All Exams >
Biotechnology Engineering (BT) >
Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2026 >
All Questions
All questions of Animal Biology for Biotechnology Engineering (BT) Exam
Secretion of HCl by gastric parietal cells is needed for- a)activation of pancreatic lipase
- b)activation of salivary lipase
- c)activation of pepsinogen to pepsin
- d)activation of intrinsic factor
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Secretion of HCl by gastric parietal cells is needed for
a)
activation of pancreatic lipase
b)
activation of salivary lipase
c)
activation of pepsinogen to pepsin
d)
activation of intrinsic factor

|
Juhi Sen answered |
Pepsinogen is secreted by the gastric chief cells and is activated to pepsin by the low pH of the stomach, created by secretion of HCl by the gastric parietal cells. Lipases are inactivated by low pH.
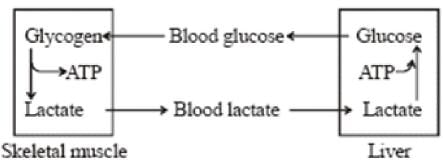
Cori cycle integrates body metabolism to- a)resynthesize glucose from lactate in the liver
- b)oxidize acetyl CoA in the muscle
- c)generate urea in the kidney
- d)generate glucose from acetyl CoA in the liver
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cori cycle integrates body metabolism to
a)
resynthesize glucose from lactate in the liver
b)
oxidize acetyl CoA in the muscle
c)
generate urea in the kidney
d)
generate glucose from acetyl CoA in the liver
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
During heavy, sternous exercise anaerobic metabolism prevails in skeletal muscles to cope with increased energy demand. During this process muscle glycogen is converted into lactate in muscle cells. Cori cycle helps transport this lactate to liver and convert the lactate back to glucose. The cycle is

In a chemical synapse, receptors for neurotransmitters are found on- a)presynaptic membranes
- b)postsynaptic membranes
- c)synaptic vesicles
- d)myelin sheaths enveloping axons
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a chemical synapse, receptors for neurotransmitters are found on
a)
presynaptic membranes
b)
postsynaptic membranes
c)
synaptic vesicles
d)
myelin sheaths enveloping axons

|
Pragati Sharma answered |
A synapse is a junction between 2 cell types. This junction provides functional continuity. The synapse have 2 types:
(i) Electrical synapse : In this, plasma membranes of cells come very close to each other but are not physically connected. This closeness is in range of 2-3 nm. In such regions cells contain barrel shaped channels made of connexin protein units. 6 units of connexin make one such channel. Connexin is an integral membrane protein. The extracellular domains of these proteins from apposing cells are tightly linked but not cells themselves. This channel allows continuous flow of molecule less than 1000 Da in size. Thus, it allows free flow of ions and provides for functional integration of cells. The flow of information by current is faster in this mode. These are also known as gap junction. E.g.: Stimulation of heart muscles for contraction in mammals, stimulation of smooth muscle cells is esophagus and intestine to generate peristaltic wave.
(ii) Chemical synapse : In this, a neuron interacts with another cell. This other cell is target cell of neuron’s actions and could be another neuron, muscle cell or gland cell. When stimulated, the action potential reaches the axon terminal membrane in neuron. This membrane is also called presynaptic membrane. After this, is a gap of 20-50 nm and called synaptic left. On other side is the membrane of target cell and is called post synaptic membrane. The action potential at presynaptic membrane causes release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. It is for this reason, they are called chemical synapse. The neurotransmitters travel across synaptic left and bind to their receptors in postsynaptic membrane.
(i) Electrical synapse : In this, plasma membranes of cells come very close to each other but are not physically connected. This closeness is in range of 2-3 nm. In such regions cells contain barrel shaped channels made of connexin protein units. 6 units of connexin make one such channel. Connexin is an integral membrane protein. The extracellular domains of these proteins from apposing cells are tightly linked but not cells themselves. This channel allows continuous flow of molecule less than 1000 Da in size. Thus, it allows free flow of ions and provides for functional integration of cells. The flow of information by current is faster in this mode. These are also known as gap junction. E.g.: Stimulation of heart muscles for contraction in mammals, stimulation of smooth muscle cells is esophagus and intestine to generate peristaltic wave.
(ii) Chemical synapse : In this, a neuron interacts with another cell. This other cell is target cell of neuron’s actions and could be another neuron, muscle cell or gland cell. When stimulated, the action potential reaches the axon terminal membrane in neuron. This membrane is also called presynaptic membrane. After this, is a gap of 20-50 nm and called synaptic left. On other side is the membrane of target cell and is called post synaptic membrane. The action potential at presynaptic membrane causes release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. It is for this reason, they are called chemical synapse. The neurotransmitters travel across synaptic left and bind to their receptors in postsynaptic membrane.
True statements about macula lutea are- a)It is also called fovea centralis
- b)It is point of sharpest vision
- c)It has high concentration of rod cells
- d)It has no rod cells but high concentration of cone cells
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
True statements about macula lutea are
a)
It is also called fovea centralis
b)
It is point of sharpest vision
c)
It has high concentration of rod cells
d)
It has no rod cells but high concentration of cone cells

|
Rutuja Choudhary answered |
Fovea centralis : At the posterior pole of eye there is a yellowish pigmented spot, macula lutea. In this region rod cells are completely absent and cone cells are densely packed. There are no cells or blood vessels lying over the photoreceptors. It is the point of greatest vision or visual activity. It is called fovea centralis. This region of greatest visual sharpness is highly developed in humans.
Identify the hormone secreted by the pituitary gland that causes the smooth muscle of the uterus to contract during parturition in mammals- a)Vasopressin
- b)Oxytocin
- c)Prolactin
- d)Gonadotropins
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the hormone secreted by the pituitary gland that causes the smooth muscle of the uterus to contract during parturition in mammals
a)
Vasopressin
b)
Oxytocin
c)
Prolactin
d)
Gonadotropins

|
Niti Mukherjee answered |
Pituitary gland is located at the base of brain just below hypothalanus. It has two parts viz. anterior pituitary and posterior pituitary. In posterior pituitary, many neurons of hypothalanus end. The endings are axonal terminals of neurons that originate in hypothalamus. They produce two peptide hormones called vasopressin and oxytocin. These move down into posterior pituitary via axonal endings and stored in secretory vesicles for release. It is the oxytocin hormone released from posterior pituitary that contracts the smooth muscle cells in uterus during parturition (child birth) in mammals. It also contracts mammary glands during lactation.
Embryonic stem cells are derived from- a)Undifferentiated inner cell mass of embryo
- b)Differentiated inner cell mass of embryo
- c)Undifferentiated trophoblast cells
- d)Differentiated trophoblast cells
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Embryonic stem cells are derived from
a)
Undifferentiated inner cell mass of embryo
b)
Differentiated inner cell mass of embryo
c)
Undifferentiated trophoblast cells
d)
Differentiated trophoblast cells

|
Ameya Reddy answered |
Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent and derived from inner mass of blastocyst which is undifferentiated.
In a bicoid mutant Drosophila ................... will form ?- a)2 head on either side
- b)2 tail on either side
- c)Head-Tail-Tail
- d)Tail-Head-Tail
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a bicoid mutant Drosophila ................... will form ?
a)
2 head on either side
b)
2 tail on either side
c)
Head-Tail-Tail
d)
Tail-Head-Tail

|
Sagarika Yadav answered |
Caudal gene shows its effect in anterior side also as bicoid won’t be able to inhibit its transcription. Hence, tail will form at both the sides.
Which of the floral whorls is affected in agamous (ag) mutants ?- a)Sepals and petals
- b)Petals and stamens
- c)Stamens and carpels
- d)Sepals and carpels
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the floral whorls is affected in agamous (ag) mutants ?
a)
Sepals and petals
b)
Petals and stamens
c)
Stamens and carpels
d)
Sepals and carpels

|
Anshul Mehra answered |
Agamous is present at the B and its mutation effect both petals and stamens.
In Hydra, if any part is lost remaining portion re-patterns itself and gives rise to complete organism. Such a pattern of development is termed as- a)Morphallaxis
- b)Epimorphosis
- c)Regeneration
- d)Healing
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In Hydra, if any part is lost remaining portion re-patterns itself and gives rise to complete organism. Such a pattern of development is termed as
a)
Morphallaxis
b)
Epimorphosis
c)
Regeneration
d)
Healing

|
Nilotpal Basu answered |
This type of regeneration is called as morphallaxis.
The accessory inspiratory muscles are- a)sternocleidomastoid
- b)Scalene
- c)Pectoralis major
- d)Ciliary muscles
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
The accessory inspiratory muscles are
a)
sternocleidomastoid
b)
Scalene
c)
Pectoralis major
d)
Ciliary muscles

|
Srishti Khanna answered |
We have the ability to increase the strength of inspiration and expiration with the help of additional accessory muscles of respiration. This is seen during labored breathing. Additional ‘accessory muscles of respiration’ are typically only used under conditions of high metabolic demand (e.g. exercise) or respiratory dysfunction (e.g. an asthma attack). The accessory inspiratory muscles are the sternocleidomastoid, the scalene muscles, the pectoralis major and minor etc.
Primary spermatocyte undergoes 2nd meiotic divisions to produce how many haploid spermatids _______ [Answer in integer]
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
Primary spermatocyte undergoes 2nd meiotic divisions to produce how many haploid spermatids _______ [Answer in integer]

|
Aryan Gupta answered |
After second meiotic division the primary spermatocyte forms 4 haploid spermatids.
Fast block to polyspermy in Sea Urchin is- a)accompanied by an exocytosis of cortical granules
- b)accompanied by an electric change in the egg cell membrane
- c)accompanied by release of 20 hydrolytic enzymes simultaneously
- d)accompanied by the formation of non-permeable jelly layer
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Fast block to polyspermy in Sea Urchin is
a)
accompanied by an exocytosis of cortical granules
b)
accompanied by an electric change in the egg cell membrane
c)
accompanied by release of 20 hydrolytic enzymes simultaneously
d)
accompanied by the formation of non-permeable jelly layer

|
Partho Gupta answered |
Fast block to polyspermy in Sea Urchin:
The fast block to polyspermy is a mechanism that prevents multiple sperm from fertilizing an egg. In sea urchins, this process is accompanied by the exocytosis of cortical granules.
Exocytosis of cortical granules:
- Sea urchin eggs contain cortical granules in their cytoplasm, located just beneath the plasma membrane.
- When a sperm binds to the egg's jelly coat, it triggers a series of events that lead to the exocytosis of cortical granules.
- Exocytosis is the process by which the granules fuse with the egg's plasma membrane and release their contents into the extracellular space.
- The cortical granules contain enzymes and other molecules that are released into the space between the egg and the jelly coat.
Function of cortical granules:
- The released enzymes and molecules cause several changes that block polyspermy.
- The first change is the formation of a fertilization envelope, which is a non-permeable layer between the egg and the jelly coat.
- The fertilization envelope physically prevents other sperm from reaching the egg.
- Additionally, the released enzymes modify the jelly coat, making it less attractive to sperm and reducing their ability to bind to the egg.
Significance of fast block to polyspermy:
- Polyspermy, the fertilization of an egg by multiple sperm, can be detrimental to the development of an embryo.
- In sea urchins, polyspermy can lead to abnormal development and death of the embryo.
- The fast block to polyspermy ensures that only a single sperm can fertilize the egg, thereby preventing polyspermy and promoting normal embryonic development.
Conclusion:
The fast block to polyspermy in sea urchins is accompanied by the exocytosis of cortical granules. The release of enzymes and molecules from the cortical granules leads to the formation of a fertilization envelope and modification of the jelly coat, preventing multiple sperm from fertilizing the egg. This mechanism ensures the successful fertilization of a single sperm and promotes normal embryonic development.
The fast block to polyspermy is a mechanism that prevents multiple sperm from fertilizing an egg. In sea urchins, this process is accompanied by the exocytosis of cortical granules.
Exocytosis of cortical granules:
- Sea urchin eggs contain cortical granules in their cytoplasm, located just beneath the plasma membrane.
- When a sperm binds to the egg's jelly coat, it triggers a series of events that lead to the exocytosis of cortical granules.
- Exocytosis is the process by which the granules fuse with the egg's plasma membrane and release their contents into the extracellular space.
- The cortical granules contain enzymes and other molecules that are released into the space between the egg and the jelly coat.
Function of cortical granules:
- The released enzymes and molecules cause several changes that block polyspermy.
- The first change is the formation of a fertilization envelope, which is a non-permeable layer between the egg and the jelly coat.
- The fertilization envelope physically prevents other sperm from reaching the egg.
- Additionally, the released enzymes modify the jelly coat, making it less attractive to sperm and reducing their ability to bind to the egg.
Significance of fast block to polyspermy:
- Polyspermy, the fertilization of an egg by multiple sperm, can be detrimental to the development of an embryo.
- In sea urchins, polyspermy can lead to abnormal development and death of the embryo.
- The fast block to polyspermy ensures that only a single sperm can fertilize the egg, thereby preventing polyspermy and promoting normal embryonic development.
Conclusion:
The fast block to polyspermy in sea urchins is accompanied by the exocytosis of cortical granules. The release of enzymes and molecules from the cortical granules leads to the formation of a fertilization envelope and modification of the jelly coat, preventing multiple sperm from fertilizing the egg. This mechanism ensures the successful fertilization of a single sperm and promotes normal embryonic development.
In case of chick development, primary organizer is called- a)Hensen’s node
- b)Dorsal lip of blastopore
- c)Nieuwkoop centre
- d)Primitive groove
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In case of chick development, primary organizer is called
a)
Hensen’s node
b)
Dorsal lip of blastopore
c)
Nieuwkoop centre
d)
Primitive groove

|
Anisha Pillai answered |
In chick development, primary organizer is called Hensen’s node which forms the fate map further.
If a sperm cell contains 8 chromosomes, it comes from an animal that has ______________ chromosomes. [Answer in integer]
Correct answer is '16'. Can you explain this answer?
If a sperm cell contains 8 chromosomes, it comes from an animal that has ______________ chromosomes. [Answer in integer]
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
Both the gametes (either sperm or egg) from each parent should contain half the total number of chromosomes for that species.
Which of the following maternal effect genes regulate anterior axis development?- a)Bicoid
- b)Nanos
- c)Caudal
- d)Hunchback
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following maternal effect genes regulate anterior axis development?
a)
Bicoid
b)
Nanos
c)
Caudal
d)
Hunchback

|
Juhi Sen answered |
There are around 50 maternal genes which are involved in anterior-posterior axis specification, but out of the 50 genes, 4 genes are particularly important because their product form gradient along the axis and play important role.


As mammalian zygotes divide, all cells are totipotent upto the ________________ celled stage. [Answer in integer]
Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?
As mammalian zygotes divide, all cells are totipotent upto the ________________ celled stage. [Answer in integer]

|
Yashvi Roy answered |
As embryo development progresses to the 8 cell stage and beyond depending on the species, the individual blastomeres that comprise the embryo gradually lose their totipotency.
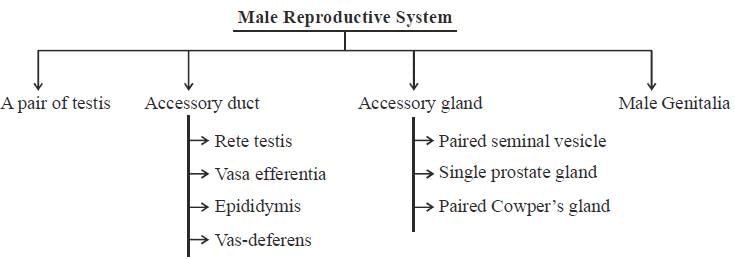
With respect to male reproductive system in humans, find out the correct statements.- a)Accessory gland includes single seminal vesicle, paired prostate gland, paired Cowper’s gland
- b)Accessory gland includes paired seminal vesicle, single prostate gland and paired Cowper’s gland
- c)Accessory duct includes only Epididymis
- d)Accessory duct includes Rete testis, Vasa efferentia, Epididymis and Vas-deferens
Correct answer is option 'B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
With respect to male reproductive system in humans, find out the correct statements.
a)
Accessory gland includes single seminal vesicle, paired prostate gland, paired Cowper’s gland
b)
Accessory gland includes paired seminal vesicle, single prostate gland and paired Cowper’s gland
c)
Accessory duct includes only Epididymis
d)
Accessory duct includes Rete testis, Vasa efferentia, Epididymis and Vas-deferens
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
The only cell that can give rise to a complete new organism is- a)Pluripotent
- b)Multipotent
- c)Totipotent
- d)Corticopotent
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The only cell that can give rise to a complete new organism is
a)
Pluripotent
b)
Multipotent
c)
Totipotent
d)
Corticopotent

|
Sanaya Kulkarni answered |
The only cell that can give rise to a complete new organism is the fertilized egg (zygote) and this is described as totipotent
Which one of the following hormones shows photoperiodicity?- a)Thyroxine
- b)Melatonin
- c)Cortisol
- d)Relaxin
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following hormones shows photoperiodicity?
a)
Thyroxine
b)
Melatonin
c)
Cortisol
d)
Relaxin

|
Harshitha Sharma answered |
In amniote animals, pineal and parietal bodies regulate photoperiodism. Melatonin secreted pineal gland has an anti-gonadotrophic effect. Its secretion is in a circadian rhythm.

Note: Amniote is any land vertebrate which possesses an amnion, chorion and allantois. It includes reptiles, birds and mammals.

Note: Amniote is any land vertebrate which possesses an amnion, chorion and allantois. It includes reptiles, birds and mammals.
Concentration of bone morphogenetic protein is higher at- a)dorsal side
- b)ventral side
- c)anterior side
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Concentration of bone morphogenetic protein is higher at
a)
dorsal side
b)
ventral side
c)
anterior side
d)
none of these

|
Bhavana Dasgupta answered |
Concentration of BMP-4 is same at all the sides.
Function of Noggin gene- a)Help in formation of neural ectoderm
- b)Help in formation of skin endoderm
- c)Acts as antagonic for BMP proteins
- d)Acts as agonist for BMP proteins
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Function of Noggin gene
a)
Help in formation of neural ectoderm
b)
Help in formation of skin endoderm
c)
Acts as antagonic for BMP proteins
d)
Acts as agonist for BMP proteins

|
Sarthak Chavan answered |
Noggin is an antagonist of BMP and heeps in neural ectoderm not in skin ectoderm.
Find out the correctly matched options- a)Radial cleavage - Amphioxus
- b)Spiral cleavage - Annelids
- c)Rotational cleavage - Nematodes
- d)Bilateral cleavage - Tunicates
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find out the correctly matched options
a)
Radial cleavage - Amphioxus
b)
Spiral cleavage - Annelids
c)
Rotational cleavage - Nematodes
d)
Bilateral cleavage - Tunicates

|
Niharika Choudhary answered |
Holoblastic cleavage:
1) Radial cleavage - Ampliioxus. Echinodenns
2) Spiral cleavage - Annelids. Molluscs
3) Bilateral cleavage - Tunicates
4) Rotational cleavage - Mammals. Nematodes
2) Spiral cleavage - Annelids. Molluscs
3) Bilateral cleavage - Tunicates
4) Rotational cleavage - Mammals. Nematodes
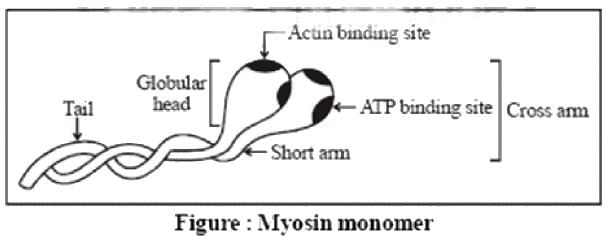
Correct facts for thick filaments are- a)It is made up of monomers called meromyosin
- b)HMM has a globular head that has ATPase activity.
- c)HMM has a globular head with no ATPase activity
- d)LMM makes the head region.
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
Correct facts for thick filaments are
a)
It is made up of monomers called meromyosin
b)
HMM has a globular head that has ATPase activity.
c)
HMM has a globular head with no ATPase activity
d)
LMM makes the head region.

|
Sahana Sharma answered |
Thick filament : It is made from myosin protein and extends from one end of A-band to other. Myosin is oligomeric and its monomers are called meromyosin. Each meromyosin has 2 parts. Heavy meromyosin (HMM) making its globular head with a short arm. Its head can bind and hydrolyze ATP, thus, is said to have ATPase activity. Light meromyosin (LMM) making the tail region.

Hormones that act on cells near the point of their synthesis and not transported through blood circulation are- a)prostaglandins and thromboxane
- b)estradiol and coitisol
- c)prednisolone and prednisone
- d)thyroxine and glucagon
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Hormones that act on cells near the point of their synthesis and not transported through blood circulation are
a)
prostaglandins and thromboxane
b)
estradiol and coitisol
c)
prednisolone and prednisone
d)
thyroxine and glucagon

|
Akshat Saini answered |
Hormones that act near their site of production and secretion are called as paracrine hormones. They are different from endocrine hormones as Latter are transported through out body by circulatory system as they are produced at a single site. The paracrine hormones are produced at many sites in body and act in their vicinity than being transported to their site of action. E.g. Prostaglandins and thromobxanes.
Correct option is (a)
Note : Prednisolone and prednisone are steriod drugs used for many different treatments. Hormones in options (b) and (d) are endocrine hormones and transported to their site of action by circulatory system.
Correct option is (a)
Note : Prednisolone and prednisone are steriod drugs used for many different treatments. Hormones in options (b) and (d) are endocrine hormones and transported to their site of action by circulatory system.
Nuclear determinants are also called as- a)Inducers
- b)Organizers
- c)Morphogens
- d)Maternal genes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Nuclear determinants are also called as
a)
Inducers
b)
Organizers
c)
Morphogens
d)
Maternal genes

|
Priya Saha answered |
Nuclear determinants are called morphogens which determine morphogenesis.
In a 35 day menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs on which day _________.
Correct answer is '21'. Can you explain this answer?
In a 35 day menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs on which day _________.

|
Rashi Choudhury answered |
Menses occurs 14 days after ovulation, regardless of the cycle length. Therefore in a 35 days menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs on day 21.
Maternal effect genes are :- a)exclusively contributed by mother
- b)defines polarity of egg
- c)mutation in such genes are lethal
- d)gene product of these genes are work as transcription factor for further development
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Maternal effect genes are :
a)
exclusively contributed by mother
b)
defines polarity of egg
c)
mutation in such genes are lethal
d)
gene product of these genes are work as transcription factor for further development

|
Lekshmi Deshpande answered |
Maternal effect genes have all the characteristic present in options.
Electrical synapses are- a)Found everywhere in body
- b)Release neurotransmitters
- c)Found in cardiac muscles
- d)Made of connexin proteins
Correct answer is option 'C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Electrical synapses are
a)
Found everywhere in body
b)
Release neurotransmitters
c)
Found in cardiac muscles
d)
Made of connexin proteins

|
Aashna Shah answered |
Electrical synapse : In this, adjacent cells are connected by direct open fluid channels called gap junctions. These are made up of connexin protein. These gap junctions are areas of low electrical resistance so that impulses can be regenerated from one cell to the next. The impulse is conducted bidirectionally in this synapse. These synapses are used to transmit action potential among cardiac muscle fibers and smooth muscle fibers. However, these are scarce in CNS.
Which one of the following is NOT a neurotransmitter?- a)Glutamine
- b)Glutamate
- c)Glycine
- d)Acetylcholine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is NOT a neurotransmitter?
a)
Glutamine
b)
Glutamate
c)
Glycine
d)
Acetylcholine

|
Rishabh Mehta answered |
A neurotransmitter is an endogenous chemical that enables neurotransmission. They transmit signals across target neuron/muscle/gland cell. Chemically, they are of two types :
1. Small molecule transmitters : These are rapidly acting and cause most acute response of nervous system by diffusing across synaptic cleft. Their examples are : Acetylcholine, glutamate (glutamic acid), glycine, gamma-amino butyric acid (GABA), epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin and histamine. Glycine and GABA are most common inhibitory neurotranomitters.
2. Neuropeptides : These cause more prolonged action in nervous system such as long term changes in number and size of synapses. E.g. Enkephlins, endorphins etc. Since glutamine is not found in synapses. It is not a neurotransmitter.
1. Small molecule transmitters : These are rapidly acting and cause most acute response of nervous system by diffusing across synaptic cleft. Their examples are : Acetylcholine, glutamate (glutamic acid), glycine, gamma-amino butyric acid (GABA), epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin and histamine. Glycine and GABA are most common inhibitory neurotranomitters.
2. Neuropeptides : These cause more prolonged action in nervous system such as long term changes in number and size of synapses. E.g. Enkephlins, endorphins etc. Since glutamine is not found in synapses. It is not a neurotransmitter.
A 50 year old man has a mean arterial blood pressure of 130 mmHg, a heart rate of 78 beats/min, a right arterial pressure of 2mmHg and a cardiac output of 3.5 L/min. The total peripheral vascular resistance (mm Hg/L/min) in this man is ______________
Correct answer is '37'. Can you explain this answer?
A 50 year old man has a mean arterial blood pressure of 130 mmHg, a heart rate of 78 beats/min, a right arterial pressure of 2mmHg and a cardiac output of 3.5 L/min. The total peripheral vascular resistance (mm Hg/L/min) in this man is ______________

|
Shail Ghoshal answered |
Mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) is a measure of the average pressure in the arteries during one cardiac cycle. It is calculated using the formula: MAP = diastolic pressure + 1/3 (systolic pressure - diastolic pressure). In this case, the MAP is given as 130 mmHg.
Heart rate refers to the number of times the heart beats per minute. In this case, the heart rate is given as 78 beats per minute.
Right arterial pressure (RAP) is the pressure in the right atrium of the heart. In this case, the RAP is given as 2 mmHg.
Cardiac output (CO) is the volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute. It is calculated using the formula: CO = heart rate × stroke volume. In this case, the CO is given as 3.5 L/min.
Total peripheral vascular resistance (TPVR) is a measure of the resistance to blood flow in the peripheral vasculature. It is calculated using the formula: TPVR = (MAP - RAP) / CO.
Calculating Total Peripheral Vascular Resistance (TPVR):
- MAP is given as 130 mmHg
- RAP is given as 2 mmHg
- CO is given as 3.5 L/min
TPVR = (130 - 2) / 3.5
TPVR = 128 / 3.5
TPVR ≈ 36.57 ≈ 37 mm Hg/L/min
Therefore, the total peripheral vascular resistance in this man is approximately 37 mm Hg/L/min.
Heart rate refers to the number of times the heart beats per minute. In this case, the heart rate is given as 78 beats per minute.
Right arterial pressure (RAP) is the pressure in the right atrium of the heart. In this case, the RAP is given as 2 mmHg.
Cardiac output (CO) is the volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute. It is calculated using the formula: CO = heart rate × stroke volume. In this case, the CO is given as 3.5 L/min.
Total peripheral vascular resistance (TPVR) is a measure of the resistance to blood flow in the peripheral vasculature. It is calculated using the formula: TPVR = (MAP - RAP) / CO.
Calculating Total Peripheral Vascular Resistance (TPVR):
- MAP is given as 130 mmHg
- RAP is given as 2 mmHg
- CO is given as 3.5 L/min
TPVR = (130 - 2) / 3.5
TPVR = 128 / 3.5
TPVR ≈ 36.57 ≈ 37 mm Hg/L/min
Therefore, the total peripheral vascular resistance in this man is approximately 37 mm Hg/L/min.
In developmental biology, morula is ________cell stage. [Answer in integer]
Correct answer is '16'. Can you explain this answer?
In developmental biology, morula is ________cell stage. [Answer in integer]

|
Maitri Sen answered |
Morula is 16 celled stage.
Which of the following ligament(s) is/are attached to ovary?
P) Ovarian ligaments
Q) Suspensory ligaments R. broad ligaments- a)only P
- b)only P and Q
- c)only P and R
- d)P, Q and R
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following ligament(s) is/are attached to ovary?
P) Ovarian ligaments
Q) Suspensory ligaments R. broad ligaments
P) Ovarian ligaments
Q) Suspensory ligaments R. broad ligaments
a)
only P
b)
only P and Q
c)
only P and R
d)
P, Q and R

|
Rishabh Mehta answered |
Ovary in humans is a paired organ in females. It is located one on each side of uterus in pelvic cavity. It is supported by ligaments in following manner:
Ovarian ligament : It connects ovary with uterus.
Suspensory ligament : It connects ovary to body wall.
Broad ligament : It connects uterus sides with wall and floor of pelvis. In this process, it also covers ovary. So, all three ligaments are attached to ovary.
Ovarian ligament : It connects ovary with uterus.
Suspensory ligament : It connects ovary to body wall.
Broad ligament : It connects uterus sides with wall and floor of pelvis. In this process, it also covers ovary. So, all three ligaments are attached to ovary.
A class of spermicides (used for contraception) inhibits the flagellar motion of the sperm thereby preventing it from swimming towards the egg. This is achieved by- a)inhibiting the motor protein dynein
- b)inhibiting the motor protein kinesin
- c)disrupting the microfilaments
- d)depolymerizing microtubules
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A class of spermicides (used for contraception) inhibits the flagellar motion of the sperm thereby preventing it from swimming towards the egg. This is achieved by
a)
inhibiting the motor protein dynein
b)
inhibiting the motor protein kinesin
c)
disrupting the microfilaments
d)
depolymerizing microtubules

|
Hrishikesh Verma answered |
Gossypol is a polyphenolic pigment isolated from cotton plant. It was used as male oral contraceptive in China. Its use has been stopped due to high toxicity. It made sperms immobile by inhibiting the motor protein dynein. Dynein is an ATPase found associated with microtubules in sperm flagella. It hydrolyzes ATP, whose energy is used for sperm motility. If dynein ATPase is inhibited, sperm is immobile and can not swim to ova for fertilization. This leads to contraceptive effects.
Choose the combination of statements that are correct for the cerebrum of the human brain
P. It is the largest part of brain
Q. Controls the pituitary hormone secretion
R. Involved in coordinating the movements of the body
S. Receives and processes the sensory information- a)PQ
- b)QR
- c)PS
- d)QS
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the combination of statements that are correct for the cerebrum of the human brain
P. It is the largest part of brain
Q. Controls the pituitary hormone secretion
R. Involved in coordinating the movements of the body
S. Receives and processes the sensory information
P. It is the largest part of brain
Q. Controls the pituitary hormone secretion
R. Involved in coordinating the movements of the body
S. Receives and processes the sensory information
a)
PQ
b)
QR
c)
PS
d)
QS

|
Jaya Sen answered |
Brain has three parts viz. forebrain, mid brain and hind brain.
Cerebrum : It is part of forebrain and largest part of brain. It is divided into two halves called cerebral hemispheres. These halves are connected by a tract of nerve fibers called corpus callosum. It contains major areas seasory and processing.
Hypothalamus : It is part of forebrain and found below thalamus, hence its name. It produces hypothalamic hormones that control secretion of pituitary gland hormones. It also controls body temperature and urge for eating and drinking.
Cerebellum : It is found in hind brain. It is major part involved in coordinating the movements of body. Thus, statements P and S are correct for cerebrum.
Cerebrum : It is part of forebrain and largest part of brain. It is divided into two halves called cerebral hemispheres. These halves are connected by a tract of nerve fibers called corpus callosum. It contains major areas seasory and processing.
Hypothalamus : It is part of forebrain and found below thalamus, hence its name. It produces hypothalamic hormones that control secretion of pituitary gland hormones. It also controls body temperature and urge for eating and drinking.
Cerebellum : It is found in hind brain. It is major part involved in coordinating the movements of body. Thus, statements P and S are correct for cerebrum.
With respect to development of any organism autonomous specification would result in which type of development?- a)Regulative
- b)Mosaic
- c)Syncytial
- d)Definitive
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
With respect to development of any organism autonomous specification would result in which type of development?
a)
Regulative
b)
Mosaic
c)
Syncytial
d)
Definitive

|
Vandana Chopra answered |
During development, each cell is said to undergo autonomous specification i.e., if removed from the embryo, each cell develops according to its intrinsic instruction. It is also known as mosaic development.
In amphibians, at puberty, nuclear membrane of primary oocyte breaks down by the influence of- a)Progestrone
- b)Estrogen
- c)Both
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In amphibians, at puberty, nuclear membrane of primary oocyte breaks down by the influence of
a)
Progestrone
b)
Estrogen
c)
Both
d)
None

|
Rashi Choudhury answered |
Progesterone breaks the nuclear membrane of primary oocyte.
Supporting cells in CNS include- a)Oligodendrocytes
- b)Microglia
- c)Astrocytes
- d)Ependymal cells
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Supporting cells in CNS include
a)
Oligodendrocytes
b)
Microglia
c)
Astrocytes
d)
Ependymal cells

|
Sahil Kapoor answered |
Supporting cells in CNS : There are 4 types :
• Oligodendrocytes that form myelin sheath around axons of the CNS, producing white matter.
• Microglia that wander through the CNS and phagocytose foreign and degenerated material.
• Astrocytes that cover capil laries of the CNS and induce the blood brain barrier. Thus, these help regulate the external milieu of neurons in CNS.
• Ependymal cells that line the ventricles of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord. Recent research has shown that ependymal cells can function as neural stem cells, i.e. they can divide to become new nervous and neuroglial cells. All these cells are together called as neuroglial cells.
• Oligodendrocytes that form myelin sheath around axons of the CNS, producing white matter.
• Microglia that wander through the CNS and phagocytose foreign and degenerated material.
• Astrocytes that cover capil laries of the CNS and induce the blood brain barrier. Thus, these help regulate the external milieu of neurons in CNS.
• Ependymal cells that line the ventricles of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord. Recent research has shown that ependymal cells can function as neural stem cells, i.e. they can divide to become new nervous and neuroglial cells. All these cells are together called as neuroglial cells.
Rolling of sheet of cells over other cells during gastrulation is called as :- a)Involution
- b)Ingression
- c)Epiboly
- d)Invagination
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Rolling of sheet of cells over other cells during gastrulation is called as :
a)
Involution
b)
Ingression
c)
Epiboly
d)
Invagination

|
Mihir Singh answered |
Epiboly in gastrulation movement which is characteristic by rolling of sheet of cells leading to its thinning and spreading of cell layers.
Choose the correct match from A, B, C and D

- a)
- b)
- c)
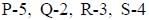
- d)
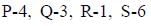
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct match from A, B, C and D


a)
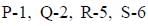
b)
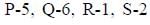
c)
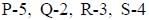
d)
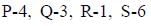

|
Hrishikesh Verma answered |

Water reabsorption is promoted by vasopressin hormone from posterior pituitary.
Thyroid hormone synthesis is initiated by thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) secreted by anterior pituitary.
Chapter doubts & questions for Animal Biology - Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2026 2025 is part of Biotechnology Engineering (BT) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Biotechnology Engineering (BT) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Biotechnology Engineering (BT) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Animal Biology - Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2026 in English & Hindi are available as part of Biotechnology Engineering (BT) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Biotechnology Engineering (BT) Exam by signing up for free.
Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2026
7 docs|34 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily