All Exams >
NEET >
Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Biological Classification for NEET Exam
Red tide is caused by
- a)Taceratium
- b)Ceratium
- c)Gonyaulax
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Red tide is caused by
a)
Taceratium
b)
Ceratium
c)
Gonyaulax
d)
All of these
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Gonyaulax is a Dinoflagellate and sometimes the number of these Dinoflagellates increases tremendously in the sea and that area of the sea appears little red because of the pigments they have that means they are responsible for Red tide.
Ceratium is one of few Dinoflagellates which show sexual reproduction (Reproduction is by zygotic meiosis). Ceratium is not responsible for causing red tides. So, this option is incorrect.
Triceratium too is not responsible for causing red tides. So, this too is an incorrect option.
Ceratium is one of few Dinoflagellates which show sexual reproduction (Reproduction is by zygotic meiosis). Ceratium is not responsible for causing red tides. So, this option is incorrect.
Triceratium too is not responsible for causing red tides. So, this too is an incorrect option.

The five kingdom classification was proposed by
a)Hutchinson
b)Bentham and Hooker
c)Engler and Prantl
d)WhittakerCorrect answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)Hutchinson
b)Bentham and Hooker
c)Engler and Prantl
d)Whittaker
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
The first major break from the Linnean model came from Thomas Whittaker. In 1969 Whittaker proposed a "five kingdom" system in which three kingdoms were added to the animals and plants: Monera (bacteria), Protista, and Fungi.
Five kingdom system of classification suggested by R.H. Whittaker is based on: [2014]
- a)All of these
- b)Mode of nutrition.
- c)Presence or absence of a well defined nucleus.
- d)Complexity of body organisation.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Five kingdom system of classification suggested by R.H. Whittaker is based on: [2014]
a)
All of these
b)
Mode of nutrition.
c)
Presence or absence of a well defined nucleus.
d)
Complexity of body organisation.
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Correct option is A. All of these
R. H. Whittaker recommended the Five Kingdom Classification in 1969. He partitioned living creatures into five realms Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. The grouping depended on the cell structure like a prokaryotic cell or eukaryotic cell, cell divider constituents, and so forth body organization, method of sustenance (autotrophic, heterotrophic), propagation, and phylogenetic connections.
R. H. Whittaker recommended the Five Kingdom Classification in 1969. He partitioned living creatures into five realms Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. The grouping depended on the cell structure like a prokaryotic cell or eukaryotic cell, cell divider constituents, and so forth body organization, method of sustenance (autotrophic, heterotrophic), propagation, and phylogenetic connections.
Final answer: The Five Kingdom Classification suggested by R. H. Whittaker was based on the complexity of body organization, mode of nutrition, and presence or absence of a well-defined nucleus.
Classification given by Bentham and Hooker is- a)artificial
- b)natural
- c)phylogenetic
- d)numerical.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Classification given by Bentham and Hooker is
a)
artificial
b)
natural
c)
phylogenetic
d)
numerical.
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Classification given by Bentham and Hooker is Natural System. Monocots were placed after dicots, closely related families were seperated, gymnosperms were placed between dicots and monocots.
Identify the virus in figure given below
- a)HIV
- b)Retrovirus
- c)Bacteriophage
- d)TMV
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the virus in figure given below
a)
HIV
b)
Retrovirus
c)
Bacteriophage
d)
TMV

|
Sarthak Verma answered |
A bacteriophage is a type of virus that infects bacteria. In fact, the word "bacteriophage" literally means "bacteria eater," because bacteriophages destroy their host cells. All bacteriophages are composed of a nucleic acid molecule that is surrounded by a protein structure.
Single-celled eukaryotes are included in- a)Archaea
- b)Monera
- c)Fungi
- d)Protista
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Single-celled eukaryotes are included in
a)
Archaea
b)
Monera
c)
Fungi
d)
Protista
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Protista
Kingdom - Protista includes all unicellular eukaryotic organisms like flagellates, diatoms, dinoflagellate, slime mould, Sarcodina, etc.
Fungi represent a group of eukaryotic achlorophyllous, non - photosynthetic heterotrophic organisms of diverse forms, sizes, physiology and mode of reproduction. The members of Archaea (Archaebacteria) are prokaryotes and include the extreme halophiles, the thermoacidophiles and the methanogens.
Monera is the kingdome, that in older classifications contain all prokaryotes.
Identify from the following, the only taxonomic category that has a real existence.- a)Phylum
- b)Species
- c)Genus
- d)Kingdom
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify from the following, the only taxonomic category that has a real existence.
a)
Phylum
b)
Species
c)
Genus
d)
Kingdom
|
|
Mrinalini Basak answered |
Explanation:
Archaebacteria are microorganisms that belong to the domain Archaea. They are prokaryotic organisms, meaning they lack a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles that are common in eukaryotic cells. Archaebacteria are known to survive in extreme environmental conditions that would be lethal for most other organisms. This is due to several factors, but the most important one is their rigid cell wall.
Rigid Cell Wall:
Archaebacteria have a unique cell wall composition that is different from that found in other bacteria. Their cell walls are made up of a complex polysaccharide called pseudomurein, which is more resistant to heat, acids, and other harsh environmental conditions than the peptidoglycan found in other bacterial cell walls. This rigid cell wall provides the archaebacteria with a protective barrier that helps them to withstand extreme temperatures, pH levels, and pressures.
Other Factors:
Apart from the rigid cell wall, there are several other factors that contribute to the ability of archaebacteria to survive in extreme environments. These include:
1. Unique metabolic pathways: Archaebacteria have evolved unique metabolic pathways that allow them to extract energy and nutrients from the environment in which they live. These pathways allow them to survive in environments that would be toxic to other organisms.
2. Resistance to radiation: Some archaebacteria are known to be resistant to high levels of radiation, which allows them to survive in environments such as hot springs and deep-sea hydrothermal vents.
3. Adaptability: Archaebacteria are highly adaptable and can adjust their metabolism and other cellular processes in response to changes in their environment. This allows them to survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, archaebacteria can survive in extreme conditions because of their unique cell wall composition, as well as other factors such as their metabolic pathways, radiation resistance, and adaptability. Their ability to survive in extreme environments makes them important models for studying the origin and evolution of life on Earth.
Archaebacteria are microorganisms that belong to the domain Archaea. They are prokaryotic organisms, meaning they lack a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles that are common in eukaryotic cells. Archaebacteria are known to survive in extreme environmental conditions that would be lethal for most other organisms. This is due to several factors, but the most important one is their rigid cell wall.
Rigid Cell Wall:
Archaebacteria have a unique cell wall composition that is different from that found in other bacteria. Their cell walls are made up of a complex polysaccharide called pseudomurein, which is more resistant to heat, acids, and other harsh environmental conditions than the peptidoglycan found in other bacterial cell walls. This rigid cell wall provides the archaebacteria with a protective barrier that helps them to withstand extreme temperatures, pH levels, and pressures.
Other Factors:
Apart from the rigid cell wall, there are several other factors that contribute to the ability of archaebacteria to survive in extreme environments. These include:
1. Unique metabolic pathways: Archaebacteria have evolved unique metabolic pathways that allow them to extract energy and nutrients from the environment in which they live. These pathways allow them to survive in environments that would be toxic to other organisms.
2. Resistance to radiation: Some archaebacteria are known to be resistant to high levels of radiation, which allows them to survive in environments such as hot springs and deep-sea hydrothermal vents.
3. Adaptability: Archaebacteria are highly adaptable and can adjust their metabolism and other cellular processes in response to changes in their environment. This allows them to survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, archaebacteria can survive in extreme conditions because of their unique cell wall composition, as well as other factors such as their metabolic pathways, radiation resistance, and adaptability. Their ability to survive in extreme environments makes them important models for studying the origin and evolution of life on Earth.
Nuclear membrane is absent in- a)Fungi
- b)Protista
- c)Plantae
- d)Monera
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Nuclear membrane is absent in
a)
Fungi
b)
Protista
c)
Plantae
d)
Monera

|
Dilip Chaurasiya answered |
In kingdom monera nucleus is absent so nuclear membrane is also absent....
Which is the possible region of respiration in bacteria- a)Mitochondria
- b)Cell wall
- c)Nucleoid
- d)Mesosome
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the possible region of respiration in bacteria
a)
Mitochondria
b)
Cell wall
c)
Nucleoid
d)
Mesosome
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
Mesosomes or chondrioids are folded invaginations in the plasma membrane of bacteria that are produced by the chemical fixation techniques used to prepare samples for electron microscopy.
Bacteria have a cell wall, a simple nuclear body without a nuclear membrane, ribosomes and mesosomes in the cytoplasm, and sometimes granules of reserve material, but no endoplasmic reticulum or organelles such as mitochondria or chloroplasts.
Who proposed the five kingdom classification?- a)Schwann and Schleiden
- b)R. H. Whittaker
- c)Virchow
- d)Carl Linnaeus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who proposed the five kingdom classification?
a)
Schwann and Schleiden
b)
R. H. Whittaker
c)
Virchow
d)
Carl Linnaeus

|
Madhurima Dasgupta answered |
Linnaeus later classified all living organisms into two kingdoms – Plantae and Animalia. Whittaker proposed an elaborate five kingdom classification – Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia.
All eukaryotic unicellular organisms belong to- a)Monera
- b)Fungi
- c)Protista
- d)Bacteria
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
All eukaryotic unicellular organisms belong to
a)
Monera
b)
Fungi
c)
Protista
d)
Bacteria
|
|
Sharmistha Giri answered |
Monera are unicellular and prokaryotic , fungi are multicellular and eukaryotic then bacteria is taken under Monera . and protista are unicellular eukaryotic..
AIDS is caused due to:
- a)Deficiency of T-4 lymphocytes
- b)High blood pressure
- c)Deficiency of Riboflavin
- d)Bacterial Infection
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
AIDS is caused due to:
a)
Deficiency of T-4 lymphocytes
b)
High blood pressure
c)
Deficiency of Riboflavin
d)
Bacterial Infection

|
Dilip Chaurasiya answered |
Aids is due to deficiency of T helper cells or T lymphocytes.
One of these is not a characteristic feature of cyanobacteria.- a)They form colonies.
- b)They can fix atmospheric nitrogen.
- c)They are multicellular.
- d)They form blooms in polluted water.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
One of these is not a characteristic feature of cyanobacteria.
a)
They form colonies.
b)
They can fix atmospheric nitrogen.
c)
They are multicellular.
d)
They form blooms in polluted water.
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Multicellular organisms are organisms that consist of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organisms. Multicellular organisms arise in various ways, for example by cell division or by aggregation of many single cells.
In five kingdom of classification, Whittaker assigned eukaryotes to- a)Only two of five kingdoms
- b)All five kingdoms
- c)Only three of five kingdoms
- d)Only four of five kingdoms
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In five kingdom of classification, Whittaker assigned eukaryotes to
a)
Only two of five kingdoms
b)
All five kingdoms
c)
Only three of five kingdoms
d)
Only four of five kingdoms
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
- In Whittaker’s five kingdom of classification, kingdom protista, kingdom fungi, kingdom plantae and kingdom animalia are eukaryotic organisms.
- The kingdom monera includes prokaryotic organisms.
The causative agent of mad-cow disease is a- a)Prion
- b)Worm [2006]
- c)Bacterium
- d)Virus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The causative agent of mad-cow disease is a
a)
Prion
b)
Worm [2006]
c)
Bacterium
d)
Virus

|
Akshat Chavan answered |
Mad cow disease is actually Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy or BSE. In this disease cattles in Britain got their brain become spongy & ultimately gradual degradation of nervous system. It is caused by some virus like but nucleic acid devoid proteinaceous particles called prions (proteinaceous infectious particle).
Can you explain the answer of this question below:All prokaryotic, unicellular organisms are included under kingdomA:FungiB:MoneraC:ProtistaD:AnimaliaThe answer is b.
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
- Monera is a kingdom that contains unicellular organisms with a prokaryotic (is a unicellular organism that lacks a membrane- bound nucleus, mitocondria, or any other membrane- bound organelle.) cell organization, like bacteria.
- They are single- celled organisms with no true nuclear membrane. The taxon Monera was first proposed as a phylum by Ernst Haeckel in 1866.
Which one is important in nutrient recycle and act as decomposer and mineralisers of the biosphere?
- a)Bacteria:- Chemosynthetic autotrophic bacteria
Fungi:- ascomycetes, Phycomycetes
- b)Bacteria:- Photosynthetic autotrophic bacteria
Fungi:- Basidiomycetes, deuteromycetes
- c)Bacteria:- Heterotrophic bacteria
Fungi:- Phycomycetes, Basidiomycetes
- d)Bacteria:- Heterotrophic bacteria
Fungi:- ascomycetes, deuteromycetes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is important in nutrient recycle and act as decomposer and mineralisers of the biosphere?
a)
Bacteria:- Chemosynthetic autotrophic bacteria
Fungi:- ascomycetes, Phycomycetes
b)
Bacteria:- Photosynthetic autotrophic bacteria
Fungi:- Basidiomycetes, deuteromycetes
c)
Bacteria:- Heterotrophic bacteria
Fungi:- Phycomycetes, Basidiomycetes
d)
Bacteria:- Heterotrophic bacteria
Fungi:- ascomycetes, deuteromycetes
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Heterotrophic bacteria are most abundant in nature. The majority are important decomposers.
Commonly known as sac-fungi, the ascomycetes are mostly multicellular, e.g., Penicillium, or rarelyunicellular, e.g., yeast (Saccharomyces). They are saprophytic, decomposers, parasitic or coprophilous (growing on dung).
Some members of deuteromycetes are saprophytes or parasites while a large number of them are decomposers of litter and help in mineral cycling. Some examples are Alternaria, Colletotrichum and Trichoderma.
Which of the following statements is correct? (2021)- a)Organisms that depend on living plants are called saprophytes.
- b)Some of the organisms can fix atmospheric nitrogen in specialized cells called sheath cells.
- c)The fusion of two cells is called Karyogamy.
- d)Fusion of protoplasms between two motile on non-motile gametes is called plasmogamy.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is correct? (2021)
a)
Organisms that depend on living plants are called saprophytes.
b)
Some of the organisms can fix atmospheric nitrogen in specialized cells called sheath cells.
c)
The fusion of two cells is called Karyogamy.
d)
Fusion of protoplasms between two motile on non-motile gametes is called plasmogamy.
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
- Some of these organisms can fix atmospheric nitrogen in specialised cells called heterocysts, e.g., Nostoc and Anabaena.
- Most fungi are heterotrophic and absorb soluble organic matter from dead substrates and hence are called saprophytes.
(i) Fusion of protoplasms between two motile or non-motile gametes called plasmogamy.
(ii) Fusion of two nuclei called karyogamy.
Virus envelope is known as: [2010]- a)Capsid
- b)Virion
- c)Nucleoprotein
- d)Core
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Virus envelope is known as: [2010]
a)
Capsid
b)
Virion
c)
Nucleoprotein
d)
Core

|
Aniket Chawla answered |
Virus envelope is known as capsid. The capsid is composed of protein subunits called capsomere.
Which of the following are wall les procaryotes:-- a)Mycoplasma
- b)Bacteria
- c)Cyanobacteria
- d)Slime molds
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are wall les procaryotes:-
a)
Mycoplasma
b)
Bacteria
c)
Cyanobacteria
d)
Slime molds
|
|
Suyash Jain answered |
**Introduction:**
Prokaryotes are a group of organisms that lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They are unicellular organisms that include bacteria and archaea. Prokaryotes have a cell wall that provides structural support and protection. However, there is one group of prokaryotes that is wall-less, known as Mycoplasma.
**Mycoplasma:**
Mycoplasma is a genus of bacteria that belong to the class Mollicutes. They are unique among prokaryotes because they lack a cell wall. Instead, they have a flexible cell membrane that gives them a pleomorphic (varying in shape) appearance. This absence of a cell wall makes Mycoplasma highly adaptable, allowing them to colonize a wide range of environments, including the human body.
**Bacteria:**
Bacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms that have a cell wall made up of peptidoglycan. The cell wall provides shape, protection, and structural support to the bacteria. It helps them withstand changes in osmotic pressure and prevents them from bursting. The cell wall also plays a role in bacterial pathogenesis, as it can interact with the host immune system.
**Cyanobacteria:**
Cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae, are a group of photosynthetic prokaryotes. They have a cell wall that contains peptidoglycan and other complex polysaccharides. The cell wall provides them with structural support and protection. Cyanobacteria are capable of oxygenic photosynthesis and are responsible for the production of a significant amount of the Earth's oxygen.
**Slime molds:**
Slime molds are not prokaryotes but rather a type of eukaryotic organism. They belong to the kingdom Protista and are known for their unique life cycle. Slime molds can exist as free-living single-celled amoeboid organisms or as a multicellular mass called a plasmodium. They do not possess a cell wall like prokaryotes or most other eukaryotes.
**Conclusion:**
Among the options given, Mycoplasma is the only wall-less prokaryote. Bacteria and cyanobacteria have cell walls, while slime molds are not prokaryotes. Mycoplasma's lack of a cell wall gives it unique characteristics and allows it to thrive in various environments.
Prokaryotes are a group of organisms that lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They are unicellular organisms that include bacteria and archaea. Prokaryotes have a cell wall that provides structural support and protection. However, there is one group of prokaryotes that is wall-less, known as Mycoplasma.
**Mycoplasma:**
Mycoplasma is a genus of bacteria that belong to the class Mollicutes. They are unique among prokaryotes because they lack a cell wall. Instead, they have a flexible cell membrane that gives them a pleomorphic (varying in shape) appearance. This absence of a cell wall makes Mycoplasma highly adaptable, allowing them to colonize a wide range of environments, including the human body.
**Bacteria:**
Bacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms that have a cell wall made up of peptidoglycan. The cell wall provides shape, protection, and structural support to the bacteria. It helps them withstand changes in osmotic pressure and prevents them from bursting. The cell wall also plays a role in bacterial pathogenesis, as it can interact with the host immune system.
**Cyanobacteria:**
Cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae, are a group of photosynthetic prokaryotes. They have a cell wall that contains peptidoglycan and other complex polysaccharides. The cell wall provides them with structural support and protection. Cyanobacteria are capable of oxygenic photosynthesis and are responsible for the production of a significant amount of the Earth's oxygen.
**Slime molds:**
Slime molds are not prokaryotes but rather a type of eukaryotic organism. They belong to the kingdom Protista and are known for their unique life cycle. Slime molds can exist as free-living single-celled amoeboid organisms or as a multicellular mass called a plasmodium. They do not possess a cell wall like prokaryotes or most other eukaryotes.
**Conclusion:**
Among the options given, Mycoplasma is the only wall-less prokaryote. Bacteria and cyanobacteria have cell walls, while slime molds are not prokaryotes. Mycoplasma's lack of a cell wall gives it unique characteristics and allows it to thrive in various environments.
Can you explain the answer of this question below: Who proposed the five kingdom classification?
- A:
Schwann and Schleiden
- B:
R. H. Whittaker
- C:
Virchow
- D:
Carl Linnaeus
The answer is b.
Who proposed the five kingdom classification?
Schwann and Schleiden
R. H. Whittaker
Virchow
Carl Linnaeus

|
Neha Choudhury answered |
Linnaeus later classified all living organisms into two kingdoms – Plantae and Animalia. Whittaker proposed an elaborate five kingdom classification – Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia.
In which class of fungi the mushroom belongs to?
- a)Ascomycetes
- b)Basidiomycetes
- c)Deuteromycetes
- d)Phycomycetes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which class of fungi the mushroom belongs to?
a)
Ascomycetes
b)
Basidiomycetes
c)
Deuteromycetes
d)
Phycomycetes
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
- Mushrooms are the commonly known form of Basidiomycetes, called bracket fungi or puffballs.
- They grow in soil, on logs and tree stumps and in living plant bodies as parasites, e.g., rusts and smuts.

Hence, the correct option is B
NCERT Reference: Topic Basidiomycetes” of chapter "Biological Classification" of NCERT.
Soap box like cell wall is characteristic of :-- a)Archae bacteria
- b)Diatoms
- c)Dinoflagellates
- d)Euglenoids
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Soap box like cell wall is characteristic of :-
a)
Archae bacteria
b)
Diatoms
c)
Dinoflagellates
d)
Euglenoids
|
|
Amrita Choudhary answered |
The cell walls construction of diatoms is known as Frustule which consists of two thin overlapping shells fitting into each other just as a soap-box. Their walls are made up of silica. When the diatoms die, the silica in their cell walls gets deposited in the form of diatomaceous earth. This diatomaceous earth is very soft and quite inert. It is used in filtration of oils, sugars, and for other industrial purposes.
The shape of the cocci bacteria is- a)Spiral
- b)Rod-shaped
- c)Spherical
- d)Comma-shaped
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The shape of the cocci bacteria is
a)
Spiral
b)
Rod-shaped
c)
Spherical
d)
Comma-shaped
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
A coccus (plural cocci) is any bacterium or archea on that has a spherical, ovoid, or generally round shape. It is one of the three distinct bacterial shapes, the other two being bacillus (rod-shaped) and spiral-shaped cells.
Chrysophytes, Euglenoids, Dinoflagellates and Slime moulds are included in the kingdom [2016]- a)Monera
- b)Protista
- c)Fungi
- d)Animalia
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Chrysophytes, Euglenoids, Dinoflagellates and Slime moulds are included in the kingdom [2016]
a)
Monera
b)
Protista
c)
Fungi
d)
Animalia

|
Rajat Roy answered |
(b) All unicellular eukaryotic organism like diatoms, desmids (chrysophytes), euglenoids, dinoflagellates and slime mould are included in Protista.
Causes of water bloom is :-- a)Green algae
- b)Blue green algae
- c)Bacteria
- d)Hydrilla
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Causes of water bloom is :-
a)
Green algae
b)
Blue green algae
c)
Bacteria
d)
Hydrilla

|
Ambition Institute answered |
These are a result of blue-green algae, which are actually bacteria (cyanobacteria). Some algal blooms are the result of an excess of nutrients (particularly phosphorus and nitrogen) in waters and higher concentrations of these nutrients in water cause increased growth of algae and green plants.
Pick up the wrong statement [2015]a) Prostista have photosynthetic and heterotrophic modes of nutritionb) Some fungi are ediblec) Nuclear membrane is present in Monerad) Cell wall is absent in AnimaliaCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Moumita Khanna answered |
(c) The kingdom Monera possesses unicellular organisms (e.g - bacteria) having no nuclear membrane.
Halophiles, methanogens and thermoacidophils are- a)Cyanobacteria
- b)Eubacteria
- c)Actinomycetes
- d)Archaebacteria
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Halophiles, methanogens and thermoacidophils are
a)
Cyanobacteria
b)
Eubacteria
c)
Actinomycetes
d)
Archaebacteria
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Methanogens , Halophiles , Thermoacidophils , all belong to ARCHAEBACTERIA. They are primitive organisms which means they were the first to inhabit earth . They are often called LIVING FOSSILS. Methanogens are found in Rumen of cattles , Halophiles are found in salt lakes , Thermoacidophils are found in hot sulphur springs and Archaebacteria are found in some of the harsh climatic conditions where no other life form could survive.
The structures that help some bacteria to attach to rocks and / or host tissues are: [2015]- a)Fimbriae
- b)Mesosomes
- c)Holdfast
- d)Rhizoids
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The structures that help some bacteria to attach to rocks and / or host tissues are: [2015]
a)
Fimbriae
b)
Mesosomes
c)
Holdfast
d)
Rhizoids

|
Rajat Roy answered |
(a) Fimbriae assist to some bacteria to get attachment with rocks or host body to get establishment and nutrition.
The cell wall of fungi consist of- a)Cellulose
- b)Chitin
- c)Glycopeptides
- d)Starch
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The cell wall of fungi consist of
a)
Cellulose
b)
Chitin
c)
Glycopeptides
d)
Starch
|
|
Om Desai answered |
- Chitin is a long-chain N-acetylglucosamine polymer and is a glucose derivative.
- This polysaccharide is a primary component of cell walls in the fungi, arthropod exoskeletons such as crustaceans and insects, mollusc's radula, cephalopod beaks, and fish.
- The cell wall of plants are made up of cellulose.
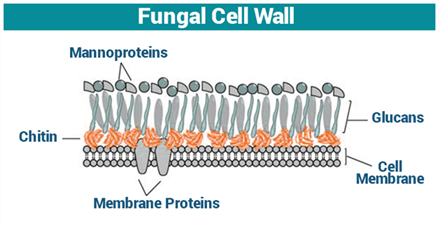
Desmids are also called- a)Mycoplasma
- b)Slime moulds
- c)Golden algae
- d)Blue-green algae
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Desmids are also called
a)
Mycoplasma
b)
Slime moulds
c)
Golden algae
d)
Blue-green algae
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
Diatoms are the phytoplanktons algae. These are found in very large numbers on earth. Some features of diatoms are as follows:- Cell wall forms two thin overlapping shells. Walls embedded with silica, and thus, indestructible. Fossilized remains of diatoms are referred to as ‘diatomaceous earth’. These are mostly photosynthetic & chief producers of the ocean.
Golden algae These belong to class chrysophyceae, also known as chrysophytes. These are unicellular, free swimming organisms found mainly in fresh water. These are important in maintaining the ecosystem of lake an they are the chief source of food for zooplanktons. They are generally photosynthetic but in the absence of sufficient light they start feeding on other organisms or on their remains.
Match the following and choose the correct combination from the options given
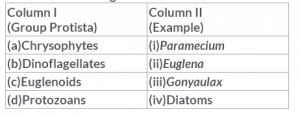
- a)(a)- (iv), (b) – (iii), (c) – (ii), (d) – (i)
- b)(a)- (iv), (b) – (ii), (c) – (iii), (d) – (i)
- c)(a)- (i), (b) – (iii), (c) – (ii), (d) – (iv)
- d)(a)- (iii), (b) – (iv), (c) – (i), (d) – (ii)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following and choose the correct combination from the options given

a)
(a)- (iv), (b) – (iii), (c) – (ii), (d) – (i)
b)
(a)- (iv), (b) – (ii), (c) – (iii), (d) – (i)
c)
(a)- (i), (b) – (iii), (c) – (ii), (d) – (iv)
d)
(a)- (iii), (b) – (iv), (c) – (i), (d) – (ii)
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
-Chrysophytes includes diatoms ,desmids
-dinoflagellate includes gymnodium, gonyaulax ,noctiula..
-euglenoids includes euglena
-protozoans includes amoeba,paramecium,trypanosoma etc..
hence correct answer is A..
-dinoflagellate includes gymnodium, gonyaulax ,noctiula..
-euglenoids includes euglena
-protozoans includes amoeba,paramecium,trypanosoma etc..
hence correct answer is A..
Which one of the following fungi contains hallucinogens? [2014]- a)Morchella esculenta
- b)Amanita muscaria
- c)Neurospora sp.
- d)Ustilago sp.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following fungi contains hallucinogens? [2014]
a)
Morchella esculenta
b)
Amanita muscaria
c)
Neurospora sp.
d)
Ustilago sp.
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Several mushrooms such as Amanita muscaria, Psilocybe mexicana and Panaeolus spp. secrete hallucinogenic substances like psilocybin and psilocin. These substances may destroy brain cells and the perception power of human beings.
Amanita Muscaria:

Viruses have: [2014]
a) either DNA or RNA
b) Prokaryotic nucleus
c) Single chromosome
d) DNA enclosed in a protein coat
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Prashanth Dasgupta answered |
(a) All viruses are nucleoprotein (Nucleic acid + Protein) in the structure. The nucleic acid (DNA and RNA) is genetic material. In a particular virus either DNA or RNA is genetic material never both are present in a virus.Single stranded RNA or ss RNA - Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) Virus envelope is known as capsid. The capsid is composed of protein subunits called capsomere.
Which one of the following statements is wrong? [2016]- a)Cyanobacteria are also called blue-green algae
- b)Golden algae are also called desmids
- c)Eubacteria are also called false bacteria
- d)Phycomycetes are also called algal fungi
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is wrong? [2016]
a)
Cyanobacteria are also called blue-green algae
b)
Golden algae are also called desmids
c)
Eubacteria are also called false bacteria
d)
Phycomycetes are also called algal fungi

|
Sonal Kulkarni answered |
(c) Eubacteria are the True bacteria.
The most efficient locomotion in protista is through :-- a)Pseudopodia
- b)Flagella
- c)Cilia
- d)Tentacles
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The most efficient locomotion in protista is through :-
a)
Pseudopodia
b)
Flagella
c)
Cilia
d)
Tentacles
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Cilia are mostly present in hundreds, projecting out of the holes of the pellicle since basal bodies of all cilia are linked to common kinetodesmata. They beat in the coordinated rhythmic manner to produce paddle stroke effect. Due to their occurrence all over the body, they perform the fastest locomotion i.e., 400-2000 micrometer/second. So, they are the most efficient organs of locomotion.
The asexual reproduction in fungi takes place by- a)endospore
- b)gametangia
- c)exospores
- d)conidiospore
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The asexual reproduction in fungi takes place by
a)
endospore
b)
gametangia
c)
exospores
d)
conidiospore
|
|
Prisha Bajaj answered |
Asexual Reproduction in Fungi by Conidiophores:
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction in which offspring arise from a single organism, and inherit the genes of that parent only. Fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually. Asexual reproduction in fungi takes place through conidiophores.
Conidiophores:
Conidiophores are specialized structures that produce conidia or conidiospores. These are asexually produced spores that develop on the surface of the conidiophore. Conidiophores are produced by many different types of fungi, including both molds and yeasts.
How Conidiophores work:
Conidiophores are produced by the mycelium of the fungus. They are typically found in clusters, and can grow to be several millimeters in length. The conidiophore is composed of several cells, including a basal cell, a stalk cell, and a terminal cell. The terminal cell is where the conidia are produced.
The conidia are formed by a process called conidiation. This process involves the development of a small bud on the surface of the terminal cell. As the bud grows, it becomes surrounded by a protective layer of cells, which eventually break apart to release the conidiospore.
Advantages of Asexual Reproduction:
Asexual reproduction has several advantages for fungi. First, it allows for rapid reproduction, since no mating is required. This is particularly important in environments where conditions are favorable for growth, but may not be stable over a long period of time.
Second, asexual reproduction allows for the production of large numbers of offspring that are genetically identical to the parent. This can be advantageous in environments where the parent organism is well adapted to the local conditions, since the offspring will also be well adapted.
Third, asexual reproduction allows for the spread of fungi over long distances, since the conidia can be carried by wind or other means.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the asexual reproduction in fungi takes place by conidiophores. These specialized structures produce conidia or conidiospores, which are asexually produced spores that develop on the surface of the conidiophore. This type of reproduction has several advantages for fungi, including rapid reproduction, large numbers of offspring, and the ability to spread over long distances.
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction in which offspring arise from a single organism, and inherit the genes of that parent only. Fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually. Asexual reproduction in fungi takes place through conidiophores.
Conidiophores:
Conidiophores are specialized structures that produce conidia or conidiospores. These are asexually produced spores that develop on the surface of the conidiophore. Conidiophores are produced by many different types of fungi, including both molds and yeasts.
How Conidiophores work:
Conidiophores are produced by the mycelium of the fungus. They are typically found in clusters, and can grow to be several millimeters in length. The conidiophore is composed of several cells, including a basal cell, a stalk cell, and a terminal cell. The terminal cell is where the conidia are produced.
The conidia are formed by a process called conidiation. This process involves the development of a small bud on the surface of the terminal cell. As the bud grows, it becomes surrounded by a protective layer of cells, which eventually break apart to release the conidiospore.
Advantages of Asexual Reproduction:
Asexual reproduction has several advantages for fungi. First, it allows for rapid reproduction, since no mating is required. This is particularly important in environments where conditions are favorable for growth, but may not be stable over a long period of time.
Second, asexual reproduction allows for the production of large numbers of offspring that are genetically identical to the parent. This can be advantageous in environments where the parent organism is well adapted to the local conditions, since the offspring will also be well adapted.
Third, asexual reproduction allows for the spread of fungi over long distances, since the conidia can be carried by wind or other means.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the asexual reproduction in fungi takes place by conidiophores. These specialized structures produce conidia or conidiospores, which are asexually produced spores that develop on the surface of the conidiophore. This type of reproduction has several advantages for fungi, including rapid reproduction, large numbers of offspring, and the ability to spread over long distances.
Classification based on comparative cytological studies, number of chromosome and behaviour of chromosome is called- a)Numerical taxonomy
- b)Cytotaxonomy
- c)Chemotaxonomy
- d)Artificial taxonomy
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Classification based on comparative cytological studies, number of chromosome and behaviour of chromosome is called
a)
Numerical taxonomy
b)
Cytotaxonomy
c)
Chemotaxonomy
d)
Artificial taxonomy
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Cytotaxonomy is the classification on the basis of comparative cytological studies, number of chromosomes and behavior of chromosomes.
Most common method of reproduction in prokaryotes :-
- a) Budding
- b) Binary fission
- c) Transduction
- d) Conjugation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most common method of reproduction in prokaryotes :-
a)
Buddingb)
Binary fissionc)
Transductiond)
Conjugation

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
Binary fission ("division in half") is a kind of asexual reproduction. It is the most common form of reproduction in prokaryotes such as bacteria. It occurs in some single-celled Eukaryotes like the Amoeba and the Paramoecium. In binary fission, DNA replication and segregation occur simultaneously.
Photosynthetic prokaryotic organism is:-- a)Rhizobium
- b)Nostoc
- c)Pseudomonas
- d)Staphylococcus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Photosynthetic prokaryotic organism is:-
a)
Rhizobium
b)
Nostoc
c)
Pseudomonas
d)
Staphylococcus
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Nostoc, is genus of blue-green algae with cells arranged in beadlike chains that are grouped together in a gelatinous mass. Like most blue-green algae,Nostoc contains two pigments, blue phycocyanin and red phycoerythrin, as well as chlorophyll, and has the ability to fix nitrogen in specialized cells called heterocysts. This makes them photosynthetic.
Which of the following are likely to be present in deep sea water ? [NEET 2013]- a)Eubacteria
- b)Blue-green algae
- c)Saprophytic fungi
- d)Archaebacteria
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are likely to be present in deep sea water ? [NEET 2013]
a)
Eubacteria
b)
Blue-green algae
c)
Saprophytic fungi
d)
Archaebacteria

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
Archaebactera live in some of the most harsh habitats such as extreme salty areas (halophiles), hot springs (thermoacidophiles) and marshy areas (methanogens) and in deep sea water.
The motile bacteria are able to move by: [2014]- a)Fimbriae
- b)Flagella
- c)Cilia
- d)Pili
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The motile bacteria are able to move by: [2014]
a)
Fimbriae
b)
Flagella
c)
Cilia
d)
Pili
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
In Bacteria the generalised mode of locomotion is flagella. hair A flagellum is a hair like appen dage that rptrudes fro the cell body. Its primary function is locomotion. A bacterial flagella is made up ofprotein flagella. the bacterial flagellum is deriven by rotary engine made up of protein and is powered by flow of protons (hydrogen) across the bocterial cell.
The literal meaning of virus is a:
- a)Poison
- b)Venome
- c)Secretion
- d)Both A and B
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The literal meaning of virus is a:
a)
Poison
b)
Venome
c)
Secretion
d)
Both A and B
|
|
Sethulakshmi E.d Dinesan answered |
Virus means VENOM or POISONOUS FLUID.(11th ncert page no 26.3rd line)
Which system of classification was developed during Linnaeus time?- a)Five kingdom of classification
- b)Three kingdom of classification
- c)Four kingdom of classificaition
- d)Two kingdom of classification
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which system of classification was developed during Linnaeus time?
a)
Five kingdom of classification
b)
Three kingdom of classification
c)
Four kingdom of classificaition
d)
Two kingdom of classification

|
Dipika Das answered |
In Linnaeus' time a TwoKingdomsystem of classification with Plantaeand Animaliakingdoms was developed that included all plants and animals respectively. This system was used till very recently.
Which one is wrong statement? [2015]
- a)Mucor has biflagellate zoospores.
- b)Haploid endosperm is a typical feature of gymnosperms.
- c)Brown algae have chlorophyll a and c and fucoxanthin.
- d)Archegonia are found in Bryophyta, Pteridophyta and Gymnosperms.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is wrong statement? [2015]
a)
Mucor has biflagellate zoospores.
b)
Haploid endosperm is a typical feature of gymnosperms.
c)
Brown algae have chlorophyll a and c and fucoxanthin.
d)
Archegonia are found in Bryophyta, Pteridophyta and Gymnosperms.
|
|
Lalit Yadav answered |
- Mucor belongs to the Kingdom Fungi and division zygomycota. Zygomycota have sexual spores called zygo- spores and most of them lack flagella.
- Gymnosperms don't have double fertilization, the endosperm is haploid and is formed by the repeated division of haploid megaspores and later develops into female gametophyte with haploid chromosomes.
- Brown algae are also known as Phaeophyceae. It is a group of marine multi-cellular algae, which play a critical role in marine environments. Its brown color is due to the presence of pigment fucoxanthin. It also consist of pigment chlorophyll a and c.
- Archegonia is the female reproductive part of flask-shaped structure. It contains of neck and swollen base, where neck consist of one or more layers of cells and swollen part contains of egg. It is found in Bryophytes (eg: ferns and mosses), gymnosperms (eg: cycads and conifers), and Pteridophyta (eg: azolla).
Hence, the correct option is A
NCERT Reference: Page no. 23 of topic “2.3.1 Phycomycetes”of chapter 2 of NCERT
NCERT Reference: Page no. 23 of topic “2.3.1 Phycomycetes”of chapter 2 of NCERT
The imperfect fungi which are decomposer of litter and help in mineral cycling belong to: [2015]- a)Basidiomycetes
- b)Phycomycetes
- c)Ascomycetes
- d)Deuteromycetes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The imperfect fungi which are decomposer of litter and help in mineral cycling belong to: [2015]
a)
Basidiomycetes
b)
Phycomycetes
c)
Ascomycetes
d)
Deuteromycetes

|
Sarthak Saini answered |
(d) Class- deuteromycetes contains imperfect fungi which play role in decomposition of organic wastes.
Chapter doubts & questions for Biological Classification - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Biological Classification - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup













