All Exams >
NEET >
NEET Past Year Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Cell Cycle and Cell Division for NEET Exam
When does synapsis occur during meiosisa)Leptoteneb)Zygotenec)DiploteneD)Pachytene Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
In meiosis I, synapsis formation occurs in the zygotene stage of prophase-I. It is the second stage of prophase-I. During this stage, the chromosomes start pairing together and this process of association called synapsis. Such paired chromosomes are called homologous chromosomes. This synapsis is accompanied by the formation of synaptonemal complex formed by bivalent or tetrad chromosomes.
In cell cycle, DNA replication takes place in[1996, 2000]- a)G1 phase
- b)G2 phase
- c)mitotic metaphase
- d)S phase
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In cell cycle, DNA replication takes place in
[1996, 2000]
a)
G1 phase
b)
G2 phase
c)
mitotic metaphase
d)
S phase

|
Arya Khanna answered |
G1 phase, also called Gap I phase is characterized by increase in cell size. In the S phase or synthetic phase DNA molecules replicate. G2 is the second growth phase. Gap II where in there is intensive formation of RNAs and proteins. In the mitotic metaphase, the chromosomes are arranged at the equatorial plate.
Which one of the following structures will not be common to mitotic cells of higher plants?[1997]- a)cell plate
- b)centriole
- c)centromere
- d)spindle fibres
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following structures will not be common to mitotic cells of higher plants?
[1997]
a)
cell plate
b)
centriole
c)
centromere
d)
spindle fibres

|
Arya Khanna answered |
Plants cells do not have centrioles. Cell plate appears during cytokinesis in dividing cells. Centromere holds the sister chromatids in a chromosome. Spindle fibres appear during metaphase.
Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division due to- a)pairing of homologous chromosomes
- b)crossing over
- c)separation of chromatids
- d)disjunction of homologous chromo
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division due to
a)
pairing of homologous chromosomes
b)
crossing over
c)
separation of chromatids
d)
disjunction of homologous chromo
|
|
Aditi Singh answered |
Explanation:
Meiosis I is the first stage of meiosis, where the homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through crossing over. This stage is known as reductional division because it reduces the number of chromosomes in the cell by half. Meiosis II, on the other hand, is equational division because it divides the sister chromatids into two separate cells, resulting in four haploid cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
The correct answer is option C, separation of chromatids. During meiosis II, the sister chromatids separate from each other and move towards opposite poles of the cell. This is referred to as chromatid disjunction and results in the formation of four haploid cells.
Option A, pairing of homologous chromosomes, is a characteristic of meiosis I, where homologous chromosomes pair up to form bivalents.
Option B, crossing over, also occurs during meiosis I, where homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material.
Option D, disjunction of homologous chromosomes, occurs during meiosis I, where homologous chromosomes separate from each other and move towards opposite poles of the cell.
Meiosis I is the first stage of meiosis, where the homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through crossing over. This stage is known as reductional division because it reduces the number of chromosomes in the cell by half. Meiosis II, on the other hand, is equational division because it divides the sister chromatids into two separate cells, resulting in four haploid cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
The correct answer is option C, separation of chromatids. During meiosis II, the sister chromatids separate from each other and move towards opposite poles of the cell. This is referred to as chromatid disjunction and results in the formation of four haploid cells.
Option A, pairing of homologous chromosomes, is a characteristic of meiosis I, where homologous chromosomes pair up to form bivalents.
Option B, crossing over, also occurs during meiosis I, where homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material.
Option D, disjunction of homologous chromosomes, occurs during meiosis I, where homologous chromosomes separate from each other and move towards opposite poles of the cell.
Mitotic anaphase differs from metaphase in possessing[1991]- a)same number of chromosomes and same number of chromatids
- b)half number of chromosomes and half number of chromatids
- c)half number of chromosomes and same number of chromatids
- d)same number of chromosomes and half number of chromatids
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Mitotic anaphase differs from metaphase in possessing
[1991]
a)
same number of chromosomes and same number of chromatids
b)
half number of chromosomes and half number of chromatids
c)
half number of chromosomes and same number of chromatids
d)
same number of chromosomes and half number of chromatids

|
Raghav Khanna answered |
In mitotic anaphase, the sister chromatids separate from each other and begin to move towards the opposite poles.
Colchicine is employed to diploidize a haploid cell as it[1996]- a)inhibits mitosis
- b)inhibits formation of mitotic spindle
- c)allows replication of DNA twice in one cell cycle
- d)inhibits formation of centromere
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Colchicine is employed to diploidize a haploid cell as it
[1996]
a)
inhibits mitosis
b)
inhibits formation of mitotic spindle
c)
allows replication of DNA twice in one cell cycle
d)
inhibits formation of centromere

|
Ruchi Chakraborty answered |
Colchicine is a mitotic poison which inhibits the appearance of spindle fibres.
During which phase(s) of cell cycle, amount of DNA in a cell remains at 4C level if the initial amount is denoted as 2C? [2014]- a)G0 and G1
- b)G1 and S
- c)Only G2
- d)G2 and M
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During which phase(s) of cell cycle, amount of DNA in a cell remains at 4C level if the initial amount is denoted as 2C? [2014]
a)
G0 and G1
b)
G1 and S
c)
Only G2
d)
G2 and M

|
Tejas Chavan answered |
(c) In M-phase both 4C and 2C of DNA are present in different stages.
Choose the correct option for the following events of meiosis in correct sequence: [2015 RS](A) Crossing over
(B) Synapsis
(C) Terminalisation of chiasmata
(D) Disappearance of nucleolus- a)B → A → C→ D
- b)A → B→ C →D
- c)A→ B→D → C
- d)D → C → B → A
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct option for the following events of meiosis in correct sequence: [2015 RS]
(A) Crossing over
(B) Synapsis
(C) Terminalisation of chiasmata
(D) Disappearance of nucleolus
(B) Synapsis
(C) Terminalisation of chiasmata
(D) Disappearance of nucleolus
a)
B → A → C→ D
b)
A → B→ C →D
c)
A→ B→D → C
d)
D → C → B → A

|
Lekshmi Banerjee answered |
(a) Synapsis → Crossing over → Terminalisation of chiasmata → Disappearance of nucleolus
Best stage to observe shape, size and number of chromosomes is[1994]- a)interphase
- b)metaphase
- c)prophase
- d)telophase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Best stage to observe shape, size and number of chromosomes is
[1994]
a)
interphase
b)
metaphase
c)
prophase
d)
telophase

|
Swara Desai answered |
During metaphase, the centomeres of the chromosome lie on the equatorial plate according to their size and spatial arrangement. So it is the best time to count the number and study the morphology of chromosomes.
A bacterium divides every 35 minutes. If a culture containing 105 cells per ml is grown for 175 minutes, what will be the cell concentration per ml after 175 minutes?[1998]- a)5 × 105cells
- b)35 × 105cells
- c)32 × 105cells
- d)175 × 105cells
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A bacterium divides every 35 minutes. If a culture containing 105 cells per ml is grown for 175 minutes, what will be the cell concentration per ml after 175 minutes?
[1998]
a)
5 × 105cells
b)
35 × 105cells
c)
32 × 105cells
d)
175 × 105cells

|
Jatin Chakraborty answered |
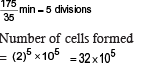
In human females, meiosis-II is not complete until? [2015 RS]- a)fertilization
- b)uterine implantation
- c)birth
- d)puberty
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In human females, meiosis-II is not complete until? [2015 RS]
a)
fertilization
b)
uterine implantation
c)
birth
d)
puberty

|
Moumita Khanna answered |
(a) Meiosis-II does not complete untill fertilization occurs in females (in human being).
How many mitotic divisions are needed for a single cell to make 128 cells? [1997]
a) 7
b) 14
c) 28
d) 64
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Here's your answer !!!
7 mitotic divisions ...
During mitotic divisions :
▶1 cell ➡ 2cells (1st mitosis)
▶2cells ➡4cells (2nd mitosis )
▶4 cells ➡ 8cells (3rd mitosis )
▶8 cells ➡ 16 cells (4th mitosis)
▶16 cells ➡ 32 cells (5th mitosis)
▶32 cells ➡64 cells (6th mitosis )
▶64 cells ➡ 128 cells (7th mitosis )
Hence , 7 mitotic divisions are needed to form 128 cells from 1 cell in plants.
Which of the following statements is not true for cancer cells in relation to mutations ? [2016]- a)Mutations in proto-oncogenes accelerate the cell cycle.
- b)Mutations destroy telomerase inhibitor.
- c)Mutations inactive the cell control.
- d)Mutations inhibit production of telomerase.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not true for cancer cells in relation to mutations ? [2016]
a)
Mutations in proto-oncogenes accelerate the cell cycle.
b)
Mutations destroy telomerase inhibitor.
c)
Mutations inactive the cell control.
d)
Mutations inhibit production of telomerase.
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta G answered |
The ability to maintain functional telomeres may be one mechanism that allows cancer cells to grow in vitro for decades. Telomerase activity is necessary to preserve many cancer types and is inactive in somatic cells, creating the possibility that telomerase inhibition could selectively repress cancer cell growth with minimal side effects. Mutation can inhibit telomerase in cancer cells, the telomeres of successive generations will progressively shorten, limiting tumor growth.
So the correct option is 'Mutations inhibit the production of telomerase'.
So the correct option is 'Mutations inhibit the production of telomerase'.
If a diploid cell is treated with colchicine then it becomes[2002]- a)triploid
- b)tetraploid
- c)diploid
- d)monoploid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a diploid cell is treated with colchicine then it becomes
[2002]
a)
triploid
b)
tetraploid
c)
diploid
d)
monoploid

|
Charvi Shah answered |
Colchicine inhibits spindle formation, due to which chromatids are unable to separate during anaphase which results in doubling of chromosomes. So, if a diploid cell is treated with colchicine, there is doubling of chromosomes and it becomes tetraploid,. Its an alkaloid obtained from Colchicum autumnale.
Segregation of mendelian factor (Aa) occurs during[1990]- a)Diplotene
- b)Anaphase I
- c)Zygotene/Pachytene
- d)Anaphase II
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Segregation of mendelian factor (Aa) occurs during
[1990]
a)
Diplotene
b)
Anaphase I
c)
Zygotene/Pachytene
d)
Anaphase II
|
|
Ritika Reddy answered |
The correct answer is option B, Anaphase I.
Explanation:
Mendelian factors or genes segregate during the process of meiosis. Meiosis is a type of cell division that occurs in the reproductive cells of sexually reproducing organisms. During meiosis, the chromosome number is reduced by half, from diploid (2n) to haploid (n).
The segregation of Mendelian factors occurs during the first division of meiosis, which is called meiosis I. Meiosis I consists of four stages: prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, and telophase I.
During prophase I, the homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange segments of DNA through a process called crossing over. This results in the formation of new combinations of genes on the chromosomes.
During metaphase I, the homologous chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell.
During anaphase I, the homologous chromosomes separate and move towards opposite poles of the cell. This is the stage where the segregation of Mendelian factors occurs. Each chromosome contains two copies of each gene, one from each parent. During anaphase I, the homologous chromosomes separate and each daughter cell receives only one copy of each gene.
During telophase I, the chromosomes reach the opposite poles of the cell and the cell divides into two daughter cells. Each daughter cell contains half the number of chromosomes as the original cell.
In conclusion, the segregation of Mendelian factors occurs during anaphase I of meiosis.
Explanation:
Mendelian factors or genes segregate during the process of meiosis. Meiosis is a type of cell division that occurs in the reproductive cells of sexually reproducing organisms. During meiosis, the chromosome number is reduced by half, from diploid (2n) to haploid (n).
The segregation of Mendelian factors occurs during the first division of meiosis, which is called meiosis I. Meiosis I consists of four stages: prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, and telophase I.
During prophase I, the homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange segments of DNA through a process called crossing over. This results in the formation of new combinations of genes on the chromosomes.
During metaphase I, the homologous chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell.
During anaphase I, the homologous chromosomes separate and move towards opposite poles of the cell. This is the stage where the segregation of Mendelian factors occurs. Each chromosome contains two copies of each gene, one from each parent. During anaphase I, the homologous chromosomes separate and each daughter cell receives only one copy of each gene.
During telophase I, the chromosomes reach the opposite poles of the cell and the cell divides into two daughter cells. Each daughter cell contains half the number of chromosomes as the original cell.
In conclusion, the segregation of Mendelian factors occurs during anaphase I of meiosis.
A somatic cell that has just completed the S phase of its cell cycle, as compared to gamete of the same species, has : [2015 RS]
- a)twice the number of chromosomes and four times the amount of DNA
- b)same number of chromosomes but twice the amount of DNA
- c)four times the number of chromosomes and twice the amount of DNA
- d)twice the number of chromosomes and twice the amount of DNA
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A somatic cell that has just completed the S phase of its cell cycle, as compared to gamete of the same species, has : [2015 RS]
a)
twice the number of chromosomes and four times the amount of DNA
b)
same number of chromosomes but twice the amount of DNA
c)
four times the number of chromosomes and twice the amount of DNA
d)
twice the number of chromosomes and twice the amount of DNA

|
Arindam Khanna answered |
The correct option is Option B.
A somatic cell that has just completed the S phase of its cell cycle has replicated its DNA but has not yet undergone cell division (mitosis). Therefore, it has the same number of chromosomes as before S phase but twice the amount of DNA, because each chromosome has been replicated into two sister chromatids.
A cell plate is laid down during- a)Cytokinesis
- b)Interphase
- c)Karyokinesis
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A cell plate is laid down during
a)
Cytokinesis
b)
Interphase
c)
Karyokinesis
d)
None of these
|
|
Ramesh Chand answered |
Cytokinesis in terrestrial plants occurs by cell plate formation. This process entails the delivery of Golgi derived and endosomal vesicles carrying cell wall and cell membrane components to the plane of cell division and the subsequent fusion of these vesicles within this plate.
In meiosis crossing over is initiated at [2016]- a)Pachytene
- b)Leptotene
- c)Zygotene
- d)Diplotene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In meiosis crossing over is initiated at [2016]
a)
Pachytene
b)
Leptotene
c)
Zygotene
d)
Diplotene

|
Prashanth Dasgupta answered |
(a) Meiosis is a process (discovered by German biologist, Oscar Hertwig) where a single cell divides twice to produce four cells containing half the original amount of genetic information. These cells are our sex cells - sperm in males, eggs in females. Crossing over is the process by which two chromosomes, exchange some distal part of their DNA. This process occurs in the Pachytene stage of Prophase I of meiosis.
At what stage of the cell cycle are histone proteins synthesized in a eukaryotic cell?[2005]- a)During G-2 stage of prophase
- b)During S-phase
- c)During entire prophase
- d)During telophase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
At what stage of the cell cycle are histone proteins synthesized in a eukaryotic cell?
[2005]
a)
During G-2 stage of prophase
b)
During S-phase
c)
During entire prophase
d)
During telophase

|
Swara Desai answered |
Histone proteins are synthesized during Sphase of cell cycle. Sphase or Synthetic phase.
Histone proteins are basic proteins and are used in packing of eukaryotic (absent in prokaryotes) DNA. DNA and histones together comprise chromatin, forming bulk of the eukaryotic chromosomes. Histones are of five major kinds
H1,H2A,H2B,H3
and
H4H1
histones link neighbouring nucleosomes (fundamental packing units of an eukaryotic chromosome), while other are elements of nucleosome structure. During S-phase of cell cycle synthesis of histone proteins take place because at this stage number of chromosomes become double to that of somatic number
Which one of the following precedes reformation of the nuclear envelope during M phase of the cell cycle
[2004]
- a)Transcription from chromosome and reassembly of the nuclear lamina
- b)Decondensation from chromosome and reassembly of the nuclear lamina
- c)Formation of the contractile ring, and formation of the phragmoplast
- d)Formation of the contractile ring, and transcription from chromosomes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following precedes reformation of the nuclear envelope during M phase of the cell cycle
[2004]
a)
Transcription from chromosome and reassembly of the nuclear lamina
b)
Decondensation from chromosome and reassembly of the nuclear lamina
c)
Formation of the contractile ring, and formation of the phragmoplast
d)
Formation of the contractile ring, and transcription from chromosomes

|
Maitri Mukherjee answered |
At the beginning of M phase or mitotic phase the nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear. The decondensation of chromosomes occur. But when nuclear envelop restart forming then nuclear lamina assemble and chromosomes start condensing.
Given below is a schematic breakup of the phases / stages of cell cycle: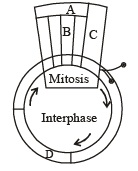 Which one of the following is the correct indication of the stage/phase in the cell cycle?[2009]
Which one of the following is the correct indication of the stage/phase in the cell cycle?[2009] - a)C - Karyokinesis
- b)D - Synthetic phase
- c)A - Cytokinesis
- d)B - Metaphase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Given below is a schematic breakup of the phases / stages of cell cycle:

Which one of the following is the correct indication of the stage/phase in the cell cycle?
[2009]
a)
C - Karyokinesis
b)
D - Synthetic phase
c)
A - Cytokinesis
d)
B - Metaphase

|
Ayush Chavan answered |
In schematic breakup of the phases/ stages of cell cycle, D synthetic phase is the correct indicat
Meiosis is evolutionary significant because it result in[1994]- a)genetically similar daughters
- b)four daughter cells
- c)eggs and sperms
- d)recombinations
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Meiosis is evolutionary significant because it result in
[1994]
a)
genetically similar daughters
b)
four daughter cells
c)
eggs and sperms
d)
recombinations

|
Arya Khanna answered |
Meiosis provides a chance for new combinations of chromosomes mainly by the phenomenon of crossing over and random distribution of homologous chromosomes between daughter cells.
In meiosis, the daughter cells differ from parent cell as well as amongst themselves due to[1991]- a)segregation, independent assortment and crossing over
- b)segregation and crossing over
- c)independent assortment and crossing over
- d)segregation and independent assortment
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In meiosis, the daughter cells differ from parent cell as well as amongst themselves due to
[1991]
a)
segregation, independent assortment and crossing over
b)
segregation and crossing over
c)
independent assortment and crossing over
d)
segregation and independent assortment

|
Shruti Chauhan answered |
Due to segregation, independent assortment and crossing over at the time of meiosis, daughter cells exhibit variation.
Lampbrush chromosomes occur during[1996]- a)prophase of mitosis
- b)diplotene of meiosis
- c)metaphase of meiosis
- d)interphase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Lampbrush chromosomes occur during
[1996]
a)
prophase of mitosis
b)
diplotene of meiosis
c)
metaphase of meiosis
d)
interphase

|
Prisha Singh answered |
Lampbrush chromosomes are highly elongated bivalent chromosomes of diplotene stage, which are held together by chiasmata and have a large number of lateral loops for rapid transcription.
During cell division in apical meristem the nuclear membrane appears in[1997]- a)metaphase
- b)anaphase
- c)telophase
- d)cytokinesis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During cell division in apical meristem the nuclear membrane appears in
[1997]
a)
metaphase
b)
anaphase
c)
telophase
d)
cytokinesis

|
Priyanka Iyer answered |
Metaphase in characterized by the appearance of spindle fibres. Anaphase involves movement of chromatids towards the poles. Cytokinesis marks the division of the cytoplasm of the parent cell into daughter cells.
The nuclear membrane is present at prophase, when the cell moves from prophase it disappers and again it reappears in telophase.
The exchange of genetic material between chromatids of paired homologous chromosomes during first meiotic division is called[1996]- a)transformation
- b)chiasmata
- c)crossing over
- d)synapsis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The exchange of genetic material between chromatids of paired homologous chromosomes during first meiotic division is called
[1996]
a)
transformation
b)
chiasmata
c)
crossing over
d)
synapsis

|
Swara Desai answered |
The points of attachment between homologous chromosomes after their separation in diplotene are called chiasmata. The process of pairing of homologous chromosomes is called synapsis the phenomenon by which DNA isolated from one type of cell, when introduced into another type, is able to bestow some of the properties of the former to the latter is known as transformation.
Best material for the study of mitosis in laboratory is[2002]- a)anther
- b)root tip
- c)leaf tip
- d)ovary
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Best material for the study of mitosis in laboratory is
[2002]
a)
anther
b)
root tip
c)
leaf tip
d)
ovary

|
Shruti Chauhan answered |
Anther cells are used to study mitosis.
The stage during which separation of the paired homologous chromosomes begins is [2018]- a)Pachytene
- b)Diplotene
- c)Diakinesis
- d)Zygotene
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The stage during which separation of the paired homologous chromosomes begins is [2018]
a)
Pachytene
b)
Diplotene
c)
Diakinesis
d)
Zygotene
|
|
Ashish Ghosh answered |
Diplotene
The correct stage during which separation of the paired homologous chromosomes begins is the diplotene stage. This stage is a sub-phase of meiosis, specifically occurring during the first meiotic division.
Explanation:
1. Diplotene Stage:
- The diplotene stage is characterized by the separation of the paired homologous chromosomes, which were initially paired during the preceding prophase I stages (leptotene, zygotene, and pachytene).
- During diplotene, the homologous chromosomes begin to move apart but are still connected at points called chiasmata, where genetic recombination has occurred.
- This stage allows for the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes, leading to genetic diversity in the resulting gametes.
Comparison with Other Prophase I Stages:
- Leptotene: The chromosomes start to condense.
- Zygotene: Homologous chromosomes begin to pair up.
- Pachytene: Pairing of homologous chromosomes is complete, and crossing over occurs.
- Diakinesis: Chromosomes condense further, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
Significance:
- The separation of homologous chromosomes during diplotene is crucial for ensuring that each resulting gamete receives a unique combination of genetic material.
- This genetic diversity is essential for evolution and adaptation in sexually reproducing organisms.
In conclusion, the diplotene stage of meiosis is where the separation of paired homologous chromosomes begins, setting the stage for the subsequent events in meiotic division.
The correct stage during which separation of the paired homologous chromosomes begins is the diplotene stage. This stage is a sub-phase of meiosis, specifically occurring during the first meiotic division.
Explanation:
1. Diplotene Stage:
- The diplotene stage is characterized by the separation of the paired homologous chromosomes, which were initially paired during the preceding prophase I stages (leptotene, zygotene, and pachytene).
- During diplotene, the homologous chromosomes begin to move apart but are still connected at points called chiasmata, where genetic recombination has occurred.
- This stage allows for the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes, leading to genetic diversity in the resulting gametes.
Comparison with Other Prophase I Stages:
- Leptotene: The chromosomes start to condense.
- Zygotene: Homologous chromosomes begin to pair up.
- Pachytene: Pairing of homologous chromosomes is complete, and crossing over occurs.
- Diakinesis: Chromosomes condense further, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
Significance:
- The separation of homologous chromosomes during diplotene is crucial for ensuring that each resulting gamete receives a unique combination of genetic material.
- This genetic diversity is essential for evolution and adaptation in sexually reproducing organisms.
In conclusion, the diplotene stage of meiosis is where the separation of paired homologous chromosomes begins, setting the stage for the subsequent events in meiotic division.
Microtubule is involved in the[1998]- a)cell division
- b)muscle contraction
- c)membrane architecture
- d)dNA recognition
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Microtubule is involved in the
[1998]
a)
cell division
b)
muscle contraction
c)
membrane architecture
d)
dNA recognition

|
Arpita Tiwari answered |
The spindle fibres involved in cell division is made of microtubules
Identify the correct statement with regard to G1 phase (Gap I) of interphase [2020]- a)Cell is metabolically active, grows but does not replicate its DNA
- b)Nuclear division takes place
- c)DNA synthesis or replication takes place
- d)Reorganisation of all cell components takes place
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the correct statement with regard to G1 phase (Gap I) of interphase [2020]
a)
Cell is metabolically active, grows but does not replicate its DNA
b)
Nuclear division takes place
c)
DNA synthesis or replication takes place
d)
Reorganisation of all cell components takes place
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
G1 Phase is metabolically active stage of cell cycle. Different type of amino acid RNA, Protein synthesis take place in G1 phase but DNA replication does not take place, (Note :- DNA replication occur in S-Phase)
Which of the following is not a characteristic feature during mitosis in somatic cells ? [2016]- a)Spindle fibres
- b)Disappearance of nucleolus
- c)Chromosome movement
- d)Synapsis
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a characteristic feature during mitosis in somatic cells ? [2016]
a)
Spindle fibres
b)
Disappearance of nucleolus
c)
Chromosome movement
d)
Synapsis

|
Muskaan Basak answered |
(d) Synapsis is the pairing of two homologous chromosomes that occurs during meiosis. It allows matching-up of homologous pairs prior to their segregation, and possible chromosomal crossover between them. Synapsis takes place during prophase I, Zygotene of meiosis.
Which of the following stages of meiosis involves division of centromere? [2021]- a)Anaphase II
- b)Telophase II
- c)Metaphase I
- d)Metaphase II
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following stages of meiosis involves division of centromere? [2021]
a)
Anaphase II
b)
Telophase II
c)
Metaphase I
d)
Metaphase II
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Anaphase II: It begins with the simultaneous splitting of the centromere of each chromosome (which was holding the sister chromatids together), allowing them to move toward opposite poles of the cell by shortening of microtubules attached to kinetochores.
Cells in GO phase [2019]
- a)Foramtion of new cell
- b)Exit the cell cycle
- c)Enter the cell cycle
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cells in GO phase [2019]
a)
Foramtion of new cell
b)
Exit the cell cycle
c)
Enter the cell cycle
d)
None of these
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Cells in the G0 phase have exited the cell cycle and are not actively dividing. However, they are still metabolically active and capable of responding to stimuli that can cause them to reenter the cell cycle and divide. The G0 phase is also referred to as the "quiescent phase," as the cells are in a state of relative rest or quiescence. Cells in the G0 phase may be found in tissues that do not require frequent cell division, such as fully developed organs, or in cells that have undergone cellular senescence and are no longer able to divide. The G0 phase is a normal part of the cell cycle and is not necessarily a terminal phase; cells can return to the G1 phase and reenter the cell cycle if the appropriate signals are received.
In ‘S’ phase of the cell cycle: [2014]- a)Amount of DNA doubles in each cell.
- b)Amount of DNA remains same in each cell.
- c)Chromosome number is increased.
- d)Amount of DNA is reduced to half in each cell.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In ‘S’ phase of the cell cycle: [2014]
a)
Amount of DNA doubles in each cell.
b)
Amount of DNA remains same in each cell.
c)
Chromosome number is increased.
d)
Amount of DNA is reduced to half in each cell.

|
Arnav Iyer answered |
(a) During S or synthesis phase, replication or duplication of chromosomal DNA and synthesis of histone proteins takes place. During this time the amount of DNA per cell doubles.
Which of the following options gives the correct sequence of events during mitosis? [2017]- a)Condensation → Nuclear membrane disassembly → Arrangement at equator → Centromere division → Segregation → Telophase
- b)Condensation → Crossing over → Nuclear membrane disassembly → Segregation → Telophase
- c)Condensation → Arrangement at equator → Centromere division → Segregation → Telophase
- d)Condensation → Nuclear membrane disassembly → Crossing over → Segregation → Telophase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following options gives the correct sequence of events during mitosis? [2017]
a)
Condensation → Nuclear membrane disassembly → Arrangement at equator → Centromere division → Segregation → Telophase
b)
Condensation → Crossing over → Nuclear membrane disassembly → Segregation → Telophase
c)
Condensation → Arrangement at equator → Centromere division → Segregation → Telophase
d)
Condensation → Nuclear membrane disassembly → Crossing over → Segregation → Telophase
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Mitosis is divided into four phase prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. During prophase, the indistinct and intertwined DNA molecule condenses to form elongated chromosomes. The nuclear membrane disintegrates during prometaphase During metaphase, the chromosomes align themselves at the equatorial plate. During anaphase, centromere of each chromosome divides into two so that each chromosome come to have its own centromere Chromatids move towards opposite poles along the path of their chromosome fibres. Finally, during telophase, two chromosome groups reorganise to form two nuclei. Nuclear envelope reappears, Golgi complex and endoplasmic reticulum are reformed Crossing over occurs during meiosis.
Option (c) also gives the correct sequence of event but it misses step II (nuclear membrane disassembly). Hence, is ruled out as best appropriate answer is option (a).
Option (c) also gives the correct sequence of event but it misses step II (nuclear membrane disassembly). Hence, is ruled out as best appropriate answer is option (a).
Meiosis II performs[1993]- a)separation of sex chromosomes
- b)synthesis of DNA and centromere
- c)separation of homologous chromosomes
- d)separation of chromatids
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Meiosis II performs
[1993]
a)
separation of sex chromosomes
b)
synthesis of DNA and centromere
c)
separation of homologous chromosomes
d)
separation of chromatids

|
Srishti Sen answered |
Meiosis II is homotypic division specially for maintanence of the haploid number, separating the chromatids from each other in a chromosome.
In the somatic cell cycle[2004]- a)In G1 phase DNA content is double the amount of DNA present in the original cell
- b)DNA replication takes place in Sphase
- c)a short interphase is followed by a long mitotic phase
- d)G2 phase follows mitotic phase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the somatic cell cycle
[2004]
a)
In G1 phase DNA content is double the amount of DNA present in the original cell
b)
DNA replication takes place in Sphase
c)
a short interphase is followed by a long mitotic phase
d)
G2 phase follows mitotic phase

|
Dipanjan Mehta answered |
DNA replication is restricted to S phase of interphase. G2 phase is followed by the mitotic phase which is shorter than the inter phase. In G2 phase DNA content is double than the amount present in the original cell.
If you are provided with roottips of onion in your class and are asked to count the chromosomes, which of the following stages can you most conveniently look into?[2004]- a)Metaphase
- b)Telophase
- c)Anaphase
- d)Prophase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If you are provided with roottips of onion in your class and are asked to count the chromosomes, which of the following stages can you most conveniently look into?
[2004]
a)
Metaphase
b)
Telophase
c)
Anaphase
d)
Prophase

|
Arya Khanna answered |
Chromosomes are most distinct in the metaphase stage. In the telophase stage they regain their coiled composition. In anaphase the chromatids separate and move towards opposite poles. In prophase stage the chromosomes appear thread like and individual chromatids cannot be seen.
During cell division, the spindle fibres attach to the chromosome at a region called[2000]- a)chromocentre
- b)kinetochore
- c)centriole
- d)chromomere
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During cell division, the spindle fibres attach to the chromosome at a region called
[2000]
a)
chromocentre
b)
kinetochore
c)
centriole
d)
chromomere

|
Arya Khanna answered |
Kinetochore is the proteinaceous covering of centriole, to which spindle fibers attach.
Spindle fibres attach on to [2016]- a)Telomere of the chromosome
- b)Kinetochore of the chromosome
- c)Centromere of the chromosome
- d)Kinetosome of the chromosome
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Spindle fibres attach on to [2016]
a)
Telomere of the chromosome
b)
Kinetochore of the chromosome
c)
Centromere of the chromosome
d)
Kinetosome of the chromosome

|
Harshitha Dey answered |
(b) Attachment of microtubules to chromosomes is mediated by kinetochores, which actively monitor spindle formation and prevent premature anaphase onset during mitosis.
Chapter doubts & questions for Cell Cycle and Cell Division - NEET Past Year Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Cell Cycle and Cell Division - NEET Past Year Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









