All Exams >
NEET >
NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions >
All Questions
All questions of Biodiversity and its Conservation for NEET Exam
Which one of the following fish is being illegally introduced for aquaculture purposes and is posing a threat to the indigenous catfishes of Indian rivers?- a)Clarias gariepinus
- b)Nile perch
- c)Climbing perch
- d)Protopterus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following fish is being illegally introduced for aquaculture purposes and is posing a threat to the indigenous catfishes of Indian rivers?
a)
Clarias gariepinus
b)
Nile perch
c)
Climbing perch
d)
Protopterus
|
|
Hardik Singh answered |
Clarias Gariepinus
Character of a stable community is that it
(a) should not show too much variations in year-to-year productivity
(b) must be resistant to occasional natural or man-made disturbances
(c) should be resistant to invasions by alien species
(d) all of these- a)should not show too much variations in year-to-year productivity
- b)must be resistant to occasional natural or man-made disturbances
- c)should be resistant to invasions by alien species
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Character of a stable community is that it
(a) should not show too much variations in year-to-year productivity
(b) must be resistant to occasional natural or man-made disturbances
(c) should be resistant to invasions by alien species
(d) all of these
(a) should not show too much variations in year-to-year productivity
(b) must be resistant to occasional natural or man-made disturbances
(c) should be resistant to invasions by alien species
(d) all of these
a)
should not show too much variations in year-to-year productivity
b)
must be resistant to occasional natural or man-made disturbances
c)
should be resistant to invasions by alien species
d)
all of these
|
|
Dishani Chavan answered |
Character of a stable community
A stable community refers to a balanced and functioning ecosystem where various species interact with each other and their environment. The character of a stable community can be determined by several factors, including its productivity, resilience to disturbances, and ability to resist invasions by alien species.
1. Year-to-year productivity
A stable community should not show too much variation in its year-to-year productivity. This means that the overall productivity of the community remains relatively constant over time. Fluctuations in productivity can disrupt the balance of the ecosystem and affect the populations of different species. Therefore, a stable community strives to maintain a consistent level of productivity to support the organisms living within it.
2. Resistance to natural or man-made disturbances
Another important characteristic of a stable community is its ability to withstand occasional natural or man-made disturbances. Natural disturbances such as hurricanes, wildfires, or droughts can temporarily disrupt the community's balance. Similarly, human activities like deforestation, pollution, or habitat destruction can also have negative impacts on the ecosystem. A stable community is resilient and can recover from such disturbances, returning to its original state over time.
3. Resistance to invasions by alien species
Invasions by alien species, also known as invasive species, can pose a significant threat to the stability of a community. These species are typically introduced from outside the ecosystem and can outcompete native species for resources, disrupt ecological interactions, and alter the overall structure and function of the community. A stable community has mechanisms in place to resist invasion by alien species, either through competitive exclusion or by maintaining a diverse and robust native species population that can resist the establishment of invaders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the character of a stable community encompasses several key features. It should exhibit minimal year-to-year variations in productivity, be resilient to natural or man-made disturbances, and have the ability to resist invasions by alien species. These traits ensure the long-term sustainability and functioning of the ecosystem, allowing the various species within the community to thrive.
A stable community refers to a balanced and functioning ecosystem where various species interact with each other and their environment. The character of a stable community can be determined by several factors, including its productivity, resilience to disturbances, and ability to resist invasions by alien species.
1. Year-to-year productivity
A stable community should not show too much variation in its year-to-year productivity. This means that the overall productivity of the community remains relatively constant over time. Fluctuations in productivity can disrupt the balance of the ecosystem and affect the populations of different species. Therefore, a stable community strives to maintain a consistent level of productivity to support the organisms living within it.
2. Resistance to natural or man-made disturbances
Another important characteristic of a stable community is its ability to withstand occasional natural or man-made disturbances. Natural disturbances such as hurricanes, wildfires, or droughts can temporarily disrupt the community's balance. Similarly, human activities like deforestation, pollution, or habitat destruction can also have negative impacts on the ecosystem. A stable community is resilient and can recover from such disturbances, returning to its original state over time.
3. Resistance to invasions by alien species
Invasions by alien species, also known as invasive species, can pose a significant threat to the stability of a community. These species are typically introduced from outside the ecosystem and can outcompete native species for resources, disrupt ecological interactions, and alter the overall structure and function of the community. A stable community has mechanisms in place to resist invasion by alien species, either through competitive exclusion or by maintaining a diverse and robust native species population that can resist the establishment of invaders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the character of a stable community encompasses several key features. It should exhibit minimal year-to-year variations in productivity, be resilient to natural or man-made disturbances, and have the ability to resist invasions by alien species. These traits ensure the long-term sustainability and functioning of the ecosystem, allowing the various species within the community to thrive.
On a logarithmic scale, the species area relationship is a straight line described by the equation log S = log C + Z log A.
What does S, C, Z and A represent in the given equation? Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Species richness = 1
Slope of the line = 2
Y- intercept = 3
Area = 4- a)1 - C; 2 - S; 3 - Z; 4 - A
- b)1 - S; 2 - Z; 3 - C; 4 - A
- c)1 - Z; 2 - S; 3 - C; 4 - A
- d)1 - A; 2 - C; 3 - S; 4 - Z
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
On a logarithmic scale, the species area relationship is a straight line described by the equation log S = log C + Z log A.
What does S, C, Z and A represent in the given equation? Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Species richness = 1
Slope of the line = 2
Y- intercept = 3
Area = 4
What does S, C, Z and A represent in the given equation? Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Species richness = 1
Slope of the line = 2
Y- intercept = 3
Area = 4
a)
1 - C; 2 - S; 3 - Z; 4 - A
b)
1 - S; 2 - Z; 3 - C; 4 - A
c)
1 - Z; 2 - S; 3 - C; 4 - A
d)
1 - A; 2 - C; 3 - S; 4 - Z
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
The relationship between species richness and area is rectangular hyperbola for a wide variety of taxa whether they are birds, bats, freshwater fishes or flowering plants and the equation can be given as S = CAZ. On a logarithmic scale it is straight line described by the equation logS = logC + ZlogA. Where S is species richness, Z is slope of line or regression coefficient, C is Y-intercept while A is area.
What is the decreasing order of the number of animals species as far as India is concerned?- a)Mammals>Aves>Reptiles,>Amphibians
- b)Aves>Reptiles>Mammals>Amphibians
- c)Mammals>Reptiles>Amphibians>Aves
- d)Reptiles>Amphibians>Mammals>Aves
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the decreasing order of the number of animals species as far as India is concerned?
a)
Mammals>Aves>Reptiles,>Amphibians
b)
Aves>Reptiles>Mammals>Amphibians
c)
Mammals>Reptiles>Amphibians>Aves
d)
Reptiles>Amphibians>Mammals>Aves
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
The number of species of aves, reptiles, amphibians and mammals are 1232, 456, 209 and 300 respectively.
An exotic species that is introduced to a new area, spreads rapidly and eliminates native species is called- a)immigrant species
- b)invasive species
- c)destructive species
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An exotic species that is introduced to a new area, spreads rapidly and eliminates native species is called
a)
immigrant species
b)
invasive species
c)
destructive species
d)
none of these
|
|
Akash Saini answered |
Understanding Invasive Species
Invasive species are organisms that are introduced to a new environment where they are not native. These species can disrupt the local ecosystem, leading to several ecological issues. Here’s a detailed look at invasive species:
Definition of Invasive Species
- An invasive species is an exotic (non-native) species that spreads rapidly in its new habitat.
- These species often lack natural predators or controls in their new environment, allowing them to thrive.
Impact on Native Species
- Invasive species can outcompete native species for resources such as food, water, and space.
- They may introduce diseases that native species are not equipped to handle.
- The result can be the decline or extinction of native species, disrupting the ecological balance.
Characteristics of Invasive Species
- Rapid reproduction: They often reproduce quickly, leading to large populations.
- Adaptability: These species can thrive in various environmental conditions.
- Aggressive growth: They may grow faster than native plants, overshadowing them and limiting their sunlight access.
Examples of Invasive Species
- Zebra mussels in North America: They clog waterways and disrupt local aquatic ecosystems.
- Kudzu in the southeastern United States: This plant grows aggressively, choking out native flora.
- Burmese python in Florida: This predator threatens local wildlife populations.
Conclusion
Recognizing and managing invasive species is crucial for preserving biodiversity and maintaining the health of ecosystems. Conservation efforts aim to control or eradicate these species to protect native wildlife and habitats.
Invasive species are organisms that are introduced to a new environment where they are not native. These species can disrupt the local ecosystem, leading to several ecological issues. Here’s a detailed look at invasive species:
Definition of Invasive Species
- An invasive species is an exotic (non-native) species that spreads rapidly in its new habitat.
- These species often lack natural predators or controls in their new environment, allowing them to thrive.
Impact on Native Species
- Invasive species can outcompete native species for resources such as food, water, and space.
- They may introduce diseases that native species are not equipped to handle.
- The result can be the decline or extinction of native species, disrupting the ecological balance.
Characteristics of Invasive Species
- Rapid reproduction: They often reproduce quickly, leading to large populations.
- Adaptability: These species can thrive in various environmental conditions.
- Aggressive growth: They may grow faster than native plants, overshadowing them and limiting their sunlight access.
Examples of Invasive Species
- Zebra mussels in North America: They clog waterways and disrupt local aquatic ecosystems.
- Kudzu in the southeastern United States: This plant grows aggressively, choking out native flora.
- Burmese python in Florida: This predator threatens local wildlife populations.
Conclusion
Recognizing and managing invasive species is crucial for preserving biodiversity and maintaining the health of ecosystems. Conservation efforts aim to control or eradicate these species to protect native wildlife and habitats.
Western ghats have a greater number of amphibian species than the Eastern ghats. What kind of diversity does it represent?- a)Species diversity
- b)Genetic diversity
- c)Ecological diversity
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Western ghats have a greater number of amphibian species than the Eastern ghats. What kind of diversity does it represent?
a)
Species diversity
b)
Genetic diversity
c)
Ecological diversity
d)
None of these
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Species diversity is the variety in the number and richness of the species of a region. Western ghats have greater amphibian species diversity as compared to Eastern ghats. The number of the species per unit area is called species richness. Number of individuals of different species represent species evenness or species equitability.
_______National Park was the first national park of India.- a)Jim Corbett
- b)Nanda Devi
- c)Kaziranga
- d)Jaldapara
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
_______National Park was the first national park of India.
a)
Jim Corbett
b)
Nanda Devi
c)
Kaziranga
d)
Jaldapara
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Jim Corbett National Park (District Nainital, Uttrakhand) is the first national park of India, established in 1936.
The narrowly utilitarian arguments for biodiversity conservation include which of the following from the given list?
(i) Industrial products like dyes, lubricants
(ii) Ecosystem services like photosynthesis
(iii) Pollinators layer of bees, birds and bats
(iv) Firewood, fibre and construction material
(v) The aesthetic pleasure of walking through thick woods
(vi) Products of medicinal importance
(vii) Watching spring flowers in full bloom- a) (i), (ii), (v) and (vii)
- b)(ii), (iii), (v) and (vii)
- c)(i), (iv) and (vi)
- d)(ii), (v), (vi) and (vii)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The narrowly utilitarian arguments for biodiversity conservation include which of the following from the given list?
(i) Industrial products like dyes, lubricants
(ii) Ecosystem services like photosynthesis
(iii) Pollinators layer of bees, birds and bats
(iv) Firewood, fibre and construction material
(v) The aesthetic pleasure of walking through thick woods
(vi) Products of medicinal importance
(vii) Watching spring flowers in full bloom
(i) Industrial products like dyes, lubricants
(ii) Ecosystem services like photosynthesis
(iii) Pollinators layer of bees, birds and bats
(iv) Firewood, fibre and construction material
(v) The aesthetic pleasure of walking through thick woods
(vi) Products of medicinal importance
(vii) Watching spring flowers in full bloom
a)
(i), (ii), (v) and (vii)
b)
(ii), (iii), (v) and (vii)
c)
(i), (iv) and (vi)
d)
(ii), (v), (vi) and (vii)
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Narrowly utilitarian arguments for biodiversity conservation include direct benefits from organisms. Industrual products, firewood, fibre, construction material and medicinal products are all included under narrowly utilitarian category.
Presently india has ____ biosphere reserves_____national park and ___wildlife sancturies
- a)20; 90; 500
- b)14; 85; 348
- c)14; 90; 448
- d)11; 91; 500
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Presently india has ____ biosphere reserves_____national park and ___wildlife sancturies
a)
20; 90; 500
b)
14; 85; 348
c)
14; 90; 448
d)
11; 91; 500
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
India now has 14 biosphere reserves, 90 national parks and 448 wildlife sanctuaries. Biosphere reserves, national parks and wildlife sanctuaries are all examples of in-situ conservation.
Species diversity______as we move away from the _______towards_____.- a)decreases, equator, poles
- b)increases, equator, poles
- c)decreases, poles, equator
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Species diversity______as we move away from the _______towards_____.
a)
decreases, equator, poles
b)
increases, equator, poles
c)
decreases, poles, equator
d)
none of these
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Barring arid/semi-arid and aquatic habitat, biodiversite shows a latitudinal and altitudinal gradients. There is little biodiversity at the poles. It increases in temperate areas but reaches the maximum in tropical rain forests at equator. It is because the tropical rain forests have favorable environmental conditions not only for speciation but also for supporting both variety and number of organisms.
Which of these organisms are protected by people of 'Bishnoi' community of Rajasthan?- a)Prosopis cineraria
- b)Black buck
- c)Bhojpatra
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these organisms are protected by people of 'Bishnoi' community of Rajasthan?
a)
Prosopis cineraria
b)
Black buck
c)
Bhojpatra
d)
Both (a) and (b)
|
|
Kirti Khanna answered |
Organisms Protected by the Bishnoi Community of Rajasthan
The Bishnoi community of Rajasthan is known for its deep-rooted traditions and religious beliefs that emphasize environmental conservation and protection of wildlife. They have been actively involved in safeguarding various organisms and habitats from harm. Two key organisms that are protected by the Bishnoi community are the Prosopis cineraria tree and the Black buck.
1. Prosopis cineraria:
The Prosopis cineraria, commonly known as the Khejri tree, is a native species to the arid regions of Rajasthan. It holds immense importance in the lives of the Bishnoi people. They consider the Khejri tree as sacred and worship it as part of their religious rituals. The Bishnoi community has been actively involved in the conservation and protection of this tree species for centuries. They believe that cutting down a Khejri tree is equivalent to killing a person from their own community. The Bishnoi community has played a significant role in preventing the indiscriminate felling of Khejri trees and raising awareness about their ecological importance.
2. Black buck:
The Black buck (Antilope cervicapra) is a species of antelope found in the Indian subcontinent, including the arid regions of Rajasthan. It is known for its distinctive black coat and spiraled horns in males. The Bishnoi community holds the Black buck in high regard and considers it a symbol of grace, beauty, and peace. They have a deep connection with this species and have taken several measures to protect it from hunting and poaching. The Bishnoi community has historically resisted the killing of Black bucks and has even sacrificed their lives to protect them. They have set up sanctuaries and conservation areas to provide a safe habitat for these animals.
Conclusion:
The Bishnoi community of Rajasthan plays a crucial role in the conservation and protection of various organisms, especially the Prosopis cineraria tree and the Black buck. Their religious beliefs and deep-rooted traditions guide their commitment to environmental conservation. Through their collective efforts, the Bishnoi community has successfully contributed to the preservation of these species and their habitats, ensuring a sustainable future for both nature and mankind.
The Bishnoi community of Rajasthan is known for its deep-rooted traditions and religious beliefs that emphasize environmental conservation and protection of wildlife. They have been actively involved in safeguarding various organisms and habitats from harm. Two key organisms that are protected by the Bishnoi community are the Prosopis cineraria tree and the Black buck.
1. Prosopis cineraria:
The Prosopis cineraria, commonly known as the Khejri tree, is a native species to the arid regions of Rajasthan. It holds immense importance in the lives of the Bishnoi people. They consider the Khejri tree as sacred and worship it as part of their religious rituals. The Bishnoi community has been actively involved in the conservation and protection of this tree species for centuries. They believe that cutting down a Khejri tree is equivalent to killing a person from their own community. The Bishnoi community has played a significant role in preventing the indiscriminate felling of Khejri trees and raising awareness about their ecological importance.
2. Black buck:
The Black buck (Antilope cervicapra) is a species of antelope found in the Indian subcontinent, including the arid regions of Rajasthan. It is known for its distinctive black coat and spiraled horns in males. The Bishnoi community holds the Black buck in high regard and considers it a symbol of grace, beauty, and peace. They have a deep connection with this species and have taken several measures to protect it from hunting and poaching. The Bishnoi community has historically resisted the killing of Black bucks and has even sacrificed their lives to protect them. They have set up sanctuaries and conservation areas to provide a safe habitat for these animals.
Conclusion:
The Bishnoi community of Rajasthan plays a crucial role in the conservation and protection of various organisms, especially the Prosopis cineraria tree and the Black buck. Their religious beliefs and deep-rooted traditions guide their commitment to environmental conservation. Through their collective efforts, the Bishnoi community has successfully contributed to the preservation of these species and their habitats, ensuring a sustainable future for both nature and mankind.
The exotic species, which when introduced in India became notorious weed(s), is/are- a)Lantana camara
- b)Eicchornia crassipes
- c)Parthenium hysterophorus
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The exotic species, which when introduced in India became notorious weed(s), is/are
a)
Lantana camara
b)
Eicchornia crassipes
c)
Parthenium hysterophorus
d)
All of these
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Lantana, Eichhornia and Parthenium are all exotic species, which had been introduced in India. Lantana camara has replaced many species in forests of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh. Eichhornia (Water hyacinth) has clogged water bodies including wetlands resulting in death of servral aquatic plants and animals. Parthenium has pushed out several herbs and shrubs from open places in the plains.
Of all the plant species recorded which class has the minimum number of species?- a)Angiosperms
- b)Fungi
- c)Lichens
- d)Algae
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Of all the plant species recorded which class has the minimum number of species?
a)
Angiosperms
b)
Fungi
c)
Lichens
d)
Algae

|
Lead Academy answered |
- The mutualistic relationship between a fungus and photosynthesizing algae is called lichens.
- Of all the plant species recorded, lichens have the minimum number of species.
- They are used in the food industry, making dyes and have medicinal use.
Which of the following statements describe natural extinction?
(i) Extinctions abetted by human activities
(ii) Slow replacement of existing species
(iii) Also known as background extinction
(iv) A small population is most likely to be extinct- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(i), (ii) and (iii)
- c)(ii), (iii) and (iv)
- d)(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements describe natural extinction?
(i) Extinctions abetted by human activities
(ii) Slow replacement of existing species
(iii) Also known as background extinction
(iv) A small population is most likely to be extinct
(i) Extinctions abetted by human activities
(ii) Slow replacement of existing species
(iii) Also known as background extinction
(iv) A small population is most likely to be extinct
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
c)
(ii), (iii) and (iv)
d)
(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Natural or background extinction is a slow process of replacement of existing species with the better adapted species due to alternate evolution, changes in environmental conditions, predators and diseases. A small population due to inbreeding depression (reduces genetic variability) and normal population fluctuations during unfavourable periods like drought, harsh winter or severe summer.
Genetic variations affect the production of the drug reserpine in the medicinal plant Rauwolfia vomitoria growing in different Himalayan ranges. What kind of diversity does it indicate?- a)Species diversity
- b)Genetic diversity
- c)Ecological diversity
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Genetic variations affect the production of the drug reserpine in the medicinal plant Rauwolfia vomitoria growing in different Himalayan ranges. What kind of diversity does it indicate?
a)
Species diversity
b)
Genetic diversity
c)
Ecological diversity
d)
None of these
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Genetic diversity is the diversity in the numbers and types of genes as well as chromosomes present in different species and the variations in the genes and their alleles in the same species. The genetic variation in Rauwolfia vomitoria growing in different Himalayan range indicates genetic diversity. Another example is of presence of more than 50,000 genetically different strains of rice, and 1000 varieties of mango in India.
Which of the following statements regarding the estimates of number of species found on earth is not correct?- a)Total number of species present on earth are considered to be about 7 million as estimated by Robert May.
- b)Plants constitute more than 70% of all the species recorded, whereas animals constitute less than 22% of the total number of species.
- c)Insects constitute more than 70% of all the animal species.
- d)None of these.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements regarding the estimates of number of species found on earth is not correct?
a)
Total number of species present on earth are considered to be about 7 million as estimated by Robert May.
b)
Plants constitute more than 70% of all the species recorded, whereas animals constitute less than 22% of the total number of species.
c)
Insects constitute more than 70% of all the animal species.
d)
None of these.

|
Himanshu Das answered |
B) as plants have evolved earlier on the earth than animals and as plants are autotrophs ( they can produce their own food with the help of inorganic substances) plants are therefore found mostly in every part of the eart and outnumber animal species which depends on plants to get their foods,,
Ex situ conservation is used for the conservation of- a)all plants
- b)all animals
- c)threatened animals and plants
- d)both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Ex situ conservation is used for the conservation of
a)
all plants
b)
all animals
c)
threatened animals and plants
d)
both (a) and (b)
|
|
Gaurav Basu answered |
Ex situ conservation is a conservation method where threatened or endangered species of animals and plants are conserved outside their natural habitat. This method involves the removal of individuals from the wild and placing them in a controlled environment to protect them from threats or to support breeding programs. The correct answer to the question is option (c) because ex situ conservation is mainly used for the conservation of threatened animals and plants.
Reasons why ex situ conservation is used for threatened animals and plants:
1. Protection from threats: Ex situ conservation provides a controlled environment where endangered species can be protected from threats such as habitat destruction, pollution, hunting, and disease.
2. Breeding programs: Ex situ conservation can involve breeding programs where individuals are selected for their genetic diversity to increase the chances of producing healthy offspring. This can help to increase the population size of threatened species.
3. Research: Ex situ conservation provides an opportunity for researchers to study endangered species and their behavior in a controlled environment. This can help to develop conservation strategies for the species in the wild.
Examples of ex situ conservation:
1. Zoos and aquariums: These facilities often have breeding programs for endangered species and provide education for the public about the importance of conservation.
2. Botanical gardens: These gardens can house endangered plant species and provide opportunities for research and education.
3. Seed banks: These facilities store seeds from endangered plant species for future use in conservation efforts.
In conclusion, ex situ conservation is an important conservation method used to protect threatened animals and plants. It provides a controlled environment where breeding programs, research, and education can take place to increase the chances of survival for endangered species.
Reasons why ex situ conservation is used for threatened animals and plants:
1. Protection from threats: Ex situ conservation provides a controlled environment where endangered species can be protected from threats such as habitat destruction, pollution, hunting, and disease.
2. Breeding programs: Ex situ conservation can involve breeding programs where individuals are selected for their genetic diversity to increase the chances of producing healthy offspring. This can help to increase the population size of threatened species.
3. Research: Ex situ conservation provides an opportunity for researchers to study endangered species and their behavior in a controlled environment. This can help to develop conservation strategies for the species in the wild.
Examples of ex situ conservation:
1. Zoos and aquariums: These facilities often have breeding programs for endangered species and provide education for the public about the importance of conservation.
2. Botanical gardens: These gardens can house endangered plant species and provide opportunities for research and education.
3. Seed banks: These facilities store seeds from endangered plant species for future use in conservation efforts.
In conclusion, ex situ conservation is an important conservation method used to protect threatened animals and plants. It provides a controlled environment where breeding programs, research, and education can take place to increase the chances of survival for endangered species.
India relishes a history of relishes a history of religious and culture traditions which emphasised the protection of nature. In many cultures, tracts of forest were set aside, all the trees and wildlife within were venerated and given total protection. Such areas are refferred to as- a)hotspots
- b)ethical groves
- c)sacred groves
- d)protected areas
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
India relishes a history of relishes a history of religious and culture traditions which emphasised the protection of nature. In many cultures, tracts of forest were set aside, all the trees and wildlife within were venerated and given total protection. Such areas are refferred to as
a)
hotspots
b)
ethical groves
c)
sacred groves
d)
protected areas
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Sacred forests (= sacred groves) are forest patches around places of worship which are held in high esteem by tribal communities. They are the most undisturbed forest patches (island of pristine forests) which are often surrounded by highly degraded landscapes. They are found in several parts of India, e.g., Karnataka, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, etc. Many endemic species which are of have become extinct elsewhere can be seen to flourish here.
'Broadly utilitarian' argument for the conservation of biodiversity does not include- a)bioprospecting
- b)pollination
- c)aesthetic value
- d)climatic regulation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
'Broadly utilitarian' argument for the conservation of biodiversity does not include
a)
bioprospecting
b)
pollination
c)
aesthetic value
d)
climatic regulation
|
|
Amar Dasgupta answered |
Bioprospecting
Bioprospecting refers to the exploration of biodiversity for new resources, such as medicinal plants or compounds. While bioprospecting can lead to valuable discoveries, it is not a broadly utilitarian argument for the conservation of biodiversity. This is because bioprospecting focuses on the potential benefits that humans can derive from biodiversity, rather than considering the intrinsic value of biodiversity itself.
Pollination
Pollination is a key ecosystem service provided by biodiversity. Many plants rely on pollinators to reproduce, and without them, food production would be severely impacted. By conserving biodiversity, we ensure that pollinators continue to thrive and support agricultural systems.
Aesthetic Value
The aesthetic value of biodiversity is another important reason for conservation efforts. Many people derive joy and inspiration from the beauty of nature, whether it's through observing diverse plant and animal species or exploring natural landscapes. Preserving biodiversity allows for future generations to experience and appreciate the wonders of the natural world.
Climatic Regulation
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth's climate. Forests, for example, act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and helping to mitigate climate change. By protecting biodiversity, we can maintain these important ecosystem functions and contribute to global efforts to address climate change.
In conclusion, while bioprospecting focuses on human-centric benefits, the broader utilitarian argument for the conservation of biodiversity includes pollination, aesthetic value, and climatic regulation as key reasons for preserving the diversity of life on Earth.
Bioprospecting refers to the exploration of biodiversity for new resources, such as medicinal plants or compounds. While bioprospecting can lead to valuable discoveries, it is not a broadly utilitarian argument for the conservation of biodiversity. This is because bioprospecting focuses on the potential benefits that humans can derive from biodiversity, rather than considering the intrinsic value of biodiversity itself.
Pollination
Pollination is a key ecosystem service provided by biodiversity. Many plants rely on pollinators to reproduce, and without them, food production would be severely impacted. By conserving biodiversity, we ensure that pollinators continue to thrive and support agricultural systems.
Aesthetic Value
The aesthetic value of biodiversity is another important reason for conservation efforts. Many people derive joy and inspiration from the beauty of nature, whether it's through observing diverse plant and animal species or exploring natural landscapes. Preserving biodiversity allows for future generations to experience and appreciate the wonders of the natural world.
Climatic Regulation
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth's climate. Forests, for example, act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and helping to mitigate climate change. By protecting biodiversity, we can maintain these important ecosystem functions and contribute to global efforts to address climate change.
In conclusion, while bioprospecting focuses on human-centric benefits, the broader utilitarian argument for the conservation of biodiversity includes pollination, aesthetic value, and climatic regulation as key reasons for preserving the diversity of life on Earth.
Which of the given statements is true?- a)National parks are meant for the protection of fauna only
- b)Wildlife sanctuaries are meant for the protection of both flora and fauna
- c)Activities like collection of forest products, harvesting of timber, private ownership of land, etc. are allowed in national parks
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the given statements is true?
a)
National parks are meant for the protection of fauna only
b)
Wildlife sanctuaries are meant for the protection of both flora and fauna
c)
Activities like collection of forest products, harvesting of timber, private ownership of land, etc. are allowed in national parks
d)
None of these
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
National parks are meant for protection of entire ecosystem (both flora and fauna). Wildlife sanctuaries are ecosystem tracts of land where wild animals (fauna) can take refuge without being hunted. Activities such as collection of forest products, harvesting of timber, private ownership of land, etc. are not allowed in national parks.
Read the given statement and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Tropical rainforests are disappearing fastly from developing countries such as India.
Statement 2: No value is attached to these forests because these are poor in biodiversity- a)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1
- b)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1
- c)Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect
- d)Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statement and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Tropical rainforests are disappearing fastly from developing countries such as India.
Statement 2: No value is attached to these forests because these are poor in biodiversity
Statement 1: Tropical rainforests are disappearing fastly from developing countries such as India.
Statement 2: No value is attached to these forests because these are poor in biodiversity
a)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1
b)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1
c)
Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect
d)
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
|
|
Dishani Chavan answered |
Statement 1: Tropical rainforests are disappearing rapidly from developing countries such as India.
Statement 2: No value is attached to these forests because they are poor in biodiversity.
The correct option is C: Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
Explanation:
- The first statement is correct, as tropical rainforests are indeed disappearing rapidly from developing countries like India. This is due to various factors such as deforestation, urbanization, agriculture expansion, logging, and infrastructure development.
- However, the second statement is incorrect. Tropical rainforests are extremely rich in biodiversity, making them one of the most valuable ecosystems on Earth. They are home to a diverse array of plant and animal species, many of which are unique and found nowhere else. Rainforests play a crucial role in maintaining global climate stability, providing habitat for wildlife, and sustaining local communities.
- The biodiversity found in tropical rainforests is invaluable in terms of ecological services and potential for scientific discoveries. These forests support a complex web of interdependent species, contributing to the overall health of the planet. The loss of these forests has far-reaching consequences for both local and global ecosystems.
- Therefore, it is incorrect to say that no value is attached to tropical rainforests due to their supposed lack of biodiversity. On the contrary, their high biodiversity is one of the main reasons why these forests deserve protection and conservation efforts.
In conclusion, statement 1 is correct, but statement 2 is incorrect as tropical rainforests are highly valued for their rich biodiversity and ecological importance.
Statement 2: No value is attached to these forests because they are poor in biodiversity.
The correct option is C: Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
Explanation:
- The first statement is correct, as tropical rainforests are indeed disappearing rapidly from developing countries like India. This is due to various factors such as deforestation, urbanization, agriculture expansion, logging, and infrastructure development.
- However, the second statement is incorrect. Tropical rainforests are extremely rich in biodiversity, making them one of the most valuable ecosystems on Earth. They are home to a diverse array of plant and animal species, many of which are unique and found nowhere else. Rainforests play a crucial role in maintaining global climate stability, providing habitat for wildlife, and sustaining local communities.
- The biodiversity found in tropical rainforests is invaluable in terms of ecological services and potential for scientific discoveries. These forests support a complex web of interdependent species, contributing to the overall health of the planet. The loss of these forests has far-reaching consequences for both local and global ecosystems.
- Therefore, it is incorrect to say that no value is attached to tropical rainforests due to their supposed lack of biodiversity. On the contrary, their high biodiversity is one of the main reasons why these forests deserve protection and conservation efforts.
In conclusion, statement 1 is correct, but statement 2 is incorrect as tropical rainforests are highly valued for their rich biodiversity and ecological importance.
Dodo, passenger pigeon and Steller's sea cow become extinct in the last 500 years due to- a)habitat destruction
- b)over-exploitation
- c)bird-flu virus inflection
- d)pollution
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Dodo, passenger pigeon and Steller's sea cow become extinct in the last 500 years due to
a)
habitat destruction
b)
over-exploitation
c)
bird-flu virus inflection
d)
pollution
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Excessive exploitation of a species, whether a plant or animal reduces size of its population such that it becomes vulnerable to extinction. Dodo, passenger pigeon and Steller's sea cow become extinct in the last 500 years due to over-exploitation by humans.
Introduction of alien species into new area poses a threat to extinction of indigenous species due to - a)their high nutrient requirement
- b)their symbiotic relationship
- c)absence of their natural predators
- d)more intraspecific competition
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Introduction of alien species into new area poses a threat to extinction of indigenous species due to
a)
their high nutrient requirement
b)
their symbiotic relationship
c)
absence of their natural predators
d)
more intraspecific competition
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
In the absence of their natural predators, exotic species flourish better and pose a threat to indigenous species.
Species diversity______as one moves from high to low altitudes.- a)increase
- b)decreases
- c)first increases then decreases
- d)first decreases then increases
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Species diversity______as one moves from high to low altitudes.
a)
increase
b)
decreases
c)
first increases then decreases
d)
first decreases then increases
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Biodiversity changes with the changes in altitude. It increases as one moves from higher to lower altitudes. Decrease in temperature and greater seasonal variability are the two major factors responsible for lower diversity at higher altitudes.
Amazon rainforests are considered as 'lungs of the planet' as they contribute______of the total oxygen in the earth's atmosphere.- a)10%
- b)15%
- c)20%
- d)30%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Amazon rainforests are considered as 'lungs of the planet' as they contribute______of the total oxygen in the earth's atmosphere.
a)
10%
b)
15%
c)
20%
d)
30%
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
About 20% of the world oxygen is produced in the amazon rainforests. They are described as the 'lungs of the planet because they provide the assential world environmental service of continously recycling CO2 into O2.
How many plant and animal species have been discovered and described so far?- a)1.5 million
- b)4.5 million
- c)1.5 billion
- d)4.5 billion
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How many plant and animal species have been discovered and described so far?
a)
1.5 million
b)
4.5 million
c)
1.5 billion
d)
4.5 billion
|
|
Nishanth Saini answered |
Introduction:
The question asks about the number of plant and animal species that have been discovered and described so far. The correct answer is option 'A', which states that 1.5 million species have been discovered and described.
Explanation:
Here is a detailed explanation of why option 'A' is the correct answer:
1. The Known Species:
- Scientists estimate that there are approximately 8.7 million species of plants and animals on Earth.
- However, the exact number is difficult to determine as new species are constantly being discovered, and some may become extinct before they are even identified.
2. Discovery and Description Process:
- Discovering and describing a new species is a complex and time-consuming process.
- Scientists rely on various methods, including fieldwork, DNA analysis, and museum collections, to identify and describe species.
- This involves studying the physical characteristics, behavior, habitat, and genetic makeup of the organisms.
3. Cataloging and Classification:
- Once a new species is discovered and described, it is cataloged and classified into the existing taxonomic system.
- The taxonomic system organizes species into groups based on their evolutionary relationships and shared characteristics.
- This helps scientists understand the diversity of life and how different species are related to each other.
4. Number of Described Species:
- As of now, scientists have described and named approximately 1.5 million species of plants and animals.
- This includes both terrestrial and marine species from various regions around the world.
- The number of described species is constantly increasing as new discoveries are made and existing species are better understood.
5. Unexplored Biodiversity:
- Despite the progress made in discovering and describing species, there is still a vast amount of biodiversity that remains unexplored.
- Many regions, especially in tropical rainforests and deep oceans, are still relatively unexplored, and countless new species are waiting to be discovered.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the number of plant and animal species that have been discovered and described so far is approximately 1.5 million. However, this represents only a fraction of the estimated 8.7 million species on Earth. The process of discovering and describing species is ongoing, and scientists continue to explore and catalog the Earth's biodiversity.
The question asks about the number of plant and animal species that have been discovered and described so far. The correct answer is option 'A', which states that 1.5 million species have been discovered and described.
Explanation:
Here is a detailed explanation of why option 'A' is the correct answer:
1. The Known Species:
- Scientists estimate that there are approximately 8.7 million species of plants and animals on Earth.
- However, the exact number is difficult to determine as new species are constantly being discovered, and some may become extinct before they are even identified.
2. Discovery and Description Process:
- Discovering and describing a new species is a complex and time-consuming process.
- Scientists rely on various methods, including fieldwork, DNA analysis, and museum collections, to identify and describe species.
- This involves studying the physical characteristics, behavior, habitat, and genetic makeup of the organisms.
3. Cataloging and Classification:
- Once a new species is discovered and described, it is cataloged and classified into the existing taxonomic system.
- The taxonomic system organizes species into groups based on their evolutionary relationships and shared characteristics.
- This helps scientists understand the diversity of life and how different species are related to each other.
4. Number of Described Species:
- As of now, scientists have described and named approximately 1.5 million species of plants and animals.
- This includes both terrestrial and marine species from various regions around the world.
- The number of described species is constantly increasing as new discoveries are made and existing species are better understood.
5. Unexplored Biodiversity:
- Despite the progress made in discovering and describing species, there is still a vast amount of biodiversity that remains unexplored.
- Many regions, especially in tropical rainforests and deep oceans, are still relatively unexplored, and countless new species are waiting to be discovered.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the number of plant and animal species that have been discovered and described so far is approximately 1.5 million. However, this represents only a fraction of the estimated 8.7 million species on Earth. The process of discovering and describing species is ongoing, and scientists continue to explore and catalog the Earth's biodiversity.
Presently, total number of biodiversity hotspots in the world is- a)25
- b)34
- c)37
- d)40
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Presently, total number of biodiversity hotspots in the world is
a)
25
b)
34
c)
37
d)
40
|
|
Deepika Khanna answered |
The correct answer is option 'B' - 34.
Biodiversity hotspots refer to areas with high levels of biodiversity that are also under significant threat from human activities. These hotspots are identified based on certain criteria such as the number of endemic species (species found nowhere else in the world), the degree of habitat loss, and the level of threat to the biodiversity present.
Here is a detailed explanation of the answer:
1. Definition of biodiversity hotspots:
- Biodiversity hotspots are regions that are biologically rich and have a high level of endemism.
- They are characterized by a large number of unique plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else in the world.
- These hotspots are also under threat due to human activities such as habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change.
2. Criteria for identifying biodiversity hotspots:
- Biodiversity hotspots are identified based on two main criteria: species richness and degree of threat.
- Species richness refers to the number of species present in an area, while the degree of threat refers to the level of risk faced by the biodiversity due to human activities.
3. Number of biodiversity hotspots:
- The concept of biodiversity hotspots was first introduced by Norman Myers in 1988.
- Initially, Myers identified 10 hotspots based on the above criteria.
- Later, the number of hotspots was revised to 25 in 1999, considering additional factors such as the importance of the areas for evolutionary processes.
- The hotspots cover only 1.4% of the Earth's land surface but support more than 60% of the world's plant, bird, mammal, reptile, and amphibian species.
4. Revision of the number of hotspots:
- In 2000, the number of hotspots was further revised to 34 to include additional regions that met the criteria.
- These additional hotspots were identified based on updated data and improved understanding of biodiversity patterns.
- The revised list includes regions such as the Western Ghats and Sri Lanka, which were not included in the original list of 10 hotspots.
In conclusion, there are currently 34 recognized biodiversity hotspots in the world. These hotspots are important for global biodiversity conservation efforts as they harbor a significant proportion of the Earth's species and are under threat from human activities.
Biodiversity hotspots refer to areas with high levels of biodiversity that are also under significant threat from human activities. These hotspots are identified based on certain criteria such as the number of endemic species (species found nowhere else in the world), the degree of habitat loss, and the level of threat to the biodiversity present.
Here is a detailed explanation of the answer:
1. Definition of biodiversity hotspots:
- Biodiversity hotspots are regions that are biologically rich and have a high level of endemism.
- They are characterized by a large number of unique plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else in the world.
- These hotspots are also under threat due to human activities such as habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change.
2. Criteria for identifying biodiversity hotspots:
- Biodiversity hotspots are identified based on two main criteria: species richness and degree of threat.
- Species richness refers to the number of species present in an area, while the degree of threat refers to the level of risk faced by the biodiversity due to human activities.
3. Number of biodiversity hotspots:
- The concept of biodiversity hotspots was first introduced by Norman Myers in 1988.
- Initially, Myers identified 10 hotspots based on the above criteria.
- Later, the number of hotspots was revised to 25 in 1999, considering additional factors such as the importance of the areas for evolutionary processes.
- The hotspots cover only 1.4% of the Earth's land surface but support more than 60% of the world's plant, bird, mammal, reptile, and amphibian species.
4. Revision of the number of hotspots:
- In 2000, the number of hotspots was further revised to 34 to include additional regions that met the criteria.
- These additional hotspots were identified based on updated data and improved understanding of biodiversity patterns.
- The revised list includes regions such as the Western Ghats and Sri Lanka, which were not included in the original list of 10 hotspots.
In conclusion, there are currently 34 recognized biodiversity hotspots in the world. These hotspots are important for global biodiversity conservation efforts as they harbor a significant proportion of the Earth's species and are under threat from human activities.
Which of the following statements regarding biodiversity hotspots are incorrect?
(i) High endemism
(ii) High level of species richness
(iii) Total number is 34 in the world
(iv) Five of these occur in India
(v) High alien species invasion
(vi) Cover less than 2% of the earth's land area, but if properly conserved, they can reduce extinctions by about 30%- a)(iii) and (iv)
- b)(iv) and (v)
- c)(iv), (v) and (vi)
- d)(iii), (iv), (v) and (vi)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements regarding biodiversity hotspots are incorrect?
(i) High endemism
(ii) High level of species richness
(iii) Total number is 34 in the world
(iv) Five of these occur in India
(v) High alien species invasion
(vi) Cover less than 2% of the earth's land area, but if properly conserved, they can reduce extinctions by about 30%
(i) High endemism
(ii) High level of species richness
(iii) Total number is 34 in the world
(iv) Five of these occur in India
(v) High alien species invasion
(vi) Cover less than 2% of the earth's land area, but if properly conserved, they can reduce extinctions by about 30%
a)
(iii) and (iv)
b)
(iv) and (v)
c)
(iv), (v) and (vi)
d)
(iii), (iv), (v) and (vi)
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Exotic species tend to cause a threat to biodiversity. They are not found in hotspots which are regions of high biodiversity. In India, 3 hotspots are found, i.e., Western Ghats and Sri Lanka, Indo-Burma (N-E India) and Himalayas.
'Which of the following is not an objective of Convention of Biodiversity?
- a)Conservation of biodiversity
- b)Sustainable use of biodiversity
- c)Fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising out of genetic resources
- d)Selective hunting of dangerous and threatening species
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
'Which of the following is not an objective of Convention of Biodiversity?
a)
Conservation of biodiversity
b)
Sustainable use of biodiversity
c)
Fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising out of genetic resources
d)
Selective hunting of dangerous and threatening species
|
|
Pranav Roy answered |
The correct answer is option 'D', which states that selective hunting of dangerous and threatening species is not an objective of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD). The CBD is an international treaty that aims to promote the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity, as well as the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from the utilization of genetic resources.
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) was adopted in 1992 during the Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. It has three primary objectives:
1. Conservation of Biodiversity:
The CBD seeks to conserve biodiversity, which refers to the variety of life on Earth, including ecosystems, species, and genetic diversity. It recognizes the intrinsic value of biodiversity and the need to maintain its ecological integrity. The conservation objective focuses on protecting and preserving natural habitats, ecosystems, and species to ensure their long-term survival.
2. Sustainable Use of Biodiversity:
The CBD promotes the sustainable use of biodiversity, which involves utilizing natural resources in a way that maintains their availability for future generations. It recognizes that human activities, such as agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and tourism, can have an impact on biodiversity. Therefore, the CBD encourages the adoption of sustainable practices that minimize negative impacts and ensure the continued provision of ecosystem services.
3. Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits:
The CBD emphasizes the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from the utilization of genetic resources. Genetic resources are the heritable material of plants, animals, and microorganisms that have potential value for human use. The CBD recognizes that the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity should be accompanied by the fair and equitable sharing of the benefits derived from accessing and utilizing these resources. This objective aims to ensure that countries and communities that hold genetic resources are fairly compensated for their contribution to scientific research, innovation, and commercialization.
Selective hunting of dangerous and threatening species, as mentioned in option 'D', does not align with the objectives of the CBD. The Convention focuses on conservation, sustainable use, and benefit-sharing rather than promoting hunting practices that may endanger species or disrupt ecosystems. The CBD aims to protect biodiversity as a whole and promote the long-term sustainability of ecosystems and the services they provide to humanity.
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) was adopted in 1992 during the Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. It has three primary objectives:
1. Conservation of Biodiversity:
The CBD seeks to conserve biodiversity, which refers to the variety of life on Earth, including ecosystems, species, and genetic diversity. It recognizes the intrinsic value of biodiversity and the need to maintain its ecological integrity. The conservation objective focuses on protecting and preserving natural habitats, ecosystems, and species to ensure their long-term survival.
2. Sustainable Use of Biodiversity:
The CBD promotes the sustainable use of biodiversity, which involves utilizing natural resources in a way that maintains their availability for future generations. It recognizes that human activities, such as agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and tourism, can have an impact on biodiversity. Therefore, the CBD encourages the adoption of sustainable practices that minimize negative impacts and ensure the continued provision of ecosystem services.
3. Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits:
The CBD emphasizes the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from the utilization of genetic resources. Genetic resources are the heritable material of plants, animals, and microorganisms that have potential value for human use. The CBD recognizes that the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity should be accompanied by the fair and equitable sharing of the benefits derived from accessing and utilizing these resources. This objective aims to ensure that countries and communities that hold genetic resources are fairly compensated for their contribution to scientific research, innovation, and commercialization.
Selective hunting of dangerous and threatening species, as mentioned in option 'D', does not align with the objectives of the CBD. The Convention focuses on conservation, sustainable use, and benefit-sharing rather than promoting hunting practices that may endanger species or disrupt ecosystems. The CBD aims to protect biodiversity as a whole and promote the long-term sustainability of ecosystems and the services they provide to humanity.
Which of the following fish led to the extinction of an ecologically unique assemblage of more than 200 species of cichlid fish in the take Victoria of E. Africa?- a)Catla catla
- b)Dog fish
- c)Nile perch
- d)African catfish
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following fish led to the extinction of an ecologically unique assemblage of more than 200 species of cichlid fish in the take Victoria of E. Africa?
a)
Catla catla
b)
Dog fish
c)
Nile perch
d)
African catfish
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Nile Perch (a predator fish) was introduced in lake Victoria of East Africa. It killed and eliminated ecoligically unique assemblage of over 200 native species of small cichild fish.
Keystone species deserve protection because these- a)are capable of surviving in harsh environmental conditions
- b)indicate presence of certain minerals in the soil
- c)have become rare due to overexploitation
- d)play an important role in supporting other species
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Keystone species deserve protection because these
a)
are capable of surviving in harsh environmental conditions
b)
indicate presence of certain minerals in the soil
c)
have become rare due to overexploitation
d)
play an important role in supporting other species
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Keystone species are those which have significant and disproportionately large influence on the community structure and characteristics. It has often considerably low abundance and biomass as compared to dominant species. Removal of such species causes serious disruption in structure and function of community.
When a species becomes extinct, the plant and animal species associated with it in an obligatory way also become extinct. This phenomenon is referred to as- a)Fragmentation
- b)Alien species invasion
- c)Over-exploitation
- d)Co-extinction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When a species becomes extinct, the plant and animal species associated with it in an obligatory way also become extinct. This phenomenon is referred to as
a)
Fragmentation
b)
Alien species invasion
c)
Over-exploitation
d)
Co-extinction
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Extinction of one species automatically causes extinction of the other species in certain obligatory mutualistic relationships. This is called co-extinction, e.g., mutualism between Pronuba yuccasella and Yucca.
The reason behind conserving biodiversity have been grouped into which of the following categories?- a)Narrowly utilitarian
- b)Broadly utilitarian
- c)Ethical
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The reason behind conserving biodiversity have been grouped into which of the following categories?
a)
Narrowly utilitarian
b)
Broadly utilitarian
c)
Ethical
d)
All of these
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
We should conserve biodiversity. The reason for this can be broadly divided into three categories.
(i) Narrowly utilltarian (Humans derive a major part of their requirement from organisms).
(ii) Broadly utilitarian (Biodiversity is fundamental to ecosystem services of nature).
(iii) Ethical (Every living species has an intrinsic value, it is our moral duty not to destory them).
(i) Narrowly utilltarian (Humans derive a major part of their requirement from organisms).
(ii) Broadly utilitarian (Biodiversity is fundamental to ecosystem services of nature).
(iii) Ethical (Every living species has an intrinsic value, it is our moral duty not to destory them).
In a national park, protection is provided to- a)flora and fauna
- b)entire ecosystem
- c)fauna only
- d)flora only
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a national park, protection is provided to
a)
flora and fauna
b)
entire ecosystem
c)
fauna only
d)
flora only
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
National park is a reserved area used for conservation purposes. It is maintained by government. Cultivation, grazing, forestry and habitat manipulation are not allowed. Protection is provided to the entire ecosystem.
Select the incorrectly matched pair.- a)UNESCO = United nations Educational Scientific and cultural Organisation
- b)CITES = Convention in International Trade in Elite Species
- c)IUCN = International Union of Conservation for Nature and Natural Resources
- d)WWF =World Wide Fund for Nature
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the incorrectly matched pair.
a)
UNESCO = United nations Educational Scientific and cultural Organisation
b)
CITES = Convention in International Trade in Elite Species
c)
IUCN = International Union of Conservation for Nature and Natural Resources
d)
WWF =World Wide Fund for Nature
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
CITES is Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora.
Biodiversity Act of India was passed by the Parliament in the year- a)1992
- b)1996
- c)2000
- d)2002
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Biodiversity Act of India was passed by the Parliament in the year
a)
1992
b)
1996
c)
2000
d)
2002
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The bidiversity Act provids support for conservation of biological diversity, sustainable use of its components and equitable sharing of the benefits arising out of the use of biological resources. The Biological Act of ndia was passed in 2002. This act of pailiament received the assent of President of India on the 5th February 2003.
First 'Earth Summit' for Convention on Biological Diversity' (CBD) was held at- a)Johanneberg (2002), South Africa.
- b)Rio de Janeiro (1992), Brazil.
- c)Dehradun (1992), India.
- d)New York (2000), U.S.A.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
First 'Earth Summit' for Convention on Biological Diversity' (CBD) was held at
a)
Johanneberg (2002), South Africa.
b)
Rio de Janeiro (1992), Brazil.
c)
Dehradun (1992), India.
d)
New York (2000), U.S.A.
|
|
Deepika Khanna answered |
First Earth Summit for Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) was held at Rio de Janeiro (1992), Brazil.
The First Earth Summit for the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) was held in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil in 1992. The summit, also known as the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), brought together representatives from 172 countries, as well as numerous organizations and NGOs, to discuss global environmental issues and create a plan for sustainable development.
Key Points:
- Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: The summit was held in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, which is known for its rich biodiversity and environmental conservation efforts. The city provided a fitting backdrop for the discussions on the Convention on Biological Diversity.
- United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED): The Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro was also known as the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED). The conference aimed to address pressing environmental issues and promote sustainable development at a global level.
- Representatives from 172 countries: The summit brought together representatives from 172 countries, highlighting the international recognition of the need to address biodiversity loss and promote conservation efforts. The diverse participation ensured that a wide range of perspectives and experiences were considered during the discussions.
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD): The main focus of the summit was the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), an international treaty aimed at conserving and sustainably using the Earth's biodiversity. The CBD seeks to promote the conservation of ecosystems, species, and genetic resources, as well as the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from their use.
- Objectives of the Summit: The Earth Summit had several objectives, including the adoption of the CBD and the negotiation of other agreements related to environmental protection and sustainable development. The summit also aimed to raise awareness about the importance of biodiversity and promote international cooperation in conserving and managing natural resources.
- Legacy of the Earth Summit: The Rio Earth Summit was a landmark event in the history of environmental governance. It led to the adoption of the CBD, which has since been ratified by nearly all countries. The summit also resulted in the creation of the Global Environment Facility (GEF) and the establishment of the Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD), both of which play important roles in promoting sustainable development worldwide.
The First Earth Summit for the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) was held in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil in 1992. The summit, also known as the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), brought together representatives from 172 countries, as well as numerous organizations and NGOs, to discuss global environmental issues and create a plan for sustainable development.
Key Points:
- Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: The summit was held in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, which is known for its rich biodiversity and environmental conservation efforts. The city provided a fitting backdrop for the discussions on the Convention on Biological Diversity.
- United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED): The Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro was also known as the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED). The conference aimed to address pressing environmental issues and promote sustainable development at a global level.
- Representatives from 172 countries: The summit brought together representatives from 172 countries, highlighting the international recognition of the need to address biodiversity loss and promote conservation efforts. The diverse participation ensured that a wide range of perspectives and experiences were considered during the discussions.
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD): The main focus of the summit was the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), an international treaty aimed at conserving and sustainably using the Earth's biodiversity. The CBD seeks to promote the conservation of ecosystems, species, and genetic resources, as well as the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from their use.
- Objectives of the Summit: The Earth Summit had several objectives, including the adoption of the CBD and the negotiation of other agreements related to environmental protection and sustainable development. The summit also aimed to raise awareness about the importance of biodiversity and promote international cooperation in conserving and managing natural resources.
- Legacy of the Earth Summit: The Rio Earth Summit was a landmark event in the history of environmental governance. It led to the adoption of the CBD, which has since been ratified by nearly all countries. The summit also resulted in the creation of the Global Environment Facility (GEF) and the establishment of the Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD), both of which play important roles in promoting sustainable development worldwide.
What is the global species diversity according to Robert May?- a)7 million
- b)70 million
- c)2 million
- d)20 million
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the global species diversity according to Robert May?
a)
7 million
b)
70 million
c)
2 million
d)
20 million

|
Imk Pathsala answered |
- Robert McCredie May is a theoretical ecologist and promoter of science.
- He estimated that there are almost 7 million species globally.
The given pie diagram represents the proportionate number of species of major taxa of vertebrates. Identify the group A and B.
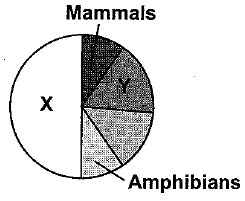
- a)A - Reptiles, B - Birds
- b)A - Fish, B - Birds
- c)A - Birds, B - Fish
- d)A - Birds, B - Reptiles
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The given pie diagram represents the proportionate number of species of major taxa of vertebrates. Identify the group A and B.


a)
A - Reptiles, B - Birds
b)
A - Fish, B - Birds
c)
A - Birds, B - Fish
d)
A - Birds, B - Reptiles
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Among vertebrates, fish account for the maximum share with approximately 26,959 species. Birds have 9,700 identified species and reptiles have 7,150 species.
There are four major causes of accelerated rates of species extinction, which are collectively called as 'the evil quartet'. Which one of the following is not included in 'the evil quartet'?- a)Over exploitation
- b)Pollution
- c)Co-extinctions
- d)Alien species invasions
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
There are four major causes of accelerated rates of species extinction, which are collectively called as 'the evil quartet'. Which one of the following is not included in 'the evil quartet'?
a)
Over exploitation
b)
Pollution
c)
Co-extinctions
d)
Alien species invasions
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
The world is facing acceleration rates of species extinctions, largely due to human interference. There are four major causes collectively called as the evil quarter, it includes (i) Habitat loss and fragmentation, (ii) Oven exploitation, (iii) Alien species invasions and (iv) Co-extinctions.
Identify the groups of organism marked A and B in the given pie diagram representing the proportionate number of species of major taxa of plants.
- a)A - Bryophytes, B - Gymnosperms
- b)A - Fungi, B - Gymnosperms
- c)A - Fungi, B - Angiospems
- d)A - Alage, B - Angiosperms
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the groups of organism marked A and B in the given pie diagram representing the proportionate number of species of major taxa of plants.


a)
A - Bryophytes, B - Gymnosperms
b)
A - Fungi, B - Gymnosperms
c)
A - Fungi, B - Angiospems
d)
A - Alage, B - Angiosperms
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
There are 2,70,000 species of higher plants and 72,000 species of fungi and in the world.
Oragnisation responsible for maintaining Red Data Book is- a)IUCN
- b)WWF
- c)CITES
- d)IBWL
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Oragnisation responsible for maintaining Red Data Book is
a)
IUCN
b)
WWF
c)
CITES
d)
IBWL
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
IUCN is International Union of Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources, which is now called world conservation Union (WCU). It has its headquarters at Morges, Switzerland. It maintains a Red Data Book or Red List which is a catalogue of taxa facing risk of extinction.
Cryopreservation is the reservation of germplasm at very low temperature of around- a)−121∘C
- b)−196∘C
- c)0∘C
- d)−101∘C
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cryopreservation is the reservation of germplasm at very low temperature of around
a)
−121∘C
b)
−196∘C
c)
0∘C
d)
−101∘C
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Cryopreservation is preservation at −196∘C (liquid nitrogen). It can maintain tissue culture, embryos, animal cells/ tissues, spermatozoa indefinitely. The cryopreserved material is revived through special technique when required.
Which of the following is not an example of in situ conservation?- a)Bioshpere reserves
- b)National parks
- c)Wildlife sanctuaries
- d)Zoological parks
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an example of in situ conservation?
a)
Bioshpere reserves
b)
National parks
c)
Wildlife sanctuaries
d)
Zoological parks
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
In situ (on site) conservation is conservation and protection of the whole ecosystem and its biodiversity at all levels in order to protect the treatened species. Two methods are being used to save biodiversity, hotspots and protected areas. Protected areas include national parks, sanctuaries, biosphere reserves and sacred forests. Zoological parks serve the purpose of ex-situ conservation.
Refer to the given figure representing different zones of a biosphere reserve.
Choose the correct answer as per the statements given below:
(i) Limited human activity is allowed such as for research and education.
(ii) An active co-operation occurs between reserve management and local people for activities like cropping, settlements, etc.
(iii) No human activity is allowed.- a)(i) - A; (ii) - B; (iii) - C
- b)(i) - B; (ii) - C; (iii) - A
- c)(i) - C; (ii) - A; (iii) - B
- d)(i) - C; (ii) - B; (iii) - A
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Refer to the given figure representing different zones of a biosphere reserve.

Choose the correct answer as per the statements given below:
(i) Limited human activity is allowed such as for research and education.
(ii) An active co-operation occurs between reserve management and local people for activities like cropping, settlements, etc.
(iii) No human activity is allowed.

Choose the correct answer as per the statements given below:
(i) Limited human activity is allowed such as for research and education.
(ii) An active co-operation occurs between reserve management and local people for activities like cropping, settlements, etc.
(iii) No human activity is allowed.
a)
(i) - A; (ii) - B; (iii) - C
b)
(i) - B; (ii) - C; (iii) - A
c)
(i) - C; (ii) - A; (iii) - B
d)
(i) - C; (ii) - B; (iii) - A
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
A − Core area
B − Buffer zone
C − Transition zone
B − Buffer zone
C − Transition zone
India is one of the 17 megadiversity countries of the world and is being divided into______biogeographical regions.- a)8
- b)10
- c)16
- d)18
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
India is one of the 17 megadiversity countries of the world and is being divided into______biogeographical regions.
a)
8
b)
10
c)
16
d)
18
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
India is one of the twelve of the twelve megadiversity regions of the world with 8.1% of genetic resources of the world. Wildlife Insitute of India has divided the country into 10 biogeographical regions-1. Trans-Himalayas, 2. Himalayas, 3. Desert, 4. Semi-arid, 5. Western Ghats, 6. Deccan Peninsula, 7. Gangetic Plain, 8. North East, 9. Coasts, 10. Island.
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
- a)A-(iv), B-(i), C-(iii), D-(ii), E-(iv)
- b)A-(iii), B-(i), C-(v), D-(ii), E-(iv)
- c)A-(iii), B-(i), C-(v), D-(iv), E-(ii)
- d)A-(v), B-(i), C-(iii), D-(iv), E-(ii)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.

a)
A-(iv), B-(i), C-(iii), D-(ii), E-(iv)
b)
A-(iii), B-(i), C-(v), D-(ii), E-(iv)
c)
A-(iii), B-(i), C-(v), D-(iv), E-(ii)
d)
A-(v), B-(i), C-(iii), D-(iv), E-(ii)
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
A. Beta diversity - Between community diversity
B. Rich biodiversity - Tropical areas
C. Gamma diversity - Diversity of whole geographical region
D. Extinct species - Dodo
E. Critically endangered species - Great Indian bustard
B. Rich biodiversity - Tropical areas
C. Gamma diversity - Diversity of whole geographical region
D. Extinct species - Dodo
E. Critically endangered species - Great Indian bustard
Given pie diagram represents the proportionate number of species of major groups of invertebrates. Identify the groups A and B.
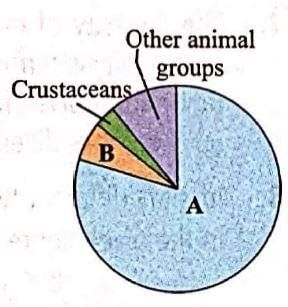
- a)A = Insects, B = Molluscs
- b)A = Molluscs, B = Insects
- c)A = Insects, B = Annelids
- d)A = Molluscs, B = Annelids
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Given pie diagram represents the proportionate number of species of major groups of invertebrates. Identify the groups A and B.


a)
A = Insects, B = Molluscs
b)
A = Molluscs, B = Insects
c)
A = Insects, B = Annelids
d)
A = Molluscs, B = Annelids
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Among all the species in the world, approximately 70% are animals and 22% are plants. In animals, insects account for 70% -80%, which is the maximum (represented as A). According to, IUCN (2009) there are 10,25,000 species of insects and 70,000 species of molluscs (represented as B).
Chapter doubts & questions for Biodiversity and its Conservation - NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Biodiversity and its Conservation - NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily










