All Exams >
NEET >
Organic Chemistry for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Organic Chemistry : Some Basic Principles & Techniques for NEET Exam
The most stable free radical among the following Is- a)
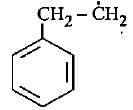
- b)

- c)
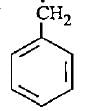
- d)
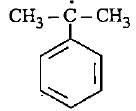
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The most stable free radical among the following Is
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Muskan Sharma answered |
In option D there is 6 alpha - H is present where as in option A only 2 alpha - H, option B 3 alpha - H and option C no alpha - H is present. This is because of hyperconjugation, more alpha - H more stability therefore option D is more stable.
Which among the following defines Meso forms of isomers?
- a)Meso form is optically inactive due to external compensation.
- b)The molecules of the meso isomers are chiral.
- c)It can be separated into optically active enantiomeric pairs.
- d)It is a single compound.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following defines Meso forms of isomers?
a)
Meso form is optically inactive due to external compensation.
b)
The molecules of the meso isomers are chiral.
c)
It can be separated into optically active enantiomeric pairs.
d)
It is a single compound.
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Meso forms of isomers are single compounds and their molecules are achiral hence they cannot be separated into pairs.
Additional Information: A meso compound or meso isomer is a non-optically active member of a set of stereoisomers, at least two of which are optically active. This means that despite containing two or more stereogenic centers, the molecule is not chiral.
If chlorocyclohexane is subjected to further chlorination, how many different isomers (geometrical plus structural only) of dichiorocyclohexane would be produced? - a)3
- b)5
- c)6
- d)7
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If chlorocyclohexane is subjected to further chlorination, how many different isomers (geometrical plus structural only) of dichiorocyclohexane would be produced?
a)
3
b)
5
c)
6
d)
7

|
Learners Habitat answered |
The correct answer is option D
There will be three constitutional isomers i.e. 1,2 dichloro cyclohexane,1,3 dichloro cyclohexane and1,4 dichloro cyclohexane.Each constitutional isomer will have cis and trans configuration thereby making six isomers in all.Also there will be two optically active isomers.
You can understand it better through these infographics
1,2 dichloro cyclohexane
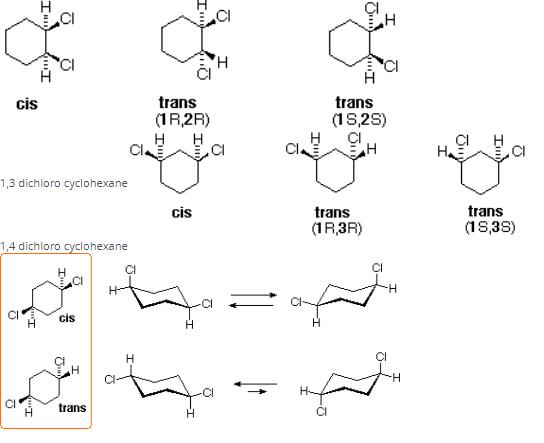
There will be three constitutional isomers i.e. 1,2 dichloro cyclohexane,1,3 dichloro cyclohexane and1,4 dichloro cyclohexane.Each constitutional isomer will have cis and trans configuration thereby making six isomers in all.Also there will be two optically active isomers.
You can understand it better through these infographics
1,2 dichloro cyclohexane

- a)3
- b)4
- c)5
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
3
b)
4
c)
5
d)
6
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
General formula of ketone = CnH2nO
12x+2x+16 = 100
x = 6
So, the formula of compound is C6H12O. We have to make ketone only. These are as follow
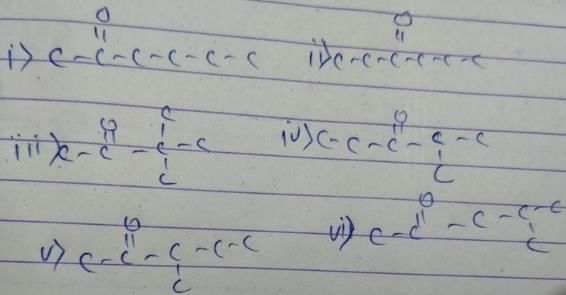
12x+2x+16 = 100
x = 6
So, the formula of compound is C6H12O. We have to make ketone only. These are as follow
- a)3
- b)4
- c)5
- d)7
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
3
b)
4
c)
5
d)
7
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The compounds with each doubly bonded carbon attached to two different groups (like Cab=Cab, Cab=Ccd) exhibit geometrical isomerism i.e., cis and trans forms. The geometrical isomerism arises due to restricted rotation of double bond.
However, even though there is restricted rotation for triple bond, alkynes do not exhibit geometrical isomerism, since the triply bonded carbons are attached to one group each only.

- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Optical purity = optical rotation of mixture/optical rotation of pure compound .
(mixture) [α]D25 = +6.76°
+[α]D = +13.57°
Since rotation of two enantiomers cancel each other, so rotation is due to enantiomeric excess.
Enantiomeric excess = observed specific rotation/max. Specific rotation = 6.76/13.52×100
= 50%
Therefore, %age of each enantiomer is given by,
If we have (+) (-) mixture(+) is in excess,
%(+) = ee/2 + 50%
= 75 % (s)
%(-) = 25% (s)
(mixture) [α]D25 = +6.76°
+[α]D = +13.57°
Since rotation of two enantiomers cancel each other, so rotation is due to enantiomeric excess.
Enantiomeric excess = observed specific rotation/max. Specific rotation = 6.76/13.52×100
= 50%
Therefore, %age of each enantiomer is given by,
If we have (+) (-) mixture(+) is in excess,
%(+) = ee/2 + 50%
= 75 % (s)
%(-) = 25% (s)
The observed order of the stability of the cabocation is:- a)(CH3)2CH+ < (CH3)3C+ 3+ < CH3CH2+
- b)CH3+ < CH3CH2+ <(CH3)2CH+ < (CH3)3C+
- c)CH3CH2+ <(CH3)2CH+ < (CH3)3C+ < CH3+
- d)CH3+ < CH3CH2+ < (CH3)3C+ <(CH3)2CH+
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The observed order of the stability of the cabocation is:
a)
(CH3)2CH+ < (CH3)3C+ 3+ < CH3CH2+
b)
CH3+ < CH3CH2+ <(CH3)2CH+ < (CH3)3C+
c)
CH3CH2+ <(CH3)2CH+ < (CH3)3C+ < CH3+
d)
CH3+ < CH3CH2+ < (CH3)3C+ <(CH3)2CH+
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Alkyl groups directly attached to the +vely charged carbon stabilize the carbocations due to inductive and hyperconjugation effects.
Inductive effect:
→ Stability of carbocation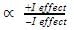
→ More number of +I group more stable carbocation.
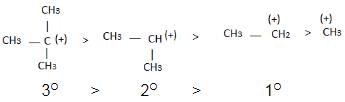
Hyperconjugation:
Inductive effect:
→ Stability of carbocation
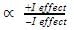
→ More number of +I group more stable carbocation.
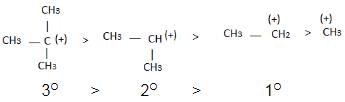
Hyperconjugation:
Stability
∝Number of canonical structures
∝Number of H (alpha hydrogen)
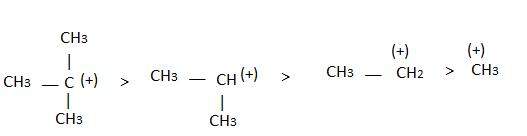
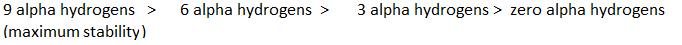
∝Number of canonical structures
∝Number of H (alpha hydrogen)
Which is true about conformers of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane?Which is true about conformers of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane?
a) The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
b) In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
c) In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
d) The most stable conformer is non-polar - a)The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
- b)In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
- c)In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
- d)The most stable conformer is non-polar
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is true about conformers of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane?
Which is true about conformers of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane?
a) The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
b) In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
c) In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
d) The most stable conformer is non-polar
a) The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
b) In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
c) In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
d) The most stable conformer is non-polar
a)
The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
b)
In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
c)
In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
d)
The most stable conformer is non-polar
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The correct answer is option D
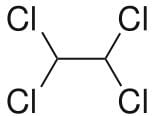
This molecule is non-polar two Cl atoms in one carbon atom cancel the polarity other two Cl atoms on the next carbon.
Also all the Cl atoms are at max distance from each other so max. Stability due to less repulsion between Cl atoms. Dihedral angle between H and Cl is 60°

This molecule is non-polar two Cl atoms in one carbon atom cancel the polarity other two Cl atoms on the next carbon.
Also all the Cl atoms are at max distance from each other so max. Stability due to less repulsion between Cl atoms. Dihedral angle between H and Cl is 60°
Pick the odd one out:- a)Napthalene
- b)Sodium chloride
- c)Ammonium chloride
- d)Camphor
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Pick the odd one out:
a)
Napthalene
b)
Sodium chloride
c)
Ammonium chloride
d)
Camphor

|
Shrikrushna Mali answered |
Other 3 are sublimating substance except NaCl
- a)3
- b)4
- c)5
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
3
b)
4
c)
5
d)
6
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
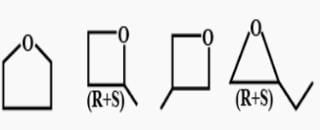
First, we will check the Double bond equivalent. In C7H8O, DBE = 4,this means that we will have 3 double bonds and a ring and no additional double bond outside the ring.
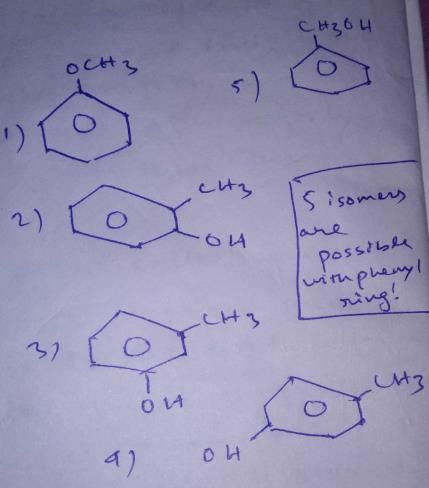
These are the structural isomers that exists for C7H8O

These are the structural isomers that exists for C7H8O
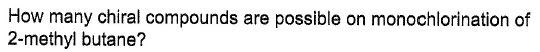 [AIEEE 2012]
[AIEEE 2012]- a)8
- b)2
- c)4
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
[AIEEE 2012]
a)
8
b)
2
c)
4
d)
6
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The positions are numbered. Note that 4 and α are the same for this purpose.
The organic compound given below is one of the four options given below. Choose the most appropriate one. 
- a)aromatic heteroyclic compound
- b)aliphatic heteroyclic compound
- c)alicyclic compound
- d)ring compound
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The organic compound given below is one of the four options given below. Choose the most appropriate one.
a)
aromatic heteroyclic compound
b)
aliphatic heteroyclic compound
c)
alicyclic compound
d)
ring compound

|
Rohit Joshi answered |
this is aliphatic heterocyclic compound.

- a)3
- b)5
- c)7
- d)8
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
3
b)
5
c)
7
d)
8
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
5 isomers are possible. C5H10(CnH2n). Molecules having the CnH2n formulas are most likely to be cyclic alkanes. The five isomers are:
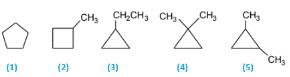
(1) Cyclopentane
(2) 1-Methylcyclobutane
(3) 1-Ethylcyclopropane
(4) 1,1-Dimethylcyclopropane
(5) 1,2-Dimethylcyclopropane
5 isomers are possible. C5H10(CnH2n). Molecules having the CnH2n formulas are most likely to be cyclic alkanes. The five isomers are:

(1) Cyclopentane
(2) 1-Methylcyclobutane
(3) 1-Ethylcyclopropane
(4) 1,1-Dimethylcyclopropane
(5) 1,2-Dimethylcyclopropane
What is the minimum number of carbon atoms of an alkane must have to form an isomer?- a)4
- b)3
- c)2
- d)1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the minimum number of carbon atoms of an alkane must have to form an isomer?
a)
4
b)
3
c)
2
d)
1
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
An alkane with minimum four carbon atoms can show isomerism.
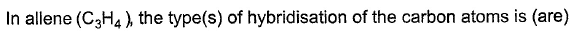
 [JEE Main 2014 Online Exam]
[JEE Main 2014 Online Exam]- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
[JEE Main 2014 Online Exam]
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Siddharth Mehra answered |
The correct answer is option 'B' - sp2 and sp.
Explanation:
In allene (C3H4), there are two carbon atoms, each with three sigma bonds. To determine the hybridization of the carbon atoms, we need to look at their bonding and lone pairs of electrons.
1. Hybridization of the first carbon atom:
- The first carbon atom is bonded to two other carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom.
- It has three sigma bonds, which means it will have three hybrid orbitals.
- The carbon atom also has one lone pair of electrons.
- The presence of three sigma bonds and one lone pair indicates sp2 hybridization.
- Therefore, the first carbon atom is sp2 hybridized.
2. Hybridization of the second carbon atom:
- The second carbon atom is also bonded to two other carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom.
- It also has three sigma bonds, which means it will have three hybrid orbitals.
- The carbon atom does not have any lone pairs of electrons.
- The presence of only three sigma bonds indicates sp hybridization.
- Therefore, the second carbon atom is sp hybridized.
In summary, in allene (C3H4), the type of hybridization of the carbon atoms is sp2 and sp.
Explanation:
In allene (C3H4), there are two carbon atoms, each with three sigma bonds. To determine the hybridization of the carbon atoms, we need to look at their bonding and lone pairs of electrons.
1. Hybridization of the first carbon atom:
- The first carbon atom is bonded to two other carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom.
- It has three sigma bonds, which means it will have three hybrid orbitals.
- The carbon atom also has one lone pair of electrons.
- The presence of three sigma bonds and one lone pair indicates sp2 hybridization.
- Therefore, the first carbon atom is sp2 hybridized.
2. Hybridization of the second carbon atom:
- The second carbon atom is also bonded to two other carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom.
- It also has three sigma bonds, which means it will have three hybrid orbitals.
- The carbon atom does not have any lone pairs of electrons.
- The presence of only three sigma bonds indicates sp hybridization.
- Therefore, the second carbon atom is sp hybridized.
In summary, in allene (C3H4), the type of hybridization of the carbon atoms is sp2 and sp.
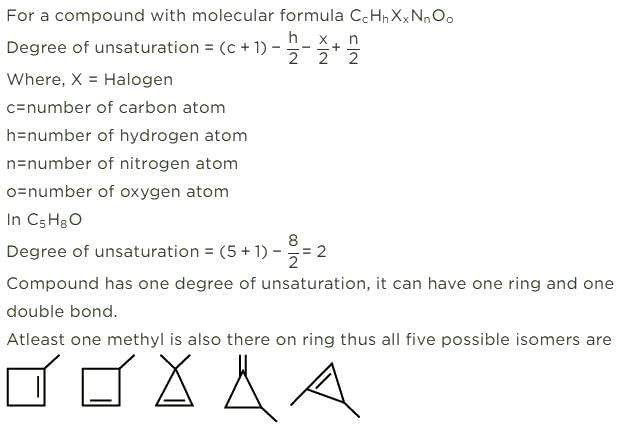
Consider all possible isomeric ketones, including stereoisomers of Molecular weight 100. All these isomers are independently reacted with NaBH4
(Note stereoisomers are also reacted separately). The total number of ketones that give a racemic product(s) is/are
[JEE Advanced 2014] - a)3
- b)4
- c)5
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider all possible isomeric ketones, including stereoisomers of Molecular weight 100. All these isomers are independently reacted with NaBH4
(Note stereoisomers are also reacted separately). The total number of ketones that give a racemic product(s) is/are
(Note stereoisomers are also reacted separately). The total number of ketones that give a racemic product(s) is/are
[JEE Advanced 2014]
a)
3
b)
4
c)
5
d)
6
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
The general formula of isomeric ketone having molecular mass 100 is C6H12O [6×12+12×1+16].
The possible structure will be :
The number of ketones that gives racemic mixture with NaBH4 is 5 as the ketone with chiral center will give diastereoisomer with NaBH4
The isomer of ethanol is:
- a)Dimethyl ether
- b)Diethyl ether
- c)Methanol
- d)Acetone
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The isomer of ethanol is:
a)
Dimethyl ether
b)
Diethyl ether
c)
Methanol
d)
Acetone
|
|
Pranavi Kulkarni answered |
The isomer of ethanol(CH3-CH2-OH) is dimethyl ether(CH3-O-CH3). This is a functional isomer of ethanol.
Explanation:
- Functional isomers are the ones with the same molecular formula but different functional groups.
- The molecular formula for dimethyl ether is C2H6O similar to ethanol.
- Dimethyl ether has the structural formula CH3OCH3 and ethanol has the structural formula CH3CH2OH.
- Therefore, dimethyl ether is the functional isomer of ethanol as both have the same molecular formula but one is ether and the other is alcohol.
Write the state of hybridisation of carbon in H2C=O.- a)sp3 hybridised carbon, trigonal
- b)sp2 hybridised carbon, trigonal planar
- c)sp3 hybridised carbon, tetrahedral
- d)sp hybridised carbon, linear
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Write the state of hybridisation of carbon in H2C=O.
a)
sp3 hybridised carbon, trigonal
b)
sp2 hybridised carbon, trigonal planar
c)
sp3 hybridised carbon, tetrahedral
d)
sp hybridised carbon, linear
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
C in H2C=O is sp2 hybridised and geometry is planar.


- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
1 and 2 are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. So, according to the options given, 1 and 2 are enantiomers of each other.
Some meta-directing substituents in aromatic substitution are given. Which one is most deactivating? [NEET 2013]- a)–SO3H
- b)–COOH
- c)–NO2
- d)–C ≡ N
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Some meta-directing substituents in aromatic substitution are given. Which one is most deactivating? [NEET 2013]
a)
–SO3H
b)
–COOH
c)
–NO2
d)
–C ≡ N

|
Anu Bajaj answered |
Decreasing order of deactivating effect of the given m-directing group is > NO2 > – CN > – SO3H > – COOH
—NO2 group is most deactivating group due to strong – E, – I and – M effects.
—NO2 group is most deactivating group due to strong – E, – I and – M effects.
What can be said with certainty if a compound has  ?
?- a)The compound has atleast one chiral centre
- b)The compound has R-configuration
- c)The compound is not a meso-isomer
- d)The optical purity of compound is less than 100%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What can be said with certainty if a compound has 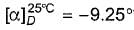 ?
?
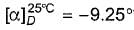 ?
?a)
The compound has atleast one chiral centre
b)
The compound has R-configuration
c)
The compound is not a meso-isomer
d)
The optical purity of compound is less than 100%
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
The correct answer is Option C.
A meso compound is optically inactive with zero specific rotation.
Nitration of benzene is:- a)Free radical substitution reaction
- b)Nucleophilic addition reaction
- c)Nucleophilic substitution reaction
- d)Electrophilic substitution reaction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Nitration of benzene is:
a)
Free radical substitution reaction
b)
Nucleophilic addition reaction
c)
Nucleophilic substitution reaction
d)
Electrophilic substitution reaction
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
Nitration and sulfonation of benzene are two examples of electrophilic aromatic substitution. The nitronium ion (NO2+) and sulfur trioxide (SO3) are the electrophiles and individually react with benzene to give nitrobenzene and benzenesulfonic acid respectively.
How many structural isomers are possible with molecular formula C4H10O ?- a)3
- b)5
- c)7
- d)8
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many structural isomers are possible with molecular formula C4H10O ?
a)
3
b)
5
c)
7
d)
8
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The formula that these isomers contain no rings or double bonds. The isomers must be alcohols and ethers.
Let's start by drawing the alcohols.
Start with four carbons in a row and put an OH group in every possible position.
This gives us
1. CH3CH2CH2CH2OH, butan 1-ol
and
2. CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3, butan-2-ol
Now use a 3-carbon chain with a CH3 on the middle carbon.
This gives
(CH3)2CHCH2OH, 2-methylpropan-1-ol
and
(CH3)3COH, 2-methylpropan-2-ol.
Now for the ethers.
Let's start with five atoms in a row.
This gives
CH3CH2CH2OCH3, 1-methoxypropane
and
CH3CH2OCH2CH3 , ethoxyethane
Finally, the only choice for a branched-chain ether is
(CH3)2CHOCH3 , 2-methoxpropane.
And there are your seven isomers of C4H10O.
A pair of enantiomers is possible for _______ isomer of 2,2-dibromobicyclo [2.2.1] heptane.
- a)cis
- b)trans
- c)both cis and trans
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A pair of enantiomers is possible for _______ isomer of 2,2-dibromobicyclo [2.2.1] heptane.
a)
cis
b)
trans
c)
both cis and trans
d)
none of the above
|
|
Tejas Verma answered |
Only one pair of enantiomers is possible for cis-2,2-dibromobicyclo [2.2.1] heptane. The trans arrangement of one carbon bridge is structurally impossible. Such a molecule would have too much strain.
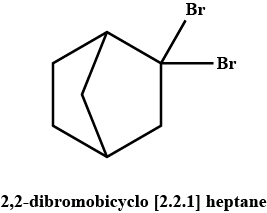
Which of the following is the correct IUPAC name?
- a)5-Ethyl-4, 4-dimethylheptane
- b)4, 4-Dimethyl-3-ethylheptane
- c)3-Ethyl-4, 4-dimethylheptane
- d)4, 4-Bis(methyl)-3-ethylheptane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the correct IUPAC name?


a)
5-Ethyl-4, 4-dimethylheptane
b)
4, 4-Dimethyl-3-ethylheptane
c)
3-Ethyl-4, 4-dimethylheptane
d)
4, 4-Bis(methyl)-3-ethylheptane
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
While writing IUPAC name, the alkyl groups are written in alphabetical order. Thus lower locant 3 is assigned to ethyl. Prefix, di, tri, and tetra are not included in alphabetical order.
Which compound below is capable of showing geometrical isomerism ?- a)CH3 - CH = C = CH - CH3
- b)CH3 - CH = C = C = CH - CH3
- c)
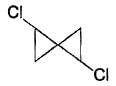
- d)
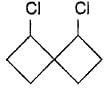
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which compound below is capable of showing geometrical isomerism ?
a)
CH3 - CH = C = CH - CH3
b)
CH3 - CH = C = C = CH - CH3
c)

d)


|
Kamna Science Academy answered |
The correct answer is option B
CH3 – CH = C = C = CH – CH3 will show geometrical isomerism because it is odd cumulene (3 pie bond) and odd cumulene always shows geometrical isomerism
CH3 – CH = C = C = CH – CH3 will show geometrical isomerism because it is odd cumulene (3 pie bond) and odd cumulene always shows geometrical isomerism
The increasing order of electron donating inductive effect of alkyl groups is- a)- H < - CH3 < - C2H5 < - C3H7
- b)- H > - CH3 > - C2H5 > - C3H7
- c)- H < - C2H5 < - CH3 < - C3H7
- d)-H>-C2H5>-CH3>-C3H7
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The increasing order of electron donating inductive effect of alkyl groups is
a)
- H < - CH3 < - C2H5 < - C3H7
b)
- H > - CH3 > - C2H5 > - C3H7
c)
- H < - C2H5 < - CH3 < - C3H7
d)
-H>-C2H5>-CH3>-C3H7
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The order of +I effect of alkyl group is given as
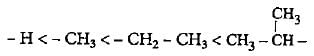
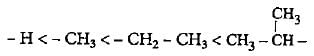
C3H6O represents an aldehyde and a ketone, is a type of:
- a)Chain isomerism
- b)Functional group isomerism
- c)Metamerism
- d)Position isomerism
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
C3H6O represents an aldehyde and a ketone, is a type of:
a)
Chain isomerism
b)
Functional group isomerism
c)
Metamerism
d)
Position isomerism
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The aldehyde and ketone that can be represented by molecular formula C3H6O are propanal and propanone respectively.
Aldehyde - Propanal - CH3CH2CHO
Ketone - Propanone - CH3COCH3
These two carbon compounds are called functional isomers. They do not have the same physical properties since their functional group is different.
When hydrogen is present on one side of C=O group and other side is R, (RCHO), then it is an aldehyde group. When R is present on both sides of C=O group, then it is a ketone.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 9) This section contains 9 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q.
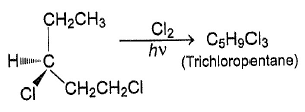
- a)3
- b)5
- c)7
- d)9
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 9) This section contains 9 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q.
a)
3
b)
5
c)
7
d)
9

|
Kamna Science Academy answered |
The number of optically active isomers = 2n−1−2n−1/2 =23−1−23−1/2 =2.
Heterolytic cleavage is a way to cleave the:- a)Non-ionic bonds
- b)Ionic bonds
- c)Covalent bonds
- d)Polar bonds
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Heterolytic cleavage is a way to cleave the:
a)
Non-ionic bonds
b)
Ionic bonds
c)
Covalent bonds
d)
Polar bonds
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
In heterolytic cleavage, a covalent bond breaks in such a way that one fragment gets both of the shared electrons. In homolytic cleavage, a covalent bond breaks in such a way that each fragment gets one of the shared electrons. The word heterolytic comes from the Greek heteros, "different", and lysis, "loosening".
The number of optical isomers possible for 2, 3-pentanediol is:
- a)2
- b)3
- c)4
- d)5
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of optical isomers possible for 2, 3-pentanediol is:
a)
2
b)
3
c)
4
d)
5
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
2 optical centers.
Total optically active isomers =22
=4
Total optically active isomers =22
=4
Which of the following statements are correct?
I. A pair of positional isomers differs in the position of the same functional group.
II. A pair of. structural isomers have the same relative molar mass.
Ill. A pair of functional group isomers belongs to different homologous series.
- a)I, II and Ill
- b)I and Ill
- c)II and III
- d)I and II
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements are correct?
I. A pair of positional isomers differs in the position of the same functional group.
II. A pair of. structural isomers have the same relative molar mass.
Ill. A pair of functional group isomers belongs to different homologous series.
II. A pair of. structural isomers have the same relative molar mass.
Ill. A pair of functional group isomers belongs to different homologous series.
a)
I, II and Ill
b)
I and Ill
c)
II and III
d)
I and II
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
According to me all statements are correct. For statement I, positional isomers have the same functional group. They just differ in the position of that group.
Statenmen II- Structural isomers have the same relative molar mass. Actually relative mass means the mass of one isomer is samee relative to another. Structural isomers differ in the structure of molecules. However they have the same molecular formula and hence; same molar mass.
Statement III- According to me, this statement is correct. As homologous series must contain the same functional group with the same physical & chemical properties. Also functional group isomers differ in the functional group attached with them. So, functional group isomers belong to different homologous series.
Statenmen II- Structural isomers have the same relative molar mass. Actually relative mass means the mass of one isomer is samee relative to another. Structural isomers differ in the structure of molecules. However they have the same molecular formula and hence; same molar mass.
Statement III- According to me, this statement is correct. As homologous series must contain the same functional group with the same physical & chemical properties. Also functional group isomers differ in the functional group attached with them. So, functional group isomers belong to different homologous series.
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
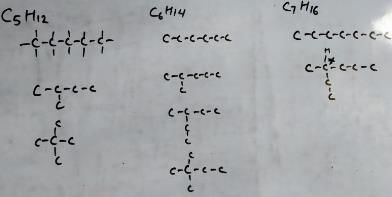
I have drawn only skeleton. It can be known that for C5H12 and C6H14, we have no isomerism. For C7H16 we have one isomer. So, the minimum carbon required for an alkane is C7H16.
How many different isomers of alkene with molecular formula C7H14, on catalytic hydrogenation, can give 3-methyl hexane?
Correct answer is '9'. Can you explain this answer?
How many different isomers of alkene with molecular formula C7H14, on catalytic hydrogenation, can give 3-methyl hexane?
|
|
Pranavi Banerjee answered |
Explanation:
Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms in space. In this case, we are looking for isomers of an alkene with the molecular formula C7H14 that can give 3-methyl hexane on catalytic hydrogenation.
Step 1: Draw the structural formula of 3-methyl hexane
3-methyl hexane has the structural formula:

Step 2: Draw the structural formula of the alkene
The alkene has the molecular formula C7H14, which means it has two fewer hydrogen atoms than 3-methyl hexane. Therefore, we can start by drawing all the possible ways to add a double bond to a chain of seven carbon atoms.

Step 3: Identify the isomers that can give 3-methyl hexane on catalytic hydrogenation
We can now check each of these isomers to see if they can give 3-methyl hexane on catalytic hydrogenation. If an isomer can give 3-methyl hexane, it means that it has a methyl group (CH3) attached to the third carbon atom from the double bond.
- Isomer 1: This isomer cannot give 3-methyl hexane on catalytic hydrogenation because it does not have a methyl group attached to the third carbon atom from the double bond.
- Isomer 2: This isomer can give 3-methyl hexane on catalytic hydrogenation because it has a methyl group attached to the third carbon atom from the double bond.
- Isomer 3: This isomer cannot give 3-methyl hexane on catalytic hydrogenation because it does not have a methyl group attached to the third carbon atom from the double bond.
- Isomer 4: This isomer can give 3-methyl hexane on catalytic hydrogenation because it has a methyl group attached to the third carbon atom from the double bond.
- Isomer 5: This isomer cannot give 3-methyl hexane on catalytic hydrogenation because it does not have a methyl group attached to the third carbon atom from the double bond.
- Isomer 6: This isomer can give 3-methyl hexane on catalytic hydrogenation because it has a methyl group attached to the third carbon atom from the double bond.
- Isomer 7: This isomer cannot give 3-methyl hexane on catalytic hydrogenation because it does not have a methyl group attached to the third carbon atom from the double bond.
- Isomer 8: This isomer can give 3-methyl hexane on catalytic hydrogenation because it has a methyl group attached to the third carbon atom from the double bond.
- Isomer 9: This isomer can
How many geometrical isomers exist for the molecule shown below ?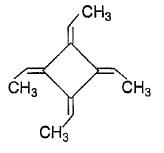
- a)2
- b)3
- c)5
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many geometrical isomers exist for the molecule shown below ?

a)
2
b)
3
c)
5
d)
6

|
EduRev JEE answered |
The correct answer is option B
Threegeometrical isomers exits of the molecule given cis-cis, tran-trans and cis-trans.
Threegeometrical isomers exits of the molecule given cis-cis, tran-trans and cis-trans.
An organic acid containing carbon, oxygen and hydrogen only has molar mass of 132 g. 6.6 g of this acid require 80 mL 1.25 M NaOH for complete neutralisation. How many carboxylic groups are present in one molecule of this acid? - a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An organic acid containing carbon, oxygen and hydrogen only has molar mass of 132 g. 6.6 g of this acid require 80 mL 1.25 M NaOH for complete neutralisation. How many carboxylic groups are present in one molecule of this acid?
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Let us consider organic acid as ‘A’.
Moles of A = mass of A/Molar mass = 6.6/132 = 0.05
Molarity of NaOH = 1.25M
And volume of NaOH = 80 mL
Therefore, moles of NaOH = molarity × Volume
= 1.25×80×10-3 = 0.1 moles.
SO, 0.05 moles of A requires 0.1 moles of NaOH
1 mole of acid requires x moles of NaOH
x = 0.1/0.05×1 = 2
So for neutralisation of 1 mole of A, we need 2 moles of NaOH. Therefore given acid is dibasic and contains 2 -COOH groups.
Moles of A = mass of A/Molar mass = 6.6/132 = 0.05
Molarity of NaOH = 1.25M
And volume of NaOH = 80 mL
Therefore, moles of NaOH = molarity × Volume
= 1.25×80×10-3 = 0.1 moles.
SO, 0.05 moles of A requires 0.1 moles of NaOH
1 mole of acid requires x moles of NaOH
x = 0.1/0.05×1 = 2
So for neutralisation of 1 mole of A, we need 2 moles of NaOH. Therefore given acid is dibasic and contains 2 -COOH groups.
Impure sample of Naphthalene can be purified by:- a)Distillation
- b)Chromatography
- c)Crystallisation
- d)Sublimation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Impure sample of Naphthalene can be purified by:
a)
Distillation
b)
Chromatography
c)
Crystallisation
d)
Sublimation
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Impure sample of Naphthalene can be purified by Sublimation.
If 3-ethylpentane is subjected to free radical chlorination, how many different monochlorination product would be produced?
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
If 3-ethylpentane is subjected to free radical chlorination, how many different monochlorination product would be produced?

|
Tarun Kaushik answered |
The correct answer is 4 Since there are three different types of H and it gives three monochlorinated product. One of them is optically active and exists as an enatiomeric pair. So there is a total of four different products.
Which of the following are not functional isomers of each other?
- a)CH3CH2NO2 and CH3CH2ON=O
- b)C2H5CHO and CH3COCH3
- c)CH3CH2NH2 and CH3NHCH3
- d)C3H7NH2 and (CH3)2CHNH2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are not functional isomers of each other?
a)
CH3CH2NO2 and CH3CH2ON=O
b)
C2H5CHO and CH3COCH3
c)
CH3CH2NH2 and CH3NHCH3
d)
C3H7NH2 and (CH3)2CHNH2
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Functional isomers are structural isomers that have the same molecular formula (that is, the same number of atoms of the same elements), but the atoms are connected in different ways so that the groupings are dissimilar or different functional groups.
10 amine to different 10 amines are not functional isomers.
Hence, option ′d′ is the answer.

The number of isomers of C6H14 is:- a)4
- b)5
- c)6
- d)7
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of isomers of C6H14 is:
a)
4
b)
5
c)
6
d)
7
|
|
Anu Mukherjee answered |
**Explanation:**
To determine the number of isomers of C6H14, we need to consider the different ways in which carbon atoms can be arranged and the different ways in which hydrogen atoms can be distributed among these carbon atoms.
**1. Straight-chain isomers:**
The simplest isomer is the straight chain, where the carbon atoms are arranged in a linear sequence. For C6H14, there is only one straight-chain isomer.
**2. Branched-chain isomers:**
In branched-chain isomers, the carbon atoms are arranged in a branched manner. To determine the number of possible branched-chain isomers, we need to consider the different ways in which the branches can be arranged and the different positions at which the branches can be attached to the main chain.
In this case, one of the carbons in the straight chain can have three branches attached to it. We can have three different arrangements of these branches, which are:
- One branch attached to the first carbon and two branches attached to the second carbon.
- Two branches attached to the first carbon and one branch attached to the second carbon.
- Three branches attached to the first carbon and no branches attached to the second carbon.
For each of these arrangements, there are different possibilities for the positions of the branches along the main chain. Therefore, for the branched-chain isomers, there are a total of three possibilities.
**3. Cycloalkane isomers:**
Cycloalkanes are ring structures where the carbon atoms are arranged in a closed loop. For C6H14, we can have cycloalkane isomers with different ring sizes.
- Cyclohexane: In this case, all six carbon atoms form a single ring. There is only one possibility.
- Cyclopentane: In this case, five carbon atoms form a ring and the remaining carbon atom is attached to one of the carbons in the ring. There is only one possibility.
Therefore, the total number of isomers of C6H14 is the sum of the straight-chain isomer, branched-chain isomers, and cycloalkane isomers, which is 1 + 3 + 2 = 6.
Therefore, the correct answer is option **c) 6**.
To determine the number of isomers of C6H14, we need to consider the different ways in which carbon atoms can be arranged and the different ways in which hydrogen atoms can be distributed among these carbon atoms.
**1. Straight-chain isomers:**
The simplest isomer is the straight chain, where the carbon atoms are arranged in a linear sequence. For C6H14, there is only one straight-chain isomer.
**2. Branched-chain isomers:**
In branched-chain isomers, the carbon atoms are arranged in a branched manner. To determine the number of possible branched-chain isomers, we need to consider the different ways in which the branches can be arranged and the different positions at which the branches can be attached to the main chain.
In this case, one of the carbons in the straight chain can have three branches attached to it. We can have three different arrangements of these branches, which are:
- One branch attached to the first carbon and two branches attached to the second carbon.
- Two branches attached to the first carbon and one branch attached to the second carbon.
- Three branches attached to the first carbon and no branches attached to the second carbon.
For each of these arrangements, there are different possibilities for the positions of the branches along the main chain. Therefore, for the branched-chain isomers, there are a total of three possibilities.
**3. Cycloalkane isomers:**
Cycloalkanes are ring structures where the carbon atoms are arranged in a closed loop. For C6H14, we can have cycloalkane isomers with different ring sizes.
- Cyclohexane: In this case, all six carbon atoms form a single ring. There is only one possibility.
- Cyclopentane: In this case, five carbon atoms form a ring and the remaining carbon atom is attached to one of the carbons in the ring. There is only one possibility.
Therefore, the total number of isomers of C6H14 is the sum of the straight-chain isomer, branched-chain isomers, and cycloalkane isomers, which is 1 + 3 + 2 = 6.
Therefore, the correct answer is option **c) 6**.
Which among the following is not an aromatic compound(in specific)- a)Naphthalene
- b)Aniline
- c)Pyridine
- d)Tropolone
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is not an aromatic compound(in specific)
a)
Naphthalene
b)
Aniline
c)
Pyridine
d)
Tropolone

|
Sai Mishra answered |
Pyridine is heterocyclic aromatic compound. Whereas naphthalene and aniline are benzenoid aromatic compounds and tropolone is a non-benzenoid aromatic compound.
Organic compounds are broadly classified as
- a)alicyclic compounds and acyclic compounds
- b)Open chain compounds and linear chain compounds
- c)Cyclic compounds and alicyclic compounds
- d)Open chain compounds and closed compounds
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Organic compounds are broadly classified as
a)
alicyclic compounds and acyclic compounds
b)
Open chain compounds and linear chain compounds
c)
Cyclic compounds and alicyclic compounds
d)
Open chain compounds and closed compounds

|
Arpita Nambiar answered |
The correct answer is option D
Organic compounds are broadly classified into open chain and closed chain compounds. Explanation: open chain compounds or acyclic compounds are otherwise called as aliphatic compounds.
Organic compounds are broadly classified into open chain and closed chain compounds. Explanation: open chain compounds or acyclic compounds are otherwise called as aliphatic compounds.
Which is not true regarding conformers of ethane?- a)Theoretically infinite conformers exist
- b)Staggered conformer has lower torsional strain than eclipsed one
- c)Increasing temperature increases the percentage of eclipsed conformer
- d)By precise experimental setup, staggered conformer can be separated out of system
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is not true regarding conformers of ethane?
a)
Theoretically infinite conformers exist
b)
Staggered conformer has lower torsional strain than eclipsed one
c)
Increasing temperature increases the percentage of eclipsed conformer
d)
By precise experimental setup, staggered conformer can be separated out of system
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
The correct answer is Option D.
Although conformers differ in potential energy and stability, the difference is so small that it does not allow their practical separation.
Although conformers differ in potential energy and stability, the difference is so small that it does not allow their practical separation.
Direction (Q. Nos. 7 and 14) This section contains 8 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)Q.
How many stereoisomers exist in the compound 1-methyl-3-(1-propenyl) cyclohexane ?
Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 7 and 14) This section contains 8 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q.
How many stereoisomers exist in the compound 1-methyl-3-(1-propenyl) cyclohexane ?
How many stereoisomers exist in the compound 1-methyl-3-(1-propenyl) cyclohexane ?
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
The correct answer is 8
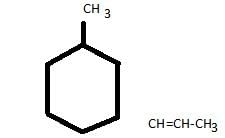
Chiral Carbon
Carbon no.1 is chiral carbon so H Show 2 optical isomers
Carbon no.3 is also chiral carbon
Hence, shows two optical isomers
Carbon 1 & carbon 3 shows G.I. due to 1 stereocenter
Propenyl shows 2 G.I.
Total 8 isomers are shown here.

Chiral Carbon
Carbon no.1 is chiral carbon so H Show 2 optical isomers
Carbon no.3 is also chiral carbon
Hence, shows two optical isomers
Carbon 1 & carbon 3 shows G.I. due to 1 stereocenter
Propenyl shows 2 G.I.
Total 8 isomers are shown here.
which compound does not possess a plane of symmetry ?
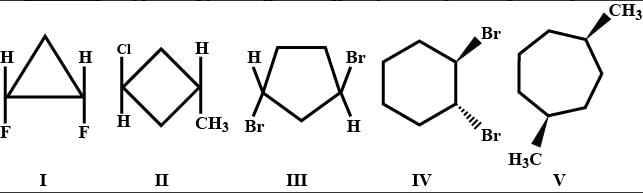
- a)I , II and V
- b)I, III and IV
- c)II, III and IV
- d)III and IV
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
which compound does not possess a plane of symmetry ?

a)
I , II and V
b)
I, III and IV
c)
II, III and IV
d)
III and IV
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Refer to image III
It does not contain plane of symmetry as molecular can not divide into turn identical names by any plane.
Refer to image IV
It also does not contain plane of symmetry.
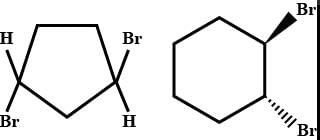

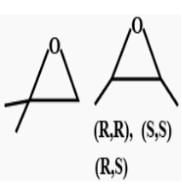
of the compounds, which correspond to the general name dichlorocyclobutane how many are optically active ?- a)0
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
of the compounds, which correspond to the general name dichlorocyclobutane how many are optically active ?
a)
0
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
The correct answer is option B
2 are optically active
2 are optically active

For (i) I–, (ii) Cl–, (iii) Br–, the increasing order of nucleophilicity would be [2007]- a)Cl– < Br– < I–
- b)I– < Cl– < Br–
- c)Br– < Cl–< I–
- d)I– < Br– < Cl–
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For (i) I–, (ii) Cl–, (iii) Br–, the increasing order of nucleophilicity would be [2007]
a)
Cl– < Br– < I–
b)
I– < Cl– < Br–
c)
Br– < Cl–< I–
d)
I– < Br– < Cl–

|
Harshitha Dey answered |
Nucleophilicity increases down the periodic table. I- > Br- > Cl- > F-
Chapter doubts & questions for Organic Chemistry : Some Basic Principles & Techniques - Organic Chemistry for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Organic Chemistry : Some Basic Principles & Techniques - Organic Chemistry for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily