Dropper Course for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Human Health & Diseases for NEET Exam
The chemical test that is used for diagnosis of typhoid is:- a)ESR-Test
- b)PCR-Test
- c)Widal-Test
- d)ELISA-Test
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The chemical test that is used for diagnosis of typhoid is:
a)
ESR-Test
b)
PCR-Test
c)
Widal-Test
d)
ELISA-Test

|
Jeeshan Ahmed answered |
The Widal test is one method that may be used to help make a presumptive diagnosis of enteric fever, also known as typhoid fever.The test was based on demonstrating the presence of agglutinin (antibody) in the serum of an infected patient, against the H (flagellar) and O (somatic) antigens ofSalmonella typhi.
The chemical test that is used for diagnosis of typhoid is:- a)ESR-Test
- b)PCR-Test
- c)Widal-Test
- d)ELISA-Test
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The chemical test that is used for diagnosis of typhoid is:
a)
ESR-Test
b)
PCR-Test
c)
Widal-Test
d)
ELISA-Test

|
Dilip answered |
Its given in 12th NCERT.... widal test for typhoid
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The disease chikunguniya is transmitted by- A:Cockroach
- B:Aedes mosquitoes
- C:House flies
- D:Female Anopheles
The answer is b.
The disease chikunguniya is transmitted by
A:
Cockroach
B:
Aedes mosquitoes
C:
House flies
D:
Female Anopheles
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
When a mosquito feeds on an infected person, the mosquito can become infected and can bite and infect others. The Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes transmit chikungunya. They also transmit dengue fever, another disease caused by a virus.
The disease causing microorganisms are called?- a)Microbes
- b)Fungi
- c)Allotropes
- d)Pathogen
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The disease causing microorganisms are called?
a)
Microbes
b)
Fungi
c)
Allotropes
d)
Pathogen
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Most microbes belong to four major groups: bacteria, viruses, protozoa or fungi. (To find out more, see the “Bacteria/Viruses/Protozoa” fact sheets). Disease-causing microbes can also be called pathogens, germs or bugs and are responsible for causing infectious diseases.
Which part of the tobacco plant is infected by Meloidogyne incognita ?[2016]- a)Flower
- b)Leaf
- c)Stem
- d)Root
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of the tobacco plant is infected by Meloidogyne incognita ?
[2016]
a)
Flower
b)
Leaf
c)
Stem
d)
Root

|
Rhea Sarkar answered |
(d) Meloidogyne incognita is a nematode (roundworm) in the family Heteroderidae. It is commonly called the "southern rootknot nematode" or the "cotton root-knot nematode".
Antibodies are produced by:- a)T-cells
- b)B-cells
- c)Monocytes
- d)Phagocytes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Antibodies are produced by:
a)
T-cells
b)
B-cells
c)
Monocytes
d)
Phagocytes
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Antibodies are produced by specialized white blood cells called B lymphocytes (or B cells). When an antigen binds to the B-cell surface, it stimulates the B cell to divide and mature into a group of identical cells called a clone.
Formation of antibodies within our body is called:- a)Innate immunity
- b)Acquired immunity
- c)Passive immunity
- d)Active immunity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Formation of antibodies within our body is called:
a)
Innate immunity
b)
Acquired immunity
c)
Passive immunity
d)
Active immunity
|
|
Shalini Basu answered |
The combination of antibodies and complement promotes rapid clearing of pathogens. The production of antibodies by plasma cells in response to an antigen is called active immunity and describes the host's active response of theimmune system to an infection or to a vaccination.
The sporozoites that cause infection, when a female Anopheles mosquito bites a person, are stored in
- a)Liver of person
- b)RBCs of mosquito
- c)Salivary glands of mosquito
- d)Intestine of person
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The sporozoites that cause infection, when a female Anopheles mosquito bites a person, are stored in
a)
Liver of person
b)
RBCs of mosquito
c)
Salivary glands of mosquito
d)
Intestine of person
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
- Sporozoites enter the female Anopheles mosquito when they bite an infected person where these sporozoite fertilise and multiply in the stomach wall of the female Anopheles and stored in the salivary gland of mosquito till it is again transferred to the human body by a mosquito bite.
- After entering the human body the sporozoites reach the liver cells, where they multiply. This is followed by their attack on red blood cells resulting in their rupture. The ruptured RBCs release a toxin called haemozoin, which is responsible for high recurring fever, chills and shivering.
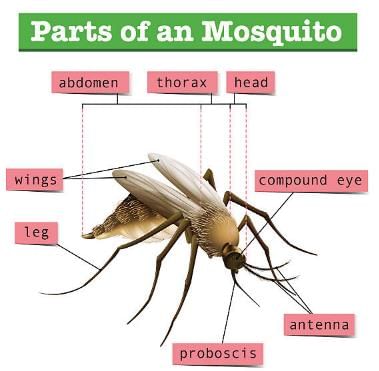
- Mosquito Anatomy:
Grafted kidney may be rejected in a patient due to :[2015 RS]- a)Cell-midiated immune response
- b)Passive immune response
- c)Innate immune response
- d)Humoral immune response
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Grafted kidney may be rejected in a patient due to :
[2015 RS]
a)
Cell-midiated immune response
b)
Passive immune response
c)
Innate immune response
d)
Humoral immune response

|
Dipika Das answered |
(a) Cell-midiated immune response is a system which is specialized for a particular person.
Immuno-deficiency syndrome could develop due to- a)Defective liver
- b)AIDS virus
- c)Defective thymus
- d)Weak immune system
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Immuno-deficiency syndrome could develop due to
a)
Defective liver
b)
AIDS virus
c)
Defective thymus
d)
Weak immune system
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).Following initial infection, a person may not notice any symptoms or may experience a brief period of influenza-like illness. Typically, this is followed by a prolonged period with no symptoms. As the infection progresses, it interferes more with the immune system, increasing the risk of developing common infections such as tuberculosis, as well as other opportunistic infections, and tumors that rarely affect people who have working immune systems.[5] These late symptoms of infection are referred to as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).This stage is often also associated with unintended weight loss.
Where memory cells are formed?- a)Monocytes
- b)Neutrophils
- c)Eosinophil
- d)Lymphocytes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Where memory cells are formed?
a)
Monocytes
b)
Neutrophils
c)
Eosinophil
d)
Lymphocytes
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
B lymphocytes are the cells of the immune system that make antibodies to invading pathogens like viruses. They form memory cells that remember the same pathogen for faster antibody production in future infections.
MALT constitutes about..........per cent of the lymphoid tissue in human body.- a)50%
- b)20%
- c)70%
- d)10%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
MALT constitutes about..........per cent of the lymphoid tissue in human body.
a)
50%
b)
20%
c)
70%
d)
10%
|
|
Mohammad Nomaan answered |
MALT constitute about 50% of the lymphoid tissue in human body.
Marijuana, hashish, charas and ganga are group of drugs collectively called?- a)Cannabinoids
- b)Opioids
- c)Coke
- d)Crack
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Marijuana, hashish, charas and ganga are group of drugs collectively called?
a)
Cannabinoids
b)
Opioids
c)
Coke
d)
Crack
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Marijuana, hashish, charas, and ganja contain chemicals called cannabinoids. They are generally, taken as inhalation or oral ingestion to effects cardiovascular system of the body.
Where will you look for the sporozoites of the malarial parasite?- a)Saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquito
- b)Spleen of infected humans
- c)Salivary glands of freshly moulted female Anopheles mosquito
- d)Red blood corpuscles of human suffering from malaria
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Where will you look for the sporozoites of the malarial parasite?
a)
Saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquito
b)
Spleen of infected humans
c)
Salivary glands of freshly moulted female Anopheles mosquito
d)
Red blood corpuscles of human suffering from malaria
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Sporozoite is the infective stage of the malarial parasite. They are present in the saliva of infected female anopheles mosquito.
In higher vertebrates, the immune system can distinguish self-cells and non-self. If this property is lost due to genetic abnormality and it attacks self-cells, then it leads to[2016]- a)allergic response
- b)graft rejection
- c)auto-immune disease
- d)active immunity
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In higher vertebrates, the immune system can distinguish self-cells and non-self. If this property is lost due to genetic abnormality and it attacks self-cells, then it leads to
[2016]
a)
allergic response
b)
graft rejection
c)
auto-immune disease
d)
active immunity

|
Shruti Chauhan answered |
(c) An autoimmune disease is a pathological state arising from an abnormal immune response of the body to substances and tissues that are normally present in the body
Which one of the following is a matching pair of a drug and its category?- a)Heroin – psychotropic
- b)Benzodiazepines – pain killer
- c)Lysergic acid dimethyl amide – narcotic
- d)Amphetamines – stimulant
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is a matching pair of a drug and its category?
a)
Heroin – psychotropic
b)
Benzodiazepines – pain killer
c)
Lysergic acid dimethyl amide – narcotic
d)
Amphetamines – stimulant

|
Shivani Rane answered |
Amphetamines is kind of drug which is used as stimulant. It is a strong CNS stimulant that is used in the treatment of ADHD. Lysergic acid dimethyl amide is not a narcotic and heroin is not a psychotropic agent.
Which of the following is the unit of immune system?- a)Chondrocyte
- b)Erythrocyte
- c)Lymphocyte
- d)Parasite
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the unit of immune system?
a)
Chondrocyte
b)
Erythrocyte
c)
Lymphocyte
d)
Parasite

|
Pankaj Banerjee answered |
Lymphocytes are one of several different types of white blood cells. Lymphocytes are of two types B cells and T cells. When a macrophage engulfs organisms, B cells (humoral immunity) release antibodies which cause the destruction of bacteria. The T cells (cell-mediated immunity) destroy the infectious organisms by killing the body cells that are affected. Hence lymphocytes is a unit of the immune system.
So, the correct answer is 'Lymphocytes'.
Anti venom against snake poison contains:- a)Antigens
- b)Enzymes
- c)Antigen-antibody complexes
- d)Antibodies
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Anti venom against snake poison contains:
a)
Antigens
b)
Enzymes
c)
Antigen-antibody complexes
d)
Antibodies
|
|
Madhavan Ghosh answered |
Anti venom against snake poison contains antibodies.
Explanation:
Anti venom is a serum that is used to treat snake bites. It contains antibodies that are specifically produced to neutralize the venom of a particular snake species. The antibodies are produced by injecting a small amount of the snake venom into an animal, usually a horse, and then collecting the blood serum from the animal after a certain period of time. This serum contains the antibodies that have been produced in response to the venom.
The antibodies in the anti venom work by binding to the venom molecules and neutralizing their toxic effects. This prevents the venom from causing damage to the body and allows the body's own immune system to clear the venom from the bloodstream.
It is important to note that anti venom is specific to the species of snake that produced the venom. This means that anti venom for one species of snake will not be effective against the venom of another species. It is also important to administer anti venom as soon as possible after a snake bite, as the venom can rapidly spread through the body and cause severe damage if left untreated.
Explanation:
Anti venom is a serum that is used to treat snake bites. It contains antibodies that are specifically produced to neutralize the venom of a particular snake species. The antibodies are produced by injecting a small amount of the snake venom into an animal, usually a horse, and then collecting the blood serum from the animal after a certain period of time. This serum contains the antibodies that have been produced in response to the venom.
The antibodies in the anti venom work by binding to the venom molecules and neutralizing their toxic effects. This prevents the venom from causing damage to the body and allows the body's own immune system to clear the venom from the bloodstream.
It is important to note that anti venom is specific to the species of snake that produced the venom. This means that anti venom for one species of snake will not be effective against the venom of another species. It is also important to administer anti venom as soon as possible after a snake bite, as the venom can rapidly spread through the body and cause severe damage if left untreated.
Which is the particular type of drug that is obtained from the plant whose one flowering branch is shown below? [2014]
- a)Hallucinogen
- b)Depressant
- c)Stimulant
- d)Pain - killer
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the particular type of drug that is obtained from the plant whose one flowering branch is shown below? [2014]

a)
Hallucinogen
b)
Depressant
c)
Stimulant
d)
Pain - killer

|
Charvi Shah answered |
(a) The plant illustrated in diagram is Datura which has hallucinogenic properties. Hallucinogen is a substance that produces psychological effects normally associated only with dreams, schizophrenia, or religious visions. It produces changes in perception (ranging from distortions in what is sensed to perceptions of objects where there are none), thought, and feeling.
The function of IgE is- a)Protection from inhaled/ingested pathogens
- b)Mediate in allergic response
- c)Activation of B-cells
- d)Stimulation of complement system, passive immunity to foetus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The function of IgE is
a)
Protection from inhaled/ingested pathogens
b)
Mediate in allergic response
c)
Activation of B-cells
d)
Stimulation of complement system, passive immunity to foetus
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
The function of IgE antibody as mediators in allergic reactions of Type I is explained by their ability to interact both with antigen and with receptor molecules on the membrane of blood basophils and tissue mast cells. However, it is not understood how the interaction of an allergen with cell-bound IgE antibody will induce basophil (mast) cells to release a great number of biologically active substances of which some will be further discussed at this meeting, nor is it known what role the IgE-mast cell system plays in the development and control of a normal immune response.
Japanese encephalitis is transmitted by- a)Tse tse fly
- b)Sand fly
- c)Housefly
- d)Mosquito
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Japanese encephalitis is transmitted by
a)
Tse tse fly
b)
Sand fly
c)
Housefly
d)
Mosquito
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Japanese encephalitis (JE) virus, a flavivirus, is closely related to West Nile and St. Louis encephalitis viruses. JE virus is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected Culex species mosquitoes, particularly Culex tritaeniorhynchus.
The virus is maintained in a cycle between mosquitoes and vertebrate hosts, primarily pigs and wading birds. Humans are incidental or dead-end hosts, because they usually do not develop high enough concentrations of JE virus in their bloodstreams to infect feeding mosquitoes.
JE virus transmission occurs primarily in rural agricultural areas, often associated with rice production and flooding irrigation. In some areas of Asia, these conditions can occur near urban centers.
In temperate areas of Asia, JE virus transmission is seasonal. Human disease usually peaks in the summer and fall. In the subtropics and tropics, transmission can occur year-round, often with a peak during the rainy season.
At which stage of HIV infection does one usually show symptoms of AIDS:- [2014]- a)Within 15 days of sexual contact with an infected person.
- b)When the infected retro virus enters host cells.
- c)When HIV damages large number of helper T-Lymphocytes.
- d)When the viral DNA is produced by reverse transcriptase.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
At which stage of HIV infection does one usually show symptoms of AIDS:- [2014]
a)
Within 15 days of sexual contact with an infected person.
b)
When the infected retro virus enters host cells.
c)
When HIV damages large number of helper T-Lymphocytes.
d)
When the viral DNA is produced by reverse transcriptase.

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
(c) HIV infection does usually show symptoms of AIDS When HIV damages large number of helper T-Lymphocytes (CD4 cells). AIDS is the stage of HIV infection that occurs when one immune system is badly damaged and one become vulnerable to infections and infection-related cancers called opportunistic infections. When the number of ones CD4 cells falls below 200 cells per cubic millimetre of blood (200 cells/mm3), one is considered to have progressed to AIDS.
The primary and secondary immune response are carried out with the help of two special types of lymphocytes present in our blood called?- a)B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes
- b)Lymphocytes and monocytes
- c)T-lymphocytes and A-lymphocytes
- d)B-lymphocytes and M-lymphocytes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The primary and secondary immune response are carried out with the help of two special types of lymphocytes present in our blood called?
a)
B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes
b)
Lymphocytes and monocytes
c)
T-lymphocytes and A-lymphocytes
d)
B-lymphocytes and M-lymphocytes
|
|
Anaswara Rajput answered |
The primary immune response can be described as the first response of our body system to a newly introduced foreign agent, while the secondary immune response is defined as an intensified immune response to this previously exposed antigen. The primary and secondary immune response is carried out by following two types of lymphocytes;
1)B-Lymphocytes: responsible for the production of antibodies in our blood. the type of antibodies is IgA. IgD, IgE, IgG, IgM.
2)T-Lymphocytes: These are mediators cell-mediated immunity.
So, the correct answer is 'Option A
1)B-Lymphocytes: responsible for the production of antibodies in our blood. the type of antibodies is IgA. IgD, IgE, IgG, IgM.
2)T-Lymphocytes: These are mediators cell-mediated immunity.
So, the correct answer is 'Option A
Which of the following endoparasites of humans does show viviparity ? [2015 RS]- a)Enterobius vermicularis
- b)Trichinella spiralis
- c)Ascaris lumbricoides
- d)Ancylostoma duodenale
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following endoparasites of humans does show viviparity ? [2015 RS]
a)
Enterobius vermicularis
b)
Trichinella spiralis
c)
Ascaris lumbricoides
d)
Ancylostoma duodenale

|
Anagha Sharma answered |
(b) Trichinella spiralis is an endoparasite found in human intestine. It is the smallest nematode producing larvae in large number. These larvae bore the intestine of human being and enter the blood and lymphatic systems.
Use of antihistamines and steroids give a quick relief from[2009]- a)allergy
- b)nausea
- c)cough
- d)Headache
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Use of antihistamines and steroids give a quick relief from
[2009]
a)
allergy
b)
nausea
c)
cough
d)
Headache

|
Aman Sharma answered |
Allergy is the hypersensitiveness of a person to some foreign substances coming in contact with or entering the body. The common allergens are dust, pollen mould, spores, fabricates, bacteria, etc. During an allergic reaction, there is increased the release of histamine from mast cells. Use of antihistamines and from mast cells. Use of antihistamine and steroids give a quick relief from allergy.
Which one of the following immunoglobulins does constitute the largest percentage in human milk? [2015 RS]
- a)lgM
- b)lgA
- c)lgG
- d)lgD
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following immunoglobulins does constitute the largest percentage in human milk? [2015 RS]
a)
lgM
b)
lgA
c)
lgG
d)
lgD

|
Arnab Iyer answered |
(b) Colostrum contains high levels of lgA, which gives passive immunity to foetus.
Asthma may be attributed to- a)bacterial infection of the lungs.
- b)allergic reaction of the mast cell in the lungs
- c)inflammation of the trachea
- d)accumulation of fluid in the lungs
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Asthma may be attributed to
a)
bacterial infection of the lungs.
b)
allergic reaction of the mast cell in the lungs
c)
inflammation of the trachea
d)
accumulation of fluid in the lungs

|
Charvi Shah answered |
(b) A mast cell or a mastocyte is typically a white blood cell. It is a special kind of granulocyte, which is a part of the immune system and laden with histamine and heparin. Besides these, mast cells also secrete the prostaglandin (PG) D2, and leukotriene (LT) C4, which are capable of inducing bronchoconstriction and mucosal edema, both features of asthma.
Select the correct statement from the ones given below?[2010]- a)Barbiturates when given to criminals make them tell the truth
- b)Morphine is often given to persons who have undergone surgery as a pain killer
- c)Chewing tobacco lowers blood pressure and heart rate
- d)Cocaine is given to patients after surgery as it stimulates recovery
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement from the ones given below?
[2010]
a)
Barbiturates when given to criminals make them tell the truth
b)
Morphine is often given to persons who have undergone surgery as a pain killer
c)
Chewing tobacco lowers blood pressure and heart rate
d)
Cocaine is given to patients after surgery as it stimulates recovery

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
Morphine is potent opioid analgesic that is often given to persons (who have undergone surgery) as a pain killer. It is mainly used to relieve severe and persistent pain. It is administrated by mouth, injection or suppositories.
Cancer cells are more damaged by radiations while others are not because cancer cells are
a) Undergoing rapid divisions
b) Different in nature
c) Starved
d) None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Tapsee Choudhary answered |
Always undifferentiated , quickly dividing and metabolically more active cells be sensitive for radiations... and cancer cells undergo rapid division and and more active metabolically.....
so they can damaged easily by radiations....
so they can damaged easily by radiations....
AIDS day is________.- a)May 1
- b)December 1
- c)June 1
- d)December 20
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
AIDS day is________.
a)
May 1
b)
December 1
c)
June 1
d)
December 20
|
|
Dorri answered |
Since 1988, 1st December is celebrated as International AIDS day to raise awareness about it's spread.
HIV originated from CHIMPANZEES to Humans cross, in Democratic Republic of CONGO (known currently). Chimps who carried SIV(closely related to HIV) were being hunted & then eaten by people living there in 1920s.
Which one of the following statements is correct?[2009]- a)Benign tumours show the property of metastasis.
- b)Heroin accelerates body functions.
- c)Malignant tumours ours may exhibit metastasis.
- d)Patients who have undergone surgery are given cannabinoids to relieve pain.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is correct?
[2009]
a)
Benign tumours show the property of metastasis.
b)
Heroin accelerates body functions.
c)
Malignant tumours ours may exhibit metastasis.
d)
Patients who have undergone surgery are given cannabinoids to relieve pain.

|
Arnab Iyer answered |
Malignant tumours may exhibit metastasis. Cancer (medical term: malignant neoplasm) is a class of diseases in which a group of cells display uncontrolled growth (division beyond the normal limits), invasion (intrusion on and destruction of adjacent tissues), and sometimes metastasis spread to other locations in the body via lymph or blood.
Anti-venom is used for the treatment of snake bite. The treatment of snake bite by anti-venom is an example of- a)Artificially acquired active immunity
- b)Specific natural immunity
- c)Naturally acquired passive immunity
- d)Artificially acquired passive immunity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Anti-venom is used for the treatment of snake bite. The treatment of snake bite by anti-venom is an example of
a)
Artificially acquired active immunity
b)
Specific natural immunity
c)
Naturally acquired passive immunity
d)
Artificially acquired passive immunity
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
The treatment of snake bite by anit-venom is an example of artificial acquired passive immunity. Anti-venom neutralize the effect of venom in the body.
AIDS is caused by Human immuno deficiency virus (HIV) which is a member of group of virus called?- a)Mono virus
- b)Retro virus
- c)Miso virus
- d)Micro virus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
AIDS is caused by Human immuno deficiency virus (HIV) which is a member of group of virus called?
a)
Mono virus
b)
Retro virus
c)
Miso virus
d)
Micro virus

|
Ishani Patel answered |
AIDS is caused by the Human immunodeficiency virus of a member of the group of virus called retrovirus. It is a type of RNA virus that inserts a copy of its genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell.
HIV that causes AIDS, first starts destroying: [2015 RS]- a)Leucocytes
- b)Helper T- Lymphocytes
- c)Thrombocytes
- d)B- Lymphocytes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
HIV that causes AIDS, first starts destroying: [2015 RS]
a)
Leucocytes
b)
Helper T- Lymphocytes
c)
Thrombocytes
d)
B- Lymphocytes

|
Rhea Sarkar answered |
(b) After infection, HIV starts to destroy the Tcells (T-helper lymphocytes). T. cells are very important for the immune system. In the early stage of infection, the decline in numbers of T.cells is observed.
Motile zygote of Plasmodium occurs in__________.- a)Human RBCs
- b)Human liver
- c)Salivary glands of Anopheles
- d)Gut of female Anopheles
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Motile zygote of Plasmodium occurs in__________.
a)
Human RBCs
b)
Human liver
c)
Salivary glands of Anopheles
d)
Gut of female Anopheles
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Gut of female Anopheles
When female Anopheles, sucks the blood of an infected person, the gametocytes of plasmodium are picked up by the mosquito. Now sexual reproduction of Plasmodium occurs inside mosquito. The outer envelope of gametocyte is dissolved and its contents are liberated into the cavity of gut. These content undergo gametogony, i.e., formation of microgametes and macroagamete. The nuclei of both fuse and a synkaryon or zygote is formed. This zygote is motionless and spherical for sometime and vermiform very soon. Now, it is called vermicule or ookinete. Ookinete pierces the stomach wall and forms a cyst(oocyst) on its outer surface which has about 1000 sporozoites. The latter pass into salivary glands of the mosquito.
Which property is not exhibited by a disease-causing pathogen?- a)Invasiveness
- b)Toxigenicity
- c)Virulence
- d)Co-operation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which property is not exhibited by a disease-causing pathogen?
a)
Invasiveness
b)
Toxigenicity
c)
Virulence
d)
Co-operation
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
A. Invasiveness of a pathogen is its ability to gain entry into a host and grow.
B. Toxigenicity is the power of a pathogen to form toxins capable of damaging host cells.
C. Virulence is the ability of a pathogen to produce disease.
D. Co-operation is a property not exhibited by a pathogen.
Hence, the correct answer is option D: Co-operation
Human Immunodeficiency Virus causes aids by attacking a type of white blood cell called- a)CD4
- b)CD3
- c)CD8
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Human Immunodeficiency Virus causes aids by attacking a type of white blood cell called
a)
CD4
b)
CD3
c)
CD8
d)
None of these
|
|
Bhaskar Ala answered |
"HIV " Attacks CD4 cells (T- helper, T- cells) .. this cells plays important role in immune system..
Development of vaccine is difficult for AIDS because HIV gene- a)Integrates into large number of host genes
- b)Undergoes mutation at rapid
- c)Undergoes reverse transcriptase
- d)Integrates its genome into that of helper T cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Development of vaccine is difficult for AIDS because HIV gene
a)
Integrates into large number of host genes
b)
Undergoes mutation at rapid
c)
Undergoes reverse transcriptase
d)
Integrates its genome into that of helper T cells
|
|
Kekan Dp answered |
It damage our immunity system from which any bacteria or virus can affect on us it's difficult to choose one tablet
Who discovered the technique of preparing vaccine from attenuated pathogen and in which year?- a)Edward Jenner, 1796
- b)Louis Pasteur, 1879
- c)Robert Downey, 1856
- d)Von Behring, 1950
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who discovered the technique of preparing vaccine from attenuated pathogen and in which year?
a)
Edward Jenner, 1796
b)
Louis Pasteur, 1879
c)
Robert Downey, 1856
d)
Von Behring, 1950
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Louis Pasteur discovered the technique of preparing vaccine from an attenuated pathogen in 1879. This was the first true vaccine consisting of weakened micro-organisms against the disease chicken cholera.
The antibody which can cross placental barrier is- a)IgA
- b)IgE
- c)IgM
- d)IgG
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The antibody which can cross placental barrier is
a)
IgA
b)
IgE
c)
IgM
d)
IgG

|
Yash answered |
IgG immunoglobin me sabse jyada 80% paye jate h . ye sbse chote imuno globin hote h kyuki enme paratopes kevel 2 hote h upr se ye monovalant hote h. chote size ke karan ye placenta ko cross kr jate h
Where will you look for the sporozoites of the malarial parasite?[2011]- a)Saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquito
- b)Red blood corpuscles of humans suffering from malaria
- c)Spleen of infected humans
- d)Salivary glands of freshly moulted female Anopheles mosquito
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Where will you look for the sporozoites of the malarial parasite?
[2011]
a)
Saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquito
b)
Red blood corpuscles of humans suffering from malaria
c)
Spleen of infected humans
d)
Salivary glands of freshly moulted female Anopheles mosquito

|
Aashna Mukherjee answered |
Sporozoites of malarial parasite are found in saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquito.
A person likely to develop tetanus is immunised by administering[2009]- a)weakened germs
- b)wide spectrum antibiotics
- c)preformed antibodies
- d)dead germs
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A person likely to develop tetanus is immunised by administering
[2009]
a)
weakened germs
b)
wide spectrum antibiotics
c)
preformed antibodies
d)
dead germs
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
The person is immunised by administering performed antibodies which is artificial passive immunity
Widal Test is carried out to test :[2012]- a)Malaria
- b)diabetes mellitus
- c)HIV/AIdS
- d)Typhoid fever
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Widal Test is carried out to test :
[2012]
a)
Malaria
b)
diabetes mellitus
c)
HIV/AIdS
d)
Typhoid fever

|
Sneha Basak answered |
Widal test is carried out to test typhoid fever caused by Salmonella typhii bacteria. Typhoid vaccine is available.
The drug which binds to specific opioid receptors present in our central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract is:- a)Smack
- b)Opioids
- c)Cannabinoids
- d)Heroine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The drug which binds to specific opioid receptors present in our central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract is:
a)
Smack
b)
Opioids
c)
Cannabinoids
d)
Heroine
|
|
Maitri Tiwari answered |
Opioids are drugs that act on the central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract by binding to specific opioid receptors. These receptors are present in various parts of the body, including the brain, spinal cord, and digestive tract.
Mechanism of Action:
When opioids bind to the receptors, they activate a series of chemical reactions that lead to pain relief, sedation, and a sense of euphoria. Opioids work by mimicking the body's natural pain-relieving chemicals, such as endorphins.
Types of Opioids:
There are several types of opioids, including natural, semi-synthetic, and synthetic opioids. Examples of natural opioids include morphine and codeine, while semi-synthetic opioids include oxycodone and hydrocodone. Synthetic opioids include fentanyl and tramadol.
Medical Uses:
Opioids are commonly used in medical settings to treat pain, such as after surgery or for chronic pain conditions. They may also be used to treat coughing and diarrhea.
Risks and Side Effects:
However, opioids can be highly addictive and can lead to dependence, tolerance, and overdose. They can also cause a range of side effects, including drowsiness, constipation, nausea, and respiratory depression.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, opioids are a class of drugs that bind to specific opioid receptors in the central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract. They are commonly used to treat pain, but can also be highly addictive and have a range of side effects. It is important to use opioids only as prescribed and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Mechanism of Action:
When opioids bind to the receptors, they activate a series of chemical reactions that lead to pain relief, sedation, and a sense of euphoria. Opioids work by mimicking the body's natural pain-relieving chemicals, such as endorphins.
Types of Opioids:
There are several types of opioids, including natural, semi-synthetic, and synthetic opioids. Examples of natural opioids include morphine and codeine, while semi-synthetic opioids include oxycodone and hydrocodone. Synthetic opioids include fentanyl and tramadol.
Medical Uses:
Opioids are commonly used in medical settings to treat pain, such as after surgery or for chronic pain conditions. They may also be used to treat coughing and diarrhea.
Risks and Side Effects:
However, opioids can be highly addictive and can lead to dependence, tolerance, and overdose. They can also cause a range of side effects, including drowsiness, constipation, nausea, and respiratory depression.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, opioids are a class of drugs that bind to specific opioid receptors in the central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract. They are commonly used to treat pain, but can also be highly addictive and have a range of side effects. It is important to use opioids only as prescribed and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Heroin is commonly called smack is chemically:- a)Diacetylchloride
- b)Diacetylmorphine
- c)Dichlordiethyl acetone
- d)Cocaine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Heroin is commonly called smack is chemically:
a)
Diacetylchloride
b)
Diacetylmorphine
c)
Dichlordiethyl acetone
d)
Cocaine

|
Swara Desai answered |
Heroine or smack is chemically diacetylmorphine which is a white, odourless, bitter crystalline compound.
AIDS can be transmitted by- a)Blood transfusion
- b)Handshake
- c)Courtship
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
AIDS can be transmitted by
a)
Blood transfusion
b)
Handshake
c)
Courtship
d)
All of the above

|
Sarthak Saini answered |
AIDS can be transmitted from infected person to healthy person through blood transfusion. The most common way of transmission of AIDS is during sexual intercourse with multiple partners without protection.
Which of the following is a pair of viral diseases?- a)Ringworm, AIDS
- b)Dysentery, Common Cold
- c)Common Cold, AIDS
- d)Typhoid, Tuberculosis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a pair of viral diseases?
a)
Ringworm, AIDS
b)
Dysentery, Common Cold
c)
Common Cold, AIDS
d)
Typhoid, Tuberculosis
|
|
Muskan Sethi answered |
Ringworm - fungal infection
AIDS- HIV virus
Common cold - Rhino Virus
typhoid - Salmonella typhi ( bacteria)
tuberculosis - mycobacterium tuberculosis ( bacteria)
dysentery - it is of two types bacterial and amoebic
therefore the viral diseases are AIDS and Common cold
At which stage of HIV infection does one usually show symptoms of AIDS?[2011]- a)When the infecting retrovirus enters host cells
- b)When viral dNA is produced by reverse trancriptase
- c)When HIV replicates rapidly in helper T-lymphocytes and damages large number of these
- d)Within 15 day of sexual contact with an infected person.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
At which stage of HIV infection does one usually show symptoms of AIDS?
[2011]
a)
When the infecting retrovirus enters host cells
b)
When viral dNA is produced by reverse trancriptase
c)
When HIV replicates rapidly in helper T-lymphocytes and damages large number of these
d)
Within 15 day of sexual contact with an infected person.

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
When HIV replicates rapidly in helper T-lymphocytes and damages large number of these cells, at this stage infected persons start showing symptoms of AIDS.
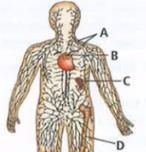
Given below is the diagram of human lymphatic system, where A, B, C and D are lymphoid organs. Select incorrect option regarding the lymphoid organs labelled as A, B, C and D.
- a)T cells mature in B
- b)B and T cells undergo maturation in C
- c)B and T cells undergo proliferation and differentiation in A
- d)B cells mature in D
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Given below is the diagram of human lymphatic system, where A, B, C and D are lymphoid organs. Select incorrect option regarding the lymphoid organs labelled as A, B, C and D.

a)
T cells mature in B
b)
B and T cells undergo maturation in C
c)
B and T cells undergo proliferation and differentiation in A
d)
B cells mature in D
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
'A'-lymph nodes, 'B'-Thymus, 'C'-spleen, 'D'-Bone marrow. Thymus and bone marrow are the primary lymphoid organs where maturation of T-cells and B-cells take place respectively. Lymph nodes and spleen are the secondary lymphoid organs where T-cells and B-cells undergo proliferation and differentiation.
Which of these glands is large at the time of birth but in adults, it reduces to a very small size?- a)Thyroid
- b)Adrenal
- c)Thymus
- d)Spleen
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these glands is large at the time of birth but in adults, it reduces to a very small size?
a)
Thyroid
b)
Adrenal
c)
Thymus
d)
Spleen
|
|
Krithika Ahuja answered |
Thymus gland is the correct option as it is large at the time of birth but reduces to a very small size in adults.
Explanation:
Thymus gland is a specialized gland of the lymphatic system that plays an important role in the development of the immune system. It is located in the upper thorax, behind the sternum, and in front of the heart. The thymus gland is large at the time of birth and continues to grow until puberty. After puberty, the thymus gland begins to shrink and is replaced by fatty tissue. By the age of 20, the thymus gland has reduced to about one-third of its maximum size, and by the age of 50, it has reduced to only a few grams of fatty tissue.
Why is Thymus gland large at the time of birth?
The thymus gland is very active during fetal development and plays a crucial role in the development of the immune system. The thymus gland produces T-lymphocytes, which are immune cells that play a crucial role in fighting infections and diseases. The thymus gland is essential for the development of T-lymphocytes, which are responsible for recognizing and attacking foreign substances in the body. The thymus gland is particularly important during fetal development because the fetus does not have a fully developed immune system and relies on the mother's immune system for protection.
Why does Thymus gland reduce in size in adults?
The thymus gland begins to shrink after puberty because the production of T-lymphocytes decreases with age. As a result, the thymus gland is no longer required to produce large numbers of T-lymphocytes, and its function gradually declines. The thymus gland is gradually replaced by fatty tissue, which is an irreversible process. However, the T-lymphocytes that are produced by the thymus gland during fetal development and childhood continue to circulate in the body and play a crucial role in the immune system throughout life.
Explanation:
Thymus gland is a specialized gland of the lymphatic system that plays an important role in the development of the immune system. It is located in the upper thorax, behind the sternum, and in front of the heart. The thymus gland is large at the time of birth and continues to grow until puberty. After puberty, the thymus gland begins to shrink and is replaced by fatty tissue. By the age of 20, the thymus gland has reduced to about one-third of its maximum size, and by the age of 50, it has reduced to only a few grams of fatty tissue.
Why is Thymus gland large at the time of birth?
The thymus gland is very active during fetal development and plays a crucial role in the development of the immune system. The thymus gland produces T-lymphocytes, which are immune cells that play a crucial role in fighting infections and diseases. The thymus gland is essential for the development of T-lymphocytes, which are responsible for recognizing and attacking foreign substances in the body. The thymus gland is particularly important during fetal development because the fetus does not have a fully developed immune system and relies on the mother's immune system for protection.
Why does Thymus gland reduce in size in adults?
The thymus gland begins to shrink after puberty because the production of T-lymphocytes decreases with age. As a result, the thymus gland is no longer required to produce large numbers of T-lymphocytes, and its function gradually declines. The thymus gland is gradually replaced by fatty tissue, which is an irreversible process. However, the T-lymphocytes that are produced by the thymus gland during fetal development and childhood continue to circulate in the body and play a crucial role in the immune system throughout life.
Chapter doubts & questions for Human Health & Diseases - 1 Year Dropper Course for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Human Health & Diseases - 1 Year Dropper Course for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









