All Exams >
NEET >
Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Principles of Inheritance & Variation for NEET Exam
In a cross between a pure tall plant with green pod and a pure short plant with yellow pod. How many short plants are produced in F2 generation out of 16? - a)1
- b)4
- c)9
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a cross between a pure tall plant with green pod and a pure short plant with yellow pod. How many short plants are produced in F2 generation out of 16?
a)
1
b)
4
c)
9
d)
3

|
Vaibhav Kaushik answered |
Ratio is 9.3.3.1
where last 3.1 is drawf and green . drawf and yellow
4 answer
where last 3.1 is drawf and green . drawf and yellow
4 answer
XO type of sex determination is found in________.- a)Grasshopper
- b)Elephant
- c)Human beings
- d)Dog
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
XO type of sex determination is found in________.
a)
Grasshopper
b)
Elephant
c)
Human beings
d)
Dog
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
In grasshopper, sex determination is of XO type, in which the males have only one X-chromosome besides the autosomes whereas females have a pair of X-chromosomes.
Who is regarded as the father of genetics?- a)Mendel
- b)Morgan
- c)Watson
- d)Bateson
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Who is regarded as the father of genetics?
a)
Mendel
b)
Morgan
c)
Watson
d)
Bateson
|
|
Riyα answered |
Option {A}
Gregor Johann Mandel...
cz it's gave the idea of heredity...
The innate tendency of offspring to resemble their parents is called?- a)Resemblance
- b)Heredity
- c)Variation
- d)Inheritance
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The innate tendency of offspring to resemble their parents is called?
a)
Resemblance
b)
Heredity
c)
Variation
d)
Inheritance
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The innate tendency of offspring to resemble their parents is called heredity. The offspring resembles to parent due to same genetic combination inherited from parents.
A normal-visioned man whose father was colour¬blind, marries a woman whose father was also colour-blind. They have their first child as a daughter. What are the chances that this child would be colour-blind? [2012]
- a)100%
- b)zero percent
- c)25%
- d)50 %
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A normal-visioned man whose father was colour¬blind, marries a woman whose father was also colour-blind. They have their first child as a daughter. What are the chances that this child would be colour-blind? [2012]
a)
100%
b)
zero percent
c)
25%
d)
50 %

|
Nayanika Reddy answered |
Colour blindness is a X-linked disease. So, woman whose father was colourblind will be carrier for the disease. So, possibility of a colourblind daughter (i.e., XcXc in F1 generation is 0%.)

Which of the following is an example of co-dominance?- a)Skin pigmentation in humans
- b)Sex-linkage in humans
- c)Pink flowers of Snapdragon
- d)The ABO blood groups in human
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of co-dominance?
a)
Skin pigmentation in humans
b)
Sex-linkage in humans
c)
Pink flowers of Snapdragon
d)
The ABO blood groups in human
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Co-dominance is the phenomenon that deviates from Mendel’s law of inheritance. Both the alleles appear in offspring instead of one as in Mendel’s experiment. ABO blood grouping in human being is example of co-dominance in which both IA and IB appear simultaneously to form AB blood type.
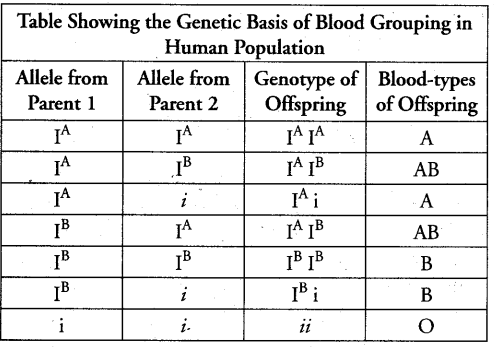
For ABO system of blood groups, allele IA produces N-acetylgalactosamine transferase enzyme which recognises H- antigen present in RBC membrane and adds N-acetylgalactosamine to sugar parts of H antigens to form A antigen.
The allele IB produces galactosyl transferase enzyme which recognized H antigen to form B antigens. Allele i does not produce any sugar or antigen.
IA and IB are completely dominant over i, in other words antigens A and B are produced. This is because of co-dominance. These antigens determine the type of blood group. Blood group A has antigens B have antigen, AB has both antigens while blood group. Blood group A have antigen A, group B have antigen B, AB has both antigens while blood group O do not carry any antigens.
Thus, six genotypes and four phenotypes are possible.
Dihybrid cross proves the law of________.- a)Segregation
- b)Purity of gametes
- c)Law of independent assortment
- d)Dominance
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Dihybrid cross proves the law of________.
a)
Segregation
b)
Purity of gametes
c)
Law of independent assortment
d)
Dominance

|
Deepak Joshi answered |
Dihybrid cross proves the law of independent assortment. Mendel found that each pair of alleles segregates independently of the other pairs of alleles during gamete formation. This is known as Law of independent assortment. Dihybrid cross - cross between two parents that differ by two pairs of alleles (AABB X aabb). The formation of gametes is an application of this law.
In human beings, if ovum fertilizes with a sperm carrying X-chromosome the zygote develops into______.- a)Male
- b)Female
- c)Sterile
- d)Any of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In human beings, if ovum fertilizes with a sperm carrying X-chromosome the zygote develops into______.
a)
Male
b)
Female
c)
Sterile
d)
Any of the above

|
Atharva Goyal answered |
Ovum fertilization and development of zygote into female
When an ovum (egg) is fertilized by a sperm carrying an X-chromosome, the resulting zygote will develop into a female. This is because the female sex is determined by the presence of two X-chromosomes (XX).
Explanation:
During sexual reproduction, the father contributes a sperm cell carrying either an X or a Y chromosome, while the mother always contributes an X chromosome through her ovum. If the sperm carrying an X chromosome fertilizes the ovum, the resulting zygote will have two X chromosomes (XX), which leads to the development of a female individual.
Genetic basis:
The sex chromosomes, X and Y, determine the individual's sex. Females have two X chromosomes (XX), while males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY). The presence of the Y chromosome triggers the development of male characteristics.
Sex determination:
The sex of an individual is determined at the moment of fertilization when the sperm carrying either an X or Y chromosome fuses with the ovum. If the sperm carries an X chromosome, it will result in an XX zygote, leading to the development of a female. On the other hand, if the sperm carries a Y chromosome, it will result in an XY zygote, leading to the development of a male.
Exceptions:
While the majority of individuals follow this pattern of sex determination, there are some exceptions. For example, individuals with variations in sex chromosome composition such as XXY or XO may not fit neatly into the binary male-female classification. These conditions may lead to variations in sexual development and reproductive abilities.
In conclusion, when an ovum is fertilized by a sperm carrying an X-chromosome, the resulting zygote develops into a female. This is due to the presence of two X chromosomes (XX) in females, which is the genetic basis for their sexual development.
When an ovum (egg) is fertilized by a sperm carrying an X-chromosome, the resulting zygote will develop into a female. This is because the female sex is determined by the presence of two X-chromosomes (XX).
Explanation:
During sexual reproduction, the father contributes a sperm cell carrying either an X or a Y chromosome, while the mother always contributes an X chromosome through her ovum. If the sperm carrying an X chromosome fertilizes the ovum, the resulting zygote will have two X chromosomes (XX), which leads to the development of a female individual.
Genetic basis:
The sex chromosomes, X and Y, determine the individual's sex. Females have two X chromosomes (XX), while males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY). The presence of the Y chromosome triggers the development of male characteristics.
Sex determination:
The sex of an individual is determined at the moment of fertilization when the sperm carrying either an X or Y chromosome fuses with the ovum. If the sperm carries an X chromosome, it will result in an XX zygote, leading to the development of a female. On the other hand, if the sperm carries a Y chromosome, it will result in an XY zygote, leading to the development of a male.
Exceptions:
While the majority of individuals follow this pattern of sex determination, there are some exceptions. For example, individuals with variations in sex chromosome composition such as XXY or XO may not fit neatly into the binary male-female classification. These conditions may lead to variations in sexual development and reproductive abilities.
In conclusion, when an ovum is fertilized by a sperm carrying an X-chromosome, the resulting zygote develops into a female. This is due to the presence of two X chromosomes (XX) in females, which is the genetic basis for their sexual development.
The term ‘Genetics’ was proposed by- a)Johannsen
- b)Morgan
- c)Mendel
- d)Bateson
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The term ‘Genetics’ was proposed by
a)
Johannsen
b)
Morgan
c)
Mendel
d)
Bateson
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Bateson co-discovered genetic linkage with Reginald Punnett and Edith Saunders, and he and Punnett founded the Journal of Genetics in 1910. Bateson also coined the term "epistasis" to describe the genetic interaction of two independent loci.
A human male produces sperms with the genotypes AB, Ab, aB, ab pertaining to two diallelic characters in equal proportions. What is the corresponding genotype of this person?- a)AABB
- b)AaBb
- c)AABb
- d)AaBB
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A human male produces sperms with the genotypes AB, Ab, aB, ab pertaining to two diallelic characters in equal proportions. What is the corresponding genotype of this person?
a)
AABB
b)
AaBb
c)
AABb
d)
AaBB
|
|
Om Desai answered |
If the genotype is AaBb the alleles that will be produced will be AB, Ab, aB, ab, since there are two diallelic characters in the genotypes the person must be heterozygous for both genes. AABB is homozygous. So, the correct answer is "AaBb".
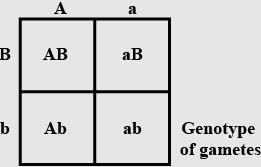

If a colour blind woman marries a normal visioned man, their sons will be[2006]- a)one - half colour blind and one - half normal
- b)three-fourths colour blind and one-fourth normal
- c)all colour blind
- d)all normal visioned
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If a colour blind woman marries a normal visioned man, their sons will be
[2006]
a)
one - half colour blind and one - half normal
b)
three-fourths colour blind and one-fourth normal
c)
all colour blind
d)
all normal visioned

|
Shanaya Rane answered |
Colour blindness in a X-chromosome linked character. So they’ll be having all colour blind sons and carrier daughters.
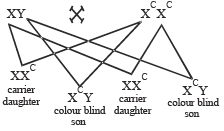
Sex determination in human being is______.- a)XY type
- b)XX type
- c)XXY type
- d)YY type
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Sex determination in human being is______.
a)
XY type
b)
XX type
c)
XXY type
d)
YY type

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
- In humans, the males are heterogametic as they have XY sex chromosomes, so they make 50% sperms with X chromosome and 50% sperms with Y chromosome. Females are homogametic. All gametes made by them have X chromosomes. So, humans show XX-XY type of sex determination.
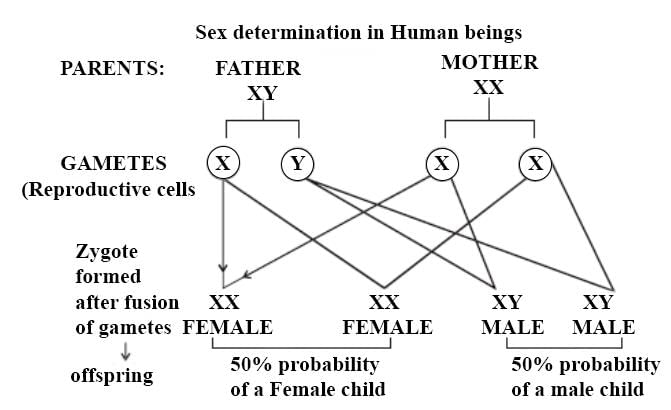
Hence, the correct option is A.
NCERT Reference: Topic SEX DETERMINATION of chapter "Principles of Inheritance and Variation" OF NCERT.
NCERT Reference: Topic SEX DETERMINATION of chapter "Principles of Inheritance and Variation" OF NCERT.
Material used for conducting experiments on genetic traits by Mendel was______.- a)Lathyrusodaratus
- b)Oryza sativa
- c)Pisumsativum
- d)Mirabilis jalappa
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Material used for conducting experiments on genetic traits by Mendel was______.
a)
Lathyrusodaratus
b)
Oryza sativa
c)
Pisumsativum
d)
Mirabilis jalappa
|
|
Kadambala Hemalatha answered |
Option c is correct.. mendel conducted experiment's on pisumsativum (garden pea)...mirabilus jalapa is also called 4'o clock plant, oryza sativa (rice)...
The physical expression or appearance of a character is called as? - a)Phenotype
- b)Morphology
- c)Ecotype
- d)Genotype
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The physical expression or appearance of a character is called as?
a)
Phenotype
b)
Morphology
c)
Ecotype
d)
Genotype

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
The physical appearance of a character is called as phenotype. The genetic make of individual is called genotype. Tallness, round, wrinkled, yellow etc. are physical appearance.
The genotypes of a husband and wife are IA IB and IAi. Among the blood types of their children how many different genotypes and phenotypes are possible?- a)3 Genotypes; 3 Phenotypes
- b)4 Genotypes; 3 Phenotypes
- c)3 Genotypes; 4 Phenotypes
- d)4 Genotypes; 4 Phenotypes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The genotypes of a husband and wife are IA IB and IAi. Among the blood types of their children how many different genotypes and phenotypes are possible?
a)
3 Genotypes; 3 Phenotypes
b)
4 Genotypes; 3 Phenotypes
c)
3 Genotypes; 4 Phenotypes
d)
4 Genotypes; 4 Phenotypes

|
Nilotpal Gupta answered |
A cross between two individuals, one with AB blood group and other with A blood group will produce four genotypes and three phenotypes.
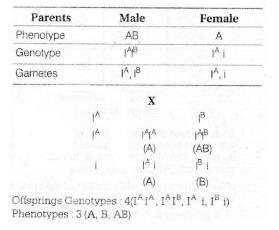

In pea plants, yellow seeds are dominant to green, If a heterozygous yellow seeded plant is crossed with a green seeded plants, what ratio of yellow and green seeded plants would you expect in F1 generation?- a)9:1
- b)3:1
- c)50:50
- d)1:3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In pea plants, yellow seeds are dominant to green, If a heterozygous yellow seeded plant is crossed with a green seeded plants, what ratio of yellow and green seeded plants would you expect in F1 generation?
a)
9:1
b)
3:1
c)
50:50
d)
1:3

|
Mehul Iyer answered |
If a heterozygous yellow seeded plant is crossed with green seeded plants, the ratio of yellow and green seeded plants are 50:50 or 1:1 similar to test cross.
Which of the following conditions is called monosomic?- a)n + 1
- b)2n + 1
- c)2n + 2
- d)2n − 1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following conditions is called monosomic?
a)
n + 1
b)
2n + 1
c)
2n + 2
d)
2n − 1
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
Monosomics (2n - 1) one chromosomes less then diploid set of somatic chromosome number.
When two genes are situated very close to one another on a chromosome________.- a)Hardly any cross-overs are produced
- b)The percentage of crossing over between them is very high
- c)No crossing over can take place
- d)Only double cross-over can occur between them
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When two genes are situated very close to one another on a chromosome________.
a)
Hardly any cross-overs are produced
b)
The percentage of crossing over between them is very high
c)
No crossing over can take place
d)
Only double cross-over can occur between them
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
- When two genes are situated very close to one another on chromosome, hardly any cross-over are produced.
- Such genes are called linkage and do not separate from each other during gamete formation.
Assertion: The cross between red and white flower bearing snapdragon plants results into pink coloured flower.Reason: Incomplete dominance of red and white flower results into pink coloured flower.- a)Both assertion and reason are correct
- b)Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect
- c)Both assertion and reason are incorrect
- d)Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion: The cross between red and white flower bearing snapdragon plants results into pink coloured flower.
Reason: Incomplete dominance of red and white flower results into pink coloured flower.
a)
Both assertion and reason are correct
b)
Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect
c)
Both assertion and reason are incorrect
d)
Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
- In Snapdragon flower, cross between true-breeding white and red coloured flower produce pink coloured flower in the F1 generation.
- This happens due to the incomplete dominance of alleles over the other.
A pure tall and a pure dwarf plant were crossed to produce offspring. Offspring were self-crossed. Find out the ratio between true breeding tall to true breeding dwarf.- a)3:1
- b)1:1
- c)2:1
- d)1:2:1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A pure tall and a pure dwarf plant were crossed to produce offspring. Offspring were self-crossed. Find out the ratio between true breeding tall to true breeding dwarf.
a)
3:1
b)
1:1
c)
2:1
d)
1:2:1
|
|
Rajesh Chatterjee answered |
As true tall breeding and true dwarf breeding is seen only a single time in F2 generation, and the remaining are hybtid tall...so the ratio becomes 1:2:2:1.But 1:1 is the ratio for only true tall breeding nd true dwarf breeding in F2 generation.
F2 generation is obtained by______.- a)Crossing of F1 and F2
- b)Selfing of F1
- c)Selfing of F2
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
F2 generation is obtained by______.
a)
Crossing of F1 and F2
b)
Selfing of F1
c)
Selfing of F2
d)
None of these
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
F2 generation is obtained by selfing of F1 progeny..where F1 generation is obtained by crossing two parents..option B
The gene which controls many characters is called- a)Pleiotropic gene
- b)Co-dominant gene
- c)Multiple gene
- d)Polygene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The gene which controls many characters is called
a)
Pleiotropic gene
b)
Co-dominant gene
c)
Multiple gene
d)
Polygene
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
A single gene may have two or more phenotypic expressions. The multiple phenotypic effect of a single gene is called pleiotropism. Hence the gene associated with this phenomenon is called Pleiotropic gene.
Sickle cell anaemia is:
[2009]
- a)caused by a change in a single base pair of DNA
- b)caused by substitution of glutamic acid by valine in the beta globin chain of haemoglobin
- c)characterized by elongated sickle like RBCs with a nucleus
- d)an autosomal linked dominant trait
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Sickle cell anaemia is:
[2009]
a)
caused by a change in a single base pair of DNA
b)
caused by substitution of glutamic acid by valine in the beta globin chain of haemoglobin
c)
characterized by elongated sickle like RBCs with a nucleus
d)
an autosomal linked dominant trait

|
Krish Saha answered |
Sickle cell anaemia is caused by a change in a single base pair of DNA. Sickle-cell anaemia is the name of a specific form of sickle-cell disease in which there is homozygosity for the mutation that causes HbS. Sickle-cell disease, or sicklecell anaemia (or drepanocytosis), is a life-long blood disorder characterized by red blood cells that assume an abnormal, rigid, sickle shape. Sickling decreases the cells flexibility and results in a risk of various complications. ‘
Fruit colour in squash in an example of: [2014]- a)Recessive epistasis
- b)Dominant epistasis
- c)Complementary genes
- d)Inhibitory genes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Fruit colour in squash in an example of: [2014]
a)
Recessive epistasis
b)
Dominant epistasis
c)
Complementary genes
d)
Inhibitory genes

|
Raghav Khanna answered |
(b) Epistasis is the phenomenon of suppression of phenotypic expression of gene by a nonallelic gene which shows its own effect. A dominant epistatic allele suppresses the expression ofa nonallelic gene whether the latter is dominant or recessive. For example, fruit colour of Summer Squash (Cucurbita pepo) is governed by a gene which pruduces yellow colour in dominant state (Y-) and green colour in recessive state (yy).
Klinefelter’s syndrome is due to- a)One Y only
- b)One X only
- c)Two X and one Y
- d)One X and two Y
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Klinefelter’s syndrome is due to
a)
One Y only
b)
One X only
c)
Two X and one Y
d)
One X and two Y

|
Kritika Singh answered |
In klinefelter syndrome One X chromosome increases... show the situation is XXY
The crossing of F1 to any one of the parents is called?- a)Back cross
- b)F1 cross
- c)Test cross
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The crossing of F1 to any one of the parents is called?
a)
Back cross
b)
F1 cross
c)
Test cross
d)
All of these
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
The crossing of F1 to any one of the parents is called back cross. It is used to check the purity of individual. When F1 is crossed with recessive parent, it is called test cross.
Down’s syndrome is due to- a)Linkage
- b)Non-disjunction of chromosome
- c)Crossing over
- d)Sex-linked inheritance
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Down’s syndrome is due to
a)
Linkage
b)
Non-disjunction of chromosome
c)
Crossing over
d)
Sex-linked inheritance
|
|
Lakshmi Pillai answered |
Explanation:
Down syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21. This additional genetic material alters the course of development and causes the characteristic features of Down syndrome.
Non-disjunction of chromosome:
The most common cause of Down syndrome is non-disjunction of chromosome 21 during meiosis. Non-disjunction occurs when the chromosomes fail to separate properly during cell division, resulting in an abnormal distribution of chromosomes in the resulting cells. In the case of Down syndrome, non-disjunction of chromosome 21 occurs either during the formation of the egg or sperm, resulting in an extra copy of chromosome 21 in the fertilized egg.
Key Points:
- Non-disjunction of chromosome 21 during meiosis is the most common cause of Down syndrome.
- Non-disjunction can occur during the formation of the egg or sperm.
- Non-disjunction leads to an abnormal distribution of chromosomes in the resulting cells, resulting in an extra copy of chromosome 21.
Other Causes:
While non-disjunction is the primary cause of Down syndrome, there are other rare genetic variations that can also result in the condition. These include translocation, mosaicism, and partial trisomy.
- Translocation: In some cases, a piece of chromosome 21 breaks off and attaches to another chromosome, typically chromosome 14. This is called a translocation. If a person has a translocation involving chromosome 21, they may have a higher risk of having a child with Down syndrome.
- Mosaicism: Mosaicism occurs when there is a mixture of cells with a normal number of chromosomes and cells with an extra copy of chromosome 21. This can result in milder symptoms or features of Down syndrome.
- Partial Trisomy: In rare cases, a person may have only a portion of chromosome 21 duplicated, leading to a condition known as partial trisomy. This can result in a milder form of Down syndrome, as only a subset of genes on chromosome 21 is affected.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the most common cause of Down syndrome is non-disjunction of chromosome 21 during meiosis. This results in an extra copy of chromosome 21 in the fertilized egg, leading to the characteristic features of Down syndrome. Other rare genetic variations, such as translocation, mosaicism, and partial trisomy, can also result in Down syndrome but are less common.
Down syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21. This additional genetic material alters the course of development and causes the characteristic features of Down syndrome.
Non-disjunction of chromosome:
The most common cause of Down syndrome is non-disjunction of chromosome 21 during meiosis. Non-disjunction occurs when the chromosomes fail to separate properly during cell division, resulting in an abnormal distribution of chromosomes in the resulting cells. In the case of Down syndrome, non-disjunction of chromosome 21 occurs either during the formation of the egg or sperm, resulting in an extra copy of chromosome 21 in the fertilized egg.
Key Points:
- Non-disjunction of chromosome 21 during meiosis is the most common cause of Down syndrome.
- Non-disjunction can occur during the formation of the egg or sperm.
- Non-disjunction leads to an abnormal distribution of chromosomes in the resulting cells, resulting in an extra copy of chromosome 21.
Other Causes:
While non-disjunction is the primary cause of Down syndrome, there are other rare genetic variations that can also result in the condition. These include translocation, mosaicism, and partial trisomy.
- Translocation: In some cases, a piece of chromosome 21 breaks off and attaches to another chromosome, typically chromosome 14. This is called a translocation. If a person has a translocation involving chromosome 21, they may have a higher risk of having a child with Down syndrome.
- Mosaicism: Mosaicism occurs when there is a mixture of cells with a normal number of chromosomes and cells with an extra copy of chromosome 21. This can result in milder symptoms or features of Down syndrome.
- Partial Trisomy: In rare cases, a person may have only a portion of chromosome 21 duplicated, leading to a condition known as partial trisomy. This can result in a milder form of Down syndrome, as only a subset of genes on chromosome 21 is affected.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the most common cause of Down syndrome is non-disjunction of chromosome 21 during meiosis. This results in an extra copy of chromosome 21 in the fertilized egg, leading to the characteristic features of Down syndrome. Other rare genetic variations, such as translocation, mosaicism, and partial trisomy, can also result in Down syndrome but are less common.
Which of the following is not a Mendelian disorder?- a)Haemophilia
- b)Turner’s syndrome
- c)Cystic fibrosis
- d)Colour blindness
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a Mendelian disorder?
a)
Haemophilia
b)
Turner’s syndrome
c)
Cystic fibrosis
d)
Colour blindness
|
|
Devanshi Mehta answered |
All humans have 46 chromosomes, which determine who and what we are genetically. Boys have an X and Y chromosome. Girls have 2 X chromosomes. Turner Syndrome is a chromosomal disorder in girls in which part or all of one of the X-chromosomes is missing.
This loss of genetic material causes 2 primary features: namely, short stature and underdeveloped ovaries causing delayed or absent puberty. It is usually diagnosed when a girl is noted to be very short and a chromosome blood test is obtained. It should also be suspected if a girl has not developed breasts by 13-14 years of age or had her menstrual period by 15-16 years of age. Effective hormonal treatment is available for both the short stature and to stimulate normal pubertal changes.
This loss of genetic material causes 2 primary features: namely, short stature and underdeveloped ovaries causing delayed or absent puberty. It is usually diagnosed when a girl is noted to be very short and a chromosome blood test is obtained. It should also be suspected if a girl has not developed breasts by 13-14 years of age or had her menstrual period by 15-16 years of age. Effective hormonal treatment is available for both the short stature and to stimulate normal pubertal changes.
Which organism’s male contain a pair of Z chromosome as sex chromosome besides autosomes?- a)Insects
- b)Human beings
- c)Lizards
- d)Birds
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which organism’s male contain a pair of Z chromosome as sex chromosome besides autosomes?
a)
Insects
b)
Human beings
c)
Lizards
d)
Birds
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
In birds male contain a pair of Z chromosome as sex chromosome besides autosomes while female contain one Z and one W chromosome.
In a given plant, red colour (R) of fruits is dominant over white fruit (r); and tallness (T) is dominant over dwarfness (t). If a plant with genotype RrTt is crossed with a plant of genotype rrtt, what will be the percentage of tall plants with red fruits in the next generation?- a)20%
- b)40%
- c)50%
- d)60%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a given plant, red colour (R) of fruits is dominant over white fruit (r); and tallness (T) is dominant over dwarfness (t). If a plant with genotype RrTt is crossed with a plant of genotype rrtt, what will be the percentage of tall plants with red fruits in the next generation?
a)
20%
b)
40%
c)
50%
d)
60%

|
Universal Academy answered |
According to question, tallness (T) is dominant over dwarfism (t) and red colour (R) is dominant over white (r) fruit colour.
Parent Generation; P1 : RRTt x rrtt
F1 generation :
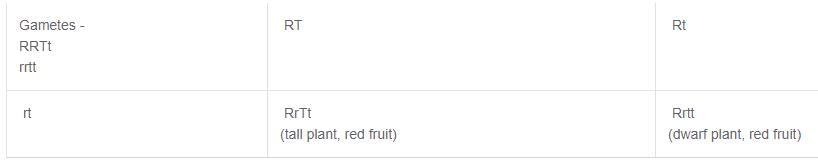
Phenotypic ratio = 1 (tall plant, red fruit)
: 1 (dwarf plant, red fruit)
; thus, percent of tall plant with red fruit is 50%.

Phenotypic ratio = 1 (tall plant, red fruit)
: 1 (dwarf plant, red fruit)
; thus, percent of tall plant with red fruit is 50%.
Inheritances of skin colour in humans is an example of[2007]- a)point mutation
- b)polygenic inheritance
- c)codominance
- d)chromosomal aberration.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Inheritances of skin colour in humans is an example of
[2007]
a)
point mutation
b)
polygenic inheritance
c)
codominance
d)
chromosomal aberration.

|
Surbhi Das answered |
Inheritance of skin colour in human is controlled by three genes, A B and C which is polygenic inheritance.
In order to find out the different types of gametes produced by a pea plant having the genotype AaBb, it should be crossed to a plant with the genotype:[2005]- a)AABB
- b)AaBb
- c)aabb
- d)aaBB
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In order to find out the different types of gametes produced by a pea plant having the genotype AaBb, it should be crossed to a plant with the genotype:
[2005]
a)
AABB
b)
AaBb
c)
aabb
d)
aaBB

|
Surbhi Das answered |
In order to find out the gamete or the genotype of an unknown individual, Scientists perform a test cross. In test cross the individual in question is crossed with the homozygous recessive parent. Hence the answer is aabb.
Match the terms in Column-I with their description in Column-II and choose the correct option : [2016]
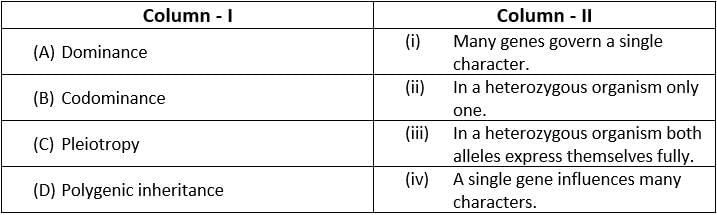
- a)(A) - (ii), (B) - (i), (C) - (iv), (D) - (iii)
- b)(A) - (ii), (B) - (iii), (C) - (iv), (D) - (i)
- c)(A) - (iv), (B) - (i), (C) - (ii), (D) - (iii)
- d)(A) - (iv), (B) - (iii), (C) - (i), (D) - (ii)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the terms in Column-I with their description in Column-II and choose the correct option : [2016]


a)
(A) - (ii), (B) - (i), (C) - (iv), (D) - (iii)
b)
(A) - (ii), (B) - (iii), (C) - (iv), (D) - (i)
c)
(A) - (iv), (B) - (i), (C) - (ii), (D) - (iii)
d)
(A) - (iv), (B) - (iii), (C) - (i), (D) - (ii)

|
Ibus Ibus answered |
Difference between pleiotropy and multiple alleles
Which one of the following conditions in humans. is correctly matched with its chromosomal abnormality/linkage?[2008]- a)Klinefelters syndrome-44 autosomes + XXY
- b)Colour blindness - Y-linked
- c)Erythroblastosis foetalis - X-linked
- d)Downs syndrome - 44 autosomes + XO
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following conditions in humans. is correctly matched with its chromosomal abnormality/linkage?
[2008]
a)
Klinefelters syndrome-44 autosomes + XXY
b)
Colour blindness - Y-linked
c)
Erythroblastosis foetalis - X-linked
d)
Downs syndrome - 44 autosomes + XO

|
Mahi Shah answered |
Klinefelter's syndrome is a genetic disorder affecting men in which an individual gains an extra X chromosome, so that the usual Karyotype of XY is replaced by one of XXY. Symptoms of Klinefelter's syndrome named after us physician H.P. Klinefelter, include female characteristics (such as breast enlargement).
If two pea plants having red (dominant) coloured flowers with unknown genotypes are crossed, 75% of the flowers are red and 25% are white. The genotypic constitution of the parents having red coloured flowers will be- a)Both heterozygous
- b)One homozygous and other heterozygous
- c)Both homozygous
- d)Both hemizygous
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If two pea plants having red (dominant) coloured flowers with unknown genotypes are crossed, 75% of the flowers are red and 25% are white. The genotypic constitution of the parents having red coloured flowers will be
a)
Both heterozygous
b)
One homozygous and other heterozygous
c)
Both homozygous
d)
Both hemizygous

|
Rosy Kumar answered |
What will be expected blood groups in the off spring when there is a cross between AB blood group mother and heterozygous B blood group father?- a)25% AB, 25% A, 50%B
- b)50% AB, 25% A, 25%B
- c)25% AB, 50% O, 25%A
- d)25% O, 25% A, 50%B
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What will be expected blood groups in the off spring when there is a cross between AB blood group mother and heterozygous B blood group father?
a)
25% AB, 25% A, 50%B
b)
50% AB, 25% A, 25%B
c)
25% AB, 50% O, 25%A
d)
25% O, 25% A, 50%B
|
|
Suresh Kumar answered |
Given;
Mother is with "AB" blood group....i.e. it means the genotypes are 'IAIB' ..
For "B" blood group genotypes are:-'IBIB'(homozygous condition);'IBIO'(Heterozygous condition)..
In question it is said that Father is with "B" heterozygous blood group...So;the genotypes are 'IBIO' ...
When cross is done between Mother with 'IAIB' & father with 'IBIO'..
the possible genotypes of the progeny are :-
'IAIB'(i.e."AB" blood group);'IAIO'(i.e."A" blood group);'IBIB'(i.e."B" blood group);'IBIO'(i.e."B" blood group)..
% of "AB" blood group=>1×100/4 =>25% of progeny with "AB" blood group..
% of "A" blood group=>1×100/4 =>25% of progeny with "A" blood group..
% of "B" blood group =>2×100/4 =>50% of progeny with "B" blood group....
Hence;option _'A'_holds true here...
Study the pedigree chart given below: What does it show?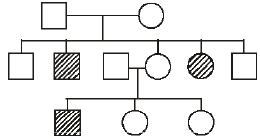 [2009]
[2009]- a)Inheritance of a condition like phenylketonuria as an autosomal recessive trait
- b)The pedigree chart is wrong as this is not possible
- c)Inheritance of a recessive sex - linked disease like haemophilia
- d)Inheritance of a sex -linked inborn error of metabolism like phenylketonuria
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the pedigree chart given below: What does it show?

[2009]
a)
Inheritance of a condition like phenylketonuria as an autosomal recessive trait
b)
The pedigree chart is wrong as this is not possible
c)
Inheritance of a recessive sex - linked disease like haemophilia
d)
Inheritance of a sex -linked inborn error of metabolism like phenylketonuria

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
The chart shows the inheritance of a condition like phenylketonuria as an autosomal recessive trait. Parents’ needs to be heterozygous as two of their children are known to be sufferer of the disease. It cannot be recessive sex linked inheritance because then the male parent would also be sufferer.
Which of the following statements is not true of two genes that show 50% recombination frequency?[NEET 2013]- a)The genes are tightly linked
- b)The genes show independent assortment
- c)If the genes are present on the same chromosome, they undergo more than one crossovers in every meiosis
- d)The genes may be on different chromosomes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not true of two genes that show 50% recombination frequency?
[NEET 2013]
a)
The genes are tightly linked
b)
The genes show independent assortment
c)
If the genes are present on the same chromosome, they undergo more than one crossovers in every meiosis
d)
The genes may be on different chromosomes

|
Krish Saha answered |
Tightly linked genes show more linkage then crossing over.
Mutations which arise suddenly in nature are called- a)Spontaneous mutations
- b)Gene mutations
- c)Induced mutations
- d)Chromosomal mutations
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mutations which arise suddenly in nature are called
a)
Spontaneous mutations
b)
Gene mutations
c)
Induced mutations
d)
Chromosomal mutations
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Gene mutation is defined as a sudden discrete change in the genetic material of gene which is heritable. Mutations when they arise suddenly in nature are called spontaneous mutations.
A man whose father was colour blind marries a woman who had a colour blind mother and normal father. What percentage of male children of this couple will be colour blind? [2013]
- a)25%
- b)0%
- c)50%
- d)75%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A man whose father was colour blind marries a woman who had a colour blind mother and normal father. What percentage of male children of this couple will be colour blind? [2013]
a)
25%
b)
0%
c)
50%
d)
75%

|
Shivani Rane answered |
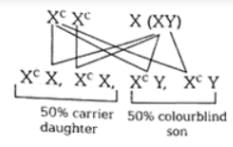
As color blindness is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder, for it is present at X -chromosome. Thus, according to the situation given in the question, a man whose father was color blind (will be, i.e, XY normal) marries a woman whose mother was color blind and father was normal (i.e, this woman will be a carrier) according to the cross given in the first figure.
Thus, when marriage will happen between a normal man and a carrier woman, in that case, the percentage of a male child to be colorblind is 25% (this can be easily observed from the second figure).So, the correct answer is '50%'.
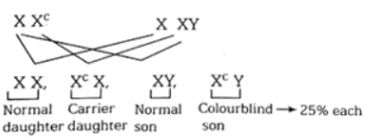
Thus, when marriage will happen between a normal man and a carrier woman, in that case, the percentage of a male child to be colorblind is 25% (this can be easily observed from the second figure).So, the correct answer is '50%'.

Test cross in plants or in Drosophila involves crossing[2011M]- a)between two genotypes with recessive trait
- b)between two F1 hybrids
- c)the F1 hybrid with a double recessive genotype.
- d)between two genotypes with dominant trait
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Test cross in plants or in Drosophila involves crossing
[2011M]
a)
between two genotypes with recessive trait
b)
between two F1 hybrids
c)
the F1 hybrid with a double recessive genotype.
d)
between two genotypes with dominant trait

|
Pooja Saha answered |
In test cross, genotype of an organism showing dominant phenotype is determined by crossing it with homozygous recessive genotype.
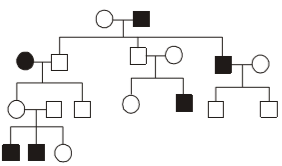
In the following human pedigree, the filled symbols represent the affected individuals. Identify the type of given pedigree. [2015 RS]
- a)X- linked recessive
- b)Autosomal recessive
- c)X-linked dominant
- d)Autosomal dominant
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following human pedigree, the filled symbols represent the affected individuals. Identify the type of given pedigree. [2015 RS]


a)
X- linked recessive
b)
Autosomal recessive
c)
X-linked dominant
d)
Autosomal dominant

|
Rohan Unni answered |
(b) Autosomal recessive is a type of disorder in which two copies of an abnormal gene must be found for the disease in the affected person.
Which of the following statements are correct about Klinefelter’s Syndrome? (NEET 2023)
A. This disorder was first described by Langdon Down (1866).
B. Such an individual has overall masculine development. However, the feminine developement is also expressed.
C. The affected individual is short statured.
D. Physical, psychomotor and mental development is retarded.
E. Such individuals are sterile.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- a)A and B only
- b)C and D only
- c)B and E only
- d)A and E only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements are correct about Klinefelter’s Syndrome? (NEET 2023)
A. This disorder was first described by Langdon Down (1866).
B. Such an individual has overall masculine development. However, the feminine developement is also expressed.
C. The affected individual is short statured.
D. Physical, psychomotor and mental development is retarded.
E. Such individuals are sterile.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A. This disorder was first described by Langdon Down (1866).
B. Such an individual has overall masculine development. However, the feminine developement is also expressed.
C. The affected individual is short statured.
D. Physical, psychomotor and mental development is retarded.
E. Such individuals are sterile.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
a)
A and B only
b)
C and D only
c)
B and E only
d)
A and E only

|
Top Rankers answered |
B. Such an individual has overall masculine development. However, the feminine development is also expressed. People with Klinefelter syndrome are male (XY), but they often have certain physical characteristics that may be typically associated with female development, such as wider hips, less body hair, and sometimes breast tissue development.
E. Such individuals are sterile. Often, individuals with Klinefelter syndrome produce little to no sperm and are therefore usually infertile. However, there are cases where fertility treatments can help some men with Klinefelter syndrome to father children.
For the other options :
A. This disorder was first described by Langdon Down (1866). This is incorrect. Klinefelter's syndrome was first described by Dr. Harry Klinefelter in the 1940s, not by Langdon Down.
C. The affected individual is short statured. This is incorrect. In fact, individuals with Klinefelter's syndrome are often taller than average.
D. Physical, psychomotor and mental development is retarded. This is also incorrect. While individuals with Klinefelter syndrome may have some learning difficulties or delays, particularly with language and speech, it is not accurate or appropriate to say that their physical, psychomotor, and mental development is "retarded". They may face some challenges, but with support they can lead healthy, productive lives.
E. Such individuals are sterile. Often, individuals with Klinefelter syndrome produce little to no sperm and are therefore usually infertile. However, there are cases where fertility treatments can help some men with Klinefelter syndrome to father children.
For the other options :
A. This disorder was first described by Langdon Down (1866). This is incorrect. Klinefelter's syndrome was first described by Dr. Harry Klinefelter in the 1940s, not by Langdon Down.
C. The affected individual is short statured. This is incorrect. In fact, individuals with Klinefelter's syndrome are often taller than average.
D. Physical, psychomotor and mental development is retarded. This is also incorrect. While individuals with Klinefelter syndrome may have some learning difficulties or delays, particularly with language and speech, it is not accurate or appropriate to say that their physical, psychomotor, and mental development is "retarded". They may face some challenges, but with support they can lead healthy, productive lives.
Alleles are : [2015 RS]- a)true breeding homozygotes
- b)different molecular forms of a gene
- c)heterozygotes
- d)different phenotype
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Alleles are : [2015 RS]
a)
true breeding homozygotes
b)
different molecular forms of a gene
c)
heterozygotes
d)
different phenotype

|
Abhiram Nair answered |
(b) Alleles are defined as alternative form of same gene.
The test cross is used to determine the________.- a)Genotype of the plant
- b)Phenotype of the plant
- c)Both a and b
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The test cross is used to determine the________.
a)
Genotype of the plant
b)
Phenotype of the plant
c)
Both a and b
d)
None of these

|
Arpita Tiwari answered |
The test cross is used to determine the genotype of the plant in which F1 plant is crossed with homozygous recessive plants. If the ratio is 1:1 the plant is homozygous.
Monohybrid ratio is_____.- a)9:3:1
- b)3:1
- c)9:3:3:1
- d)9:1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Monohybrid ratio is_____.
a)
9:3:1
b)
3:1
c)
9:3:3:1
d)
9:1

|
Dipika Das answered |
Monohybrid ratio is the ratio of different phenotypic traits obtained on hybridizing single pair of trait. It is 3:1. When tall pea plant is crossed with dwarf, the offspring obtained are in ¾ tall and ¼ dwarf.
Turner syndrome is- a)XYY
- b)XO
- c)XXX
- d)XXY
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Turner syndrome is
a)
XYY
b)
XO
c)
XXX
d)
XXY

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
Turner syndrome (TS), also known 45,X, or 45,X0, is a genetic condition in which a female is partly or completely missing an X chromosome. Signs and symptoms vary among those affected.
Chapter doubts & questions for Principles of Inheritance & Variation - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Principles of Inheritance & Variation - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup