All Exams >
Civil Engineering (CE) >
SSC JE Civil Engineering 2025 Mock Test Series >
All Questions
All questions of Geomatics Engineering (Surveying) for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam
In setting up a plane table at any station
- a)orientation is done first.
- b)Mapping is done first
- c)Levelling is done first
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In setting up a plane table at any station
a)
orientation is done first.
b)
Mapping is done first
c)
Levelling is done first
d)
None of these

|
Akshat Datta answered |
Setting up a Plane Table
A plane table is an instrument used for surveying and mapping purposes. It consists of a flat table or board with a leveling head and a sighting device. To set up a plane table at any station, the following steps are followed:
1. Levelling and Centering:
The first step is to level and center the plane table. This is done by adjusting the screws on the leveling head until the bubble in the spirit level is centered. The table is then placed on the tripod and leveled in all directions using the leveling screws on the tripod.
2. Orientation:
Once the table is level, it is oriented to the true north using a compass or a theodolite. The table is then clamped in position.
3. Sighting:
The next step is to sight the target using the sighting device. The surveyor looks through the sighting device and lines it up with the target. The position of the target is then marked on the table using a pencil or a pin.
4. Sketching:
After the position of the target is marked, the surveyor sketches the surrounding details on the table. This is done by sighting and marking the position of several other targets and drawing lines between them.
5. Calculation:
Once the sketch is complete, the surveyor calculates the position of the targets and other features using trigonometry and other mathematical calculations.
In conclusion, leveling and centering are done simultaneously while setting up a plane table. This is to ensure that the table is stable and accurate while sighting and sketching the targets.
A plane table is an instrument used for surveying and mapping purposes. It consists of a flat table or board with a leveling head and a sighting device. To set up a plane table at any station, the following steps are followed:
1. Levelling and Centering:
The first step is to level and center the plane table. This is done by adjusting the screws on the leveling head until the bubble in the spirit level is centered. The table is then placed on the tripod and leveled in all directions using the leveling screws on the tripod.
2. Orientation:
Once the table is level, it is oriented to the true north using a compass or a theodolite. The table is then clamped in position.
3. Sighting:
The next step is to sight the target using the sighting device. The surveyor looks through the sighting device and lines it up with the target. The position of the target is then marked on the table using a pencil or a pin.
4. Sketching:
After the position of the target is marked, the surveyor sketches the surrounding details on the table. This is done by sighting and marking the position of several other targets and drawing lines between them.
5. Calculation:
Once the sketch is complete, the surveyor calculates the position of the targets and other features using trigonometry and other mathematical calculations.
In conclusion, leveling and centering are done simultaneously while setting up a plane table. This is to ensure that the table is stable and accurate while sighting and sketching the targets.
A dumpy level is set up with its eyepiece vertically over a peg A. The height from the top of peg A to the centre of the eyepiece is 1.540 m and the reading on peg B is 0.705 m. The level is then set up over B. The height of the eyepiece above peg B is 1.490 m and a reading on A is 2.195 m. The difference in level between A and B is ________.
- a)2.900 m
- b)3.030 m
- c)0.770 m
- d)0.785 m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A dumpy level is set up with its eyepiece vertically over a peg A. The height from the top of peg A to the centre of the eyepiece is 1.540 m and the reading on peg B is 0.705 m. The level is then set up over B. The height of the eyepiece above peg B is 1.490 m and a reading on A is 2.195 m. The difference in level between A and B is ________.
a)
2.900 m
b)
3.030 m
c)
0.770 m
d)
0.785 m

|
Engineers Adda answered |
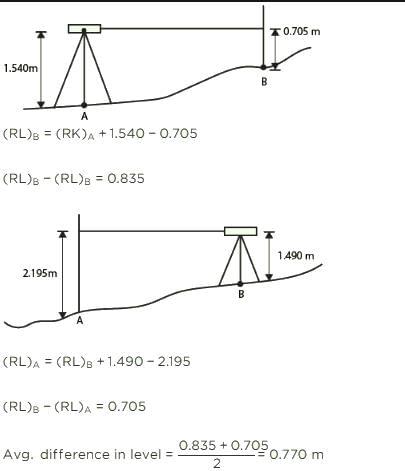
If cross sectional area of an embankment at 30 m intervals are 20, 40, 60, 50 and 30 m2 respectively, then volume of the embankment on the basis of prismoidal rule is:- a)5300 m2
- b)8300 m2
- c)4300 m2
- d)6300 m2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If cross sectional area of an embankment at 30 m intervals are 20, 40, 60, 50 and 30 m2 respectively, then volume of the embankment on the basis of prismoidal rule is:
a)
5300 m2
b)
8300 m2
c)
4300 m2
d)
6300 m2

|
Varun Mukherjee answered |
Volume of embankment is given by:
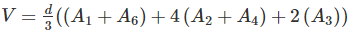
d = 30 m
A1 = 20 m2
A2 = 40 m2
A3 = 60 m2
A4 = 50 m2
A5 = 30 m2
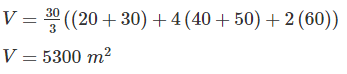
If the vertical curve connects a 1% upgrade with 1.4% downgrade, and the rate of change of grade is to be 0.06% per 20 m stations, the length of a vertical curve is- a)133.3 m
- b)40 m
- c)400 m
- d)800 m
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If the vertical curve connects a 1% upgrade with 1.4% downgrade, and the rate of change of grade is to be 0.06% per 20 m stations, the length of a vertical curve is
a)
133.3 m
b)
40 m
c)
400 m
d)
800 m

|
Naina Das answered |
Deflection angle, 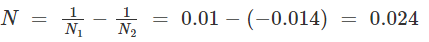
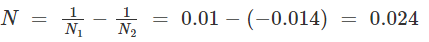
Length of the vertical curve, 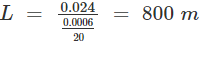
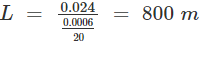
Direct ranging is possible only when the end stations are:- a)Close to each other
- b)Not more than 100 m apart
- c)Mutually intervisible
- d)Located at highest point in the sea.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direct ranging is possible only when the end stations are:
a)
Close to each other
b)
Not more than 100 m apart
c)
Mutually intervisible
d)
Located at highest point in the sea.

|
Jay Sharma answered |
The process of establishing or developing intermediate points between two terminal points or end points on a straight line is known as ranging.
Direct Ranging: The ranging in which intermediate ranging rods are placed in a straight line by direct observation from either end.
Direct ranging is possible only when the end stations are intervisible.
If the engineer’s scale of a drawing is state as 1 cm = 5 m, then the fraction scale would be 1: x, where x is:- a)0.5
- b)500.0
- c)50.0
- d)5.0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the engineer’s scale of a drawing is state as 1 cm = 5 m, then the fraction scale would be 1: x, where x is:
a)
0.5
b)
500.0
c)
50.0
d)
5.0

|
Naina Das answered |
Engineer's Scale is given as:
1 cm = 5 m
Now,
Representative fraction = 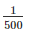
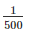
Hence x = 500
Parallax bar is used to measure- a)Parallax
- b)Parallax difference
- c)Difference in elevation
- d)Reduced level of a point
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Parallax bar is used to measure
a)
Parallax
b)
Parallax difference
c)
Difference in elevation
d)
Reduced level of a point

|
Baishali Bajaj answered |
The parallax bar is an instrument designed for use with a mirror stereoscope that has a stereo base of ten inches or less. The bar
is used to determine the height difference of natural and man made features when viewing stereoscopic photographs.
The following consecutive readings were taken with a dumpy level and a 3 m staff on a continuous sloping ground:0.425, 1.035, 1.950, 2.360, 2.950, 0.750, 1.565, 2.455.Which of the following readings are back sights?- a)0.425, 2.950, 0.750
- b)0.425, 2.360, 0.750
- c)0.425, 0.750
- d)0.425, 2.950, 0.750, 1.565
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The following consecutive readings were taken with a dumpy level and a 3 m staff on a continuous sloping ground:
0.425, 1.035, 1.950, 2.360, 2.950, 0.750, 1.565, 2.455.
Which of the following readings are back sights?
a)
0.425, 2.950, 0.750
b)
0.425, 2.360, 0.750
c)
0.425, 0.750
d)
0.425, 2.950, 0.750, 1.565

|
Ashwin Kulkarni answered |
Given information:
Consecutive readings taken with a dumpy level and a 3 m staff on a continuous sloping ground: 0.425, 1.035, 1.950, 2.360, 2.950, 0.750, 1.565, 2.455.
To determine which readings are back sights.
Backsight:
A backsight is a reading taken on a point of known level or elevation, also known as a bench mark, which is used as a reference height for other readings.
Solution:
To determine which readings are back sights, we need to identify the points for which we have a known level or elevation. From the given readings, we can identify that:
- The initial reading of 0.425 is not a backsight as it is the starting point of the survey and there is no known level or elevation for this point.
- The reading of 2.950 is not a backsight as there is no indication that this point is a known level or elevation.
- The reading of 0.750 is a backsight as it is immediately followed by the reading of 1.565, which is higher. This indicates that the point with reading 0.750 is at a lower level or elevation and is a point of known height.
- The final reading of 2.455 is not a backsight as there is no indication that this point is a known level or elevation.
Therefore, the readings that are backsights are:
Option C: 0.425, 0.750.
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Consecutive readings taken with a dumpy level and a 3 m staff on a continuous sloping ground: 0.425, 1.035, 1.950, 2.360, 2.950, 0.750, 1.565, 2.455.
To determine which readings are back sights.
Backsight:
A backsight is a reading taken on a point of known level or elevation, also known as a bench mark, which is used as a reference height for other readings.
Solution:
To determine which readings are back sights, we need to identify the points for which we have a known level or elevation. From the given readings, we can identify that:
- The initial reading of 0.425 is not a backsight as it is the starting point of the survey and there is no known level or elevation for this point.
- The reading of 2.950 is not a backsight as there is no indication that this point is a known level or elevation.
- The reading of 0.750 is a backsight as it is immediately followed by the reading of 1.565, which is higher. This indicates that the point with reading 0.750 is at a lower level or elevation and is a point of known height.
- The final reading of 2.455 is not a backsight as there is no indication that this point is a known level or elevation.
Therefore, the readings that are backsights are:
Option C: 0.425, 0.750.
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
The indirect method of contouring has all the following advantages over direct method except:- a)Economy
- b)Suitability
- c)Accuracy
- d)Suitability for large projects
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The indirect method of contouring has all the following advantages over direct method except:
a)
Economy
b)
Suitability
c)
Accuracy
d)
Suitability for large projects

|
Megha Choudhury answered |
**Explanation:**
The indirect method of contouring is a technique used in surveying to determine the shape of the land surface, particularly in areas with uneven terrain. It involves the use of contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation, to create a contour map.
The indirect method of contouring has several advantages over the direct method, which involves physically measuring the elevation at each point on the ground. These advantages include:
**1. Economy:**
- The indirect method is generally more economical than the direct method because it requires fewer field measurements.
- It relies on the interpolation of elevation values between known points, reducing the need for extensive field work.
**2. Suitability:**
- The indirect method is suitable for areas with complex terrain or limited access.
- It can be used in situations where it is difficult or impractical to measure the elevation at every point on the ground.
**3. Suitability for large projects:**
- The indirect method is particularly well-suited for large projects that cover a wide area.
- It allows for the efficient collection of elevation data over a large extent of land.
However, the indirect method of contouring does have one disadvantage compared to the direct method:
**4. Accuracy:**
- The indirect method may not be as accurate as the direct method because it relies on interpolation and estimation.
- It assumes that the elevation values between known points vary smoothly and continuously, which may not always be the case.
- In areas with abrupt changes in elevation or irregular topography, the indirect method may produce less accurate results.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C' - Accuracy. The indirect method of contouring does not have an advantage in terms of accuracy compared to the direct method.
The indirect method of contouring is a technique used in surveying to determine the shape of the land surface, particularly in areas with uneven terrain. It involves the use of contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation, to create a contour map.
The indirect method of contouring has several advantages over the direct method, which involves physically measuring the elevation at each point on the ground. These advantages include:
**1. Economy:**
- The indirect method is generally more economical than the direct method because it requires fewer field measurements.
- It relies on the interpolation of elevation values between known points, reducing the need for extensive field work.
**2. Suitability:**
- The indirect method is suitable for areas with complex terrain or limited access.
- It can be used in situations where it is difficult or impractical to measure the elevation at every point on the ground.
**3. Suitability for large projects:**
- The indirect method is particularly well-suited for large projects that cover a wide area.
- It allows for the efficient collection of elevation data over a large extent of land.
However, the indirect method of contouring does have one disadvantage compared to the direct method:
**4. Accuracy:**
- The indirect method may not be as accurate as the direct method because it relies on interpolation and estimation.
- It assumes that the elevation values between known points vary smoothly and continuously, which may not always be the case.
- In areas with abrupt changes in elevation or irregular topography, the indirect method may produce less accurate results.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C' - Accuracy. The indirect method of contouring does not have an advantage in terms of accuracy compared to the direct method.
Which one is the CORRECT sequence for the temporary adjustment of the theodolite?- a)Centering, elimination of parallax, leveling, and setting
- b)Centering, setting, elimination of parallax and leveling
- c)Setting, centering, leveling and elimination of parallax
- d)Setting, leveling, elimination of parallax and centering
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is the CORRECT sequence for the temporary adjustment of the theodolite?
a)
Centering, elimination of parallax, leveling, and setting
b)
Centering, setting, elimination of parallax and leveling
c)
Setting, centering, leveling and elimination of parallax
d)
Setting, leveling, elimination of parallax and centering

|
Priyanka Shah answered |
Temporary Adjustment of Theodolite:
Firstly, Instrument is at set-up at concerned station, Then
1. Cantering: To place the vertical axis exactly over the station mark
2. Levelling: Levelling adjustment of the theodolite is done using levelling screws or foot screws. The objective of levelling in surveying is to make the vertical axis of the instrument truly vertical.
3. Elimination of Parallax: Parallax is the condition arising when the image formed by the objective is not in the plane of crosshairs. This one of important steps in the temporary adjustment of theodolite or telescope.
The needle of a magnetic compass is generally supported on a:- a)Bush Bearing
- b)Ball Bearing
- c)Needle Bearing
- d)Jewel Bearing
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The needle of a magnetic compass is generally supported on a:
a)
Bush Bearing
b)
Ball Bearing
c)
Needle Bearing
d)
Jewel Bearing

|
Kaavya Sengupta answered |
The needle of magnetic compass is generally supported on a Jewel Bearing. A jewel bearing is a plain bearing in which a metal spindle turns in a jewel-lined pivot hole.
The hole is typically shaped like a torus and is slightly larger than the shaft diameter.
The back sight reading on bench mark of R.L 500.00 m is 2.685 m. If foresight reading on the point is 1.345 m, the reduced level of the point is?- a)502.68 m
- b)501.315 m
- c)501.340 m
- d)504.030 m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The back sight reading on bench mark of R.L 500.00 m is 2.685 m. If foresight reading on the point is 1.345 m, the reduced level of the point is?
a)
502.68 m
b)
501.315 m
c)
501.340 m
d)
504.030 m

|
Ankit Joshi answered |
Given data:
- Backsight reading on benchmark = 2.685 m
- Foresight reading on the point = 1.345 m
- Reduced level of benchmark = 500.00 m
We need to find the reduced level of the point.
Steps to find reduced level:
1. Calculate the height of instrument (HI):
- HI = Benchmark RL + Backsight reading
- HI = 500.00 m + 2.685 m
- HI = 502.685 m
2. Calculate the Reduced Level (RL) of the point:
- RL = HI - Foresight reading
- RL = 502.685 m - 1.345 m
- RL = 501.340 m
Therefore, the reduced level of the point is 501.340 m.
Hence, option (c) is the correct answer.
- Backsight reading on benchmark = 2.685 m
- Foresight reading on the point = 1.345 m
- Reduced level of benchmark = 500.00 m
We need to find the reduced level of the point.
Steps to find reduced level:
1. Calculate the height of instrument (HI):
- HI = Benchmark RL + Backsight reading
- HI = 500.00 m + 2.685 m
- HI = 502.685 m
2. Calculate the Reduced Level (RL) of the point:
- RL = HI - Foresight reading
- RL = 502.685 m - 1.345 m
- RL = 501.340 m
Therefore, the reduced level of the point is 501.340 m.
Hence, option (c) is the correct answer.
Every 20 m chain should be accurate to within- a)± 8 mm
- b)± 2 mm
- c)± 5 mm
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Every 20 m chain should be accurate to within
a)
± 8 mm
b)
± 2 mm
c)
± 5 mm
d)
None of these

|
Dhruba Jain answered |
As the chain is a metal made, it may undergo many changes due to temperature effect or human error and etc. So for all lengths of chain a tolerance is given:
1. 5 meter chain: + or – 3 mm
2. 10 meter chain: + or – 3 mm
3. 20 meter chain: + or – 5 mm
4. 30 meter chain: + or – 8 mm
In chain surveying the lateral measurements that are taken form the chainage to the objects are called:- a)Backsights
- b)Check lengths
- c)Offsets
- d)Laterals
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In chain surveying the lateral measurements that are taken form the chainage to the objects are called:
a)
Backsights
b)
Check lengths
c)
Offsets
d)
Laterals

|
Garima Basak answered |
Offsets: Lateral measurements to chain lines for locating ground features are known as offsets.
Backsights: A measurement or reading taken back towards a point of known elevation, used to calculate the height of the surveying instrument is known as backsights.
Principle of plane tabling is:-- a)Parallelism
- b)Triangulation
- c)Traversing
- d)Centering
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Principle of plane tabling is:-
a)
Parallelism
b)
Triangulation
c)
Traversing
d)
Centering

|
Garima Basak answered |
Plane table surveying is the graphical method of survey in which the field observations and plotting are done simultaneously. Plane table surveying is based on the principle that lines drawn during plotting always lie parallel to the corresponding lines actually present on the ground i.e the principle of plane table surveying is parallelism.
The least count of a Vernier is the:- a)Value of the division on the main scale
- b)Value of the division on the vernier scale
- c)Sum of values of one Vernier scale and one main scale divisions
- d)Difference between the value of one main scale division and Vernier scale division.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The least count of a Vernier is the:
a)
Value of the division on the main scale
b)
Value of the division on the vernier scale
c)
Sum of values of one Vernier scale and one main scale divisions
d)
Difference between the value of one main scale division and Vernier scale division.

|
Debolina Chavan answered |
The minimum length that can be measured using the Vernier callipers is called its least count.

A level, when set up 25 m from peg A and 50 m from peg B, reads 2.853 m on a staff held on A and 4.462 m on a staff held on B, keeping the bubble at its centre while reading. If the reduced levels of A and B are 283.665 m and 285.295m respectively, what is the collimation error per 100.0 m?- a)0.015 m
- b)0.021 m
- c)0.045 m
- d)0.060 m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A level, when set up 25 m from peg A and 50 m from peg B, reads 2.853 m on a staff held on A and 4.462 m on a staff held on B, keeping the bubble at its centre while reading. If the reduced levels of A and B are 283.665 m and 285.295m respectively, what is the collimation error per 100.0 m?
a)
0.015 m
b)
0.021 m
c)
0.045 m
d)
0.060 m

|
Partho Jain answered |
Actual difference between A and B = 285.295 - 283.665 = 1.630 m
Apparent difference between A and B = 4.462 - 2.853 = 1.609 m
Error in collimation = 1.63 - 1.609 = 0.021 m
To orient a plane table at a point with two inaccessible points, the method generally adopted is:- a)Intersection
- b)Resection
- c)Radiation
- d)Two-point problem
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
To orient a plane table at a point with two inaccessible points, the method generally adopted is:
a)
Intersection
b)
Resection
c)
Radiation
d)
Two-point problem

|
Prasad Desai answered |
Two Point Problem: It is basically a resection method. In the two-point problem, two points are sighted from other point corresponding to the points given in plane table sheet.
In the method of intersection, the plotted position of stations is known, and the plotted position of objects are obtained by intersection.
In the method of resection, the plotted position of objects is known, and the plotted position of station is obtained.
When the curve is to be set out over a rough ground, the method used is- a)Two Theodolite method
- b)Rankine method
- c)Tachometric method
- d)Either 1 or 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When the curve is to be set out over a rough ground, the method used is
a)
Two Theodolite method
b)
Rankine method
c)
Tachometric method
d)
Either 1 or 3

|
Simran Mukherjee answered |
Two theodolite method: In this method, curves are staked out by angular measurements only. Accuracy attained in this method is quite high. Thus, the method is used when higher accuracy is required and when the topography is rough or field condition is difficult. Whenever curve is to be set out over rough ground this method is adopted.
Tacheometric Method: This method is sometimes used when the ground is rough and chaining cannot be done accurately. The usual table of tangential angles can be used to obtain the direction of the respective points on the curve.
Which one of the following statement is CORRECT?- a)The nature of combined correction due to curvature and refraction is additive.
- b)The figure on the staff are distinct if the staff is kept near to the level.
- c)In levelling, if the previous reading is less than the next consecutive reading, it indicates a rise.
- d)The effect of curvature and refraction can be neglected, if the instrument is kept midway.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statement is CORRECT?
a)
The nature of combined correction due to curvature and refraction is additive.
b)
The figure on the staff are distinct if the staff is kept near to the level.
c)
In levelling, if the previous reading is less than the next consecutive reading, it indicates a rise.
d)
The effect of curvature and refraction can be neglected, if the instrument is kept midway.

|
Srestha Datta answered |
Curvature correction is negative and refraction correction is positive. If previous reading is less than the next consecutive reading then it will indicate a falling gradient.
Which one of the following is the largest scale?- a)1 : 500
- b)1 : 1000
- c)1 : 2500
- d)1 : 50000
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the largest scale?
a)
1 : 500
b)
1 : 1000
c)
1 : 2500
d)
1 : 50000

|
Preethi Datta answered |
Upon solving,
1/500 = 0.002
1/1000 = 0.001
1/2500 = 0.0004
1/50000 = 0.00002
Largest is 0.002 i.e. 1/500
The instrument which is used in plane tabling for obtaining horizontal and vertical distances directly without resorting to chaining, is known as- a)Plane alidade
- b)Telescopic alidade
- c)Clinometer
- d)Tacheometer
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The instrument which is used in plane tabling for obtaining horizontal and vertical distances directly without resorting to chaining, is known as
a)
Plane alidade
b)
Telescopic alidade
c)
Clinometer
d)
Tacheometer

|
Bibek Mehra answered |
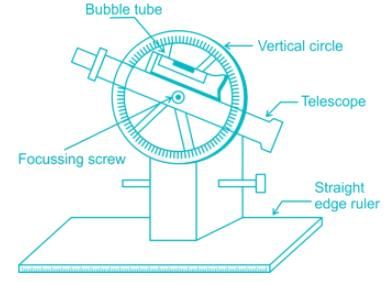
Telescopic alidade consists of a telescope mounted on a column fixed to the ruler. The line of sight through the telescope is kept parallel to the bevelled edge of the ruler. The telescope is provided with a level tube and vertical graduation arc. If the horizontal sight is required, bubble in the level tube is kept at the centre.
If inclined sights are required, vertical graduation helps in noting the inclination of the line of sight. By providing telescope the range and the accuracy of the line of sight are increased.
Formula used in correction for curvature (Cc):where, d is the distance in km and Cc is in meter- a)0.007849 d2
- b)0.07849 d2
- c)0.7849 d2
- d)7.849 d2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Formula used in correction for curvature (Cc):
where, d is the distance in km and Cc is in meter
a)
0.007849 d2
b)
0.07849 d2
c)
0.7849 d2
d)
7.849 d2

|
Shounak Saini answered |
Curvature correction is negative and is given by:
Cc = -0.07849 d2
where,
d is the distance in km
Cc is in meter
The least count of prismatic compass is:- a)1°
- b)30'
- c)15'
- d)20"
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The least count of prismatic compass is:
a)
1°
b)
30'
c)
15'
d)
20"

|
Subham Unni answered |
The smallest value that can be measured by the measuring instrument is called its Least Count.
Least count of Prismatic Compass = 30 minutes = 30’
Least Count of surveyor’s Compass = 15 minutes = 15’
A 30 m metric chain is found to be 20 cm too long throughout a measurement. If the distance measured is recorded as 300 m, what is the actual distance?- a)300.1m
- b)300.2 m
- c)298.0 m
- d)302.0 m
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A 30 m metric chain is found to be 20 cm too long throughout a measurement. If the distance measured is recorded as 300 m, what is the actual distance?
a)
300.1m
b)
300.2 m
c)
298.0 m
d)
302.0 m

|
Sarthak Menon answered |
True length of chain × true measurement = incorrect length of chain × incorrect measurement
Hence, True measurement = 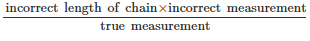
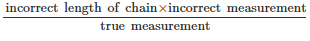
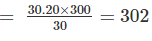
If whole circle bearing of any line is W1, that of the preceding line is W2 and “d” is the deflection angles to the right, then choose the correct expression:- a)W1 = W2 + d
- b)W1 = W2 - d
- c)W1 = W2 + 2d
- d)W1 = W2 - 2d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If whole circle bearing of any line is W1, that of the preceding line is W2 and “d” is the deflection angles to the right, then choose the correct expression:
a)
W1 = W2 + d
b)
W1 = W2 - d
c)
W1 = W2 + 2d
d)
W1 = W2 - 2d

|
Bhavya Ahuja answered |
The included angle between the two lines is A, then the whole circle bearing of the new line formed by extending the preceding line by the included angle A is:
W3 = W1 + A - 180°
Note: This formula assumes that the angles are measured in degrees and that the bearings are given in the whole circle notation (i.e. from 0° to 360°).
W3 = W1 + A - 180°
Note: This formula assumes that the angles are measured in degrees and that the bearings are given in the whole circle notation (i.e. from 0° to 360°).
As applied to staff readings, the corrections for curvature and refraction are respectively- a)+ and -
- b)- and +
- c)+ and +
- d)- and -
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
As applied to staff readings, the corrections for curvature and refraction are respectively
a)
+ and -
b)
- and +
c)
+ and +
d)
- and -

|
Anjana Mukherjee answered |
The curvature increases the staff reading, hence its correction is negative. The rays of light when passing through atmosphere bend down and follows a curved path, hence correction is positive.
Correction due to curvature = -0.0785D2
Correction due to refraction = 0.0112D2
Combined correction = -0.0673D2
Which of the following surveys is employed for collecting data related to transfer of land property from one owner to another?- a)Geodetic survey
- b)Property survey
- c)City survey
- d)Cadastral survey
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following surveys is employed for collecting data related to transfer of land property from one owner to another?
a)
Geodetic survey
b)
Property survey
c)
City survey
d)
Cadastral survey

|
Aditi Chakraborty answered |
Cadastral survey : The cadastral survey are made incident to the fixing of property lines, the calculation of land area, or the transfer of land property from one owner to another. They are also made to fix the boundaries of municipalities and of state and federal jurisdictions.
Basically, Cadastral surveying is the discipline of land surveying that relates to the laws of land ownership and the definition of property boundaries.
Geodetic survey is the survey in which curvature of the earth is taken in to considerations in the field.
City survey: They are made in connection with the construction of streets, water supply systems, sewers and other works.
Calculate the volume of the earthwork (in cubic meter) using trapezoidal method if the cross section areas of the three section of embankment at an interval of 20 m are 40 square meters, 50 square meters and 80 square meters.- a)1067
- b)1700
- c)2200
- d)3200
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the volume of the earthwork (in cubic meter) using trapezoidal method if the cross section areas of the three section of embankment at an interval of 20 m are 40 square meters, 50 square meters and 80 square meters.
a)
1067
b)
1700
c)
2200
d)
3200

|
Ishani Basu answered |
h(internal) = 20 m
A1 = 40 m2
A2 = 50 m2
A3 = 80 m3
Using trapezoidal formula
Volumeofearthwork=h 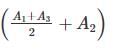
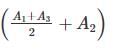
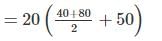
V = 2200 m3
An object on the top of a hill 100 m high is just visible above the horizon from a station at sea level. The distance between the station and the object is:- a)38.53 km
- b)3.853 km
- c)3853 km
- d)385.3 km
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An object on the top of a hill 100 m high is just visible above the horizon from a station at sea level. The distance between the station and the object is:
a)
38.53 km
b)
3.853 km
c)
3853 km
d)
385.3 km

|
Navya Saha answered |
Distance between the station and the object is given by:
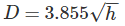
Where,
h = height of visible horizon (meters)
D = Distance of visible horizon (km)
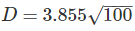
D = 38.53 km.
Which of the following is the most appropriate well conditioned traingle?- a)Isosceles Traingle
- b)Equilateral Traingle
- c)Right angle traingle
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the most appropriate well conditioned traingle?
a)
Isosceles Traingle
b)
Equilateral Traingle
c)
Right angle traingle
d)
None of these

|
Sarthak Kulkarni answered |
Understanding Well-Conditioned Triangles
In civil engineering, the concept of well-conditioned triangles is critical for stability and structural integrity. A well-conditioned triangle ensures that calculations involving angles and lengths yield reliable results.
Defining Well-Conditioned Triangles
A well-conditioned triangle is typically characterized by having angles that are not too acute or too obtuse, which helps avoid computational errors in structural analysis.
Key Triangle Types
- Isosceles Triangle: This triangle has two equal sides and two equal angles. While it can be stable, the presence of two equal angles may lead to less predictable behavior under certain conditions.
- Equilateral Triangle: An equilateral triangle has all sides and angles equal (60 degrees each). This uniformity provides excellent structural properties and minimizes the risk of deformation or failure. It is considered the most stable configuration due to its symmetry.
- Right Angle Triangle: This triangle has one angle of 90 degrees. While useful in various applications, the presence of a right angle can sometimes lead to less favorable conditions for stability compared to equilateral triangles.
Conclusion
Given this analysis, the correct answer is option 'B', the Equilateral Triangle. It is the most appropriate well-conditioned triangle due to its uniformity in angles and sides, which enhances structural stability and predictability in calculations.
For civil engineering applications, choosing an equilateral triangle can significantly impact the reliability of structural designs and analyses.
In civil engineering, the concept of well-conditioned triangles is critical for stability and structural integrity. A well-conditioned triangle ensures that calculations involving angles and lengths yield reliable results.
Defining Well-Conditioned Triangles
A well-conditioned triangle is typically characterized by having angles that are not too acute or too obtuse, which helps avoid computational errors in structural analysis.
Key Triangle Types
- Isosceles Triangle: This triangle has two equal sides and two equal angles. While it can be stable, the presence of two equal angles may lead to less predictable behavior under certain conditions.
- Equilateral Triangle: An equilateral triangle has all sides and angles equal (60 degrees each). This uniformity provides excellent structural properties and minimizes the risk of deformation or failure. It is considered the most stable configuration due to its symmetry.
- Right Angle Triangle: This triangle has one angle of 90 degrees. While useful in various applications, the presence of a right angle can sometimes lead to less favorable conditions for stability compared to equilateral triangles.
Conclusion
Given this analysis, the correct answer is option 'B', the Equilateral Triangle. It is the most appropriate well-conditioned triangle due to its uniformity in angles and sides, which enhances structural stability and predictability in calculations.
For civil engineering applications, choosing an equilateral triangle can significantly impact the reliability of structural designs and analyses.
The instrument which is used in plane tabling for obtaining horizontal and vertical distance directly without resorting to changing, is known as:- a)Planimeter
- b)Plane alidade
- c)Telescopic alidade
- d)Clinometer
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The instrument which is used in plane tabling for obtaining horizontal and vertical distance directly without resorting to changing, is known as:
a)
Planimeter
b)
Plane alidade
c)
Telescopic alidade
d)
Clinometer

|
Aditi Sarkar answered |
Telescopic Alidade: It consist of a telescope as an arrangement for sighting. The telescope is fitted with a stadia diaphragm and can be used as tachometer also for computations of horizontal and vertical elevations.
Planimeter: It is a measuring instrument used to determine the area of an arbitrary two dimensional shape.
Clinometer: It is an instrument for measuring angles of slope (or tilt), elevation or depression of an object with respect to gravity
In plane table survey, the error due to centering should not exceed the scale divided by..........- a)25
- b)40
- c)50
- d)80
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In plane table survey, the error due to centering should not exceed the scale divided by..........
a)
25
b)
40
c)
50
d)
80

|
Anuj Verma answered |
Error due to Centering in Plane Table Survey
In plane table surveying, the process of centering involves setting up the plane table over a point on the ground from where the survey is to be conducted. It is essential to ensure that the table is accurately centered to minimize errors in the survey measurements. One such error is the misplacement of the station point, which can lead to inaccuracies in the plotted positions of the various survey points.
Significance of Scale in Plane Table Survey
The scale is an important aspect of a plane table survey as it determines the ratio between the distances on the map or drawing and the actual distances on the ground. It allows for the representation of large areas on a smaller piece of paper. The scale is usually expressed as a representative fraction (RF) or a graphic scale.
Error Due to Centering
The error due to centering in plane table surveying occurs when the station point is not accurately positioned on the ground. This misplacement can lead to the incorrect plotting of survey points and subsequent errors in the survey measurements. The error due to centering is dependent on various factors such as the accuracy of the centering process and the scale used in the survey.
Relation Between Error Due to Centering and Scale
The error due to centering should not exceed the scale divided by a certain factor. This factor represents the maximum allowable error due to centering, beyond which the accuracy of the survey may be compromised.
Calculation of Maximum Allowable Error
To calculate the maximum allowable error due to centering, the scale is divided by the factor specified in the question. In this case, the correct answer is option 'B,' which states that the error due to centering should not exceed the scale divided by 40.
For example, if the scale of the survey is 1:5000, the maximum allowable error due to centering would be 1/40 * 5000 = 125 units. This means that the misplacement of the station point should not exceed 125 units on the ground.
Importance of Limiting the Error Due to Centering
Limiting the error due to centering is crucial in achieving accurate survey measurements. Any misplacement of the station point can lead to cumulative errors in the plotted positions of the survey points. These errors can affect the overall reliability and precision of the survey data, leading to incorrect interpretations and decisions based on the survey results.
Conclusion
In plane table surveying, it is important to minimize the error due to centering to ensure the accuracy of the survey measurements. The maximum allowable error due to centering is determined by dividing the scale by a specified factor. Option 'B' in this question correctly states that the error due to centering should not exceed the scale divided by 40. By adhering to this criterion, surveyors can obtain reliable and precise survey data for various engineering and construction projects.
In plane table surveying, the process of centering involves setting up the plane table over a point on the ground from where the survey is to be conducted. It is essential to ensure that the table is accurately centered to minimize errors in the survey measurements. One such error is the misplacement of the station point, which can lead to inaccuracies in the plotted positions of the various survey points.
Significance of Scale in Plane Table Survey
The scale is an important aspect of a plane table survey as it determines the ratio between the distances on the map or drawing and the actual distances on the ground. It allows for the representation of large areas on a smaller piece of paper. The scale is usually expressed as a representative fraction (RF) or a graphic scale.
Error Due to Centering
The error due to centering in plane table surveying occurs when the station point is not accurately positioned on the ground. This misplacement can lead to the incorrect plotting of survey points and subsequent errors in the survey measurements. The error due to centering is dependent on various factors such as the accuracy of the centering process and the scale used in the survey.
Relation Between Error Due to Centering and Scale
The error due to centering should not exceed the scale divided by a certain factor. This factor represents the maximum allowable error due to centering, beyond which the accuracy of the survey may be compromised.
Calculation of Maximum Allowable Error
To calculate the maximum allowable error due to centering, the scale is divided by the factor specified in the question. In this case, the correct answer is option 'B,' which states that the error due to centering should not exceed the scale divided by 40.
For example, if the scale of the survey is 1:5000, the maximum allowable error due to centering would be 1/40 * 5000 = 125 units. This means that the misplacement of the station point should not exceed 125 units on the ground.
Importance of Limiting the Error Due to Centering
Limiting the error due to centering is crucial in achieving accurate survey measurements. Any misplacement of the station point can lead to cumulative errors in the plotted positions of the survey points. These errors can affect the overall reliability and precision of the survey data, leading to incorrect interpretations and decisions based on the survey results.
Conclusion
In plane table surveying, it is important to minimize the error due to centering to ensure the accuracy of the survey measurements. The maximum allowable error due to centering is determined by dividing the scale by a specified factor. Option 'B' in this question correctly states that the error due to centering should not exceed the scale divided by 40. By adhering to this criterion, surveyors can obtain reliable and precise survey data for various engineering and construction projects.
Angles of 45° with a chain line may be set out with:- a)Optical square
- b)French square
- c)Open cross staff
- d)Prismatic square
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Angles of 45° with a chain line may be set out with:
a)
Optical square
b)
French square
c)
Open cross staff
d)
Prismatic square

|
Tanishq Rane answered |
1. For 45° → French square
2. For 90° → Optical square
3. Open cross staff is commonly used for setting out long offsets
Which type of errors introduces due to clogging of chain rings with mud?- a)Compensating error
- b)Positive error
- c)Negative error
- d)Can be positive or negative error
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of errors introduces due to clogging of chain rings with mud?
a)
Compensating error
b)
Positive error
c)
Negative error
d)
Can be positive or negative error

|
Neha Mukherjee answered |
Due to clogging of chain rings with mud, actual length of the chain will become less than nominal length of chain. Therefore, measured value is greater than true value.
Error in measurement = Measured value – True value
Error = +ve
Identify the incorrect statement:- a)Change point is a point denoting shifting of level
- b)For levelling work both centering and levelling of a dumpy level prerequisite
- c)Bench mark is a point whose RL is always known
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the incorrect statement:
a)
Change point is a point denoting shifting of level
b)
For levelling work both centering and levelling of a dumpy level prerequisite
c)
Bench mark is a point whose RL is always known
d)
None of these

|
Puja Sharma answered |
Bench mark is a permanent reference point whose R.L is always known to us.
It is our first step to adjust the level for its temporary adjustment (centering, levelling) before start to take reading from a level.
Change point is a point which denotes shifting of level either due to inability to take reading or due to some obstruction.
The theodolite employed for Tacheometry by stadia system differs from an ordinary transit only in having the diaphragm fixed with:- a)Two additional horizontal hairs
- b)Two additional vertical hairs
- c)Two additional horizontal and two additional vertical hairs
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The theodolite employed for Tacheometry by stadia system differs from an ordinary transit only in having the diaphragm fixed with:
a)
Two additional horizontal hairs
b)
Two additional vertical hairs
c)
Two additional horizontal and two additional vertical hairs
d)
None of the above

|
Anand Mehta answered |
The stadia diaphragm essentially consists of one stadia hair above and the other an equal distance below the horizontal crosshair i.e a crosshair with two horizontal
The stadia hair being mounted in the same ring and in the same vertical plane as the horizontal and vertical cross-hair. In stadia systems, staff intercepts, at a pair of stadia hairs present at the diaphragm.
In the stadia system, Targets on the staff are fixed at a known interval and the stadia hairs are adjusted to bisect the upper target at the upper hair and the lower target at the lower hair.
In ordinary transit system, observations are not taken on stadia hairs.
A scale of 1 inch = 50 ft. is mentioned on an old map. What is the corresponding equivalent scale?- a)1 cm = 5 m
- b)1 cm = 6 m
- c)1 cm = 10 m
- d)1 cm = 12 m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A scale of 1 inch = 50 ft. is mentioned on an old map. What is the corresponding equivalent scale?
a)
1 cm = 5 m
b)
1 cm = 6 m
c)
1 cm = 10 m
d)
1 cm = 12 m

|
Sakshi Basak answered |
1 feet = 12 inches
1 inch = 2.54 cm
50 feet = 12 x 50 x 2.54 cm = 1524 cm = 15.24 m
So, 2.54 cm = 15.24 m
Hence 1 cm = 6 m
During chaining along a straight line, the leader of the survey party has three arrows and while follower has five arrows, the distance of the follower from the starting point will be _________.- a)Three chains
- b)Four chains
- c)Five chains
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During chaining along a straight line, the leader of the survey party has three arrows and while follower has five arrows, the distance of the follower from the starting point will be _________.
a)
Three chains
b)
Four chains
c)
Five chains
d)
None of these

|
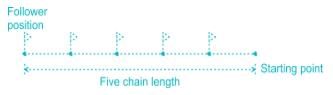
Debolina Chavan answered |
Arrows are used for counting the number of chains while measuring a chain line. An arrow is inserted into the ground after every chain length measured on the ground. After completion of a chain the leader inserts an arrow and follower picked that one on next chaining operation. As the follower has 5 arrows so the distance between the follower and the starting point will be five chains.
The difference between face left and face right observation of a theodolite is 3’. The error is:- a)45”
- b)1’30”
- c)3’
- d)0’
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The difference between face left and face right observation of a theodolite is 3’. The error is:
a)
45”
b)
1’30”
c)
3’
d)
0’

|
Puja Sharma answered |
Error is half the difference between the face left and face right observation.
Error = 3'/2 = 1'30"
The operation of levelling in which only backsight and foresight readings are taken at every step of the level is called…….levelling.- a)Fly
- b)Reciprocal
- c)Compound
- d)Profile
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The operation of levelling in which only backsight and foresight readings are taken at every step of the level is called…….levelling.
a)
Fly
b)
Reciprocal
c)
Compound
d)
Profile

|
Tanishq Rane answered |
Fly levelling is conducted when the benchmark is very far from the work station. In such case, a temporary bench mark is located at the work station which is located based on the original benchmark. Even it is not highly precise it is used for determining approximate level. In fly levelling only backsight and foresight readings are taken at every step of the level.
Reciprocal levelling: When it is not possible to locate the levelling instrument in between the inter visible points, reciprocal levelling is performed. This case appears in case of ponds or rivers etc. In case of reciprocal levelling, instrument is set nearer to 1st station and sighted towards 2nd station.
Profile leveling is generally adopted to find elevation of points along a line such as for road, rails or rivers etc. In this type of levelling, readings of intermediate stations are taken and reduced level of each station is found.
The horizontal angle between the true meridian and magnetic at a place is called:- a)Magnetic bearing
- b)Local attraction
- c)Declination
- d)Azimuth
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The horizontal angle between the true meridian and magnetic at a place is called:
a)
Magnetic bearing
b)
Local attraction
c)
Declination
d)
Azimuth

|
Yash Joshi answered |
Explanation:
The horizontal angle between the true meridian and magnetic at a place is called declination.
Declination:
- The Earth has a magnetic field that varies from place to place.
- The magnetic north pole and the geographic north pole are not located at the same point on the Earth's surface.
- The angle between the true meridian (geographic north) and the magnetic meridian (magnetic north) at a specific location is known as declination.
Causes of Declination:
- The Earth's magnetic field is generated by the movement of molten iron in its outer core.
- This movement is influenced by various factors such as the rotation of the Earth and the interaction with the Sun's magnetic field.
- As a result, the magnetic field is not perfectly aligned with the Earth's rotational axis, leading to declination.
Measurement of Declination:
- Declination is measured in degrees east or west.
- If the magnetic meridian is to the east of the true meridian, the declination is positive (+).
- If the magnetic meridian is to the west of the true meridian, the declination is negative (-).
Importance of Declination:
- Declination is an important parameter for navigation and surveying.
- It is used to convert magnetic bearings to true bearings and vice versa.
- Without considering declination, there can be errors in direction and positioning.
Other Options:
- Magnetic bearing: The direction of a line measured with respect to the magnetic meridian.
- Local attraction: Disturbances in a compass needle caused by nearby magnetic substances or structures.
- Azimuth: The horizontal angle measured clockwise from a reference direction, usually the north.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C' - Declination.
In a solution of the three-point problem in plane table surveying, the converging of error is attained through- a)Concyclic concept
- b)Bessel’s Method
- c)Triangle of error
- d)Tracing paper method
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a solution of the three-point problem in plane table surveying, the converging of error is attained through
a)
Concyclic concept
b)
Bessel’s Method
c)
Triangle of error
d)
Tracing paper method

|
Tanishq Rane answered |
In three point problem, if the orientation of the plane table is not proper, the intersection of the resectors through the three points will not meet at a point but will form a triangle, known as triangle of error. The size of the triangle of error depends upon the amount of angular error in the orientation. This triangle of error will reduce to a point by trial and error.
GIS deals with which kind of data:- a)Numeric Data
- b)Binary data
- c)Spatial data
- d)Complex data
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
GIS deals with which kind of data:
a)
Numeric Data
b)
Binary data
c)
Spatial data
d)
Complex data

|
Sanskriti Datta answered |
GIS (Geographic Information System) deals with spatial data.
Spatial Data:
Spatial data refers to data that is associated with a specific location or geographical area. It represents the physical features and characteristics of objects in the real world. Spatial data can include information such as coordinates, boundaries, distances, and relationships between objects.
GIS and Spatial Data:
GIS is a powerful tool that allows us to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, and visualize spatial data. It combines hardware, software, and data to create a digital representation of the real world. GIS enables users to view, understand, and interpret data in a geographic context.
Spatial data in GIS is typically represented using points, lines, or polygons. Points represent specific locations, such as the coordinates of a building or a landmark. Lines can represent roads, rivers, or boundaries, while polygons are used to represent areas such as land parcels, administrative boundaries, or land use zones.
Key Points:
- GIS deals with spatial data.
- Spatial data is associated with a specific location or geographical area.
- Spatial data represents the physical features and characteristics of objects in the real world.
- It includes information such as coordinates, boundaries, distances, and relationships between objects.
- GIS allows us to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, and visualize spatial data.
- Spatial data in GIS is represented using points, lines, or polygons.
In conclusion, GIS primarily deals with spatial data, which is essential for various applications such as urban planning, environmental management, transportation, and natural resource analysis. By leveraging spatial data and GIS technology, professionals can make informed decisions and gain valuable insights into the spatial relationships and patterns within their data.
Spatial Data:
Spatial data refers to data that is associated with a specific location or geographical area. It represents the physical features and characteristics of objects in the real world. Spatial data can include information such as coordinates, boundaries, distances, and relationships between objects.
GIS and Spatial Data:
GIS is a powerful tool that allows us to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, and visualize spatial data. It combines hardware, software, and data to create a digital representation of the real world. GIS enables users to view, understand, and interpret data in a geographic context.
Spatial data in GIS is typically represented using points, lines, or polygons. Points represent specific locations, such as the coordinates of a building or a landmark. Lines can represent roads, rivers, or boundaries, while polygons are used to represent areas such as land parcels, administrative boundaries, or land use zones.
Key Points:
- GIS deals with spatial data.
- Spatial data is associated with a specific location or geographical area.
- Spatial data represents the physical features and characteristics of objects in the real world.
- It includes information such as coordinates, boundaries, distances, and relationships between objects.
- GIS allows us to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, and visualize spatial data.
- Spatial data in GIS is represented using points, lines, or polygons.
In conclusion, GIS primarily deals with spatial data, which is essential for various applications such as urban planning, environmental management, transportation, and natural resource analysis. By leveraging spatial data and GIS technology, professionals can make informed decisions and gain valuable insights into the spatial relationships and patterns within their data.
Using two theodolite method, setting out a curve is known as:- a)Linear measurements only
- b)One linear and one angular measurement
- c)Two angular measurements only
- d)One linear and two angular measurements
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Using two theodolite method, setting out a curve is known as:
a)
Linear measurements only
b)
One linear and one angular measurement
c)
Two angular measurements only
d)
One linear and two angular measurements

|
Shail Rane answered |
In a two theodolite method, curves are staked out by angular measurements only. Accuracy attained in this method is quite high. Thus the method is used when higher accuracy is required and when the topography is rough or field condition is difficult.
When the whole circle bearing of a traverse line is between 90° and 180° then:- a)The latitude is positive and departure is negative
- b)The departure is positive and latitude is negative
- c)Both the latitude and departure are positive
- d)Both the latitude and departure are negative
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When the whole circle bearing of a traverse line is between 90° and 180° then:
a)
The latitude is positive and departure is negative
b)
The departure is positive and latitude is negative
c)
Both the latitude and departure are positive
d)
Both the latitude and departure are negative

|
Samarth Ghoshal answered |
When the whole circle bearing of a traverse line is between 90° and 180°, it means that the line is oriented in the southeast direction.
Which one of the following statements is CORRECT?- a)The height of the instrument method is better as compared to the rise and fall method.
- b)The length of a metric used in levelling is 2.0 m.
- c)The rise and fall method for the reduction of levels provided checks on all sights.
- d)The effect of curvature is to cause the object to appear the same as they really are.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is CORRECT?
a)
The height of the instrument method is better as compared to the rise and fall method.
b)
The length of a metric used in levelling is 2.0 m.
c)
The rise and fall method for the reduction of levels provided checks on all sights.
d)
The effect of curvature is to cause the object to appear the same as they really are.

|
Charvi Kaur answered |
The correct statement is option C: The rise and fall method for the reduction of levels provided checks on all sights.
Explanation:
The rise and fall method is a commonly used method in surveying for determining the reduced levels of points. It involves taking readings of the staff at different points and applying corrections to account for errors and variations in the measurements. This method provides checks on all sights, ensuring the accuracy of the levelling process.
Here is a detailed explanation of the rise and fall method for the reduction of levels:
1. Procedure:
- The surveyor sets up the instrument at a known benchmark or reference point.
- The staff is placed at the desired points where readings are to be taken.
- The surveyor looks through the telescope of the instrument and reads the staff at each point.
- The readings are recorded, and corrections are applied to account for various factors.
2. Backsight and Foresight:
- The first reading taken on the staff is called the backsight. It is taken on a staff held at a point of known reduced level.
- The backsight reading helps to establish a starting point for the levelling process.
- The subsequent readings taken on the staff are called foresights. They are taken on staffs held at points whose reduced levels need to be determined.
3. Rise and Fall Calculation:
- After taking the backsight and foresights, the surveyor performs a calculation known as the "rise and fall" to determine the reduced levels of the foresight points.
- The rise and fall is the algebraic sum of the differences between each foresight reading and the preceding backsight reading.
- This calculation ensures that any errors or mistakes in the readings are identified and corrected.
4. Accuracy and Checks:
- The rise and fall method provides checks on all sights, which means that the accuracy of the levelling process can be verified.
- By comparing the calculated reduced levels of the foresight points with their actual known reduced levels (if available), the surveyor can check for any discrepancies or errors.
- This helps to ensure the reliability and accuracy of the levelling results.
In summary, the rise and fall method in levelling provides checks on all sights, allowing for the verification and correction of errors in the readings. This makes it a valuable and widely used method in surveying.
Explanation:
The rise and fall method is a commonly used method in surveying for determining the reduced levels of points. It involves taking readings of the staff at different points and applying corrections to account for errors and variations in the measurements. This method provides checks on all sights, ensuring the accuracy of the levelling process.
Here is a detailed explanation of the rise and fall method for the reduction of levels:
1. Procedure:
- The surveyor sets up the instrument at a known benchmark or reference point.
- The staff is placed at the desired points where readings are to be taken.
- The surveyor looks through the telescope of the instrument and reads the staff at each point.
- The readings are recorded, and corrections are applied to account for various factors.
2. Backsight and Foresight:
- The first reading taken on the staff is called the backsight. It is taken on a staff held at a point of known reduced level.
- The backsight reading helps to establish a starting point for the levelling process.
- The subsequent readings taken on the staff are called foresights. They are taken on staffs held at points whose reduced levels need to be determined.
3. Rise and Fall Calculation:
- After taking the backsight and foresights, the surveyor performs a calculation known as the "rise and fall" to determine the reduced levels of the foresight points.
- The rise and fall is the algebraic sum of the differences between each foresight reading and the preceding backsight reading.
- This calculation ensures that any errors or mistakes in the readings are identified and corrected.
4. Accuracy and Checks:
- The rise and fall method provides checks on all sights, which means that the accuracy of the levelling process can be verified.
- By comparing the calculated reduced levels of the foresight points with their actual known reduced levels (if available), the surveyor can check for any discrepancies or errors.
- This helps to ensure the reliability and accuracy of the levelling results.
In summary, the rise and fall method in levelling provides checks on all sights, allowing for the verification and correction of errors in the readings. This makes it a valuable and widely used method in surveying.
Which of the following is not a temporary adjustment to a compass used for land surveying?- a)Focusing the prism
- b)Making the pivot exactly vertically over the ground station mark
- c)Center of the pivot coincides with geometrical center of graduated ring
- d)Levelling
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a temporary adjustment to a compass used for land surveying?
a)
Focusing the prism
b)
Making the pivot exactly vertically over the ground station mark
c)
Center of the pivot coincides with geometrical center of graduated ring
d)
Levelling

|
Sagarika Patel answered |
Station or temporary adjustments of the prismatic compass
1.centering 2. Levelling 3. Focusing of the prism
The horizontal angle between the true meridian and the survey line measured in a clockwise direction is called as:- a)Magnetic Bearing
- b)True bearing
- c)Grid Meridian
- d)Arbitrary Meridian
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The horizontal angle between the true meridian and the survey line measured in a clockwise direction is called as:
a)
Magnetic Bearing
b)
True bearing
c)
Grid Meridian
d)
Arbitrary Meridian

|
Bhavya Ahuja answered |
True Bearing: It is horizontal distance between the true meridian and the survey line measured in a clockwise direction.
Azimuth: it is the horizontal angle or direction of a compass bearing.
Arbitrary Meridian: Any convenient direction from a survey station to some well defined permanent object is known as arbitrary meridian. This is used for small area survey or to determine the relative directions of small traverse.
Grid Meridian: For survey of country, the true meridian passing through the central place is sometimes taken as a reference meridian for the whole country. Such a meridian is known as Grid meridian.
Chapter doubts & questions for Geomatics Engineering (Surveying) - SSC JE Civil Engineering 2025 Mock Test Series 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Geomatics Engineering (Surveying) - SSC JE Civil Engineering 2025 Mock Test Series in English & Hindi are available as part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
SSC JE Civil Engineering 2025 Mock Test Series
1 videos|1 docs|64 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup











