All Exams >
NEET >
Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Excretory Products and their Elimination for NEET Exam
When a fresh-water protozoan possessing a contractile vacuole, is placed in a glass containing marine water, the vacuole will [2004]
- a) increase in number
- b) disappear
- c) increase in size
- d) decrease in size
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When a fresh-water protozoan possessing a contractile vacuole, is placed in a glass containing marine water, the vacuole will [2004]
a)
increase in numberb)
disappearc)
increase in sized)
decrease in size|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Contractile vacuole is responsible to throw excess water that comes from outside to inside the cell. In presence of marine water, due to exosmosis cell start losing water. So, there is a need to preserve water. In that situation, the presence of contractile vacuole will dehydrate the cell. So, contractile vacuole will be disappeared.
If kidney fail to reabsorb water, the effect on tissue would [1994]- a)remain unaffected
- b)shrink and shrivel
- c)absorb water from blood plasma
- d)take more O2 from blood
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If kidney fail to reabsorb water, the effect on tissue would [1994]
a)
remain unaffected
b)
shrink and shrivel
c)
absorb water from blood plasma
d)
take more O2 from blood

|
Sonal Kulkarni answered |
If kidneys fail to reabsorb water the urine will be diluted causing polyuria (frequent urination). Then the body tissues get dehydrated & the cell will loose water content & shrink.
Which one of the following characteristics is common to both in humans and adult frogs? [2012M] - a)Four - chambered heart
- b)Internal fertilization
- c)Nucleated RBCs
- d)Ureotelic mode of excretion
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following characteristics is common to both in humans and adult frogs? [2012M]
a)
Four - chambered heart
b)
Internal fertilization
c)
Nucleated RBCs
d)
Ureotelic mode of excretion

|
Abhiram Nair answered |
Adult frog and human exhibit ureotelism because there excretory waste product is urea.
Which one of the following statements in regard to the excretion by the human kidneys is correct? [2010]- a)Descending limb of Loop of Henle is impermeable to water
- b)Distal convoluted tubule is incapable of reabsorbing HCO3
- c)Nearly 99 per cent of the glomer ular filtrate is reabsorbed by the renal tubules
- d)Ascending limb of Loop of Henle is impermeable to electrolytes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements in regard to the excretion by the human kidneys is correct? [2010]
a)
Descending limb of Loop of Henle is impermeable to water
b)
Distal convoluted tubule is incapable of reabsorbing HCO3
c)
Nearly 99 per cent of the glomer ular filtrate is reabsorbed by the renal tubules
d)
Ascending limb of Loop of Henle is impermeable to electrolytes

|
Abhiram Nair answered |
Urine formation involves three main process called, glomerular filtration, reabsorption and secretion. A comparison of the volume of the filtrate formed per day (which is 180 litres per day) with that of urine released (about 1.5 litres) suggest that nearly 99 percent of the glomerular filtrate is resorbed by the renal tubules. The descending limb of loop of Henle is permeable to water but impermeable to electrolytes.
The ascending limb is impermeable to water but allows transport of electrolytes.
Reabsorption of sodium ions and water takes place in distal convoluted tubule.
Also, it is capable of reabsorption of HCO3.
The ascending limb is impermeable to water but allows transport of electrolytes.
Reabsorption of sodium ions and water takes place in distal convoluted tubule.
Also, it is capable of reabsorption of HCO3.
The enteronephric nephridia of earthworm are concerned with [2000]- a)osmoregulation
- b)excretion of nitrogenous wastes
- c)digestion
- d)respiration
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The enteronephric nephridia of earthworm are concerned with [2000]
a)
osmoregulation
b)
excretion of nitrogenous wastes
c)
digestion
d)
respiration

|
Sarthak Saini answered |
The nephridia are the excretory organs. The nephridia in earthworm are – Septal nephridia, Pharyngeal nephridia and Integumentary nephridia. The septal nephridia do not discharge excretory fluid to the exterior rather it pour them into the intestine. Hence these are also called Enteronephric nephridia.
Solenocytes are the main excretory structures in[1998]- a)Platyhelminthes
- b)Annelids
- c)Molluscs
- d)Echinodermates
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Solenocytes are the main excretory structures in[1998]
a)
Platyhelminthes
b)
Annelids
c)
Molluscs
d)
Echinodermates

|
Moumita Khanna answered |
Solenocytes or flame cells or protonephridia are excretory organs in Platyhelminthes (Flatworms). They excrete ammonia. In Annelids excretory structure are nephridia. In Molluscs sac like kidneys are excretory. In Echinodermata nitrogenous wastes are excreted through gills.
Part not belonging to uriniferous tubule is- a)Glomerulus [1994]
- b)Henle’s loop
- c)Distal convoluted tubule
- d)Connecting tubule
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Part not belonging to uriniferous tubule is
a)
Glomerulus [1994]
b)
Henle’s loop
c)
Distal convoluted tubule
d)
Connecting tubule

|
Pragati Mishra answered |
Connecting tubules/duct is not considered a part of uriniferous tubule (as it is common to many nephrons)
A person is undergoing prolonged fasting. His urine will be found to contain abnormal quantities of: [2005]
- a) fats
- b) amino acids
- c) glucose
- d) ketones
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A person is undergoing prolonged fasting. His urine will be found to contain abnormal quantities of: [2005]
a)
fatsb)
amino acidsc)
glucosed)
ketones|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
If a person is undergoing prolonged fasting, his urine will be found to contain abnormal quantities of ketones. During fasting energy is obtained by the oxidation of reserved fats. As a result of fatty acid oxidation large amount of ketone bodies are produced such as acetoacetate, (3-hydroxybutyrate and acetone.
In the renal tubules the permeability of the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct to water is controlled by [1999]- a)Vasopressin
- b)Aldosterone
- c)Growth hormone
- d)Renin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the renal tubules the permeability of the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct to water is controlled by [1999]
a)
Vasopressin
b)
Aldosterone
c)
Growth hormone
d)
Renin

|
Soumya Ahuja answered |
Growth hormone, released by the anterior lobe of pituitary brings about body growth by synthesis and deposition of proteins in tissues. Renin secreted by special cells in kidneys regulates blood pressure. Aldosterone reduces Na+ elimination by helping active reabsorption from the nephric filtrate.
The basic functional unit of the human kidney is[1997]- a)nephron
- b)nephridia
- c)pyramid
- d)Henle's loop
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The basic functional unit of the human kidney is[1997]
a)
nephron
b)
nephridia
c)
pyramid
d)
Henle's loop

|
Sarthak Saini answered |
The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. Each nephron is composed of a renal corpuscle, the initial filtering component; and a renal tubule that processes and carries away the filtered fluid.
Uric acid is the chief nitrogenous component of the excretory products of [2009]- a)earthworm
- b)cockroach
- c)frog
- d) man
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Uric acid is the chief nitrogenous component of the excretory products of [2009]
a)
earthworm
b)
cockroach
c)
frog
d)
man
|
|
Rocky Handsome answered |
•Cockroach excretes uric acid as the chief nitrogenous excretory product.
•Man excretes urea as the chief nitrogenous excretory product.
•Earthworm excretes 40% urea, 20% ammonia and 40% amino acids.
Frog excretes urea as the chief nitrogenous product.
•Man excretes urea as the chief nitrogenous excretory product.
•Earthworm excretes 40% urea, 20% ammonia and 40% amino acids.
Frog excretes urea as the chief nitrogenous product.
If Henle's loop were absent from mammalian nephron, which of the following is to be expected? [2003]- a)The urine will be more dilute
- b)There will be no urine formation
- c)There will be hardly any change in the quality and quantity of urine formed
- d)The urine will be more concentrated
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If Henle's loop were absent from mammalian nephron, which of the following is to be expected? [2003]
a)
The urine will be more dilute
b)
There will be no urine formation
c)
There will be hardly any change in the quality and quantity of urine formed
d)
The urine will be more concentrated

|
Krish Khanna answered |
The main function of the Henle's loop is to absorb water from the tubular lumen, thus making the urine concentrated. If loop of Henle becomes absent then the urine becomes more dilute.
Which one of the following statements is correct with respect to kidney function regulation ? [2011]- a)When someone drinks lot of water,ADH release is suppressed.
- b)Exposure to cold temperature blood flow stimulates formation of Angiotensin II.
- c)An increase in glomer ular blood flow stimulates formation of Angiotensin II.
- d)During summer when body loses lot of water by evaporation, the release of ADH is suppressed.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is correct with respect to kidney function regulation ? [2011]
a)
When someone drinks lot of water,ADH release is suppressed.
b)
Exposure to cold temperature blood flow stimulates formation of Angiotensin II.
c)
An increase in glomer ular blood flow stimulates formation of Angiotensin II.
d)
During summer when body loses lot of water by evaporation, the release of ADH is suppressed.

|
Pankaj Kulkarni answered |
When some one drinks lots of water, kidney release of ADH is suppressed.
Which one of the following correctly explains the function of a specific part of a human nephron ? [2011]- a)Podocytes : create minute spaces (slite pores) for the filtration of blood into the Bowman’s capsule
- b)Henle’s loop : most reabsorption of the major substances from the glomerular filtrate
- c)Distal convoluted tubule : reabsorption of K+ ions into the surrounding blood capillaries
- d)Afferent arteriole : carries the blood away from the glomerular towards renal vein.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following correctly explains the function of a specific part of a human nephron ? [2011]
a)
Podocytes : create minute spaces (slite pores) for the filtration of blood into the Bowman’s capsule
b)
Henle’s loop : most reabsorption of the major substances from the glomerular filtrate
c)
Distal convoluted tubule : reabsorption of K+ ions into the surrounding blood capillaries
d)
Afferent arteriole : carries the blood away from the glomerular towards renal vein.
|
|
Parth Sharma answered |
Glome podocytes are highly specialized cells with a complex cytoarchitecture plays a major role in establishing the selective permeability of glomerular filtration barrier.
Which of the following factors is responsible for the formation of concentrated urine? [2019]- a)Hydrostatic pressure during glomerular filtration.
- b)Low levels of antidiuretic hormone.
- c)Maintaining liyperosmolarity towards the medullary interstitium in the kidneys.
- d)Secretion of erythropoietin by Juxtaglomerular complex
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following factors is responsible for the formation of concentrated urine? [2019]
a)
Hydrostatic pressure during glomerular filtration.
b)
Low levels of antidiuretic hormone.
c)
Maintaining liyperosmolarity towards the medullary interstitium in the kidneys.
d)
Secretion of erythropoietin by Juxtaglomerular complex
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
The counter current mechanism helps to maintain a concentration gradient in the medullary mterstitium. The proximity between the Henle’s loop and vasa recta, as well as the counter current in them help in maintaining an increasing osmolarity towards the inner medullary interstitium, i.e., from 300 mOsmoIL-1 in the cortex to about 1200 mOsmolL-1 m the inner medulla. This gradient is mainly caused by NaCl and urea. Presence of such interstitial gradient helps in an easy passage of water from the collecting tubule thereby concentrating the filtrate (urine).
Figure shown human urinar y system with structures labelled A to D. Select option which correctly identifies them and gives their characteristics and /or functions. [NEET 2013]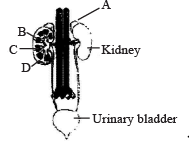
- a)B-pelvis-broad funnel shaped space inner to hilum, directly connected to loops of Henle.
- b)C-Medulla-inner zone of kidney and contains complex nephrons.
- c)D - Cortex - outer part of kidney and do not contain any part of nephrons
- d)A-Adrenal gland - located at the anterior part of kidney. Secrete Catecholamines which stimulate glycogen breakdown.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Figure shown human urinar y system with structures labelled A to D. Select option which correctly identifies them and gives their characteristics and /or functions. [NEET 2013]

a)
B-pelvis-broad funnel shaped space inner to hilum, directly connected to loops of Henle.
b)
C-Medulla-inner zone of kidney and contains complex nephrons.
c)
D - Cortex - outer part of kidney and do not contain any part of nephrons
d)
A-Adrenal gland - located at the anterior part of kidney. Secrete Catecholamines which stimulate glycogen breakdown.

|
Devansh Mehra answered |
A-Adrenal gland,
B-Renal pelvis,
C- Medulla,
D-Cortex.
Under normal conditions which one is completely reabsorbed in the renal tubule? [1991]- a)Urea
- b)Uric acid
- c)Salts
- d)Glucose
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Under normal conditions which one is completely reabsorbed in the renal tubule? [1991]
a)
Urea
b)
Uric acid
c)
Salts
d)
Glucose
|
|
Raghavendra Roy answered |
Overview:
The renal tubule is a part of the nephron, which is the functional unit of the kidney. It is responsible for reabsorbing certain substances from the filtrate back into the bloodstream. The reabsorption process helps maintain the body's homeostasis by selectively retaining essential substances while eliminating waste products.
Explanation:
Under normal conditions, the renal tubule completely reabsorbs glucose. This is because glucose is an essential nutrient that needs to be conserved by the body.
Reabsorption of Glucose:
1. Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT): The majority of glucose reabsorption occurs in the PCT. Glucose is reabsorbed via secondary active transport using sodium-glucose cotransporters (SGLT). SGLT1 is responsible for the reabsorption of glucose from the filtrate into the epithelial cells lining the PCT, while SGLT2 reabsorbs it from the epithelial cells back into the bloodstream.
2. Loop of Henle: The loop of Henle is responsible for reabsorbing water and salts, but it does not reabsorb glucose.
3. Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) and Collecting Duct: In the DCT and collecting duct, glucose is not reabsorbed under normal conditions. Instead, it remains in the filtrate and is excreted in the urine. This occurs because the reabsorption of glucose in the PCT is highly efficient, and there is usually no glucose left to be reabsorbed in the DCT and collecting duct.
Reabsorption of Other Substances:
- Urea: Urea is partially reabsorbed in the renal tubule. Approximately 50% of filtered urea is reabsorbed, while the remaining 50% is excreted in the urine.
- Uric Acid: Uric acid is both filtered and secreted in the renal tubule. A small amount may be reabsorbed, but the majority is excreted in the urine.
- Salts: Salts, such as sodium and chloride, are reabsorbed in varying amounts depending on the body's needs. The reabsorption of salts helps maintain electrolyte balance in the body.
In conclusion, under normal conditions, glucose is completely reabsorbed in the renal tubule, while urea, uric acid, and salts are only partially reabsorbed or excreted in the urine.
The renal tubule is a part of the nephron, which is the functional unit of the kidney. It is responsible for reabsorbing certain substances from the filtrate back into the bloodstream. The reabsorption process helps maintain the body's homeostasis by selectively retaining essential substances while eliminating waste products.
Explanation:
Under normal conditions, the renal tubule completely reabsorbs glucose. This is because glucose is an essential nutrient that needs to be conserved by the body.
Reabsorption of Glucose:
1. Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT): The majority of glucose reabsorption occurs in the PCT. Glucose is reabsorbed via secondary active transport using sodium-glucose cotransporters (SGLT). SGLT1 is responsible for the reabsorption of glucose from the filtrate into the epithelial cells lining the PCT, while SGLT2 reabsorbs it from the epithelial cells back into the bloodstream.
2. Loop of Henle: The loop of Henle is responsible for reabsorbing water and salts, but it does not reabsorb glucose.
3. Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) and Collecting Duct: In the DCT and collecting duct, glucose is not reabsorbed under normal conditions. Instead, it remains in the filtrate and is excreted in the urine. This occurs because the reabsorption of glucose in the PCT is highly efficient, and there is usually no glucose left to be reabsorbed in the DCT and collecting duct.
Reabsorption of Other Substances:
- Urea: Urea is partially reabsorbed in the renal tubule. Approximately 50% of filtered urea is reabsorbed, while the remaining 50% is excreted in the urine.
- Uric Acid: Uric acid is both filtered and secreted in the renal tubule. A small amount may be reabsorbed, but the majority is excreted in the urine.
- Salts: Salts, such as sodium and chloride, are reabsorbed in varying amounts depending on the body's needs. The reabsorption of salts helps maintain electrolyte balance in the body.
In conclusion, under normal conditions, glucose is completely reabsorbed in the renal tubule, while urea, uric acid, and salts are only partially reabsorbed or excreted in the urine.
Consider the following four statements (i-iv) regarding kidney transplant and select the two correct ones out of these. [2010]
(i) Even if a kidney transplant is proper the recipient may need to take immune suppresants for a long time
(ii) The cell mediated immune response is responsible for the graft rejection
iii) The B lymphocytes are responsible for rejection of the graft
(iv) The acceptance or rejection of a kidney transplant depends on specific interferons
The two correct statements are:- a)(ii) and (iii)
- b)(iii) and (iv)
- c)(i) and (iii)
- d)(i) and (ii)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following four statements (i-iv) regarding kidney transplant and select the two correct ones out of these. [2010]
(i) Even if a kidney transplant is proper the recipient may need to take immune suppresants for a long time
(ii) The cell mediated immune response is responsible for the graft rejection
iii) The B lymphocytes are responsible for rejection of the graft
(iv) The acceptance or rejection of a kidney transplant depends on specific interferons
The two correct statements are:
(i) Even if a kidney transplant is proper the recipient may need to take immune suppresants for a long time
(ii) The cell mediated immune response is responsible for the graft rejection
iii) The B lymphocytes are responsible for rejection of the graft
(iv) The acceptance or rejection of a kidney transplant depends on specific interferons
The two correct statements are:
a)
(ii) and (iii)
b)
(iii) and (iv)
c)
(i) and (iii)
d)
(i) and (ii)

|
Soumya Ahuja answered |
Tissue and blood group matching are essential before undertaking kidney transplant. Even if kidney transplant is proper, the recipient may need to take immuno suppresant all his/her life. The ability of body to differentiate self and nonself and the cell-mediated immune response is responsible for graft rejection.
The maximum amount of electrolytes and water (70 - 80 percent) from the glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed in which part of the nephron ? [2012]- a)Ascending limb of loop of Henle
- b)Distal convoluted tubule
- c)Proximal convoluted tubule
- d)Descending limb of loop of Henle
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The maximum amount of electrolytes and water (70 - 80 percent) from the glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed in which part of the nephron ? [2012]
a)
Ascending limb of loop of Henle
b)
Distal convoluted tubule
c)
Proximal convoluted tubule
d)
Descending limb of loop of Henle

|
Subhankar Datta answered |
From the Bowman's capsule, the glomerular filtrate enters the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT). PCT is surrounded by a network of peritubular capillaries and is the seat of reabsorption. About 75% of glomerular filtrate is normally reabsorbed in PCT before reaching the loop of Henle. The reabsorbed materials include glucose, amino acids, vitamins, hormones, sodium, potassium, chlorides, phosphates, bicarbonates, most of water and some urea etc.
Hair present in the skin are [1993]- a)epidermal in origin and made of dead cells
- b)epidermal in origin and made of living cells
- c)der mal in origin and made of living cells
- d)dermal in origin and made of dead cells
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Hair present in the skin are [1993]
a)
epidermal in origin and made of dead cells
b)
epidermal in origin and made of living cells
c)
der mal in origin and made of living cells
d)
dermal in origin and made of dead cells

|
Arnav Iyer answered |
Each hair is present in a tubular pit called hair follicle. Living cells are only present at the base of hair known as hair papilla, rest of the hair is dead and divisible into outer cuticle, middle cortex & inner medulla.
In Or nithine cycle, which one pair of the following wastes are removed from the blood?[1996]- a)CO2 and urea
- b)CO2 and ammonia
- c)Ammonia and urea
- d)Urea and sodium salts
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In Or nithine cycle, which one pair of the following wastes are removed from the blood?[1996]
a)
CO2 and urea
b)
CO2 and ammonia
c)
Ammonia and urea
d)
Urea and sodium salts

|
Sneha Basak answered |
In ureotelic animals urea is formed from ammonia by Ornithine cycle.
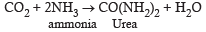
Which one of the following is a matching pair?[2000]- a)Tears-excretion of salts
- b)Sweat-thermoregulation
- c)Saliva-tasting food
- d)Sebum-sex attraction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is a matching pair?[2000]
a)
Tears-excretion of salts
b)
Sweat-thermoregulation
c)
Saliva-tasting food
d)
Sebum-sex attraction

|
Krish Patel answered |
Sweat regulates body temperature. Sweating also called perspiration or sometimes transpiration is the production and evaporation of a fluid, consisting primarily of water as well as a smaller amount of sodium chloride the main constituent of “table salt”, that is excreted by the sweat glands in the skin of mammals.
The principal nitrogenous excretory compound in humans is synthesised [2010]- a)in kidneys but eliminated mostly through liver
- b)in kidneys as well as eliminated by kidneys
- c)in liver and also eliminated by the same through bile
- d)in the liver, but eliminated mostly through kidneys
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The principal nitrogenous excretory compound in humans is synthesised [2010]
a)
in kidneys but eliminated mostly through liver
b)
in kidneys as well as eliminated by kidneys
c)
in liver and also eliminated by the same through bile
d)
in the liver, but eliminated mostly through kidneys

|
Pankaj Kulkarni answered |
The principal nitrogenous excretory compound in humans is urea. It is synthesized in the mitrochondrial matrix and cytosol of liver cells and eliminated through kidneys.
Brush border is characteristic of [1990]- a)neck of nephron
- b)collecting tube
- c)proximal convoluted tubule
- d)all the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Brush border is characteristic of [1990]
a)
neck of nephron
b)
collecting tube
c)
proximal convoluted tubule
d)
all the above

|
Vijivenkat N answered |
The proximal convoluted tubule lined by brush border cells increase surface area for absorption of electrolytes like glucose, amino acids, NaCl, water, K+, HCO3-, urea. Along with these, phosphates, lactates and citrates are also reabsorbed.
Uricotelic mode of passing out nitrogenous wastes is found in [2011]- a)Reptiles and Bird
- b)Birds and Annelids
- c)Amphibians and Reptiles
- d)Insects and Amphibians
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Uricotelic mode of passing out nitrogenous wastes is found in [2011]
a)
Reptiles and Bird
b)
Birds and Annelids
c)
Amphibians and Reptiles
d)
Insects and Amphibians

|
Abhiram Nair answered |
An uricotelic organism produces uric acid as a result of de-amination. Examples of such organism are birds and insects.
Uric acid is nitrogenous waste in [1994]- a)Mammals and molluscs
- b)Birds and lizards
- c)Frog and cartilaginous fishes
- d)Insects and bony fishes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Uric acid is nitrogenous waste in [1994]
a)
Mammals and molluscs
b)
Birds and lizards
c)
Frog and cartilaginous fishes
d)
Insects and bony fishes

|
Krish Patel answered |
The excretion of uric acidis called uricotelism. The excretion of uric acid is advantageous for those animals which have to conserve water for their survival like birds and lizards.
In Hydra waste material of food digestion and nitrogenous waste material removed from- a)mouth and body wall [2001]
- b)mouth and tentacles
- c)mouth and nematocyst
- d)body wall and tentacles
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In Hydra waste material of food digestion and nitrogenous waste material removed from
a)
mouth and body wall [2001]
b)
mouth and tentacles
c)
mouth and nematocyst
d)
body wall and tentacles

|
Rhea Sarkar answered |
Hydra being a coelenterate, has blind sac body plan. It has only one mouth which serves as the opening for ingestion and waste elimination besides diffusion across body wall.
Which one of the following options gives the correct categorization of six animals according to the type of nitrogenous wastes (A, B, C), they give out? [2012M]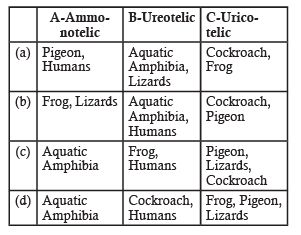
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following options gives the correct categorization of six animals according to the type of nitrogenous wastes (A, B, C), they give out? [2012M]

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Deepak Joshi answered |
Those animals that excrete ammonia are called as ammonotelic, eg. aquatic amphibia. Those animals that excrete urea are called as ureotelic, eg. frog, humans.
Those animals that excrete uric acid are called as uricotelic, eg. pigeon, lizards, and cockroach.
Those animals that excrete uric acid are called as uricotelic, eg. pigeon, lizards, and cockroach.
In ureotelic animals, urea is formed by the [1997, 2000]- a)Arginine cycle
- b)Cori's cycle
- c)Ornithine cycle
- d)EM pathway
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In ureotelic animals, urea is formed by the [1997, 2000]
a)
Arginine cycle
b)
Cori's cycle
c)
Ornithine cycle
d)
EM pathway

|
Bhargavi Choudhury answered |
In ureotelic animals urea is formed by Ornithine cycle. Urea is formed in the liver where two molecules of ammonia combine with one molecule of CO2 in presence of Ornithine, citrulline, arginine and enzyme arginase. This is called Ornithine cycle.
Uricotelism is found in [2004]- a)Mammals and birds
- b)Fishes and fresh water protozoans
- c)Birds, reptiles and insects
- d)Frogs and toads
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Uricotelism is found in [2004]
a)
Mammals and birds
b)
Fishes and fresh water protozoans
c)
Birds, reptiles and insects
d)
Frogs and toads
|
|
Ashwin Majumdar answered |
Understanding Uricotelism
Uricotelism is a biological term referring to the excretion of nitrogenous waste primarily in the form of uric acid. This adaptation is crucial for organisms that need to conserve water, which is particularly important in arid environments.
Key Characteristics of Uricotelism
- Water Conservation: Uricotelic organisms excrete uric acid as a semi-solid paste, which minimizes water loss compared to urea or ammonia, making it an efficient method for maintaining water balance.
- Evolutionary Adaptation: This adaptation is particularly beneficial for animals that inhabit environments where water is scarce, allowing them to thrive in terrestrial ecosystems.
Organisms Exhibiting Uricotelism
- Birds: Birds are a prime example of uricotelism. Their ability to excrete uric acid helps them conserve water, which is vital for survival, especially during flight.
- Reptiles: Similar to birds, reptiles such as lizards and snakes also excrete uric acid. They have adapted to terrestrial life where water availability may be limited.
- Insects: Many insects utilize uricotelism, excreting uric acid to efficiently manage water resources in their often variable environments.
Conclusion
In summary, uricotelism is primarily found in birds, reptiles, and insects due to its evolutionary advantages in water conservation, particularly in dry habitats. This characteristic is essential for their survival and adaptation to terrestrial life.
Uricotelism is a biological term referring to the excretion of nitrogenous waste primarily in the form of uric acid. This adaptation is crucial for organisms that need to conserve water, which is particularly important in arid environments.
Key Characteristics of Uricotelism
- Water Conservation: Uricotelic organisms excrete uric acid as a semi-solid paste, which minimizes water loss compared to urea or ammonia, making it an efficient method for maintaining water balance.
- Evolutionary Adaptation: This adaptation is particularly beneficial for animals that inhabit environments where water is scarce, allowing them to thrive in terrestrial ecosystems.
Organisms Exhibiting Uricotelism
- Birds: Birds are a prime example of uricotelism. Their ability to excrete uric acid helps them conserve water, which is vital for survival, especially during flight.
- Reptiles: Similar to birds, reptiles such as lizards and snakes also excrete uric acid. They have adapted to terrestrial life where water availability may be limited.
- Insects: Many insects utilize uricotelism, excreting uric acid to efficiently manage water resources in their often variable environments.
Conclusion
In summary, uricotelism is primarily found in birds, reptiles, and insects due to its evolutionary advantages in water conservation, particularly in dry habitats. This characteristic is essential for their survival and adaptation to terrestrial life.
Presence of which of the following conditions in urine are indicative of Diabetes Mellitus? [2020]- a)Ketonuria and Glycosuria
- b)Renal calculi and Hyperglycaemia
- c)Uremia and Ketonuria
- d)Uremia and Renal Calculi
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Presence of which of the following conditions in urine are indicative of Diabetes Mellitus? [2020]
a)
Ketonuria and Glycosuria
b)
Renal calculi and Hyperglycaemia
c)
Uremia and Ketonuria
d)
Uremia and Renal Calculi
|
|
Pallavi Choudhary answered |
Presence of which of the following conditions in urine are indicative of Diabetes Mellitus?
The correct answer is option 'A' - Ketonuria and Glycosuria.
Explanation:
Diabetes Mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels due to inadequate production or utilization of insulin. It can be diagnosed by various clinical features and laboratory tests, including urine analysis. Specific changes in the urine composition can indicate the presence of diabetes mellitus.
The presence of the following conditions in urine are indicative of Diabetes Mellitus:
Ketonuria:
Ketonuria refers to the presence of ketone bodies in the urine. In a normal state, the body primarily uses glucose as a source of energy. However, in diabetes mellitus, when there is a lack of insulin or insulin resistance, the body is unable to utilize glucose effectively. As a result, the body starts breaking down fat for energy, leading to the production of ketone bodies (such as acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone). These ketone bodies are then excreted in the urine, leading to the presence of ketonuria. Ketonuria is a significant indicator of uncontrolled diabetes mellitus.
Glycosuria:
Glycosuria refers to the presence of glucose in the urine. In a normal state, the kidneys reabsorb all the filtered glucose back into the bloodstream. However, in diabetes mellitus, when blood sugar levels are elevated and exceed the renal threshold, the capacity of the kidneys to reabsorb glucose is overwhelmed. As a result, glucose spills into the urine, leading to the presence of glycosuria. Glycosuria is a sensitive indicator of diabetes mellitus and can be detected even before blood sugar levels become significantly elevated.
Therefore, the presence of both ketonuria and glycosuria in urine is highly indicative of Diabetes Mellitus. These urine changes reflect the abnormal metabolism of glucose and fat in the body due to insulin deficiency or resistance. It is important to note that the absence of these urine changes does not rule out the possibility of diabetes mellitus, as there are cases of diabetes mellitus without ketonuria or glycosuria.
The correct answer is option 'A' - Ketonuria and Glycosuria.
Explanation:
Diabetes Mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels due to inadequate production or utilization of insulin. It can be diagnosed by various clinical features and laboratory tests, including urine analysis. Specific changes in the urine composition can indicate the presence of diabetes mellitus.
The presence of the following conditions in urine are indicative of Diabetes Mellitus:
Ketonuria:
Ketonuria refers to the presence of ketone bodies in the urine. In a normal state, the body primarily uses glucose as a source of energy. However, in diabetes mellitus, when there is a lack of insulin or insulin resistance, the body is unable to utilize glucose effectively. As a result, the body starts breaking down fat for energy, leading to the production of ketone bodies (such as acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone). These ketone bodies are then excreted in the urine, leading to the presence of ketonuria. Ketonuria is a significant indicator of uncontrolled diabetes mellitus.
Glycosuria:
Glycosuria refers to the presence of glucose in the urine. In a normal state, the kidneys reabsorb all the filtered glucose back into the bloodstream. However, in diabetes mellitus, when blood sugar levels are elevated and exceed the renal threshold, the capacity of the kidneys to reabsorb glucose is overwhelmed. As a result, glucose spills into the urine, leading to the presence of glycosuria. Glycosuria is a sensitive indicator of diabetes mellitus and can be detected even before blood sugar levels become significantly elevated.
Therefore, the presence of both ketonuria and glycosuria in urine is highly indicative of Diabetes Mellitus. These urine changes reflect the abnormal metabolism of glucose and fat in the body due to insulin deficiency or resistance. It is important to note that the absence of these urine changes does not rule out the possibility of diabetes mellitus, as there are cases of diabetes mellitus without ketonuria or glycosuria.
Nitrogenous waste products are eliminated mainly as [1991]- a)urea in tadpole and ammonia in adult frog
- b)ammonia in tadpole and urea in adult frog
- c)urea in both tadpole and adult frog
- d)urea in tadpole and uric acid in adult frog
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Nitrogenous waste products are eliminated mainly as [1991]
a)
urea in tadpole and ammonia in adult frog
b)
ammonia in tadpole and urea in adult frog
c)
urea in both tadpole and adult frog
d)
urea in tadpole and uric acid in adult frog

|
Arnav Iyer answered |
Ammonia molecules are small and very soluble in water. In ammonotelic animals large amount of H2O is required to eliminate ammonia from the body, so it is found in aquatic animals like tadpole of frog. When tadpole becomes a mature frog it acquires mainly ureotelism.
Formation of concentrated (hyperosmotic) urine in vertebrates generally depends on [2000]- a)length of the proximal convoluted tubule
- b)length of Henle's loop
- c)area of Bowman's capsule epithelium
- d)capillary network forming glomerulus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Formation of concentrated (hyperosmotic) urine in vertebrates generally depends on [2000]
a)
length of the proximal convoluted tubule
b)
length of Henle's loop
c)
area of Bowman's capsule epithelium
d)
capillary network forming glomerulus

|
Arnav Iyer answered |
Henle’s loop is involved in osmoregulation and concentrating urine. Thus producing a hypertonic urine.
Select the option which shows correct matching of animal with excretory organs and excretory product [NEET Kar. 2013]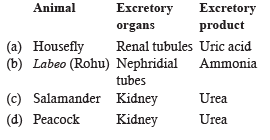
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the option which shows correct matching of animal with excretory organs and excretory product [NEET Kar. 2013]

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Pankaj Kulkarni answered |
Salamander (Amphibia; Caudata) excrete urea by help of kidneys.
A terrestrial animal must be able to [2004]- a)excrete large amounts of water in urine
- b)conserve water
- c)actively pump salts out through the skin
- d)excrete large amounts of salts in urine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A terrestrial animal must be able to [2004]
a)
excrete large amounts of water in urine
b)
conserve water
c)
actively pump salts out through the skin
d)
excrete large amounts of salts in urine
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Explanation:
Since, terrestrial animals do not have automatic access to either fresh or salt water, they must regulate water content in other ways, balancing off gains and losses.
Reabsorption of useful substances from glomerular filtrate occurs in [1989]- a)Collecting tube
- b)Loop of Henle
- c)Proximal convoluted tubule
- d)Distal convoluted tubule
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Reabsorption of useful substances from glomerular filtrate occurs in [1989]
a)
Collecting tube
b)
Loop of Henle
c)
Proximal convoluted tubule
d)
Distal convoluted tubule

|
Ritika Khanna answered |
From Bowman's capsule, glomer ular filtrate enters the proximal convolute tubule. Most of the useful substances like Glucose (all), Amino Acids (all), most of the inorganic ions (Na+, K+, Cl– etc), most of the important buffer bicarbonates are reabsorbed in Proximal Convoluted Tubule. Cells are specially adaptive for absorption having numerous microvilli & mitochondria (to provide energy for active absorption).
A patient suffering from cholera is given saline drip because [1996, 2000]- a)Cl– ions are important component of blood plasma
- b)Na+ ions help to retain water in the body
- c)Na+ ions are important in transport of substances across membrane
- d)Cl– ions help in the formation of HCl in stomach for digestion
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A patient suffering from cholera is given saline drip because [1996, 2000]
a)
Cl– ions are important component of blood plasma
b)
Na+ ions help to retain water in the body
c)
Na+ ions are important in transport of substances across membrane
d)
Cl– ions help in the formation of HCl in stomach for digestion

|
Rhea Sarkar answered |
In patients affected with cholera, a cholera enterotoxin is produced which results in increased synthesis of intracellular cyclic AMP, which in turn increases the permeability of intestinal mucosa, leading to secretion of fluid throughout the small intestine. Hence the patient is given saline drip whereby Na+ ions restore the osmotic balance by retaining water in the body.
Proximal and distal convoluted tubules are parts of [1990]- a)Seminiferous tubules
- b)Nephron
- c)Oviduct
- d)Vas deferens
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Proximal and distal convoluted tubules are parts of [1990]
a)
Seminiferous tubules
b)
Nephron
c)
Oviduct
d)
Vas deferens

|
Krish Patel answered |
Nephron is the excretory unit of human excretory system. Each nephron has a Bowman’s Capsule, a Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT), Loop of Henle (Descending & Ascending limbs) and Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) which then enter into collecting duct.
A fall in glomer ular filtration rate (GFR) activates [2012M]- a)adrenal cortex to release aldosterone.
- b)adrenal medulla to release adrenaline.
- c)juxta - glomerular cells to release renin.
- d)posterior pituitary to release vasopressin.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A fall in glomer ular filtration rate (GFR) activates [2012M]
a)
adrenal cortex to release aldosterone.
b)
adrenal medulla to release adrenaline.
c)
juxta - glomerular cells to release renin.
d)
posterior pituitary to release vasopressin.

|
Anand Jain answered |
The amount of the filtrate formed by the kidneys per minute is called glomerular filtration rate (GFR). GFR in a healthy individual is approximately 125 ml/ minute, i.e., 180 litres per day. A fall in GFR can activate the JG cells to release renin which can stimulate the glomerular blood flow and thereby the GFR back to normal. Renin converts angiotensinogen in blood to angiotensin I and further angiotensin II. Angiotensin II being powerful vasoconstrictor increases the glomerular blood pressure and thereby GFR
Chapter doubts & questions for Excretory Products and their Elimination - Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Excretory Products and their Elimination - Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










