All Exams >
JEE >
Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced >
All Questions
All questions of Organic Chemistry for JEE Exam
PVC is a type of:- a)Homopolymers
- b)Synthetic polymer
- c)Natural rubber
- d)Addition polymer
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
PVC is a type of:
a)
Homopolymers
b)
Synthetic polymer
c)
Natural rubber
d)
Addition polymer
|
|
Priyanshu Intelligent answered |
Polyvinyl chloride colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). ... PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
Name the monomer of nylon-6:- a)hexamethylene
- b)ethylene glycol
- c)Caprolactum
- d)Ethene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Name the monomer of nylon-6:
a)
hexamethylene
b)
ethylene glycol
c)
Caprolactum
d)
Ethene
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The correct answer is Option C.
Nylon 6 is synthesized by ring-opening polymerization of caprolactam. Caprolactam has 6 carbons, hence Nylon 6.
Nylon 6 is synthesized by ring-opening polymerization of caprolactam. Caprolactam has 6 carbons, hence Nylon 6.
The IUPAC name of CH3CHO is:- a)Acetaldehyde
- b)Ethanal
- c)Formaldehyde
- d)Methanal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name of CH3CHO is:
a)
Acetaldehyde
b)
Ethanal
c)
Formaldehyde
d)
Methanal

|
Ambition Institute answered |
- The functional group is an aldehyde; −CHO and the given compound has two carbon atoms.
- Thus, the IUPAC name of the compound is ethanal.
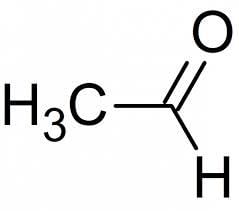
C5H11Br is least soluble in:- a)Ether
- b)Alcohol
- c)Water
- d)None of these
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
C5H11Br is least soluble in:
a)
Ether
b)
Alcohol
c)
Water
d)
None of these
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
C5H11Br is only very slightly soluble in water. It is more soluble in organic solvents.
Write the IUPAC name of (CH3)2CHCHO?- a)2,2-Dimethylpropanal
- b)3-Hydroxypropanal
- c)But-3-en-2-one
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Write the IUPAC name of (CH3)2CHCHO?
a)
2,2-Dimethylpropanal
b)
3-Hydroxypropanal
c)
But-3-en-2-one
d)
None of these
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
The IUPAC name of (CH3)2CHCHO is 2-methylpropanal and its chemical name is Isobutyraldehyde.
Which of the following is not true about optical isomers?- a)They rotate the plane polarized light.
- b)They are superimposable on their mirror image.
- c)They posses at least one chiral carbon atom.
- d)They are nonsuperimposable on their mirror image.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not true about optical isomers?
a)
They rotate the plane polarized light.
b)
They are superimposable on their mirror image.
c)
They posses at least one chiral carbon atom.
d)
They are nonsuperimposable on their mirror image.
|
|
Nisha Pillai answered |
Explanation:
Optical isomers are stereoisomers that exist in two mirror-image forms that are non-superimposable on each other. They are also known as enantiomers.
a) They rotate the plane polarized light: Optical isomers have the property of rotating the plane of polarized light in opposite directions. One isomer rotates the plane of polarized light in the clockwise direction and the other in the counterclockwise direction.
b) They are superimposable on their mirror image: This statement is false. Optical isomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. If we try to superimpose them, they will not match perfectly.
c) They possess at least one chiral carbon atom: Optical isomers possess chiral carbon atoms. Chiral carbon atoms are those carbon atoms that are attached to four different groups or atoms.
d) They are nonsuperimposable on their mirror image: As mentioned earlier, optical isomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. They have the same physical and chemical properties but differ in their biological activity, as they interact differently with other chiral molecules in living organisms.
Conclusion: Optical isomers are important in fields like medicinal chemistry, where knowing the activity of each isomer can help in designing drugs that are more effective and have fewer side effects. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the properties of optical isomers.
Optical isomers are stereoisomers that exist in two mirror-image forms that are non-superimposable on each other. They are also known as enantiomers.
a) They rotate the plane polarized light: Optical isomers have the property of rotating the plane of polarized light in opposite directions. One isomer rotates the plane of polarized light in the clockwise direction and the other in the counterclockwise direction.
b) They are superimposable on their mirror image: This statement is false. Optical isomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. If we try to superimpose them, they will not match perfectly.
c) They possess at least one chiral carbon atom: Optical isomers possess chiral carbon atoms. Chiral carbon atoms are those carbon atoms that are attached to four different groups or atoms.
d) They are nonsuperimposable on their mirror image: As mentioned earlier, optical isomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. They have the same physical and chemical properties but differ in their biological activity, as they interact differently with other chiral molecules in living organisms.
Conclusion: Optical isomers are important in fields like medicinal chemistry, where knowing the activity of each isomer can help in designing drugs that are more effective and have fewer side effects. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the properties of optical isomers.
Synthesis of protein is controlled by:- a)Nucleotide
- b)RNA
- c)DNA
- d)Nucleoside
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Synthesis of protein is controlled by:
a)
Nucleotide
b)
RNA
c)
DNA
d)
Nucleoside
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
RNA can directly control the synthesis of proteins, hence can easily express the characters. DNA, however, is dependent on RNA for synthesis of proteins. The protein synthesising machinery has evolved around RNA.
Which of the following is a tertiary halogenoalkanes?- a)2-Bromopentane
- b)2-Bromo 3-methylpentane
- c)Bromopentane
- d)2-Bromo 2-methylpentane
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a tertiary halogenoalkanes?
a)
2-Bromopentane
b)
2-Bromo 3-methylpentane
c)
Bromopentane
d)
2-Bromo 2-methylpentane
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
√Br CH3 -( CH )- CH2 - CH2 - CH3 √CH3 The carbon with which the Br is bonded is bonded with another 3 carbon atoms. So haloalkane is 3.
The drug which can act both as an analgesic and antipyretic is- a)Valium
- b)Aspirin
- c)Equanil
- d)Zantac
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The drug which can act both as an analgesic and antipyretic is
a)
Valium
b)
Aspirin
c)
Equanil
d)
Zantac
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Aspirin (Acetyl salicylic acid) is a chemical substance which lowers body temperature and reduces pain as well. Therefore it acts both as analgesic and antipyretic.
Which of the following statements are correct in case of the carbonyl bond between carbon and oxygen?- a)Carbon is the nucleophilic centre and Oxygen is the electrophilic centre.
- b)Oxygen is the nucleophilic centre and Carbon is the electrophilic centre.
- c)Carbon and Oxygen double bond is polarised.
- d)Both ‘b’ and ‘c’ are correct
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements are correct in case of the carbonyl bond between carbon and oxygen?
a)
Carbon is the nucleophilic centre and Oxygen is the electrophilic centre.
b)
Oxygen is the nucleophilic centre and Carbon is the electrophilic centre.
c)
Carbon and Oxygen double bond is polarised.
d)
Both ‘b’ and ‘c’ are correct
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The double bonds in alkenes and double bonds in carbonyl groups are VERY different in terms of reactivity. The C=C is less reactive due to C=O electronegativity attributed to the oxygen and its two lone pairs of electrons. One pair of the oxygen lone pairs are located in 2s while the other pair are in 2p orbital where its axis is directed perpendicular to the direction of the pi orbitals. The Carbonyl groups properties are directly tied to its electronic structure as well as geometric positioning. For example, the electronegativity of oxygen also polarizes the pi bond allowing the single bonded substituent connected to become electron withdrawing.
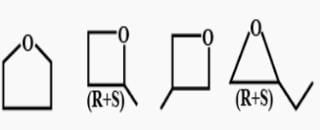
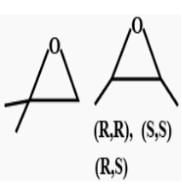
If chlorocyclohexane is subjected to further chlorination, how many different isomers (geometrical plus structural only) of dichiorocyclohexane would be produced? - a)3
- b)5
- c)6
- d)7
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If chlorocyclohexane is subjected to further chlorination, how many different isomers (geometrical plus structural only) of dichiorocyclohexane would be produced?
a)
3
b)
5
c)
6
d)
7

|
Learners Habitat answered |
The correct answer is option D
There will be three constitutional isomers i.e. 1,2 dichloro cyclohexane,1,3 dichloro cyclohexane and1,4 dichloro cyclohexane.Each constitutional isomer will have cis and trans configuration thereby making six isomers in all.Also there will be two optically active isomers.
You can understand it better through these infographics
1,2 dichloro cyclohexane
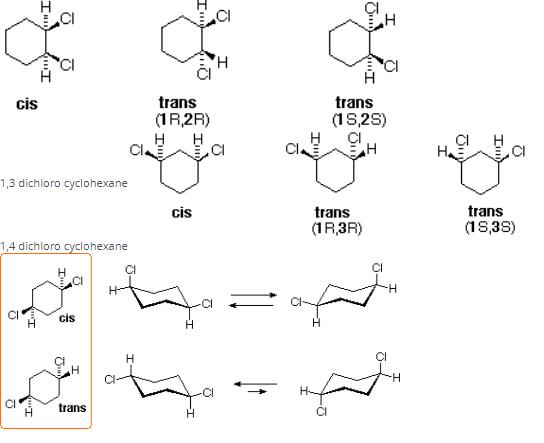
There will be three constitutional isomers i.e. 1,2 dichloro cyclohexane,1,3 dichloro cyclohexane and1,4 dichloro cyclohexane.Each constitutional isomer will have cis and trans configuration thereby making six isomers in all.Also there will be two optically active isomers.
You can understand it better through these infographics
1,2 dichloro cyclohexane
Which of the following statement about C=O and C=C is correct?- a)Both consist of a sigma and pi bond
- b)C=O is polar but C=C is non-polar
- c)Both a and b are correct
- d)Both C=O and C=C undergo nucleophilic addition reactions
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement about C=O and C=C is correct?
a)
Both consist of a sigma and pi bond
b)
C=O is polar but C=C is non-polar
c)
Both a and b are correct
d)
Both C=O and C=C undergo nucleophilic addition reactions

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
- The first bond formed is a sigma bind and the second one is a pi bond.
- O has a higher electronegativity than C and hence the electron cloud will be shifted towards the O atom, making the compound polar.
- This is not possible in C=C.
The reaction of CH3OC2H5 with one mole HI gives- a)CH3OH
- b)C2H5OH
- c)CH3I + C2H5OH
- d)C2H5I + CH3OH
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction of CH3OC2H5 with one mole HI gives
a)
CH3OH
b)
C2H5OH
c)
CH3I + C2H5OH
d)
C2H5I + CH3OH
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The correct answer is option C
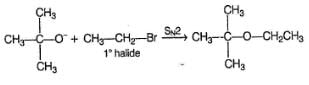
When ethers are treated with a strong acid in the presence of a nucleophile, they can be cleaved to give alcohols and alkyl halides. If the ether is on a primary carbon this may occur through an SN2 pathway. The reaction of CH3OC2H5 with HI gives CH3I+C2H5OH.
When ethers are treated with a strong acid in the presence of a nucleophile, they can be cleaved to give alcohols and alkyl halides. If the ether is on a primary carbon this may occur through an SN2 pathway. The reaction of CH3OC2H5 with HI gives CH3I+C2H5OH.
A broad spectrum antibiotic is:a)Paracetamolb)Ampicillinc)Aspirind)PenicillinCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
A broad-spectrum antibiotic acts against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, in contrast to a narrow-spectrum antibiotic, which is effective against specific families of bacteria. An example of a commonly used broad-spectrum antibiotic is ampicillin.
C2H5OH and CH3OCH3 are:- a)Position isomers
- b)Functional isomers
- c)Chain isomer
- d)Metamers
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
C2H5OH and CH3OCH3 are:
a)
Position isomers
b)
Functional isomers
c)
Chain isomer
d)
Metamers
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
Alkyl alcohol and ether having same molecular formula ( Here C2H6O) are functional isomers of each other. As both having different functional group first one has -OH & second one has -O- functional group in the same carbon chain respectively .
Among the following functional groups, which of these is not a carbonyl compound?- a)alcohols
- b)aldehydes
- c)Carboxylic acid
- d)ketones
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following functional groups, which of these is not a carbonyl compound?
a)
alcohols
b)
aldehydes
c)
Carboxylic acid
d)
ketones
|
|
Pari answered |
In carbonyl compound C=O is present bt in alchol OH is present. So alchol is not a carbonyl compound
Which intermolecular force is present in Nylon 6,6?- a)Copolymers
- b)Hydrogen bonding
- c)Dipole-dipole interaction
- d)van der Waals forces
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which intermolecular force is present in Nylon 6,6?
a)
Copolymers
b)
Hydrogen bonding
c)
Dipole-dipole interaction
d)
van der Waals forces
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
Van der Waals forces include attraction and repulsions between atoms, molecules, and surfaces.
Hydrogen bonding is a special type of attraction between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as N, O, or F atom and another very electronegative atom.
Dipole-dipole interactions occur when the partial charges formed within one molecule are attracted to an opposite partial charge in a nearby molecule.
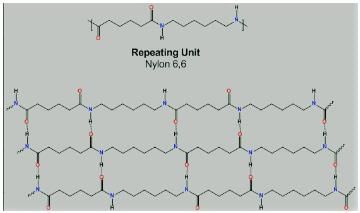
From the picture of Nylon-6,6, we can see there is hydrogen bonding between oxygen and hydrogen atom.
Though hydrogen bonds are also one type of dipole-dipole attraction, here, a more appropriate answer will be - The intermolecular forces present in nylon-6,6 are hydrogen bonding.
Hydrogen bonding is a special type of attraction between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as N, O, or F atom and another very electronegative atom.
Dipole-dipole interactions occur when the partial charges formed within one molecule are attracted to an opposite partial charge in a nearby molecule.

From the picture of Nylon-6,6, we can see there is hydrogen bonding between oxygen and hydrogen atom.
Though hydrogen bonds are also one type of dipole-dipole attraction, here, a more appropriate answer will be - The intermolecular forces present in nylon-6,6 are hydrogen bonding.

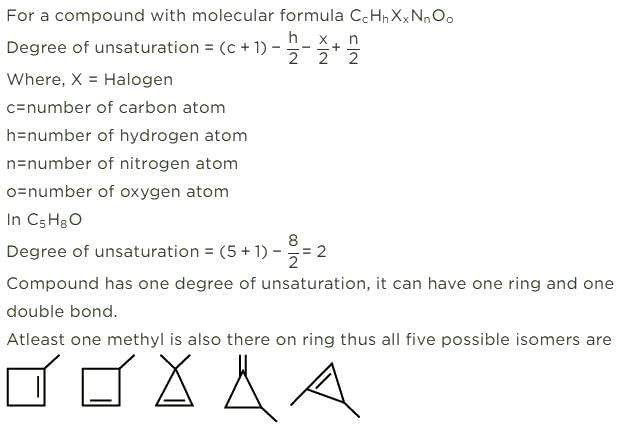
- a)3
- b)4
- c)5
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
3
b)
4
c)
5
d)
6
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
General formula of ketone = CnH2nO
12x+2x+16 = 100
x = 6
So, the formula of compound is C6H12O. We have to make ketone only. These are as follow
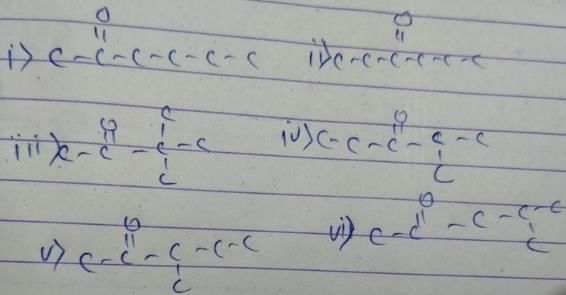
12x+2x+16 = 100
x = 6
So, the formula of compound is C6H12O. We have to make ketone only. These are as follow
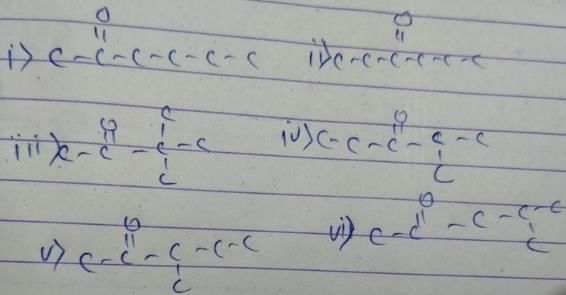
Acetone is isomeric to:- a)n-propyl alcohol
- b)propanal
- c)ethyl methyl ether
- d)isopropyl alcohol
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Acetone is isomeric to:
a)
n-propyl alcohol
b)
propanal
c)
ethyl methyl ether
d)
isopropyl alcohol
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Acetone (CH3COCH3) and Propanal (CH3CH2CHO) are functional isomers.
- Acetone:
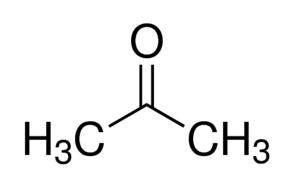
- Propanal:

In amines ,the hybridisation state of N is:- a)sp
- b)sp2d
- c)sp2
- d)sp3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In amines ,the hybridisation state of N is:
a)
sp
b)
sp2d
c)
sp2
d)
sp3
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Hybridisation of N in amine is sp3 with nitrogen having a one pair and 3 bond pair. Remember that amine is RR’R”N where R, R’ and R” may be alkyl or hydrogen.
Drugs which can block the binding site of the enzyme and prevent the binding of substrate, or can inhibit the catalytic activity of the enzyme are called as:- a)Catalytic inhibitors
- b)Enzyme inhibitors
- c)Chemical inhibitors
- d)Enzyme receptors
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Drugs which can block the binding site of the enzyme and prevent the binding of substrate, or can inhibit the catalytic activity of the enzyme are called as:
a)
Catalytic inhibitors
b)
Enzyme inhibitors
c)
Chemical inhibitors
d)
Enzyme receptors
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and decreases its activity. Since blocking an enzyme's activity can kill a pathogen or correct a metabolic imbalance, many drugs are enzyme inhibitors. They are also used in pesticides.
The essential amino acid is:- a)Serine
- b)Arginine
- c)Alanine
- d)Glycine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The essential amino acid is:
a)
Serine
b)
Arginine
c)
Alanine
d)
Glycine
|
|
Ritika Sengupta answered |
Essential Amino Acids
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. There are 20 different amino acids that make up proteins, and they can be classified into two groups: essential and non-essential.
- Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained through the diet.
- Non-essential amino acids can be synthesized by the body.
Arginine as an Essential Amino Acid
Arginine is one of the essential amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained through the diet.
Functions of Arginine
Arginine has several important functions in the body, including:
- Acting as a precursor for the synthesis of nitric oxide, which helps to relax blood vessels and improve blood flow.
- Stimulating the release of growth hormone, which is important for muscle growth and repair.
- Supporting immune function.
- Playing a role in wound healing.
Food Sources of Arginine
Arginine can be found in a variety of foods, including:
- Meat and poultry
- Fish and seafood
- Dairy products
- Nuts and seeds
- Legumes and beans
Conclusion
Arginine is an essential amino acid that plays important roles in the body, including supporting immune function, stimulating growth hormone release, and aiding in wound healing. It can be obtained through a variety of dietary sources, including meat, fish, dairy, nuts, and legumes.
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. There are 20 different amino acids that make up proteins, and they can be classified into two groups: essential and non-essential.
- Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained through the diet.
- Non-essential amino acids can be synthesized by the body.
Arginine as an Essential Amino Acid
Arginine is one of the essential amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained through the diet.
Functions of Arginine
Arginine has several important functions in the body, including:
- Acting as a precursor for the synthesis of nitric oxide, which helps to relax blood vessels and improve blood flow.
- Stimulating the release of growth hormone, which is important for muscle growth and repair.
- Supporting immune function.
- Playing a role in wound healing.
Food Sources of Arginine
Arginine can be found in a variety of foods, including:
- Meat and poultry
- Fish and seafood
- Dairy products
- Nuts and seeds
- Legumes and beans
Conclusion
Arginine is an essential amino acid that plays important roles in the body, including supporting immune function, stimulating growth hormone release, and aiding in wound healing. It can be obtained through a variety of dietary sources, including meat, fish, dairy, nuts, and legumes.
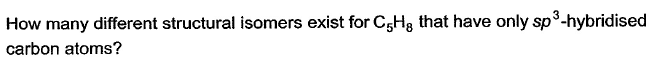
- a)3
- b)4
- c)5
- d)7
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
3
b)
4
c)
5
d)
7
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The compounds with each doubly bonded carbon attached to two different groups (like Cab=Cab, Cab=Ccd) exhibit geometrical isomerism i.e., cis and trans forms. The geometrical isomerism arises due to restricted rotation of double bond.
However, even though there is restricted rotation for triple bond, alkynes do not exhibit geometrical isomerism, since the triply bonded carbons are attached to one group each only.
Deficiency of vitamin A results in:- a)Scurvy
- b)Night blindness
- c)Beri-beri
- d)Rickets
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Deficiency of vitamin A results in:
a)
Scurvy
b)
Night blindness
c)
Beri-beri
d)
Rickets
|
|
Mr.perfect answered |
Yup... causes hardening of cornea.
Which of the following is intermediate in Sandmeyer’s reaction?- a)Diazonium salt
- b)Hydronium ion
- c)Ammonium salt
- d)Nitronium ion
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is intermediate in Sandmeyer’s reaction?
a)
Diazonium salt
b)
Hydronium ion
c)
Ammonium salt
d)
Nitronium ion
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Diazonium salt is intermediate in Sandmeyer’s reaction.
What is the major bromination product in the following reaction? 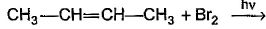
- a)
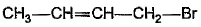
- b)
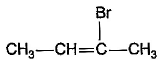
- c)
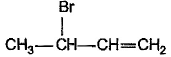
- d)
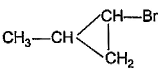
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the major bromination product in the following reaction?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
The correct answer is option c
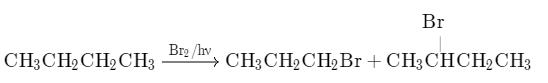
Thus, a racemic mixture is obtained. A racemic mixture is one that has an equal amount of left and right handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule.
Thus, a racemic mixture is obtained. A racemic mixture is one that has an equal amount of left and right handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule.
Phenol is acidic due to resonance stabilization of its conjugate base :- a)O-H
- b)Benzyl alcohol
- c)Alkoxide ion
- d)Phenoxide ion
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Phenol is acidic due to resonance stabilization of its conjugate base :
a)
O-H
b)
Benzyl alcohol
c)
Alkoxide ion
d)
Phenoxide ion
|
|
Rishika Patel answered |
Polarity of Phenol
Phenol, also known as benzenol or carbolic acid, is an aromatic compound that consists of a benzene ring bonded to a hydroxyl group (-OH). The presence of the hydroxyl group makes phenol a polar molecule because oxygen is more electronegative than carbon and hydrogen.
Acidity of Phenol
Phenol is considered an acid because it can donate a proton (H+) and form a conjugate base. The acidity of phenol is attributed to resonance stabilization of its conjugate base, the phenoxide ion.
Resonance Stabilization of Phenoxide Ion
When phenol loses a proton, it forms the phenoxide ion (C6H5O-). The phenoxide ion is resonance stabilized, which means that the negative charge can be delocalized over the entire ring system through resonance structures.
Resonance Structures of Phenoxide Ion
The resonance structures of the phenoxide ion can be represented as follows:
1. In the first resonance structure, the lone pair on the oxygen atom forms a double bond with carbon, while the negative charge is located on the oxygen atom.
2. In the second resonance structure, the lone pair on the oxygen atom forms a double bond with one of the carbon atoms in the ring, while the negative charge is located on that carbon atom.
3. In the third resonance structure, the lone pair on the oxygen atom forms a double bond with another carbon atom in the ring, while the negative charge is located on that carbon atom.
The resonance structures demonstrate that the negative charge of the phenoxide ion is delocalized over the entire ring system, resulting in stability.
Comparison with Other Options
a) O-H: The O-H bond in phenol is the source of acidity, but it does not explain the resonance stabilization of the conjugate base.
b) Benzyl alcohol: While benzyl alcohol also has an -OH group, it lacks the aromatic ring required for resonance stabilization of the conjugate base.
c) Alkoxide ion: Alkoxide ions are formed when an alcohol loses a proton, but they do not have the same resonance stabilization as the phenoxide ion.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'D' (Phenoxide ion) because the resonance stabilization of the phenoxide ion is responsible for the acidity of phenol. The delocalization of the negative charge over the aromatic ring system increases the stability of the conjugate base, making phenol acidic.
Phenol, also known as benzenol or carbolic acid, is an aromatic compound that consists of a benzene ring bonded to a hydroxyl group (-OH). The presence of the hydroxyl group makes phenol a polar molecule because oxygen is more electronegative than carbon and hydrogen.
Acidity of Phenol
Phenol is considered an acid because it can donate a proton (H+) and form a conjugate base. The acidity of phenol is attributed to resonance stabilization of its conjugate base, the phenoxide ion.
Resonance Stabilization of Phenoxide Ion
When phenol loses a proton, it forms the phenoxide ion (C6H5O-). The phenoxide ion is resonance stabilized, which means that the negative charge can be delocalized over the entire ring system through resonance structures.
Resonance Structures of Phenoxide Ion
The resonance structures of the phenoxide ion can be represented as follows:
1. In the first resonance structure, the lone pair on the oxygen atom forms a double bond with carbon, while the negative charge is located on the oxygen atom.
2. In the second resonance structure, the lone pair on the oxygen atom forms a double bond with one of the carbon atoms in the ring, while the negative charge is located on that carbon atom.
3. In the third resonance structure, the lone pair on the oxygen atom forms a double bond with another carbon atom in the ring, while the negative charge is located on that carbon atom.
The resonance structures demonstrate that the negative charge of the phenoxide ion is delocalized over the entire ring system, resulting in stability.
Comparison with Other Options
a) O-H: The O-H bond in phenol is the source of acidity, but it does not explain the resonance stabilization of the conjugate base.
b) Benzyl alcohol: While benzyl alcohol also has an -OH group, it lacks the aromatic ring required for resonance stabilization of the conjugate base.
c) Alkoxide ion: Alkoxide ions are formed when an alcohol loses a proton, but they do not have the same resonance stabilization as the phenoxide ion.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'D' (Phenoxide ion) because the resonance stabilization of the phenoxide ion is responsible for the acidity of phenol. The delocalization of the negative charge over the aromatic ring system increases the stability of the conjugate base, making phenol acidic.
Which polymerisation occurs among the molecules containing double bonds?- a)Condensation polymerization
- b)Natural polymer
- c)Synthetic polymer
- d)Addition polymer
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which polymerisation occurs among the molecules containing double bonds?
a)
Condensation polymerization
b)
Natural polymer
c)
Synthetic polymer
d)
Addition polymer
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Addition polymerization takes place when the monomer molecule contains double carbon bonds, as in alkenes, or triple carbon bonds, as in alkynes. In this lesson we will consider alkene monomers.
The enzyme pepsin hydrolyses:- a)polysaccharides to monosaccharides
- b)glucose to ethyl alcohol
- c)proteins to amino acids
- d)fats to fatty acids
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The enzyme pepsin hydrolyses:
a)
polysaccharides to monosaccharides
b)
glucose to ethyl alcohol
c)
proteins to amino acids
d)
fats to fatty acids
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option C
Pepsin hydrolyses proteins to amino acid(polypeptide chains) and initiates protein digestion in the digestion process in humans.
Pepsin hydrolyses proteins to amino acid(polypeptide chains) and initiates protein digestion in the digestion process in humans.
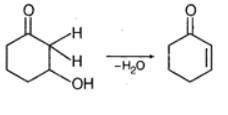
Maximum dehydration takes place that of [aieee-2002]- a)
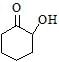
- b)
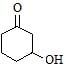
- c)
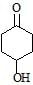
- d)
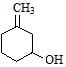
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Maximum dehydration takes place that of [aieee-2002]
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Dehydrated product will be conjugated with −C=O that's why more tendency and as carbocation is more stable further to C=O that's why (b)

Alpha helix is found in- a)RNA
- b)Lipid
- c)Carbohydrates
- d)secondary proteins
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Alpha helix is found in
a)
RNA
b)
Lipid
c)
Carbohydrates
d)
secondary proteins
|
|
Ræjû Bhæï answered |
The alpha helix (α-helix) is a common motif in the secondary structure of proteins and is a right hand-helix conformation in which every backbone N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone C=O. group of the amino acid located three or four residues earlier along the protein sequence.
Paul Muller of Geigy Pharmaceuticals in Switzerland discovered the effectiveness of DDT as:- a)Insecticides
- b)Fertilizers
- c)Anaesthetics
- d)Antiseptics
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Paul Muller of Geigy Pharmaceuticals in Switzerland discovered the effectiveness of DDT as:
a)
Insecticides
b)
Fertilizers
c)
Anaesthetics
d)
Antiseptics
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
Paul Hermann Muller, Swiss chemist who received the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1948 for discovering the potent toxic effects on insects of DDT. With its chemical derivatives, DDT became the most widely used insecticide for more than 20 years and was a major factor in increased world food production and the suppression of insect-borne diseases.
Paul Hermann Muller, Swiss chemist who received the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1948 for discovering the potent toxic effects on insects of DDT. With its chemical derivatives, DDT became the most widely used insecticide for more than 20 years and was a major factor in increased world food production and the suppression of insect-borne diseases.
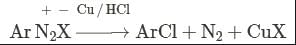
- a)Sandmeyers reaction
- b)Gattermanns reaction
- c)Dehydrogenation reaction
- d)Esterification reaction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
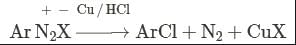
a)
Sandmeyers reaction
b)
Gattermanns reaction
c)
Dehydrogenation reaction
d)
Esterification reaction
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
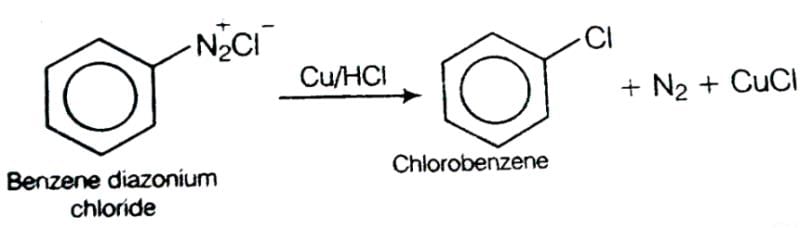 This reaction is called Gattermann reaction. In this reaction, Cl, Br and CN can be introduced into the benzene ring by simply treating diazonium salts with HCl, HBr, KCN. Respectively in presnce of copper powder instead of using Cu(I) salts.
This reaction is called Gattermann reaction. In this reaction, Cl, Br and CN can be introduced into the benzene ring by simply treating diazonium salts with HCl, HBr, KCN. Respectively in presnce of copper powder instead of using Cu(I) salts.Propanone and prop-2-en-1-ol are examples of which type of isomerism?
- a)Functional isomers
- b)Chain isomers
- c)Tautomers
- d)Position isomers
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Propanone and prop-2-en-1-ol are examples of which type of isomerism?
a)
Functional isomers
b)
Chain isomers
c)
Tautomers
d)
Position isomers
|
|
Gayatri Banerjee answered |
Functional isomers
Explanation: Propanone (CH3COCH3) and prop-2-en-1-ol (CH2=CHCH2OH) are examples of functional isomers because they have the same molecular formula (C3H6O) but different functional groups. Propanone has a carbonyl group (C=O) while prop-2-en-1-ol has an alcohol group (OH) and a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C).
Explanation: Propanone (CH3COCH3) and prop-2-en-1-ol (CH2=CHCH2OH) are examples of functional isomers because they have the same molecular formula (C3H6O) but different functional groups. Propanone has a carbonyl group (C=O) while prop-2-en-1-ol has an alcohol group (OH) and a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C).
Ethers are :- a)Basic
- b)Amphoteric substances
- c)Acidic
- d)Neutral
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ethers are :
a)
Basic
b)
Amphoteric substances
c)
Acidic
d)
Neutral
|
|
Sandeep Kumar Chaudhary answered |
O
HAS LONE PAIR IN ETHER SO IT CAN ACCEPT H+.
SO IT IS BEHAVES AS BASE
HAS LONE PAIR IN ETHER SO IT CAN ACCEPT H+.
SO IT IS BEHAVES AS BASE
Which one of the following is 1-bromo-3-methyl butane?- a)(CH3)2CHCHBrCH3
- b)(CH3)2CHCH2CH2Br
- c)CH3CH2CH2CH(Br)CH3
- d)CH3CH2CH(Br)CH2CH3
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is 1-bromo-3-methyl butane?
a)
(CH3)2CHCHBrCH3
b)
(CH3)2CHCH2CH2Br
c)
CH3CH2CH2CH(Br)CH3
d)
CH3CH2CH(Br)CH2CH3
|
|
Advait Ghosh answered |
Explanation:
To name the given compound, we need to identify the longest carbon chain and number it from the end nearest to the substituent. Here, the longest chain is 5 carbon atoms long, and it is numbered from the end that is closest to the bromine atom.
The name of the compound is given as 1-bromo-3-methyl butane. Let's break down each part of the name to understand how it is derived:
1. The prefix "1-bromo" indicates that the bromine atom is attached to the first carbon atom of the chain.
2. The suffix "-ane" indicates that the compound is an alkane, which means it contains only single bonds between carbon atoms.
3. The prefix "but-" indicates that the longest chain contains four carbon atoms.
4. The prefix "3-methyl" indicates that there is a methyl group attached to the third carbon atom of the chain.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B, which represents (CH3)2CHCH2CH2Br.
To name the given compound, we need to identify the longest carbon chain and number it from the end nearest to the substituent. Here, the longest chain is 5 carbon atoms long, and it is numbered from the end that is closest to the bromine atom.
The name of the compound is given as 1-bromo-3-methyl butane. Let's break down each part of the name to understand how it is derived:
1. The prefix "1-bromo" indicates that the bromine atom is attached to the first carbon atom of the chain.
2. The suffix "-ane" indicates that the compound is an alkane, which means it contains only single bonds between carbon atoms.
3. The prefix "but-" indicates that the longest chain contains four carbon atoms.
4. The prefix "3-methyl" indicates that there is a methyl group attached to the third carbon atom of the chain.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B, which represents (CH3)2CHCH2CH2Br.

- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Optical purity = optical rotation of mixture/optical rotation of pure compound .
(mixture) [α]D25 = +6.76°
+[α]D = +13.57°
Since rotation of two enantiomers cancel each other, so rotation is due to enantiomeric excess.
Enantiomeric excess = observed specific rotation/max. Specific rotation = 6.76/13.52×100
= 50%
Therefore, %age of each enantiomer is given by,
If we have (+) (-) mixture(+) is in excess,
%(+) = ee/2 + 50%
= 75 % (s)
%(-) = 25% (s)
(mixture) [α]D25 = +6.76°
+[α]D = +13.57°
Since rotation of two enantiomers cancel each other, so rotation is due to enantiomeric excess.
Enantiomeric excess = observed specific rotation/max. Specific rotation = 6.76/13.52×100
= 50%
Therefore, %age of each enantiomer is given by,
If we have (+) (-) mixture(+) is in excess,
%(+) = ee/2 + 50%
= 75 % (s)
%(-) = 25% (s)
Which one of the following is likely to give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution?- a)CHCl3
- b)(CH3)3CCl
- c)CH2=CH-Cl
- d)CCl4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is likely to give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution?
a)
CHCl3
b)
(CH3)3CCl
c)
CH2=CH-Cl
d)
CCl4
|
|
Gargi Ahuja answered |
Precipitation Reaction
A precipitation reaction is a chemical reaction that produces a precipitate, which is an insoluble solid that forms from the reaction of two soluble compounds.
AgNO3 Solution
AgNO3 is a soluble salt that dissociates to give Ag+ and NO3- ions in an aqueous solution.
Likely Precipitate
A compound is likely to give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution if it contains Cl- ions, as AgCl is insoluble in water and will form a white precipitate.
Analysis of Options
a) CHCl3
CHCl3 does not contain Cl- ions and will not give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution.
b) (CH3)3CCl
(CH3)3CCl contains Cl- ions and will give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution.
c) CH2=CH-Cl
CH2=CH-Cl does not contain Cl- ions and will not give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution.
d) CCl4
CCl4 does not contain Cl- ions and will not give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution.
Conclusion
Out of the given options, only (CH3)3CCl contains Cl- ions and will give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution, making option 'B' the correct answer.
A precipitation reaction is a chemical reaction that produces a precipitate, which is an insoluble solid that forms from the reaction of two soluble compounds.
AgNO3 Solution
AgNO3 is a soluble salt that dissociates to give Ag+ and NO3- ions in an aqueous solution.
Likely Precipitate
A compound is likely to give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution if it contains Cl- ions, as AgCl is insoluble in water and will form a white precipitate.
Analysis of Options
a) CHCl3
CHCl3 does not contain Cl- ions and will not give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution.
b) (CH3)3CCl
(CH3)3CCl contains Cl- ions and will give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution.
c) CH2=CH-Cl
CH2=CH-Cl does not contain Cl- ions and will not give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution.
d) CCl4
CCl4 does not contain Cl- ions and will not give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution.
Conclusion
Out of the given options, only (CH3)3CCl contains Cl- ions and will give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution, making option 'B' the correct answer.
Which of the following is major product of following reaction?
CH3CH = CH2 + HBr 
- a)2-Bromo propene
- b)1-Bromo propane
- c)1-Bromo propene
- d)2-Bromo propane
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is major product of following reaction?
CH3CH = CH2 + HBr
CH3CH = CH2 + HBr

a)
2-Bromo propene
b)
1-Bromo propane
c)
1-Bromo propene
d)
2-Bromo propane

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
The correct answer is Option D.
As HBr in the presence of a peroxide follows antimarkonikoff rule where the negative group should attach to the carbon having less no of hydrogen atoms.

As HBr in the presence of a peroxide follows antimarkonikoff rule where the negative group should attach to the carbon having less no of hydrogen atoms.
In the following sequence of reactions, CH3CH2OH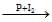 A
A 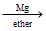 B
B  C
C 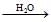 D, then compound `D' is - [AIEEE 2007]
D, then compound `D' is - [AIEEE 2007]- a)Butanal
- b)N-butyl alcohol
- c)N-propyl alcohol
- d)Propanal
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following sequence of reactions, CH3CH2OH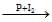 A
A 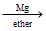 B
B  C
C 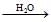 D, then compound `D' is - [AIEEE 2007]
D, then compound `D' is - [AIEEE 2007]
a)
Butanal
b)
N-butyl alcohol
c)
N-propyl alcohol
d)
Propanal
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Correct Answer is option C
When ethanol is treated with a mixture of phosphorus and iodine, ethyl iodide CH3CH2I is obtained.
Compound A on reaction with Mg metal in ether forms ethyl magnesium iodide CH3CH2 MgI.
The compound B reacts with formaldehyde to form compound C; CH3CH2−CH2−OMgX which on hydrolysis gives n propyl alcohol CH3CH2CH2−OH.
The compound D is n-propyl alcohol.
Hence, option C is correct.
When ethanol is treated with a mixture of phosphorus and iodine, ethyl iodide CH3CH2I is obtained.
Compound A on reaction with Mg metal in ether forms ethyl magnesium iodide CH3CH2 MgI.
The compound B reacts with formaldehyde to form compound C; CH3CH2−CH2−OMgX which on hydrolysis gives n propyl alcohol CH3CH2CH2−OH.
The compound D is n-propyl alcohol.
Hence, option C is correct.
Which class of drugs share common structural features and often have similar pharmacological activity?- a)Aspirin
- b)Paracetamol
- c)Caffine
- d)Sulphonamides
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which class of drugs share common structural features and often have similar pharmacological activity?
a)
Aspirin
b)
Paracetamol
c)
Caffine
d)
Sulphonamides
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Drugs can also be classified on the basis of their action on a particular biochemical process.
Ex: Antihistamines inhibit the action of the inflammation-causing compound, histamine.
Drugs classified according to their chemical structure share common structural features and often have similar pharmacological activity.
Ex: All sulphonamides have a common structural feature.
Sulphonamides are anti-bacterial drugs used to treat bacterial infections.
Drugs usually interact with bio-molecules like carbohydrates, lipids, protein and nucleic acids. These bio-molecules are called drug targets (or) simply target molecules. Drugs with similar structures have similar mechanisms of action on bio-molecular targets.
Nitration of anisole gives majorly:- a)Nitroanisole
- b)para-Nitroanisole
- c)ortho-Nitroanisole
- d)meta-Nitroanisole
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Nitration of anisole gives majorly:
a)
Nitroanisole
b)
para-Nitroanisole
c)
ortho-Nitroanisole
d)
meta-Nitroanisole

|
Prasenjit Malik answered |
When anisole is nitrated with a mixture of conc HNO3 and H2SO4 it gives a mixture of ortho-Nitroanisole and para-Nitroanisole (major) products.


Organic compounds can be classified even based upon the function groups. Identify the one which is not a functional group
- a)Isocyanide
- b)Isocyano
- c)Carboxyl
- d)Carbonyl
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Organic compounds can be classified even based upon the function groups. Identify the one which is not a functional group
a)
Isocyanide
b)
Isocyano
c)
Carboxyl
d)
Carbonyl
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Isocyanide is a compound and it is not a functional group.
Chapter doubts & questions for Organic Chemistry - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Organic Chemistry - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced in English & Hindi are available as part of JEE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup