All Exams >
NEET >
NEET Past Year Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Molecular Basis of Inheritance for NEET Exam
Transformation was discovered by: [2014]- a)Meselson and Stahl
- b)Hershey and Chase
- c)Griffith
- d)Watson and Crick
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Transformation was discovered by: [2014]
a)
Meselson and Stahl
b)
Hershey and Chase
c)
Griffith
d)
Watson and Crick

|
Yash Saha answered |
(c) Frederick Griffith (in 1928), a British Medical officer described the phenomenon of bacterial transformation. He carried out experiment with Streptococcus pneumoniae (bacterium causing pneumonia) which is used to infect mice. By using S Strain (heat killed) and R strain (live) it was concluded that R strain has been transformed by some material of S strain which makes R strain virulent and enable to synthesize smooth polysachharide.
Which one of the following is wrongly matched? [2014]- a)Transcription – Writing information from DNA to tRNA.
- b)Translation – Using information in mRNA to make protein
- c)Repressor protein – Binds to operator to stop enzyme synthesis.
- d)Operon – Structural genes, operator and promoter
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is wrongly matched? [2014]
a)
Transcription – Writing information from DNA to tRNA.
b)
Translation – Using information in mRNA to make protein
c)
Repressor protein – Binds to operator to stop enzyme synthesis.
d)
Operon – Structural genes, operator and promoter

|
Aman Sharma answered |
(a) Process of copying genetic information from DNA to RNA is called transcription. At a time only one DNA strand is being transcribed into RNA. The strand of DNA with polarity 3' → 5' act as template strand and the DNA strand with polarity 5' → 3' act as coding strand.
Commonly used vectors for human genome sequencing are: [2014]- a)T-DNA
- b)BAC and YAC
- c)Expression Vectors
- d)T/A Cloning Vectors
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Commonly used vectors for human genome sequencing are: [2014]
a)
T-DNA
b)
BAC and YAC
c)
Expression Vectors
d)
T/A Cloning Vectors

|
Anirudh Datta answered |
(b) Human genome sequencing is a process that determines the complete DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This requires sequencing all of an organism's chromosomal DNA as well as DNA contained in the mitochondria and, for plants, in the chloroplast. Commonly used vectors for human genome sequencing are BAC (Bacterial artificial chromosomes) and YAC (Yeast artificial chromosomes).
An abnormal human baby with 'XXX' sex chromosomes was born due to- a)formation of abnormal sperms in the father
- b)formation of abnormal ova in the mother
- c)fusion of two ova and one sperm
- d)fusion of two sperms and one ovum
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An abnormal human baby with 'XXX' sex chromosomes was born due to
a)
formation of abnormal sperms in the father
b)
formation of abnormal ova in the mother
c)
fusion of two ova and one sperm
d)
fusion of two sperms and one ovum

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
Alleles are different molecular forms of a gene, representing altemate forms of a given character.
Height of a pea plant-T for tallness and t for dwarfness.
T and t are altemate forms for given character of height.
Heterozygotes and homozygotes refers to inheritance of two different and similar travels for a character respectively.
A complex of ribosomes attached to a single strand of RNA is known as [2016]- a)Polysome
- b)Polymer
- c)Polypeptide
- d)Okazaki fragment
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A complex of ribosomes attached to a single strand of RNA is known as [2016]
a)
Polysome
b)
Polymer
c)
Polypeptide
d)
Okazaki fragment

|
Dipika Das answered |
(a) A polysome or polyribosome is a complex of an mRNA molecule and two or more ribosomes, which is formed during the active translation process. They were initially named as ergosomes in 1963. However, further research by Jonathan Warner and Alex Rich characterized polysome.
A pleiotropic gene: [2015 RS]- a)is a gene evolved during Pliocene.
- b)controls a trait only in combination with another gene
- c)controls multiple traits in an individual.
- d)is expressed only in primitive plants
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A pleiotropic gene: [2015 RS]
a)
is a gene evolved during Pliocene.
b)
controls a trait only in combination with another gene
c)
controls multiple traits in an individual.
d)
is expressed only in primitive plants

|
Arindam Khanna answered |
(c) A pleiotropic gene regulates multiple traits (characte- ristics) in an individual.
Which of the following important biochemical reactions in living systems is catalyzed by a ribozyme?
a)Formation of peptide bondb)Repair of DNAc)Electron transfer chaind)Organization of MTOC during cell divisonCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
In prokaryotes (bacteria) the 23srRNA of the larger subunit of ribosome is the enzyme ribozyme that catalyzes peptide bond formation.
Hence, the correct option is A.
NCERT Reference: Page no. 115 of topic “6.7 TRANSLATION” of chapter 6.
NCERT Reference: Page no. 115 of topic “6.7 TRANSLATION” of chapter 6.
The chromosomes in which centromere is situated close to one end are: [2015 RS]- a)Acrocentric
- b)Telocentric
- c)Sub-metacentric
- d)Metacentric
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The chromosomes in which centromere is situated close to one end are: [2015 RS]
a)
Acrocentric
b)
Telocentric
c)
Sub-metacentric
d)
Metacentric

|
Aman Sharma answered |
(a) In acrocentric chromosomes, one arm is very short but another is long.
In sea urchin DNA, which is double stranded, 17% of the bases were shown to be cytosine. The percentages of the other three bases expected to be present in this DNA are :- [2015 RS]- a)G 17%, A 16.5%, T 32.5%
- b)G 17%, A 33%, T 33%
- c)G 8.5%, A 50%, T 24.5%
- d)G 34%, A 24.5%, T 24.5%
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In sea urchin DNA, which is double stranded, 17% of the bases were shown to be cytosine. The percentages of the other three bases expected to be present in this DNA are :- [2015 RS]
a)
G 17%, A 16.5%, T 32.5%
b)
G 17%, A 33%, T 33%
c)
G 8.5%, A 50%, T 24.5%
d)
G 34%, A 24.5%, T 24.5%

|
Diya Datta answered |
(b) Chargaff's rule states that A = T and G º C. The molar amount of adenine = molar amount of thymine. The molar amount of guanine = molar amount of cytosine. Hence, G is 17%, so, C = 17% A = 33%, so, T = 33%
Which of the following is not required for any of the techniques of DNA fingerprinting available at present ? [2016]- a)Polymerase chain reaction
- b)Zinc finger analysis
- c)Restriction enzymes
- d)DNA-DNA hybridization
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not required for any of the techniques of DNA fingerprinting available at present ? [2016]
a)
Polymerase chain reaction
b)
Zinc finger analysis
c)
Restriction enzymes
d)
DNA-DNA hybridization

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
(b) Zinc-finger analysis is used for protein analysis. The zinc finger proteins are a super family of proteins involved in numerous activities of plant growth and development.
Which one of the following also acts as a catalyst in a bacterial cell ?[2011]- a)5 sr RNA
- b)sn RNA
- c)hn RNA
- d)23 sr RNA
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following also acts as a catalyst in a bacterial cell ?
[2011]
a)
5 sr RNA
b)
sn RNA
c)
hn RNA
d)
23 sr RNA

|
Abhishek Choudhary answered |
23sr RNA acts as a catalyst in a bacterial cell.
Which one of the following pairs of nitrogenous bases of nucleic acids, is wrongly matched with the category mentioned against it?[2008]- a)Thymine, Uracil - Pyrimidines
- b)Uracil, Cytosine - Pyrimidines
- c)Guanine, Adenine - Purines
- d)Adenine, Thymine - Purines
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pairs of nitrogenous bases of nucleic acids, is wrongly matched with the category mentioned against it?
[2008]
a)
Thymine, Uracil - Pyrimidines
b)
Uracil, Cytosine - Pyrimidines
c)
Guanine, Adenine - Purines
d)
Adenine, Thymine - Purines

|
Lekshmi Banerjee answered |
Purine is an organic nitrogenous base sparingly soluble in water, that gives rise to a group of biologically important derivatives, notably adenine and guanine, which occur in nucleotides and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA).
Which one of the following is not applicable to RNA? [2015 RS]- a)5' phosphoryl and 3' hydroxyl ends
- b)Heterocyclic nitrogenous bases
- c)Chargaff's rule
- d)Complementary base pairing
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not applicable to RNA? [2015 RS]
a)
5' phosphoryl and 3' hydroxyl ends
b)
Heterocyclic nitrogenous bases
c)
Chargaff's rule
d)
Complementary base pairing

|
Priyanka Iyer answered |
(c) Chargaff's rule is not applicable to RNA
A man with blood group 'A' marries a woman with blood group 'B'. What are all the possible blood groups of their offsprings ? [2015 RS]- a)A,B and AB only
- b)A,B,AB and O
- c)O only
- d)A and B only
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A man with blood group 'A' marries a woman with blood group 'B'. What are all the possible blood groups of their offsprings ? [2015 RS]
a)
A,B and AB only
b)
A,B,AB and O
c)
O only
d)
A and B only

|
Shruti Chauhan answered |
(b) Possible × Possible genotype genotype of man with blood of woman with group A blood group B I A IA, IA IO × IB IB, IB IO If the genotype is I A IO × IB IO The possibility of resultant blood group may be A, B, AB and O.
Removal of introns and joining the exons in a defined order in a transcription unit is called:[2009]- a)tailing
- b)transformation
- c)capping
- d)splicing
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Removal of introns and joining the exons in a defined order in a transcription unit is called:
[2009]
a)
tailing
b)
transformation
c)
capping
d)
splicing

|
Ayush Choudhury answered |
Splicing is the removal of introns and joining the exons in a defined order in a transcription unit. In molecular biology, splicing is a modification of RNA after transcription, in which introns are removed and exons are joined.
Multiple alleles are present : [2015 RS]- a)At different loci on the same chromosome
- b)At the same locus of the chromosome
- c)On non-sister chromatids
- d)On different chromosomes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Multiple alleles are present : [2015 RS]
a)
At different loci on the same chromosome
b)
At the same locus of the chromosome
c)
On non-sister chromatids
d)
On different chromosomes

|
Krish Patel answered |
(b) All alleles of a gene are situated on the same loci of chromosome in organisms.
Gene regulation governing lactose operon of E.coli that involves the lac I gene product is : [2015 RS]- a)Negative and inducible because repressor protein prevents transcription
- b)Negative and repressible because repressor protein prevents transcription
- c)Feedback inhibition because excess of bgalactosidase can switch off trascription
- d)Positive and inducible because it can be induced by lactose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Gene regulation governing lactose operon of E.coli that involves the lac I gene product is : [2015 RS]
a)
Negative and inducible because repressor protein prevents transcription
b)
Negative and repressible because repressor protein prevents transcription
c)
Feedback inhibition because excess of bgalactosidase can switch off trascription
d)
Positive and inducible because it can be induced by lactose
|
|
Raza Great answered |
In negative inducible operons, a regulatory repressor protein is normally bound to the operator, which prevents the transcription of the genes in the operon. If an inducer molecule is present, it binds to the repressor and changes its conformation so that it is unable to bind to the operator. This allows for expression of the operon. The lac operon is a negatively controlled inducible operon, where the inducer molecule is allolactose
The movement of a gene from one linkage group to another is called : [2015 RS]- a)Duplication
- b)Translocation
- c)Crossing over
- d)Inversion
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The movement of a gene from one linkage group to another is called : [2015 RS]
a)
Duplication
b)
Translocation
c)
Crossing over
d)
Inversion

|
Harshitha Dey answered |
(b) In translocation, the movement of a gene takes place from one linkage group to another between non-homologous chromosomes.
A gene showing codominance has: [2015 RS]- a)alleles tightly linked on the same chromosome
- b)alleles that are recessive to each other
- c)both alleles independently expressed in the heterozygote
- d)one allele dominant on the other
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A gene showing codominance has: [2015 RS]
a)
alleles tightly linked on the same chromosome
b)
alleles that are recessive to each other
c)
both alleles independently expressed in the heterozygote
d)
one allele dominant on the other

|
Diya Datta answered |
(c) In codominance both alleles are independently expressed in the heterozygote
Which one of the following is the starter codon? [2016]- a)AUG
- b)UGA
- c)UAA
- d)UAG
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the starter codon? [2016]
a)
AUG
b)
UGA
c)
UAA
d)
UAG

|
Aman Sharma answered |
(a) The start codon is the first codon of a messenger RNA (mRNA) transcript translated by a ribosome. The start codon always codes for methionine in eukaryotes and a modified Met (fMet) in prokaryotes. The most common start codon is AUG
In the DNA molecule[2008]- a)the total amount of purine nucleotides and pyrimidine nucleotides is not always equal
- b)there are two strands which run parallel in the 5′ → 3′ direction
- c)the proportion of Adenine in relation to thymine varies with the organism
- d)there are two strands which run anti parallel one in 5′ → 3′ direction and other in 3′ → 5′
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the DNA molecule
[2008]
a)
the total amount of purine nucleotides and pyrimidine nucleotides is not always equal
b)
there are two strands which run parallel in the 5′ → 3′ direction
c)
the proportion of Adenine in relation to thymine varies with the organism
d)
there are two strands which run anti parallel one in 5′ → 3′ direction and other in 3′ → 5′

|
Subham Chavan answered |
In the DNA molecule, there are two strands which run anti parallel one is 5' - 3' direction and other in 3' -5' direction, the two chains are held together by hydrogen bonds between their bases. Adenine (A), a purine of one chain his exactly opposite thymine (T), a pyramidine of the other chain. Similarly, cytosine (C), a pyrimidine lies opposite guanine (G), a purine. This allows a sort of lock & key arrangment between large sized purine & small sized pyrimidine. It is strengthened by the appearance of hydrogen bonds between the two.
Semi-conservative replication of DNA was first demonstrated in:[2009]- a)Escherichia coli
- b)Streptococcus pneumoniae
- c)Salmonella typhimurium
- d)Drosophila melanogaster
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Semi-conservative replication of DNA was first demonstrated in:
[2009]
a)
Escherichia coli
b)
Streptococcus pneumoniae
c)
Salmonella typhimurium
d)
Drosophila melanogaster

|
Harshitha Dey answered |
Semiconservative replication of DNA was first demonstrated in Escherichia coli. E. coli is a common type of bacteria that can get into food, like beef and vegetables. The strange thing about these bacteria is that they are not always harmful to you. E. coli normally lives inside your intestines, where it helps your body breakdown and digest the food you eat.
Satellite DNA is useful tool in:[2010]- a)organ transplantation
- b)sex determination
- c)forensic science
- d)genetic engineering
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Satellite DNA is useful tool in:
[2010]
a)
organ transplantation
b)
sex determination
c)
forensic science
d)
genetic engineering

|
Lekshmi Banerjee answered |
Satellite DNA is useful in forensic science. The polymorphism of minisatellite, microsatellite and minivariant repeats is analysed for DNA finger printing, DNA profiling. It helps in the resolution of crimes, legal disputes etc.
The term 'linkage' was coined by : [2015 RS]- a)T. Boveri
- b)G. Mendel
- c)W. Sutton
- d)T.H. Morgan
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The term 'linkage' was coined by : [2015 RS]
a)
T. Boveri
b)
G. Mendel
c)
W. Sutton
d)
T.H. Morgan

|
Subham Chavan answered |
(d) Thomas Hunt Morgan won the Nobel Prize (1933) in physiology or medicine for the function of chromosomes in heredity
Which of the following features of genetic code does allow bacteria to produce human insulin by recombinant DNA technology? [2019]- a)Genetic code is specific.
- b)Genetic code is not ambiguous.
- c)Genetic code is redundant.
- d)Genetic code is nearly universal.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following features of genetic code does allow bacteria to produce human insulin by recombinant DNA technology? [2019]
a)
Genetic code is specific.
b)
Genetic code is not ambiguous.
c)
Genetic code is redundant.
d)
Genetic code is nearly universal.
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
As genetic code is nearly universal means almost all organism (from a virus, bacteria to a tree or human being) will have amino acids coded by same kind of codons as given in checkerboard. So, this properties is utilised to produce human insulin using bacteria.
The experimental proof for semi-conservative replication of DNA was first shown in a [2018]- a)Fungus
- b)Bacterium
- c)Plant
- d)Virus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The experimental proof for semi-conservative replication of DNA was first shown in a [2018]
a)
Fungus
b)
Bacterium
c)
Plant
d)
Virus
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Semiconservative replication of DNA was proved by the work of Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl (1958) using bacterium Escherichia coli.
Transposons can be used during which one of the following? (NEET 2022)- a)Polymerase Chain Reaction
- b)Gene Silencing
- c)Autoradiography
- d)Gene sequencing
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Transposons can be used during which one of the following? (NEET 2022)
a)
Polymerase Chain Reaction
b)
Gene Silencing
c)
Autoradiography
d)
Gene sequencing
|
|
Devika Singh answered |
Understanding Transposons
Transposons, or "jumping genes," are sequences of DNA that can move around within the genome. They play a significant role in genetic variation and can influence gene expression and function.
Transposons in Gene Silencing
Transposons can be utilized for gene silencing through the following mechanisms:
Other Applications
While transposons play a crucial role in gene silencing, they are not typically used in:
In conclusion, transposons are powerful tools in gene silencing, providing insights into gene function and regulation.
Transposons, or "jumping genes," are sequences of DNA that can move around within the genome. They play a significant role in genetic variation and can influence gene expression and function.
Transposons in Gene Silencing
Transposons can be utilized for gene silencing through the following mechanisms:
- Insertional Mutagenesis: When a transposon integrates into a gene, it can disrupt that gene’s function, effectively silencing it. This is a common method for studying gene function.
- Regulatory Element Modulation: Transposons can carry regulatory elements that influence the expression of nearby genes. By inserting these elements, researchers can alter the expression levels and study the resulting phenotypic changes.
- RNA Interference: Certain transposable elements can give rise to small RNAs that participate in the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway, leading to the silencing of complementary mRNA transcripts.
- Vector for Gene Silencing Tools: Transposons can serve as vectors to deliver gene silencing constructs, such as short interfering RNAs (siRNAs) or short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs), into target cells, enhancing the efficiency of gene silencing.
Other Applications
While transposons play a crucial role in gene silencing, they are not typically used in:
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): This technique amplifies DNA but does not involve transposons.
- Autoradiography: This method is used for visualizing radiolabeled molecules, unrelated to transposon activity.
- Gene Sequencing: Though transposons can impact genomic sequences, they are not directly used in sequencing methodologies.
In conclusion, transposons are powerful tools in gene silencing, providing insights into gene function and regulation.
Name the enzyme that facilitates opening of DNA helix during transcription. [2020]- a)DNA polymerase
- b)RNA polymerase
- c)DNA ligase
- d)DNA helicase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Name the enzyme that facilitates opening of DNA helix during transcription. [2020]
a)
DNA polymerase
b)
RNA polymerase
c)
DNA ligase
d)
DNA helicase
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
RNA polymerase holoenzyme binds to the promoter, unwinds DNA (open complex) and form phospodiester links between the initating nucleotides. DNA polymerase, DNA ligase & DNA helicase are involved in the process of replication and not transcription.
If the length of a DNA molecule is 1.1 metres, what will be the approximate number of base pairs? (NEET 2022)- a)6.6 x 109 bp
- b)3.3 x 106 bp
- c)6.6 x 106 bp
- d)3.3 x 109 bp
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If the length of a DNA molecule is 1.1 metres, what will be the approximate number of base pairs? (NEET 2022)
a)
6.6 x 109 bp
b)
3.3 x 106 bp
c)
6.6 x 106 bp
d)
3.3 x 109 bp

|
Lead Academy answered |
The two chains of DNA are coiled in a right-handed helicle fashion. The pitch of the helix is 3.4 nm and has a diameter of 2 nm. In the B-form of DNA, the distance between a bp in a helix is approximately 0.34 nm which means there are about 10 nucleotides present in a complete turn.
The total length of DNA molecule in nm = 1.1 × 109 nm.
The approximate number of base pairs = 1.1 × 109/ 0.34
= 3.3 × 109
The total length of DNA molecule in nm = 1.1 × 109 nm.
The approximate number of base pairs = 1.1 × 109/ 0.34
= 3.3 × 109
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) refers to (NEET 2023)- a)All genes that are expressed as RNA.
- b)All genes that are expressed as proteins.
- c)All genes whether expressed or unexpressed.
- d)Certain important expressed genes.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) refers to (NEET 2023)
a)
All genes that are expressed as RNA.
b)
All genes that are expressed as proteins.
c)
All genes whether expressed or unexpressed.
d)
Certain important expressed genes.
|
|
Janani Iyer answered |
Understanding Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs)
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) are short, single-stranded sequences derived from cDNA (complementary DNA) that represent portions of expressed genes. They play a crucial role in gene discovery and functional genomics.
Key Characteristics of ESTs:
- Representation of Expressed Genes:
ESTs are essentially fragments of mRNA that have been reverse-transcribed into cDNA. They provide a snapshot of the genes that are being actively expressed in a given tissue or under specific conditions.
- RNA Expression:
Since ESTs are derived from mRNA, they directly relate to genes that are transcribed into RNA. This means that only the genes that are actively expressed at the time of sample collection will produce ESTs.
- Gene Discovery:
By analyzing ESTs, researchers can identify novel genes, study gene expression patterns, and explore alternative splicing events. This makes ESTs vital for understanding the complexity of gene expression.
Why Option 'A' is Correct:
- Option 'A' states that ESTs refer to "All genes that are expressed as RNA." This is accurate because ESTs specifically represent the RNA transcripts that have been produced from the active genes in a specific cellular environment.
- In contrast, the other options do not accurately capture the essence of what ESTs are:
- Option 'B' (All genes that are expressed as proteins) is misleading as it overlooks the RNA stage.
- Option 'C' (All genes whether expressed or unexpressed) is incorrect since ESTs only reflect expressed genes.
- Option 'D' (Certain important expressed genes) fails to encompass the broader spectrum of expressed genes captured by ESTs.
In conclusion, ESTs are a valuable tool for understanding the expression of genes in biological research, making option 'A' the correct answer.
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) are short, single-stranded sequences derived from cDNA (complementary DNA) that represent portions of expressed genes. They play a crucial role in gene discovery and functional genomics.
Key Characteristics of ESTs:
- Representation of Expressed Genes:
ESTs are essentially fragments of mRNA that have been reverse-transcribed into cDNA. They provide a snapshot of the genes that are being actively expressed in a given tissue or under specific conditions.
- RNA Expression:
Since ESTs are derived from mRNA, they directly relate to genes that are transcribed into RNA. This means that only the genes that are actively expressed at the time of sample collection will produce ESTs.
- Gene Discovery:
By analyzing ESTs, researchers can identify novel genes, study gene expression patterns, and explore alternative splicing events. This makes ESTs vital for understanding the complexity of gene expression.
Why Option 'A' is Correct:
- Option 'A' states that ESTs refer to "All genes that are expressed as RNA." This is accurate because ESTs specifically represent the RNA transcripts that have been produced from the active genes in a specific cellular environment.
- In contrast, the other options do not accurately capture the essence of what ESTs are:
- Option 'B' (All genes that are expressed as proteins) is misleading as it overlooks the RNA stage.
- Option 'C' (All genes whether expressed or unexpressed) is incorrect since ESTs only reflect expressed genes.
- Option 'D' (Certain important expressed genes) fails to encompass the broader spectrum of expressed genes captured by ESTs.
In conclusion, ESTs are a valuable tool for understanding the expression of genes in biological research, making option 'A' the correct answer.
Against the codon 5' UAC 3', what would be the sequence of anticodon on tRNA? (NEET 2022 Phase 2)- a)5' GUA 3'
- b)5' AUG 3'
- c)5' ATG 3'
- d)5' GTA 3'
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Against the codon 5' UAC 3', what would be the sequence of anticodon on tRNA? (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
a)
5' GUA 3'
b)
5' AUG 3'
c)
5' ATG 3'
d)
5' GTA 3'
|
|
Aaditya Roy answered |
Understanding Codons and Anticodons
In molecular biology, codons and anticodons are integral to the process of translation, where mRNA is translated into proteins.
What is a Codon?
- A codon is a sequence of three nucleotides on mRNA that corresponds to a specific amino acid.
- In this case, the codon given is 5' UAC 3'.
What is an Anticodon?
- An anticodon is a complementary sequence of three nucleotides on tRNA that pairs with the codon during translation.
- The pairing is based on complementary base pairing rules: A pairs with U, and C pairs with G.
Finding the Anticodon for UAC
1. Complementary Base Pairing:
- For the codon 5' UAC 3', we will find the complementary bases.
- U (Uracil) pairs with A (Adenine).
- A (Adenine) pairs with U (Uracil).
- C (Cytosine) pairs with G (Guanine).
2. Constructing the Anticodon:
- Pairing U with A gives A.
- Pairing A with U gives U.
- Pairing C with G gives G.
- Therefore, the complementary sequence is 3' AUG 5'.
3. Writing in the Correct Orientation:
- Anticodons are typically written in the 5' to 3' direction.
- Thus, the anticodon corresponding to the codon 5' UAC 3' is 5' AUG 3'.
Conclusion
- The correct sequence of the anticodon on tRNA for the codon 5' UAC 3' is indeed 5' AUG 3'.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B'.
In molecular biology, codons and anticodons are integral to the process of translation, where mRNA is translated into proteins.
What is a Codon?
- A codon is a sequence of three nucleotides on mRNA that corresponds to a specific amino acid.
- In this case, the codon given is 5' UAC 3'.
What is an Anticodon?
- An anticodon is a complementary sequence of three nucleotides on tRNA that pairs with the codon during translation.
- The pairing is based on complementary base pairing rules: A pairs with U, and C pairs with G.
Finding the Anticodon for UAC
1. Complementary Base Pairing:
- For the codon 5' UAC 3', we will find the complementary bases.
- U (Uracil) pairs with A (Adenine).
- A (Adenine) pairs with U (Uracil).
- C (Cytosine) pairs with G (Guanine).
2. Constructing the Anticodon:
- Pairing U with A gives A.
- Pairing A with U gives U.
- Pairing C with G gives G.
- Therefore, the complementary sequence is 3' AUG 5'.
3. Writing in the Correct Orientation:
- Anticodons are typically written in the 5' to 3' direction.
- Thus, the anticodon corresponding to the codon 5' UAC 3' is 5' AUG 3'.
Conclusion
- The correct sequence of the anticodon on tRNA for the codon 5' UAC 3' is indeed 5' AUG 3'.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B'.
Which one of the following pairs of codons is correctly matched with their function or the signal for the particular amino acid?[2008]- a)GUU, GCU-Alanine
- b)UAG, UGA-Stop
- c)AUG, ACG-Start/Methionine
- d)UUA, UCA-Leucine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pairs of codons is correctly matched with their function or the signal for the particular amino acid?
[2008]
a)
GUU, GCU-Alanine
b)
UAG, UGA-Stop
c)
AUG, ACG-Start/Methionine
d)
UUA, UCA-Leucine

|
Anirudh Datta answered |
GCU indicates alanine but GUU indicates valine. Stop codons are UAG, UGA and UAA AUG is the most common start codon which does for methionine. UUA indicates leucine but UCA indicates serine.
During DNA replication, Okazaki fragments are used to elongate [2017]- a)The lagging strand towards replication fork
- b)The leading strand away from replication fork
- c)The lagging strand away from the replication fork
- d)The leading strand towards replication fork.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During DNA replication, Okazaki fragments are used to elongate [2017]
a)
The lagging strand towards replication fork
b)
The leading strand away from replication fork
c)
The lagging strand away from the replication fork
d)
The leading strand towards replication fork.
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Lagging strand is a replicated strand 0f DNA which is formed in short segments called Okazaki fragments. Its growth is discontinuous. The direction of growth of the lagging strand is 3' → 5’ though in each Okazaki fragment it is 5’ → 3’.
E.coli cells with a mutated z gene of the lac operon cannot grow in medium containing only lactose as the source of energy because:[2005]- a)the lac operon is constitutively active in these cells
- b)they cannot synthesize functional betagalactosidase
- c)in the presence of glucose, E.coli cells do not utilize lactose
- d)they cannot transport lactose from the medium into the cell
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
E.coli cells with a mutated z gene of the lac operon cannot grow in medium containing only lactose as the source of energy because:
[2005]
a)
the lac operon is constitutively active in these cells
b)
they cannot synthesize functional betagalactosidase
c)
in the presence of glucose, E.coli cells do not utilize lactose
d)
they cannot transport lactose from the medium into the cell

|
Raghav Khanna answered |
Operons are segments of genetic material which function as regulated unit or units that can be switched on and switched off. An operon consists of one to several structural genes. (Three in lac operon) These are genes which produce mRNAs for forming polypeptides / proteins / enzymes. Z (produces enzyme β galactosidase for splitting lactose into glucose and galactose). Y (produces enzyme galactoside permease required in entry of lactose) A (produces enzyme thiogalactoside trans- acetylase).
The three structural genes of the operon produce a single polycistronic mRNA.
The three structural genes of the operon produce a single polycistronic mRNA.
Given below are two statements: (NEET 2023)Statement I: In prokaryotes, the positively charged DNA is held with some negatively charged proteins in a region called nucleoid.
Statement II: In eukaryotes, the negatively charged DNA is wrapped around the positively charged histone octamer to form nucleosome.In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is false.
- d)Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is true.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Given below are two statements: (NEET 2023)
Statement I: In prokaryotes, the positively charged DNA is held with some negatively charged proteins in a region called nucleoid.
Statement II: In eukaryotes, the negatively charged DNA is wrapped around the positively charged histone octamer to form nucleosome.
Statement II: In eukaryotes, the negatively charged DNA is wrapped around the positively charged histone octamer to form nucleosome.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is false.
d)
Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is true.

|
Ambition Institute answered |
- In prokaryotes, the negatively charged DNA is held with some positively charged proteins in a region termed as nucleoid.
- In eukaryotes, the negatively charged DNA is wrapped around the positively charged histone octamer to form a structure called nucleosome.
Ten E.coli cells with 15N - dsDNA are incubated in medium containing 14N nucleotide. After 60 minutes, how many E.coli cells will have DNA totally free from 15N? (NEET 2022)- a)20 cells
- b)40 cells
- c)60 cells
- d)80 cells
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Ten E.coli cells with 15N - dsDNA are incubated in medium containing 14N nucleotide. After 60 minutes, how many E.coli cells will have DNA totally free from 15N? (NEET 2022)
a)
20 cells
b)
40 cells
c)
60 cells
d)
80 cells
|
|
Sonal Khanna answered |
Understanding the Experiment
In this experiment, we start with ten E. coli cells containing 15N-labeled dsDNA. When these cells are incubated in a medium with 14N nucleotides, the following processes occur during DNA replication.
DNA Replication Process
1. First Generation:
- Each E. coli cell will replicate its DNA using the 14N nucleotides.
- As a result, the new DNA strands will be composed of 14N, while the original strands remain 15N.
- This leads to two types of DNA: 50% hybrid (15N-14N) and 50% original (15N-15N).
2. Second Generation:
- Each hybrid DNA (15N-14N) replicates. The original 15N strand pairs with new 14N nucleotides.
- This results in:
- 50% of the cells producing DNA with both strands as 14N (14N-14N).
- 50% producing hybrid DNA (15N-14N).
Calculating Total E. coli Cells
- Initially, we have 10 E. coli cells.
- After the first hour (1 generation):
- Total cells = 10 (each cell divides)
- Hybrid DNA cells (15N-14N) = 10
- Original DNA cells (15N-15N) = 0
- After the second hour (2 generations):
- Total cells = 20 (10 from the first generation divide)
- Cells with 14N-14N = 10 (half of 20)
- Cells with 15N-14N = 10 (the other half)
- After the third hour (3 generations):
- Total cells = 40
- Cells with 14N-14N = 20 (half of 40)
- Cells with 15N-14N = 20 (the other half)
By the end of 60 minutes, 20 cells will have DNA totally free from 15N.
Final Answer
Thus, the correct option is C) 60 cells with 14N-14N DNA, as each cell continues to replicate, doubling with each division.
In this experiment, we start with ten E. coli cells containing 15N-labeled dsDNA. When these cells are incubated in a medium with 14N nucleotides, the following processes occur during DNA replication.
DNA Replication Process
1. First Generation:
- Each E. coli cell will replicate its DNA using the 14N nucleotides.
- As a result, the new DNA strands will be composed of 14N, while the original strands remain 15N.
- This leads to two types of DNA: 50% hybrid (15N-14N) and 50% original (15N-15N).
2. Second Generation:
- Each hybrid DNA (15N-14N) replicates. The original 15N strand pairs with new 14N nucleotides.
- This results in:
- 50% of the cells producing DNA with both strands as 14N (14N-14N).
- 50% producing hybrid DNA (15N-14N).
Calculating Total E. coli Cells
- Initially, we have 10 E. coli cells.
- After the first hour (1 generation):
- Total cells = 10 (each cell divides)
- Hybrid DNA cells (15N-14N) = 10
- Original DNA cells (15N-15N) = 0
- After the second hour (2 generations):
- Total cells = 20 (10 from the first generation divide)
- Cells with 14N-14N = 10 (half of 20)
- Cells with 15N-14N = 10 (the other half)
- After the third hour (3 generations):
- Total cells = 40
- Cells with 14N-14N = 20 (half of 40)
- Cells with 15N-14N = 20 (the other half)
By the end of 60 minutes, 20 cells will have DNA totally free from 15N.
Final Answer
Thus, the correct option is C) 60 cells with 14N-14N DNA, as each cell continues to replicate, doubling with each division.
Select the two correct statements out of the four (a–d) given below about lac operon.
(i) Glucose or galactose may bind with the repressor and inactivate it
(ii) In the absence of lactose the repressor binds with the operator region
(iii) The z-gene codes for permease
(iv) This was elucidated by Francois Jacob and Jacque Monod
The correct statements are:
[2010]
- a)(ii) and (iii)
- b)(i) and (iii)
- c)(ii) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (ii)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the two correct statements out of the four (a–d) given below about lac operon.
(i) Glucose or galactose may bind with the repressor and inactivate it
(ii) In the absence of lactose the repressor binds with the operator region
(iii) The z-gene codes for permease
(iv) This was elucidated by Francois Jacob and Jacque Monod
(ii) In the absence of lactose the repressor binds with the operator region
(iii) The z-gene codes for permease
(iv) This was elucidated by Francois Jacob and Jacque Monod
The correct statements are:
[2010]
a)
(ii) and (iii)
b)
(i) and (iii)
c)
(ii) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (ii)

|
Subham Chavan answered |
In lac operon, lactose acts as the inducer that binds with the repressor and inactivates it. This enables the operator to carry out the translation of the genes and produce enzymes. If glucose is present in the system there is no need of lac operon as it is the preferred substrate. Since galactose is not an inducer it cannot bind with the repressor.
In the absence of lactose repressor binds with the operator and does not allow translation of the genes and hence no enzymes will be formed.
The lac z gene codes for galactosidase enzyme. Permease is encoded by lac y gene.
Taylor conducted the experiments to prove semiconservative mode of chromosome replication on [2016]- a)Vinca rosea
- b)Vicia faba
- c)Drosophila melanogaster
- d)E. coli
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Taylor conducted the experiments to prove semiconservative mode of chromosome replication on [2016]
a)
Vinca rosea
b)
Vicia faba
c)
Drosophila melanogaster
d)
E. coli
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Taylor et al. (1957) conducted experiment on Vicia faba (broad bean) to prove semiconservative replication of DNA. He fed dividing cells of root tips of Vicia faba with radioactive 3H containing thymine instead of normal thymine and found that all the chromosomes became radioactive. Labelled thymine was then replaced with normal one. Next generation came to have radioactivity in one of the two chromatids of each chromosome while in subsequent generation radioactivity was present in 50% of the chromosomes. This is possible only if out of the two strands of a chromosome, one is formed afresh while the other is conserved at each replication.
DNA Polymorphism forms the basis of: (NEET 2022)- a)DNA finger printing
- b)Both genetic mapping and DNA finger printing
- c)Translation
- d)Genetic mapping
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
DNA Polymorphism forms the basis of: (NEET 2022)
a)
DNA finger printing
b)
Both genetic mapping and DNA finger printing
c)
Translation
d)
Genetic mapping
|
|
Ujwal Sen answered |
Understanding DNA Polymorphism
DNA polymorphism refers to the variations in the DNA sequence among individuals. These variations can be single nucleotide changes, insertions, deletions, or larger structural changes. The significance of these polymorphisms is profound in genetics, especially in applications like genetic mapping and DNA fingerprinting.
Role in Genetic Mapping
- Definition: Genetic mapping involves identifying the location of genes on chromosomes.
- Function of Polymorphism: Polymorphisms serve as genetic markers, helping researchers locate genes associated with traits or diseases.
- Linkage Analysis: By analyzing the inheritance patterns of polymorphic markers, scientists can determine the proximity of genes on a chromosome, aiding in constructing genetic maps.
Role in DNA Fingerprinting
- Definition: DNA fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals based on unique patterns in their DNA.
- Polymorphisms as Markers: Variations in DNA sequences are crucial for distinguishing between individuals. The higher the number of polymorphisms analyzed, the more accurate the identification.
- Applications: This technique is widely used in forensic science, paternity testing, and biodiversity studies, showcasing the uniqueness of genetic profiles.
Conclusion
Both genetic mapping and DNA fingerprinting leverage DNA polymorphisms for their processes. While genetic mapping uses polymorphisms to locate genes, DNA fingerprinting uses them to identify individuals uniquely. Therefore, option 'B' is the correct answer as it encompasses both applications of DNA polymorphism.
DNA polymorphism refers to the variations in the DNA sequence among individuals. These variations can be single nucleotide changes, insertions, deletions, or larger structural changes. The significance of these polymorphisms is profound in genetics, especially in applications like genetic mapping and DNA fingerprinting.
Role in Genetic Mapping
- Definition: Genetic mapping involves identifying the location of genes on chromosomes.
- Function of Polymorphism: Polymorphisms serve as genetic markers, helping researchers locate genes associated with traits or diseases.
- Linkage Analysis: By analyzing the inheritance patterns of polymorphic markers, scientists can determine the proximity of genes on a chromosome, aiding in constructing genetic maps.
Role in DNA Fingerprinting
- Definition: DNA fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals based on unique patterns in their DNA.
- Polymorphisms as Markers: Variations in DNA sequences are crucial for distinguishing between individuals. The higher the number of polymorphisms analyzed, the more accurate the identification.
- Applications: This technique is widely used in forensic science, paternity testing, and biodiversity studies, showcasing the uniqueness of genetic profiles.
Conclusion
Both genetic mapping and DNA fingerprinting leverage DNA polymorphisms for their processes. While genetic mapping uses polymorphisms to locate genes, DNA fingerprinting uses them to identify individuals uniquely. Therefore, option 'B' is the correct answer as it encompasses both applications of DNA polymorphism.
During transcription holoenzyme RNA polymerase binds to a DNA sequence and the DNA assumes a saddle like structure at that point. What is that sequence called?[2005]- a)AAAT box
- b)TATA box
- c)GGTT box
- d)CAAT box
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During transcription holoenzyme RNA polymerase binds to a DNA sequence and the DNA assumes a saddle like structure at that point. What is that sequence called?
[2005]
a)
AAAT box
b)
TATA box
c)
GGTT box
d)
CAAT box
|
|
Jyoti Shah answered |
Introduction:
In molecular biology, AUG is a codon that plays a crucial role in protein synthesis. The information carried by AUG is significant for the initiation of translation, and it is also responsible for coding the amino acid methionine. This question asks which statements about AUG are true.
Explanation:
To determine the correct answer, let's evaluate each option one by one:
a) It codes for methionine only:
This statement is incorrect. AUG codes for methionine, but it can also serve as a start codon for protein synthesis. In some cases, AUG can be used to code for methionine within the middle of a protein sequence, but its primary function is as an initiation codon.
b) It is an initiation codon:
This statement is correct. AUG is the most common initiation codon used to start protein synthesis. When an mRNA molecule is translated into a protein, the ribosome recognizes AUG as the start codon and begins the translation process from that point.
c) It codes for methionine in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes:
This statement is correct. The genetic code is nearly universal, meaning that the same codons code for the same amino acids across different organisms. AUG consistently codes for methionine in both prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (organisms with a distinct nucleus).
d) All of the above:
This statement is correct. Option D includes all the true statements mentioned above. AUG codes for methionine, serves as an initiation codon, and codes for methionine in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Therefore, option D is the correct answer.
Conclusion:
In summary, AUG is an important codon in protein synthesis. It codes for methionine, serves as an initiation codon, and is conserved across different organisms. Therefore, option D, "All of the above," is the correct answer.
In molecular biology, AUG is a codon that plays a crucial role in protein synthesis. The information carried by AUG is significant for the initiation of translation, and it is also responsible for coding the amino acid methionine. This question asks which statements about AUG are true.
Explanation:
To determine the correct answer, let's evaluate each option one by one:
a) It codes for methionine only:
This statement is incorrect. AUG codes for methionine, but it can also serve as a start codon for protein synthesis. In some cases, AUG can be used to code for methionine within the middle of a protein sequence, but its primary function is as an initiation codon.
b) It is an initiation codon:
This statement is correct. AUG is the most common initiation codon used to start protein synthesis. When an mRNA molecule is translated into a protein, the ribosome recognizes AUG as the start codon and begins the translation process from that point.
c) It codes for methionine in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes:
This statement is correct. The genetic code is nearly universal, meaning that the same codons code for the same amino acids across different organisms. AUG consistently codes for methionine in both prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (organisms with a distinct nucleus).
d) All of the above:
This statement is correct. Option D includes all the true statements mentioned above. AUG codes for methionine, serves as an initiation codon, and codes for methionine in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Therefore, option D is the correct answer.
Conclusion:
In summary, AUG is an important codon in protein synthesis. It codes for methionine, serves as an initiation codon, and is conserved across different organisms. Therefore, option D, "All of the above," is the correct answer.
A sequential expression of a set of human genes[2007]- a)messenger RNA
- b)DNA sequence
- c)ribosome
- d)transfer RNA.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A sequential expression of a set of human genes
[2007]
a)
messenger RNA
b)
DNA sequence
c)
ribosome
d)
transfer RNA.

|
Abhishek Choudhary answered |
A sequential expression of a set of human genes is the DNA sequence. Because gene is the functional part of DNA sequence.
What is the role of RNA polymerase III in the process of transcription in eukaryotes? (2021)- a)Transcribes precursor of mRNA
- b)Transcribes only snRNAs
- c)Transcribes rRNAs (28S, 18S and 5.8S)
- d)Transcribes tRNA, 5s rRNA and snRNA
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the role of RNA polymerase III in the process of transcription in eukaryotes? (2021)
a)
Transcribes precursor of mRNA
b)
Transcribes only snRNAs
c)
Transcribes rRNAs (28S, 18S and 5.8S)
d)
Transcribes tRNA, 5s rRNA and snRNA
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The RNA polymerase I transcribes rRNAs (28S, 18S, and 5.8S), whereas the RNA polymerase III is responsible for transcription of tRNA, 5srRNA, and snRNAs (small nuclear RNAs).
The length of DNA molecule greatly exceeds the dimensions of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. How is this DNA accommodated?[2007]- a)super-coiling in nucleosomes
- b)DNase digestion
- c)through elimination of repititive DNA
- d)deletion of non-essential genes.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The length of DNA molecule greatly exceeds the dimensions of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. How is this DNA accommodated?
[2007]
a)
super-coiling in nucleosomes
b)
DNase digestion
c)
through elimination of repititive DNA
d)
deletion of non-essential genes.

|
Harshitha Dey answered |
The nucleosome model explains the packaging of histone proteins and DNA in the chromatin material which forms the chromosome.
The process of translation of mRNA to proteins begins as soon as: (NEET 2022)- a)The larger subunit of ribosome encounters mRNA
- b)Both the subunits join together to bind with mRNA
- c)The tRNA is activated and the larger subunit of ribosome encounters mRNA
- d)The small subunit of ribosome encounters mRNA
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The process of translation of mRNA to proteins begins as soon as: (NEET 2022)
a)
The larger subunit of ribosome encounters mRNA
b)
Both the subunits join together to bind with mRNA
c)
The tRNA is activated and the larger subunit of ribosome encounters mRNA
d)
The small subunit of ribosome encounters mRNA

|
Bs Academy answered |
When the small subunit of ribosome encounters an mRNA, the process of translation of the mRNA to protein begins. This process is followed by the binding of bigger/larger subunit.
t-RNA is activated by the addition of amino acid prior to the attachment or ribosome, in the first phase.
t-RNA is activated by the addition of amino acid prior to the attachment or ribosome, in the first phase.
In lac operon, z gene codes for (NEET 2022 Phase 2)- a)Transacetylase
- b)β-galactosidase
- c)Permease
- d)Repressor
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In lac operon, z gene codes for (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
a)
Transacetylase
b)
β-galactosidase
c)
Permease
d)
Repressor

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
In lac operon, z gene codes for β-galactosidase.
Transacetylase, permease and repressor protein are coded by genes 'a', 'y' and 'i' respectively.
Transacetylase, permease and repressor protein are coded by genes 'a', 'y' and 'i' respectively.
Match List - I with List - II. (NEET 2022 Phase 2)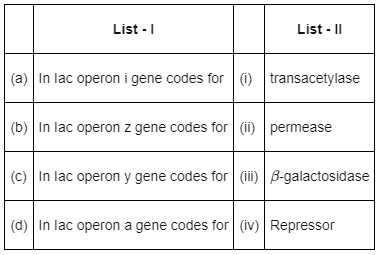 Choose the correct answer from the options given below
Choose the correct answer from the options given below- a)(a) - (iii), (b) - (i), (c) - (iv), (d) - (ii)
- b)(a) - (iii), (b) - (ii), (c) - (i), (d) - (iv)
- c)(a) - (iv), (b) - (iii), (c) - (ii), (d) - (i)
- d)(a) - (iv), (b) - (i), (c) - (iii), (d) - (ii)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Match List - I with List - II. (NEET 2022 Phase 2)

Choose the correct answer from the options given below
a)
(a) - (iii), (b) - (i), (c) - (iv), (d) - (ii)
b)
(a) - (iii), (b) - (ii), (c) - (i), (d) - (iv)
c)
(a) - (iv), (b) - (iii), (c) - (ii), (d) - (i)
d)
(a) - (iv), (b) - (i), (c) - (iii), (d) - (ii)

|
Lead Academy answered |
In Iac operon,
- The i gene codes for repressor protein.
- The z gene codes for β-galactosidase.
- The y gene codes for permease and the a gene codes for transacetylase.
The association of histone H1 with a nucleosome indicates that [2017]- a)DNA replication is occurring
- b)The DNA is condensed into a chromatin fibre
- c)The DNA double helix is exposed
- d)Transcription is occurring
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The association of histone H1 with a nucleosome indicates that [2017]
a)
DNA replication is occurring
b)
The DNA is condensed into a chromatin fibre
c)
The DNA double helix is exposed
d)
Transcription is occurring
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Histones help in packaging of DNA. In eukaryotes, DNA packaging is carried out with the help of positively charged basic proteins called histones. Histones are of five types - H1 H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. H1 is attached over the linker DNA. Histone contains a large proportion of the positively charged (basic) amino acids, lysine and arginine in their structure. DNA is negatively charged due to the phosphate groups on its backbone. The result of these opposite charges is strong attraction and therefore, high binding affinity between histones and DNA.
What is not true for genetic code?[2009]- a)It is nearly universal
- b)It is degenerate
- c)It is unambiguous
- d)A codon in mRNA is read in a non contiguous fashion
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is not true for genetic code?
[2009]
a)
It is nearly universal
b)
It is degenerate
c)
It is unambiguous
d)
A codon in mRNA is read in a non contiguous fashion

|
Kunal Rane answered |
The genetic code consists of 64 triplets of nucleotides. These triplets are called codons. With three exceptions, each codon encodes for one of the 20 amino acids used in the synthesis of proteins. That produces some redundancy in the code. Most of the amino acids being encoded by more than one codon. The genetic code can be expressed as either RNA codons or DNA codons.
Match List I with List II: (NEET 2024)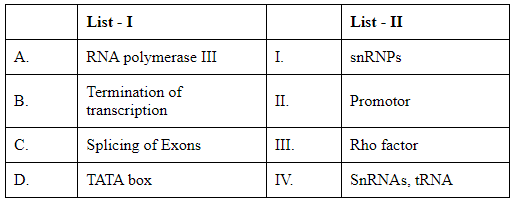
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :- a)A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
- b)A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I
- c)A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
- d)A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Match List I with List II: (NEET 2024)

Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
a)
A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
b)
A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I
c)
A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
d)
A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The goal is to correctly match the terms in List I with the descriptions in List II. Let's analyze and match each term from List I with its appropriate partner in List II:
List I:
A. RNA polymerase III: This enzyme is primarily responsible for transcribing DNA to synthesize tRNA, 5S rRNA, and other small RNAs.
B. Termination of transcription: In prokaryotes, specific termination factors such as the Rho factor are involved in stopping transcription. In eukaryotes, different mechanisms and sequences are used.
C. Splicing of Exons: The process involving the removal of introns and joining of exons during mRNA processing. Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) are critical components in this process.
D. TATA box: A DNA sequence within the promoter region, which is crucial for forming the transcription initiation complex.
A. RNA polymerase III: This enzyme is primarily responsible for transcribing DNA to synthesize tRNA, 5S rRNA, and other small RNAs.
B. Termination of transcription: In prokaryotes, specific termination factors such as the Rho factor are involved in stopping transcription. In eukaryotes, different mechanisms and sequences are used.
C. Splicing of Exons: The process involving the removal of introns and joining of exons during mRNA processing. Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) are critical components in this process.
D. TATA box: A DNA sequence within the promoter region, which is crucial for forming the transcription initiation complex.
List II:
I. snRNPs: Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins involved in mRNA splicing.
II. Promoter: A region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene, typically containing sequences like the TATA box.
III. Rho factor: A protein essential for terminating transcription in prokaryotes.
IV. SnRNAs, tRNA: Molecules transcribed primarily by RNA polymerase III.
I. snRNPs: Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins involved in mRNA splicing.
II. Promoter: A region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene, typically containing sequences like the TATA box.
III. Rho factor: A protein essential for terminating transcription in prokaryotes.
IV. SnRNAs, tRNA: Molecules transcribed primarily by RNA polymerase III.
Matching these descriptions:
A (RNA polymerase III) matches with IV (SnRNAs, tRNA).
B (Termination of transcription) matches with III (Rho factor).
C (Splicing of Exons) matches with I (snRNPs).
D (TATA box) matches with II (Promoter).
Therefore, the correct matches according to options listed are: Option D: A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
A (RNA polymerase III) matches with IV (SnRNAs, tRNA).
B (Termination of transcription) matches with III (Rho factor).
C (Splicing of Exons) matches with I (snRNPs).
D (TATA box) matches with II (Promoter).
Therefore, the correct matches according to options listed are: Option D: A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
Match List-I with List-II: (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
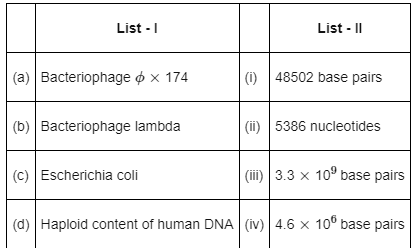 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- a)(a)-(i), (b)-(ii), (c)-(iv), (d)-(iii)
- b)(a)-(i), (b)-(ii), (c)-(iii), (d)-(iv)
- c)(a)-(ii), (b)-(iv), (c)-(i), (d)-(iii)
- d)(a)-(ii), (b)-(i), (c)-(iv), (d)-(iii)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Match List-I with List-II: (NEET 2022 Phase 2)


Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
a)
(a)-(i), (b)-(ii), (c)-(iv), (d)-(iii)
b)
(a)-(i), (b)-(ii), (c)-(iii), (d)-(iv)
c)
(a)-(ii), (b)-(iv), (c)-(i), (d)-(iii)
d)
(a)-(ii), (b)-(i), (c)-(iv), (d)-(iii)

|
Top Rankers answered |
Genetic material of –
- Bacteriophage ∅ × 174 contains 5386 nucleotides
- Bacteriophage lambda contains 48502 base pairs
- Escherichia coli contains 4.6 × 106 base pairs
- Haploid content of human DNA contains 3.3 × 109 base pairs
Chapter doubts & questions for Molecular Basis of Inheritance - NEET Past Year Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Molecular Basis of Inheritance - NEET Past Year Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









