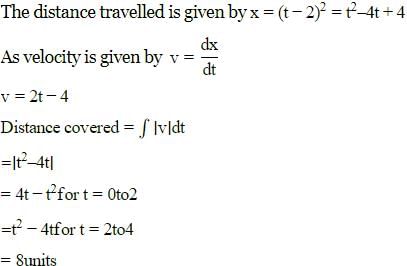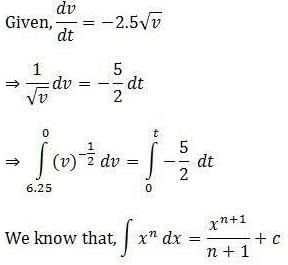All Exams >
JEE >
Physics for JEE Main & Advanced >
All Questions
All questions of Motion in a Straight Line for JEE Exam
A man starts from his home with a speed of 4 km/h on a straight road up to his office 5 km away and returns to home, then the path length covered is:
- a)-5 km
- b)5 km
- c)0
- d)10 km
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A man starts from his home with a speed of 4 km/h on a straight road up to his office 5 km away and returns to home, then the path length covered is:
a)
-5 km
b)
5 km
c)
0
d)
10 km
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
5 km is the distance covered while going and 5 km while coming back.
⇒ Total path travelled = 10 km
⇒ Total path travelled = 10 km
A particle is moving along a circle of radius R such that it completes one revolution in 40 seconds. What will be the displacement after 2 minutes 20 seconds?
- a)6R
- b)2R
- c)4R
- d)R
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle is moving along a circle of radius R such that it completes one revolution in 40 seconds. What will be the displacement after 2 minutes 20 seconds?
a)
6R
b)
2R
c)
4R
d)
R
|
|
Bhargavi Bajaj answered |
Given:
- Particle is moving along a circle of radius R
- It completes one revolution in 40 seconds
- Time = 2 minutes 20 seconds = 140 seconds
To find: Displacement of the particle after 2 minutes 20 seconds
Solution:
- One revolution is completed in 40 seconds
- Therefore, in 1 second, the particle covers 1/40th of the circumference of the circle
- Circumference of a circle = 2πR
- Therefore, in 1 second, the particle covers 2πR/40 distance
- In 140 seconds, the particle covers (2πR/40) x 140 distance
- Simplifying, we get the displacement as (7πR/2) or 3.5πR
- Option B says the displacement is 2R
- This is not equal to (7πR/2) or 3.5πR
- Therefore, option B is incorrect
- Option A says the displacement is 6R
- This is not equal to (7πR/2) or 3.5πR
- Therefore, option A is incorrect
- Option C says the displacement is 4R
- This is not equal to (7πR/2) or 3.5πR
- Therefore, option C is incorrect
- Option D says the displacement is R
- This is not equal to (7πR/2) or 3.5πR
- Therefore, option D is incorrect
- Hence, the correct answer is option B, which says the displacement is 2R.
- Particle is moving along a circle of radius R
- It completes one revolution in 40 seconds
- Time = 2 minutes 20 seconds = 140 seconds
To find: Displacement of the particle after 2 minutes 20 seconds
Solution:
- One revolution is completed in 40 seconds
- Therefore, in 1 second, the particle covers 1/40th of the circumference of the circle
- Circumference of a circle = 2πR
- Therefore, in 1 second, the particle covers 2πR/40 distance
- In 140 seconds, the particle covers (2πR/40) x 140 distance
- Simplifying, we get the displacement as (7πR/2) or 3.5πR
- Option B says the displacement is 2R
- This is not equal to (7πR/2) or 3.5πR
- Therefore, option B is incorrect
- Option A says the displacement is 6R
- This is not equal to (7πR/2) or 3.5πR
- Therefore, option A is incorrect
- Option C says the displacement is 4R
- This is not equal to (7πR/2) or 3.5πR
- Therefore, option C is incorrect
- Option D says the displacement is R
- This is not equal to (7πR/2) or 3.5πR
- Therefore, option D is incorrect
- Hence, the correct answer is option B, which says the displacement is 2R.
The ratio of magnitude of velocity and speed is always:- a)Equal to or less than one
- b)Less than one
- c)One
- d)Equal to or greater than one
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The ratio of magnitude of velocity and speed is always:
a)
Equal to or less than one
b)
Less than one
c)
One
d)
Equal to or greater than one
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
The displacement of the body in given time is always equal to or less than distance covered, because, velocity is displacement per unit time and speed is distance covered per unit time, therefore, ratio of magnitude of velocity and speed is always equal to or less than one.
Which of the following is not an example of a rectilinear motion?
- a)A car moving on a straight road.
- b)A rain drop falling towards the earth.
- c)A car moving in a circular path.
- d)A wooden block sliding down the inclined plane.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an example of a rectilinear motion?
a)
A car moving on a straight road.
b)
A rain drop falling towards the earth.
c)
A car moving in a circular path.
d)
A wooden block sliding down the inclined plane.
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Rectilinear motion is another name for straight-line motion.
A body is said to experience rectilinear motion if any two particles of the body travel the same distance along two parallel straight lines.
A body is said to experience rectilinear motion if any two particles of the body travel the same distance along two parallel straight lines.
A car moving in a circular path changes its direction at every instant. Thus, it is not the rectilinear motion.
36 km/h is equal to:
- a)129. 6 ms-1
- b)600 ms-1
- c)10 ms-1
- d)12.96 ms-1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
36 km/h is equal to:
a)
129. 6 ms-1
b)
600 ms-1
c)
10 ms-1
d)
12.96 ms-1
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
1 km = 1000 m and 1 hr = 3600 sec.
Therefore,

If a body does not change its direction during the course of its motion, then ______.
- a)Displacement is greater than path length.
- b)Path length and displacement are equal.
- c)Path length is greater than displacement.
- d)Path length is either greater or equal to displacement.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a body does not change its direction during the course of its motion, then ______.
a)
Displacement is greater than path length.
b)
Path length and displacement are equal.
c)
Path length is greater than displacement.
d)
Path length is either greater or equal to displacement.
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Since the object does not change its direction it means that the object is traveling in a straight line.
⇒ The path length and displacement will be equal.
⇒ The path length and displacement will be equal.
The numerical ratio of velocity to speed is:- a)Either less than or equal to 1
- b)Equal to 1
- c)Greater than 1
- d)Less than 1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The numerical ratio of velocity to speed is:
a)
Either less than or equal to 1
b)
Equal to 1
c)
Greater than 1
d)
Less than 1
|
|
Charvi Mehta answered |
When an object is moving along a straight path, magnitude of average velocity is equal to the average speed. Therefore, numerical ratio of average velocity to average speed is one in a straight line motion.
But, during curved motion, the displacement<distance covered, so the velocity<speed.
A vehicle travels half the distance L with speed V1and the other half with speed V2, then its average speed is
- a)
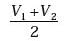
- b)
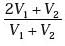
- c)
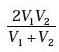
- d)
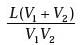
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A vehicle travels half the distance L with speed V1and the other half with speed V2, then its average speed is
a)
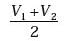
b)
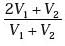
c)
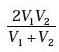
d)
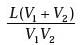
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
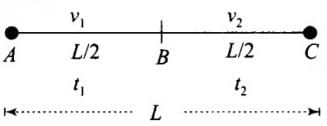
Let the vehicle travels from A to B. Distances, velocities, and time taken are shown. To calculate average speed we will calculate the total distance covered and will divide it by the time interval in which it covers that total distance.
Time taken to travel first half distance t1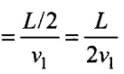
Time taken to travel first half distance t1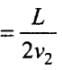
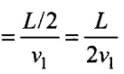
Time taken to travel first half distance t1
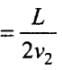
Total time taken = t1 + t2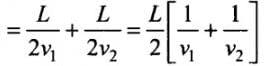
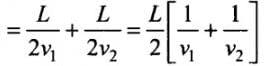
We know that vav = Average speed = Total Distance / Total Time
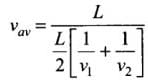
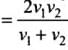
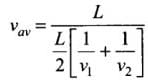
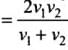
A truck has a velocity of 2 m /s at time t=0. It accelerates at 2 m / s2 on seeing police .What is its velocity in m/s at a time of 2 sec- a)6
- b)7
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A truck has a velocity of 2 m /s at time t=0. It accelerates at 2 m / s2 on seeing police .What is its velocity in m/s at a time of 2 sec
a)
6
b)
7
c)
3
d)
4
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Explanation:
Initial velocity u = 2 m/s
final velocity = v m/s
Time duration = final time - initial time = 2-0 = 2 s
acceleration a = 2 m/s2
We know,
v = u + at
=> v = 2+2x2
=> v = 6 m/s
A car covers a distance of 5 km in 5 mins, its average speed is equal to- a)1 km ⁄ h
- b)25 km ⁄ h
- c)60 km ⁄ h
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A car covers a distance of 5 km in 5 mins, its average speed is equal to
a)
1 km ⁄ h
b)
25 km ⁄ h
c)
60 km ⁄ h
d)
None of the above
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
5 km in 5 mins, which means 1 km in 1 min
Hence, it will travel 60 km in 60 mins, i.e. speed = 60km/hr
Hence, it will travel 60 km in 60 mins, i.e. speed = 60km/hr
The displacement of a particle starting from rest (at t = 0) is given by s = 6t2-t3 . The time in seconds at which the particle will attain zero velocity again, is
- a)6
- b)4
- c)2
- d)8
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The displacement of a particle starting from rest (at t = 0) is given by s = 6t2-t3 . The time in seconds at which the particle will attain zero velocity again, is
a)
6
b)
4
c)
2
d)
8
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
v = ds/dt
v = 12t - 3t2
0 = 3t (4 - t)
⇒ t = 0 or 4
Here t = 0 is not realistic so at t = 4 the velocity will be zero.
Thus, the particle will attain zero velocity at the time of 4 seconds.
⇒ t = 0 or 4
Here t = 0 is not realistic so at t = 4 the velocity will be zero.
Thus, the particle will attain zero velocity at the time of 4 seconds.
The ratio of displacement to distance is- a)Greater than 1
- b)Either less than or equal to 1
- c)Less than 1
- d)Equal to 1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The ratio of displacement to distance is
a)
Greater than 1
b)
Either less than or equal to 1
c)
Less than 1
d)
Equal to 1
|
|
Saumya Dey answered |
Ratio of Displacement to Distance
Displacement and distance are two terms used in physics to describe the motion of an object. Displacement refers to the change in position of an object from its initial to final position, whereas distance refers to the total path covered by the object during its motion.
Ratio of Displacement to Distance Formula
The ratio of displacement to distance is given by:
Displacement / Distance
This ratio is used to determine the efficiency of an object's motion. If the ratio is equal to 1, it means that the object has moved in a straight line from its initial to final position. If the ratio is less than 1, it means that the object has taken a longer path to reach its final position, and if the ratio is greater than 1, it means that the object has moved back and forth before reaching its final position.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer to the question is option B, which states that the ratio of displacement to distance is either less than or equal to 1. This is because an object can never cover a greater distance than its displacement. The displacement represents the shortest distance between the initial and final positions of an object, whereas the distance represents the total path covered by the object.
Therefore, the displacement can be equal to or less than the distance covered by the object, but it can never be greater than the distance. This is the reason why the ratio of displacement to distance is either less than or equal to 1.
Displacement and distance are two terms used in physics to describe the motion of an object. Displacement refers to the change in position of an object from its initial to final position, whereas distance refers to the total path covered by the object during its motion.
Ratio of Displacement to Distance Formula
The ratio of displacement to distance is given by:
Displacement / Distance
This ratio is used to determine the efficiency of an object's motion. If the ratio is equal to 1, it means that the object has moved in a straight line from its initial to final position. If the ratio is less than 1, it means that the object has taken a longer path to reach its final position, and if the ratio is greater than 1, it means that the object has moved back and forth before reaching its final position.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer to the question is option B, which states that the ratio of displacement to distance is either less than or equal to 1. This is because an object can never cover a greater distance than its displacement. The displacement represents the shortest distance between the initial and final positions of an object, whereas the distance represents the total path covered by the object.
Therefore, the displacement can be equal to or less than the distance covered by the object, but it can never be greater than the distance. This is the reason why the ratio of displacement to distance is either less than or equal to 1.
On velocity-time graph when two curves coincide, the objects will have- a)Same acceleration
- b)Same velocity
- c)Different velocity
- d)Different acceleration
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
On velocity-time graph when two curves coincide, the objects will have
a)
Same acceleration
b)
Same velocity
c)
Different velocity
d)
Different acceleration
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
On velocity-time graph, the point at which two curves coincide will indicate that both the objects have same velocity at that instant.
If the position- time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis- a)The velocity is zero
- b)The velocity is decreasing
- c)The velocity is increasing
- d)The velocity is constant but non zero
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If the position- time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis
a)
The velocity is zero
b)
The velocity is decreasing
c)
The velocity is increasing
d)
The velocity is constant but non zero
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Explanation:Position-time graph of horizontal straight line parallel to time axis represents that the position of the body does not changes with the passage of time. So it represents the rest state of motion.It means velocity of object is zero.
A car moving with a speed of 50 km/h, can be stopped by brakes after at least 6m. If the same car is moving at a speed of 100 km/h, the minimum stopping distance is [AIEEE 2003]- a)12 m
- b) 18 m
- c) 24 m
- d)6 m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A car moving with a speed of 50 km/h, can be stopped by brakes after at least 6m. If the same car is moving at a speed of 100 km/h, the minimum stopping distance is [AIEEE 2003]
a)
12 m
b)
18 m
c)
24 m
d)
6 m
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
We know that retardation of a car with an initial speed of 50kmph stops after 6 m.
We know that v2 - u2 = 2as (third equation of motion)
► 0 - 502 = 2 * a * 6
► a = - 502 / 12
Hence when the initial speed is 100 kmph
We get,
► -1002 = 2 * a * s
► 2 * s = 12 * (1002 / 502)
Thus we get s = 24 m.
We know that v2 - u2 = 2as (third equation of motion)
► 0 - 502 = 2 * a * 6
► a = - 502 / 12
Hence when the initial speed is 100 kmph
We get,
► -1002 = 2 * a * s
► 2 * s = 12 * (1002 / 502)
Thus we get s = 24 m.
Suppose our school is 1 km away from our house, and we go to school in the morning, and in the afternoon we come back. Then, the total displacement for the entire trip is- a)1 km
- b)2 km
- c)-1 km
- d)0 km
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Suppose our school is 1 km away from our house, and we go to school in the morning, and in the afternoon we come back. Then, the total displacement for the entire trip is
a)
1 km
b)
2 km
c)
-1 km
d)
0 km
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The displacement is 0 because the initial and final position are the same, i.e. the home, and hence, displacement is 0.
If a moving body comes to rest, then its acceleration is______.
- a)Positive
- b)Both of these depending upon the initial velocity
- c)Constant
- d)Negative
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If a moving body comes to rest, then its acceleration is______.
a)
Positive
b)
Both of these depending upon the initial velocity
c)
Constant
d)
Negative
|
|
Karthik Namboothiri answered |
But, I think it should be (c) because: it was initially moving with a speed and then, it came to rest.
So, the speed must decrease with time to become 0m/s (to become at rest). so, the acceleration must be negative so that it can decrease with time ( as the change in velocity will become negative only when the speed decreases).
So, I think the answer is (C)
Please correct me if I am wrong🤔
Two balls of equal mass and of Perfectly inelastic material are lying on the floor. One of the balls with velocity V is made to strike the second ball. Both the balls after impact will move with a velocity
- a)v
- b)v/8
- c)v/4
- d)v/2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two balls of equal mass and of Perfectly inelastic material are lying on the floor. One of the balls with velocity V is made to strike the second ball. Both the balls after impact will move with a velocity
a)
v
b)
v/8
c)
v/4
d)
v/2
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Given:
Let two balls A and B have mass mA, mB respectively, and their initial velocities are uA and uB. After the collision, they will move with the same velocity, vo.
Given that mass of both balls are same.
So mA = mB = m
uA = V, uB = 0
From the Concept of Momentum Conservation:
mAuA + mBuB = (m+m)vo
mV = 2mvo
vo = V/2
Both the balls after impact will move with velocity v/2.
Choose the correct option:- a)distance is a scalar, velocity is a vector , acceleration is a vector.
- b)distance is a vector, velocity is a scalar, acceleration is a vector.
- c)distance is a vector, velocity is a vector, acceleration is a vector.
- d)distance is a scalar, velocity is a vector, acceleration is a scalar.
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct option:
a)
distance is a scalar, velocity is a vector , acceleration is a vector.
b)
distance is a vector, velocity is a scalar, acceleration is a vector.
c)
distance is a vector, velocity is a vector, acceleration is a vector.
d)
distance is a scalar, velocity is a vector, acceleration is a scalar.
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
- Distance is a scalar quantity that refers to "how much ground an object has covered" during its motion.
- Acceleration is a vector quantity that is defined as the rate at which an object changes its velocity.
- Velocity is a vector quantity that refers to the speed of an object in a particular direction.
A boy throws a ball up and catches it when the ball falls back. In which part of the motion the ball is accelerating?- a)During downward motion
- b)When the ball comes to rest
- c)During upward motion
- d)When the boy catches the ball
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A boy throws a ball up and catches it when the ball falls back. In which part of the motion the ball is accelerating?
a)
During downward motion
b)
When the ball comes to rest
c)
During upward motion
d)
When the boy catches the ball
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
- When the ball moves upward, the force of gravitation is acting in the opposite direction of the ball that is why in that case acceleration is negative or in other words deceleration takes place.
- But when the ball is moving downwards the force of gravitation is in the same direction of the motion of the ball thus acceleration takes place in this case.
The ratio of C.G.S. to M.K.S. unit of acceleration is:- a)1:10
- b)1:1
- c)1:100
- d)10:1
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The ratio of C.G.S. to M.K.S. unit of acceleration is:
a)
1:10
b)
1:1
c)
1:100
d)
10:1
|
|
Vikram Khanna answered |
M.K.S. unit of acceleration = 1m/^s2
C.G.S unit of acceleration/ M,K.S unit of acceleration =
1cm/^s2 / 1m/^s2
= 1cm / 100 cm
= 1/100
=1:100
The acceleration at any instant is the slope of the tangent of the ________ curve at that instant:- a)a-t
- b)v-t
- c)x-v
- d)x-t
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The acceleration at any instant is the slope of the tangent of the ________ curve at that instant:
a)
a-t
b)
v-t
c)
x-v
d)
x-t
|
|
Om Desai answered |
This can be verified graphically
ObtaIning instantaneous acceleration from graph
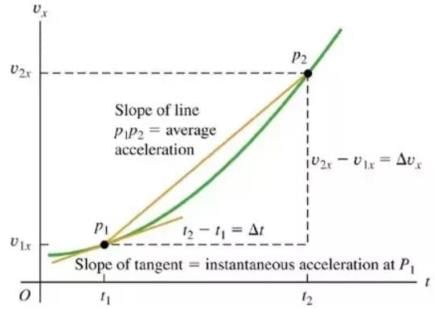

Figure shows the displacement – time graph of a particle moving along X – axis.

- a)particle moves at a variable velocity
- b)particle moves at a constant velocity upto a time t0 and then stops
- c)particle moves at a constant velocity upto a time t0 and then velocity increases
- d)particle moves at increasing velocity upto t0 and then velocity becomes constant
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Figure shows the displacement – time graph of a particle moving along X – axis.
a)
particle moves at a variable velocity
b)
particle moves at a constant velocity upto a time t0 and then stops
c)
particle moves at a constant velocity upto a time t0 and then velocity increases
d)
particle moves at increasing velocity upto t0 and then velocity becomes constant
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Because velocity is the slope of the x-t graph.(dx/dt=V) and by looking at the graph it can be seen that upto time T0 slope is constant so velocity will be constant and after time T0 slope is zero ( line is parallel to X axis) so the velocity will be zero.
From a building two balls A and B are thrown such that A is thrown upwards and B downwards (both vertically with same velocity). If vA and vB are their respective velocities on reaching the ground,then [AIEEE 2002]- a)

- b)
- c)
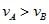
- d)Their velocities depend on their masses
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
From a building two balls A and B are thrown such that A is thrown upwards and B downwards (both vertically with same velocity). If vA and vB are their respective velocities on reaching the ground,then
[AIEEE 2002]
a)
b)
c)
d)
Their velocities depend on their masses
|
|
Om Desai answered |
From the conservation of energy, potential energy at height h = kinetic energy at the ground.
Therefore, at height h, PE of ball A, PE = mAgh
Therefore, at height h, PE of ball A, PE = mAgh
The velocity of a particle is 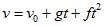 . If its position is x = 0 at t = 0, then its displacement after unit time (t = 1) is [AIEEE 2007]
. If its position is x = 0 at t = 0, then its displacement after unit time (t = 1) is [AIEEE 2007]- a)
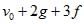
- b)
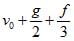
- c)
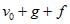
- d)
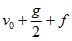
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The velocity of a particle is 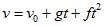 . If its position is x = 0 at t = 0, then its displacement after unit time (t = 1) is
. If its position is x = 0 at t = 0, then its displacement after unit time (t = 1) is
[AIEEE 2007]
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
v = v0 + gt + ft2
∫0x dx = ∫01(v0 + gt + ft2) dt
► x = v0 + g/2 + f/3
∫0x dx = ∫01(v0 + gt + ft2) dt
► x = v0 + g/2 + f/3
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is always perpendicular to the velocity of the particle. The motion of the particle takes place in a plane, it follows that [AIEEE 2004]
- A:
Its velocity is constant
- B:
Its acceleration is constant
- C:
Its kinetic energy is constant
- D:
It moves in straight line
The answer is c.
A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is always perpendicular to the velocity of the particle. The motion of the particle takes place in a plane, it follows that [AIEEE 2004]
Its velocity is constant
Its acceleration is constant
Its kinetic energy is constant
It moves in straight line
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
When a force of constant magnitude acts on the velocity of a particle perpendicularly, then there is no change in the kinetic energy of the particle. Hence, kinetic energy remains constant.
The S.I. unit of acceleration is:- a) ms2
- b)ms
- c)ms-2
- d)m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The S.I. unit of acceleration is:
a)
ms2
b)
ms
c)
ms-2
d)
m
|
|
Shambhavi Singh answered |
Calculating acceleration involves dividing velocity by time Or we can say, dividing the meter per second by the second. i.e.
[ m/s2 = m/s / s ]
Therefore, option ( c) ms-2 is the correct answer.
An object is said to be in uniform motion in a straight line if its displacement- a)is decreasing in equal intervals of time
- b)is increasing in equal intervals of time
- c)is equal in equal intervals of time.
- d)is equal in not equal intervals of time.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An object is said to be in uniform motion in a straight line if its displacement
a)
is decreasing in equal intervals of time
b)
is increasing in equal intervals of time
c)
is equal in equal intervals of time.
d)
is equal in not equal intervals of time.
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Explanation:Uniform motion is the kind of motion in which a body covers equal displacement in equal intervals of time. It does not matter how small the time intervals are, as long as the displacements covered are equal.
If a body is involved in rectilinear motion and the motion is uniform, then the acceleration of the body must be zero.
Jagadeesh, on driving his way to school, calculates the speed for the trip to be 20 km/hr. After reaching the school he found the school was closed. So he immediately started returning home. While on his return trip, due to less traffic, he calculates the speed to be 40 km/hr. Calculate Jagadeesh's average speed for the entire journey.
- a)26.67 kmhr-1
- b)33.34 kmhr-1
- c)50 kmhr-1
- d)30 kmhr-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Jagadeesh, on driving his way to school, calculates the speed for the trip to be 20 km/hr. After reaching the school he found the school was closed. So he immediately started returning home. While on his return trip, due to less traffic, he calculates the speed to be 40 km/hr. Calculate Jagadeesh's average speed for the entire journey.
a)
26.67 kmhr-1
b)
33.34 kmhr-1
c)
50 kmhr-1
d)
30 kmhr-1

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Let t1 and t2 be the time taken for Jagadeesh to go to school and then back home. If s is the displacement, then

Total time taken
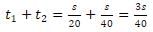
Total displacement=2 s
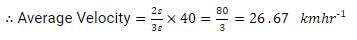

Total time taken
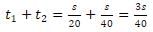
Total displacement=2 s
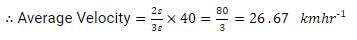
Speed time graph of a particle moving along a fixed direction is shown in the figure below. The average speed of the particle over the interval: t = 0 s to 10 s.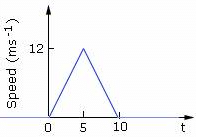
- a)16 m/s
- b)6 m/s
- c)10 m/s
- d)0.6 m/s
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Speed time graph of a particle moving along a fixed direction is shown in the figure below. The average speed of the particle over the interval: t = 0 s to 10 s.
a)
16 m/s
b)
6 m/s
c)
10 m/s
d)
0.6 m/s
|
|
Om Desai answered |
From the given graph we get that the area of the given graph is total distance covered that is
= ½ x 10 x 12
= 60m
And total time taken is 10 sec
Thus average speed is 60m / 10sec
= 6 m/s
= ½ x 10 x 12
= 60m
And total time taken is 10 sec
Thus average speed is 60m / 10sec
= 6 m/s
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of:- a)Distance
- b)Velocity
- c)Speed
- d)Displacement
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of:
a)
Distance
b)
Velocity
c)
Speed
d)
Displacement
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Acceleration is a vector quantity that is defined as the rate at which an object changes its velocity. An object is accelerating if it is changing its velocity.
If a body losses half of its velocity on penetrating 3 cm in a wooden block, then how much will it penetrate more before coming to rest ? [AIEEE 2002]- a)1 cm
- b)2cm
- c)3cm
- d)4cm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If a body losses half of its velocity on penetrating 3 cm in a wooden block, then how much will it penetrate more before coming to rest ? [AIEEE 2002]
a)
1 cm
b)
2cm
c)
3cm
d)
4cm

|
Ayush Joshi answered |
Let the initial velocity of the body be u. Its velocity becomes u/2 after penetrating 3 cm in the block. We can calculate the deceleration of the body using these.
v2= u2 +2as
u2/4 = u2 + 2ax3
-3u2/4 = 6a
a = -u2/8
Now, we can calculate the distance the body travels till it comes to rest.
v2 = u2 + 2as
0 = u2 +2x(-u2/8)xs
u2 = u2s/4
s = 4 cm
Therefore, the body penetrates 1 cm (4-3=1cm) more before coming to rest.
I hope you understand the concept.
Two escalators move people up and down between floors of a shopping mall at the same rate, either up or down. What of the following statements regarding the motion of the escalators is true?- a)The escalators have different speeds and velocities.
- b)The escalators have the same velocity, but different speeds.
- c)The escalators have the same speed and velocity.
- d)The escalators have the same speed, but different velocities.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two escalators move people up and down between floors of a shopping mall at the same rate, either up or down. What of the following statements regarding the motion of the escalators is true?
a)
The escalators have different speeds and velocities.
b)
The escalators have the same velocity, but different speeds.
c)
The escalators have the same speed and velocity.
d)
The escalators have the same speed, but different velocities.
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
As the particles are moving at the same rate, their speed is the same but velocities will be different beacuse their directions will be different.
An automobile travelling with a speed of 60 km/h, can brake to stop within a distance of 20 m. If the car is going twice as fast, i.e. 120 km/h, the stopping distance will be [AIEEE 2004]- a)20 m
- b)40 m
- c)60m
- d)80 m
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An automobile travelling with a speed of 60 km/h, can brake to stop within a distance of 20 m. If the car is going twice as fast, i.e. 120 km/h, the stopping distance will be [AIEEE 2004]
a)
20 m
b)
40 m
c)
60m
d)
80 m
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
The initial speed of the car in 1st case = 60kmph = 50/3 m/s
Final speed = 0
Let the deceleration be a
We have
(0)^2 - (50/3)^2 = 2ax(20)
=>a = -(50/3)^2/40 = - 6.94 ms^-2 (approx)
Considering the acceleration to be same in both case
The initial speed at the second case = 120kmph=100/3 m/s
Let the distance be x
Final speed = 0
We have
v^2-u^2 =2ax
=>0^2 – (100/3)^2 =2x (-6.94)x
=>x = 80 m
Slope of displacement time graph or x-t graph gives us the particles’ ____________.- a)displacement
- b)deceleration
- c)velocity
- d)acceleration
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Slope of displacement time graph or x-t graph gives us the particles’ ____________.
a)
displacement
b)
deceleration
c)
velocity
d)
acceleration
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Velocity is a physical vector quantity; both magnitude and direction are needed to define it. The scalar absolute value (magnitude) of velocity is called "speed", being a coherent derived unit whose quantity is measured in the SI (metric system) as metres per second (m/s) or as the SI base unit of (m⋅s−1).
A ball whose kinetic energy is E, is projected at an angle of 45° to the horizontal. The kinetic energy of the ball at the highest point of its flight will be [AIEEE 2002] - a)E
- b)
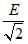
- c)
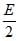
- d)zero
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A ball whose kinetic energy is E, is projected at an angle of 45° to the horizontal. The kinetic energy of the ball at the highest point of its flight will be
[AIEEE 2002]
a)
E
b)
c)
d)
zero
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
At the highest point of its flight, the vertical component of velocity is zero and the only horizontal component is left which is ux = u cosθ
Given θ = 450
Given θ = 450
A particle is moving with velocity 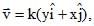 where k is a constant. The general equation for its path is [AIEEE 2010]
where k is a constant. The general equation for its path is [AIEEE 2010]- a)y = x2 + constant
- b)y2 = x + constant
- c)xy = constant
- d)y2 = x2 + constant
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle is moving with velocity 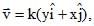 where k is a constant. The general equation for its path is
where k is a constant. The general equation for its path is
[AIEEE 2010]
a)
y = x2 + constant
b)
y2 = x + constant
c)
xy = constant
d)
y2 = x2 + constant
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
As, v = k(yi + xi)
vx = Ky → dx/dt = Ky
vy = Kx → dy/dt = Kx
Dividing both equations,
► dy/dx = dy/dt divided by dx/dt = Kx / Ky = x/y
► ydy = xdx
Integrating the equation,
► y2/ 2 = x2/2 + c
► y2 = x2 + constant
vx = Ky → dx/dt = Ky
vy = Kx → dy/dt = Kx
Dividing both equations,
► dy/dx = dy/dt divided by dx/dt = Kx / Ky = x/y
► ydy = xdx
Integrating the equation,
► y2/ 2 = x2/2 + c
► y2 = x2 + constant
Linear inequalities are graphically represented on Cartesian plane by a- a)negative full space
- b)closed half space
- c)open half space
- d)positive full space
- e)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Linear inequalities are graphically represented on Cartesian plane by a
a)
negative full space
b)
closed half space
c)
open half space
d)
positive full space
e)
|
|
Muskaan Kumar answered |
The graph of an inequality in two variables is the set of points that represents all solutions to the inequality. A linear inequality divides the coordinate plane into two halves by a boundary line where one half represents the solutions of the inequality. The boundary line is dashed for > and < and solid for ≤ and ≥.
A body moving along a straight line at 20m/s undergoes an acceleration of -4m/s2. After two seconds its speed will be- a)-8 m/s
- b)12 m/s
- c)16 m/s
- d)24 m/s
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A body moving along a straight line at 20m/s undergoes an acceleration of -4m/s2. After two seconds its speed will be
a)
-8 m/s
b)
12 m/s
c)
16 m/s
d)
24 m/s

|
Aaditya Nair answered |
V = 20 m/s, a = 4 m/s^2, u = 0 m/s
by using the formula 2as = v^2 - u^2 we get s = 50 m
then using the formula s = ut + 1/2at2 we get t = 5 s then after two seconds is 5+2 = 7 s
now using formula v = u + at we get v( speed ) = 28 m/s
Can you explain the answer of this question below:If the upward direction is taken as positive what is the sign of velocity and acceleration when a body falls freely from a height.- A:positive acceleration and negative velocity
- B:positive acceleration and positive velocity
- C:negative acceleration and positive velocity.
- D:negative acceleration and negative velocity
The answer is d.
If the upward direction is taken as positive what is the sign of velocity and acceleration when a body falls freely from a height.
A:
positive acceleration and negative velocity
B:
positive acceleration and positive velocity
C:
negative acceleration and positive velocity.
D:
negative acceleration and negative velocity
|
|
Ananya Sharma answered |
Both velocity and acceleration are in the downward direction. Thus, they will be considered negative as they are vectors and the upward direction is positive.
A ball is thrown from a point with a speed v0 at an angle fo projection 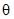 . From the same point and at the same instant, a person starts running with a constant speed
. From the same point and at the same instant, a person starts running with a constant speed 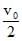 to catch the ball. Will the person be able to catch the ball? If yes, what should be the angle of projection ?[AIEEE 2004]
to catch the ball. Will the person be able to catch the ball? If yes, what should be the angle of projection ?[AIEEE 2004]- a)Yes, 60°
- b) Yes, 30°
- c)No
- d)Yes, 45°
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A ball is thrown from a point with a speed v0 at an angle fo projection 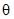 . From the same point and at the same instant, a person starts running with a constant speed
. From the same point and at the same instant, a person starts running with a constant speed 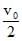 to catch the ball. Will the person be able to catch the ball? If yes, what should be the angle of projection ?
to catch the ball. Will the person be able to catch the ball? If yes, what should be the angle of projection ?
[AIEEE 2004]
a)
Yes, 60°
b)
Yes, 30°
c)
No
d)
Yes, 45°

|
Gowri Chavan answered |
Man will catch the ball, if the horizontal component of velocity becomes equal to the constant speed of man ie.
vo cos θ = vo/2
or Cos θ = 1/2
or θ = 60o
A boy playing on the roof of a 10 m high building throws a ball with a speed of 10 m/s at an angle 30° with the horizontal. How far from the throwing point will the ball be at the height of 10 m from the ground ? [g = 10 m/s2, sin 30° = 1/2, cos 30° = 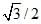 ] [AIEEE 2003]
] [AIEEE 2003]- a)5.20 m
- b)4.33 m
- c) 2.60 m
- d) 8.66 m
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A boy playing on the roof of a 10 m high building throws a ball with a speed of 10 m/s at an angle 30° with the horizontal. How far from the throwing point will the ball be at the height of 10 m from the ground ? [g = 10 m/s2, sin 30° = 1/2, cos 30° = 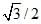 ]
]
[AIEEE 2003]
a)
5.20 m
b)
4.33 m
c)
2.60 m
d)
8.66 m
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
We have to simply calculate the range of the projectile.
► R = u2sin2θ/g
► R = (10)2 * sin (2 * 30º) / 10
► R = 10 * (√3/2) = 8.66 m
► R = u2sin2θ/g
► R = (10)2 * sin (2 * 30º) / 10
► R = 10 * (√3/2) = 8.66 m
Chapter doubts & questions for Motion in a Straight Line - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Motion in a Straight Line - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced in English & Hindi are available as part of JEE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup