NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II...
Start Learning for Free
Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division due to
- a)pairing of homologous chromosomes
- b)crossing over
- c)separation of chromatids
- d)disjunction of homologous chromo
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division d...
Explanation:
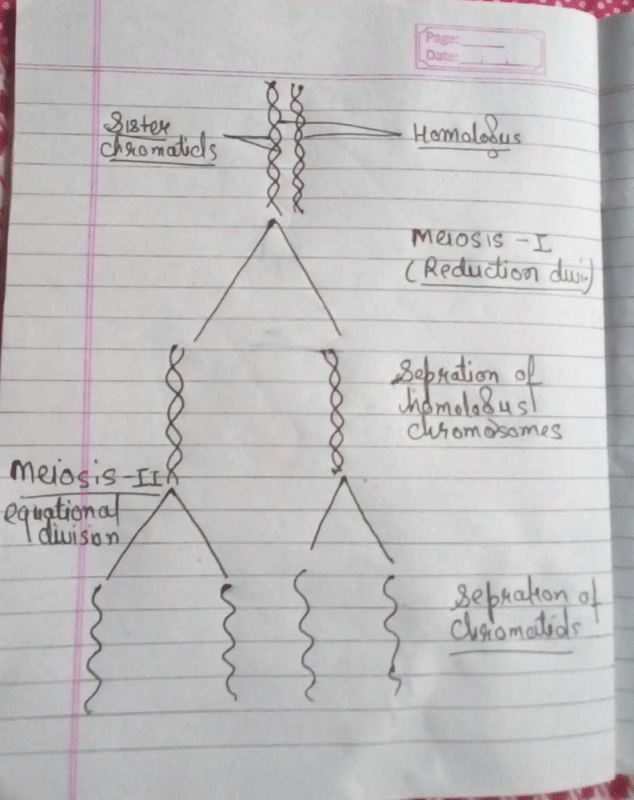
Meiosis I is the first stage of meiosis, where the homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through crossing over. This stage is known as reductional division because it reduces the number of chromosomes in the cell by half. Meiosis II, on the other hand, is equational division because it divides the sister chromatids into two separate cells, resulting in four haploid cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
The correct answer is option C, separation of chromatids. During meiosis II, the sister chromatids separate from each other and move towards opposite poles of the cell. This is referred to as chromatid disjunction and results in the formation of four haploid cells.
Option A, pairing of homologous chromosomes, is a characteristic of meiosis I, where homologous chromosomes pair up to form bivalents.
Option B, crossing over, also occurs during meiosis I, where homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material.
Option D, disjunction of homologous chromosomes, occurs during meiosis I, where homologous chromosomes separate from each other and move towards opposite poles of the cell.
Meiosis I is the first stage of meiosis, where the homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through crossing over. This stage is known as reductional division because it reduces the number of chromosomes in the cell by half. Meiosis II, on the other hand, is equational division because it divides the sister chromatids into two separate cells, resulting in four haploid cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
The correct answer is option C, separation of chromatids. During meiosis II, the sister chromatids separate from each other and move towards opposite poles of the cell. This is referred to as chromatid disjunction and results in the formation of four haploid cells.
Option A, pairing of homologous chromosomes, is a characteristic of meiosis I, where homologous chromosomes pair up to form bivalents.
Option B, crossing over, also occurs during meiosis I, where homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material.
Option D, disjunction of homologous chromosomes, occurs during meiosis I, where homologous chromosomes separate from each other and move towards opposite poles of the cell.
Free Test
| FREE | Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division d...

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Question Description
Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division due toa)pairing of homologous chromosomesb)crossing overc)separation of chromatidsd)disjunction of homologous chromoCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division due toa)pairing of homologous chromosomesb)crossing overc)separation of chromatidsd)disjunction of homologous chromoCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division due toa)pairing of homologous chromosomesb)crossing overc)separation of chromatidsd)disjunction of homologous chromoCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division due toa)pairing of homologous chromosomesb)crossing overc)separation of chromatidsd)disjunction of homologous chromoCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division due toa)pairing of homologous chromosomesb)crossing overc)separation of chromatidsd)disjunction of homologous chromoCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division due toa)pairing of homologous chromosomesb)crossing overc)separation of chromatidsd)disjunction of homologous chromoCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division due toa)pairing of homologous chromosomesb)crossing overc)separation of chromatidsd)disjunction of homologous chromoCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division due toa)pairing of homologous chromosomesb)crossing overc)separation of chromatidsd)disjunction of homologous chromoCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division due toa)pairing of homologous chromosomesb)crossing overc)separation of chromatidsd)disjunction of homologous chromoCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division due toa)pairing of homologous chromosomesb)crossing overc)separation of chromatidsd)disjunction of homologous chromoCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division due toa)pairing of homologous chromosomesb)crossing overc)separation of chromatidsd)disjunction of homologous chromoCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division due toa)pairing of homologous chromosomesb)crossing overc)separation of chromatidsd)disjunction of homologous chromoCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















