All Exams >
UPSC >
Old & New NCERTs for IAS Preparation (Must Read) >
All Questions
All questions of Class 9 Geography for UPSC CSE Exam
Standard meridian of India is __________________.- a)82°50'E
- b)7°30'E
- c)68°7'E
- d)23°30'E
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Standard meridian of India is __________________.
a)
82°50'E
b)
7°30'E
c)
68°7'E
d)
23°30'E
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The standard meridian of India is 82°30'E. It passes through Mirzapur (Uttar Pradesh). The time of this meridian is taken as the standard time for the whole country.
Which of the following age group is that of the working-age group?
- a)15-30 years
- b)15-40 years
- c)15-59 years
- d)15-64 years
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following age group is that of the working-age group?
a)
15-30 years
b)
15-40 years
c)
15-59 years
d)
15-64 years

|
Anisha Shah answered |
The working age population is defined as those aged 15 to 59. The basic indicator for employment is the proportion of the working age population aged 15-59 who are employed. The age dependency ratio is the ratio of dependents (people younger than 15 or older than 59) to the working-age population.
Time of Arunachal Pradesh is __________________ hour ahead from Jaisalmer.
- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Time of Arunachal Pradesh is __________________ hour ahead from Jaisalmer.
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4
|
|
Shrushti Barure answered |
Due to the longitudinal extent there is a time lag of 2 hours
What helped India to established close contacts with West Asia, Africa and Europe from the west coast and with southeast and east Asia from the east coast?
- a)The central location
- b)All the these
- c)Indian landmass
- d)Deccan Peninsula
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What helped India to established close contacts with West Asia, Africa and Europe from the west coast and with southeast and east Asia from the east coast?
a)
The central location
b)
All the these
c)
Indian landmass
d)
Deccan Peninsula
|
|
Anshul Roy answered |
The peninsular situation, central location, and Indian landmass helped India to establish close contacts with West Asia, Africa, and Europe from the west coast and with southeast and east Asia from the east coast. The Indian landmass has a focal area in East and West Asia. India is toward the south expansion of the Asian mainland. The trans-Indian Ocean courses, which associate the nations of Europe in the West with East Asia, give an important focal area to India. The Deccan peninsula juts into the Indian Ocean, helping India to lay out close contact with West Asia, Africa, and Europe from the Western coast and South-East and East Asia from the Eastern coast. No other nation has a long shore on the Indian Ocean as India has. In this way, India's prominent situation in the Indian Ocean legitimises the naming of a sea after it.
Basically migration can be classified into- a)2
- b)6
- c)3
- d)1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Basically migration can be classified into
a)
2
b)
6
c)
3
d)
1
|
|
Ankita answered |
Emigration. Immigration (migration is classified) ^-^
Kavaratti is the capital of Andaman and Nicobar Islands.- a)False
- b)True
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Kavaratti is the capital of Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
a)
False
b)
True
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Port Blair is the capital of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
The total number of tiger reserves in India is- a)20
- b)8
- c)50
- d)40
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The total number of tiger reserves in India is
a)
20
b)
8
c)
50
d)
40
|
|
Nehmat Kaur answered |
The correct answer is option 'C', which states that there are 50 tiger reserves in India.
Explanation:
**Tiger Reserves in India:**
India is home to a significant population of tigers, and to protect these majestic creatures and their habitats, tiger reserves have been established across the country. Tiger reserves are designated areas where conservation efforts are focused on safeguarding the tiger population and their ecosystems.
**Number of Tiger Reserves in India:**
As of now, India has a total of 50 tiger reserves, spread across various states. These reserves have been established under the Project Tiger initiative, which was launched in 1973 by the Government of India. The objective of this project is to ensure the conservation and sustainable management of the tiger population in the country.
**Purpose of Tiger Reserves:**
Tiger reserves play a crucial role in the conservation of tigers and their habitats. These reserves provide protected areas where tigers can thrive and breed without facing significant threats from poaching, habitat destruction, or human-wildlife conflict. By designating specific areas as tiger reserves, the government aims to create a safe and conducive environment for the survival and growth of the tiger population.
**Project Tiger:**
Project Tiger is a comprehensive wildlife conservation program implemented by the Government of India. It focuses on the protection and management of tiger reserves, research and monitoring, habitat improvement, wildlife law enforcement, and community participation. The project has been instrumental in reviving the tiger population in India, which was once on the brink of extinction.
**Importance of Tiger Reserves:**
Tiger reserves not only safeguard the tiger population but also contribute to the overall biodiversity conservation of the respective regions. These reserves protect the ecosystems that support tigers, which in turn benefit numerous other species of flora and fauna. Additionally, tiger reserves attract tourists, generating revenue and supporting local economies through ecotourism.
In conclusion, India has a total of 50 tiger reserves, which are crucial for the conservation and protection of the tiger population and their habitats. These reserves serve as safe havens for tigers and contribute to the overall biodiversity conservation efforts in the country.
Explanation:
**Tiger Reserves in India:**
India is home to a significant population of tigers, and to protect these majestic creatures and their habitats, tiger reserves have been established across the country. Tiger reserves are designated areas where conservation efforts are focused on safeguarding the tiger population and their ecosystems.
**Number of Tiger Reserves in India:**
As of now, India has a total of 50 tiger reserves, spread across various states. These reserves have been established under the Project Tiger initiative, which was launched in 1973 by the Government of India. The objective of this project is to ensure the conservation and sustainable management of the tiger population in the country.
**Purpose of Tiger Reserves:**
Tiger reserves play a crucial role in the conservation of tigers and their habitats. These reserves provide protected areas where tigers can thrive and breed without facing significant threats from poaching, habitat destruction, or human-wildlife conflict. By designating specific areas as tiger reserves, the government aims to create a safe and conducive environment for the survival and growth of the tiger population.
**Project Tiger:**
Project Tiger is a comprehensive wildlife conservation program implemented by the Government of India. It focuses on the protection and management of tiger reserves, research and monitoring, habitat improvement, wildlife law enforcement, and community participation. The project has been instrumental in reviving the tiger population in India, which was once on the brink of extinction.
**Importance of Tiger Reserves:**
Tiger reserves not only safeguard the tiger population but also contribute to the overall biodiversity conservation of the respective regions. These reserves protect the ecosystems that support tigers, which in turn benefit numerous other species of flora and fauna. Additionally, tiger reserves attract tourists, generating revenue and supporting local economies through ecotourism.
In conclusion, India has a total of 50 tiger reserves, which are crucial for the conservation and protection of the tiger population and their habitats. These reserves serve as safe havens for tigers and contribute to the overall biodiversity conservation efforts in the country.
Goa is the smallest state in India.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Goa is the smallest state in India.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Pankaj Chawla answered |
Yes, the correct answer is option 'A', which means that the statement "Goa is the smallest state in India" is true. Let's discuss why.
Geographical Location of Goa
Goa is a state situated in the western region of India, along the Arabian Sea coastline. It is bounded by the states of Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to the east and south. The state capital is Panaji, and the largest city is Vasco da Gama.
Size of Goa
As per the census of 2011, the total area of Goa is 3,702 square kilometers. This makes it the smallest state in India in terms of area.
Comparison with Other States
To understand this better, let's compare the size of Goa with other states in India:
- The largest state in India is Rajasthan, which has an area of around 342,239 square kilometers.
- The second smallest state in India is Sikkim, which has an area of around 7,096 square kilometers, which is almost twice the size of Goa.
- The third smallest state is Tripura, which has an area of around 10,486 square kilometers, which is almost three times the size of Goa.
Conclusion
From the above comparisons, it is evident that Goa is indeed the smallest state in India in terms of its geographical area.
Geographical Location of Goa
Goa is a state situated in the western region of India, along the Arabian Sea coastline. It is bounded by the states of Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to the east and south. The state capital is Panaji, and the largest city is Vasco da Gama.
Size of Goa
As per the census of 2011, the total area of Goa is 3,702 square kilometers. This makes it the smallest state in India in terms of area.
Comparison with Other States
To understand this better, let's compare the size of Goa with other states in India:
- The largest state in India is Rajasthan, which has an area of around 342,239 square kilometers.
- The second smallest state in India is Sikkim, which has an area of around 7,096 square kilometers, which is almost twice the size of Goa.
- The third smallest state is Tripura, which has an area of around 10,486 square kilometers, which is almost three times the size of Goa.
Conclusion
From the above comparisons, it is evident that Goa is indeed the smallest state in India in terms of its geographical area.
The Himalayan mountain ranges run in the north-south direction from Indus to the Brahmaputra.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The Himalayan mountain ranges run in the north-south direction from Indus to the Brahmaputra.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Himalayan mountain range runs west-northwest to east-southeast in an arc 2,400 km (1,500 mi) long.
Which of the following states shares an international boundary? - a)Haryana
- b)Uttar pradesh
- c)Jharkhand
- d)Madhya Pradesh
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following states shares an international boundary?
a)
Haryana
b)
Uttar pradesh
c)
Jharkhand
d)
Madhya Pradesh
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
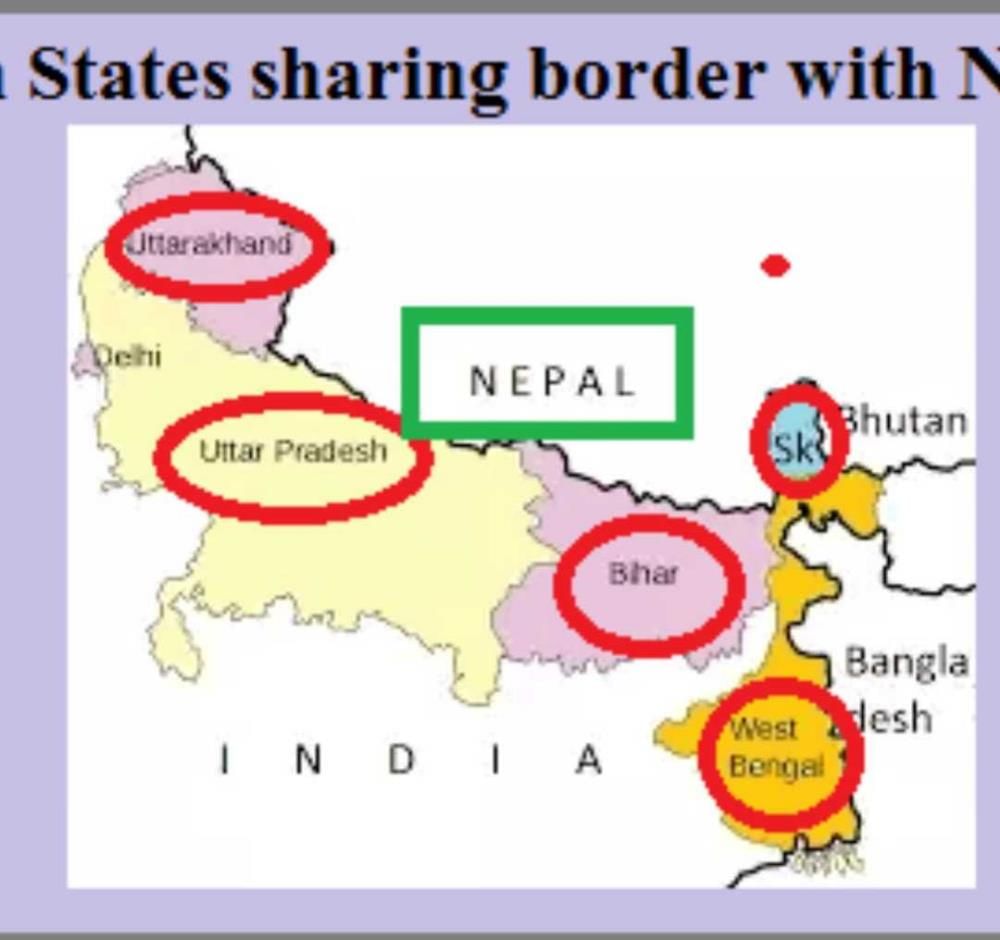
Uttar pradesh shares an international boundary with Nepal.
Which is the southern most point of the Indian Union?- a)Nehru point
- b)Gandhi point
- c)Indira point
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the southern most point of the Indian Union?
a)
Nehru point
b)
Gandhi point
c)
Indira point
d)
None of the above
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Indira point is the name of the southernmost point of Republic of India. It is situated on Great Nicobar Island in the Nicobar Islands, which are located in the eastern Indian Ocean at 6°45'10″N and 93°49'36″E. This is not on the Indian mainland, but within the Union Territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Which one of the following lakes differs from the rest in the group?- a)Dal Lake
- b)Nainital Lake
- c)The Guru Gobind Sagar Lake
- d)Bhimtal Lake
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following lakes differs from the rest in the group?
a)
Dal Lake
b)
Nainital Lake
c)
The Guru Gobind Sagar Lake
d)
Bhimtal Lake
|
|
Geetika Chopra answered |
The Guru Gobind Sagar Lake differs from the rest of the lakes in the group.
Reasons:
Location:
- The Guru Gobind Sagar Lake is located in the state of Himachal Pradesh, while the other lakes are located in Uttarakhand and Jammu and Kashmir.
Origin:
- The Guru Gobind Sagar Lake is a man-made reservoir, created by the Bhakra Dam on the Sutlej River. In contrast, the other lakes are natural or semi-natural.
Purpose:
- The Guru Gobind Sagar Lake was created primarily for hydroelectric power generation, irrigation, and drinking water supply. The other lakes do not have such a specific purpose.
Size:
- The Guru Gobind Sagar Lake is much larger than the other lakes, with a surface area of about 170 square kilometers. In comparison, Dal Lake has a surface area of about 18 square kilometers, Nainital Lake has a surface area of about 1.5 square kilometers, and Bhimtal Lake has a surface area of about 1.2 square kilometers.
Tourism:
- While the other lakes are popular tourist destinations, the Guru Gobind Sagar Lake is not as well-known as a tourist spot. It is mainly visited by people interested in water sports and fishing.
In conclusion, the Guru Gobind Sagar Lake differs from the rest of the lakes in the group due to its location, origin, purpose, size, and popularity as a tourist destination.
Reasons:
Location:
- The Guru Gobind Sagar Lake is located in the state of Himachal Pradesh, while the other lakes are located in Uttarakhand and Jammu and Kashmir.
Origin:
- The Guru Gobind Sagar Lake is a man-made reservoir, created by the Bhakra Dam on the Sutlej River. In contrast, the other lakes are natural or semi-natural.
Purpose:
- The Guru Gobind Sagar Lake was created primarily for hydroelectric power generation, irrigation, and drinking water supply. The other lakes do not have such a specific purpose.
Size:
- The Guru Gobind Sagar Lake is much larger than the other lakes, with a surface area of about 170 square kilometers. In comparison, Dal Lake has a surface area of about 18 square kilometers, Nainital Lake has a surface area of about 1.5 square kilometers, and Bhimtal Lake has a surface area of about 1.2 square kilometers.
Tourism:
- While the other lakes are popular tourist destinations, the Guru Gobind Sagar Lake is not as well-known as a tourist spot. It is mainly visited by people interested in water sports and fishing.
In conclusion, the Guru Gobind Sagar Lake differs from the rest of the lakes in the group due to its location, origin, purpose, size, and popularity as a tourist destination.
The western part of the northern plains is dominated by:- a)Doabs
- b)Bhabhar
- c)Terai
- d)Ox-bow lakes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The western part of the northern plains is dominated by:
a)
Doabs
b)
Bhabhar
c)
Terai
d)
Ox-bow lakes
|
|
Aditi Sharma answered |
The western part of the northern plains are dominated by the river Indus and its tributaries are responsible for forming it.
Which of the following features is the distinct feature of the Peninsular plateau?- a)Alluvial soil
- b)Bhabar
- c)Terai
- d)Black soil
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following features is the distinct feature of the Peninsular plateau?
a)
Alluvial soil
b)
Bhabar
c)
Terai
d)
Black soil
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
One of the distinct features of the peninsular plateau is the black soil area known as Deccan Trap.
Most of the Peninsular rivers are perennial.
- a)False
- b)True
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Most of the Peninsular rivers are perennial.
a)
False
b)
True
|
|
Aravind Jain answered |
False
Explanation:
Perennial rivers are those rivers which flow throughout the year. Most of the Peninsular rivers are not perennial in nature. These rivers depend on rainfall for their flow and hence, they dry up during summers. Some of the major Peninsular rivers such as Godavari, Krishna, Cauvery, etc. have a seasonal flow and are not perennial. However, some of the Peninsular rivers such as Narmada and Tapti have a perennial flow as they originate from the mountains and are not solely dependent on rainfall. Hence, the statement that most of the Peninsular rivers are perennial is false.
Explanation:
Perennial rivers are those rivers which flow throughout the year. Most of the Peninsular rivers are not perennial in nature. These rivers depend on rainfall for their flow and hence, they dry up during summers. Some of the major Peninsular rivers such as Godavari, Krishna, Cauvery, etc. have a seasonal flow and are not perennial. However, some of the Peninsular rivers such as Narmada and Tapti have a perennial flow as they originate from the mountains and are not solely dependent on rainfall. Hence, the statement that most of the Peninsular rivers are perennial is false.
Which one of the following water bodies separates Sri Lanka from India? - a)Palk Strait and Gulf of Khambat
- b)Palk Strait and Gulf of Mannar
- c)Gulf of Mannar and 10° Channel
- d)10° Channel and Gulf of Khambat
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following water bodies separates Sri Lanka from India?
a)
Palk Strait and Gulf of Khambat
b)
Palk Strait and Gulf of Mannar
c)
Gulf of Mannar and 10° Channel
d)
10° Channel and Gulf of Khambat
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Sri Lanka is separated from India by a narrow channel of sea formed by the Palk Strait and the Gulf of Mannar.
At which parallel of latitude does India begin to taper towards the south?- a)22° N
- b)23°30' N
- c)8°4 N
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
At which parallel of latitude does India begin to taper towards the south?
a)
22° N
b)
23°30' N
c)
8°4 N
d)
None of these
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
At 22°N latitude, India begins to taper towards South. The shape of India does begin to taper into a triangular shape. It extends into the Indian ocean and divides the ocean into two seas; the Arabian Sea to the West and the Bay of Bengal to the East.
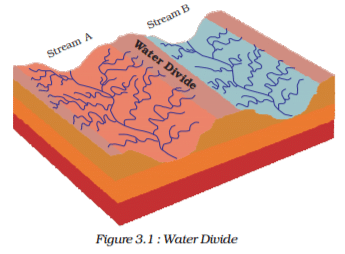
The area drained by a single river system is called a – - a)Water shed
- b)Drainage basin
- c)Water divide
- d)Drainage Line
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The area drained by a single river system is called a –
a)
Water shed
b)
Drainage basin
c)
Water divide
d)
Drainage Line
|
|
Ravi Verma answered |
The term drainage describes the river system of an area. Look at the physical map. You will notice that small streams flowing from different directions come together to form the main river, which ultimately drains into a large water body such as a lake or a sea or an ocean. The area drained by a single river system is called a drainage basin. A closer observation on a map will indicate that any elevated area, such as a mountain or an upland, separates two drainage basins. Such an upland is known as a water divide (Figure 3.1).
The Aravalis are young-fold mountains.- a)False
- b)True
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Aravalis are young-fold mountains.
a)
False
b)
True
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
In ancient times, Aravalli were extremely high but since have worn down almost completely by millions of years of weathering, where as the Himalayas being young fold mountains are still continuously rising.
Since the opening of the Suez Canal in 1869, India’s distance from Europe has been reduced by 7000 km.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Since the opening of the Suez Canal in 1869, India’s distance from Europe has been reduced by 7000 km.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Because, before the opening of Suez Canal, to reach Europe one had to cover almost half the east and whole of west coast of African continent taking a round through the Cape of Good Hope.
Which country shares land boundaries with India in the west?- a)China
- b)Nepal
- c)Bhutan
- d)Pakistan
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which country shares land boundaries with India in the west?
a)
China
b)
Nepal
c)
Bhutan
d)
Pakistan
|
|
Pranav Desai answered |
Land boundaries of India in the west
India is surrounded by seven countries and shares land boundaries with six of them. The country that shares land boundaries with India in the west is Pakistan.
India-Pakistan Border
The India-Pakistan border is one of the most significant borders in the world, and it is also known as the International Border (IB). The border between India and Pakistan runs through the states of Punjab, Rajasthan, and Gujarat. The length of the India-Pakistan border is approximately 3,323 km.
The India-Pakistan border is divided into three sectors: the Western Sector, the Eastern Sector, and the Northern Sector. The Western Sector stretches from Gujarat to Jammu, the Eastern Sector from Jammu to West Bengal, and the Northern Sector from Jammu to the Karakoram Pass.
The India-Pakistan border is a heavily guarded boundary, and there is a constant presence of military forces on both sides of the border. The border has witnessed many conflicts and skirmishes, and both countries have fought three major wars in 1947, 1965, and 1971.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Pakistan shares land boundaries with India in the west. The India-Pakistan border is one of the most significant borders in the world and has witnessed many conflicts and skirmishes. The border is heavily guarded, and both countries maintain a constant presence of military forces.
India is surrounded by seven countries and shares land boundaries with six of them. The country that shares land boundaries with India in the west is Pakistan.
India-Pakistan Border
The India-Pakistan border is one of the most significant borders in the world, and it is also known as the International Border (IB). The border between India and Pakistan runs through the states of Punjab, Rajasthan, and Gujarat. The length of the India-Pakistan border is approximately 3,323 km.
The India-Pakistan border is divided into three sectors: the Western Sector, the Eastern Sector, and the Northern Sector. The Western Sector stretches from Gujarat to Jammu, the Eastern Sector from Jammu to West Bengal, and the Northern Sector from Jammu to the Karakoram Pass.
The India-Pakistan border is a heavily guarded boundary, and there is a constant presence of military forces on both sides of the border. The border has witnessed many conflicts and skirmishes, and both countries have fought three major wars in 1947, 1965, and 1971.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Pakistan shares land boundaries with India in the west. The India-Pakistan border is one of the most significant borders in the world and has witnessed many conflicts and skirmishes. The border is heavily guarded, and both countries maintain a constant presence of military forces.
Which of the following country share a land boundary with India in the north?- a)Myanmar
- b)Sri Lanka
- c)Bangladesh
- d)Nepal
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following country share a land boundary with India in the north?
a)
Myanmar
b)
Sri Lanka
c)
Bangladesh
d)
Nepal
|
|
Sarika Singh answered |
**Explanation:**
India shares a land boundary with several countries in different directions. In the north, it shares a land boundary with Nepal.
**Nepal:**
- Nepal is a landlocked country located in the Himalayas, bordered by China to the north and India to the south, east, and west.
- The India-Nepal border is approximately 1,751 kilometers long and is defined by the Himalayan mountain range.
- The border between India and Nepal is open and allows for the free movement of people and goods between the two countries.
- Some of the major border crossings between India and Nepal include Sunauli-Bhairahawa, Raxaul-Birgunj, and Panitanki-Kakarbhitta.
The other options listed in the question do not share a land boundary with India in the north:
**Myanmar:**
- Myanmar is located to the east of India and shares a border with India's northeastern states of Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, and Mizoram.
- The border between India and Myanmar is defined by rivers, mountains, and forests.
**Sri Lanka:**
- Sri Lanka is an island nation located to the south of India, separated by the Palk Strait.
- There is no land boundary between India and Sri Lanka.
**Bangladesh:**
- Bangladesh is located to the east of India and shares a border with the Indian states of West Bengal, Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram.
- The India-Bangladesh border is defined by rivers, including the Brahmaputra, Ganges, and Meghna.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D, Nepal, as it shares a land boundary with India in the north.
India shares a land boundary with several countries in different directions. In the north, it shares a land boundary with Nepal.
**Nepal:**
- Nepal is a landlocked country located in the Himalayas, bordered by China to the north and India to the south, east, and west.
- The India-Nepal border is approximately 1,751 kilometers long and is defined by the Himalayan mountain range.
- The border between India and Nepal is open and allows for the free movement of people and goods between the two countries.
- Some of the major border crossings between India and Nepal include Sunauli-Bhairahawa, Raxaul-Birgunj, and Panitanki-Kakarbhitta.
The other options listed in the question do not share a land boundary with India in the north:
**Myanmar:**
- Myanmar is located to the east of India and shares a border with India's northeastern states of Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, and Mizoram.
- The border between India and Myanmar is defined by rivers, mountains, and forests.
**Sri Lanka:**
- Sri Lanka is an island nation located to the south of India, separated by the Palk Strait.
- There is no land boundary between India and Sri Lanka.
**Bangladesh:**
- Bangladesh is located to the east of India and shares a border with the Indian states of West Bengal, Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram.
- The India-Bangladesh border is defined by rivers, including the Brahmaputra, Ganges, and Meghna.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D, Nepal, as it shares a land boundary with India in the north.
Luni is the only river which drains the- a)Desert Region of India
- b)Peninsular Region
- c)Central Highland
- d)Malabar Coast
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Luni is the only river which drains the
a)
Desert Region of India
b)
Peninsular Region
c)
Central Highland
d)
Malabar Coast
|
|
Aditya Shah answered |
Luni is the river in Rajasthan. It originates in Pushkar valley of Aravali range near Ajmer, passes through the southeastern portion of the Thar Desert and ends in the marshy lands of Rann of Kutch in Gujarat after travelling a distance of 495 km.
In which of the following water bodies are Lakshadweep islands situated?- a)Arabian Sea
- b)Bay of Bengal
- c)Indian Ocean
- d)Atlantic Ocean
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following water bodies are Lakshadweep islands situated?
a)
Arabian Sea
b)
Bay of Bengal
c)
Indian Ocean
d)
Atlantic Ocean
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Lakshadweep, formerly the Laccadives, is a group of islands situated some 400 km off India's west coast in the Arabian sea. They are India's only coral atolls and geologically a part of the same chain as the Maldives.
Which of the following states suffer from loo?
- a)Gujarat
- b)Both (A) and (C)
- c)Uttar Pradesh
- d)Tamil Nadu
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following states suffer from loo?
a)
Gujarat
b)
Both (A) and (C)
c)
Uttar Pradesh
d)
Tamil Nadu
|
|
Bably Bhatt answered |
The summer, hot winds called loos blow across the plains during the day. Trees shed their leaves to avoid excessive moisture loss. The dry, hot weather is broken occasionally by dust storms and thunderstorms that temporarily lower the temperature.
Which of the following island groups of India lies to its south-east?- a)Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- b)Lakshadweep
- c)Daman and Diu
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following island groups of India lies to its south-east?
a)
Andaman and Nicobar Islands
b)
Lakshadweep
c)
Daman and Diu
d)
All the above
|
|
Ananya Yadav answered |
The correct answer is option 'A', which states that the Andaman and Nicobar Islands lie to the south-east of India.
Explanation:
India is a country in South Asia with a vast coastline that extends over 7,500 km. The country has several island groups located off its coast, which include:
1. Andaman and Nicobar Islands - These islands are a group of more than 500 islands located in the Bay of Bengal. The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are the only union territory of India that lies to the south-east of the country.
2. Lakshadweep - Lakshadweep is a group of islands located in the Arabian Sea. It is the smallest union territory of India and lies to the west of Kerala.
3. Daman and Diu - Daman and Diu are two small union territories located on the western coast of India. They are separated by the Gulf of Khambhat and lie to the north-west of the country.
Hence, the correct answer is option 'A', as the Andaman and Nicobar Islands lie to the south-east of India.
Explanation:
India is a country in South Asia with a vast coastline that extends over 7,500 km. The country has several island groups located off its coast, which include:
1. Andaman and Nicobar Islands - These islands are a group of more than 500 islands located in the Bay of Bengal. The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are the only union territory of India that lies to the south-east of the country.
2. Lakshadweep - Lakshadweep is a group of islands located in the Arabian Sea. It is the smallest union territory of India and lies to the west of Kerala.
3. Daman and Diu - Daman and Diu are two small union territories located on the western coast of India. They are separated by the Gulf of Khambhat and lie to the north-west of the country.
Hence, the correct answer is option 'A', as the Andaman and Nicobar Islands lie to the south-east of India.
Which Indian states have maximum and minimum forest cover area?- a)Arunachal Pradesh and Haryana
- b)Himachal Pradesh and Haryana
- c)Tripura and Rajasthan
- d)Manipur and Gujarat
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which Indian states have maximum and minimum forest cover area?
a)
Arunachal Pradesh and Haryana
b)
Himachal Pradesh and Haryana
c)
Tripura and Rajasthan
d)
Manipur and Gujarat
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
The state which have maximum forest cover area is arunachal pradesh and minimum is haryana
The total length of River Ganga drainage basin is- a)2500 km
- b)2900 km
- c)2700 km
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The total length of River Ganga drainage basin is
a)
2500 km
b)
2900 km
c)
2700 km
d)
None of these
|
|
Shail Kapoor answered |
Length of River Ganga Drainage Basin
The total length of River Ganga drainage basin is 2500 km.
Explanation
The River Ganga is one of the largest rivers in India and has a significant impact on the country's culture, economy, and environment. The river flows through several states in northern India, including Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, and West Bengal. The Ganga basin is also one of the most densely populated regions in the world.
The River Ganga drainage basin is the area of land drained by the river and its tributaries. The length of the drainage basin is measured from the source of the river in the Himalayas to the point where it meets the Bay of Bengal. The total length of the River Ganga drainage basin is approximately 2,500 km.
The River Ganga is considered holy by Hindus and is a significant pilgrimage site. It is also an essential source of water for agriculture, industry, and domestic use. However, the river is facing several challenges, including pollution, climate change, and overuse. The Indian government has launched several initiatives to clean up the river and prevent further degradation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the total length of the River Ganga drainage basin is 2,500 km. The river is an essential resource for India and its people, but it is also facing significant challenges. It is crucial to take steps to protect and preserve the river for future generations.
The total length of River Ganga drainage basin is 2500 km.
Explanation
The River Ganga is one of the largest rivers in India and has a significant impact on the country's culture, economy, and environment. The river flows through several states in northern India, including Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, and West Bengal. The Ganga basin is also one of the most densely populated regions in the world.
The River Ganga drainage basin is the area of land drained by the river and its tributaries. The length of the drainage basin is measured from the source of the river in the Himalayas to the point where it meets the Bay of Bengal. The total length of the River Ganga drainage basin is approximately 2,500 km.
The River Ganga is considered holy by Hindus and is a significant pilgrimage site. It is also an essential source of water for agriculture, industry, and domestic use. However, the river is facing several challenges, including pollution, climate change, and overuse. The Indian government has launched several initiatives to clean up the river and prevent further degradation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the total length of the River Ganga drainage basin is 2,500 km. The river is an essential resource for India and its people, but it is also facing significant challenges. It is crucial to take steps to protect and preserve the river for future generations.
Which of the following divisions of India has the oldest landmass?- a)The peninsular part
- b)The Himalayan mountain
- c)The Vindhya mountain
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following divisions of India has the oldest landmass?
a)
The peninsular part
b)
The Himalayan mountain
c)
The Vindhya mountain
d)
All the above
|
|
Gargi Das answered |
Oldest Landmass in India:
India has a diverse topography with different landforms and divisions. The country can be broadly divided into three geological divisions- the peninsular part, the Himalayan mountain range, and the Indo-Gangetic plain. Out of these three divisions, the peninsular part has the oldest landmass.
The Peninsular Part:
The peninsular part of India is a vast region that comprises the Deccan Plateau and the Eastern and Western Ghats. It covers the southern part of India and is surrounded by water on three sides- the Arabian Sea to the west, the Bay of Bengal to the east, and the Indian Ocean to the south.
The peninsular part of India is made up of ancient rocks, some of which are more than a billion years old. These rocks were formed during the Precambrian era and were part of the Gondwana landmass.
The peninsular region of India consists of several plateaus and hill ranges, including the Malwa Plateau, the Satpura Range, the Vindhya Range, and the Eastern and Western Ghats. These landforms have been formed due to various geological processes over millions of years.
The Himalayan Mountain Range:
The Himalayan mountain range is the youngest landform in India and is still being formed. The range is located in the northern part of India and stretches for over 2,400 kilometers from the Indus River in the west to the Brahmaputra River in the east.
The Himalayas were formed due to the collision of the Indian and Eurasian tectonic plates. This collision caused the upliftment of the Himalayan range, which is still continuing at a rate of 5mm to 10mm per year.
The Himalayan range is home to some of the highest peaks in the world, including Mount Everest, K2, and Kangchenjunga.
The Vindhya Mountain Range:
The Vindhya mountain range is a range of hills and mountains that stretches for over 1,000 kilometers across central India. The range separates the northern part of India from the Deccan Plateau.
The Vindhya range is made up of sedimentary rocks that were formed during the Cenozoic era. These rocks are relatively younger than the rocks in the peninsular part of India.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the peninsular part of India has the oldest landmass. The region is made up of ancient rocks that were formed during the Precambrian era and were part of the Gondwana landmass. The Himalayan range is the youngest landform in India and is still being formed, while the Vindhya range is relatively younger than the rocks in the peninsular part of India.
India has a diverse topography with different landforms and divisions. The country can be broadly divided into three geological divisions- the peninsular part, the Himalayan mountain range, and the Indo-Gangetic plain. Out of these three divisions, the peninsular part has the oldest landmass.
The Peninsular Part:
The peninsular part of India is a vast region that comprises the Deccan Plateau and the Eastern and Western Ghats. It covers the southern part of India and is surrounded by water on three sides- the Arabian Sea to the west, the Bay of Bengal to the east, and the Indian Ocean to the south.
The peninsular part of India is made up of ancient rocks, some of which are more than a billion years old. These rocks were formed during the Precambrian era and were part of the Gondwana landmass.
The peninsular region of India consists of several plateaus and hill ranges, including the Malwa Plateau, the Satpura Range, the Vindhya Range, and the Eastern and Western Ghats. These landforms have been formed due to various geological processes over millions of years.
The Himalayan Mountain Range:
The Himalayan mountain range is the youngest landform in India and is still being formed. The range is located in the northern part of India and stretches for over 2,400 kilometers from the Indus River in the west to the Brahmaputra River in the east.
The Himalayas were formed due to the collision of the Indian and Eurasian tectonic plates. This collision caused the upliftment of the Himalayan range, which is still continuing at a rate of 5mm to 10mm per year.
The Himalayan range is home to some of the highest peaks in the world, including Mount Everest, K2, and Kangchenjunga.
The Vindhya Mountain Range:
The Vindhya mountain range is a range of hills and mountains that stretches for over 1,000 kilometers across central India. The range separates the northern part of India from the Deccan Plateau.
The Vindhya range is made up of sedimentary rocks that were formed during the Cenozoic era. These rocks are relatively younger than the rocks in the peninsular part of India.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the peninsular part of India has the oldest landmass. The region is made up of ancient rocks that were formed during the Precambrian era and were part of the Gondwana landmass. The Himalayan range is the youngest landform in India and is still being formed, while the Vindhya range is relatively younger than the rocks in the peninsular part of India.
The river Narmada has its source at- a)Amarkantak
- b)Vindhya range
- c)Satpura range
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The river Narmada has its source at
a)
Amarkantak
b)
Vindhya range
c)
Satpura range
d)
All the above
|
|
Poulomi Chavan answered |
**The source of the river Narmada is Amarkantak.**
The river Narmada, one of the major rivers in India, originates from the Amarkantak plateau. It is located in the Maikal Mountains, which is part of the Vindhya Range. Amarkantak is a pilgrimage town situated at an altitude of around 1065 meters in the Anuppur district of Madhya Pradesh.
**Amarkantak**:
- Amarkantak is considered a sacred place by Hindus as it is believed to be the meeting point of the Vindhya Range and the Satpura Range, which are two important mountain ranges in central India.
- It is believed that the Narmada River emerges as a result of the union of two small streams, namely, the Sonbhadra and the Johila, at the origin point in Amarkantak.
- The Sonbhadra stream originates from the east while the Johila stream originates from the west. They converge at the Amarkantak plateau to form the Narmada River.
**Vindhya Range**:
- The Vindhya Range is a range of hills and mountains that runs parallel to the Narmada River in central India.
- It extends from eastern Gujarat through Madhya Pradesh and into southeastern Uttar Pradesh.
- The Vindhya Range acts as a watershed between the rivers flowing into the Arabian Sea and those flowing into the Bay of Bengal.
- It is a prominent feature in the landscape of central India and is known for its rich biodiversity and scenic beauty.
**Satpura Range**:
- The Satpura Range is another important mountain range in central India.
- It runs parallel to the Vindhya Range and forms the southern boundary of the Narmada River basin.
- The Satpura Range is known for its dense forests, wildlife sanctuaries, and hill stations.
- Several rivers, including the Tapti and the Narmada, originate from this range.
In conclusion, the river Narmada has its source at Amarkantak, which is located in the Maikal Mountains of the Vindhya Range. The belief that the Narmada River is formed by the union of the Sonbhadra and Johila streams at Amarkantak makes it a significant pilgrimage site for Hindus.
The river Narmada, one of the major rivers in India, originates from the Amarkantak plateau. It is located in the Maikal Mountains, which is part of the Vindhya Range. Amarkantak is a pilgrimage town situated at an altitude of around 1065 meters in the Anuppur district of Madhya Pradesh.
**Amarkantak**:
- Amarkantak is considered a sacred place by Hindus as it is believed to be the meeting point of the Vindhya Range and the Satpura Range, which are two important mountain ranges in central India.
- It is believed that the Narmada River emerges as a result of the union of two small streams, namely, the Sonbhadra and the Johila, at the origin point in Amarkantak.
- The Sonbhadra stream originates from the east while the Johila stream originates from the west. They converge at the Amarkantak plateau to form the Narmada River.
**Vindhya Range**:
- The Vindhya Range is a range of hills and mountains that runs parallel to the Narmada River in central India.
- It extends from eastern Gujarat through Madhya Pradesh and into southeastern Uttar Pradesh.
- The Vindhya Range acts as a watershed between the rivers flowing into the Arabian Sea and those flowing into the Bay of Bengal.
- It is a prominent feature in the landscape of central India and is known for its rich biodiversity and scenic beauty.
**Satpura Range**:
- The Satpura Range is another important mountain range in central India.
- It runs parallel to the Vindhya Range and forms the southern boundary of the Narmada River basin.
- The Satpura Range is known for its dense forests, wildlife sanctuaries, and hill stations.
- Several rivers, including the Tapti and the Narmada, originate from this range.
In conclusion, the river Narmada has its source at Amarkantak, which is located in the Maikal Mountains of the Vindhya Range. The belief that the Narmada River is formed by the union of the Sonbhadra and Johila streams at Amarkantak makes it a significant pilgrimage site for Hindus.
What is the rank of India among the population of different countries of the world?
- a)Second
- b)First
- c)Third
- d)Fourth
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the rank of India among the population of different countries of the world?
a)
Second
b)
First
c)
Third
d)
Fourth

|
Suyash Zunake answered |
Yes India was at the second position, but now it already crossed China in 2023. Now we r the highest populous country in the world.
Which canal shortened the distance between India and Europe?- a)Suez canal
- b)Gobind Sagar canal
- c)Chilika lake
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which canal shortened the distance between India and Europe?
a)
Suez canal
b)
Gobind Sagar canal
c)
Chilika lake
d)
All the above
|
|
Sakshi Das answered |
The correct answer is option 'A', Suez Canal.
Explanation:
The Suez Canal is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez. It was opened in November 1869, and since then it has shortened the distance between India and Europe. The canal has reduced the distance between the ports of Mumbai and London by approximately 7,000 kilometers. Before the Suez Canal, ships had to travel around the southern tip of Africa to reach Europe from India, which took a longer time and was more dangerous due to adverse weather conditions.
Advantages of the Suez Canal:
1. Reduced travel time: The Suez Canal has reduced the travel time between India and Europe by providing a direct route through the Isthmus of Suez.
2. Reduced transportation cost: The shorter distance and reduced travel time have reduced transportation costs significantly.
3. Boosted trade: The canal has boosted trade between India and Europe, as it has made the transportation of goods faster and cheaper.
4. Improved global connectivity: The Suez Canal has improved global connectivity by providing a direct route between the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea.
In conclusion, the Suez Canal has shortened the distance between India and Europe, reducing travel time, transportation costs, and boosting trade between the two regions.
Explanation:
The Suez Canal is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez. It was opened in November 1869, and since then it has shortened the distance between India and Europe. The canal has reduced the distance between the ports of Mumbai and London by approximately 7,000 kilometers. Before the Suez Canal, ships had to travel around the southern tip of Africa to reach Europe from India, which took a longer time and was more dangerous due to adverse weather conditions.
Advantages of the Suez Canal:
1. Reduced travel time: The Suez Canal has reduced the travel time between India and Europe by providing a direct route through the Isthmus of Suez.
2. Reduced transportation cost: The shorter distance and reduced travel time have reduced transportation costs significantly.
3. Boosted trade: The canal has boosted trade between India and Europe, as it has made the transportation of goods faster and cheaper.
4. Improved global connectivity: The Suez Canal has improved global connectivity by providing a direct route between the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea.
In conclusion, the Suez Canal has shortened the distance between India and Europe, reducing travel time, transportation costs, and boosting trade between the two regions.
Which of the following statement is not correct in respect of the population of India?- a)India has a very large population
- b)When a low annual rate is applied to a very large population, it yields a large absolute increase
- c)India’s annual increase in population is not enough to neutralise efforts to conserve the resource endowment and environment
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is not correct in respect of the population of India?
a)
India has a very large population
b)
When a low annual rate is applied to a very large population, it yields a large absolute increase
c)
India’s annual increase in population is not enough to neutralise efforts to conserve the resource endowment and environment
d)
None of the above
|
|
Raj Malik answered |
Has a high population growth rate compared to other countries
d)India's population is evenly distributed across all regions.
d)India's population is evenly distributed across all regions.
In which of the following places, the annual precipitation is over 400 cm?- a)UP
- b)West Bengal
- c)Meghalaya
- d)Madhya Pradesh
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following places, the annual precipitation is over 400 cm?
a)
UP
b)
West Bengal
c)
Meghalaya
d)
Madhya Pradesh
|
|
Amrutha Anoop answered |
The western coast and North-Eastern India receive over about 400 cm of rainfall annually. However, it is less than 60 cm in western Rajasthan and adjoining parts of Gujarat, Haryana and Punjab. Rainfall is equally low in the interior of the Deccan plateau, and east of the Sahyadris
Which of the following crops is associated with the winter rainfall?- a)Zaid
- b)Rabi
- c)Kharif
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following crops is associated with the winter rainfall?
a)
Zaid
b)
Rabi
c)
Kharif
d)
None of these
|
|
Partho Iyer answered |
Explanation:
The answer to the question is option B, which is "Rabi".
Explanation:
1. Rabi Crops:
Rabi crops are the crops that are sown in the winter season, which typically starts in October or November and lasts until March or April. These crops are associated with the winter rainfall, also known as the "northeast monsoon" or the "retreating monsoon". The winter rainfall is crucial for the growth and development of these crops.
Rabi crops include wheat, barley, oats, gram, mustard, peas, etc. These crops are well-adapted to the prevailing weather conditions during the winter season, and they require cool weather and a sufficient amount of water for their growth.
2. Kharif Crops:
Kharif crops, on the other hand, are sown in the rainy season, typically around June or July. These crops are associated with the southwest monsoon, which brings heavy rainfall to the regions during the summer season. Kharif crops include rice, maize, millet, cotton, etc.
3. Zaid Crops:
Zaid crops are the crops that are grown in the summer season, between the harvesting of the rabi crops and the sowing of the kharif crops. These crops are mainly grown in regions with sufficient irrigation facilities and are not dependent on monsoon rainfall. Zaid crops include watermelon, muskmelon, cucumber, bitter gourd, etc.
Conclusion:
Based on the above explanation, it is clear that the crop associated with winter rainfall is the "Rabi" crop. Rabi crops are sown in the winter season and require the winter rainfall for their growth and development.
The answer to the question is option B, which is "Rabi".
Explanation:
1. Rabi Crops:
Rabi crops are the crops that are sown in the winter season, which typically starts in October or November and lasts until March or April. These crops are associated with the winter rainfall, also known as the "northeast monsoon" or the "retreating monsoon". The winter rainfall is crucial for the growth and development of these crops.
Rabi crops include wheat, barley, oats, gram, mustard, peas, etc. These crops are well-adapted to the prevailing weather conditions during the winter season, and they require cool weather and a sufficient amount of water for their growth.
2. Kharif Crops:
Kharif crops, on the other hand, are sown in the rainy season, typically around June or July. These crops are associated with the southwest monsoon, which brings heavy rainfall to the regions during the summer season. Kharif crops include rice, maize, millet, cotton, etc.
3. Zaid Crops:
Zaid crops are the crops that are grown in the summer season, between the harvesting of the rabi crops and the sowing of the kharif crops. These crops are mainly grown in regions with sufficient irrigation facilities and are not dependent on monsoon rainfall. Zaid crops include watermelon, muskmelon, cucumber, bitter gourd, etc.
Conclusion:
Based on the above explanation, it is clear that the crop associated with winter rainfall is the "Rabi" crop. Rabi crops are sown in the winter season and require the winter rainfall for their growth and development.
Which of the following statements is correct about the Tropic of Cancer?- a)The Tropic of Cancer passes through the middle of Kerala
- b)The Tropic of Cancer passes through the middle of the country from Rann of Kuchchh in the west to Mizoram in the east
- c)The Tropic of Cancer passed through the middle of Delhi to Arunachal Pradesh
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is correct about the Tropic of Cancer?
a)
The Tropic of Cancer passes through the middle of Kerala
b)
The Tropic of Cancer passes through the middle of the country from Rann of Kuchchh in the west to Mizoram in the east
c)
The Tropic of Cancer passed through the middle of Delhi to Arunachal Pradesh
d)
None of the above
|
|
Samaira Reddy answered |
Tropic of Cancer and its location in India
What is Tropic of Cancer?
Tropic of Cancer is an imaginary line that circles the Earth at 23.5 degrees north of the Equator. This line marks the farthest northern point at which the Sun appears directly overhead at noon.
Location of Tropic of Cancer in India
The Tropic of Cancer passes through the middle of India, dividing it into two halves. It enters India through the Rann of Kutch in Gujarat in the west and moves towards the east passing through Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, West Bengal, and Tripura before leaving the Indian mainland at Mizoram.
Incorrect statements about Tropic of Cancer
Option A states that the Tropic of Cancer passes through the middle of Kerala, which is incorrect. Kerala is located south of the Tropic of Cancer.
Option C states that the Tropic of Cancer passes through the middle of Delhi to Arunachal Pradesh, which is also incorrect. While the Tropic of Cancer does pass through the state of Arunachal Pradesh, it does not pass through Delhi.
Correct statement about Tropic of Cancer
Option B states that the Tropic of Cancer passes through the middle of the country from Rann of Kuchchh in the west to Mizoram in the east, which is correct.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
What is Tropic of Cancer?
Tropic of Cancer is an imaginary line that circles the Earth at 23.5 degrees north of the Equator. This line marks the farthest northern point at which the Sun appears directly overhead at noon.
Location of Tropic of Cancer in India
The Tropic of Cancer passes through the middle of India, dividing it into two halves. It enters India through the Rann of Kutch in Gujarat in the west and moves towards the east passing through Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, West Bengal, and Tripura before leaving the Indian mainland at Mizoram.
Incorrect statements about Tropic of Cancer
Option A states that the Tropic of Cancer passes through the middle of Kerala, which is incorrect. Kerala is located south of the Tropic of Cancer.
Option C states that the Tropic of Cancer passes through the middle of Delhi to Arunachal Pradesh, which is also incorrect. While the Tropic of Cancer does pass through the state of Arunachal Pradesh, it does not pass through Delhi.
Correct statement about Tropic of Cancer
Option B states that the Tropic of Cancer passes through the middle of the country from Rann of Kuchchh in the west to Mizoram in the east, which is correct.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
An example of pull factor is ___________.- a)Hunger
- b)Education
- c)Health
- d)Employment
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An example of pull factor is ___________.
a)
Hunger
b)
Education
c)
Health
d)
Employment
|
|
Puja Dey answered |
Pull Factors: Explanation and Examples
Pull factors refer to the reasons or factors that attract people to move to a particular place or country. These factors are usually positive and can be economic, social, cultural or political in nature. Here are some examples of pull factors:
Employment Opportunities:
Employment opportunities are one of the main factors that attract people to move to another country or place. If a country or region has a strong economy with many job opportunities, people from other countries or regions will be attracted to move there. For example, people from developing countries often migrate to developed countries in search of better job opportunities and higher wages.
Education:
Education is another factor that can attract people to move to a particular place. If a place has a good education system with quality schools and universities, people will be attracted to move there to study. For example, many students from developing countries often move to developed countries to pursue higher education.
Healthcare:
Access to quality healthcare is also a pull factor that can attract people to move to a particular place. If a place has a good healthcare system with quality hospitals and medical facilities, people will be attracted to move there for better healthcare services. For example, people often migrate to developed countries with advanced healthcare systems for better medical care.
Cultural and Social Factors:
Cultural and social factors can also be a pull factor that attracts people to move to a particular place. If a place has a rich cultural heritage or is known for its tolerant and inclusive society, people will be attracted to move there to experience the culture and lifestyle. For example, people often migrate to cosmopolitan cities like New York or London for their diverse and multicultural environments.
In conclusion, pull factors are important in determining patterns of migration and population movement. People are often attracted to places that offer better economic, social, cultural or political opportunities and benefits. Understanding these factors is essential for policymakers to design effective migration policies and programs.
Pull factors refer to the reasons or factors that attract people to move to a particular place or country. These factors are usually positive and can be economic, social, cultural or political in nature. Here are some examples of pull factors:
Employment Opportunities:
Employment opportunities are one of the main factors that attract people to move to another country or place. If a country or region has a strong economy with many job opportunities, people from other countries or regions will be attracted to move there. For example, people from developing countries often migrate to developed countries in search of better job opportunities and higher wages.
Education:
Education is another factor that can attract people to move to a particular place. If a place has a good education system with quality schools and universities, people will be attracted to move there to study. For example, many students from developing countries often move to developed countries to pursue higher education.
Healthcare:
Access to quality healthcare is also a pull factor that can attract people to move to a particular place. If a place has a good healthcare system with quality hospitals and medical facilities, people will be attracted to move there for better healthcare services. For example, people often migrate to developed countries with advanced healthcare systems for better medical care.
Cultural and Social Factors:
Cultural and social factors can also be a pull factor that attracts people to move to a particular place. If a place has a rich cultural heritage or is known for its tolerant and inclusive society, people will be attracted to move there to experience the culture and lifestyle. For example, people often migrate to cosmopolitan cities like New York or London for their diverse and multicultural environments.
In conclusion, pull factors are important in determining patterns of migration and population movement. People are often attracted to places that offer better economic, social, cultural or political opportunities and benefits. Understanding these factors is essential for policymakers to design effective migration policies and programs.
Which of the following plays a major role in determining the climate of place?
- a)Altitude
- b)Relief
- c)Latitude
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following plays a major role in determining the climate of place?
a)
Altitude
b)
Relief
c)
Latitude
d)
None of these
|
|
Atharva Roy answered |
Importance of Relief in Determining Climate
Relief, also known as topography, plays a major role in determining the climate of a place, along with other factors such as latitude, altitude, wind patterns, ocean currents, and distance from the sea. Relief refers to the physical features of the land, such as mountains, valleys, and plateaus, which affect the distribution of temperature, precipitation, and vegetation.
Elevation and Temperature
One of the most important ways in which relief affects climate is through elevation. As altitude increases, temperature decreases, and vice versa. This is because air becomes thinner and less dense at higher altitudes, which means that it can hold less heat. Therefore, mountainous regions tend to be cooler than low-lying areas at the same latitude. For example, the Himalayas in Asia and the Andes in South America are much colder than the surrounding regions.
Mountain Barriers and Precipitation
Relief also affects precipitation patterns because mountains can act as barriers to the movement of air masses. When warm, moist air from the ocean encounters a mountain range, it is forced to rise and cool, which causes the water vapor to condense and form clouds. These clouds can then produce precipitation on the windward side of the mountain, which is the side facing the prevailing winds. The leeward side of the mountain, on the other hand, tends to be dry because the descending air is warmed and dries out.
Coastal vs. Inland Climate
Another way in which relief affects climate is through its influence on the proximity of a place to the sea. Coastal areas tend to have milder and more moderate climates than inland areas, which are subject to greater temperature extremes. This is because the sea has a moderating effect on temperature, which means that it takes longer to warm up and cool down than the land. Therefore, coastal areas have cooler summers and warmer winters than inland areas at the same latitude. Additionally, coastal areas tend to have higher humidity and more precipitation than inland areas because of the presence of moist sea air.
In conclusion, relief plays a major role in determining the climate of a place. It affects temperature, precipitation, and vegetation by influencing factors such as elevation, mountain barriers, and proximity to the sea. Therefore, it is important to consider relief when studying and predicting climate patterns.
Relief, also known as topography, plays a major role in determining the climate of a place, along with other factors such as latitude, altitude, wind patterns, ocean currents, and distance from the sea. Relief refers to the physical features of the land, such as mountains, valleys, and plateaus, which affect the distribution of temperature, precipitation, and vegetation.
Elevation and Temperature
One of the most important ways in which relief affects climate is through elevation. As altitude increases, temperature decreases, and vice versa. This is because air becomes thinner and less dense at higher altitudes, which means that it can hold less heat. Therefore, mountainous regions tend to be cooler than low-lying areas at the same latitude. For example, the Himalayas in Asia and the Andes in South America are much colder than the surrounding regions.
Mountain Barriers and Precipitation
Relief also affects precipitation patterns because mountains can act as barriers to the movement of air masses. When warm, moist air from the ocean encounters a mountain range, it is forced to rise and cool, which causes the water vapor to condense and form clouds. These clouds can then produce precipitation on the windward side of the mountain, which is the side facing the prevailing winds. The leeward side of the mountain, on the other hand, tends to be dry because the descending air is warmed and dries out.
Coastal vs. Inland Climate
Another way in which relief affects climate is through its influence on the proximity of a place to the sea. Coastal areas tend to have milder and more moderate climates than inland areas, which are subject to greater temperature extremes. This is because the sea has a moderating effect on temperature, which means that it takes longer to warm up and cool down than the land. Therefore, coastal areas have cooler summers and warmer winters than inland areas at the same latitude. Additionally, coastal areas tend to have higher humidity and more precipitation than inland areas because of the presence of moist sea air.
In conclusion, relief plays a major role in determining the climate of a place. It affects temperature, precipitation, and vegetation by influencing factors such as elevation, mountain barriers, and proximity to the sea. Therefore, it is important to consider relief when studying and predicting climate patterns.
Chapter doubts & questions for Class 9 Geography - Old & New NCERTs for IAS Preparation (Must Read) 2025 is part of UPSC CSE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the UPSC CSE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for UPSC CSE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Class 9 Geography - Old & New NCERTs for IAS Preparation (Must Read) in English & Hindi are available as part of UPSC CSE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UPSC CSE Exam by signing up for free.
Old & New NCERTs for IAS Preparation (Must Read)
3 videos|706 docs|517 tests
|
Related UPSC CSE Content
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup