All Exams >
NEET >
NEET Past Year Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Coordination Compounds for NEET Exam
Earth's atmosphere is richest in :- a)ultraviolet
- b)infrared
- c)X-rays
- d)microwaves
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Earth's atmosphere is richest in :
a)
ultraviolet
b)
infrared
c)
X-rays
d)
microwaves
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
Earth 's atmosphere is richest in infrared radiation or IR.
* The earth emits huge amounts of infrared radiation and thereby makes the atmosphere richest in infrared rays.
* When sunlight (solar radiation) hits the earth, some of the energy is absorbed by the earth that ultimately heats up the earth.
* This heat gets radiated by the earth in the form of infrared radiation.
Earth 's atmosphere is richest in infrared radiation or IR.
* The earth emits huge amounts of infrared radiation and thereby makes the atmosphere richest in infrared rays.
* When sunlight (solar radiation) hits the earth, some of the energy is absorbed by the earth that ultimately heats up the earth.
* This heat gets radiated by the earth in the form of infrared radiation.
Which one of the following is expected to exhibit optical isomerism? (en = eth ylen ediamine) [2 00 5]- a)cis [Pt(NH3)2 Cl2]
- b)trans [Pt(NH3)2Cl2]
- c)cis [Co(en)2Cl2]
- d)trans [Co(en)2Cl2]
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is expected to exhibit optical isomerism? (en = eth ylen ediamine) [2 00 5]
a)
cis [Pt(NH3)2 Cl2]
b)
trans [Pt(NH3)2Cl2]
c)
cis [Co(en)2Cl2]
d)
trans [Co(en)2Cl2]

|
Shivani Rane answered |
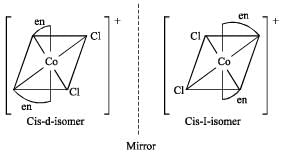
Transform of [M(AA)2 a2]n± does not shows optical isomerism.
23. One projectile moving with velocity v in space get burst into 2 parts of masses in the ratio of 1 : 2. The smaller part becomes stationary, velocity of other part is : - a)uv
- b)3v/2
- c)4v/3
- d)2v/3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
23. One projectile moving with velocity v in space get burst into 2 parts of masses in the ratio of 1 : 2. The smaller part becomes stationary, velocity of other part is :
a)
uv
b)
3v/2
c)
4v/3
d)
2v/3
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Let the mass =m
Apply law of momentum conservation
mv = m/4*0 + 2mv1/3
v = 2v1/3
v1 = 3v/2
Apply law of momentum conservation
mv = m/4*0 + 2mv1/3
v = 2v1/3
v1 = 3v/2
Which of the following complex ion is not expected to absorb visible light ? [2010]- a)Ni(CN)42
- b)Cr(NH3)6 3
- c)2Fe(H2 O)6
- d)Ni(H2O)62
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following complex ion is not expected to absorb visible light ? [2010]
a)
Ni(CN)42
b)
Cr(NH3)6 3
c)
2Fe(H2 O)6
d)
Ni(H2O)62

|
Mahesh Saini answered |
Absorption of visual light is associated with an energy difference between two orbitals — one occupied, one unoccupied — and electrons must be able to be excited from one to the other.
In coordination complexes, these excitations typically happen within the metal’s d subshell, so it is usually sufficient to examine that and approximately determine which excitations are possible. The main selection rules are:
the spin rule. The electron must be excitable without a spin-flip
the Laporte rule. Basically, d to d transitions are forbidden in octahedral complexes
The spin rule is very strongly observed. The color of manganese(II) whose transition is spin-forbidden is extremely faint. The Laporte rule only holds true as long as the complex is inversion-symmetric, so any asymmetric vibration is enough to make it void; thus, Laporte-forbidden transitions are typically still visible but somewhat faint.
Let’s examine the complexes:
[Ni(CN)4]2−This is expected to be square planar and d8. The energy difference between the two highest orbitals — dxy and dx2−y2 — is expected to be high. The former is expected to be fully populated, the latter to be unpopulated.
[Cr(NH3)6]3+ This is a d3 system. It is expected to be octahedral with a standard difference between the lower and higher energy levels.
[Fe(H2O)6]2+This is a d6 octahedral system. There is no reason to assume a low spin state. The energy difference is expected to be slightly less than in the previous case.
[Ni(H2O)6]2+ this is expected to be a high-spin d8system and octahedral. The same expectation regarding energy levels as on the previous case applies.
We realize that the of our complexes are average high spin octahedral complexes. For these, visible light absorption is always expected. Only one case is different. In that different case, the HOMO-LUMO difference is large. While we can still expect absorption, it seems most reasonable to assign this absorption band an ultraviolet wavelength.
Thus, [Ni(CN)4]2− is the answer.
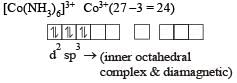
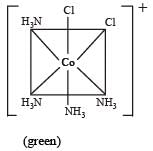
Which one of the following is an outer orbital complex and exhibits paramagnetic behaviour ? [2012]- a)[Ni(NH3)6]2+
- b)[Zn(NH3)6)]2+
- c)[Cr(NH3)6]3+
- d)[CO(NH3)6]3+
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is an outer orbital complex and exhibits paramagnetic behaviour ? [2012]
a)
[Ni(NH3)6]2+
b)
[Zn(NH3)6)]2+
c)
[Cr(NH3)6]3+
d)
[CO(NH3)6]3+

|
Muskaan Basak answered |
[Ni(NH3)6]2+
Ni2+ = 3d8, according to 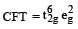 therefore, hybridisation is sp3d2 & complex is paramagnetic.
therefore, hybridisation is sp3d2 & complex is paramagnetic.
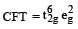 therefore, hybridisation is sp3d2 & complex is paramagnetic.
therefore, hybridisation is sp3d2 & complex is paramagnetic.The d electron configurations of Cr2+, Mn2+, Fe2+ and Ni2+ are 3d4, 3d5, 3d6 and 3d8 respectively. Which one of the following aqua complexes will exhibit the minimum paramagnetic behaviour? [2007] (At. No. Cr = 24, Mn = 25, Fe = 26, Ni = 28)- a)[Fe(H2O)6]2+
- b)[Ni(H2O)6]2+
- c)[Cr(H2O)6]2+
- d)[Mn(H2O)6]2+
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The d electron configurations of Cr2+, Mn2+, Fe2+ and Ni2+ are 3d4, 3d5, 3d6 and 3d8 respectively. Which one of the following aqua complexes will exhibit the minimum paramagnetic behaviour? [2007] (At. No. Cr = 24, Mn = 25, Fe = 26, Ni = 28)
a)
[Fe(H2O)6]2+
b)
[Ni(H2O)6]2+
c)
[Cr(H2O)6]2+
d)
[Mn(H2O)6]2+
|
|
Lalit Yadav answered |
Lesser is the number of unpaired electrons smaller will be the paramagnetic behaviour.
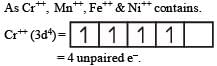


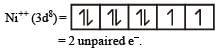
As Ni++ has minimum no. of unpaired e– thus this is least paramagnetic.
29. A body of mass m1 is moving with velocity u. It collides with another stationary body of mass m2. They get embedded. At the point of collision, the velocity of the system :- a)increases
- b)decreases but does not become zero
- c)remains same
- d)zero
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
29. A body of mass m1 is moving with velocity u. It collides with another stationary body of mass m2. They get embedded. At the point of collision, the velocity of the system :
a)
increases
b)
decreases but does not become zero
c)
remains same
d)
zero
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
The correct answer is Option B
Just before the collision the velocity of the center of mass will be
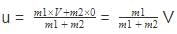
after the collision if the system moves with velocity V0 then on conserving the momentum
we will get m1V + 0=(m1 + m2)V0
or V0 =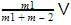 we can notice that both V0 and u are the same, due to absence of external force on the system.
we can notice that both V0 and u are the same, due to absence of external force on the system.
Just before the collision the velocity of the center of mass will be
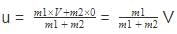
after the collision if the system moves with velocity V0 then on conserving the momentum
we will get m1V + 0=(m1 + m2)V0
or V0 =
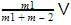 we can notice that both V0 and u are the same, due to absence of external force on the system.
we can notice that both V0 and u are the same, due to absence of external force on the system.Which of the following does not show optical isomerism? [2009]- a)[Co(NH3)3Cl3]0
- b)[Co (en) Cl2 (NH3)2]+
- c)[Co (en)3]3+
- d)[Co (en)2Cl2]+ (en = ethylenediamine)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following does not show optical isomerism? [2009]
a)
[Co(NH3)3Cl3]0
b)
[Co (en) Cl2 (NH3)2]+
c)
[Co (en)3]3+
d)
[Co (en)2Cl2]+ (en = ethylenediamine)

|
Kajal Bose answered |
The octahedral coordination compounds of the type MA3B3 exhibit fac-mer isomerism.
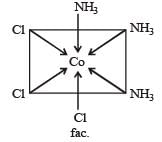
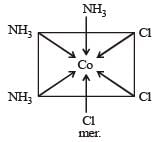
21. A body is orbitting around earth at a mean radius which is two times as greater as the parking orbit of a satellite, the period of body is : - a)4 days
- b)2√2 days
- c)16 days
- d)64 days
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
21. A body is orbitting around earth at a mean radius which is two times as greater as the parking orbit of a satellite, the period of body is :
a)
4 days
b)
2√2 days
c)
16 days
d)
64 days
|
|
Advait Singh answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
By Kepler's third law of planetary motion,
We have,
T2 ∝ a3
Given, T1=1 day (geostationary)
By Kepler's third law of planetary motion,
We have,
T2 ∝ a3
Given, T1=1 day (geostationary)
a1 = a, a2 = 2a
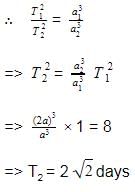
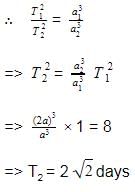
Th e complexes [Co(NH3)6] [Cr (CN)6] and [Cr(NH3)6] [Co(CN)6] are the examples of which type of isomerism? [2011]- a)Linkage isomerism
- b)Ionization isomerism
- c)Coordination isomerism
- d)Geometrical isomerism
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Th e complexes [Co(NH3)6] [Cr (CN)6] and [Cr(NH3)6] [Co(CN)6] are the examples of which type of isomerism? [2011]
a)
Linkage isomerism
b)
Ionization isomerism
c)
Coordination isomerism
d)
Geometrical isomerism

|
Abhijeet Goyal answered |
Coordination isomerism occurs when cationic and anionic complexes of different metal ions are present in a salt. Interchange of ligand between the complexes give isomers e.g. [Co (NH3)6] [Cr (CN)6] is an isomer of [Co (CN)6] [Cr (NH3)6]
30. A body of weight mg is hanging on a string which extends in length by l. The work done in extending the string is :- a)mgl
- b)mgl/2
- c)2 mgl
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
30. A body of weight mg is hanging on a string which extends in length by l. The work done in extending the string is :
a)
mgl
b)
mgl/2
c)
2 mgl
d)
none of these
|
|
Yash Patel answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
L = h
The gravitational force is a conservative field.
The work done by the body to extend the string is equivalent to
Potential E = mgh = mgL
The gravitational force is a conservative field.
The work done by the body to extend the string is equivalent to
Potential E = mgh = mgL
15. If a Carnot engine is working with source temperature 227°C and sink temperature 27°C, its efficiency will be :- a)40 %
- b)10 %
- c)67 %
- d)50 %
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
15. If a Carnot engine is working with source temperature 227°C and sink temperature 27°C, its efficiency will be :
a)
40 %
b)
10 %
c)
67 %
d)
50 %
|
|
Ram Mohith answered |
The efficiency of a Carnot engine is given by,
n = 1 - (t/T) where, t = temperature of sink (in K) = 300 K
T = temperature of source (in K) = 500 K
n = 1 - (300/500)
= 1 - 0.6
= 0.4
Therefore, the efficiency of this Carnot engine is 40%
Among [ Ni(CO)4],[ Ni(CN) 4]2- ,[ NiCl4]2- species, the hybridization states of the Ni atom are, respectively(At. No. of Ni = 28) [2004]- a)sp3, dsp2, dsp2
- b)sp3, dsp2, sp3
- c)sp3, sp3, dsp2
- d)dsp2 , sp3 , sp3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Among [ Ni(CO)4],[ Ni(CN) 4]2- ,[ NiCl4]2- species, the hybridization states of the Ni atom are, respectively(At. No. of Ni = 28) [2004]
a)
sp3, dsp2, dsp2
b)
sp3, dsp2, sp3
c)
sp3, sp3, dsp2
d)
dsp2 , sp3 , sp3
|
|
User3973420 answered |
In Ni(CO)4, nickel is sp3 hybridised because in it
oxidation state of Ni is zero. So, configuration of
28Ni=1s2,2s22p6,3s23p63d8,4s2
(CO is a strong field ligand, hence does pairing of
electrons)
In [Ni(CN)4]2−nickel is present as Ni2+, so its
configuration = 1s2,2s22p6,3s23p63d8
CN− is strong field ligand, hence it makes
Ni2+ electrons to be paired up.
In [NiCl4]2−, nickel is present as Ni2+ , so its
configuration = 1s2,2s22p6,3s23p6,3d8
Cl− is a weak field ligand, hence in Ni2+ electrons
are not paired....
oxidation state of Ni is zero. So, configuration of
28Ni=1s2,2s22p6,3s23p63d8,4s2
(CO is a strong field ligand, hence does pairing of
electrons)
In [Ni(CN)4]2−nickel is present as Ni2+, so its
configuration = 1s2,2s22p6,3s23p63d8
CN− is strong field ligand, hence it makes
Ni2+ electrons to be paired up.
In [NiCl4]2−, nickel is present as Ni2+ , so its
configuration = 1s2,2s22p6,3s23p6,3d8
Cl− is a weak field ligand, hence in Ni2+ electrons
are not paired....
Which of the following coordination compounds would exhibit optical isomerism? [2004]- a)pentamminenitrocobalt(III) iodide
- b)diamminedichloroplatinum(II)
- c)trans-dicyanobis (ethylenediamine) chromium (III) chloride
- d)tris-(ethylendiamine) cobalt (III) bromide
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following coordination compounds would exhibit optical isomerism? [2004]
a)
pentamminenitrocobalt(III) iodide
b)
diamminedichloroplatinum(II)
c)
trans-dicyanobis (ethylenediamine) chromium (III) chloride
d)
tris-(ethylendiamine) cobalt (III) bromide

|
Shivani Tiwari answered |
The optical isomers are pair of molecules which are non super imposable mirror images of each other
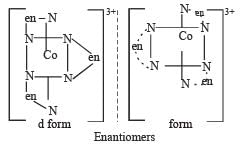
The two optically active isomers are collectivity called enantiomers.
[Co(NH3)4 (NO2)2] Cl exhibits [2006]- a)linkage isomerism, ionization isomerism and geometrical isomerism
- b)ionization isomerism, geometrical isomerism and optical isomerism
- c)linkage isomerism, geometrical isomerism and optical isomerism
- d)linkage isomerism, ionization isomerism and optical isomerism
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
[Co(NH3)4 (NO2)2] Cl exhibits [2006]
a)
linkage isomerism, ionization isomerism and geometrical isomerism
b)
ionization isomerism, geometrical isomerism and optical isomerism
c)
linkage isomerism, geometrical isomerism and optical isomerism
d)
linkage isomerism, ionization isomerism and optical isomerism

|
Naveen Menon answered |
The given compound may have lin kage isomerism due to presence of NO2 group which may be in the form –NO2 or –ONO.
It may have ionisation isomerism due to presence of two ionisable group –NO2 & – Cl. It may have geometrical isomerism in the form of form as follows :
It may have ionisation isomerism due to presence of two ionisable group –NO2 & – Cl. It may have geometrical isomerism in the form of form as follows :
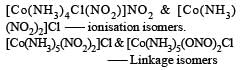
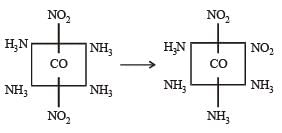
Geometrical isomers
Considering H2O as a weak field ligand, the number of unpaired electrons in [Mn(H2O)6]2+ will be (At. no. of Mn = 25) [2004] - a)three
- b)five
- c)two
- d)four
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Considering H2O as a weak field ligand, the number of unpaired electrons in [Mn(H2O)6]2+ will be (At. no. of Mn = 25) [2004]
a)
three
b)
five
c)
two
d)
four

|
Sushant Goyal answered |
Since H2O is a weak ligand, it will not cause pairing of electrons in the metal ion Mn2+.
Thus electronic configuration of the metal (Mn2+) in the complex will be
Thus electronic configuration of the metal (Mn2+) in the complex will be
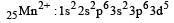
i.e s unpaired electrons.
The complex, [Pt(Py)(NH3)BrCl] will have how many geometrical isomers ? [2011]- a)3
- b)4
- c)0
- d)2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The complex, [Pt(Py)(NH3)BrCl] will have how many geometrical isomers ? [2011]
a)
3
b)
4
c)
0
d)
2

|
Sneha Basak answered |
Complexes of the type MABCD may exist in three isomeric forms.
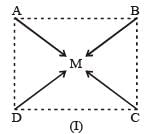
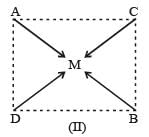
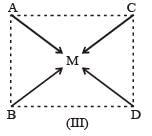
Similarly, [Pt (Py) (NH3) BrCl] may exist in three isomeric form in which M = Pt A = Py, B = NH3, C = Br, D = Cl.
Which of the following does not have a metalcarbon bond? [2004]- a)Al(OC2 H5)3
- b)C2 H5MgBr
- c)K[Pt (C2H4)Cl3]
- d)Ni(CO)4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following does not have a metalcarbon bond? [2004]
a)
Al(OC2 H5)3
b)
C2 H5MgBr
c)
K[Pt (C2H4)Cl3]
d)
Ni(CO)4

|
Ishaan Menon answered |
Triethoxyaluminium has no Al – C linkage
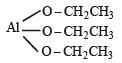
Which is diamagnetic? [NEET Kar. 2013]- a)[Fe(CN)6]3–
- b)[Co(F6)]3–
- c)[Ni(CN)4]2–
- d)[NiCl4]2–
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is diamagnetic? [NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
[Fe(CN)6]3–
b)
[Co(F6)]3–
c)
[Ni(CN)4]2–
d)
[NiCl4]2–

|
Swara Desai answered |

CN– is a strong ligand and causes pairing of 3 electrons of Ni2+.
∴ It is diamagnetic.
Which of the following carbonyls will have the strongest C – O bond ? [2011 M]- a)Mn (CO)6+
- b)Cr (CO)6
- c)V (CO)6–
- d)Fe (CO)5
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following carbonyls will have the strongest C – O bond ? [2011 M]
a)
Mn (CO)6+
b)
Cr (CO)6
c)
V (CO)6–
d)
Fe (CO)5

|
Mehul Iyer answered |
As + ve charge on the central metal atom increases, the less readily the metal can donate electron density into the π* orbitals of CO ligand to weaken the C – O bond.
Hence, the C – O bond would be strongest in Mn(CO)6+.
Hence, the C – O bond would be strongest in Mn(CO)6+.
Which of the following complexes exhibits the highest paramagnetic behaviour ? [2008] where gly = glycine, en = ethylenediamine and bpy = bipyridyl moities) (At.nosTi = 22, V = 23, Fe = 26, Co = 27)- a)[V(gly)2(OH)2(NH3)2]+
- b)[Fe(en)(bpy)(NH3)2]2+
- c)[Co(OX)2(OH)2]–
- d)[Ti(NH3)6]3+
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following complexes exhibits the highest paramagnetic behaviour ? [2008] where gly = glycine, en = ethylenediamine and bpy = bipyridyl moities) (At.nosTi = 22, V = 23, Fe = 26, Co = 27)
a)
[V(gly)2(OH)2(NH3)2]+
b)
[Fe(en)(bpy)(NH3)2]2+
c)
[Co(OX)2(OH)2]–
d)
[Ti(NH3)6]3+

|
Rajat Roy answered |
More the number of unpaired electrons present in a complex more is its paramagnetic behaviour.
To find unpaired electrons let us calculate the oxidation states of elements in each complex and then write the electronic configuration for that oxidation state to find the number of unpaired electrons in it.
We find that in their complexes V, Fe, Co and Ti are in + 3, + 2, + 5, and + 3 oxidation states respectively. In these state the number of unpaired electrons present in them are 2, 4, 4 and 1 respectively. Since the maximum number of unpaired electrons are in cobalt complex so it has highest paramagnetic behaviour i.e. choice (c) is correct answer.
To find unpaired electrons let us calculate the oxidation states of elements in each complex and then write the electronic configuration for that oxidation state to find the number of unpaired electrons in it.
We find that in their complexes V, Fe, Co and Ti are in + 3, + 2, + 5, and + 3 oxidation states respectively. In these state the number of unpaired electrons present in them are 2, 4, 4 and 1 respectively. Since the maximum number of unpaired electrons are in cobalt complex so it has highest paramagnetic behaviour i.e. choice (c) is correct answer.
Which of the following complex ions is expected to absorb visible light? [2009] (At. no. Zn = 30, Sc = 21, Ti = 22, Cr = 24)- a)[Ti (en)2(NH3)2]4+
- b)[Cr (NH3)6]3+
- c)[Zn (NH3)6]2+
- d)[Sc (H2O)3 (NH3)3]3+
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following complex ions is expected to absorb visible light? [2009] (At. no. Zn = 30, Sc = 21, Ti = 22, Cr = 24)
a)
[Ti (en)2(NH3)2]4+
b)
[Cr (NH3)6]3+
c)
[Zn (NH3)6]2+
d)
[Sc (H2O)3 (NH3)3]3+

|
Mohit Patel answered |
Explanation:
To determine which complex ion is expected to absorb visible light, we need to consider the electronic configuration and the nature of the ligands in each complex ion. The absorption of visible light occurs when an electron in a transition metal complex ion is excited from a lower energy level (ground state) to a higher energy level (excited state). This excitation is possible when the energy of the incident light matches the energy difference between the two levels.
[Ti (en)2(NH3)2]4:
- The complex ion contains the ligands ethylenediamine (en) and ammonia (NH3).
- The central metal ion is titanium (Ti) with an atomic number of 22.
- The electronic configuration of Ti in its ground state is [Ar]3d24s2.
- The complex ion has a d2 configuration, which means it will have a weak absorption in the visible region.
- However, the ligands en and NH3 are not strong-field ligands, so the energy difference between the d orbitals is not significant enough to absorb visible light.
- Therefore, this complex ion is not expected to absorb visible light.
[Cr (NH3)6]3:
- The complex ion contains the ligand ammonia (NH3).
- The central metal ion is chromium (Cr) with an atomic number of 24.
- The electronic configuration of Cr in its ground state is [Ar]3d54s1.
- The complex ion has a d4 configuration, which means it will have a strong absorption in the visible region.
- The ligand NH3 is a strong-field ligand, causing a significant energy difference between the d orbitals.
- Therefore, this complex ion is expected to absorb visible light.
[Zn (NH3)6]2:
- The complex ion contains the ligand ammonia (NH3).
- The central metal ion is zinc (Zn) with an atomic number of 30.
- The electronic configuration of Zn in its ground state is [Ar]3d104s2.
- The complex ion has a d10 configuration, which means it will not have any absorption in the visible region.
- The ligand NH3 is not a strong-field ligand, so the energy difference between the d orbitals is not significant enough to absorb visible light.
- Therefore, this complex ion is not expected to absorb visible light.
[Sc (H2O)3 (NH3)3]3:
- The complex ion contains the ligands water (H2O) and ammonia (NH3).
- The central metal ion is scandium (Sc) with an atomic number of 21.
- The electronic configuration of Sc in its ground state is [Ar]3d14s2.
- The complex ion has a d1 configuration, which means it will have a weak absorption in the visible region.
- However, the ligands H2O and NH3 are not strong-field ligands, so the energy difference between the d orbitals is not significant enough to absorb visible light.
- Therefore, this complex ion is not expected to absorb visible light.
Therefore, the complex ion [Cr (NH3)6]3 is expected to absorb visible light.
To determine which complex ion is expected to absorb visible light, we need to consider the electronic configuration and the nature of the ligands in each complex ion. The absorption of visible light occurs when an electron in a transition metal complex ion is excited from a lower energy level (ground state) to a higher energy level (excited state). This excitation is possible when the energy of the incident light matches the energy difference between the two levels.
[Ti (en)2(NH3)2]4:
- The complex ion contains the ligands ethylenediamine (en) and ammonia (NH3).
- The central metal ion is titanium (Ti) with an atomic number of 22.
- The electronic configuration of Ti in its ground state is [Ar]3d24s2.
- The complex ion has a d2 configuration, which means it will have a weak absorption in the visible region.
- However, the ligands en and NH3 are not strong-field ligands, so the energy difference between the d orbitals is not significant enough to absorb visible light.
- Therefore, this complex ion is not expected to absorb visible light.
[Cr (NH3)6]3:
- The complex ion contains the ligand ammonia (NH3).
- The central metal ion is chromium (Cr) with an atomic number of 24.
- The electronic configuration of Cr in its ground state is [Ar]3d54s1.
- The complex ion has a d4 configuration, which means it will have a strong absorption in the visible region.
- The ligand NH3 is a strong-field ligand, causing a significant energy difference between the d orbitals.
- Therefore, this complex ion is expected to absorb visible light.
[Zn (NH3)6]2:
- The complex ion contains the ligand ammonia (NH3).
- The central metal ion is zinc (Zn) with an atomic number of 30.
- The electronic configuration of Zn in its ground state is [Ar]3d104s2.
- The complex ion has a d10 configuration, which means it will not have any absorption in the visible region.
- The ligand NH3 is not a strong-field ligand, so the energy difference between the d orbitals is not significant enough to absorb visible light.
- Therefore, this complex ion is not expected to absorb visible light.
[Sc (H2O)3 (NH3)3]3:
- The complex ion contains the ligands water (H2O) and ammonia (NH3).
- The central metal ion is scandium (Sc) with an atomic number of 21.
- The electronic configuration of Sc in its ground state is [Ar]3d14s2.
- The complex ion has a d1 configuration, which means it will have a weak absorption in the visible region.
- However, the ligands H2O and NH3 are not strong-field ligands, so the energy difference between the d orbitals is not significant enough to absorb visible light.
- Therefore, this complex ion is not expected to absorb visible light.
Therefore, the complex ion [Cr (NH3)6]3 is expected to absorb visible light.
Which of the following will give a pair of enantiomorphs? [2007]- a)[Cr(NH3)6][Co(CN)6]
- b)[Co(en)2Cl2]Cl
- c)[Pt(NH3)4] [PtCl6]
- d)[Co(NH3)4Cl2]NO2. (en =NH2CH2CH2NH2)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following will give a pair of enantiomorphs? [2007]
a)
[Cr(NH3)6][Co(CN)6]
b)
[Co(en)2Cl2]Cl
c)
[Pt(NH3)4] [PtCl6]
d)
[Co(NH3)4Cl2]NO2. (en =NH2CH2CH2NH2)

|
Shalini Saha answered |
Non superimposable mirror images are called optical isomers and may be described as “chiral’. They are also called enantiomers and rotate plane polarised light in opposite directions.
Crystal field stabilization energy for high spin 4 octahedral complex is: [2010]- a)– 1.8 Δ0
- b)– 1.6 Δ0 + P
- c)– 1.2 Δ0
- d)– 0.6 Δ0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Crystal field stabilization energy for high spin 4 octahedral complex is: [2010]
a)
– 1.8 Δ0
b)
– 1.6 Δ0 + P
c)
– 1.2 Δ0
d)
– 0.6 Δ0

|
Prasenjit Pillai answered |
4 in high spin octahedral complex
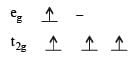
CFSE = [0.6 × 1] + [–0.4 × 3] = – 0.6 Δ0
In which of the following coordination entities the magnitude Δ0 (CFSE in octahedral field) will be maximum? [2008]- a)[Co(H2O)6]3+
- b)[Co(NH3)6]3+
- c)[Co(CN)6]3–
- d)[Co (C2O4)3]3– (At. No. Co = 27)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following coordination entities the magnitude Δ0 (CFSE in octahedral field) will be maximum? [2008]
a)
[Co(H2O)6]3+
b)
[Co(NH3)6]3+
c)
[Co(CN)6]3–
d)
[Co (C2O4)3]3– (At. No. Co = 27)

|
Abhijeet Goyal answered |
In octahedral field the crystal field splitting of d- orbitals of a metal ion depends upon the field produced by the ligands.
In general ligands can be arranged in a series in the order of increasing fields and splittings which they produce around a central metal ion. A portion of the series is given below. cyanide > ethylene - diamine > ammonia > pyridine>thiocyanate > water> fluoride > oxalate > hydroxide> chloride> bromide > iodide.
Out of the given ligands water, ammonia, cyanide and oxalate, we can find from the above series of ligands that the maximum splitting will occur in case of cyanide (CN–) i.e. the magnitude of Δ0 will be maximum in case of [Co(CN)6]3+.
In general ligands can be arranged in a series in the order of increasing fields and splittings which they produce around a central metal ion. A portion of the series is given below. cyanide > ethylene - diamine > ammonia > pyridine>thiocyanate > water> fluoride > oxalate > hydroxide> chloride> bromide > iodide.
Out of the given ligands water, ammonia, cyanide and oxalate, we can find from the above series of ligands that the maximum splitting will occur in case of cyanide (CN–) i.e. the magnitude of Δ0 will be maximum in case of [Co(CN)6]3+.
[Cr(H2O)6]Cl3 (at no. of Cr = 24) has a magnetic moment of 3.83 B. M. The correct distribution of 3d electrons in the Chromium of the complex is- a)3d xy1, (3dx2 –y2)1, 3dyz1 [2006]
- b)3d xy1, 3dyz1, 3dxz1
- c)3dxy1, 3dyz1, 3dz2
- d)(3dx2 – y2)1, 3dz2 , 3dxz1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
[Cr(H2O)6]Cl3 (at no. of Cr = 24) has a magnetic moment of 3.83 B. M. The correct distribution of 3d electrons in the Chromium of the complex is
a)
3d xy1, (3dx2 –y2)1, 3dyz1 [2006]
b)
3d xy1, 3dyz1, 3dxz1
c)
3dxy1, 3dyz1, 3dz2
d)
(3dx2 – y2)1, 3dz2 , 3dxz1

|
Subhankar Datta answered |
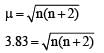
on solving n = 3
as per magnetic moment, it has three unpaired electron.
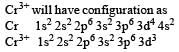
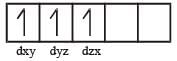
So 3dxy' 3dyz' 3dxz'
A magnetic moment of 1.73 BM will be shown by one among the following : [NEET 2013]- a)[Ni(CN)4]2-
- b)TiCl4
- c)[CoCl6]4-
- d)[Cu(NH3)4]2+
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A magnetic moment of 1.73 BM will be shown by one among the following : [NEET 2013]
a)
[Ni(CN)4]2-
b)
TiCl4
c)
[CoCl6]4-
d)
[Cu(NH3)4]2+

|
Shivani Rane answered |
[Cu(NH3)4]2+ hybridisation 2 Cu+2 – 3 9 has one unpaired e-

So magnetic moment
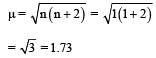
Wavelength of Kα line of X-ray spectra varies with atomic number as : - a)λ∞ Z
- b)λ∞ √Z
- c)λ∞ 1/Z 2
- d)λ∞ 1/√Z
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Wavelength of Kα line of X-ray spectra varies with atomic number as :
a)
λ∞ Z
b)
λ∞ √Z
c)
λ∞ 1/Z 2
d)
λ∞ 1/√Z
|
|
Tejas Verma answered |
The correct answer is Option C.
For characteristic X-rays
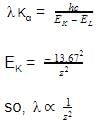
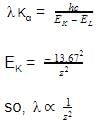
Of the following complex ions, which is diamagnetic in nature ? [2011]- a)[NiCl4]2–
- b)[Ni(CN)4]2–
- c)[CuCl4]2–
- d)[CoF6]3–
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Of the following complex ions, which is diamagnetic in nature ? [2011]
a)
[NiCl4]2–
b)
[Ni(CN)4]2–
c)
[CuCl4]2–
d)
[CoF6]3–

|
Ruchi Chopra answered |
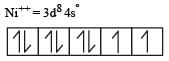
Since, the coordination number of Ni in this complex is 4, the configuration of Ni++ at first sight shows that the complex is paramagnetic with two unpaired electron. However, experiments show that the complex is diamagnetic. This is possible when the 3d electrons rearrange against the Hund’s rule as shown below. This is in accordance with the fact that the ligand involved here is strong i.e., CN– ion.
Ni++ (after rearrangement) 

Hence, now dsp2 hybridization involving one 3d, one 4s and two 4p orbitals, takes place leading to four dsp2 hybrid orbitals, each of which accepts four electron pairs from CN– ion forming [Ni (CN)4]2– ion.
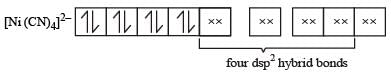
Thus, the complex is diamagnetic as it has no unpaired electron.
Which of the following complex compounds will exhibit highest paramagnetic behaviour? [2011M] (At. No. : Ti = 22, Cr = 24, Co = 27, Zn = 30)- a)[Ti (NH3)6]3+
- b)[Cr (NH3)6]3+
- c)[Co (NH3)6]3+
- d)[Zn (NH3)6]2+
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following complex compounds will exhibit highest paramagnetic behaviour? [2011M] (At. No. : Ti = 22, Cr = 24, Co = 27, Zn = 30)
a)
[Ti (NH3)6]3+
b)
[Cr (NH3)6]3+
c)
[Co (NH3)6]3+
d)
[Zn (NH3)6]2+
|
|
Akanksha Das answered |
(a) [Ti(NH3)6]3+ : 3d1 configuration and thus has one unpaired electron. (b) [Cr(NH3)6]3+ : In this complex Cr is in +3 oxidation state.
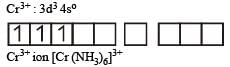

Thus, the complex is paramagnetic.
(c) [Co(NH3)6]3+ : In this complex are cobalt ion is in + 3 oxidation state with 3d6 configuration.
Co3+,[Ar]3d6
Co3+,[Ar]3d6
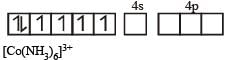
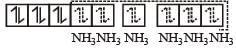
(inner orbital or d2sp3 hybrid orbital low spin complex) diamagnetic
(d) In this complex Zn exists as
Zn++ ion
Zn++ ion : 3d10 4s0
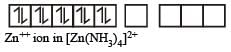
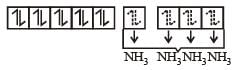
Due to presence of paired electrons complex is diamagnetic in nature.
The correct IUPAC name for [CrF2(en)2]Cl is: [NEET Kar. 2013]- a)Chloro difluoridobis (ethylene diamine) chromium (III)
- b)Chloro difluor idoeth ylen ediamin ech -romium (III) chloride
- c)Difluoridobis (ethylene diamine) chromium (III) chloride
- d)Difluorobis-(ethylene diamine) chromium (III) chloride
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct IUPAC name for [CrF2(en)2]Cl is: [NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
Chloro difluoridobis (ethylene diamine) chromium (III)
b)
Chloro difluor idoeth ylen ediamin ech -romium (III) chloride
c)
Difluoridobis (ethylene diamine) chromium (III) chloride
d)
Difluorobis-(ethylene diamine) chromium (III) chloride
|
|
Swara Sharma answered |
Explanation:
The given compound has the following coordination entities:
- Chromium (III) ion: [Cr(en)2F2]3+
- Chloride ion: Cl-
Now, let's break down the name of the compound into its individual parts:
- The first part of the name is the name of the central metal ion: chromium (III).
- The second part of the name describes the ligands that are attached to the central metal ion. In this case, the ligands are two ethylenediamine (en) molecules and two fluoride (F-) ions.
- The third part of the name describes the anion that is associated with the compound. In this case, the anion is a chloride ion (Cl-).
Putting all of this together, the correct IUPAC name for the compound [CrF2(en)2]Cl is: Difluoridobis(ethylene diamine)chromium(III)chloride.
Therefore, option C is the correct answer.
The given compound has the following coordination entities:
- Chromium (III) ion: [Cr(en)2F2]3+
- Chloride ion: Cl-
Now, let's break down the name of the compound into its individual parts:
- The first part of the name is the name of the central metal ion: chromium (III).
- The second part of the name describes the ligands that are attached to the central metal ion. In this case, the ligands are two ethylenediamine (en) molecules and two fluoride (F-) ions.
- The third part of the name describes the anion that is associated with the compound. In this case, the anion is a chloride ion (Cl-).
Putting all of this together, the correct IUPAC name for the compound [CrF2(en)2]Cl is: Difluoridobis(ethylene diamine)chromium(III)chloride.
Therefore, option C is the correct answer.
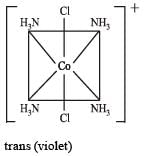
In a particular isomer of [Co(NH3)4Cl2]0, the Cl-Co-Cl angle is 90°, the isomer is known as [NEET Kar. 2013]- a)Linkage isomer
- b)Optical isomer
- c)cis-isomer
- d)Position isomer
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a particular isomer of [Co(NH3)4Cl2]0, the Cl-Co-Cl angle is 90°, the isomer is known as [NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
Linkage isomer
b)
Optical isomer
c)
cis-isomer
d)
Position isomer
|
|
Anisha Bose answered |
The correct answer is Option C.
The Cl−Co−Cl bond is at right angle.
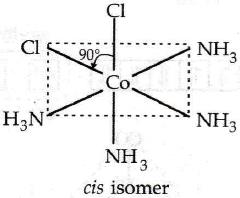
The Cl−Co−Cl bond is at right angle.
The anion of acetylacetone (a cac) for ms Co(acac)3 chelate with Co3+. The rings of the chelate are [NEET Kar. 2013]- a)three membered
- b)five membered
- c)four membered
- d)six membered
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The anion of acetylacetone (a cac) for ms Co(acac)3 chelate with Co3+. The rings of the chelate are [NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
three membered
b)
five membered
c)
four membered
d)
six membered

|
Amar Jain answered |
Explanation:
Acetylacetone:
Acetylacetone (also known as 2,4-pentanedione or acac) is a β-diketone compound with the formula CH3COCH2COCH3. It is a yellow liquid with a fruity odor. Acetylacetone is a versatile ligand that forms stable complexes with many metal ions. It acts as a bidentate ligand, meaning it can form coordination bonds with a metal ion through two oxygen atoms.
Co(acac)3:
Co(acac)3 is the coordination compound formed when 3 molecules of acetylacetone (acac) coordinate with a central cobalt (Co) ion. The cobalt ion has a charge of +3, and each acetylacetone molecule acts as a bidentate ligand, coordinating through the oxygen atoms of the carbonyl groups.
Chelate Complex:
In a chelate complex, the ligand forms a ring structure with the central metal ion. This ring structure is called a chelate ring. The chelate ring is formed by the coordination of two or more atoms of the ligand to the metal ion. In the case of Co(acac)3, the anion of acetylacetone (acac) chelates with the cobalt ion.
Ring Formation:
The question asks about the ring size of the chelate formed between the anion of acetylacetone and the Co(acac)3 complex. To determine the ring size, we need to count the number of atoms involved in the chelation.
In Co(acac)3, there are 3 acetylacetone molecules coordinating with the cobalt ion. Each acetylacetone molecule has two oxygen atoms available for coordination. Therefore, the total number of oxygen atoms available for coordination is 3 x 2 = 6.
Since the anion of acetylacetone chelates with the cobalt ion, it should coordinate with two oxygen atoms. This means that the anion of acetylacetone forms a 6-membered chelate ring with the cobalt ion.
Answer:
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - six-membered chelate ring.
Acetylacetone:
Acetylacetone (also known as 2,4-pentanedione or acac) is a β-diketone compound with the formula CH3COCH2COCH3. It is a yellow liquid with a fruity odor. Acetylacetone is a versatile ligand that forms stable complexes with many metal ions. It acts as a bidentate ligand, meaning it can form coordination bonds with a metal ion through two oxygen atoms.
Co(acac)3:
Co(acac)3 is the coordination compound formed when 3 molecules of acetylacetone (acac) coordinate with a central cobalt (Co) ion. The cobalt ion has a charge of +3, and each acetylacetone molecule acts as a bidentate ligand, coordinating through the oxygen atoms of the carbonyl groups.
Chelate Complex:
In a chelate complex, the ligand forms a ring structure with the central metal ion. This ring structure is called a chelate ring. The chelate ring is formed by the coordination of two or more atoms of the ligand to the metal ion. In the case of Co(acac)3, the anion of acetylacetone (acac) chelates with the cobalt ion.
Ring Formation:
The question asks about the ring size of the chelate formed between the anion of acetylacetone and the Co(acac)3 complex. To determine the ring size, we need to count the number of atoms involved in the chelation.
In Co(acac)3, there are 3 acetylacetone molecules coordinating with the cobalt ion. Each acetylacetone molecule has two oxygen atoms available for coordination. Therefore, the total number of oxygen atoms available for coordination is 3 x 2 = 6.
Since the anion of acetylacetone chelates with the cobalt ion, it should coordinate with two oxygen atoms. This means that the anion of acetylacetone forms a 6-membered chelate ring with the cobalt ion.
Answer:
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - six-membered chelate ring.
CN– is a strong field ligand. This is due to the fact that [2004]- a)it carries negative charge
- b)it is a pseudohalide
- c)it can accept electrons from metal species
- d)it forms high spin complexes with metal species
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
CN– is a strong field ligand. This is due to the fact that [2004]
a)
it carries negative charge
b)
it is a pseudohalide
c)
it can accept electrons from metal species
d)
it forms high spin complexes with metal species

|
Swara Desai answered |
CN– is astrong fieldlig and as it is a psuedohalide ion. These ions are strong coordinating ligands and hence have the tendency to form σ-bond (from the pseudo halide to the metal) and π-bond. (from the metal to pseudo halide)
The d-electron configurations of Cr 2+, Mn2+, Fe2+ and Co2+ are d4, d5, d6 and d7, respectively.Which one of the following will exhibit minimum paramagnetic behaviour? [2011] (At, nos. Cr = 24, Mn = 25, Fe = 26, Co = 27)- a)[Mn(H2O)6]2+
- b)[Fe(H2O)6]2+
- c)[Co(H2O)6]2+
- d)[Cr(H2O)6]2+
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The d-electron configurations of Cr 2+, Mn2+, Fe2+ and Co2+ are d4, d5, d6 and d7, respectively.Which one of the following will exhibit minimum paramagnetic behaviour? [2011] (At, nos. Cr = 24, Mn = 25, Fe = 26, Co = 27)
a)
[Mn(H2O)6]2+
b)
[Fe(H2O)6]2+
c)
[Co(H2O)6]2+
d)
[Cr(H2O)6]2+

|
Nayanika Dasgupta answered |
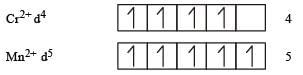
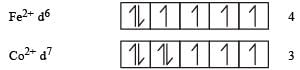
Minimum paramagnetic behaviour = [Co (H2O)6]2+
Red precipitate is obtained when ethanol solution of dimethylglyoxime is added to ammoniacal Ni(II). Which of the following statements is not true ? [2012 M]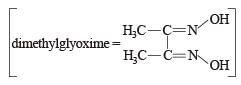
- a)Red complex has a square planar geometry.
- b)Complex has symmetrical H-bonding
- c)Red complex has a tetrahedral geometry.
- d)Dimethylglyoxime functions as bidentate ligand.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Red precipitate is obtained when ethanol solution of dimethylglyoxime is added to ammoniacal Ni(II). Which of the following statements is not true ? [2012 M]
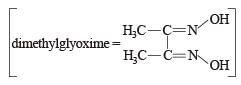
a)
Red complex has a square planar geometry.
b)
Complex has symmetrical H-bonding
c)
Red complex has a tetrahedral geometry.
d)
Dimethylglyoxime functions as bidentate ligand.

|
Shruti Chauhan answered |
Nickel ions are frequently detected by the formation of red precipitate of the complex of nickel dimethylglyoxime, when heated with dimethylglyoxime.
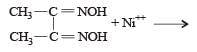
Dimethylglyoxime
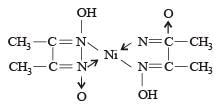
Nickel dimethylglyoxime
Which of the following is considered to be an anticancer species ? [2004]- a)
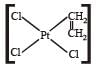
- b)
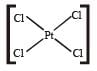
- c)
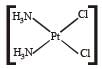
- d)
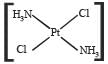
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is considered to be an anticancer species ? [2004]
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Surbhi Das answered |
Diaminodichloroplatinum (II) commonly known as - platin is found to have anticancer property.
Which one of the following complexes is not expected to exhibit isomerism? [2010]- a)
- b)
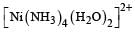
- c)
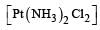
- d)
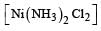
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following complexes is not expected to exhibit isomerism? [2010]
a)
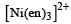
b)
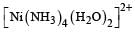
c)
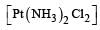
d)
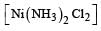

|
Rohan Unni answered |
hybridisation, thus tetrahedral in shape. Hence the four ligands are not different to exhibit optical isomerism.
∴ Correct choice : (d)
Chapter doubts & questions for Coordination Compounds - NEET Past Year Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Coordination Compounds - NEET Past Year Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup

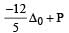
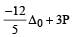
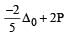
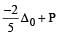
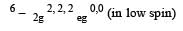
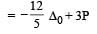






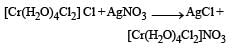

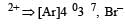 is weak ligand.
is weak ligand.







