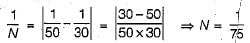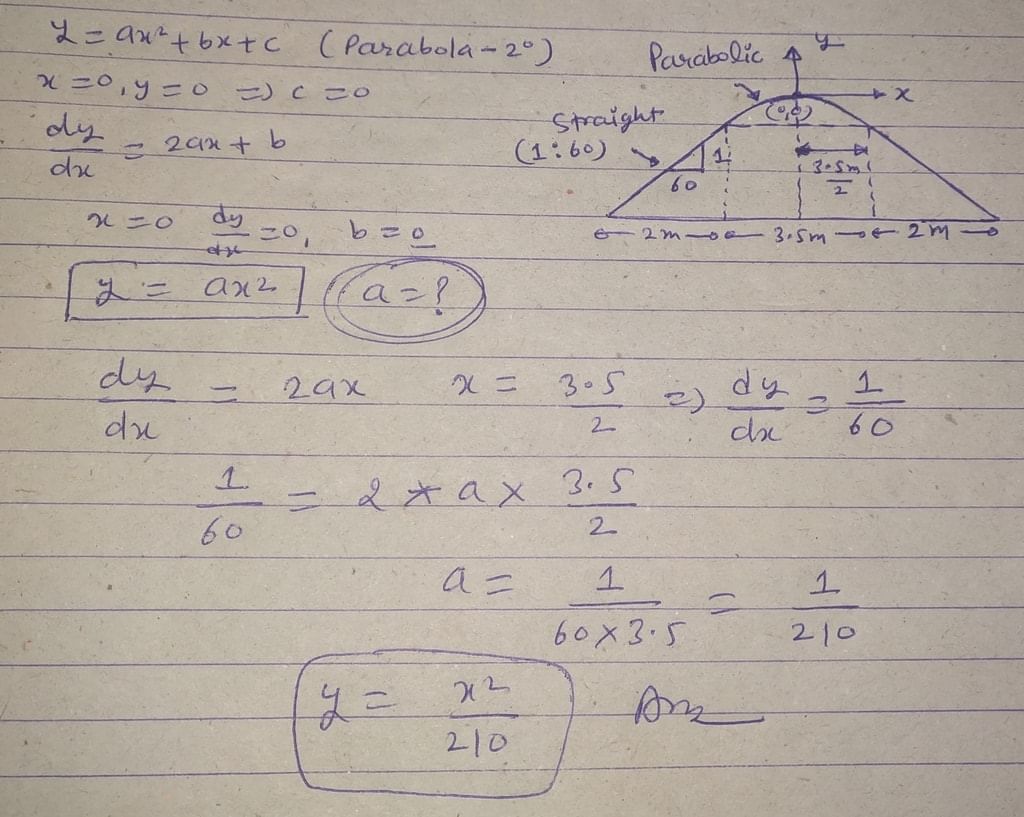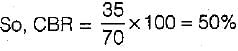All Exams >
Civil Engineering (CE) >
Topicwise Question Bank for Civil Engineering >
All Questions
All questions of Transportation Engineering for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam
An Excel workbook is a collection of:- a) Worksheet
- b) Cells
- c) Charts
- d) Worksheets
- e) None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An Excel workbook is a collection of:
a)
Worksheet
b)
Cells
c)
Charts
d)
Worksheets
e)
None of these
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
A workbook is a collection of one or more spreadsheets and charts in a single file.
Consider
1. Creation of Central Road Fund
2. National Highway Act
3. Formation of Indian Road Congress
4. Creation of Highway Research BoardThe correct chronological order of these events is- a)4, 3, 2, 1
- b)2, 1, 3, 4
- c)1 ,3 , 2 , 4
- d)2, 3, 1 ,4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider
1. Creation of Central Road Fund
2. National Highway Act
3. Formation of Indian Road Congress
4. Creation of Highway Research Board
1. Creation of Central Road Fund
2. National Highway Act
3. Formation of Indian Road Congress
4. Creation of Highway Research Board
The correct chronological order of these events is
a)
4, 3, 2, 1
b)
2, 1, 3, 4
c)
1 ,3 , 2 , 4
d)
2, 3, 1 ,4

|
Engineers Adda answered |
Creation of Central Road Fund -1929
National Highway Act -1956
Formation of Indian Road Congress - 1934
Creation of Highway Research Board - 1973
National Highway Act -1956
Formation of Indian Road Congress - 1934
Creation of Highway Research Board - 1973
Bitumen is derived from
- a)Destructive distillation of coal tar
- b)Destructive distillation of petroleum
- c)Fractional distillation of petroleum
- d)Naturally occurring ores
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Bitumen is derived from
a)
Destructive distillation of coal tar
b)
Destructive distillation of petroleum
c)
Fractional distillation of petroleum
d)
Naturally occurring ores

|
Ankit Joshi answered |
Bituminous binders used in pavement construction works include both bitumen and tar. Bitumen is a petroleum product obtained by the distillation of petroleum crude where as road tar is obtained by the destructive distillation of coal or wood.
Cant deficiency occurs when a vehicle travels around a curve at- a)equilibrium speed
- b)speeds higher than equilibrium speed
- c)speeds lower than equilibrium speed
- d)booked speed
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cant deficiency occurs when a vehicle travels around a curve at
a)
equilibrium speed
b)
speeds higher than equilibrium speed
c)
speeds lower than equilibrium speed
d)
booked speed
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Cant deficiency is the difference, between the equilibrium cant necessary for maximum permissible speed on a curve and actual cant provided. So if a vehicle travels at a speed higher than the equilibrium speed, cant deficiency occurs whereas if a vehicle travels at a speed lower than equilibrium speed, cant excess occurs.
Critical load position in a rigid pavement design is taken as- a)interior loading
- b)edge loading
- c)corner loading
- d)interior, edge and corner loading
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Critical load position in a rigid pavement design is taken as
a)
interior loading
b)
edge loading
c)
corner loading
d)
interior, edge and corner loading

|
Ashish Chakraborty answered |
For different combinations such as day/night, summer/winter, vehicle load, different combinations need to be considered on either of interior, edge or corner loading.
In the design of highway expansion and contraction joints should respectively be provided at- a)50 m and 32 m
- b)50 m and 10 m
- c)25 m and 10 m
- d)25 m and 32 m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the design of highway expansion and contraction joints should respectively be provided at
a)
50 m and 32 m
b)
50 m and 10 m
c)
25 m and 10 m
d)
25 m and 32 m

|
Rajat Patel answered |
Highway Expansion and Contraction Joints
Expansion and contraction joints are designed to allow for the thermal expansion and contraction of concrete pavement. These joints are important in preventing cracks and other types of damage to the pavement due to temperature changes. In the design of highway expansion and contraction joints, the spacing between joints is an important consideration.
Spacing of Joints
The spacing of expansion and contraction joints is determined by a number of factors, including the type of pavement, the expected temperature changes, and the traffic volume. In general, the spacing of joints is greater for concrete pavements than for asphalt pavements. The following are the recommended spacing of joints for highway expansion and contraction joints:
- Expansion joints should be provided every 50 meters (164 feet).
- Contraction joints should be provided every 10 meters (33 feet).
Reasons for Recommended Spacing
The recommended spacing of joints is based on a number of factors. The following are some reasons for the recommended spacing of joints:
- Expansion joints are provided at greater intervals because they are designed to accommodate greater movements due to temperature changes. This is because the concrete pavement expands more than it contracts due to temperature changes.
- Contraction joints are provided at smaller intervals because they are designed to accommodate smaller movements due to temperature changes. This is because the concrete pavement contracts more than it expands due to temperature changes.
- The spacing of joints is also affected by traffic volume. High traffic volumes can cause greater stresses on the pavement, which can lead to greater movement due to temperature changes. As a result, the spacing of joints may need to be reduced in areas with high traffic volumes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the recommended spacing of highway expansion and contraction joints is 50 meters for expansion joints and 10 meters for contraction joints. These spacings are based on a number of factors, including the type of pavement, the expected temperature changes, and the traffic volume. The spacing of joints is important in preventing cracks and other types of damage to the pavement due to temperature changes.
Expansion and contraction joints are designed to allow for the thermal expansion and contraction of concrete pavement. These joints are important in preventing cracks and other types of damage to the pavement due to temperature changes. In the design of highway expansion and contraction joints, the spacing between joints is an important consideration.
Spacing of Joints
The spacing of expansion and contraction joints is determined by a number of factors, including the type of pavement, the expected temperature changes, and the traffic volume. In general, the spacing of joints is greater for concrete pavements than for asphalt pavements. The following are the recommended spacing of joints for highway expansion and contraction joints:
- Expansion joints should be provided every 50 meters (164 feet).
- Contraction joints should be provided every 10 meters (33 feet).
Reasons for Recommended Spacing
The recommended spacing of joints is based on a number of factors. The following are some reasons for the recommended spacing of joints:
- Expansion joints are provided at greater intervals because they are designed to accommodate greater movements due to temperature changes. This is because the concrete pavement expands more than it contracts due to temperature changes.
- Contraction joints are provided at smaller intervals because they are designed to accommodate smaller movements due to temperature changes. This is because the concrete pavement contracts more than it expands due to temperature changes.
- The spacing of joints is also affected by traffic volume. High traffic volumes can cause greater stresses on the pavement, which can lead to greater movement due to temperature changes. As a result, the spacing of joints may need to be reduced in areas with high traffic volumes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the recommended spacing of highway expansion and contraction joints is 50 meters for expansion joints and 10 meters for contraction joints. These spacings are based on a number of factors, including the type of pavement, the expected temperature changes, and the traffic volume. The spacing of joints is important in preventing cracks and other types of damage to the pavement due to temperature changes.
A contraction joint is provided in concrete pavement to- a)prevent contraction of the pavement
- b)permit cracking at the joint
- c)lower the bending moment in the pavement in order to reduce pavement thickness
- d)lower the temperature gradient across the depth of the pavement
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A contraction joint is provided in concrete pavement to
a)
prevent contraction of the pavement
b)
permit cracking at the joint
c)
lower the bending moment in the pavement in order to reduce pavement thickness
d)
lower the temperature gradient across the depth of the pavement

|
Milan Ghosh answered |
Contraction Joint is provided to prevent contraction, Usually, steel bars and sealant material is used to form a contraction joint.
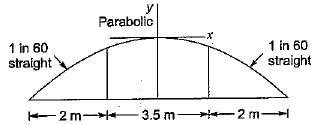
The shape of the camber, best suited for cement concrete pavements, is- a)Straight line
- b)Parabolic
- c)Elliptical
- d)Combination of straight and parabolic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The shape of the camber, best suited for cement concrete pavements, is
a)
Straight line
b)
Parabolic
c)
Elliptical
d)
Combination of straight and parabolic

|
Bhaskar Rane answered |
The camber is given a parabolic, elliptic or straight line shape in the cross-section. Parabolic or elliptic shape is given so that the profile is flat at the middle and steeper towards the edges, which is preferred by fast moving vehicles.
When very flat cross slope is provided as in cement concrete pavements, straight line shape of camber may be provided.
When very flat cross slope is provided as in cement concrete pavements, straight line shape of camber may be provided.
Stopping sight distance on a national highway at a descending gradient of 2% is where V = 80 km/h
- a)121 m
- b)132 m
- c)143 m
- d)154 m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Stopping sight distance on a national highway at a descending gradient of 2% is where V = 80 km/h
a)
121 m
b)
132 m
c)
143 m
d)
154 m

|
Raghavendra Goyal answered |
Desigmsffeed on national highway,
V = 80 km/hr
SSD = vt+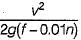
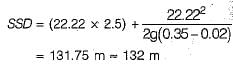
V = 80 km/hr
SSD = vt+
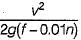
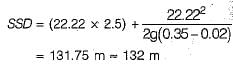
When the path travelled along the road surface is more than the circumferential movement of the wheels due to rotation, then it results in- a)slipping
- b)skidding
- c)turning
- d)revolving
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When the path travelled along the road surface is more than the circumferential movement of the wheels due to rotation, then it results in
a)
slipping
b)
skidding
c)
turning
d)
revolving
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
Skid occurs when vehicles slide without revolving or when the wheels partially revolve i.e., when the path travelled along the road surface is more than the circumferential movements of the wheels due to their rotation. Slip occurs when a wheel revolves more than the corresponding longitudinal movement along the roads.
in an airport, if 4 groups of 5 gates each located well-separated are considered for traffic and the future-to present traffic ratio is 3, then the total requirement of future gates will ,be- a)32
- b)36
- c)44
- d)68
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
in an airport, if 4 groups of 5 gates each located well-separated are considered for traffic and the future-to present traffic ratio is 3, then the total requirement of future gates will ,be
a)
32
b)
36
c)
44
d)
68
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Gate is the parking space for an aircraft. Number of Gate positions

For the present traffic 4 x 5 = 20 gates are needed. Therefore for future traffic (three times present traffic) 60 gates will be required. In addition some aircrafts will have higher occupancy time in future as they will be very big compared to the present traffic composition. Therefore 68 gates will be the correct choice.

For the present traffic 4 x 5 = 20 gates are needed. Therefore for future traffic (three times present traffic) 60 gates will be required. In addition some aircrafts will have higher occupancy time in future as they will be very big compared to the present traffic composition. Therefore 68 gates will be the correct choice.
Consider the following steps involved in the design of super elevation in practice as recommended by IRC :
1. Calculation of the allowable speed for maximum ‘e’ and design value of T
2. Calculation of the super elevation for 75% of the design speed
3. Calculation of the value of ‘e’ and recheck
4. Calculation of the value of ‘f and recheck
The correct sequence of these steps is- a)1-2-3-4
- b)3-4-1-2
- c)2-3-4-1
- d)4-3-2-1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following steps involved in the design of super elevation in practice as recommended by IRC :
1. Calculation of the allowable speed for maximum ‘e’ and design value of T
2. Calculation of the super elevation for 75% of the design speed
3. Calculation of the value of ‘e’ and recheck
4. Calculation of the value of ‘f and recheck
The correct sequence of these steps is
1. Calculation of the allowable speed for maximum ‘e’ and design value of T
2. Calculation of the super elevation for 75% of the design speed
3. Calculation of the value of ‘e’ and recheck
4. Calculation of the value of ‘f and recheck
The correct sequence of these steps is
a)
1-2-3-4
b)
3-4-1-2
c)
2-3-4-1
d)
4-3-2-1

|
Saptarshi Khanna answered |
2 - 3 - 4 - 1
The step given in 1 is an alternative of step given in 4.
The step given in 1 is an alternative of step given in 4.
For a Broad Gauge route with M+7 sleeper density, number of sleepers per rail length is- a)18
- b)19
- c)20
- d)21
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For a Broad Gauge route with M+7 sleeper density, number of sleepers per rail length is
a)
18
b)
19
c)
20
d)
21
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Length of one rail in broad gauge is equal to 13 m
Therefore, M+7 means that 13+7=20 sleepers will be used per rail on that route.
Therefore, M+7 means that 13+7=20 sleepers will be used per rail on that route.
Select the correct option for cell address:- a) 2512
- b) A 25
- c) 911
- d) 45 Z
- e) None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct option for cell address:
a)
2512
b)
A 25
c)
911
d)
45 Z
e)
None of these
|
|
Maulik Chauhan answered |
The correct option for the cell address is option 'B', which is "A25".
Explanation:
A cell address in a spreadsheet refers to the location of a specific cell. In most spreadsheet software, such as Microsoft Excel, cell addresses are represented by a combination of a letter and a number. The letter represents the column of the cell, and the number represents the row of the cell.
In this case, the correct cell address is "A25". Let's break it down further:
1. Columns: The letters in the cell address represent the columns in the spreadsheet. The first column is denoted by the letter "A", the second column by "B", and so on. In this case, the letter "A" indicates that the cell is located in the first column.
2. Rows: The numbers in the cell address represent the rows in the spreadsheet. The first row is denoted by the number 1, the second row by 2, and so on. In this case, the number "25" indicates that the cell is located in the 25th row.
Therefore, the correct cell address is "A25", which represents a cell located in the first column and the 25th row.
Explanation:
A cell address in a spreadsheet refers to the location of a specific cell. In most spreadsheet software, such as Microsoft Excel, cell addresses are represented by a combination of a letter and a number. The letter represents the column of the cell, and the number represents the row of the cell.
In this case, the correct cell address is "A25". Let's break it down further:
1. Columns: The letters in the cell address represent the columns in the spreadsheet. The first column is denoted by the letter "A", the second column by "B", and so on. In this case, the letter "A" indicates that the cell is located in the first column.
2. Rows: The numbers in the cell address represent the rows in the spreadsheet. The first row is denoted by the number 1, the second row by 2, and so on. In this case, the number "25" indicates that the cell is located in the 25th row.
Therefore, the correct cell address is "A25", which represents a cell located in the first column and the 25th row.
The length of National Highways as per 3rd 20 year (Lucknow) road plan is given by- a)area of the country/75
- b)area of the country/50
- c)area of the country/40
- d)area of the country/25
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The length of National Highways as per 3rd 20 year (Lucknow) road plan is given by
a)
area of the country/75
b)
area of the country/50
c)
area of the country/40
d)
area of the country/25

|
Tanishq Rane answered |
(i) Length of National Highways (NH) - Area of the country/50
(ii) Length of State Highways (SH) = Area of the state/25 = 62.5 x number of towns in the state - Area of the state/50
(iii) Length of the Major District Roads (MDR) = Area of the State/12.5 = 90 x number of towns in the state
(iv) Total length of all categories of roads in a district i.e.
NH + SH + MDR + ODR + VR
= Area of District x 0.82
(ii) Length of State Highways (SH) = Area of the state/25 = 62.5 x number of towns in the state - Area of the state/50
(iii) Length of the Major District Roads (MDR) = Area of the State/12.5 = 90 x number of towns in the state
(iv) Total length of all categories of roads in a district i.e.
NH + SH + MDR + ODR + VR
= Area of District x 0.82
The modulus of sub-grade reaction is evaluated from- a)plate bearing test
- b)CBR test
- c)direct shear test
- d)tri-axial test
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The modulus of sub-grade reaction is evaluated from
a)
plate bearing test
b)
CBR test
c)
direct shear test
d)
tri-axial test

|
Maulik Das answered |
Modulus of subgrade reaction (k) is calculated from plate bearing test at 0.125 cm settlement
K = Pressure (kg/cm2) / 0.125 cm
K = Pressure (kg/cm2) / 0.125 cm
The grade compensation of a 4° curve on a Broad Gauge railway track is- a)0.20%
- b)0.16%
- c)0.12%
- d)0.08%
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The grade compensation of a 4° curve on a Broad Gauge railway track is
a)
0.20%
b)
0.16%
c)
0.12%
d)
0.08%

|
Milan Ghosh answered |
For BG track grade compensation is 0.04% per degree of curve. For 4° curve grade compensation will be
= 4 x 0.04 = 0.16 % .
= 4 x 0.04 = 0.16 % .
Consider the following statements: Wind rose diagram is used for the purpose(s) of
1. runway orientation
2. estimating the runway capacity
3. geometric design of holding.apronWhich of these statements is/are correct?- a)1 and 2
- b)2 and 3
- c)1 and 3
- d)1 alone
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements: Wind rose diagram is used for the purpose(s) of
1. runway orientation
2. estimating the runway capacity
3. geometric design of holding.apron
1. runway orientation
2. estimating the runway capacity
3. geometric design of holding.apron
Which of these statements is/are correct?
a)
1 and 2
b)
2 and 3
c)
1 and 3
d)
1 alone

|
Devanshi Iyer answered |
Wind rose diagram is used for the purpose(s) of:
1. Runway orientation:
The wind rose diagram provides valuable information about the prevailing wind patterns at a specific location. By analyzing the wind rose diagram, engineers and planners can determine the most frequent wind directions and speeds. This information is crucial for the proper orientation of runways at airports. Runways are typically designed to align with the prevailing wind direction to ensure safe takeoff and landing operations. By aligning the runways with the prevailing winds, aircraft can take off and land with minimal crosswind component, which enhances safety and efficiency.
2. Estimating the runway capacity:
The wind rose diagram also aids in estimating the runway capacity. The capacity of a runway is influenced by wind conditions as well. Strong crosswinds can reduce the effective capacity of a runway, as they may require aircraft to use a different runway or limit the maximum allowable crosswind component for takeoffs and landings. By analyzing the wind rose diagram, airport operators can assess the impact of wind conditions on the runway capacity and make necessary adjustments to ensure efficient operations.
3. Geometric design of holding apron:
The wind rose diagram is not directly used for the geometric design of holding aprons. Holding aprons are areas where aircraft wait before taking off or after landing. The design of holding aprons takes into consideration factors such as aircraft size, taxiway width, and traffic flow patterns. While wind conditions can indirectly influence the design of holding aprons (e.g., providing adequate space for aircraft to maneuver in crosswind conditions), the wind rose diagram itself is not a primary tool for this purpose.
Therefore, the correct statement is:
d) 1 alone: The wind rose diagram is primarily used for runway orientation. It provides information about prevailing wind patterns, aiding in the proper alignment of runways with the prevailing winds.
1. Runway orientation:
The wind rose diagram provides valuable information about the prevailing wind patterns at a specific location. By analyzing the wind rose diagram, engineers and planners can determine the most frequent wind directions and speeds. This information is crucial for the proper orientation of runways at airports. Runways are typically designed to align with the prevailing wind direction to ensure safe takeoff and landing operations. By aligning the runways with the prevailing winds, aircraft can take off and land with minimal crosswind component, which enhances safety and efficiency.
2. Estimating the runway capacity:
The wind rose diagram also aids in estimating the runway capacity. The capacity of a runway is influenced by wind conditions as well. Strong crosswinds can reduce the effective capacity of a runway, as they may require aircraft to use a different runway or limit the maximum allowable crosswind component for takeoffs and landings. By analyzing the wind rose diagram, airport operators can assess the impact of wind conditions on the runway capacity and make necessary adjustments to ensure efficient operations.
3. Geometric design of holding apron:
The wind rose diagram is not directly used for the geometric design of holding aprons. Holding aprons are areas where aircraft wait before taking off or after landing. The design of holding aprons takes into consideration factors such as aircraft size, taxiway width, and traffic flow patterns. While wind conditions can indirectly influence the design of holding aprons (e.g., providing adequate space for aircraft to maneuver in crosswind conditions), the wind rose diagram itself is not a primary tool for this purpose.
Therefore, the correct statement is:
d) 1 alone: The wind rose diagram is primarily used for runway orientation. It provides information about prevailing wind patterns, aiding in the proper alignment of runways with the prevailing winds.
The ideal form of curve for the summit curve is
- a)spiral
- b)circle
- c)parabola
- d)lemniscate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The ideal form of curve for the summit curve is
a)
spiral
b)
circle
c)
parabola
d)
lemniscate

|
Sreemoyee Joshi answered |
Circular summit curve is ideal as the sight distance available throughout the length of circular curve is constant.
A locomotive has four pairs of driving wheels carrying an axle load of 24 x 104 N The maximum load that can be pulled if the coefficient of friction is 1/6, is- a)32 x 104 N
- b)16 x 104 N
- c)8 x 104 N
- d)4 x 104 N
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A locomotive has four pairs of driving wheels carrying an axle load of 24 x 104 N The maximum load that can be pulled if the coefficient of friction is 1/6, is
a)
32 x 104 N
b)
16 x 104 N
c)
8 x 104 N
d)
4 x 104 N

|
Devansh Banerjee answered |
Maximum load pulled
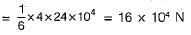
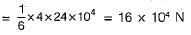
A1 type of international airport is the indicative term for - a)baste runway length and single isolated wheel load only
- b)runway length at standard conditions only
- c)strength of the runway pavement only
- d)besic unway length, maximum permissible single isolated wheel load and tyre pressure
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A1 type of international airport is the indicative term for
a)
baste runway length and single isolated wheel load only
b)
runway length at standard conditions only
c)
strength of the runway pavement only
d)
besic unway length, maximum permissible single isolated wheel load and tyre pressure

|
Simran Saha answered |
A1 type of international airport indicates: Minimum basic runway length - 2100 m
Pavement width = 45 m
Maximum longitudinal grade = 1.5%
Isolated wheel load = 45000 kg
Tyre pressure = 8.5 kg/cm2
Pavement width = 45 m
Maximum longitudinal grade = 1.5%
Isolated wheel load = 45000 kg
Tyre pressure = 8.5 kg/cm2
Which one of the following is the correct statements:
Penetration to know bitumen grade is measured in:- a)One-hundredth of mm
- b)One-tenth of mm
- c)One-tenth of an inch
- d)One micron
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the correct statements:
Penetration to know bitumen grade is measured in:
Penetration to know bitumen grade is measured in:
a)
One-hundredth of mm
b)
One-tenth of mm
c)
One-tenth of an inch
d)
One micron

|
Bhaskar Rane answered |
Penetration test determines the hardness or softness of bitumen by measuring the depth in tenths of a millimetre to which a standard loaded needle wilt penetrate vertically in five seconds.
The type of spike used for fixing chairs of bull headed rails to wooden sleepers is- a)dog spike
- b)rail screw
- c)elastic spike
- d)round spike
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The type of spike used for fixing chairs of bull headed rails to wooden sleepers is
a)
dog spike
b)
rail screw
c)
elastic spike
d)
round spike

|
Snehal Tiwari answered |
Round spikes are mainly used for fixing G.l. chairs of B.H. rails to wooden sleepers and also in switch fittings on wooden sleepers. The spikes have a blunt end and the length varies according to the gauge of the track.
if N is the algebraic difference of grades, S is the headlight sight distance in metres, then the transmission length of a valley curve (following standard codes) should roughly be equal to- a)NS2/6
- b)NS2/9.6
- c)NS2/4
- d)NS2/10
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
if N is the algebraic difference of grades, S is the headlight sight distance in metres, then the transmission length of a valley curve (following standard codes) should roughly be equal to
a)
NS2/6
b)
NS2/9.6
c)
NS2/4
d)
NS2/10

|
Jithin Choudhury answered |
The head light sight distance should be at least equal to SSD. If the vehicles are overtaking then length curve should be:
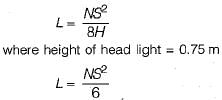
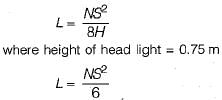
The lost time due to starting delay on a traffic signal is noted to be 3s, the actual green time is 25s and yellow time is 3s. How much is the effective green time?- a)31s
- b)28s
- c)25 s
- d)22s
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The lost time due to starting delay on a traffic signal is noted to be 3s, the actual green time is 25s and yellow time is 3s. How much is the effective green time?
a)
31s
b)
28s
c)
25 s
d)
22s

|
Abhay Banerjee answered |
Effective green time = Actual green time + Yellow time - lost time
= 25 + 3 - 3
= 25 seconds
= 25 + 3 - 3
= 25 seconds
If the normal flows on two approach roads at an intersection are respectively 500 pcu per hr and 300 pcu per hr, the saturation flows are 1600 pcu per hr on each road and the total lost time per signal cycle is 16 s, then the optimum cycle time by Webster’s method is- a)72.5 s
- b)58 s
- c)48 s
- d)19.3 s
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the normal flows on two approach roads at an intersection are respectively 500 pcu per hr and 300 pcu per hr, the saturation flows are 1600 pcu per hr on each road and the total lost time per signal cycle is 16 s, then the optimum cycle time by Webster’s method is
a)
72.5 s
b)
58 s
c)
48 s
d)
19.3 s

|
Jaideep Malik answered |
Optimum cycle time,
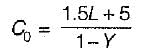
L = Total lost time per cycle = 16 sec
Y = y1 + y2
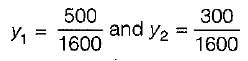
∴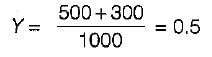
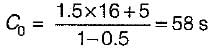
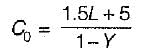
L = Total lost time per cycle = 16 sec
Y = y1 + y2
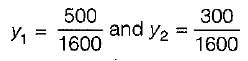
∴
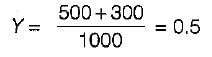
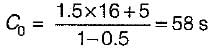
Maximum number of vehicles can be parked with- a)parallel parking
- b)30° angle parking
- c)45° angle parking
- d)90° angle parking
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Maximum number of vehicles can be parked with
a)
parallel parking
b)
30° angle parking
c)
45° angle parking
d)
90° angle parking

|
Ashwin Kulkarni answered |
Angle parking or parallel parking may be allowed in the kerb parking. Angle parking may be at angle 30, 60 or 90 degrees. Angle parking accommodates more vehicles per unit length of kerb and maximum vehicles that can be parked is with an angle of 90 degree.
The maximum harbour depth below lowest low water is generally equal to- a)loaded draft + 1.2 m when bottom is rock
- b)loaded draft + 1.8 m when bottom is soft
- c)loaded draft + 1.5 m when bottom Is soft
- d)loaded draft + 1.8m when bottom is rock
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The maximum harbour depth below lowest low water is generally equal to
a)
loaded draft + 1.2 m when bottom is rock
b)
loaded draft + 1.8 m when bottom is soft
c)
loaded draft + 1.5 m when bottom Is soft
d)
loaded draft + 1.8m when bottom is rock

|
Sreemoyee Chauhan answered |
Harbour Depth and Loaded Draft
Harbour depth is the depth of water in a harbour or port, measured at a particular point below the lowest low water level. The loaded draft is the depth of a ship below the waterline when it is fully loaded with cargo. The maximum harbour depth below the lowest low water is generally equal to the loaded draft when the ship is fully loaded.
Bottom Condition
The type of bottom in the harbour also affects the maximum depth. If the bottom is soft, the maximum depth will be less than if the bottom is rock. This is because soft bottoms are less stable and can shift or settle over time.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is option 'D' - loaded draft 1.8m when bottom is rock. This means that if the bottom of the harbour is rock, the maximum depth below the lowest low water will be equal to the loaded draft of 1.8 meters. This is because rock bottoms provide a stable foundation for the harbour and can support greater depths than soft bottoms.
Option 'A' is incorrect because a loaded draft of 1.2m would be too shallow for a harbour depth, even with a rock bottom. Option 'B' is incorrect because a loaded draft of 1.8m would be too shallow for a soft bottom. Option 'C' is also incorrect because a loaded draft of 1.5m would be too shallow for both rock and soft bottoms.
In summary, the maximum harbour depth below the lowest low water is generally equal to the loaded draft, and it is greater when the bottom of the harbour is rock than when it is soft.
Harbour depth is the depth of water in a harbour or port, measured at a particular point below the lowest low water level. The loaded draft is the depth of a ship below the waterline when it is fully loaded with cargo. The maximum harbour depth below the lowest low water is generally equal to the loaded draft when the ship is fully loaded.
Bottom Condition
The type of bottom in the harbour also affects the maximum depth. If the bottom is soft, the maximum depth will be less than if the bottom is rock. This is because soft bottoms are less stable and can shift or settle over time.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is option 'D' - loaded draft 1.8m when bottom is rock. This means that if the bottom of the harbour is rock, the maximum depth below the lowest low water will be equal to the loaded draft of 1.8 meters. This is because rock bottoms provide a stable foundation for the harbour and can support greater depths than soft bottoms.
Option 'A' is incorrect because a loaded draft of 1.2m would be too shallow for a harbour depth, even with a rock bottom. Option 'B' is incorrect because a loaded draft of 1.8m would be too shallow for a soft bottom. Option 'C' is also incorrect because a loaded draft of 1.5m would be too shallow for both rock and soft bottoms.
In summary, the maximum harbour depth below the lowest low water is generally equal to the loaded draft, and it is greater when the bottom of the harbour is rock than when it is soft.
Which of the following factors are taken into account for estimating the runway length required for aircraft landing?
1. Normal maximum temperature
2. Airport elevation
3. Maximum landing weight
4. Effective runway gradientSelect the correct answer using the codes given below: - a)1, 2, 3 and 4
- b)1, 3 and 4
- c)2 and 3
- d)1, 2 and 4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following factors are taken into account for estimating the runway length required for aircraft landing?
1. Normal maximum temperature
2. Airport elevation
3. Maximum landing weight
4. Effective runway gradient
1. Normal maximum temperature
2. Airport elevation
3. Maximum landing weight
4. Effective runway gradient
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
a)
1, 2, 3 and 4
b)
1, 3 and 4
c)
2 and 3
d)
1, 2 and 4

|
Hiral Sharma answered |
Factors for estimating runway length for aircraft landing:
1. Normal maximum temperature:
The normal maximum temperature of the region where the airport is located is an important factor in estimating the runway length required for aircraft landing. Higher temperatures affect the air density, which in turn affects the aircraft's lift and braking performance. Higher temperatures reduce the density of air, resulting in reduced lift and longer stopping distances. Therefore, the runway length needs to be increased to compensate for the reduced performance of the aircraft in hot weather conditions.
2. Airport elevation:
The elevation of the airport is another critical factor in determining the required runway length for aircraft landing. Higher elevations result in thinner air, which reduces the aircraft's lift and performance. As the air density decreases with increasing elevation, the aircraft requires a longer runway to generate sufficient lift for takeoff and landing. Therefore, airports located at higher elevations need longer runways compared to those at lower elevations.
3. Maximum landing weight:
The maximum landing weight of the aircraft plays a significant role in estimating the runway length required for landing. The weight of the aircraft affects its landing speed, braking performance, and overall stopping distance. Heavier aircraft require longer runways to safely decelerate and come to a complete stop. The landing weight is determined by factors such as fuel load, payload, and passenger count. Therefore, the runway length needs to be sufficient to accommodate the maximum landing weight of the aircraft operating at the airport.
4. Effective runway gradient:
The effective runway gradient, or slope, is also considered when estimating the required runway length for aircraft landing. A downhill gradient can assist in reducing the required runway length by providing additional deceleration. Conversely, an uphill gradient increases the required runway length as it reduces the aircraft's braking effectiveness. The gradient of the runway, along with other factors, is taken into account to determine the overall runway length required for safe landing operations.
In conclusion, the factors that are taken into account for estimating the runway length required for aircraft landing include normal maximum temperature, airport elevation, maximum landing weight, and effective runway gradient. These factors are crucial in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of aircraft at airports.
1. Normal maximum temperature:
The normal maximum temperature of the region where the airport is located is an important factor in estimating the runway length required for aircraft landing. Higher temperatures affect the air density, which in turn affects the aircraft's lift and braking performance. Higher temperatures reduce the density of air, resulting in reduced lift and longer stopping distances. Therefore, the runway length needs to be increased to compensate for the reduced performance of the aircraft in hot weather conditions.
2. Airport elevation:
The elevation of the airport is another critical factor in determining the required runway length for aircraft landing. Higher elevations result in thinner air, which reduces the aircraft's lift and performance. As the air density decreases with increasing elevation, the aircraft requires a longer runway to generate sufficient lift for takeoff and landing. Therefore, airports located at higher elevations need longer runways compared to those at lower elevations.
3. Maximum landing weight:
The maximum landing weight of the aircraft plays a significant role in estimating the runway length required for landing. The weight of the aircraft affects its landing speed, braking performance, and overall stopping distance. Heavier aircraft require longer runways to safely decelerate and come to a complete stop. The landing weight is determined by factors such as fuel load, payload, and passenger count. Therefore, the runway length needs to be sufficient to accommodate the maximum landing weight of the aircraft operating at the airport.
4. Effective runway gradient:
The effective runway gradient, or slope, is also considered when estimating the required runway length for aircraft landing. A downhill gradient can assist in reducing the required runway length by providing additional deceleration. Conversely, an uphill gradient increases the required runway length as it reduces the aircraft's braking effectiveness. The gradient of the runway, along with other factors, is taken into account to determine the overall runway length required for safe landing operations.
In conclusion, the factors that are taken into account for estimating the runway length required for aircraft landing include normal maximum temperature, airport elevation, maximum landing weight, and effective runway gradient. These factors are crucial in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of aircraft at airports.
Desire lines are drawn based on- a)spot speed studies
- b)traffic volume studies
- c)accident studies
- d)origin and destination studies
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Desire lines are drawn based on
a)
spot speed studies
b)
traffic volume studies
c)
accident studies
d)
origin and destination studies

|
Puja Sharma answered |
Desire lines are plotted which is a graphical representation prepared in almost all O and D surveys, Desire lines are straight lines connecting the origin points with destinations. The width of such desire lines is drawn proportional to the number of trips in both directions.
Squaring of sleepers through packing consists of- a)Adjusting the sleepers to be perpendicular to the rails
- b)Adjusting the ballast under sleepers to space them parallel to each other
- c)Cutting the edges of the sleepers to a square shape
- d)Adjusting the rails to be perpendicular to the sleepers
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Squaring of sleepers through packing consists of
a)
Adjusting the sleepers to be perpendicular to the rails
b)
Adjusting the ballast under sleepers to space them parallel to each other
c)
Cutting the edges of the sleepers to a square shape
d)
Adjusting the rails to be perpendicular to the sleepers

|
Akash Mukherjee answered |
In through packing the sleepers are squared and brought to specified spacing at straight lengths and on curves i.e., the ballast under the sleepers is adjusted to space them parallel to each other.
The traffic conflicts that may occur in a rotary intersection are- a)Merging and diverging
- b)Crossing and merging
- c)Crossing and diverging
- d)Crossing, merging and diverging
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The traffic conflicts that may occur in a rotary intersection are
a)
Merging and diverging
b)
Crossing and merging
c)
Crossing and diverging
d)
Crossing, merging and diverging

|
Srestha Khanna answered |
Rotary intersections, also known as roundabouts, are circular intersections that help control traffic flow and reduce collisions. However, traffic conflicts may still occur in these areas. The traffic conflicts that may occur in a rotary intersection area are:
Merging and Diverging:
- Merging refers to the act of a vehicle entering the rotary intersection from a feeder road.
- Diverging refers to the act of a vehicle leaving the rotary intersection onto a feeder road.
- Conflicts may arise when merging or diverging vehicles do not yield to circulating vehicles or when circulating vehicles do not yield to merging or diverging vehicles.
Other possible traffic conflicts in a rotary intersection area may include:
- Crossing: When a vehicle crosses the rotary intersection to reach another road or exit.
- Merging and Crossing: When a vehicle merges onto the rotary intersection and then crosses it to reach another road or exit.
- Diverging and Crossing: When a vehicle leaves the rotary intersection and then crosses another road.
However, the correct answer to this question is option 'A', which refers to merging and diverging conflicts.
Merging and Diverging:
- Merging refers to the act of a vehicle entering the rotary intersection from a feeder road.
- Diverging refers to the act of a vehicle leaving the rotary intersection onto a feeder road.
- Conflicts may arise when merging or diverging vehicles do not yield to circulating vehicles or when circulating vehicles do not yield to merging or diverging vehicles.
Other possible traffic conflicts in a rotary intersection area may include:
- Crossing: When a vehicle crosses the rotary intersection to reach another road or exit.
- Merging and Crossing: When a vehicle merges onto the rotary intersection and then crosses it to reach another road or exit.
- Diverging and Crossing: When a vehicle leaves the rotary intersection and then crosses another road.
However, the correct answer to this question is option 'A', which refers to merging and diverging conflicts.
As per ICAO, the minimum basic runway length for A and E type of airport will be- a)1500 m and 600 m
- b)2100 m and 750 m
- c)1500 m and 750 m
- d)2100 m and 600 m
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
As per ICAO, the minimum basic runway length for A and E type of airport will be
a)
1500 m and 600 m
b)
2100 m and 750 m
c)
1500 m and 750 m
d)
2100 m and 600 m

|
Ashwin Kulkarni answered |
The minimum basic length for B, C and D types of airport are 1500 m, 900 m and 750 m respectively.
In using the data from a plate bearing test for determining the modulus of sub-grade reaction, the value of settlement to be used to- a)1.25 mm
- b)2.50 mm
- c)3.75 mm
- d)1.75 mm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In using the data from a plate bearing test for determining the modulus of sub-grade reaction, the value of settlement to be used to
a)
1.25 mm
b)
2.50 mm
c)
3.75 mm
d)
1.75 mm

|
Sarthak Kulkarni answered |
Modulus of subgrade reaction (k) is calculated from plate bearing test at 0.125 cm settlement
K = Pressure (kg/cm2) / 0.125 cm
K = Pressure (kg/cm2) / 0.125 cm
Parabolic camber is preferred for- a)Slow moving vehicle
- b)Steel tyred vehicle
- c)Fast moving vehicle
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Parabolic camber is preferred for
a)
Slow moving vehicle
b)
Steel tyred vehicle
c)
Fast moving vehicle
d)
All the above

|
Aaditya Jain answered |
The camber is given a parabolic elliptic or straight line shape in the cross section parabolic or elliptic shape is given so that the profile is flat at the middle and steeper towards the edges, which is preferred by fast moving vehicles as the have to frequently cross the crown line during overtaking operation on a two lane highway.
The mechanical extra widening required for 10.5 m wide pavement on a horizontal curve of radius R metre is given by where l is the length of wheel base of vehicle in metres.- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The mechanical extra widening required for 10.5 m wide pavement on a horizontal curve of radius R metre is given by
where l is the length of wheel base of vehicle in metres.
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Rajdeep Gupta answered |
Mechanical widening 
where, n = no. of lanes
For 10.5 m wide pavement,
n=3


where, n = no. of lanes
For 10.5 m wide pavement,
n=3

Consider the following factors :
1. Magnitude of load
2. Thickness of cement concrete slab
3. Temperature distribution in the slab
4. Modulus of sub-grade reaction
Which of these should be taken into reckoning to determine the wheel load stress at critical location in a cement concrete pavement?- a)1, 2 and 3
- b)1 and 3
- c)3 and 4
- d)1, 2 and 4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following factors :
1. Magnitude of load
2. Thickness of cement concrete slab
3. Temperature distribution in the slab
4. Modulus of sub-grade reaction
Which of these should be taken into reckoning to determine the wheel load stress at critical location in a cement concrete pavement?
1. Magnitude of load
2. Thickness of cement concrete slab
3. Temperature distribution in the slab
4. Modulus of sub-grade reaction
Which of these should be taken into reckoning to determine the wheel load stress at critical location in a cement concrete pavement?
a)
1, 2 and 3
b)
1 and 3
c)
3 and 4
d)
1, 2 and 4

|
Arnab Saini answered |
To determine wheel load'stress at critical location, - Magnitude of load (P) - Thickness of slab (h) - Radius of wheel Load distribution (a), radius of relative stiffness (I) and radius of resisting section (b) are needed. 'a', 'b' and 'I’ depend upon modulus of sub - grade reaction.
If the stopping distance is 60 metres, then the minimum stopping sight distance for two lane, two way traffic is- a)30 m
- b)60 m
- c)120 m
- d)180 m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the stopping distance is 60 metres, then the minimum stopping sight distance for two lane, two way traffic is
a)
30 m
b)
60 m
c)
120 m
d)
180 m

|
Arnab Choudhury answered |
The minimum stopping sight distance should be equal to the stopping distance in one-way traffic lanes and also in two-way traffic roads when there are two or more traffic lanes.
Rapid curing cutback bitumen is produced by blending bitumen with- a)Kerosene
- b)Benzene
- c)Diesel
- d)Petrol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Rapid curing cutback bitumen is produced by blending bitumen with
a)
Kerosene
b)
Benzene
c)
Diesel
d)
Petrol

|
Milan Saha answered |
Rapid curing cutback bitumen is a type of bitumen that is blended with another substance in order to improve its curing time. In this case, the correct substance that is blended with bitumen to produce rapid curing cutback bitumen is petrol.
Petrol, also known as gasoline, is a flammable liquid mixture that is primarily used as a fuel in internal combustion engines. It is derived from crude oil through a refining process. Petrol has a low viscosity and a high volatility, making it an ideal additive for bitumen to enhance its curing properties.
Below is a detailed explanation of why petrol is used as a blending agent to produce rapid curing cutback bitumen:
1. Enhances Volatility: Petrol has a high evaporation rate due to its low boiling point. When blended with bitumen, it increases the overall volatility of the mixture. This enhanced volatility helps in the rapid evaporation of the petrol component, which accelerates the curing process of the bitumen.
2. Reduces Viscosity: Bitumen is a highly viscous material at room temperature, which makes it difficult to handle and apply. By blending it with petrol, the viscosity of the mixture is reduced, making it easier to work with. The lower viscosity also aids in the rapid penetration of the bitumen into the pavement surface, leading to faster curing.
3. Improves Adhesion: The addition of petrol improves the adhesion properties of the bitumen. It helps in better bonding between the bitumen and the aggregate particles, resulting in improved pavement performance. The enhanced adhesion also contributes to the rapid curing of the bitumen.
4. Provides Cost-effectiveness: Petrol is readily available and relatively inexpensive compared to other blending agents such as kerosene, benzene, or diesel. This makes it a cost-effective choice for producing rapid curing cutback bitumen.
In summary, petrol is used as a blending agent in the production of rapid curing cutback bitumen due to its high volatility, ability to reduce viscosity, improved adhesion properties, and cost-effectiveness. The addition of petrol enhances the curing time of bitumen, making it a suitable choice for various road construction and maintenance applications.
Petrol, also known as gasoline, is a flammable liquid mixture that is primarily used as a fuel in internal combustion engines. It is derived from crude oil through a refining process. Petrol has a low viscosity and a high volatility, making it an ideal additive for bitumen to enhance its curing properties.
Below is a detailed explanation of why petrol is used as a blending agent to produce rapid curing cutback bitumen:
1. Enhances Volatility: Petrol has a high evaporation rate due to its low boiling point. When blended with bitumen, it increases the overall volatility of the mixture. This enhanced volatility helps in the rapid evaporation of the petrol component, which accelerates the curing process of the bitumen.
2. Reduces Viscosity: Bitumen is a highly viscous material at room temperature, which makes it difficult to handle and apply. By blending it with petrol, the viscosity of the mixture is reduced, making it easier to work with. The lower viscosity also aids in the rapid penetration of the bitumen into the pavement surface, leading to faster curing.
3. Improves Adhesion: The addition of petrol improves the adhesion properties of the bitumen. It helps in better bonding between the bitumen and the aggregate particles, resulting in improved pavement performance. The enhanced adhesion also contributes to the rapid curing of the bitumen.
4. Provides Cost-effectiveness: Petrol is readily available and relatively inexpensive compared to other blending agents such as kerosene, benzene, or diesel. This makes it a cost-effective choice for producing rapid curing cutback bitumen.
In summary, petrol is used as a blending agent in the production of rapid curing cutback bitumen due to its high volatility, ability to reduce viscosity, improved adhesion properties, and cost-effectiveness. The addition of petrol enhances the curing time of bitumen, making it a suitable choice for various road construction and maintenance applications.
Consider the following statements: The failure of sub-grade of a flexible pavement is mainly attributed to
1. inadequate stability
2. loss of binding action
3. loss of base course materials
4. excessive stress concentration
Which of the statements are correct?- a)1 and 2
- b)1 and 4
- c)2 and 4
- d)2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements: The failure of sub-grade of a flexible pavement is mainly attributed to
1. inadequate stability
2. loss of binding action
3. loss of base course materials
4. excessive stress concentration
Which of the statements are correct?
1. inadequate stability
2. loss of binding action
3. loss of base course materials
4. excessive stress concentration
Which of the statements are correct?
a)
1 and 2
b)
1 and 4
c)
2 and 4
d)
2 and 3

|
Aditya Jain answered |
Two basic reasons for failure of sub-grade are:
(i) Inadequate stability
(ii) Excessive stress application.
(i) Inadequate stability
(ii) Excessive stress application.
The load transfer to lower layers in flexible pavements is by- a)bending action of layers
- b)shear deformation
- c)grain to grain contact
- d)consolidation of sub-grade
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The load transfer to lower layers in flexible pavements is by
a)
bending action of layers
b)
shear deformation
c)
grain to grain contact
d)
consolidation of sub-grade

|
Rithika Reddy answered |
Flexible pavements are those, which on the whole have low or negligible flexural strength and are flexible in their structural action under the loads. The flexible pavement layers reflects the deformation of the lower layers on-to the surface of the layer. The flexible pavement layers transmit the vertical or compressive stresses to the lower layers by grain to grain transfer through the points of contact in granular structure.
The lowest tide which occurs in half lunar month is called- a)Spring tide
- b)Neap tide
- c)Lunar tide
- d)Tidal bore
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The lowest tide which occurs in half lunar month is called
a)
Spring tide
b)
Neap tide
c)
Lunar tide
d)
Tidal bore

|
Ashish Chakraborty answered |
Spring tides occur usually at new and full moon or rather a day or two after (or twice in each lunar month). At new moon, the sun and moon have the same celestial longitude and cross a meridian of the earth at the same instant. The sun and moon are on same side of the earth. The high water level of the resulting tide is above the average, whereas the low water level is below the average.
During neap tide, the moon falls behind the sun. High water level is below the average, whereas the low water level is above the average.
During neap tide, the moon falls behind the sun. High water level is below the average, whereas the low water level is above the average.
In highway pavements emulsions are mainly used in- a)surface dressing
- b)patching and maintenance
- c)bitumen macadam
- d)asphaltic concrete
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In highway pavements emulsions are mainly used in
a)
surface dressing
b)
patching and maintenance
c)
bitumen macadam
d)
asphaltic concrete

|
Sakshi Basak answered |
A bitumen emulsion is liquid product in which a substantial amount of bitumen is suspended in a finely divided condition in an aqueous medium and stabilized by means of one more suitable materials. The function of this emulsifier is to form a protective coating around the globules of binder resisting the coalescence of the globules.
With reference to tunnelling, which of the following factors are to be considered for deciding the size of the shaft?
1. System used for hoisting
2. Size of the muck car
3. Quantity of muck to be lifted
4. Eventual use of the shaft
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:- a)1 , 2 and 3
- b)1 and 4
- c)2, 3 and 4
- d)1, 2, 3 and 4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
With reference to tunnelling, which of the following factors are to be considered for deciding the size of the shaft?
1. System used for hoisting
2. Size of the muck car
3. Quantity of muck to be lifted
4. Eventual use of the shaft
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
1. System used for hoisting
2. Size of the muck car
3. Quantity of muck to be lifted
4. Eventual use of the shaft
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
a)
1 , 2 and 3
b)
1 and 4
c)
2, 3 and 4
d)
1, 2, 3 and 4

|
Hiral Sharma answered |
Size of shaft depends upon the following factors:
(i) Quantity of muck to be handled
(ii) Nature of hoisting system
(iii) Nature of equipment used in tunnelling
(iv) Number of labourers needed for tunnelling
(v) Space required to carry pipes and wires
(vi) Eventual use of the shaft.
(i) Quantity of muck to be handled
(ii) Nature of hoisting system
(iii) Nature of equipment used in tunnelling
(iv) Number of labourers needed for tunnelling
(v) Space required to carry pipes and wires
(vi) Eventual use of the shaft.
The most suitable equipment for compacting clayey soils is a- a)smooth wheeled roller
- b)pneumatic tyred roller
- c)sheep foot roller
- d)vibrator
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The most suitable equipment for compacting clayey soils is a
a)
smooth wheeled roller
b)
pneumatic tyred roller
c)
sheep foot roller
d)
vibrator

|
Ashwin Kulkarni answered |
Clayey Soil Sheepsfoot Roller Vibrator Sands
Smooth Wheeled Roller Finishing of gravel and sand Pneumatic Tyred Rollers Coarse grained soils with some fines.
Smooth Wheeled Roller Finishing of gravel and sand Pneumatic Tyred Rollers Coarse grained soils with some fines.
Chapter doubts & questions for Transportation Engineering - Topicwise Question Bank for Civil Engineering 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Transportation Engineering - Topicwise Question Bank for Civil Engineering in English & Hindi are available as part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup