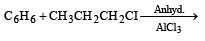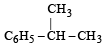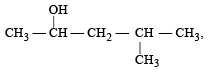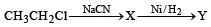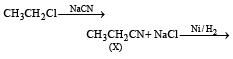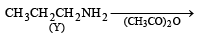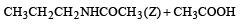All Exams >
NEET >
NEET Past Year Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes for NEET Exam
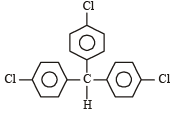
Which one is most reactive towards SN1 reaction ?- a)C6 H5CH(C6 H5 )Br [2010]
- b)C6 H5CH(CH3)Br
- c)C6 H5C(CH3)(C6 H5)Br
- d)C6 H5CH2Br
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is most reactive towards SN1 reaction ?
a)
C6 H5CH(C6 H5 )Br [2010]
b)
C6 H5CH(CH3)Br
c)
C6 H5C(CH3)(C6 H5)Br
d)
C6 H5CH2Br

|
Rajat Roy answered |
SN1 reactions involve the formation of carbocations, hence higher the stability of carbocation, more will be reactivity of the parent alkyl halide. Thus tertiary carbocation formed from (c) is stabilized by two phenyl groups and one methyl group, hence most stable.
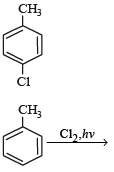
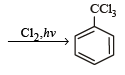
The reaction of toluene with Cl2 in presence of FeCl3 gives ' X' and reaction in presence of light gives ‘Y’. Thus, ‘X’ and ‘Y’ are : [2010]- a)X = Benzal chloride, Y = o – Chlorotoluene
- b)X = m – Chlorotoluene , Y = p – Chlorotoluene
- c)X = o –and p – Chlorotoluene, Y = Trichloromethyl – benzene
- d)X = Benzyl chloride, Y = m – Chlorotoluene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction of toluene with Cl2 in presence of FeCl3 gives ' X' and reaction in presence of light gives ‘Y’. Thus, ‘X’ and ‘Y’ are : [2010]
a)
X = Benzal chloride, Y = o – Chlorotoluene
b)
X = m – Chlorotoluene , Y = p – Chlorotoluene
c)
X = o –and p – Chlorotoluene, Y = Trichloromethyl – benzene
d)
X = Benzyl chloride, Y = m – Chlorotoluene
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
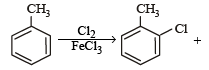
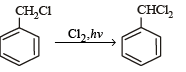
2-Bromopen tane is heated with potassium ethoxide in ethanol. The major product obtained is[1998]- a)2-ethoxypentane
- b)pentene-1
- c)trans-2-pentene
- d)cis-pentene-2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
2-Bromopen tane is heated with potassium ethoxide in ethanol. The major product obtained is[1998]
a)
2-ethoxypentane
b)
pentene-1
c)
trans-2-pentene
d)
cis-pentene-2

|
Deepak Joshi answered |
Potassium ethoxide is a strong base, and 2-bromopentane is a 2º bromide, so elimination raction predominates
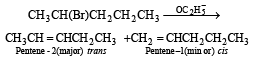
Since trans- alkene is more stable than cis.thus trans-pentene -2 is the main product.
Which of the following is responsible for depletion of the ozone layer in the upper strata of the atmosphere? [2004]- a)Polyh alogens
- b)Ferrocene
- c)Fullerenes
- d)Fr eons
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is responsible for depletion of the ozone layer in the upper strata of the atmosphere? [2004]
a)
Polyh alogens
b)
Ferrocene
c)
Fullerenes
d)
Fr eons

|
Devansh Mehra answered |
Chlorofluorocarbons, e.g. CF2Cl2, CHF2Cl2, HCF2CHCl2. These are non-inflammable colour less and stable upto 550ºC. These are emitted as propellants in aerosol spray, cans refrigerators, fire fighting reagents etc. They are chemically inert and hence do not react with any substance with which they come in contact and therefore float through the atmosphere and as a result enter the stratosphere. There theyabsorb UV-rays and due to this they produce free atomic chlorine which results decomposition of ozone which cause depletion of ozone layer.
Reactivity order of halides for dehydrohalogenation is [2002]- a)R – F > R – Cl > R – Br > R –I
- b)R –I > R – Br > R – Cl > R – F
- c)R –I > R – Cl > R – Br > R – F
- d)R – F > R –I > R – Br > R – Cl
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Reactivity order of halides for dehydrohalogenation is [2002]
a)
R – F > R – Cl > R – Br > R –I
b)
R –I > R – Br > R – Cl > R – F
c)
R –I > R – Cl > R – Br > R – F
d)
R – F > R –I > R – Br > R – Cl

|
Raghav Khanna answered |
The order of atomic size of h alogen s decrease in the order I > Br > Cl > F i.e on moving down a group atomic size increases. Further the bond length of C-X bond deccreases in the order C – I > C – Br > C – Cl > C – F and hence the bond dissociation energy decreases in the order R – F > R – Cl > R – Br > R – I hence R – I being a weakest bond break most easily. Hence R – I is most reactive.
Consider the reactions : [2011 M]
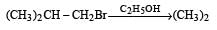
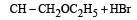
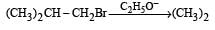
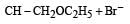 The mechanisms of reactions (i) and (ii) are respectively :
The mechanisms of reactions (i) and (ii) are respectively :
- a)SN2 and SN2
- b)SN1 and SN1
- c)SN2 and SN1
- d)SN1 and SN2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the reactions : [2011 M]
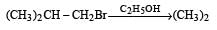
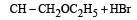
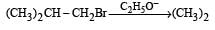
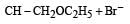
The mechanisms of reactions (i) and (ii) are respectively :
a)
SN2 and SN2
b)
SN1 and SN1
c)
SN2 and SN1
d)
SN1 and SN2

|
Devansh Mehra answered |
explanation: Since rearrangement do not occur in the given nucleophilic substitution
reactions, therefore carbocations are not the intermediate in these reactions.
Thus both the reactions occur by SN2 mechanism
reactions, therefore carbocations are not the intermediate in these reactions.
Thus both the reactions occur by SN2 mechanism
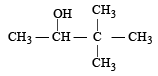
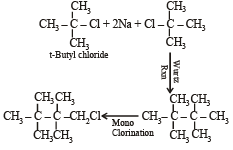
An organic compound A (C4H9Cl) on reaction with Na/diethyl ether gives a hydrocarbon which on monochlorination gives only one chloro derivative, then A is [2001]- a)tert-butyl chloride
- b)sec-butyl chloride
- c)isobutyl chloride
- d)n-butyl chloride
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An organic compound A (C4H9Cl) on reaction with Na/diethyl ether gives a hydrocarbon which on monochlorination gives only one chloro derivative, then A is [2001]
a)
tert-butyl chloride
b)
sec-butyl chloride
c)
isobutyl chloride
d)
n-butyl chloride

|
Ayush Chavan answered |
The replacement of chlorine of chlorobenzene to give phenol requires drastic conditions, but the chlorine of 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene is readily replaced since, [1997]- a)nitro groups make the aromatic ring electron rich at ortho/para positions
- b)nitro groups withdraw electrons from the meta position of the aromatic ring
- c)n itr o groups don ate electr on s at meta position
- d)nitro groups withdraw electrons from ortho/ para positions of the aromatic ring
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The replacement of chlorine of chlorobenzene to give phenol requires drastic conditions, but the chlorine of 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene is readily replaced since, [1997]
a)
nitro groups make the aromatic ring electron rich at ortho/para positions
b)
nitro groups withdraw electrons from the meta position of the aromatic ring
c)
n itr o groups don ate electr on s at meta position
d)
nitro groups withdraw electrons from ortho/ para positions of the aromatic ring

|
Prasenjit Pillai answered |
—NO2 group is electron attractive group, so it is able to deactivate the benzene ring.
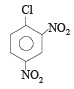
hence withdrawl of electrons from ortho & para position cause easy removal of –Cl atom due to development of +ve charge on o- and p positions.
Industrial preparation of chloroform employs acetone and [1993]- a)Phosgene
- b)Calcium hypochlorite
- c)Chlorine gas
- d)Sodium chloride.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Industrial preparation of chloroform employs acetone and [1993]
a)
Phosgene
b)
Calcium hypochlorite
c)
Chlorine gas
d)
Sodium chloride.

|
Pooja Saha answered |
By distilling ethanol or acetone with a paste of bleaching powder (laboratory and commercial method).
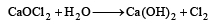
Cl2, so obtained acts as a mild oxidising as well as chlorinating agent
(a)
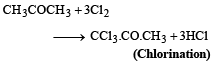
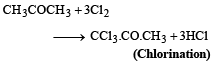
(b)
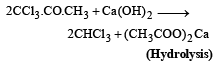
Chloropicrin is obtained by the reaction of [2004]- a)steam on carbon tetrachloride
- b)nitric acid on chlorobenzene
- c)chlorine on picric acid
- d)nitric acid on chloroform
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Chloropicrin is obtained by the reaction of [2004]
a)
steam on carbon tetrachloride
b)
nitric acid on chlorobenzene
c)
chlorine on picric acid
d)
nitric acid on chloroform

|
Abhiram Nair answered |
Chloropicrin is nitrochloroform. It is obtained by the nitration of chloroform with HNO3.
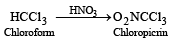
Chloropicrin is a liquids, poisonous and used as an insecticide and a war gas
In a SN2 substitution reaction of the type 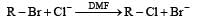 [2008] which one of the following has the highest relative rate ?
[2008] which one of the following has the highest relative rate ?- a)
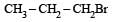
- b)
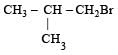
- c)

- d)CH3CH2Br
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a SN2 substitution reaction of the type 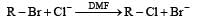 [2008] which one of the following has the highest relative rate ?
[2008] which one of the following has the highest relative rate ?
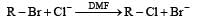 [2008] which one of the following has the highest relative rate ?
[2008] which one of the following has the highest relative rate ?a)
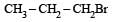
b)
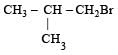
c)

d)
CH3CH2Br

|
Ayush Chavan answered |
For such a reacti on the rate of S2N substitution reaction is maximum in case of CH3CH2 Br because S2N mech an ism is followed in case of primary and secondary halides i.e., S2N reaction is favoured by small groups on the carbon atom attached to halogens so CH3 CH2 Br > CH3 CH2 CH2 Br >
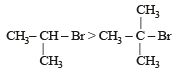
i.e. option (d) is correct.
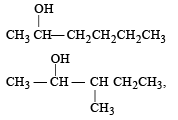
Which of the following is the correct order of boiling points for the given compounds?- a)Chloromethane < Dichloromethane < Chloroform < Carbon tetrachloride
- b)Chloromethane > Dichloromethane > Chloroform > Carbon tetrachloride
- c)Carbon tetrachloride > Chloroform > Dichloromethane > Chloromethane
- d)Chloroform > Carbon tetrachloride > Dichloromethane > Chloromethane
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the correct order of boiling points for the given compounds?
a)
Chloromethane < Dichloromethane < Chloroform < Carbon tetrachloride
b)
Chloromethane > Dichloromethane > Chloroform > Carbon tetrachloride
c)
Carbon tetrachloride > Chloroform > Dichloromethane > Chloromethane
d)
Chloroform > Carbon tetrachloride > Dichloromethane > Chloromethane

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The boiling points increase with the molecular mass and the extent of dipole-dipole interactions. Chloromethane has the lowest boiling point due to its smaller size and weaker intermolecular forces, while carbon tetrachloride has the highest boiling point.
When chlorine is passed through propene at 400°C, which of the following is formed ?[1993]- a)PVC
- b)Allyl chloride
- c)Nikyl chloride
- d)1, 2-Dichloroethane
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When chlorine is passed through propene at 400°C, which of the following is formed ?[1993]
a)
PVC
b)
Allyl chloride
c)
Nikyl chloride
d)
1, 2-Dichloroethane

|
Mehul Iyer answered |
At high temp. i.e., 400°C substitution occurs in preference to addition.
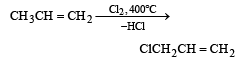
Zerevitinov’s determination of active hydrogen in a compound is based upon its reaction with[1994]- a)Na
- b)CH3MgI
- c)Zn
- d)Al.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Zerevitinov’s determination of active hydrogen in a compound is based upon its reaction with[1994]
a)
Na
b)
CH3MgI
c)
Zn
d)
Al.

|
Ashwini Khanna answered |
Number of active hydrogen in a compound corresponds to the number of moles of CH4 evolved per mole of the compound.
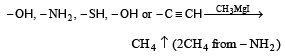
Which chloro derivative of benzene among the following would undergo hydrolysis most readily with aqueous sodium hydroxide to furnish the corresponding hydroxy derivative? [1989]- a)
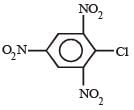
- b)
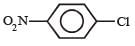
- c)
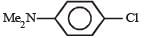
- d)C6H5Cl.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which chloro derivative of benzene among the following would undergo hydrolysis most readily with aqueous sodium hydroxide to furnish the corresponding hydroxy derivative? [1989]
a)

b)

c)

d)
C6H5Cl.

|
Anand Jain answered |
Cl in 2, 4, 6-trinitrochlorobenzene is activated by three NO2 groups at o, and p-positions and hence undergoes hydrolysis most readily.
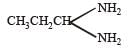
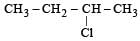 obtained by chlorination of n-butane, will be [2001]
obtained by chlorination of n-butane, will be [2001]- a)l-form
- b)d-form
- c)Meso form
- d)Racemic mixture
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
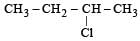 obtained by chlorination of n-butane, will be [2001]
obtained by chlorination of n-butane, will be [2001]a)
l-form
b)
d-form
c)
Meso form
d)
Racemic mixture

|
Smruti Sucharita answered |
Recemic mixture... Bcoz it contains chiral carbon... So shows optical activity...
Which of the following reactions is an example of nucleophilic substitution reaction? [2009]- a)2 RX + 2 Na → R – R + 2 NaX
- b)RX + H2 → RH + HX
- c)RX + Mg → RMgX
- d)RX + KOH → ROH + KX
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following reactions is an example of nucleophilic substitution reaction? [2009]
a)
2 RX + 2 Na → R – R + 2 NaX
b)
RX + H2 → RH + HX
c)
RX + Mg → RMgX
d)
RX + KOH → ROH + KX

|
Ashwini Khanna answered |
In nucleophilic substitution, a nucleophile provides an electron pair to the substrate and the leaving group departs with an electron pair.
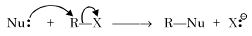
These are usually written as SN (S stands for substitution and N for nucleophilic) and are common in aliphatic compounds especially in alkyl halides and acyl halides.
Chapter doubts & questions for Haloalkanes and Haloarenes - NEET Past Year Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes - NEET Past Year Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup